Summary. Introduction
|
|
|
- Hugh Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1999) 7, OsteoArthritis Research Society International /99/ $12.00/0 Article No. joca , available online at on Meniscal subluxation: association with osteoarthritis and joint space narrowing D. R. Gale, C. E. Chaisson, S. M. S. Totterman, R. K. Schwartz, M. E. Gale and D. Felson The Department of Radiology at Boston VA Medical Center and Boston University Arthritis Center, Boston University School of Medicine and the Department of Radiology, University of Rochester Medical Center Summary Objective: Since complete meniscectomy leads to knee OA, we investigated the potential links among meniscal subluxation, joint space narrowing and symptomatic OA. Materials and methods: 233 cases with symptomatic knee OA and 58 asymptomatic controls underwent radiography and MR imaging of the knee. Joint space narrowing was measured on weight-bearing PA fluoroscopy-positioned radiographs. The amount of medial or lateral meniscal subluxation was measured on coronal MR images. The prevalence and severity of meniscal subluxation was compared in cases and controls. We evaluated the correlation of the degree of meniscal subluxation with joint space narrowing, Kellgren and Lawrence grade, and two major risk factors for the development of OA, age and weight. Results: Cases had more medial and lateral subluxation than controls. Mean medial meniscal subluxation was 5.1 mm in cases and 2.8 mm in controls (P=0.001). Modest degrees of meniscal subluxation were common in both cases and controls: 81% of cases and 64% of controls had 3 mm of subluxation; age and gender adjusted (P=0.006). Severe degrees of subluxation were almost unique to OA cases (e.g. prevalence of 7 mm, 35% cases vs. 7% controls, P<0.001). Among controls, severe degrees of subluxation were present only in those with radiographic joint space narrowing (defined as grade 1 narrowing on a 0 3 scale). In cases, there was a strong correlation between the degree of medial meniscal subluxation and the severity of medial joint space narrowing (r=0.56, P=0.0001). Similar results were present in the lateral compartment. Meniscal subluxation did not correlate with age or weight. Conclusion: Meniscal subluxation is highly associated with symptomatic knee OA. In subjects with osteoarthritis, increasing meniscal subluxation on MR correlates with the severity of joint space narrowing OsteoArthritis Research Society International Key words: Knee osteoarthritis, Meniscus. Introduction Symptomatic osteoarthritis (OA) occurs in 11% of persons aged 65 and over and approximately 6% of the overall U.S. adult population. 1 It accounts for most total knee replacements and for as much or more lower extremity disability as any disease. In the knee, the menisci function as buffers by distributing axial load and protecting the adjacent articular cartilage. 2 They also stabilize the knee. In both clinical practice and experimental models, complete meniscectomy has been shown to predispose to premature osteoarthritis. 3,4 We hypothesized that significant meniscal subluxation, displacement away from or uncovering the tibial articular cartilage, would occur more often in subjects with knee OA than controls either because it caused the OA or because laxity of supporting meniscal structures associated with OA predisposes to meniscal subluxation. In either case Received 14 January 1999; accepted 11 June Supported in part by grant from the Bayer Corporation, by NIH AR20613 and by a Clinical Sciences Grant from the Arthritis Foundation. Address reprint requests to Dr Daniel R. Gale at Boston VA Medical Center (114) 150 South Huntington Ave, Boston, MA Corresponding author: David T. Felson, Boston University Arthritis Center, 715 Albany Street, A203, Boston, MA significant meniscal subluxation may simulate a condition similar to complete meniscectomy. Joint space narrowing is a primary radiographic feature of OA. Hyaline cartilage erosion and loss are characteristic pathologic findings in OA. Arthroscopic and arthrographic studies of knee OA have suggested a moderate correlation between radiographic joint space narrowing and loss of hyaline articular cartilage. 5,6 While hyaline articular cartilage loss accounts for some joint space narrowing, menisci comprise some of the space between femur and tibia, especially along the periphery of the joint. Meniscal removal or displacement could also account for and contribute to joint space narrowing. Meniscal findings in older asymptomatic subjects have not been well studied. Recent reports have documented some association of meniscal protrusion with radiographic findings in osteoarthritis such as osteophyte formation, anterior cruciate ligament tear or joint effusion. 7,8 However, these studies have not evaluated the relationship of meniscal subluxation to the presence of osteoarthritis nor assessed the degree of subluxation and its association with joint space narrowing, a distinctive feature of OA. The link between joint space narrowing and meniscal subluxation is a matter of considerable importance because narrowing, which is commonly thought to represent hyaline articular cartilage loss, has been and continues to be used as the primary outcome measure for knee OA in clinical practice and investigative trials
2 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Vol. 7 No This study evaluated the prevalence of meniscal subluxation in symptomatic OA cases versus asymptomatic controls. In symptomatic OA cases, we tested the correlation of meniscal subluxation measured on MRI with joint space narrowing measured on weight bearing knee radiographs. In addition, we evaluated the correlation of meniscal subluxation with age and weight, two of the major risk factors for the development of OA. The focus of this investigation was subluxation in those with symptomatic OA (our cases), with the recognition that controls, while asymptomatic, may, like many older persons, have evidence of radiographic OA. Materials and methods PATIENT SELECTION The minimum age for entry into the study was 40 years for men and 50 years for women. The minimum entry age for women was older in order to lessen the chance of inadvertently obtaining radiographs on pregnant women. Male subjects were drawn from the longitudinal Veterans Health Study, a cohort study of 2425 men receiving care at regional area medical centers, designed to evaluate the relationship between chronic diseases and health outcomes. 10 Female subjects were drawn from a similar study, the Women s Health Project (N=800) that was designed to describe the health status of women veterans using ambulatory services. The human studies committee and the institutional review board approved protocols for both the parent studies and the knee osteoarthritis sub-study. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects. During assessment in these parent studies, subjects were surveyed about knee symptoms. They were asked two questions: Do you have pain, aching or stiffness in one or both knees on most days?, and Has a doctor ever told you that you have knee arthritis?. In a follow-up interview, those answering positively to both questions were asked about other types of arthritis that could cause knee symptoms. If no other forms of arthritis were identified in the interview or from review of the individual s medical record, then the individual was eligible for recruitment as a case. Controls were recruited from among those who answered in the negative to both of the above screening questions and these persons were characterized as controls irrespective of their radiographic findings. RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION In cases and controls, weight-bearing PA using the protocol of Buckland-Wright, 11 weight-bearing skyline and weight-bearing lateral radiographs were obtained. 12 For the PA view, the knee was positioned and radiographed under fluoroscopy so that the anterior and posterior medial tibial plateaus were superimposed in order to optimize the measurement of joint space narrowing. This technique improves the accuracy of joint space narrowing measurements. Radiographs were read for the presence of definite osteophytes and other features by one radiologist (DRG) using an atlas. If a definite osteophyte was present in a symptomatic knee on any one of three views, the subject was characterized as an OA case (this includes the patella). This definition meets American College of Rheumatology criteria 13 for knee OA. Symptomatic individuals without a radiographic osteophyte were excluded from this study since they met neither the criteria for knee OA nor asymptomatic control. Radiographic joint space narrowing in each tibio-femoral compartment of each knee was evaluated using both semi-quantitative and quantitative methods. These evaluations were conducted independently of one another and the readers were blinded to case status and MRI findings. The semi-quantitative measurements, developed for the Framingham Osteoarthritis Study, used a four-point scale (0 3 where 0 was no evidence of joint space narrowing and 3 represented absent joint space). 14 We defined a knee as having joint space narrowing if there was joint space narrowing ( 1 on a 0 3 scale) in at least one tibio-femoral compartment. The intraobserver agreement for this dichotomous definition of narrowing was Kappe=0.6 (P<0.001). In the quantitative method, joint space narrowing (technically the distance between femoral condyle and tibial plateau) was measured at three points in the medial and lateral compartments of each knee: the most peripheral site at which femur apposed tibia; the narrowest site; and the site measured to be at the center of the compartment (midpoint) using a previously developed protocol. 15 Joint space narrowing was measured between points using calipers with an electronic readout of the distance. Because magnification of images occurs with this imaging protocol, we used a fixed size ball bearing taped to the knee and adjusted for its magnification to compute joint space narrowing. Reproducibility of these readings was high (intraobserver ICC=ranged from across medial and lateral compartment sites). The severity of osteoarthritis on the PA projection was also scored from 0 4 using the Kellgren and Lawrence scale. 16 MRI EVALUATION Each case underwent MRI of the more symptomatic knee. For controls the dominant knee was selected for imaging. All studies were performed on a GE Signa 1.5 Tesla MR (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, Wisconsin) using a phased array knee coil. A positioning device for the ankle and knee was used to ensure uniformity between patients. The MR protocol for each subject included coronal, sagittal and axial images. Coronal spin echo fat saturated proton density and T2 weighed fat saturated images (TR 2200 TE 20/80) with a slice thickness of 3 mm, a 1-mm interslice gap, 1 NEX, field of view cm, and a matrix of were used. MRIs of the cases and controls were randomly mixed and the three MRI readers (DRG, SMST, RKS) were blinded to case status. Meniscal subluxation was measured to the nearest millimeter on the coronal images using a MR generated scale on each image (Fig. 1). Meniscal subluxation was defined as the greatest distance from the most peripheral aspect of the meniscus to the border of the tibia excluding any osteophyte on any one of the multiple coronal images. Inter- and intra-observer reliability of meniscal subluxation measurements was tested using a subset of the MRI exams. The inter-observer intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for medial subluxation was 0.85 (P<0.0001) and for lateral subluxation was 0.76 (P<0.0001). The intra-observer ICC for medial subluxation was 0.93 (P<0.0001). There were insufficient numbers of subset cases to test for intra-observer lateral subluxation. Weights were measured as part of the parent study evaluation and were obtained only in the study of men and
3 528 D. R. Gale et al.: Meniscal subluxation and knee osteoarthritis Fig. 1. (a) An AP view of the knee demonstrates grade I narrowing medially using the qualitative scale. (b) The corresponding proton density weighted fat saturation MR image demonstrates 4 mm of subluxation of the medial meniscus beyond a vertical line through the medial border of tibia. The articular cartilage is relatively well preserved. not women. Male subjects were weighed using a balance beam scale. Only one knee per subject was studied by MRI and thus the analyses are knee and subject specific. Analysis focused on the difference between proportions (chi square or Fisher s exact test when appropriate) and differences in continuous measures was tested using t test (e.g., subject age). s reported are two-sided. To adjust for age (and for gender or weight when appropriate) in comparing the prevalence of meniscal subluxation in cases versus controls, we used logistic regression using case status as the dependent variable. To evaluate the association between the amount of meniscal subluxation and joint space narrowing as well as risk factors for OA, we computed Pearson correlation coefficients. For some analyses evaluating controls, we separated controls with any tibiofemoral joint space narrowing (defined as a score of 1 on semi-quantitative scale (0 3) in either medial or lateral compartment) from those without narrowing. With controls separated into those with and without narrowing, we created three analytic groups: cases, controls with X-ray OA and narrowing (control A), and controls without narrowing (control B). To analyse whether subluxation correlated with knee symptoms, controlling for radiographic disease, we compared the mean subluxation of cases vs. control A. To evaluate whether subluxation was associated with narrowing, we compared the degree of subluxation in controls A and B. We performed both comparisons above by carrying out a multiple regression analysis in which the log-transformed value for medial subluxation was the dependent variable and independent variables included age, gender and group (a class variable: either case, control A or control B). This permitted us to compare least squares means values for medical subluxation in the three groups. Results There were a total of 203 male and 31 female cases with symptomatic and radiographic knee OA from our Veteran population, which is predominantly comprised of men. There were 27 male and 30 female controls (Table I). Female cases were similar in age to female controls, while male cases were slightly older than their controls. Male cases were slightly heavier than their respective controls. All cases and 70% of controls (67% of males and 74% of females) had some evidence of radiographic OA (at least a
4 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Vol. 7 No % 82% Percentage of the knees % 56% 35% % 17% % 3% 4% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0.0 > _ 3 mm _> 5 mm _> 7 mm _> 9 mm _> 11 mm Degree of meniscal subluxation Fig. 2. Prevalence of medial subluxation in cases and controls with and without JSN, at different levels of subluxation. ", case; with JSN; h, control without JSN. 35%, Control Table I Description of cases and controls Cases Controls (Chi-square) Men (N) Mean age (years) (±s.d.) 67 (±10) 65 (±10) 0.23 Mean weight (lbs) (±s.d.) 201 (±35) 189 (±34) 0.12 Joint space narrowing ( 1ona0 3 scale) (%) 130 (64%) 4 (15%) <0.001 Women (N) Mean age (years) (±s.d.) 66 (±10) 66 (±8) 0.78 Mean weight (lbs) (±s.d.) NA* NA NA Joint space narrowing ( 1ona0 3 scale) (%) 26 (84%) 13 (43%) <0.001 *Data not available for women. small definite osteophyte) on at least one radiographic view. In both men and women, using the semi-quantitative scale, cases were more likely than controls to demonstrate any joint space narrowing (P=0.001). The mean medial meniscal subluxation was greater in cases than controls (Table II). In men, the mean medial meniscal subluxation was 5.3 mm (±3.1) in cases and 2.9 mm (±2.2) in controls (P=0.0002), and the mean lateral meniscal subluxation was 0.62 mm (±1.8) in cases and 0.48 mm (±1.4) in controls (P=0.69). In women, the mean medial meniscal subluxation was 4.3 mm (±3.4) in cases and 2.7mm (±2.1) in controls (P=0.03), and mean lateral meniscal subluxation was 1.9 mm (±3.4) in cases and 0 mm (±0) in controls. At every level of medial meniscal subluxation, the prevalence was significantly greater for cases than controls. Medial meniscal subluxation, defined as 3 mm or greater, was present in 81% of the cases and 64% of controls (P=0.006). Further, medial subluxation of 7 mm occurred in 35% of cases and 7% of controls (P<0.001). Also, at every threshold of medial subluxation, rates were higher among both male and female cases than their respective controls. We then assessed whether the amount of meniscal subluxation differed among controls with joint space narrowing and those without joint space narrowing, and compared those rates of subluxation to those of cases. In cases and controls with and without joint space narrowing (using the semiquantitative scale score of 1 in at least one compartment), we found that more severe degrees of subluxation occurred almost uniquely in those with narrowing (Fig. 2). For example, in controls with no joint space narrowing, only 3/38 (8%) had meniscal subluxation of at least 5 mm. However, in controls with joint space narrowing, 6/17 (35%) had this degree of meniscal subluxation. The number of cases and controls demonstrating lateral subluxation was smaller; lateral subluxation of 5 mm did not occur in any controls, but occurred in 20/232 (9%) of cases. We performed an analysis comparing the degree of medial subluxation in cases and two groups of controls (those with and without narrowing) after controling for age and gender and found the adjusted mean subluxation in cases was 1.32 mm (95% CI 1.20, 1.45) For controls with narrowing, the adjusted mean subluxation was 1.22 mm (95% CI 0.75, 1.69; P=0.68 vs. cases). For controls without narrowing, the adjusted mean subluxation was 0.64 mm (95% CI 0.34, 0.95); P=0.04 vs. controls with narrowing). Meniscal subluxation was correlated with joint space narrowing (quantitative method) in both male and female
5 530 D. R. Gale et al.: Meniscal subluxation and knee osteoarthritis Table II Mean meniscal subluxation (±s.d.) in cases vs. controls Cases Controls * Medial Men 5.3 mm (±3.1) 2.9 mm (±2.2) Women 4.3 mm (±3.4) 2.7 mm (±2.1) Men and women 5.1 mm (±3.2) 2.8 mm (±2.1) Lateral Men 0.62 mm (±1.8) 0.48 mm (±1.4) 0.69 Women 1.9 mm (±3.4) 0 mm (±0) Men and women 0.8 mm (±2.1) 0.23 mm (±0.96) *Adjusted for age and when appropriate for gender and age. Unable to calculate due to lack of distribution in controls. Table III Correlation (r values) of meniscal subluxation on MRI with joint space narrowing on X-ray Mid point of compartment* Most peripheral site in compartment* Narrowest site in compartment* Medial Men Women All cases Lateral Men Women All cases *These sites are defined in Methods. Table IV Bivariate correlation (r value) of meniscal subluxation* with other factors in knee osteoarthritis cases Medial correlation coefficient Lateral correlation coefficient Men Kellgren & Lawrence Grade (0 4) Age (years) Weight (lbs) Women Kellgren & Lawrence Grade (0 4) Age (years) Weight (lbs) N/A N/A All Kellgren & Lawrence Grade (0 4) Age (years) *Degree of meniscal subluxation is assessed on a continuous scale. cases. In cases the mean joint space height at the narrowest point in the medial compartment was 3.26 mm (±1.34 s.d.) In men, there was a correlation of r=0.50 to 0.54 (P=0.0001) between medial joint space narrowing on X-ray and medial meniscal subluxation on MRI (Table III). In women there was a similar correlation in the medial joint compartment (r=0.57 to 0.64 (P=0.001)). In men, correlations between lateral joint space narrowing on X-ray and lateral subluxation on MRI were lower (r=0.28 to 0.34) than in women (r=0.43 to 0.44). In those without meniscal subluxation, joint space narrowing was very uncommon. Of the twenty controls with <3 mm of medial meniscal subluxation, only three (15%) demonstrated medial joint space narrowing ( 1 on a 0 3 scale) and of fifty-four controls with <3 mm of lateral meniscal subluxation, only three (6%) had lateral joint space narrowing. Of cases, sixteen of forty-two (38%) cases without medial meniscal subluxation (<3 mm) demonstrated medial joint space narrowing, whereas only seven of 194 (4%) cases without lateral meniscal subluxation demonstrated lateral joint space narrowing. For male cases, there was little correlation between age and the amount of medial subluxation [r=0.15 (P=0.03)] and lateral subluxation [r=0.15 (P=0.04)] (Table IV). Similarly there was no correlation between weight and the amount of medial subluxation [r=0.01 (P=0.86)] or lateral subluxation [r=0.005 (P=0.95)]. For female cases, there was no correlation between age and the amount of medial subluxation [r=0.06 (P=0.76)] but there was a moderate correlation between age and lateral subluxation [r=0.44
6 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Vol. 7 No (P=0.014)]. Kellgren and Lawrence grade was moderately correlated with the degree of meniscal subluxation. Discussion This study demonstrates that meniscal subluxation is substantially and significantly more common in symptomatic osteoarthritis cases than asymptomatic controls. Importantly, the study also indicates that the amount of medial meniscal subluxation correlates with the degree of medial joint space narrowing in both men and women, and lateral subluxation with lateral joint space narrowing in women. In men, the correlation between lateral subluxation and lateral joint space narrowing is less strong, probably because few male cases demonstrated lateral joint space narrowing. Since joint space narrowing is an essential component of the Kellgren and Lawrence scale, it is not surprising that meniscal subluxation also correlates well with Kellgren and Lawrence grade. Because our study was cross-sectional, etiologic inferences can not be drawn. Either subluxation contributes to the development of joint space narrowing and knee osteoarthritis, or conversely results from the joint space narrowing and associated osteoarthritic changes. Joint space narrowing and meniscal subluxation may be interdependent, so that once subluxation is established in a knee, progressive articular cartilage loss and joint space narrowing occurs. Only a longitudinal study will resolve whether meniscal subluxation causes joint space narrowing. Our findings are relevant to OA research, in part, because radiographic joint space narrowing is a central outcome measure in ongoing clinical trials in OA and used routinely in clinical practice. Some of the progressive joint space narrowing in these longitudinal studies may be due to meniscal subluxation and not necessarily hyaline cartilage loss. By design, this study included subjects as controls regardless of their radiographic OA status, based only on their asymptomatic state. This design permitted us to evaluate the association of subluxation with knee symptoms (cases vs. controls) and with structured OA (controls with and without X-ray OA). In controls with radiographic joint space narrowing, subluxation was common, but in controls without radiographic narrowing, severe subluxation was rare. This suggests that subluxation is associated with the development of structural osteoarthritis and does not necessarily induce symptoms in those with structural OA. A model for understanding the impact of meniscal subluxation on the development of OA can be derived from the effect of complete meniscectomy. Following complete meniscectomy, the contact area between the tibia and femur, over which compressive stress is distributed decreases by approximately 40% The contact area and the contact stress experienced by the articular cartilage are inversely proportional. Without the energy absorbing function of the meniscus, the markedly increased contact contributes significantly to articular cartilage loss as well as remodeling of bone. 20 Following complete meniscectomy there is also loss of stability within the knee joint, which may contribute to the accelerated osteoarthritis in patients with a history of complete meniscectomy. We hypothesize that with increasing meniscal subluxation, there may be increasing contact stress on the articular cartilage of the femur and tibia. We are unable to suggest a threshold that represents pathologic subluxation and suggest, for the time being, measurement on a continuum. Joint space narrowing on weight bearing radiographs has usually been ascribed to loss of articular cartilage. Experimentally, a normal meniscus compresses only 1 2 mm in height while under load. Therefore, meniscal compression contributes little to the appearance of joint space narrowing. It is possible, however, that progressive loss of meniscal volume within the joint space leads to articular cartilage wear, and that these two factors in combination account for the radiographic appearance of joint space narrowing. We suspect that early joint space narrowing may be due more to loss of meniscal height secondary to subluxation than to articular cartilage loss, especially in the periphery of the joint where hyaline cartilage is the thinnest and meniscus the thickest. This hypothesis is supported by the observation that only 15% of the controls with less than 3-mm meniscal subluxation demonstrated joint space narrowing. The type and degree of anatomic derangement necessary to permit significant medio-lateral meniscal subluxation is uncertain. The attachments of the meniscus to the surrounding bone and soft tissues are complex and probably contribute to the relative lack of significant subluxation in normals. For the medial meniscus, these include anterior and posterior attachments to the tibia, attachments to the medial collateral ligament, and to the coronary ligament. For the meniscus to translocate, there are probably several anatomic conditions necessary including laxity in the medial collateral ligament and possibly other meniscal attachments. Perhaps just as important as the surrounding soft tissues for the stability of the meniscus is the intrinsic structure of the meniscus. Circumferentially oriented collagen fibers in the meniscus provide significant resistance to hoop stress. The hoop stresses found within the meniscus counteract the compressive forces generated on the meniscus by the tibia and femur and the resultant tendency to radial meniscal displacement. A single cut or tear to the radial edge of the meniscus eliminates these hoop stresses and contributes to medio-lateral subluxation of the meniscus. 18 Many subjects with significant meniscal subluxation may have either radial tears or equivalent, specifically sufficient degenerative change within their meniscus that the circumferentially oriented collagen is disrupted. There are several limitations to the present study. First, as indicated above, the cross sectional nature of this study precludes definitive etiologic inferences. Second, the amount of meniscal subluxation may be underestimated in both cases and controls because the knee MRI exams were non-weight bearing. Third, the direction of meniscal subluxation is not exclusively medial or lateral. Because nearly all the measurements of subluxation were obtained on the anterior half of the coronal images containing the tibial plateau, there may have been a component of anterior subluxation as well. Subluxation was measured on the coronal MR images as opposed to sagittal images because of ease and reproducibility. Fourth, we did not evaluate the anatomic conditions such as joint effusion, meniscal tear or internal derangements that contribute to meniscal subluxation. Lastly, we can not be certain our results are generalizable beyond the veterans population we studied. In conclusion, our data show that meniscal subluxation is a prominent feature of knee OA and contributes to the appearance of joint space narrowing.
7 532 D. R. Gale et al.: Meniscal subluxation and knee osteoarthritis Acknowledgments We are indebted to Karen Iandoli, Sean Johnson, Josh Goldman, Kathleen Becerra, Pam McLeod and Nilsa Carrasquillo for their invaluable help on this project. References 1. Felson DT, Zhang Y. An update on the epidemiology of knee and hip ostoarthritis with a view to prevention. Arthritis Rheum 1998;41: DeHaven KE. The role of the meniscus. In: Ewing JW, Ed. Articular Cartilage and Knee Joint Function: Basic Science and Arthroscopy. New York: Raven Press, Ltd 1990: Jackson JP. Degenerative changes in the knee after meniscectomy. BMJ 1968;2: Neyret P, Donell ST, Dejour H. Osteoarthritis of the knee following meniscectomy. J Rheumatol 1994;33: Buckland-Wright JC, Macfarlane DG, Lynch JA, Jasani MK, Bradshaw CR. Joint space width measures cartilage thickness in osteoarthritis of the knee: high resolution plain film and double contrast macroradiographic investigation. Ann Rheum Dis 1995;54: Ayral X, Dougados M, Listrat V, Bonvarlet JP, Simonnet J, Amor B. Arthroscopic evaluation of chondropathy in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Rheumatol 1996;23: Miller TT, Staron RB, Feldman F, Cepel E. Meniscal position on routine MR imaging of the knee. Skeletal Radiol 1997;26: Tehranzadeh J, Patel T, Mesgarzadeh M. Relationship of the extent of meniscal subluxation of the knee the grade of osteoarthrosis at MR imaging. Radiological Society of North America. 82nd scientific assembly and annual meeting, 12/1 12/6, 1996;abstract: Altman R, Brandt K, Hochberg M, Moskowitz R, Bellamy N, Bloch DA, et al. Design and conduct of clinical trials in patients with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1996;4: Kazis LE, Miller DR, Clark J, Skinner K, Lee A, Rogers W, et al. Health related quality of life in patients served by the Department of Veterans Affairs: Results from the Veterans Health Study. Arch Intern Med 1998;158: Buckland-Wright C. Protocols for precise radioanatomicla positioning of the tibiofemoral and patellofemoral compartments of the knee. Osteoarthritis Cart 1995;3(Suppl A): McAlindon T, Zhang Y, Hannan M, Naimark A, Weissman B, Castelli W. et al. Are risk factors for patellofemoral and tibiofemoral knee osteoarthritis different? J Rheumatol 1996;23: Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstein D, Brandt K, et al. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis: Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 1986;29: Felson DT, McAlindon TE, Anderson JJ, Naimark A, Weissman BW, Aliabadi P, et al. Defining radiographic osteoarthritis for the whole knee. Osteoarthritis Cart 1997;5: Neuhauser KB, Anderson JJ, Felson DT. Rate of joint space (JS) narrowing in normal knees and knees with osteoarthritis (OA). Arthritis Rheum 1994; 37:S Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Atlas of standard radiographs: the epidemiology of chronic rheumatism. Vol. 2. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications Fukubayashi T, Kurosawa H. The contact area and pressure distribution pattern of the knee. Acta Orthop Scand 1980;51: Kurosawa H, Fukubayashi T, Nakajima H. Loadbearing mode of the knee joint: physical behavior of the knee joint with or without menisci. Clin Ortho Rel Res 1980;149: Walker PS, Erkman MJ. The role of the menisci in force transmission across the knee. Clin Ortho Rel Res 1975;109: Grood ES. Meniscal function. Adv Orthop Surg 1984;00:193 7.
The Relationship Between Cartilage Loss on Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Radiographic Progression in Men and Women With Knee Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 10, October 2005, pp 3152 3159 DOI 10.1002/art.21296 2005, American College of Rheumatology The Relationship Between Cartilage Loss on Magnetic Resonance Imaging and
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 10, October 2005, pp 3152 3159 DOI 10.1002/art.21296 2005, American College of Rheumatology The Relationship Between Cartilage Loss on Magnetic Resonance Imaging and
The Association of Meniscal Pathologic Changes With Cartilage Loss in Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 3, March 2006, pp 795 801 DOI 10.1002/art.21724 2006, American College of Rheumatology The Association of Meniscal Pathologic Changes With Cartilage Loss in Symptomatic
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 54, No. 3, March 2006, pp 795 801 DOI 10.1002/art.21724 2006, American College of Rheumatology The Association of Meniscal Pathologic Changes With Cartilage Loss in Symptomatic
BRIEF REPORT. KENNETH D. BRANDT, ROSE S. FIFE, ETHAN M. BRAUNSTEIN, and BARRY KATZ. From the Department of Medicine, the Department of
 1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1402e1407
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1402e1407 Comparison of BLOKS and WORMS scoring systems part II. Longitudinal assessment of knee MRIs for osteoarthritis and suggested approach based on their performance:
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1402e1407 Comparison of BLOKS and WORMS scoring systems part II. Longitudinal assessment of knee MRIs for osteoarthritis and suggested approach based on their performance:
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in the community: definitions and normal joint space
 Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA
 Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
Radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis in a Czech cohort
 Radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis in a Czech cohort K. Pavelka, J. Gatterova, R.D. Altman Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic; Department of Medicine, University of Miami School
Radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis in a Czech cohort K. Pavelka, J. Gatterova, R.D. Altman Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic; Department of Medicine, University of Miami School
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, A19eA31 ª 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2003.09.012 Workshop for Consensus
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, A19eA31 ª 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2003.09.012 Workshop for Consensus
2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 716 724 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00158-4 Precision and accuracy
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 716 724 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00158-4 Precision and accuracy
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, Osteoarthritis Research Society /98/ $12.00/0 Article No.
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, 252 259 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063 4584/98/040252 + 08 $12.00/0 Article No. oc980118 Quantitative evaluation of joint space width in femorotibial osteoarthritis:
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, 252 259 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063 4584/98/040252 + 08 $12.00/0 Article No. oc980118 Quantitative evaluation of joint space width in femorotibial osteoarthritis:
Arthritis & Rheumatism
 ~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN. David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging
 MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
ARTICLE IN PRESS. International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2009) jj, jjjejjj ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2008.11.014 Strong association of
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2009) jj, jjjejjj ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2008.11.014 Strong association of
Table of Contents. Overview Introduction Variables Missing Data Image Type Time Points Reading Methods...
 MULTICENTER OSTEOARTHRITIS STUDY LONGITUDINAL KNEE RADIOGRAPH ASSESSMENTS (BASELINE TO 15-MONTH, 30-MONTH, 60-MONTH AND 84-MONTH FOLLOW-UP) AND MEASUREMENTS FROM BASELINE FULL LIMB RADIOGRAPHS DATASET
MULTICENTER OSTEOARTHRITIS STUDY LONGITUDINAL KNEE RADIOGRAPH ASSESSMENTS (BASELINE TO 15-MONTH, 30-MONTH, 60-MONTH AND 84-MONTH FOLLOW-UP) AND MEASUREMENTS FROM BASELINE FULL LIMB RADIOGRAPHS DATASET
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy, MD 1,2 * ; Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan, MD 1 ; Meir Liebergall, MD 2; Andrew D. Pearle, MD 1 1Hospital for Special Surgery, Weill Medical
Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy, MD 1,2 * ; Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan, MD 1 ; Meir Liebergall, MD 2; Andrew D. Pearle, MD 1 1Hospital for Special Surgery, Weill Medical
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis
 the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi?
 Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi? #$%&' ()"*+!," Philippe Neyret E Servien S Lustig P Verdonk One or more of the authors of the next presentation have identified no potential conflicts of interest 2 Consequences
Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi? #$%&' ()"*+!," Philippe Neyret E Servien S Lustig P Verdonk One or more of the authors of the next presentation have identified no potential conflicts of interest 2 Consequences
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 542 546 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0809,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 542 546 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0809,
Selection of Knee Radiographs for Trials of Structure-Modifying Drugs in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 5, May 2005, pp 1411 1417 DOI 10.1002/art.21024 2005, American College of Rheumatology Selection of Knee Radiographs for Trials of Structure-Modifying Drugs in Patients
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 5, May 2005, pp 1411 1417 DOI 10.1002/art.21024 2005, American College of Rheumatology Selection of Knee Radiographs for Trials of Structure-Modifying Drugs in Patients
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study
 Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Measurement of Radiographic Joint Space Width in the Tibiofemoral Compartment of the Osteoarthritic Knee
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 2, February 2003, pp 378 384 DOI 10.1002/art.10773 2003, American College of Rheumatology Measurement of Radiographic Joint Space Width in the Tibiofemoral Compartment
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 2, February 2003, pp 378 384 DOI 10.1002/art.10773 2003, American College of Rheumatology Measurement of Radiographic Joint Space Width in the Tibiofemoral Compartment
The Meniscus. History. Anatomy. Anatomy. Blood Supply. Attachments
 History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping
 Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Project 15 Test-Retest Reliability of Semi-quantitative Readings from Knee Radiographs
 Project 15 Test-Retest Reliability of Semi-quantitative Readings from Knee Radiographs 1. SAS dataset... 1 2. Purpose and methods... 1 2.1 Background... 1 2.2 Reliability at single time points... 1 2.3
Project 15 Test-Retest Reliability of Semi-quantitative Readings from Knee Radiographs 1. SAS dataset... 1 2. Purpose and methods... 1 2.1 Background... 1 2.2 Reliability at single time points... 1 2.3
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1393e1401
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1393e1401 Comparison of BLOKS and scoring systems part I. Cross sectional comparison of methods to assess cartilage morphology, meniscal damage and bone marrow lesions
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1393e1401 Comparison of BLOKS and scoring systems part I. Cross sectional comparison of methods to assess cartilage morphology, meniscal damage and bone marrow lesions
OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1993) 1, 209-218 O 1993 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584193/040209 + 10 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Precision of joint space width measurement in knee osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1993) 1, 209-218 O 1993 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584193/040209 + 10 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Precision of joint space width measurement in knee osteoarthritis
Keywords Osteoarthritis; Knee; Pathology; Biopsy
 Carlos Antônio Garrido 1, Tania Clarete Fonseca Vieira Sales Sampaio 2, Frederico de Souza Ferreira 3 Objectives: To compare the modified Ahlbäck radiological classification with macroscopic analysis of
Carlos Antônio Garrido 1, Tania Clarete Fonseca Vieira Sales Sampaio 2, Frederico de Souza Ferreira 3 Objectives: To compare the modified Ahlbäck radiological classification with macroscopic analysis of
Epidemiology. Meniscal Injury & Repair. Meniscus Anatomy. Meniscus Anatomy
 Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Epidemiology 60-70/100,000 per year Meniscal Injury & Repair Arthroscopic Mensiscectomy One of the most common orthopaedic procedures 20% of all surgeries at some centers Male:Female ratio - 2-4:1 Younger
Sonographic Imaging of Meniscal Subluxation in Patients with Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sonographic Imaging of Meniscal Subluxation in Patients with Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis Chun-Hung Ko, 1 Kam-Kong Chan, 1 Hui-Ling Peng 2 Background/Purpose: This study was undertaken
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sonographic Imaging of Meniscal Subluxation in Patients with Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis Chun-Hung Ko, 1 Kam-Kong Chan, 1 Hui-Ling Peng 2 Background/Purpose: This study was undertaken
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study
 Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
T he goals of medical management of patients with
 1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair?
 Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair? Jack M. Bert, MD Adjunct Clinical Professor University of Minnesota Minnesota Bone & Joint Specialists, Ltd St. Paul, Minnesota Disclosures
Is Meniscectomy such a bad thing compared to meniscal repair? Jack M. Bert, MD Adjunct Clinical Professor University of Minnesota Minnesota Bone & Joint Specialists, Ltd St. Paul, Minnesota Disclosures
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs
 Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Disclosures. Background. Background
 Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
O steoarthritis is a joint disorder rated among the top 10
 1721 EXTENDED REPORT Patellofemoral osteoarthritis coexistent with tibiofemoral osteoarthritis in a meniscectomy population M Englund, L S Lohmander... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
1721 EXTENDED REPORT Patellofemoral osteoarthritis coexistent with tibiofemoral osteoarthritis in a meniscectomy population M Englund, L S Lohmander... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
Incidental Meniscal Findings on Knee MRI in Middle-Aged and Elderly Persons
 The new england journal of medicine original article Incidental Meniscal Findings on Knee MRI in Middle-Aged and Elderly Persons Martin Englund, M.D., Ph.D., Ali Guermazi, M.D., Daniel Gale, M.D., David
The new england journal of medicine original article Incidental Meniscal Findings on Knee MRI in Middle-Aged and Elderly Persons Martin Englund, M.D., Ph.D., Ali Guermazi, M.D., Daniel Gale, M.D., David
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty
 Rheumatology 2002;41:142 147 Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty J. F. Maillefert 1,4,A.Gueguen
Rheumatology 2002;41:142 147 Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty J. F. Maillefert 1,4,A.Gueguen
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques
 Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis Classification of Knee Arthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis of Knee
 1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
BASELINE QUESTIONNAIRE (SURGEON)
 SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
(Alternate title) Evaluation of Meniscal Extrusion with Posterior Root Disruption and Repair using Ultrasound
 Evaluation of lateral meniscal position with weight bearing: Ultrasonography to measure extrusion with intact, torn and repaired posterior root attachments (Alternate title) Evaluation of Meniscal Extrusion
Evaluation of lateral meniscal position with weight bearing: Ultrasonography to measure extrusion with intact, torn and repaired posterior root attachments (Alternate title) Evaluation of Meniscal Extrusion
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life
 Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
Dimensions of the intercondylar notch and the distal femur throughout life Poster No.: P-0089 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Hirtler, S. Röhrich, F. Kainberger; Vienna/AT Keywords:
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 361 369 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00049-9 Assessment
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 361 369 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00049-9 Assessment
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
 Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
Anterior Tibial Translation Sign: Factors Affecting Interpretation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 1): S57-S62 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Numphung
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
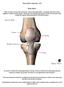 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Influence of Posterior Tibial Slope & Meniscal Tears on Preoperative Laxity in ACL-Deficient Knees
 Influence of Posterior Tibial Slope & Meniscal Tears on Preoperative Laxity in ACL-Deficient Knees Guillaume DEMEY, David DEJOUR, Marco PUNGITORE M. VALOROSO, G. LA BARBERA, S. PASQUALOTTO, J. VALLUY,
Influence of Posterior Tibial Slope & Meniscal Tears on Preoperative Laxity in ACL-Deficient Knees Guillaume DEMEY, David DEJOUR, Marco PUNGITORE M. VALOROSO, G. LA BARBERA, S. PASQUALOTTO, J. VALLUY,
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Association of Squatting With Increased Prevalence of Radiographic Tibiofemoral Knee Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 4, April 2004, pp 1187 1192 DOI 10.1002/art.20127 2004, American College of Rheumatology Association of Squatting With Increased Prevalence of Radiographic Tibiofemoral
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 4, April 2004, pp 1187 1192 DOI 10.1002/art.20127 2004, American College of Rheumatology Association of Squatting With Increased Prevalence of Radiographic Tibiofemoral
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
International Cartilage Repair Society. Introduction. Performance metrics
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, A4eA9 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.02.020 International Cartilage
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, A4eA9 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.02.020 International Cartilage
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Key Indexing Terms: KNEE ALIGNMENT OSTEOARTHRITIS CARTILAGE VOLUME CHONDRAL DEFECTS
 A Longitudinal Study of the Association Between Knee Alignment and Change in Cartilage Volume and Chondral Defects in a Largely Non-Osteoarthritic Population GUANGJU ZHAI, CHANGHAI DING, FLAVIA CICUTTINI,
A Longitudinal Study of the Association Between Knee Alignment and Change in Cartilage Volume and Chondral Defects in a Largely Non-Osteoarthritic Population GUANGJU ZHAI, CHANGHAI DING, FLAVIA CICUTTINI,
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Biomechanics of the Knee. Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital
 Biomechanics of the Knee Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital Knee Biomechanics Kinematics Range of Motion Joint Motion Kinetics Knee Stabilisers Joint Forces Axes The Mechanical Stresses to which
Biomechanics of the Knee Valerie Nuñez SpR Frimley Park Hospital Knee Biomechanics Kinematics Range of Motion Joint Motion Kinetics Knee Stabilisers Joint Forces Axes The Mechanical Stresses to which
Cartilage Repair Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Safety, feasibility, and radiographic outcomes of the anterior meniscal takedown technique to approach chondral defects on the tibia and posterior femoral
Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Safety, feasibility, and radiographic outcomes of the anterior meniscal takedown technique to approach chondral defects on the tibia and posterior femoral
W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco
 Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
Knee Pain And Injuries In Adults W. Dilworth Cannon, M.D. Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University of California San Francisco Pain Control Overview Narcotics rarely necessary after 1 st 1-2
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, Osteoarthritis Research Society /95/ $08.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
O steoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent form of
 319 EXTENDED REPORT Characterisation of size and direction of in knee osteoarthritis: a radiographic study Y Nagaosa, P Lanyon, M Doherty... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
319 EXTENDED REPORT Characterisation of size and direction of in knee osteoarthritis: a radiographic study Y Nagaosa, P Lanyon, M Doherty... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Treatment of meniscal lesions and isolated lesions of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Treatment of meniscal s and isolated s of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults June 2008 AIM OF THE GUIDELINES To encourage good practices in the areas of meniscal
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE Treatment of meniscal s and isolated s of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee in adults June 2008 AIM OF THE GUIDELINES To encourage good practices in the areas of meniscal
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective
 On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
On Field Assessment and Management of Acute Knee Injuries: A Physiotherapist s Perspective Jessica Condliffe Physiotherapist / Clinic Manager TBI Health Wellington Presentation Outline Knee anatomy review
The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment
 The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment Focus on the Meniscus Dr. Alvin J. Detterline, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Towson Orthopaedic Associates University of Maryland St. Joseph Medical
The Impact of Age on Knee Injury Treatment Focus on the Meniscus Dr. Alvin J. Detterline, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Towson Orthopaedic Associates University of Maryland St. Joseph Medical
Impact of Type of Meniscal Tear on Radiographic and Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 8, August 2003, pp 2178 2187 DOI 10.1002/art.11088 2003, American College of Rheumatology Impact of Type of Meniscal Tear on Radiographic and Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 8, August 2003, pp 2178 2187 DOI 10.1002/art.11088 2003, American College of Rheumatology Impact of Type of Meniscal Tear on Radiographic and Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2012) 43(S2), S68 S72. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Injury
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2012) 43(S2), S68 S72 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Injury journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/injury There is no relation between mild malalignment
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2012) 43(S2), S68 S72 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Injury journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/injury There is no relation between mild malalignment
Prospective evaluation of the McMurray test PETER J. EVANS,* MD, PhD, G. DOUGLAS BELL, MD, FRCS(C), AND CY FRANK, MD, FRCS(C)
 Prospective evaluation of the McMurray test PETER J. EVANS,* MD, PhD, G. DOUGLAS BELL, MD, FRCS(C), AND CY FRANK, MD, FRCS(C) From the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sport Medicine Centre, University
Prospective evaluation of the McMurray test PETER J. EVANS,* MD, PhD, G. DOUGLAS BELL, MD, FRCS(C), AND CY FRANK, MD, FRCS(C) From the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sport Medicine Centre, University
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 1081e1085 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.011 MRI of bone marrow
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 1081e1085 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.011 MRI of bone marrow
SCALENE ASIA PACIFIC SDN BHD ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN TREATMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE JOINT
 SCALENE ASIA PACIFIC SDN BHD ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN TREATMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE JOINT ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN
SCALENE ASIA PACIFIC SDN BHD ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN TREATMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE JOINT ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 849 854 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0840,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 849 854 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. 1063 4584/02/$35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2002.0840,
Patella position in the trochlea groove: comparison between supine and standing radiographs
 Patella position in the trochlea groove: comparison between supine and standing radiographs Award: Winner Poster No.: P-0098 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster N. Skou,
Patella position in the trochlea groove: comparison between supine and standing radiographs Award: Winner Poster No.: P-0098 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster N. Skou,
