arthritis.org Arthritis Answers Symptoms, treatment, prevention and risk
|
|
|
- Mabel Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 arthritis.org Arthritis Answers Symptoms, treatment, prevention and risk
2 Is It Arthritis? Chances are you or someone you know has arthritis or a related condition. Fifty million Americans, or one in five people, have been told by their doctors that they have arthritis. It affects people of all ages, including children. Arthritis and related conditions can cause pain, stiffness and swelling in or around joints. This can make it difficult to do normal everyday activities. Arthritis is usually chronic, meaning that it lasts a long time. For many people, it does not go away. But there are things you can do now to avoid arthritis or to reduce pain and keep moving. Warning Signs Pain from arthritis can be ongoing or can come and go. It may occur when you re moving or after you have been still for some time. You may feel pain in one spot or in many parts of your body. Your joints may feel stiff and be hard to move. You may find that it is hard to do daily tasks you used to do easily, such as climbing stairs or opening a jar. Pain and stiffness usually will be worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity. In some types of arthritis, the skin over the joint may appear swollen and red, and feel warm to the touch. With some types of arthritis, you may have fatigue, a poor appetite or fever. If you have any of these signs for more than two weeks, see your doctor. These symptoms can develop suddenly or slowly. Causes There are more than 100 types of arthritis and related conditions. The cause of most types of arthritis is unknown. Scientists are studying several major factors that are thought to be important in arthritis. These factors include: genetic factors that you inherit from your parents; the role of inflammation and the immune system in causing joint damage; and lifestyle factors, including injury to joints. The importance of these factors varies, depending on the type of arthritis. Warning signs of arthritis Pain Stiffness Occasional swelling and/or tenderness Difficulty moving a joint Redness around a joint 2 3
3 How Is Arthritis Diagnosed? It s important to find out what type of arthritis you have because treatments are different for the various types of arthritis. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to help slow or prevent damage to joints that can occur during the first few years with several types of arthritis. Your primary-care doctor will likely tell you that it is important that you see a rheumatologist (rooma-tahl-o-jist), a physician who specializes in diagnosis and treatment of arthritis and related conditions. See page 18 for more about rheumatologists. To find a rheumatologist in your area, visit the American College of Rheumatology s Web site, and click on Find a Member. When you see your doctor for the first time about your joint pain, expect at least three things to hap- What to tell your doctor You can help your doctor by writing down the answers to the following points before your appointment. Bring your answers when you see your doctor. Where it hurts When it hurts When it first began to hurt How long it has hurt If you have any swelling What daily tasks are hard to do now If you have ever hurt the joint in an accident or overused it on the job or in a hobby or sport If anyone in your family has had similar problems What your doctor should tell you? When you go to your doctor to get a diagnosis there are a few things you should learn. If you have arthritis or a related condition What type of arthritis it is What to expect What you can do about it pen before you get an arthritis diagnosis: First, your doctor will talk to you about your symptoms and medical history. Next, your doctor will conduct a physical examination. Finally, your doctor may order X-rays and laboratory tests. Your doctor will examine your joints to check for swelling and tender points, to see what movements cause pain, and to see if joints move through their normal ranges of motion. Your doctor also will check for other signs that may be found in some forms of arthritis including skin rashes, mouth sores, muscle weakness, eye problems or involvement of internal organs, such as the heart or lungs. Your doctor also may do some laboratory tests. These may include tests of your blood, urine or joint fluid. The doctor also may order X-rays of your joints. The results from your medical history, physical exam and tests help your doctor match your symptoms to the pattern of a specific disease or rule out other diseases. Symptoms for some types of arthritis develop slowly and may appear similar to other types in early stages. It may take several visits before your doctor can tell what type of arthritis you have. 4 5
4 Assess Your Joint Health Only a doctor can diagnose arthritis. However, by asking yourself the following questions you may be able to get a better idea of your joint health. What s Your Risk? [Circle or. Please answer each question the best you can.] 1. Are you 45 years of age or older? What Are Your Symptoms? [Circle or. Please answer each question the best you can.] 6. Has a doctor ever told you that you have arthritis? 7. During the past 12 months, have you had pain, aching, stiffness or swelling in or around a joint? 2. Have you ever had an injury to your knee severe enough to put you in bed; to force you to use a cane, crutch or brace; or to require surgery? 3. Are you more than 10 pounds ove weight? 4. Have you in the past, or do you currently, participate in greater than 3 hours per day of heavy physical activities, such as bending, lifting, or carrying items on a regular basis? 5. Did you have hip problems that caused you to limp as a child? 8. In a typical month, were these symptoms present daily for at least half of the days in that month? 9. Do you have pain in your knee or hip when climbing stairs or walking 2-3 blocks (1/4 mile) on flat ground? 10. Do you have daily pain or stiffness in your hand joints? 11. Are you now limited in any way in any activities because of joint symptoms (pain, aching, stiffness, loss of motion)? 6 7
5 12. Because of joint symptoms, rate your ability to do the following: 0 - Without ANY Difficulty 1 - With SOME Difficulty 2 - With MUCH Difficulty 3 - UNABLE To Do a. Dress yourself, including shoelaces and buttons? b. Stand up from an armless, straight chair? c. Get in and out of a car? d. Open a car door? If you answered yes to any of questions 1-5, you are at risk for arthritis. If you answered yes to two or more of questions 6-11, you might have symptoms of arthritis. *Please add the numbers shown next to each of your answers for question 12 (a+b+c+d). If you scored a 6 or more on question 12, you will likely benefit from seeing your health-care professional and should consider calling for an evaluation. Discuss your symptoms with your health-care professional at your next appointment. If you re given a diagnosis of arthritis or a related condition, there s still good news. You can do something to help take control of your arthritis. Contact your local Arthritis Foundation office or visit the Arthritis Foundation s Web site, to learn more about how you can live successfully with arthritis. Can You Prevent Arthritis? There are steps you can take to reduce your risk for getting certain types of arthritis or to reduce disability if you already have arthritis. Prevention of Arthritis It is important to stay at your recommended weight, especially as you get older. People who are overweight are more at risk for osteoarthritis (OA), the most common form of arthritis. Extra weight increases your risk for getting OA in the knees, and possibly in the hips. This is especially true for women. What if you re already overweight? Research shows that middle-aged and older women of average height who lose 11 pounds or more will decrease the risk of developing knee OA by half over time. To lose weight, exercise, eat foods low in calories and control the amount of food you eat. If you re having trouble with weight control, ask your doctor or a registered dietitian for help. Joint injuries caused by accidents, injuries or overuse can increase your risk for OA. Keeping the muscles around joints strong especially the thigh muscles that support the knee will help prevent injury. If You Have Arthritis What can you do to maintain your independence if you already have arthritis? Studies show that exercise helps reduce the pain and fatigue of many different kinds of arthritis and related diseases. Exercise keeps you moving, working and doing daily activities that help you remain independent. Read the Physical Activity section on page 23 of this booklet for tips to help you start or maintain an exercise program. 8 9
6 Which Type of Arthritis Do You Have? There are more than 100 types of arthritis and related conditions, so it is important to know which type of arthritis or related disease you have so it can be treated properly. If you don t know which type you have, make an appointment with your doctor or ask during your next visit. Arthritis most often affects areas in or around joints. Joints are where bones meet, such as your knee. The ends of the bones are covered by cartilage, a spongy material that keeps bones from rubbing together. The joint is enclosed in a capsule and lined with tissue called the synovium. This lining releases a slippery fluid that helps the joint move smoothly and easily. Muscles and tendons support the joint and help you move. Different types of arthritis can affect one or more parts of a joint to produce pain and swelling, and limit use of the joint. Certain types of arthritis also can affect other parts of the body, such as the skin, eyes, mouth and internal organs (such as the heart, lungs or kidneys). Some common types of arthritis and related conditions are described on the following pages. Osteoarthritis The most common type of arthritis is osteoarthritis (ah-stee-oh-ar-thry-tis), or OA. OA affects about 27 million Americans. OA is sometimes called degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease because it causes the breakdown of cartilage and bones over time, causing pain and stiffness. OA usually affects the fingers and weightbearing joints, including the knees, hips, back and neck, but can affect other joints and the hands. It affects both men and women and usually occurs after age 44. Treatments for OA include medication, exercise, heat or cold, joint protection, pacing activities, weight loss if overweight, self-care skills and sometimes surgery. Rheumatoid Arthritis In rheumatoid arthritis (ROO-ma-toyd ar- THRY-tis), or RA, an abnormality in the body s immune system is associated with inflammation of the joints. However, the exact cause of the disease is unknown. Inflammation begins in the joint lining (synovium) and, over time, leads to damage Bone Muscle Bursa Tendon Cartilage Destruction Joint Capsule Synovial Membrane Synovial Fluid Cartilage Bone Bone Spur Different types of arthritis can affect different parts of a joint. Joint with osteoarthritis 10 11
7 of both cartilage and bone. Rheumatoid arthritis often affects the same joints on both sides of the body. Hands, wrists, feet, knees, ankles, shoulders, neck, jaw and elbows can all have arthritis in them. RA affects about 1.5 million Americans and is more common in women than in men. Treatments include medications, exercise, rest, joint protection, pacing activites, self-management skills and sometimes surgery. Fibromyalgia In contrast to arthritis which is a disease of the joints, fibromyalgia does not affect joints but instead is a condition that involves pain in the muscles and soft tissues. Fibromyalgia (fy-bro-my- AL-ja) causes widespread pain and pain at distinct tender points. These are places on the body that are highly sensitive to touch and produce pain. People with fibromyalgia often have fatigue, Some of the tender points that are common in fi bromyalgia Neck Jaw Ankles Toes Some of the joints that may be affected by RA Shoulders Knees Elbows Hips Wrists Fingers disturbed sleep, low mood and stiffness. Fibromyalgia is a common condition that usually affects women. It does not cause muscle or joint damage. Treatments include exercise, antidepressants, tender point injections, muscle relaxants, pacing your activities and self-management skills. Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (ah-stee-oh-po-ro-sis) is one of the most common diseases related to arthritis. It causes bone to lose mass and become thin and brittle. This can lead to painful fractures, rounded shoulders and loss of height. It does not directly affect the joints as arthritis does. Osteoporosis affects or will affect more than 40 million Americans, most of whom are women. It is the major cause of bone fractures in postmenopausal women and senior citizens, including men. People with some forms of arthritis (such as 12 13
8 Lupus occurs more often in African Americans than in Caucasians, and also may occur more frequently in Asian and Latino populations. Treatments include taking medications to reduce inflammation or to reduce the immune system s activity, balancing rest with exercise and eating a proper diet. rmal bone Bone with osteoporosis Osteoporosis makes bones less dense and more susceptible to fractures. rheumatoid arthritis or lupus) also are at risk for developing osteoporosis because certain medications called corticosteroids (such as prednisone) can cause osteoporosis. Many of the steps that you can take to prevent osteoporosis also can help treat it. These steps include increasing calcium and vitamin D intake, taking medication to reduce bone loss, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Your doctor can help determine which treatments are best for you. Lupus Lupus is a disease that affects the skin and joints. In some people, lupus also affects the internal organs such as the kidneys, lungs or heart. Lupus affects women about eight to 10 times more often than men. Symptoms often first appear in women between ages 18 and 45. Some of the common symptoms include: A rash over the cheeks and across the bridge of the nose Scaly, disc-shaped sores on the face, neck and/or chest Gout Gout occurs when the body produces too much of a substance called uric acid. Gout also happens when your body can t get rid of uric acid. This leads to high levels of uric acid in the blood, which may lead to the formation of uric acid crystals in a joint, which causes severe pain and swelling. Certain foods such as sardines, anchovies and organ meats, and alcohol, especially beer, also can raise the body s uric acid level. Gout most commonly affects the big toes, ankles and knees. However, gout can develop in any joint. More men than women have gout. Treatments include anti-inflammatory and special gout drugs, weight loss if overweight, and limiting alcohol intake. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 8 million people in the United States have gout. rmal joint Uric acid crystals 14 Abnormal sun sensitivity Kidney problems Joint with gout compared with a normal joint 15
9 Low Back Pain Low back pain can be caused by a back strain or injury, or by certain types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Treatments include pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs, exercise, heat or cold, joint protection, weight loss if overweight, pacing activities and self-management skills. In addition, complementary therapies, such as yoga, acupuncture, massage and chiropractic treatment have been suggested as helpful. Bursitis and Tendinitis Bursitis and tendinitis may be caused by irritation from injuring or overusing a joint, but in many cases, occurs without a known cause. Bursitis affects a small sac called the bursa that helps cushion the muscles and tendons surrounding a joint. Tendinitis affects the tendons that attach muscle to bone. (See the illustration of a normal joint on page 10 to see where tendons and bursae are located.) Treatments include anti-inflammatory drugs, injections, heat or cold, and rest. Polymyalgia Rheumatica Polymyalgia rheumatica causes pain and stiffness in the neck, shoulders and hips. The pain and stiffness are caused by inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. Treatments include medication, exercise and rest. Other Forms of Arthritis There are many more types of arthritis and related conditions including vasculitis, scleroderma, juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and psoriatic arthritis. Contact the Arthritis Foundation at or for free, single copies of brochures on these diseases and other topics such as medication and lifestyle management. Who Will Treat You? Part of your treatment plan may involve working with health-care specialists such as those listed below. Family physicians, primary-care physicians, general practitioners, internists and pediatricians provide general medical care for adults and for children with different types of arthritis. These doctors also can help you find a specialist. Rheumatologists are specialists who treat people with arthritis and related diseases. Your primarycare doctor may refer you to this kind of specialist. Most rheumatologists are internists who have had two to three years of additional training in the care of people with arthritis and related diseases. Pediatric rheumatologists are specialists in the diagnosis and treatment of children with arthritis and related diseases. Most pediatric rheumatologists are pediatricians who have advanced training in the care of children with arthritis and related diseases. Orthopaedic surgeons have specialized training in performing surgery on the bones, joints, muscles and other parts of the musculoskeletal system. You would see an orthopaedic surgeon if you are considering a surgical procedure, such as joint replacement. Physiatrists, or medical doctors in physical medicine, physical therapists and exercise physiologists can guide your physical therapy and rehabilitation and show you exercises to help keep your muscles strong and joints flexible. Occupational therapists can teach you how to reduce strain on your joints while doing everyday activities. They can also fit you with splints and other devices to help reduce stress on your joints
10 Podiatrists are experts in foot care. If arthritis affects your feet, a podiatrist can prescribe special supports and shoes. Podiatrists also perform foot surgeries to correct foot abnormalities. Psychiatrists and psychologists can help you manage the emotional and mental distress related to your disease. Psychiatrists can prescribe medications for mood disorders that can be associated with chronic diseases. Psychologists can help you develop coping skills to maximize your life as your manage your arthritis. Ophthalmologists provide eye care and treatment. Several forms of arthritis or medications used in their treatment may cause eye problems. Once diagnosed you can talk to your doctor about how often you may need to get eye checkups. Pharmacists fill prescriptions for medicines and can explain the drugs actions and side effects. They also can tell you how different medicines work together and answer questions you have about either prescription or over-the-counter medicines. Other health-care specialists you may see include nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, social workers and dietitians. Nurse practitioners and physician assistants can provide prescriptions in most states many work closely with rheumatologists in the management of arthritis and related conditions. What Treatments Work? Before beginning your treatment, your doctor will diagnose which type of arthritis or related condition you have. There are many things that help reduce pain, relieve stiffness and keep you moving. Your care may involve more than one kind of treatment. Your doctor may prescribe medications, but there are many things you can do on your own to help manage pain and fatigue, and move more easily. Finding the right treatment may take time. Be sure to let your doctor know if a treatment is not working. Your treatment may change as your arthritis changes. Treatments for arthritis can be divided into several categories, which are described on the following pages. Medication Many different drugs are used to treat arthritis and related diseases. The ones, you should take will depend on the type of arthritis you have. Some medications are available without a prescription, but others must be prescribed by your doctor. You should always check with your doctor before taking any medication, including over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, and dietary and herbal supplements. Your doctor can tell you how much and when to take any of these for best relief. The doctor can also tell you how to avoid drug-related problems. nsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduce pain and swelling. Some NSAIDs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) and naproxen (Aleve), are available without a prescription. Others are available by only prescription. The most common side effect of these medications is stomach upset. Call your doctor if you have continuous stomach pain. NSAIDs can carry a risk of stomach ulcers 18 19
11 and bleeding. A subcategory of NSAIDs, called COX-2 inhibitors, was designed to be safer for the stomach. Both traditional NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors carry a warning that they may increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Talk to your doctor about risks before making a decision to take any medications. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone and cortisone, may be prescribed to reduce severe pain and inflammation. They are available only by prescription. They may be given in pill form or by injection into the joint or soft tissues around the joint, the muscle, or into a vein. Joint injections can bring quick relief for many forms of arthritis, but they should be used carefully because in some patients they may weaken bone, tendons and cartilage. Your doctor will carefully monitor you for side effects. Analgesics are prescribed for pain relief. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is a non-opiate analgesic commonly used for the treatment of mild to moderate pain. Opiate analgesics, including codeine, may be used for more severe forms of arthritis pain. Analgesics do not reduce the inflammation or swelling that can be associated with some forms of arthritis, but they are helpful when pain is the main problem. They are generally considered to be safer than NSAIDs for most people. Topical treatments such as ointments, creams and rubs that contain counterirritants, like Capsicum (capsaicin), or anti-inflammatory medications that can be used on the skin may provide pain relief. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist for more information. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) slow down the disease process and limit joint damage in RA and some other types of inflammatory arthritis. These medications include methotrexate, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, cyclosporine, azathioprine and penicillamine. They are available only by prescription and may take several weeks or months to work. Your doctor will carefully monitor you for side effects from taking these powerful drugs. Biologic response modifiers (BRMs), are drugs that help reduce pain and inflammation, increase physical function and slow the progression of or halt disease, especially rheumatoid arthritis and some other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), anakinra (Kineret), adalimumab (Humira), golimumab (Simponi) certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) and tocilizumab (Actemra) do this by blocking the action of cytokines that are part of the immune system. There are also two medications approved for use in people who have not found relief from other treatments. They are also effective in slowing the disease process. Abatacept (Orencia) works by blocking one of the signals by which immune cells talk to each other, and thereby can modulate or break the cellular connections that may lead to inflammation, autoimmune responses and joint damage. Rituximab (Rituxan) works by depleting or getting rid of some immune cells in the blood. It looks for certain B cells. In a normal immune system, B cells usually help the body fight infection but may also be involved in the joint inflammation that occurs in RA. Talk with your doctor to learn more about biologics. Sleep medications may help you sleep better and help your muscles relax. These drugs may be used to help people with fibromyalgia sleep better. They are available by prescription and are used at bedtime in a low dose, but taking them long-term should be avoided. Antidepressants such as amitriptyline hydrochloride (Elavil), trazadone, escitalopram oxalate (Lexapro) are also sometimes used by people with arthritis or related conditions in low doses to relieve pain. They may also be used in higher doses to help with depression that can accompany chronic 20 21
12 disease. Medications such as sertraline (Zoloft) may be used to treat depression associated with rheumatoid arthritis and other chronic diseases. Talk to your doctor for more information on these medications. Physical Activity Being physically active every day can help to keep you moving and independent. It helps lessen pain, increase movement, reduce fatigue, prevent weight gain and helps you look and feel better. People with arthritis should try to be active or exercise at least 30 minutes each day in addition to their everyday activities. Physical therapists and exercise physiologists can assist in designing exercises that minimize joint injury. There are three main types of exercises: 1. Range-of-motion exercises keep your joints flexible by moving them to their fullest extent. You should try to do these exercises daily. 2. Resistance exercises increase or maintain muscle strength and endurance. Strong muscles help keep your joints stable and make them easier to move. Try to do these exercises daily or every other day. 3. Aerobic (endurance) exercises build fitness. They help keep your heart healthy and control your weight. You should do aerobic exercises for a total of 30 minutes, five times a week, at a pace that raises or sustains your heart rate. You can build your endurance by exercising for shorter periods several times a day. Examples of aerobic exercises include walking, swimming and riding a stationary bicycle. Tips for Exercise Exercise at the time of the day when you have less stiffness or pain. Start slowly. Build up the amount of time you exercise and the number of repetitions you do. Exercise at a level that allows you to talk comfortably during the activity. If pain from exercise lasts more than two hours, you may have done too much. Reduce your level of activity next time. Stop exercising right away if you have chest pain, severe dizziness or shortness of breath, or if you feel sick to your stomach. Talk with your doctor before starting a new exercise routine. Heat and Cold Using heat or cold over joints or muscles may give you short-term relief from pain and stiffness. You also can use heat or cold to help prepare for exercise. Heat helps relax aching muscles. Sources of heat include heat packs, hot tubs or heated pools. Don t use heat with rubs or creams because this can cause skin burns. Cold numbs the area so you don t feel as much pain, and can decrease swelling and inflammation. You can apply cold with ice, cold packs or bags of frozen vegetables. It s important to use heat and cold safely. Don t use either treatment for more than 20 minutes at a time. Let your skin return to a normal temperature between applications. Pacing Your Activities Pacing yourself saves energy by switching between periods of activity and periods of rest. Pacing helps protect your joints from the stress of repeated tasks, and helps reduce fatigue. Alternate heavy or repeated tasks with easy ones. Change tasks often so that you don t hold joints in one position for a long time. Plan rest breaks during your daily activities. Joint Protection You can learn to protect your joints by using them in ways that avoid excess stress. Protecting your joints makes it easier to do daily tasks. Your rheumatologist may refer you to an occupational therapist for an assessment of your function and needs
13 Here are three methods of joint protection: 1. Paying attention to joint position means using joints in the best way to avoid excess stress on them. Use larger or stronger joints to carry things. For instance, carry your grocery bags using your forearms or palms instead of your fingers. 2. Using walking or assistive devices can help keep stress off certain joints. Your doctor may suggest using a cane, crutches or a walker to reduce stress on your hips and knees. Many assistive devices have special features to help make tasks easier. Special features, such as extra-thick pens, make them easier to hold. Longer handles and reachers give you better leverage. Lightweight items, such as plastic dishes, are easier to carry than ceramics. 3. Weight control means staying close to your recommended weight, or losing weight if you are overweight now. Weight control helps reduce your risk for developing OA in the knees. If you already have knee OA, losing weight may lessen pain by reducing stress on your joints. Exercising and reducing calories will help you lose weight. If you need to lose a lot of weight, work with your doctor and a registered or licensed dietitian to find the best weight-loss program for you. Complementary Therapies Complementary therapies including supplements (like glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate for people with moderate to severe knee OA pain), vitamins, massage, yoga, acupuncture and more may also provide relief for you. Some of these nonconventional methods have been shown to be helpful for people with arthritis. For more information or alternative therapies, call or go to Be sure to talk with your doctor about any complementary therapy you are taking or thinking about taking. Surgery Most people with arthritis will never need surgery. However, surgery can help in cases when other treatments have failed. It can reduce pain and improve function. Two common types of surgery for people with arthritis are synovectomy and total joint replacement. Synovectomy is the removal of the thickened joint membrane (synovium) that causes damage to joints in inflammatory forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis. Joint replacement replaces the damaged joint with an artificial joint. These procedures are usually effective in relieving pain and helping you maintain activities of daily living. For more information on joint surgery, call or go to for a free copy of the Arthritis Foundation s Surgery and Arthritis brochure. Self-Management Skills Arthritis and related conditions may affect you in different ways, from what you can do to how you look. Daily tasks may be harder or may take longer. You are the best manager of your arthritis. Being a good arthritis manager means understanding your disease and knowing what to expect. It also means planning your activities for when you feel best and learning to work with your doctor as a team. You can help yourself feel better by learning to manage your symptoms and how they affect your daily activities. You also can learn skills to help manage how arthritis affects your emotions and your family. Symptom-management skills use problem-solving methods to help you identify and overcome difficulties with daily tasks. Coping skills can help you manage the changes arthritis and other diseases bring to your life. Speak with your doctor for references for where you can learn such techniques
14 Our goal is to help you: Learn, be inspired and connect. Subscribe to Arthritis Today magazine to get information on everyday life with arthritis, the latest health news, tools to help you chart a winning course and much more. Go to arthritistoday.org/subscribe. The Arthritis Foundation is the Champion of. We lead the fight for the arthritis community and help you conquer your everyday battles through life-changing information and resources, access to optimal care, advancements in science and community connections. Go to or call Contact your local office about resources and events going on where you live. Go to arthritis.org, click the Local Offices tab at the top and enter your ZIP code. Raise funds to conquer arthritis in our annual events, Walk to Cure Arthritis and Jingle Bell Run. Visit arthritis.org/events. Talk about your condition. You re not alone when you connect with our community. Visit arthritis.org/community. Make your voice be heard. Go to arthritis.org/advocate and become an Arthritis Foundation Advocate for better access to health care. Acknowledgements The Arthritis Foundation appreciates the contributions of and reviews by the following: Roy Altman, MD, professor emeritus, Division of Rheumatology, Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles Susan Richmond, MS, PA-C, clinical assistant professor, Bryant University, Smithfield, Rhode Island Scott Zashin, MD, FACP FACR, clinical professor of internal medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Southwestern Medical School, University of Texas, Dallas Additional Review Provided by 2015 Arthritis Foundation. All rights reserved.
15 YOGA DESIGNED FOR YOU! only $24.95 This DVD offers easy-tofollow poses that are gentle on joints to help ease pain, increase strength and flexibility and improve well-being naturally. 60-minute full practice that includes a variety of poses Modifi cation demonstrations for poses to protect joints Sun Salutation and more! Use Promo Code: AFYOGA TO ORDER CALL OR VISIT Engage with the Arthritis Foundation community on Twitter, Facebook, Pinterest and YouTube
Pain or stiffness in joints after periods of inactivity or excessive use
 Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Joint Injuries and Disorders
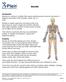
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis
 Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
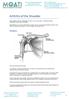
 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in How to Prevent and Treat Aches and Pains. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
Facts About Aging and. Bone Health. A Guide to Better Understanding and Well-Being. This educational information is proudly provided by
 and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well-Being This educational information is proudly provided by Aging The fact is, everyone experiences slow loss of bone strength and bone density throughout
and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well-Being This educational information is proudly provided by Aging The fact is, everyone experiences slow loss of bone strength and bone density throughout
Understanding Arthritis. Training
 Understanding Arthritis Training 1 Learning Objectives At the end of this training the learner will: Be able to define Arthritis Describe the symptoms of Arthritis Understand the impact of Arthritis Know
Understanding Arthritis Training 1 Learning Objectives At the end of this training the learner will: Be able to define Arthritis Describe the symptoms of Arthritis Understand the impact of Arthritis Know
Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA
 Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA Osteoarthritis: What Is It? Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of
Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA Osteoarthritis: What Is It? Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
What Is Back Pain? Fast Facts: An Easy-to-Read Series of Publications for the Public. Who Gets Back Pain? What Are the Causes of Back Pain?
 Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
Arthritis. that affects the joints.
 Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
You may have heard different things from your friends or from family members about arthritis.
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Talk About Arthritis You may have heard different things from your friends or from family members about arthritis. For example, you may
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Talk About Arthritis You may have heard different things from your friends or from family members about arthritis. For example, you may
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options
 Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options Pinnacle Orthopedics Pinnacle Medical Network About Pinnacle Orthopedics and Pinnacle Medical Network South Louisiana s Premier System for the Delivery of Musculoskeletal
Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options Pinnacle Orthopedics Pinnacle Medical Network About Pinnacle Orthopedics and Pinnacle Medical Network South Louisiana s Premier System for the Delivery of Musculoskeletal
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
KEEP UP THE FIGHT WITH. Little Victories
 FOR MODERATE TO SEVERE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) KEEP UP THE FIGHT WITH Little Victories Small improvements in your daily activities may be a sign that ORENCIA (abatacept) is working for you. Use this
FOR MODERATE TO SEVERE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) KEEP UP THE FIGHT WITH Little Victories Small improvements in your daily activities may be a sign that ORENCIA (abatacept) is working for you. Use this
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis What is rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause inflammation of
Rheumatoid Arthritis What is rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause inflammation of
Managing Gout A Review of the Research for Adults
 Managing Gout A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* has said that you have gout. You are age 18 or
Managing Gout A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* has said that you have gout. You are age 18 or
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions
 Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
What Is Back Pain? Can Back Pain Be Prevented? When Should I See a Doctor for Pain? How Is Back Pain Diagnosed?
 What Is Back Pain? Back pain can also occur with some conditions and diseases, such as: Scoliosis Spondylolisthesis Arthritis Spinal stenosis Pregnancy Kidney stones Infections Endometriosis Fibromyalgia.
What Is Back Pain? Back pain can also occur with some conditions and diseases, such as: Scoliosis Spondylolisthesis Arthritis Spinal stenosis Pregnancy Kidney stones Infections Endometriosis Fibromyalgia.
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Arthritis. Healthy Living with Hand & Wrist Arthritis The Orthopedic Specialty Hospital. ARTH + ITIS = Inflammation (Joint) (Inflammation) of joints
 Healthy Living with Hand & Wrist Arthritis The Orthopedic Specialty Hospital Arthritis Causes Diagnosis Medical treatment Surgical treatment Defining Arthritis ARTH + ITIS = Inflammation (Joint) (Inflammation)
Healthy Living with Hand & Wrist Arthritis The Orthopedic Specialty Hospital Arthritis Causes Diagnosis Medical treatment Surgical treatment Defining Arthritis ARTH + ITIS = Inflammation (Joint) (Inflammation)
About diet and arthritis
 About diet and arthritis Yes, the right diet can certainly help some people with arthritis and rheumatism. Recent research has also discovered several new links between arthritis and diet. This article
About diet and arthritis Yes, the right diet can certainly help some people with arthritis and rheumatism. Recent research has also discovered several new links between arthritis and diet. This article
How can I keep my joints healthy?
 Normal Joint (Representation) Muscle Cartilage Tendon Other forms of arthritis may be associated with diseases like lupus (LOO-puhs), fibromyalgia (fibro-my-al-juh), psoriasis (suh-rye-uh-sis), or certain
Normal Joint (Representation) Muscle Cartilage Tendon Other forms of arthritis may be associated with diseases like lupus (LOO-puhs), fibromyalgia (fibro-my-al-juh), psoriasis (suh-rye-uh-sis), or certain
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Arthritis. Canada s most common chronic health condition. About the Arthritis Society
 About the Arthritis Society The Arthritis Society is a national health charity, fueled by donors and volunteers, with a vision to live in a world where people are free from the devastating effects that
About the Arthritis Society The Arthritis Society is a national health charity, fueled by donors and volunteers, with a vision to live in a world where people are free from the devastating effects that
Arthritis. written by Harvard Medical School.
 Arthritis written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org Healthy Joints Your joints are engineering gems. In health, they are strong enough to support your weight, supple enough to let you move about,
Arthritis written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org Healthy Joints Your joints are engineering gems. In health, they are strong enough to support your weight, supple enough to let you move about,
Understanding treatments for knee pain.
 Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
Patient Reference Guide. Osteoarthritis. Care for Adults With Osteoarthritis of the Knee, Hip, or Hand
 Patient Reference Guide Osteoarthritis Care for Adults With Osteoarthritis of the Knee, Hip, or Hand Quality standards outline what high-quality care looks like. They focus on conditions or topics where
Patient Reference Guide Osteoarthritis Care for Adults With Osteoarthritis of the Knee, Hip, or Hand Quality standards outline what high-quality care looks like. They focus on conditions or topics where
o Your healthcare provider should test you for TB before starting CIMZIA.
 Medication Guide CIMZIA (CIM-zee-uh) (certolizumab pegol) lyophilized powder or solution for subcutaneous use Read the Medication Guide that comes with CIMZIA before you start using it, and before each
Medication Guide CIMZIA (CIM-zee-uh) (certolizumab pegol) lyophilized powder or solution for subcutaneous use Read the Medication Guide that comes with CIMZIA before you start using it, and before each
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
JOINT HEALTH. Joints are areas in the body where two or more bones meet. They have the following components:
 JOINT HEALTH Joints are areas in the body where two or more bones meet. They have the following components: Articular Cartilage: tissue covering the surface of a bone at a joint. Cartilage helps reduce
JOINT HEALTH Joints are areas in the body where two or more bones meet. They have the following components: Articular Cartilage: tissue covering the surface of a bone at a joint. Cartilage helps reduce
Arm Injuries and Disorders
 Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arthritis of the Knee
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
Total hip replacement
 Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read this
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read this
Tips for Pain Management
 Tips for Pain Management Going for the 3 Increases: Increase in Health, Increase in Happiness & Increase in Energy Strategies for Success in Health Management By: James J. Messina, Ph.D. What are the medical
Tips for Pain Management Going for the 3 Increases: Increase in Health, Increase in Happiness & Increase in Energy Strategies for Success in Health Management By: James J. Messina, Ph.D. What are the medical
Why is this important for you? Types of arthritis. Information for the public Published: 28 February 2017 nice.org.uk
 Spondyloarthritis in over 16s: diagnosis and management Information for the public Published: 28 February 2017 nice.org.uk Spondyloarthritis: the care you should expect This information explains the care
Spondyloarthritis in over 16s: diagnosis and management Information for the public Published: 28 February 2017 nice.org.uk Spondyloarthritis: the care you should expect This information explains the care
HAQ-II(Health Assessment Questionnaire-II)
 Kathy Karamlou, MD 355 Placentia Ave, suite 208 Newport Beach, CA 92663 949-631-6500 949-631-9700 NAME: DATE: DOB: HAQ-II(Health Assessment Questionnaire-II) We are interested in learning how your illness
Kathy Karamlou, MD 355 Placentia Ave, suite 208 Newport Beach, CA 92663 949-631-6500 949-631-9700 NAME: DATE: DOB: HAQ-II(Health Assessment Questionnaire-II) We are interested in learning how your illness
Helpline No:
 ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION Registered Nonprofit Organisation - No. 002-847 NPO Helpline No: 0861 30 30 30 DRUGS AND ARTHRITIS This information leaflet is published by the Arthritis Foundation as part of our
ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION Registered Nonprofit Organisation - No. 002-847 NPO Helpline No: 0861 30 30 30 DRUGS AND ARTHRITIS This information leaflet is published by the Arthritis Foundation as part of our
Considering Your Non-opioid Options for Pain
 YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Considering Your Non-opioid Options for Pain Self-Care, Chiropractic, Physical Therapy, Acupuncture and Pain Rehabilitation 2 Managing Your Pain: Options Pain If
YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Considering Your Non-opioid Options for Pain Self-Care, Chiropractic, Physical Therapy, Acupuncture and Pain Rehabilitation 2 Managing Your Pain: Options Pain If
Osteoarthritis of the Hands, Fingers and/or Wrists
 Osteoarthritis of the Hands, Fingers and/or Wrists This fact sheet has been written for people whose hands, fingers and/or wrists are affected by osteoarthritis (OA). It provides general information about
Osteoarthritis of the Hands, Fingers and/or Wrists This fact sheet has been written for people whose hands, fingers and/or wrists are affected by osteoarthritis (OA). It provides general information about
SIMPLE Targets of OA Therapy
 SIMPLE Targets of OA Therapy Helping your patient with their osteoarthritis symptoms is SIMPLE. Remember these steps to prevent and treat osteoarthritis. Symptom management (e.g. reduce pain and stiffness)
SIMPLE Targets of OA Therapy Helping your patient with their osteoarthritis symptoms is SIMPLE. Remember these steps to prevent and treat osteoarthritis. Symptom management (e.g. reduce pain and stiffness)
Source: Exercise in Arthritis
 Exercise in Arthritis Regular exercise boosts fitness and helps reverse joint stiffness with RA. Decrease Pain, Increase Energy Exercise more to decrease pain and feel more energetic? Hardly seems possible
Exercise in Arthritis Regular exercise boosts fitness and helps reverse joint stiffness with RA. Decrease Pain, Increase Energy Exercise more to decrease pain and feel more energetic? Hardly seems possible
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Managing your pain
 Managing your pain www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic pain Anxiety and stress can make
Managing your pain www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects one in six New Zealanders over the age of 15 years Arthritis is the most common cause of chronic pain Anxiety and stress can make
About Arthritis
 About Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects more than 530,000 New Zealanders. In fact, it is the greatest cause of disability in this country. Arthritis literally means inflammation
About Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects more than 530,000 New Zealanders. In fact, it is the greatest cause of disability in this country. Arthritis literally means inflammation
PAIN. Headache. enstrual Pain. Low Back Pain. Osteoarthritis. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Sprains and Strains. Taking Care of. Pain of
 Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
November 2016 A Casting Call for My Sprained Wrist Many of us would breathe a sigh of
 A Casting Call for My Sprained Wrist Many of us would breathe a sigh of relief if we heard that our wrist was only sprained instead of broken, and would look forward to a less arduous and painful treatment
A Casting Call for My Sprained Wrist Many of us would breathe a sigh of relief if we heard that our wrist was only sprained instead of broken, and would look forward to a less arduous and painful treatment
Dr. Nuelle Knee Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions
 Dr. Nuelle Knee Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your knee replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These discharge
Dr. Nuelle Knee Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your knee replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These discharge
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe
 Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Lupus. Fast facts. What is lupus? What causes lupus? Who gets lupus?
 Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA
 For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA Lenvatinib (len va' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a capsule that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA Lenvatinib (len va' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a capsule that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
Your Hemophilia A action plan from
 An everyday guide to living with Hemophilia A JOINT POINTS! Get the score on what it takes......to keep your joints in healthy shape. Your Hemophilia A action plan from An everyday guide to living with
An everyday guide to living with Hemophilia A JOINT POINTS! Get the score on what it takes......to keep your joints in healthy shape. Your Hemophilia A action plan from An everyday guide to living with
NECK OWNER S MANUAL. A Guide to the Care of the Neck
 NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
How to Protect Your Joints
 Form: D-5855 How to Protect Your Joints For people with arthritis Arthritis can be painful and make every day activities difficult. This booklet will show you how to protect your joints. This can help
Form: D-5855 How to Protect Your Joints For people with arthritis Arthritis can be painful and make every day activities difficult. This booklet will show you how to protect your joints. This can help
Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES FACTORS THAT INCREASE RISK
 Page Number: 0 Date:13/6/11 Time:20:10:06 Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Low-back strain is an injury to the muscles and tendons of the lower back. These muscles require great force
Page Number: 0 Date:13/6/11 Time:20:10:06 Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Low-back strain is an injury to the muscles and tendons of the lower back. These muscles require great force
Managing Osteoarthritis Pain With Medicines. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Managing Osteoarthritis Pain With Medicines A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Summary Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* said you have osteoarthritis (pronounced ah-stee-oharth-rye-tis). Osteoarthritis
Managing Osteoarthritis Pain With Medicines A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Summary Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* said you have osteoarthritis (pronounced ah-stee-oharth-rye-tis). Osteoarthritis
About Arthritis
 About Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects more than 530,000 New Zealanders. In fact, it is the greatest cause of disability in this country. Arthritis literally means inflammation
About Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz Did you know? Arthritis affects more than 530,000 New Zealanders. In fact, it is the greatest cause of disability in this country. Arthritis literally means inflammation
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
Vibration (i.e., driving a Lack of exercise
 What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
arthritis.org Managing Your Pain Causes of pain and tips for taking control
 arthritis.org Managing Your Pain Causes of pain and tips for taking control 2 About Arthritis Pain Coping with pain can be the hardest part of having arthritis or a related condition. In conditions like
arthritis.org Managing Your Pain Causes of pain and tips for taking control 2 About Arthritis Pain Coping with pain can be the hardest part of having arthritis or a related condition. In conditions like
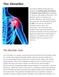
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Mistakes people make. when seeing a doctor for osteoarthritis knee pain.
 5 Mistakes people make when seeing a doctor for osteoarthritis knee pain. Are you sabotaging your own chances for having a successful appointment about your knee pain? Avoid these common mistakes to get
5 Mistakes people make when seeing a doctor for osteoarthritis knee pain. Are you sabotaging your own chances for having a successful appointment about your knee pain? Avoid these common mistakes to get
Keep moving. Self-help and daily living Keep moving. and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis.
 Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
About Arthritis
 About Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz 4298_art_AboutArthritis_flyer_4-0.indd 1 25/11/10 9:45:02 AM Did you know? Arthritis affects more than 530,000 New Zealanders. In fact, it is the greatest cause of
About Arthritis www.arthritis.org.nz 4298_art_AboutArthritis_flyer_4-0.indd 1 25/11/10 9:45:02 AM Did you know? Arthritis affects more than 530,000 New Zealanders. In fact, it is the greatest cause of
When Aimee Bower s feet started hurting during her recreational
 Pain Free at Last Providence rheumatologists provide treatments for the aches of arthritis. Written by DAWN HOFFMAN Photgraphed by MICHAEL NEVEUX When Aimee Bower s feet started hurting during her recreational
Pain Free at Last Providence rheumatologists provide treatments for the aches of arthritis. Written by DAWN HOFFMAN Photgraphed by MICHAEL NEVEUX When Aimee Bower s feet started hurting during her recreational
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is rheumatoid arthritis?...4 Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis... 5 What causes rheumatoid arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is rheumatoid arthritis?...4 Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis... 5 What causes rheumatoid arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family
Issue What is Arthritis?
 Issue 4-17. What is Arthritis? Arthritis is very common but can be very confusing for patients to understand. Arthritis is not a single disease, it is a way of referring to joint pain or joint disease.
Issue 4-17. What is Arthritis? Arthritis is very common but can be very confusing for patients to understand. Arthritis is not a single disease, it is a way of referring to joint pain or joint disease.
Appendix Surgery. (Appendectomy) Your surgery and recovery at home. This booklet belongs to: Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital
 Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO
 neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO Neck pain Neck pain is a common problem. Nearly 25 percent of adults will experience neck pain at some time in their lives. Even though neck problems can be painful and frustrating,
neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO Neck pain Neck pain is a common problem. Nearly 25 percent of adults will experience neck pain at some time in their lives. Even though neck problems can be painful and frustrating,
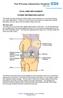
The Shoulder. The Shoulder Joint:
 The Shoulder The board certified physicians and surgeons at Orthopaedic Associates of Central Texas (OACT) are leaders in caring for the joints of the body. The shoulder joint is a complex and dynamic
The Shoulder The board certified physicians and surgeons at Orthopaedic Associates of Central Texas (OACT) are leaders in caring for the joints of the body. The shoulder joint is a complex and dynamic
Exercising with Persistent Pain
 Exercising with Persistent Pain Why You Feel Pain When you are injured, your mind and body react. They protect the weak part of your body, and you feel pain when you try to use it. This protection is important
Exercising with Persistent Pain Why You Feel Pain When you are injured, your mind and body react. They protect the weak part of your body, and you feel pain when you try to use it. This protection is important
A Patient s Guide to Nutraceuticals (Dietary Supplements)
 A Patient s Guide to Nutraceuticals (Dietary Supplements) 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Nutraceuticals (Dietary Supplements) 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
Welcome to Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis or JRA, by Connie Martin, MS, RDN; Claire Stephens, MS, RDN; and Lolita McLean, MPH, RDN...
 Welcome to Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis or JRA, by Connie Martin, MS, RDN; Claire Stephens, MS, RDN; and Lolita McLean, MPH, RDN...all of Alabama s Children s Rehabilitation Service, part of the Alabama
Welcome to Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis or JRA, by Connie Martin, MS, RDN; Claire Stephens, MS, RDN; and Lolita McLean, MPH, RDN...all of Alabama s Children s Rehabilitation Service, part of the Alabama
A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
 TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
OVERCOMING FROZEN SHOULDER
 OVERCOMING FROZEN SHOULDER Treatment to Relieve Pain and Regain Movement When You Have Frozen Shoulder Is your shoulder stiff and painful? If so, you may have frozen shoulder (sometimes called adhesive
OVERCOMING FROZEN SHOULDER Treatment to Relieve Pain and Regain Movement When You Have Frozen Shoulder Is your shoulder stiff and painful? If so, you may have frozen shoulder (sometimes called adhesive
MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you.
 Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is
For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA
 For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA Olaparib (oh lap' a rib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have
For the Patient: Olaparib tablets Other names: LYNPARZA Olaparib (oh lap' a rib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have
Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth.
 For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
Palindromic rheumatism
 1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
Patient Information. Contents. What is regenerative medicine? Is this treatment right for you? Two types of products used
 Patient Information Contents 3 3 4 7 9 10 12 What is regenerative medicine? Is this treatment right for you? Two types of products used Getting ready for your procedure Special instructions Possible side
Patient Information Contents 3 3 4 7 9 10 12 What is regenerative medicine? Is this treatment right for you? Two types of products used Getting ready for your procedure Special instructions Possible side
Osteoarthritis of the Carpometacarpal Thumb Joint
 Appendix 1. Participant s booklet. Osteoarthritis of the Carpometacarpal Thumb Joint Patient Information Booklet Study Coordinator: Sarah Meneses sarah.meneses@sydney.edu.au (02) 9463 1855 For more information
Appendix 1. Participant s booklet. Osteoarthritis of the Carpometacarpal Thumb Joint Patient Information Booklet Study Coordinator: Sarah Meneses sarah.meneses@sydney.edu.au (02) 9463 1855 For more information
Dr. Nuelle Total/Partial Hip Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions
 Dr. Nuelle Total/Partial Hip Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your hip replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These
Dr. Nuelle Total/Partial Hip Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your hip replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These
Athens Rheumatology Clinic, LLC Sana Makhdumi, MD
 Athens Rheumatology Clinic, LLC Sana Makhdumi, MD Phone: 706-850-8322 Fax: 706-850-8322 PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date of first appointment: / / Time of appointment: Birthdate: Name LAST FIRST MIDDLE INITIAL
Athens Rheumatology Clinic, LLC Sana Makhdumi, MD Phone: 706-850-8322 Fax: 706-850-8322 PATIENT HISTORY FORM Date of first appointment: / / Time of appointment: Birthdate: Name LAST FIRST MIDDLE INITIAL
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Are You Living with. Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you.
 Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Back Protection. Training Guide
 Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
April 2016 Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is
 Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is absolutely! After age 40 or so, we all begin to lose muscle strength and bone density, and our hormone production slows. While these factors
Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is absolutely! After age 40 or so, we all begin to lose muscle strength and bone density, and our hormone production slows. While these factors
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA
 For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
caring for your back DURING PREGNANCY
 caring for your back DURING PREGNANCY Low-back pain is common during pregnancy. Your doctor may have told you that you have low-back or lumbar strain, sciatica, and/or sacroiliac pain. Low back pain usually
caring for your back DURING PREGNANCY Low-back pain is common during pregnancy. Your doctor may have told you that you have low-back or lumbar strain, sciatica, and/or sacroiliac pain. Low back pain usually
