The September 3, 2001, cover story of
|
|
|
- Shanna Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EPIDEMIOLOGY, PATHOPHYSIOLOGY, AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION * Linda Kay Myers, MD ABSTRACT Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), the most common form of arthritis in children, is an idiopathic autoimmune disease that affects children worldwide. Early and accurate diagnosis is necessary to effectively treat and minimize the potentially crippling effects of JIA. Recognizing the clinical syndromes of the various types of JIA is essential to achieving the goals of therapy, which include relieving pain and inflammation, reducing joint destruction, restoring physical function and normal growth, and alleviating psychosocial burden on children. (Adv Stud Pharm. 2008;5(6): ) The September 3, 2001, cover story of Newsweek highlighted arthritis, its 21 million American sufferers, its potentially crippling effects, and its complicated treatment. 1 Arthritis, or inflammation of the joint, refers to over 100 rheumatic conditions that may also have systemic effects. The disease is distributed worldwide. Due to physical, economic, and emotional impairment, arthritis should not be minimized, and proper treatment is vital to optimal patient care. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) has been described worldwide in many races and geographic areas and is not a rare disease. Epidemiology data have defined JIA incidence as 9.2 to 13.9 cases per *Based on a presentation by Dr Myers at a roundtable held in San Antonio, Texas, on May 16, Division Chief Pediatric Rheumatology and Professor of Pediatrics, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee. Address correspondence to: Linda Kay Myers, MD, UT Medical Group, Inc., 777 Washington Avenue, Suite P110, Memphis, TN lmyers@utmem.edu. individuals per year and prevalence as 65 to cases per individuals. JIA is the most common form of chronic arthritis in children and one of the most common chronic childhood illnesses, with prevalence numbers rivaling those of diabetes and cystic fibrosis. Its physical impact can cause emotional and financial trauma in both patients and parents. CHARACTERISTICS OF JIA Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, along with adult rheumatoid arthritis (RA), seems to be a relatively modern disease whose exact etiology is unknown. In 1864, the French physician Cornil provided the first detailed description of JIA in a 29-year-old female with chronic arthritis since the age of The English physician Still presented the classic description of childhood arthritis in 1897 with his description of lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, fever, and joint swelling in 12 patients. 3 The term juvenile RA was coined by Coss and Boots in This term was later changed to juvenile arthritis or JIA to reflect its differences from adult RA. Unlike RA, JIA comprises a group of diseases, and it differs from RA in its diagnosis and clinical course. JIA can be difficult to diagnose, because typical RA tests may be unreliable in children. The clinical course of JIA differs from RA, in that the former affects normal growth and development, may have a slower rate of joint damage, and the pauciarticular form may more readily enter into spontaneous remission. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis causes joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased motility. All joints may be affected. Left untreated, JIA can eventually cause joint destruction and deformity, which may cripple physical function and disrupt normal physiological growth (eg, asymmetrical leg bone or toe growth). CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA Juvenile idiopathic arthritis classification criteria define the age of onset to be less than 16 years. 170 Vol. 5, No. 6 September 2008
2 Arthritis must be present in 1 or more joints and is defined as swelling or effusion, or the presence of 2 or more of the following signs: limitation in range of motion, tenderness or pain on motion, and increased heat. Diagnosis is confirmed when the duration of the disease is 6 weeks or longer and when other forms of arthritis are excluded. The highest incidence of JIA occurs between the ages of 1 and 3 years, with the early onset occurring more commonly in girls, but the onset can occur at any age. The 3 types of JIA are classified as polyarticular, pauciarticular, and systemic disease (Table). Polyarticular arthritis tends to be more severe and potentially destructive, particularly if rheumatoid factor is positive. Patients with systemic disease are often hospitalized due to severe symptoms and may receive their initial diagnosis upon hospitalization. In terms of ancillary manifestations (Table), morning stiffness may be present with all types of JIA, whereas rash, fever, and pericarditis tend to occur with systemic arthritis. Table. Classification and Ancillary Manifestations of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Polyarticular Arthritis ( 5 joints) 5 joints 2 subtypes: rheumatoid factor positive or negative Generally symmetric involvement of any joints Typically more severe, destructive form Pauciarticular Arthritis 4 joints Typically early childhood onset (peak between ages 1 and 3) Late-onset group (approximately age 9) More commonly male Occasionally classified as juvenile spondylar arthropathy Generally asymmetric joint involvement Systemic Disease Arthritis with intermittent fever Rash (maculopapular, salmon-pink, or blanching eruption) Enlarged lymph nodes Pleural effusion or pericardial effusion Diagnosis should rule out malignancy or infection Ancillary Manifestations Morning stiffness Cervical spondylitis Rheumatoid rash Rheumatoid nodules Intermittent fever Tenosynovitis Pericarditis Antinuclear antibodies Chronic uveitis Rheumatoid factors CHRONIC UVEITIS Chronic uveitis, or intraocular inflammation of the uvea, is an ancillary manifestation associated with all types of JIA, but is most common with pauciarticular arthritis. Typical ophthalmoscopic features include inflammatory cell migration, asymptomatic bilateral synechiae (scarring), cataracts, and band keratopathy (calcium deposition). High-risk factors for development of this complication include being female, age younger than 6 years, diagnosed with JIA for less than 2 years, and positive for antinuclear antibodies. If chronic uveitis is not treated aggressively, chronic keratitis may occur and lead to blindness. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Synovial fluid analysis of swollen joints is often used to rule out other causes of arthritis. A fluid that appears cloudy and has leukocyte counts greater than 2000 with greater than 50% neutrophils is consistent with an inflammatory-type picture. Additionally, poor mucin clot formation due to partial hyaluronic acid degradation is observed. Cultures and Gram stains should be done to exclude infectious etiologies. The presence of specific human leukocyte antigens (HLA) appears to be associated with JIA. The HLA system resides on chromosome 6 and is essential to immune function. Specifically, the class II antigens (HLA-DR, -DP, and -DQ) appear to be associated with inflammatory diseases, including JIA. The major histocompatibility complex polymorphisms appear to alter the peptide binding sites of the arthritogenic peptides that T cells recognize and, thereby, predispose these individuals to the development of autoimmune disease. The HLA type may also alter the development of pathogenic T-cell repertoires. The HLA-peptide relationship is heterogeneous and varies with the JIA type. Antigen-activated T cells release cytokines that play key roles in pathophysiology (Figure 1). 5 Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α is produced by monocytes, macrophages, B cells, T cells, and fibroblasts and is an important cytokine mediator of the inflammatory cascade. TNF-α stimulates macrophages to produce additional TNF-α and the interleukins IL-1 and IL-6. TNF-α is also a potent stimulator of IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8, which stimulate chondrocytes, osteoclasts, and fibroblasts to release metalloproteinases and, ultimately, lead to the erosion of bone and cartilage. 5-9 In RA and JIA, joint pathogenesis involves inflammation of the synovial lining, with resulting pannus University of Tennessee Advanced Studies in Pharmacy 171
3 Figure 1. Role of Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis T Cell INFLAMMATION Synovial membrane TNF-α MACROPHAGE IL-6 IL-1 TNF-α IL-1 IL-6 IL-8 Chondrocytes INFLAMMATION Pannus Capsule for JIA. Cyclooxygenase-2 specific NSAIDs may be preferred in patients who have a tendency to bleed or have gastrointestinal intolerance, although side effects must be monitored. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are typically used as second-line agents in the treatment of JIA to prevent radiographic changes associated with joint destruction. DMARDs consist of medications (eg, immunosuppressive, antimalarial, and biologic) that alter immune function. Current biologics target cytokines in the inflammatory cascade. The most common biologics currently used in JIA inhibit the cytokine TNF-α. These biologic agents have demonstrated favorable efficacy in children with JIA and have become widely used, either as US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved agents or in clinical studies. Osteoclasts Fibroblasts Production of MMPs and other effector molecules Migration of polymorphonuclear cells Bone and cartilage erosion IL = interleukin; MMP = matrix metalloproteinases; TNF = tumor necrosis factor. Reprinted with permission from Feldmann. Nature Rev. 2002;2: formation due to inflammatory cell migration (Figure 2). 6 The pannus is comprised primarily of invasive lining cells with attributes of transformed cells (open nuclei, high expression of oncogenes, and increased metalloproteinases). Simultaneously, destruction of the bone and cartilage occurs as a result of antibody deposition. One feature of JIA that distinguishes it from other inflammatory arthropathies is the propensity of the synovium to become hyperplastic and locally invasive at the synovial interface with cartilage and bone (pannus interface). Antirheumatic medications for JIA often target the rapidly dividing cells of the pannus. RATIONALE OF PHARMACOLOGIC TREATMENT A primary pharmacologic goal is the prevention of joint inflammation and further destruction of the bone and cartilage. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, prevent the inflammatory response, and are typically used as first-line agents FUTURE DIRECTIONS Historically, determining individual patient response to specific JIA therapies has been difficult. Treatment plans are a series of trial and error strategies that attempt to decrease joint pain and destruction, suppress the inflammatory response, improve physical function, and preserve normal growth and development. With the recent completion of human genome sequencing, new tools are available to study the phenotypes of patients with arthritis. Through profiles determined by microarray analysis and genome-wide association studies, researchers hope to be able to better categorize patients and subsequently tailor treatments to suit the needs of individuals. Figure 2. Joint Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial membrane Cartilage Capsule NORMAL RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Cartilage thinning Pannus Synovial fluid Inflamed synovial membrane Major cell types: T lymphocytes Macrophages Minor cell types: Fibroblasts Plasma cells Endothelium Dendritic cells Major cell type: Neutrophils Adapted with permission from Feldmann et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14: Vol. 5, No. 6 September 2008
4 DISCUSSION Dr Rich: Managed care providers often assume that drug therapy and disease management have been appropriately established by specialists, such as rheumatologists. Are patients typically referred to specialists by their primary care physicians (PCPs)? Dr Myers: In tertiary care centers, most patients are referred by PCPs, or other specialists such as allergists or orthopedists, who refer to pediatric rheumatologists to confirm diagnosis and select appropriate treatment. PCPs often vary in their level of comfort with proper differential diagnosis, initial workup, and selection of candidates for rheumatology referral. Dr Rich: Because the cost of biologic therapy is relatively high, is it appropriate for managed care providers to require diagnosis verification by a rheumatology specialist? Dr Miller: Pediatric rheumatology centers (PRCs), if available, should initiate biologic treatment, a decision with which many PCPs seem to agree. However, pediatric rheumatologists are not available in some geographic areas, and the timeliness of referral to pediatric rheumatologists can vary, particularly in children with long-standing diagnosis. Studies of practice patterns seem to show not only late referral but also late diagnosis of children with JIA. 10 Dr Myers: Rather than using a stepwise approach to treatment, physicians in more rural communities without PRCs or extensive training may be more apt to choose more costly treatments or corticosteroids based on pharmaceutical marketing or perceived ease of use. Referral to PRCs may be more cost effective because specialists methodically confirm diagnosis and choose optimal drug therapy. Dr Rich: Until clinical studies demonstrate significant disease modification with biologics, cost considerations in addition to appropriate therapy choices drive managed care decisions. When PRCs are confirming diagnoses and prescribing therapies, managed care providers are more willing to accept therapy choices. Dr Saleh: It seems that patient access to pediatric rheumatologists is impeded and may not occur until after failure to many therapies and in advanced stages of disease, which may warrant biologics and aggressive therapy. If pediatric patients were treated earlier, as with adult RA, would disease management and remission achievement be easier? Dr Myers: Early diagnosis and early treatment is unquestionably optimal for disease management. Generally, untreated patients in later stages of disease and with existing joint damage are the most difficult to manage. Dr Miller: In the adult population, patients with RA may experience exacerbation after biologic agents are discontinued. More data are needed to determine if this increase also occurs in the pediatric population. Subjectively, it seems that biologic agents may be stopped in some pediatric patients without rebound flares occurring, which suggests that biologic therapy may not be required for excessive periods in some children. Dr Myers: Pediatric rheumatologists often attempt to wean patients from biologic therapies when patients enter remission to avoid excessive time on medications. However, a significant number of children may experience rebound exacerbation of JIA symptoms. Education of PCPs and other related specialists, such as orthopedists, is optimal to JIA management. Rheumatologists should educate other physicians about JIA differential diagnosis and initial treatment so that patients are diagnosed early and treated appropriately. Dr Busbey: At the Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC), the use of biologics is restricted to rheumatologists. This restriction avoids inappropriate use by PCPs and ensures rheumatology referral. Dr Miller: Biologics should be initiated in PRCs; however, patients can return to their referral centers, or even home healthcare agencies, for future therapies provided that periodic review and coordination exists with the PRCs. One exception may be infliximab, which is possibly more suited to the day hospital setting due to stringent monitoring requirements for serious systemic adverse reactions. Dr Penna: Are there any promising diagnostic tests that may some day help determine the precise drug for individual patients? Managed care concerns include not only drug costs but also corresponding diagnostic test costs, as well as the availability of tools that help identify best therapies for individual patients. Dr Myers: Although unavailable presently, research seems to be heading toward developing such tests, which could dramatically improve patient care. Dr Miller: Although research may be investigating these tests, particularly in adults, I believe that research is heading more toward understanding the basic biology of rheumatoid conditions. Genetic phenotyping in conjunction with treatment stratification would be valuable to patient care. However, ethical and political University of Tennessee Advanced Studies in Pharmacy 173
5 questions could arise with this approach because patient privacy could be breached and insurance coverage refused. Dr Swims: As observed in adult RA, is there a window of opportunity in JIA for treatment to be most effective in preventing joint destruction? Dr Myers: Early treatment definitely results in better patient outcomes. This window of opportunity emphasizes the need to educate PCPs. Dr Saleh: Are the polyarticular and pauciarticular types of JIA considered the same disease process or 2 different phenotypes? Are these types of JIA investigated together as one disease state in clinical trials, or are they differentiated? Is there any difference between the 2 types in terms of response to therapy? Dr Myers: The joint pathophysiology of these types appears to be the same, featuring pannus formation and invasion into the cartilage and bone. However, the types differ phenotypically, which is mostly expressed as differences in disease aggression. The polyarticular form tends to be more aggressive, as seen in rheumatoid factor-positive disease. Investigators often use animal models to investigate joint pathophysiology, because they allow the investigator to simplify the variables involved in disease. Until phenotypic differences are more fully understood, treatment is typically the same for both JIA types, except that the use of aggressive therapies varies with the degree of arthritis. Dr Miller: Some gene expression studies have shown preliminary differences between systemic JIA and other febrile illnesses. 11 Dr Penna: One managed care perspective is that early aggressive treatment conflicts with the need to control cost through drug utilization review. The VAMC approach of requiring specialists to prescribe biologics is an effective method to overcome this conflict. However, in areas without readily available pediatric rheumatologists, this requirement could delay treatment inappropriately. Additionally, local PCPs may not easily accept this provision by managed care providers. Dr Myers: Unfortunately, our most effective treatments are currently the most expensive. Until therapy costs decrease, deciding when to use biologics in lieu of less expensive therapies for JIA will continue to remain challenging. The cost tier for JIA treatment is much higher since the advent of biologic therapies in the past 10 years. Dr Rich: Another issue is lifetime maximum benefits associated with health insurance. In adult patients with RA, biologic therapy discontinuation is rare because joint destruction tends to continue throughout life. Do patients with JIA require long-term biologic therapy, or are biologics able to slow disease progression to the point of therapy discontinuation? Dr Myers: A significant number of patients will go into remission, sometimes spontaneously. In children, I prefer to attempt to wean them from biologic therapy, particularly to determine remission durability. However, it is difficult to predict who will remain disease-free and who will need to restart therapy. Because therapies change as newer agents become available, predicting therapy response becomes even more complicated. Dr Miller: One issue to consider with cost of therapy is that socioeconomic consequences may result from untreated or undertreated disease. Data have shown that prior to the advent of biologic therapies, some children with polyarticular disease had difficulties entering the workforce as adults. 12 Dr Busbey: One review article reported that approximately 30% of patients with JIA did not graduate from high school. 13 Dr Myers: A large prospective observation study continues to recruit patients with JIA and other related conditions to learn more about the causes and course of these diseases. 14 Dr Rich: Although long-term studies may provide valuable information about future therapy benefits, managed care providers generally focus on studies that examine short-term therapy benefits. A primary goal of managed care is immediate or shortterm cost containment. Managed care typically covers the cost of highpriced therapies, including for some patients who have reached lifetime maximums. This blanket coverage impedes an important incentive to drive down the price of biologics and other costly therapies. Managed care providers are conflicted because denying benefits or requiring patient cost sharing for high-priced therapies could be disparaging. Dr Miller: When evaluating clinical studies, therapy success with biologics should be carefully defined. Before the first clinical trials of biologics started in adults with RA, the US FDA required a quality-of-life (QOL) component be incorporated into assessment of responsiveness before treatment approval would be granted. Completing high school and maintaining employment may also be effective ways to measure 174 Vol. 5, No. 6 September 2008
6 success of treatment. Clinical trial results that only report clinical and biologic changes after treatment do not provide QOL information. REFERENCES 1. Adler J. Arthritis: what it is, why you get it, and how to stop the pain. Newsweek. September 3, newsweek.com/id/ Accessed June 2, Cornil MV. Memoire sur les coincidences pathologiques du rhumatisme articulaire chronique. C R Mem Soc Biol (Paris). 1864;4:3 3. Still GF. On a form of chronic joint disease in children. Med Chirurg Trans. 1897;80: Coss JA, Boots RH. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Pediatr. 1946;29: Feldmann M. Development of anti-tnf therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Rev. 2002;2: Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14: Choy EHS, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344: Smith JB, Haynes MK. Rheumatoid arthritis-a molecular understanding. Ann Intern Med. 2002;136: Issekutz AC, Meager A, Otterness I, Issekutz TB. The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-1 in polymorphonuclear leukocyte and T lymphocyte recruitment to joint inflammation in adjuvant arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994;97: Foster HE, Eltringham MS, Kay LJ, et al. Delay in access to appropriate care for children presenting with musculoskeletal symptoms and ultimately diagnosed with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57: Allantaz F, Chaussabel D, Stichweh D, et al. Blood leukocyte microarrays to diagnose systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis and follow the response to IL-1 blockade. J Exp Med. 2007;204: Nigrovic PA, White PH. Care of the adult with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;55: Weiss JE, Ilowite NT. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2005;52: Studies of the Pathogenesis and Natural History of Arthritis and Related Conditions. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [database online]. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health; Available at: NCT Accessed May 29, University of Tennessee Advanced Studies in Pharmacy 175
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases
 Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is rheumatoid arthritis?...4 Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis... 5 What causes rheumatoid arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is rheumatoid arthritis?...4 Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis... 5 What causes rheumatoid arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family
Using ENBREL to Treat Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis
 Using ENBREL to Treat Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Writing White Papers class Bellevue Community College TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...2 OVERVIEW...3 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS... 3 JUVENILE RHEUMATOID
Using ENBREL to Treat Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis Writing White Papers class Bellevue Community College TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...2 OVERVIEW...3 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS... 3 JUVENILE RHEUMATOID
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
 MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis. Dr Johan Siebert
 JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition
 Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
MMS Pharmacology Lecture 2. Antirheumatic drugs. Dr Sura Al Zoubi
 MMS Pharmacology Lecture 2 Antirheumatic drugs Dr Sura Al Zoubi Revision Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition (RA): is the most common systemic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical inflammation
MMS Pharmacology Lecture 2 Antirheumatic drugs Dr Sura Al Zoubi Revision Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition (RA): is the most common systemic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical inflammation
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis?
 Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis
 Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Nausheen Khuddus, MD Melissa Elder, MD, PhD
 Nausheen Khuddus, MD Melissa Elder, MD, PhD Nausheen Khuddus, MD Pediatric Ophthalmologist and Strabismus Specialist Accent Physicians Gainesville, Florida What Is Uveitis? Uveitis is caused by inflammatory
Nausheen Khuddus, MD Melissa Elder, MD, PhD Nausheen Khuddus, MD Pediatric Ophthalmologist and Strabismus Specialist Accent Physicians Gainesville, Florida What Is Uveitis? Uveitis is caused by inflammatory
Pain or stiffness in joints after periods of inactivity or excessive use
 Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis
 Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News
 Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News Jeffrey R. Lisse, M.D. Ethel P. McChesney Bilby Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Rheumatology University of Arizona School of Medicine
Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News Jeffrey R. Lisse, M.D. Ethel P. McChesney Bilby Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Rheumatology University of Arizona School of Medicine
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904)
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for.
 Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
AUTOIMMUNITY TOLERANCE TO SELF
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness of Ustekinumab (STELARA ) in pediatric patients have not been evaluated.
 Original Issue Date (Created): January 1, 2010 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 28, 2014 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 I. POLICY Preauthorization Requirements for Ustekinumab (STELARA ) Note:
Original Issue Date (Created): January 1, 2010 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): January 28, 2014 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 I. POLICY Preauthorization Requirements for Ustekinumab (STELARA ) Note:
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
Ontario Public Drug Programs. Inflectra (infliximab) Frequently Asked Questions
 Ontario Public Drug Programs Inflectra (infliximab) Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is the funding status of Inflectra (infliximab)? Effective February 25 2016, Inflectra (infliximab) will be added
Ontario Public Drug Programs Inflectra (infliximab) Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is the funding status of Inflectra (infliximab)? Effective February 25 2016, Inflectra (infliximab) will be added
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Concordance with the British Society of Rheumatology (BSR) 2010 recommendations on eligibility criteria for the first biologic agent
 Concordance with the British Society of Rheumatology (BSR) 2010 recommendations on eligibility criteria for the first biologic agent Michela Frendo, John Paul Caruana Galizia, Andrew A Borg Abstract Aims:
Concordance with the British Society of Rheumatology (BSR) 2010 recommendations on eligibility criteria for the first biologic agent Michela Frendo, John Paul Caruana Galizia, Andrew A Borg Abstract Aims:
Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 12/15/ months or as otherwise noted by indication
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Kineret (anakinra subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Kineret (anakinra subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
HARVARD PILGRIM HEALTH CARE RECOMMENDED MEDICATION REQUEST GUIDELINES HUMIRA PEDIATRIC
 Generic Brand HICL GCN Exception/Other ADALIMUMAB HUMIRA 24800 HUMIRA PEDIATRIC GUIDELINES FOR USE INITIAL CRITERIA (NOTE: FOR RENEWAL CRITERIA SEE BELOW) 1. Is the patient currently taking Humira? If
Generic Brand HICL GCN Exception/Other ADALIMUMAB HUMIRA 24800 HUMIRA PEDIATRIC GUIDELINES FOR USE INITIAL CRITERIA (NOTE: FOR RENEWAL CRITERIA SEE BELOW) 1. Is the patient currently taking Humira? If
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary. Adalimumab (Humira) for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. National Horizon Scanning Centre.
 Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Adalimumab (Humira) for juvenile idiopathic arthritis June 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Adalimumab (Humira) for juvenile idiopathic arthritis June 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time
ORENCIA (abatacept) Demonstrates Comparable Efficacy to Humira ( adalimumab
 ORENCIA (abatacept) Demonstrates Comparable Efficacy to Humira (adalimumab) in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis in First Head-to-Head Study of These Agents ORENCIA demonstrated comparable
ORENCIA (abatacept) Demonstrates Comparable Efficacy to Humira (adalimumab) in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis in First Head-to-Head Study of These Agents ORENCIA demonstrated comparable
Contents. Welcome Address... iii EULAR 2017 Abstracts Reviewers... iv. Speakers Abstracts
 vi Welcome Address... iii EULAR 2017 Abstracts Reviewers... iv Speaker Presentations Speakers Abstracts Wednesday, 14 June 2017 SP0001 SP0004 Joint EULAR - APLAR session: novel animal models - where no
vi Welcome Address... iii EULAR 2017 Abstracts Reviewers... iv Speaker Presentations Speakers Abstracts Wednesday, 14 June 2017 SP0001 SP0004 Joint EULAR - APLAR session: novel animal models - where no
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline. Guideline for the child with possible arthritis (joint swelling/pain, loss of function)
 Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Guideline for the child with possible arthritis (joint swelling/pain, loss of function) Definition: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is defined as arthritis
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Guideline for the child with possible arthritis (joint swelling/pain, loss of function) Definition: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is defined as arthritis
Blau's Disease / Juvenile Sarcoidosis
 https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Blau's Disease / Juvenile Sarcoidosis Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS BLAU S DISEASE/JUVENILE SARCOIDOSIS 1.1 What is it? Blau syndrome is a genetic disease.
https://www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Blau's Disease / Juvenile Sarcoidosis Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS BLAU S DISEASE/JUVENILE SARCOIDOSIS 1.1 What is it? Blau syndrome is a genetic disease.
Clinical Policy: Tocilizumab (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44
 Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 09/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 09/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Level 1A, City Tower Piccadilly Plaza Manchester M1 4BD
 xxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxx - xxxxxxxxx x National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Level 1A, City Tower Piccadilly Plaza Manchester M1 4BD Dear xxxxx, 1st September 2011 Comments on the August
xxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxx - xxxxxxxxx x National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Level 1A, City Tower Piccadilly Plaza Manchester M1 4BD Dear xxxxx, 1st September 2011 Comments on the August
SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
 SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS Essam Tewfik Attwa and S. Al-Beltagy* Rheumatology & Rehabilitation Department, Zagazig University Faculty of Medicine
SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS Essam Tewfik Attwa and S. Al-Beltagy* Rheumatology & Rehabilitation Department, Zagazig University Faculty of Medicine
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the. Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis
 Home Search Browse Resources Help What's New About Purpose Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis This study is currently recruiting patients. Sponsors and Collaborators: University of Pennsylvania Amgen
Home Search Browse Resources Help What's New About Purpose Etanercept for Treatment of Hidradenitis This study is currently recruiting patients. Sponsors and Collaborators: University of Pennsylvania Amgen
Effective Health Care Program
 Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 28 Effective Health Care Program Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Children With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Executive Summary Background
Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 28 Effective Health Care Program Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Children With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Executive Summary Background
The Hospital for Sick Children Technology Assessment at SickKids (TASK)
 The Hospital for Sick Children Technology Assessment at SickKids (TASK) THE USE OF BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIERS IN POLYARTICULAR-COURSE JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Report No. 2010-01 Date: January 11,
The Hospital for Sick Children Technology Assessment at SickKids (TASK) THE USE OF BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIERS IN POLYARTICULAR-COURSE JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Report No. 2010-01 Date: January 11,
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis What is rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause inflammation of
Rheumatoid Arthritis What is rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause inflammation of
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is the most common type of joint disease. It represents a group of conditions that result in changes
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is the most common type of joint disease. It represents a group of conditions that result in changes
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
p. 70 p. 94 p. 102 p. 105 p. 108
 European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Orencia (abatacept) for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Media backgrounder
 Orencia (abatacept) for Rheumatoid Arthritis Media backgrounder What is Orencia (abatacept)? Orencia (abatacept) is the first biologic agent to be available in both an intravenous (IV) and a self-injectable,
Orencia (abatacept) for Rheumatoid Arthritis Media backgrounder What is Orencia (abatacept)? Orencia (abatacept) is the first biologic agent to be available in both an intravenous (IV) and a self-injectable,
SYSTEMIC JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS DRUG
 SYSTEMIC JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Anakinra Kineret 100mg/0.67mg pre-filled syringe For the treatment of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients who meet the following criteria; Patient
SYSTEMIC JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Anakinra Kineret 100mg/0.67mg pre-filled syringe For the treatment of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients who meet the following criteria; Patient
3. Is the prescribed dose within the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)- approved dosing for giant cell arteritis?
 Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH PESLVAIA & AETA BETTER HEALTH KIDS Actemra (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review
Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH PESLVAIA & AETA BETTER HEALTH KIDS Actemra (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review
Requirements in the Development of an Autoimmune Disease Amino Acids in the Shared Epitope
 + T cell MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ Induction of + T H 1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes APC Activated autoreactive +
+ T cell MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ Induction of + T H 1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes APC Activated autoreactive +
Regulatory Status FDA approved indication: Kineret is an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist indicated for: (1)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.50 Subject: Kineret Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 17, 2017 Kineret Description Kineret (anakinra)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.50 Subject: Kineret Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 17, 2017 Kineret Description Kineret (anakinra)
2/23/18. Disclosures. Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood. Making Room for Rheumatology. I have nothing to disclose. James J.
 Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Lupus. Fast facts. What is lupus? What causes lupus? Who gets lupus?
 Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
Lupus Systemic lupus erythematosus, referred to as SLE or lupus, is sometimes called the "great imitator." Why? Because of its wide range of symptoms, people often confuse lupus with other health problems.
Erelzi (etanercept) Frequently Asked Questions
 Erelzi (etanercept) Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is the funding status of Erelzi (etanercept)? Effective December 21, 2017, Erelzi (etanercept) will be added to the Ontario Drug Benefit (ODB) Formulary
Erelzi (etanercept) Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is the funding status of Erelzi (etanercept)? Effective December 21, 2017, Erelzi (etanercept) will be added to the Ontario Drug Benefit (ODB) Formulary
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: abatacept_orencia 4/2008 2/2018 2/2019 2/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Abatacept (Orencia ), a
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: abatacept_orencia 4/2008 2/2018 2/2019 2/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Abatacept (Orencia ), a
2017 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Monoclonal Antibodies in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Prof. John D. Isaacs
 John D Isaacs Professor of Clinical Rheumatology Director, Wilson Horne Immunotherapy Centre Newcastle University, UK 1 Rheumatoid arthritis Targeting T-cells Targeting B-cells Costimulation blockade Novel
John D Isaacs Professor of Clinical Rheumatology Director, Wilson Horne Immunotherapy Centre Newcastle University, UK 1 Rheumatoid arthritis Targeting T-cells Targeting B-cells Costimulation blockade Novel
Treatment modalities Prof Ally 2012
 Treatment modalities Prof Ally 2012 Analgesia Types of Pain Nociceptive /neuropathic nociceptive Tissue damage - trauma, inflammation Somatic (musculoskeletal): local pain referred pain Neuropathic pain:
Treatment modalities Prof Ally 2012 Analgesia Types of Pain Nociceptive /neuropathic nociceptive Tissue damage - trauma, inflammation Somatic (musculoskeletal): local pain referred pain Neuropathic pain:
Welcome to Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis or JRA, by Connie Martin, MS, RDN; Claire Stephens, MS, RDN; and Lolita McLean, MPH, RDN...
 Welcome to Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis or JRA, by Connie Martin, MS, RDN; Claire Stephens, MS, RDN; and Lolita McLean, MPH, RDN...all of Alabama s Children s Rehabilitation Service, part of the Alabama
Welcome to Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis or JRA, by Connie Martin, MS, RDN; Claire Stephens, MS, RDN; and Lolita McLean, MPH, RDN...all of Alabama s Children s Rehabilitation Service, part of the Alabama
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline
 Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline The child and young person with possible arthritis (joint swelling and/or pain, loss of function for >4 weeks) Definition: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline The child and young person with possible arthritis (joint swelling and/or pain, loss of function for >4 weeks) Definition: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel:
 Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
THE MANAGEMENT OF JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS
 THE MANAGEMENT OF JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Prof Chris Scott PAEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGIST UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN RED CROSS WAR MEMORIAL CHILDRENS S HOSPITAL Chronic Arthritis >6wks JIA No other cause
THE MANAGEMENT OF JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Prof Chris Scott PAEDIATRIC RHEUMATOLOGIST UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN RED CROSS WAR MEMORIAL CHILDRENS S HOSPITAL Chronic Arthritis >6wks JIA No other cause
Remicade. Remicade (infliximab), Inflectra (infliximab-dyyb) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.50.02 Subsection: Gastrointestinal nts Original Policy Date: May 20, 2011 Subject: Remicade Page: 1 of
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.50.02 Subsection: Gastrointestinal nts Original Policy Date: May 20, 2011 Subject: Remicade Page: 1 of
The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Information for parents 2 This information sheet is about Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA), its treatment and what it may
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Information for parents 2 This information sheet is about Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA), its treatment and what it may
Regulatory Status FDA- approved indication: Simponi and Simponi ARIA are tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers indicated for the treatment of:
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.51 Subject: Simponi / Simponi ARIA Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: March 17, 2017 Simponi / Simponi
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.51 Subject: Simponi / Simponi ARIA Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Date: March 17, 2017 Simponi / Simponi
Simponi / Simponi ARIA (golimumab)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.51 Subject: Simponi / Simponi ARIA Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 15, 2016 Simponi / Simponi
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.51 Subject: Simponi / Simponi ARIA Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 15, 2016 Simponi / Simponi
Understanding Arthritis. Training
 Understanding Arthritis Training 1 Learning Objectives At the end of this training the learner will: Be able to define Arthritis Describe the symptoms of Arthritis Understand the impact of Arthritis Know
Understanding Arthritis Training 1 Learning Objectives At the end of this training the learner will: Be able to define Arthritis Describe the symptoms of Arthritis Understand the impact of Arthritis Know
Understanding Psoriatic Arthritis
 Understanding Psoriatic Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is psoriatic arthritis?...4 Symptoms of psoriatic arthritis... 5 What causes psoriatic arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family history...11
Understanding Psoriatic Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is psoriatic arthritis?...4 Symptoms of psoriatic arthritis... 5 What causes psoriatic arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family history...11
Kineret (anakinra) When Policy Topic is covered Kineret (anakinra) requires prior authorization through the pharmacy services area.
 Kineret (anakinra) Policy Number: 5.01.622 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2017 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for Kineret (anakinra)
Kineret (anakinra) Policy Number: 5.01.622 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2017 Next Review: 3/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for Kineret (anakinra)
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling. Rheumatic Diseases
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
ACTEMRA (tocilizumab)
 ACTEMRA (tocilizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
ACTEMRA (tocilizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 RHEUMATOID THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Eman Sh.Al-Obeidy*, Shatha F. Abdullah** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
RHEUMATOID THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Eman Sh.Al-Obeidy*, Shatha F. Abdullah** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
Arthritis of the Shoulder
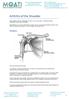 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Cimzia. Cimzia (certolizumab pegol) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.50.11 Subject: Cimzia Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 8, 2017 Cimzia Description Cimzia (certolizumab
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.50.11 Subject: Cimzia Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 8, 2017 Cimzia Description Cimzia (certolizumab
Subject: Remicade (Page 1 of 5)
 Subject: Remicade (Page 1 of 5) Objective: I. To ensure that Health Share/Tuality Health Alliance (THA) has a process by which the appropriate utilization of Remicade (Infliximab) for members whose diagnosis
Subject: Remicade (Page 1 of 5) Objective: I. To ensure that Health Share/Tuality Health Alliance (THA) has a process by which the appropriate utilization of Remicade (Infliximab) for members whose diagnosis
When Aimee Bower s feet started hurting during her recreational
 Pain Free at Last Providence rheumatologists provide treatments for the aches of arthritis. Written by DAWN HOFFMAN Photgraphed by MICHAEL NEVEUX When Aimee Bower s feet started hurting during her recreational
Pain Free at Last Providence rheumatologists provide treatments for the aches of arthritis. Written by DAWN HOFFMAN Photgraphed by MICHAEL NEVEUX When Aimee Bower s feet started hurting during her recreational
ADALIMUMAB Generic Brand HICL GCN Exception/Other ADALIMUMAB HUMIRA GUIDELINES FOR USE INITIAL CRITERIA (NOTE: FOR RENEWAL CRITERIA SEE BELOW)
 Generic Brand HICL GCN Exception/Other ADALIMUMAB HUMIRA 24800 GUIDELINES FOR USE INITIAL CRITERIA (NOTE: FOR RENEWAL CRITERIA SEE BELOW) 1. Does the patient have a diagnosis of moderate to severe rheumatoid
Generic Brand HICL GCN Exception/Other ADALIMUMAB HUMIRA 24800 GUIDELINES FOR USE INITIAL CRITERIA (NOTE: FOR RENEWAL CRITERIA SEE BELOW) 1. Does the patient have a diagnosis of moderate to severe rheumatoid
1. Background: Infliximab is administered parenterally; therefore, it is not covered under retail pharmacy benefits.
 Subject: Infliximab (Remicade ) Original Original Committee Approval: October 13, 2006 Revised Last Committee Approval: December 3, 2008 Last Review: October 19, 2007 1. Background: Infliximab is a genetically
Subject: Infliximab (Remicade ) Original Original Committee Approval: October 13, 2006 Revised Last Committee Approval: December 3, 2008 Last Review: October 19, 2007 1. Background: Infliximab is a genetically
What prescribers need to know
 HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in an Electronic Medical Record (EMR) What prescribers need to know 2 / This is your guide to identifying HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in your Electronic Medical
HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in an Electronic Medical Record (EMR) What prescribers need to know 2 / This is your guide to identifying HUMIRA Citrate-free presentations in your Electronic Medical
PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF AGE OF ONSET IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Recipient ID: RETIRED. Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed:
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic,
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic,
2. Does the patient have a diagnosis of giant cell arteritis (GCA)? Y N
 Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH EW JERSE (MEDICAID) Actemra (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign
Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH EW JERSE (MEDICAID) Actemra (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign
Remicade. Remicade (infliximab), Inflectra (infliximab-dyyb) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Remicade Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Remicade Description Remicade (infliximab),
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Remicade Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Remicade Description Remicade (infliximab),
ERROR CORRECTION FORM
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Registry Use Only Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic, syngeneic unrelated related
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Registry Use Only Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic, syngeneic unrelated related
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
INFLIXIMAB Remicade (infliximab), Inflectra (infliximab-dyyb), Renflexis (infliximab-abda)
 RATIONALE FOR INCLUSION IN PA PROGRAM Background Remicade, Renflexis and Inflectra are tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) blockers. Tumor necrosis factor is an endogenous protein that regulates a number of physiologic
RATIONALE FOR INCLUSION IN PA PROGRAM Background Remicade, Renflexis and Inflectra are tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) blockers. Tumor necrosis factor is an endogenous protein that regulates a number of physiologic
Beyond the Bowel: Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Beyond the Bowel: Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Robert Isfort, M.D. TriHealth Digestive Institute IBD Family Education Day 2019 Learning Objectives Review manifestations
Beyond the Bowel: Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Robert Isfort, M.D. TriHealth Digestive Institute IBD Family Education Day 2019 Learning Objectives Review manifestations
Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Market: Trends and Opportunities ( )
 Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Market: Trends and Opportunities (2013-2018) Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Market Report Scope of the report The report titled Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Market: Trends and Opportunities
Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Market: Trends and Opportunities (2013-2018) Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Market Report Scope of the report The report titled Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Market: Trends and Opportunities
A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Regulatory Status FDA- approved indication: Simponi and Simponi ARIA are tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers indicated for the treatment of: (2-3)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.51 Subject: Simponi / Simponi ARIA Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Simponi / Simponi
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.51 Subject: Simponi / Simponi ARIA Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Simponi / Simponi
ACTEMRA (tocilizumab)
 RATIONALE FOR INCLUSION IN PA PROGRAM Background Actemra is an agent in the class of drugs known as biologic disease modifiers. It is used to treat adult onset rheumatoid (RA) arthritis, polyarticular
RATIONALE FOR INCLUSION IN PA PROGRAM Background Actemra is an agent in the class of drugs known as biologic disease modifiers. It is used to treat adult onset rheumatoid (RA) arthritis, polyarticular
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
