Research Article FeNO as a Marker of Airways Inflammation: The Possible Implications in Childhood Asthma Management
|
|
|
- Grace Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Allergy Volume 1, Article ID 69145, 7 pages doi:1.1155/1/69145 Research Article FeNO as a Marker of Airways Inflammation: The Possible Implications in Childhood Asthma Management Marcello Verini, 1 Nicola Pietro Consilvio, 1 Sabrina Di Pillo, 1 Anna Cingolani, 1 Cynzia Spagnuolo, 1 Daniele Rapino, 1 Alessandra Scaparrotta, 1 and Francesco Chiarelli 1 Allergological and Pneumological Service, Department of Pediatric, University G. D Annunzio, 661 Chieti, Italy Department of Pediatric, University G. D Annunzio, 661 Chieti, Italy Correspondence should be addressed to Marcello Verini, mverini@alice.it Received 16 September 9; Revised 3 January 1; Accepted 1 March 1 Academic Editor: Massimo Triggiani Copyright 1 Marcello Verini et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. The aim of this study was to verify FeNO usefulness, as a marker of bronchial inflammation, in the assessment of therapeutic management of childhood asthma. We performed a prospective 1-year randomized clinical trial evaluating two groups of 3 children with allergic asthma:, in which therapy was assessed only by GINA guidelines and, who followed a therapeutic program assessed also on FeNO measurements. Asthma Severity score (ASs), Asthma Exacerbation Frequency (AEf), and Asthma Therapy score (ATs) were evaluated at the start of the study (T1), 6 months (T), and 1 year after (T3). ASs and AEf significantly decreased only in the at times T and T3 (p[t1-t] =.1, and p[t1-t3] =.1; p[t1-t] =.1; and p[t1-t3] <.1, resp.). After six months of follow-up, we found a significant increase of patients under inhaled corticosteroid and/or antileukotrienes in the compared to the (P =.). Our data show that FeNO measurements, might be a very useful additional parameter for management of asthma, which is able to avoid unnecessary inhaled corticosteroid and antileukotrienes therapies, however, mantaining a treatment sufficient to obtain a meaningful improvement of asthma. 1. Introduction Asthma is characterized by variable degrees of airway obstruction, hyperresponsiveness, and chronic inflammation [1]. Current guidelines emphasize that inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) represent the main treatment for asthma because they target the underlying airways inflammation []. Actually decisions to start ICSs and/or long-acting β- adrenergic agonist (LABA) and/or antileukotrienes (a-lt), or change the dose are mainly based on symptoms reported by the child or parents [3]. Nevertheless symptoms are nonspecific and not closely related to the presence and severity of airways inflammation [4]. Lung function tests show only marginal correlation with airways inflammation [5]. Bronchial epithelium produces Nitric Oxide (NO) [6], and its fraction in exhaled air (FeNO) is elevated in atopic asthma and reflects eosinophilic airways inflammation [7]. Many studies have shown that allergological markers correlate with FeNO levels, and particularly elevated FeNO levels have been found mainly in atopic than in nonatopic asthma [8 1]. Therefore, measurement of FeNO represents a noninvasive marker that may be a useful guide for the adjustment of ICSs treatment [11]. The hypothesis of this study was to verify if FeNO measure is useful in terms of better asthma management in children. The aim of our study was to examine whether the inclusion of repeated FeNO measurements into asthma monitoring leads to an improvement in asthma outcome, with an exacerbation reduction, clinical improvement, and therapy score reduction.. Subjects This was a prospective randomized study. We recruited 64 Caucasian children (36 males and 8 females; aged between
2 Allergy Table 1: Clinical characteristics of the population. Characteristics M/F 18/14 18/14 Age (years) 1.7 ± ±.1 Weight (Kg) Height (cm) Remission Asthma 7 7 Intermittent Asthma Persistent Asthma 7 6 Asthma Duration (years) 5.7 ± ±.7 6 and 17 years) who had been referred to the Allergological and Pneumological Unity of the Pediatric Department, University of Chieti, Italy, between January 5 and January 6. All subjects had been admitted for allergic asthma and the diagnosis was made by a pediatric respiratory physician on the basis of clinical history of repeated episodes of coughing, dyspnea, and wheezing, according to ATS-ERS criteria [1]. Patients were randomly allocated to two groups (Table 1): (i) 3 children (18 boys and 14 girls; mean age, 1.7 ±.4 years) (ii) 3 children (18 boys and 14 girls; mean age, 11.3 ±.1 years). The whole study population was assessed at baseline (T1), after a period of six months (T), and at the end of 1-year followup (T3) (Table ). At baseline and at 6 months, in the, therapy was based on symptoms, short acting β-agonist use, and lung function, according to GINA guidelines [13], while in the, therapy was assessed according also to FeNO measurements. The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Chieti. Written informed consent was obtained from all parents and oral consent from all children. 3. Methods Asthma Severity score (ASS), Asthma Exacerbation frequency (AEF), Asthma Therapy score (ATS), and immunoallergological and functional data were evaluated at the start of the study (T1), 6 months (T), and 1 year later (T3). Asthma was classified according to GINA guidelines to: Intermittent Asthma, Mild Persistent, Moderate Persistent, and Severe Persistent Asthma, considering the 6 months before the beginning of the study [13] Asthma Severity Score (ASS). It was assessed as (i) Intermittent Asthma = Score 1, (ii) Mild and Moderate Persistent Asthma = Score, (iii) Severe Persistent Asthma = Score 3. We also assessed an arbitrary implementation of asthma classification by GINA criteria, and performed the following score for these two phenotypes of asthma: (i) Remission Asthma = Score, (ii) Exercise induced Asthma = Score. 3.. Asthma Exacerbation Frequency (AEF). It was assessed with an anamnestic questionnaire evaluating frequency of asthma exacerbation (defined as the number of episodes of coughing, dyspnea, and wheezing, according to ATS-ERS criteria [1], requiring short-acting β-adrenergic agonist) during the 6 months before the beginning of the study, between T1 and T and between T and T3 evaluations Asthma Therapy Score (ATS). It was assessed with an anamnestic questionnaire and an arbitrary score, as follows: (i) Antihistamines, Ketotifen, Cromones = Score 1, (ii) Specific Immuno Therapy (SIT), long-acting β- adrenergic agonist (LABA) or antileukotrienes (a-lt) = Score, (iii) ICSs = Score Allergic Sensitization. It was evaluated by Skin Prick Test (SPT) and serum-specific IgE measurements for the most common respiratory allergens: Dust Mite (Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus, and Farinae), Grass, Parietaria, Artemisia Vulgaris, Olive, Cypress, Lime, Stone, Elm, Plane, Cat and Dog dander, Alternaria Alternata, and Aspergillus Fumigatus (moulds). Determination of Allergen-Specific IgE was made by an Immunoenzymatic Allergo-sorbent Test (Cap test Pharmacia) [14, 15] Inflammatory Cells. Peripheral blood eosinophil counts and serum eosinophil cationic protein (s-ecp) levels were measured by immunofluorescence Respiratory Function. EvaluationsweremadebyFlow/ Volume, curves, Static Lung Volume and Plethysmographic Airway Resistances determination according to ATS/ERS Guidelines [16, 17] Respiratory Inflammation. All children of the FeNO group underwent FeNO analysis. FeNO was determined with an on-line method using a single breath exhalation and a sensitive chemiluminescence assay (Ecomedics CLD 88), according to ATS-ERS [18]. Patients made an inspiration of eno-free air via a mouthpiece immediately followed by full exhalation at a constant rate (5 ml/sec) for at least 5 seconds. The mean of three readings at the end of the expiration (plateau phase) was taken as the representative value for each measurements. 1 ppb or more were considered elevated values, according to ATS-ERS criteria [19].
3 Allergy 3 Table : Study design. T1 T (6 m) T3 (1 m) Diary card R Diary card Diary card A Clinical evaluation N Clinical evaluation Clinical evaluation D O Allerg. evaluation M Allerg. Evaluation Lung Function Tests I Z A Lung Function Tests Lung Function Tests FeNO measurements T I O FeNO measurements FeNO measurements N Score therapy Score therapy Score therapy 4. Statistical Analysis All values were expressed as means and SD. We analysed differences in variables (ASS, ATS, AEF, and respiratory function test) obtained at different times between the two groups by unpaired T-test, and within each group with paired T-test. Statistical significance level was P<.5. The comparison of the differences in AEF and in ATS between the two groups was calculated also using the Chi square (χ ) Test. The number of antiasthmatic drugs used in the two groups was calculated at T1, T, and T3. In the, level of 1 ppb was the cut-off used to guide the therapeutic management [at 6 months of the follow-up study (T)], according to the ERS-ATS Statement of 1 [19]. Values above 1 ppb were considered as an indication to increase the number of drugs, whereas values below 1 ppb lead to a reduction or to a maintenance in the amount of drugs. 5. Results The two groups were similar for age, sex, weight, and height without significant differences. All the children of both groups were allergic to Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus (Df. pt). At the first assessment, patients asthma characteristics were similar between the two groups. Asthma Severity score (ASS), Asthma Exacerbations frequency (AEF), Asthma Therapy score (ATS), functional and immunoallergological (circulating eosinophils, s-ecp, total and specific IgE) parameters did not show any significant difference between the two groups at T1. ASS mean values significantly decrease in the at T and T3 (from 1.9 ±.81 to.56 ±.75 at T, p[t1-t] =.1,andto.75 ±.95 at T3, p[t1-t3] =.1, resp.), while no difference was detected in the in the corresponding times (from 1.9±.77 to.93±.61 at T, p[t1-t] =.1, and to.9 ±.8 at T3, p[t1-t3] =.1) (Figure 1). Similarly, AEF evaluation showed a significant reduction in the number of episodes in the at T and T3 (Mean values: from 1.96 ± 1.18 to 1.1 ±.96 at T, p[t1-t] =.3, and to.83 ±.98 at T3, p[t1-t3] =.1) but not in the (Mean values: from.1 ± 1.17 to 1.78 ± 1.9 at T, p[t1-t] =.8; and to 1.85 ± 1.34 at T3, p[t1-t3] =.14) (Figure ). Using the Chi-square (χ ) Test we found a significant decrease of the number of patients with asthma exacerbation only in the at T (P =.6) and at T3 (P <.5) (Figure 3). In addition in the, there was no increase in antiasthmatic therapy (Mean values of ATS were similar in the 3 evaluations), (1.5 ±.7 in T1; 1.43 ±.7 in T, and 1.53 ±.6 in T3) while in the, the treatment was significantly step up (Mean values: from 1.3 ±.9 to 1.6 ±.6 at T, p[t1-t] <.5, andto1.4 ±.7 at T3, p[t-t3] <.5; p[t1-t3] <.5), as shown in Figure 4. Using the Chi square (χ ) Test, we found a significative difference in the number of patients who did not use ICS and/or a-lt after 6 months between the (5/3 = 15%) in comparison to the (/3 = 6%) [T: P =.]. No significant difference was found between the two groups at the end of the study; nevertheless, a careful observation relative to the therapy revealed a light difference among the two groups about the anti-inflammatory drugs use. In fact, the keeps the same therapy, while the showed an increased use of ICSs and a-lt (Figure 5). TheevaluationofFeNOlevelsinFeNOgroupdemonstrated a significant reduction after 6 months of therapy, with a return at the levels of the beginning at the end of the study (Mean values of FeNO: from ± 1.31 to 9.51 ± 11.4 at T, p[t1-t] =.6, and to ± 1.74 at T3, p[t-t3] =.5; p[t1-t3]=.44). No significant difference was found between the two groups in terms of respiratory function test and of imunoallergological parameters.
4 4 Allergy P =.1 n.s. P = M T1 T T3 (a) T1 T T3 (b) Figure 1: Asthma Severity score (ASS) in FeNO and s at the first evaluation (T1) after 6 months (T) and after 1 year of therapy (T3). Mean Values ± SD. P = n.s. 3 P =.3.5 Number of episodes T1 T T3 (a) T1 T T3 (b) Figure : Asthma Exacerbation frequency (AEF) in the FeNO and s at the first evaluation (T1) after 6 months (T) and after 1 year of therapy (T3). Mean Number of episodes ± SD.
5 Allergy 5 Number of patients With Without Chi square (χ )test T1 T T3 T1 T T3 Figure 3: Number of patients with and without asthma exacerbation in FeNO and s at first evaluation (T1), after 6 months (T) and after 1 year of therapy (T3). M T1 T T3 Unpaired T-test T1 T T3 Figure 4: Antiinflammatory drugs level in both group at each evaluation. Mean Values ± SD. 6. Discussion This study shows that FeNO measurements are useful in childhood asthma management because FeNO reductions are related to improvement in clinical score with a reduction of asthma exacerbation. In our study, FeNO reductions were not related to any improvement of respiratory function but allow to keep the same therapeutic regimen in the FeNO group, while in the, we had a significant increase of number of patients who use antiinflammatory drugs (mainly ICS) without any evidence of increase in bronchial inflammation. Previous studies have shown a significant correlation between FeNO and respiratory symptoms, bronchial hyperresponsiveness (BHR), and blood eosinophilia but not with spirometric indices of lung function [, 1]. These findings are in agreement with data reported by Silvestri and coworkers [] who demonstrated that airways inflammation may not be strictly related to a reduction in lung volumes or to the degree of airflow limitation. Recent studies revealed that FeNO is a potentially useful measure to evaluate the role of airways inflammation in asthma, as it represents the forerunner of an important event in asthma: the remodelling of bronchial airway [3]. Current guidelines recommended to adjust the dose of these drugs on the basis of symptoms and LFTs results Number of patients Chi square (χ ) test P =. T1 T T3 T1 T T3 None a-lt ICS 3 8 Figure 5: Antiinflammatory drugs trend: variation of the number of patients that use antiinflammatory drugs. [13]. However, recent studies demonstrated that the use of alternative criteria, like BHR, FeNO levels, and sputum eosinophils, leads to an improvement in asthma treatment outcomes [4]. The ICSs therapy produces a rapid reduction (dosedependent) of FeNO levels in asthmatic subjects. Some studies demonstrated that the reduction of FeNO levels occurs at the same time of the reduction of sputum eosinophils [5]. The elevated sensitivity of FeNO levels to ICSs therapies shows that it can be used as a factor of prediction for antiinflammatory therapy, and could be an indicative marker to detect patients that do not have a good compliance to therapy. Also the anti-lt drugs association could improve FeNO levels, while LABA does not reduce it [6, 7]. Therefore, exhaled nitric oxide may be a valuable parameter to monitor adherence to steroids, although it is less suitable to describe physiologically relevant impairments of lung function [8]. In our study, we found a reduction of clinical symptoms and asthma exacerbations in the. Furthermore, we found also an improvement of respiratory function and therapeutic score. We demonstrated that measurement of airways inflammation is of practical value in management of asthmatic children because it allows to monitor patients from a flogistic point of view. It leads to an improvement of clinical outcome and to a reduction in number of exacerbations. Furthermore, differently from other studies, in our study FeNO measurement did not permit to reduce the use of drugs but allows us to not increase the amount of drugs as it has been done in. In particular, we underlied a mild increase of therapeutic score in due to an increase of drugs dose to reach a good clinical outcome. Only a few longitudinal studies have examined the possible clinical relevance of FeNO in asthma management. Roberts and coworkers [9] have demonstrated that FeNO relates to previous allergen exposure and asthma control. Pijnenburg et al. [3] demonstrated that FeNO is helpful in predicting asthma relapse in children who discontinue ICSs because of clinical remission. Similarly, the study of Zacharasiewicz et al. [] performed on 4 children with 6 7
6 6 Allergy stable asthma eligible for inhaled steroid reduction has showed that elevated values of sputum eosinophil and FeNO were a significant predictor for failed ICSs reduction in children with apparently well-controlled asthma. These findings suggest that monitoring airway inflammation may be useful in optimizing treatment in childhood asthma. In a recent single-blind controlled trial in adult with asthma, Smith and colleagues [31] showed that using FeNO for adjustments of ICSs leads to similar asthma control with less ICS in the FeNO-treated group compared with the group treated on conventional parameters; the FeNO levels can offer a method to adjust the doses of ICSs. Indeed, use of FeNO measurements may also help to minimize the potential long-term side effects related to ICSs, which are more likely when higher doses are used. Also in the clinical trial of Pijnenburg et al. [3], performed on 85 children with asthma, 1 year of steroids titration FeNO did not result in higher steroid doses and did improve airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation compared with titrating on symptoms only. 7. Conclusion Our results have shown that the use of noninvasive methods to monitor airway inflammation, as FeNO measure, can help to guide treatment in childhood asthma management. We demonstrate that repeated FeNO measurement can help to optimize asthma therapy with improvement in asthma severity and exacerbation. These findings confirm the important role of FeNO in the routine assessment of children with asthma in clinical practice, especially when decisions about treatment need to be made. Overall, this approach offers a logical complementary item to the use of clinical and functional data leading to a more fitted treatment in childhood asthma management to reach a good clinical outcome and a reduction of exacerbations. Our study shows that FeNO measurement does not allow only a reduction of drugs use but also a better personal fitted therapy sufficient to obtain good clinical control. Further prospective studies on lager populations of children are required to confirm these conclusions. Acknowledgment The authors thank all nurses of the Department of Pediatrics, University of Chieti, in particular Di Santo D, Di Luca D, Diomedi A, for their daily support in clinical research and care of children. References [1] F. H. Guo, S. A. A. Comhair, S. Zheng, et al., Molecular mechanisms of increased nitric oxide (NO) in asthma: evidence for transcriptional and post-translational regulation of NO synthesis, Immunology, vol. 164, no. 11, pp ,. [] A. Zacharasiewicz, N. Wilson, C. Lex, et al., Clinical use of noninvasive measurements of airway inflammation in steroid reduction in children, American Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, vol. 171, no. 1, pp , 5. [3] M. W. Pijnenburg, E. M. Bakker, W. C. Hop, and J. C. De Jongste, Titrating steroids on exhaled nitric oxide in children with asthma: a randomized controlled trial, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, vol. 17, no. 7, pp , 5. [4] L. Grönke, F. Kanniess, O. Holz, R. A. Jörres, and H. Magnussen, The relationship between airway hyperresponsiveness, markers of inflammation and lung function depends on the duration of the asthmatic disease, Clinical and Experimental Allergy, vol. 3, no. 1, pp ,. [5]S.J.Langley,S.Goldthorpe,A.Custovic,andA.Woodcock, Relationship among pulmonary function, bronchial reactivity, and exhaled nitric oxide in a large group of asthmatic patients, Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, vol. 91, no. 4, pp , 3. [6] T. L. Frank, A. Adisesh, A. C. Pickering, et al., Relationship between exhaled nitric oxide and childhood asthma, American Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, vol. 158, no. 4, pp , [7] G. L. Piacentini, A. Bodini, S. Costella, et al., Exhaled nitric oxide and sputum eosinophil markers of inflammation in asthmatic children, European Respiratory Journal, vol. 13, no. 6, pp , [8] F. Cardinale, F. M. de Benedictis, V. Muggeo, et al., Exhaled nitric oxide, total serum IgE and allergic sensitization in childhood asthma and allergic rhinitis, Pediatric Allergy and Immunology, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 36 4, 5. [9] J. D. Leuppi, S. H. Downs, S. R. Downie, G. B. Marks, and C. M. Salome, Exhaled nitric oxide levels in atopic children: relation to specific allergic sensitisation, AHR, and respiratory symptoms, Thorax, vol. 57, no. 6, pp ,. [1] M. Silvestri, F. Sabatini, D. Spallarossa, et al., Exhaled nitric oxide levels in non-allergic and allergic mono- or polysensitised children with asthma, Thorax, vol. 56, no. 11, pp , 1. [11] M. Fritsch, S. Uxa, F. Horak Jr., et al., Exhaled nitric oxide in the management of childhood asthma: a prospective 6- months study, Pediatric Pulmonology, vol. 41, no. 9, pp , 6. [1] National Asthma Education and Prevention Program, NAEPP expert panel report guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma update on selected topics, National Institutes for Health, 6. [13] GINA World Report 6, Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, or or [14] E. Terho and A. J. Frew, Type III allergy skin testing. Position statement for EAACI subcommittee on skin tests and allergen standardization, Allergy, vol. 5, no. 5, pp , [15] A.Wolkerstorfer,U.Wahn,N.I.M.Kjellman,T.L.Diepgen, M. De Longueville, and A. P. Oranje, Natural course of sensitization to cow s milk and hen s egg in childhood atopic dermatitis: ETAC study group, Clinical & Experimental Allergy, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 7 73,. [16] G. Laszlo, Standardisation of lung function testing: helpful guidance from the ATS/ERS Task Force, Thorax, vol. 61, no. 9, pp , 6. [17]J.Stocks,S.Godfrey,C.Beardsmore,E.Bar-Yishay,andR. Castile, Plethysmographic measurements of lung volume and airway resistance, European Respiratory Journal,vol.17,no., pp. 3 31, 1.
7 Allergy 7 [18] American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society, ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 5, American Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, vol. 171, no. 8, pp , 5. [19] E. Baraldi, J. C. de Jongste, B. Gaston, et al., Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide in children, 1, European Respiratory Journal, vol., no. 1, pp. 3 37,. [] P. A. Steerenberg, N. A. H. Janssen, G. de Meer, et al., Relationship between exhaled NO, respiratory symptoms, lung function, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and blood eosinophilia in school children, Thorax, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 4 45, 3. [1] P. J. Franklin, S. W. Turner, P. N. Le Souëf, and S. M. Stick, Exhaled nitric oxide and asthma: complex interactions between atopy, airway responsiveness, and symptoms in a community population of children, Thorax, vol. 58, no. 1, pp , 3. [] M. Silvestri, D. Spallarossa, E. Battistini, V. Brusasco, and G. A. Rossi, Dissociation between exhaled nitric oxide and hyperresponsiveness in children with mild intermittent asthma, Thorax, vol. 55, no. 6, pp ,. [3] I. H. van Veen, P. J. Sterk, R. Schot, et al., Alveolar nitric oxide versus measures of peripheral airway dysfunction in severe asthma, European Respiratory Journal, vol. 7, no. 5, pp , 6. [4] E. Baraldi, N. M. Azzolin, S. Zanconato, C. Dario, and F. Zacchello, Corticosteroids decrease exhaled nitric oxide in children with acute asthma, Pediatrics, vol. 131, no. 3, pp , [5] R. H. Green, C. E. Brightling, S. McKenna, et al., Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial, The Lancet, vol. 36, no. 9347, pp ,. [6] H. Bisgaard, L. Loland, and J. A. Oj, NO in exhaled air of asthmatic children is reduced by the leukotriene receptor antagonist montelukast, American Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, vol. 16, no. 4, pp , [7] H. Bisgaard, Leukotriene modifiers in pediatric asthma management, Pediatrics, vol. 17, no., pp , 1. [8] J. Beck-Ripp, M. Griese, S. Arenz, C. Köring, B. Pasqualoni, and P. Bufler, Changes of exhaled nitric oxide during steroid treatment of childhood asthma, European Respiratory Journal, vol. 19, no. 6, pp ,. [9] G. Roberts, C. Hurley, A. Bush, and G. Lack, Longitudinal study of grass pollen exposure, symptoms, and exhaled nitric oxide in childhood seasonal allergic asthma, Thorax, vol. 59, no. 9, pp , 4. [3]M.W.Pijnenburg,W.Hofhuis,W.C.Hop,andJ.C.De Jongste, Exhaled nitric oxide predicts asthma relapse in children with clinical asthma remission, Thorax, vol. 6, no. 3, pp , 5. [31] A. D. Smith, J. O. Cowan, K. P. Brassett, G. P. Herbison, and D. R. Taylor, Use of exhaled nitric oxide measurements to guide treatment in chronic asthma, The New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 35, no. 1, pp , 5.
8 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
ASTHMA TREATMENT EFFICACY ASSESSMENT BY FeNO MEASUREMENT
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 5 (54) No. 2-2012 ASTHMA TREATMENT EFFICACY ASSESSMENT BY FeNO MEASUREMENT Dana ALEXANDRESCU 1 Abstract: The author of
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 5 (54) No. 2-2012 ASTHMA TREATMENT EFFICACY ASSESSMENT BY FeNO MEASUREMENT Dana ALEXANDRESCU 1 Abstract: The author of
Exhaled nitric oxide to help manage childhood asthma reality bites
 Exhaled nitric oxide to help manage childhood asthma reality bites Peter J Franklin 1 and Stephen M Stick 2,3 1 Centre for Asthma, Allergy and Respiratory Research, University of Western Australia, 2 Respiratory
Exhaled nitric oxide to help manage childhood asthma reality bites Peter J Franklin 1 and Stephen M Stick 2,3 1 Centre for Asthma, Allergy and Respiratory Research, University of Western Australia, 2 Respiratory
Clinical Study Principal Components Analysis of Atopy-Related Traits in a Random Sample of Children
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Allergy Volume 2011, Article ID 170989, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/170989 Clinical Study Principal Components Analysis of Atopy-Related Traits in a Random Sample
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Allergy Volume 2011, Article ID 170989, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/170989 Clinical Study Principal Components Analysis of Atopy-Related Traits in a Random Sample
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
NIOX VERO. For assessment and management of airway inflammation
 NIOX VERO For assessment and management of airway inflammation NIOX VERO NIOX VERO is a point-of-care device for assessing airway inflammation in patients with respiratory problems such as asthma. NIOX
NIOX VERO For assessment and management of airway inflammation NIOX VERO NIOX VERO is a point-of-care device for assessing airway inflammation in patients with respiratory problems such as asthma. NIOX
Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide measurements between NIOX MINO â electrochemical and Ecomedics chemiluminescence analyzer
 Respiratory Medicine (2008) 102, 1667e1671 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed SHORT COMMUNICATION Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide measurements between
Respiratory Medicine (2008) 102, 1667e1671 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed SHORT COMMUNICATION Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide measurements between
Differences in Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Non- and Mono- or Polysensitised Allergic Children with Asthma Bronchiale
 30 The Open Pediatric Medicine Journal, 2008, 2, 30-34 Open Access Differences in Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Non- and Mono- or Polysensitised Allergic Children with Asthma Bronchiale Leonie Korsch, Annette
30 The Open Pediatric Medicine Journal, 2008, 2, 30-34 Open Access Differences in Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Non- and Mono- or Polysensitised Allergic Children with Asthma Bronchiale Leonie Korsch, Annette
NG80. Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80)
 Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Changes of exhaled nitric oxide during steroid treatment of childhood asthma
 Eur Respir J 2002; 19: 1015 1019 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.01582001 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Changes of exhaled nitric
Eur Respir J 2002; 19: 1015 1019 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.01582001 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Changes of exhaled nitric
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of YourCare Health Plan
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
2.6 MONITORING ASTHMA
 2.6 MONITORING ASTHMA 2.6.1 MONITORING ASTHMA IN ADULTS In the majority of patients with asthma symptom-based monitoring is adequate. Patients achieving control of symptoms with treatment have a low risk
2.6 MONITORING ASTHMA 2.6.1 MONITORING ASTHMA IN ADULTS In the majority of patients with asthma symptom-based monitoring is adequate. Patients achieving control of symptoms with treatment have a low risk
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Exhaled Nitric Oxide Today s Asthma Biomarker. Richard F. Lavi, MD FAAAAI FAAP
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide Today s Asthma Biomarker Richard F. Lavi, MD FAAAAI FAAP Objectives Describe exhaled nitric oxide physiology and pathophysiology Review the current literature regarding exhaled nitric
Exhaled Nitric Oxide Today s Asthma Biomarker Richard F. Lavi, MD FAAAAI FAAP Objectives Describe exhaled nitric oxide physiology and pathophysiology Review the current literature regarding exhaled nitric
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of Excellus Health Plan, Inc. A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MEASUREMENT OF EXHALED MARKERS OF AIRWAY INFLAMMATION IN PATIENTS WITH ASTHMA POLICY NUMBER: 2.01.41 CATEGORY: Technology Assessment EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/15/04 REVISED DATE: 02/17/05,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MEASUREMENT OF EXHALED MARKERS OF AIRWAY INFLAMMATION IN PATIENTS WITH ASTHMA POLICY NUMBER: 2.01.41 CATEGORY: Technology Assessment EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/15/04 REVISED DATE: 02/17/05,
ImmunoCAP. Specific IgE blood test
 Allergy- Specific IgE blood test provides clinicians with an accurate and convenient method of helping to rule in or rule out allergy in patients with allergy-like symptoms. Allergy- Positive About Allergy-
Allergy- Specific IgE blood test provides clinicians with an accurate and convenient method of helping to rule in or rule out allergy in patients with allergy-like symptoms. Allergy- Positive About Allergy-
B ronchial hyperresponsiveness, variable airway obstruction,
 494 ASTHMA Exhaled nitric oxide rather than lung function distinguishes preschool children with probable L P Malmberg, A S Pelkonen, T Haahtela, M Turpeinen... See end of article for authors affiliations...
494 ASTHMA Exhaled nitric oxide rather than lung function distinguishes preschool children with probable L P Malmberg, A S Pelkonen, T Haahtela, M Turpeinen... See end of article for authors affiliations...
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma
 The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Formulating hypotheses and implementing research in allergic disorders in rural Crete, Greece
 Formulating hypotheses and implementing research in allergic disorders in rural Crete, Greece Christos Lionis and Leda Chatzi, Clinic of Social and Family Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Crete,
Formulating hypotheses and implementing research in allergic disorders in rural Crete, Greece Christos Lionis and Leda Chatzi, Clinic of Social and Family Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Crete,
Exhaled carbon monoxide levels after a course of oral prednisone in children
 Exhaled carbon monoxide levels after a course of oral prednisone in children with asthma exacerbation Background: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FE NO ) and exhaled carbon monoxide (ECO) have been proposed
Exhaled carbon monoxide levels after a course of oral prednisone in children with asthma exacerbation Background: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FE NO ) and exhaled carbon monoxide (ECO) have been proposed
KEY WORDS airflow limitation, airway hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation, airway lability, peak expiratory flow rate
 Allergology International. 2013;62:343-349 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.13-oa-0543 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stratifying a Risk for an Increased Variation of Airway Caliber among the Clinically Stable Asthma Atsushi
Allergology International. 2013;62:343-349 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.13-oa-0543 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stratifying a Risk for an Increased Variation of Airway Caliber among the Clinically Stable Asthma Atsushi
Which asthma patient has allergic airway inflammation?
 Which asthma patient has allergic airway inflammation? C o n t r o l l i n g A l l e r g i c A s t h m a Several underlying diseases can present symptoms similar to asthma. Therefore, a correct diagnos
Which asthma patient has allergic airway inflammation? C o n t r o l l i n g A l l e r g i c A s t h m a Several underlying diseases can present symptoms similar to asthma. Therefore, a correct diagnos
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Nitric oxide (NO) was first measured in exhaled
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Acute Exacerbation of Asthma DINESH RAJ, RAKESH LODHA, APARNA MUKHERJEE, TAVPRITESH SETHI, *ANURAG AGRAWAL AND SUSHIL KUMAR KABRA
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Acute Exacerbation of Asthma DINESH RAJ, RAKESH LODHA, APARNA MUKHERJEE, TAVPRITESH SETHI, *ANURAG AGRAWAL AND SUSHIL KUMAR KABRA
Combined use of exhaled nitric oxide and airway hyperresponsiveness in characterizing asthma in a large population survey
 Eur Respir J 2000; 15: 849±855 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2000 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Combined use of exhaled nitric oxide and airway hyperresponsiveness
Eur Respir J 2000; 15: 849±855 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2000 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Combined use of exhaled nitric oxide and airway hyperresponsiveness
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: exhaled_nitric_oxide_measurement 2/2009 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: exhaled_nitric_oxide_measurement 2/2009 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Asthma is
Exhaled nitric oxide measurements with dynamic flow restriction in children aged 4 8 yrs
 Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 919 924 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.01282002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Exhaled nitric oxide measurements
Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 919 924 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.01282002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Exhaled nitric oxide measurements
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Evolution of asthma from childhood. Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT
 Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Determination of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) reference values in healthy Thai population
 Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Determination of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) reference values in healthy Thai population Yiwa Suksawat, Punchama Pacharn, Orathai
Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Determination of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) reference values in healthy Thai population Yiwa Suksawat, Punchama Pacharn, Orathai
COPD and Asthma: Similarities and differences Prof. Peter Barnes
 and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
Exhaled Nitric Oxide among Bulgarian Children with Asthma Exacerbation
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 6 Issue 4 April 2017 PP. 10-16 Exhaled Nitric Oxide among Bulgarian Children with Asthma
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 6 Issue 4 April 2017 PP. 10-16 Exhaled Nitric Oxide among Bulgarian Children with Asthma
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care
 Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype. Phenotypes of Severe Asthma. Cellular Phenotypes 12/7/2012
 Subbasement Membrane Thickness(µm) 12/7/212 Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype Phenotypes of Severe Asthma Most mild and to some degree moderate asthmatics respond well to currently available
Subbasement Membrane Thickness(µm) 12/7/212 Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype Phenotypes of Severe Asthma Most mild and to some degree moderate asthmatics respond well to currently available
Abstract INTRODUCTION. Keywords: atopic asthma, children, fungus sensitization ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fungus Sensitizations: Specific IgE to 4 Different Fungi among Asthmatic Children in North Taiwan Yu-Ting Yu, Shyh-Dar Shyur, Hwai-Chih Yang, Szu-Hung Chu, Yu-Hsuan Kao, Hou-Ling Lung,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fungus Sensitizations: Specific IgE to 4 Different Fungi among Asthmatic Children in North Taiwan Yu-Ting Yu, Shyh-Dar Shyur, Hwai-Chih Yang, Szu-Hung Chu, Yu-Hsuan Kao, Hou-Ling Lung,
Daily ambulatory exhaled nitric oxide measurements in asthma
 Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2006: 17: 189 193 DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2006.00394.x Ó 2006 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2006 Blackwell Munksgaard PEDIATRIC ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Daily ambulatory exhaled
Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2006: 17: 189 193 DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2006.00394.x Ó 2006 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2006 Blackwell Munksgaard PEDIATRIC ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Daily ambulatory exhaled
Asthma Phenotypes, Heterogeneity and Severity: The Basis of Asthma Management
 Asthma Phenotypes, Heterogeneity and Severity: The Basis of Asthma Management Eugene R. Bleecker, MD Professor and Director, Center for Genomics & Personalized Medicine Research Professor, Translational
Asthma Phenotypes, Heterogeneity and Severity: The Basis of Asthma Management Eugene R. Bleecker, MD Professor and Director, Center for Genomics & Personalized Medicine Research Professor, Translational
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Identifying Biologic Targets to Attenuate or Eliminate Asthma Exacerbations
 Identifying Biologic Targets to Attenuate or Eliminate Exacerbations exacerbations are a major cause of disease morbidity and costs. For both children and adults, viral respiratory infections are the major
Identifying Biologic Targets to Attenuate or Eliminate Exacerbations exacerbations are a major cause of disease morbidity and costs. For both children and adults, viral respiratory infections are the major
Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 03/03/2010
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Xolair (omalizumab) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP HMO/PPO/CDHP: Rx
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Xolair (omalizumab) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP HMO/PPO/CDHP: Rx
A systematic review and meta-analysis: tailoring asthma treatment on eosinophilic markers (exhaled nitric oxide or sputum eosinophils)
 See Editorial, p 191 < Additional material is published online only. To view this file please visit the journal online (http://throax.bmj.com/ content/67/3.toc). 1 Queensland Children s Respiratory Centre
See Editorial, p 191 < Additional material is published online only. To view this file please visit the journal online (http://throax.bmj.com/ content/67/3.toc). 1 Queensland Children s Respiratory Centre
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
The exacerbation risk prediction by fractional exhaled nitric oxide in younger and elder children with bronchial asthma
 Kawasaki Medical Journal 40(1):41-46,2014 doi:10.11482/kmj-e40(1)41 41 The risk prediction by fractional exhaled nitric oxide in younger and elder children with bronchial asthma Tokio WAKABAYASHI 1), Tetsuya
Kawasaki Medical Journal 40(1):41-46,2014 doi:10.11482/kmj-e40(1)41 41 The risk prediction by fractional exhaled nitric oxide in younger and elder children with bronchial asthma Tokio WAKABAYASHI 1), Tetsuya
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
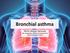 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma?
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Exhaled Breath Condensate in the Management of Respiratory Disorders
 Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date... 2/15/2018 Next Review Date... 2/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 0439 Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Exhaled Breath Condensate in the Management of Respiratory Disorders
Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date... 2/15/2018 Next Review Date... 2/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 0439 Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Exhaled Breath Condensate in the Management of Respiratory Disorders
Exhaled nitric oxide levels in asthma: Personal best versus reference values
 Exhaled nitric oxide levels in asthma: Personal best versus reference values Andrew D. Smith, MRCP(UK), Jan O. Cowan, and D. Robin Taylor, MD Dunedin, New Zealand Background: Factors affecting the fraction
Exhaled nitric oxide levels in asthma: Personal best versus reference values Andrew D. Smith, MRCP(UK), Jan O. Cowan, and D. Robin Taylor, MD Dunedin, New Zealand Background: Factors affecting the fraction
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Does rhinitis. lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma
 Does rhinitis lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma For a better management of allergies in Europe Allergy
Does rhinitis lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma For a better management of allergies in Europe Allergy
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier
 Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Diagnostics Assessment Programme. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide concentration in asthma; NIOX MINO and NObreath. Final scope
 Diagnostics Assessment Programme Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide concentration in asthma; NIOX MINO and NObreath Final scope February 2013 1. Introduction The Medical Technologies Advisory Committee
Diagnostics Assessment Programme Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide concentration in asthma; NIOX MINO and NObreath Final scope February 2013 1. Introduction The Medical Technologies Advisory Committee
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma
 Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit)
 Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Measure breath nitric oxide for airway inflammation with the NObreath FeNO monitor
 Measure breath nitric oxide for airway inflammation with the NObreath FeNO monitor British technology Improving asthma management, one breath at a time. www.bedfont.com w on 01622 851122 or email ask@bedfont.com
Measure breath nitric oxide for airway inflammation with the NObreath FeNO monitor British technology Improving asthma management, one breath at a time. www.bedfont.com w on 01622 851122 or email ask@bedfont.com
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers?
 Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma
 Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Exhaled nitric oxide measurements: clinical application and interpretation ...
 817 OCCASIONAL REVIEW Exhaled nitric oxide measurements: clinical application and interpretation D R Taylor, M W Pijnenburg, A D Smith, J C De Jongste... The use of exhaled nitric oxide measurements (F
817 OCCASIONAL REVIEW Exhaled nitric oxide measurements: clinical application and interpretation D R Taylor, M W Pijnenburg, A D Smith, J C De Jongste... The use of exhaled nitric oxide measurements (F
(Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
10801 Sixth St, Rancho Cucamonga, CA Tel (909) Fax (909) Visit our web site at:
 for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma and Other Pulmonary Disorders IEHP Policy: Based on a review of the currently available literature, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of FE NO
for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma and Other Pulmonary Disorders IEHP Policy: Based on a review of the currently available literature, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of FE NO
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Clinical Benefits of FeNO Monitoring in Asthma RYAN BURTON, MS, RPFT
 Clinical Benefits of FeNO Monitoring in Asthma RYAN BURTON, MS, RPFT Disclosures I am an employee of Circassia Pharmaceuticals. Objectives Nitric Oxide Inflammation in Asthma Phenotyping Personalized Medicine
Clinical Benefits of FeNO Monitoring in Asthma RYAN BURTON, MS, RPFT Disclosures I am an employee of Circassia Pharmaceuticals. Objectives Nitric Oxide Inflammation in Asthma Phenotyping Personalized Medicine
Relationship between Methacholine Challenge Testing and exhaled Nitric Oxide in adult patients with suspected bronchial asthma
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E S Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol Vol 46, N 3, 109-113, 2014 M. Giovannini, M. Valli, V. Ribuffo, R. Melara, G. Cappiello, E. Businarolo, A. Andreani Relationship between Methacholine
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E S Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol Vol 46, N 3, 109-113, 2014 M. Giovannini, M. Valli, V. Ribuffo, R. Melara, G. Cappiello, E. Businarolo, A. Andreani Relationship between Methacholine
Fractional exhaled Nitric Oxide monitoring in paediatric asthma management Horizon Scan Report 0047 September 2016
 Diagnostic Evidence Co-operative Oxford Fractional exhaled Nitric Oxide monitoring in paediatric asthma management Horizon Scan Report 0047 September 2016 Clinical Questions: Does monitoring of childhood
Diagnostic Evidence Co-operative Oxford Fractional exhaled Nitric Oxide monitoring in paediatric asthma management Horizon Scan Report 0047 September 2016 Clinical Questions: Does monitoring of childhood
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies
 Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Definition and Pathology CHAPTER 1. John Rees
 CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
7/7/2015. Somboon Chansakulporn, MD. History of variable respiratory symptoms. 1. Documented excessive variability in PFT ( 1 test)
 Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
THE COPD-ASTHMA OVERLAP SYNDROME
 THE COPD-ASTHMA OVERLAP SYNDROME NICOLA A. HANANIA, MD, MS, FRCP(C), FCCP, FACP ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIRECTOR OF ASTHMA & COPD CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE HOUSTON, TX
THE COPD-ASTHMA OVERLAP SYNDROME NICOLA A. HANANIA, MD, MS, FRCP(C), FCCP, FACP ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE DIRECTOR OF ASTHMA & COPD CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE HOUSTON, TX
Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma
 Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma Dr Andrew Tai FRACP, PhD Paediatric Respiratory and Sleep Specialist Women's and Children's Hospital, Adelaide Approaching the patient Check the diagnosis
Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma Dr Andrew Tai FRACP, PhD Paediatric Respiratory and Sleep Specialist Women's and Children's Hospital, Adelaide Approaching the patient Check the diagnosis
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2017?
 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Asthma-COPD overlap The word syndrome has been removed from the previous term asthma-copd overlap syndrome
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Asthma-COPD overlap The word syndrome has been removed from the previous term asthma-copd overlap syndrome
LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE
 LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE Azienda Ospedaliera Pisana Università degli Studi di Pisa Pierluigi Paggiaro GINA International Executive Committee, Chairman GINA ITaly Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department,
LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE Azienda Ospedaliera Pisana Università degli Studi di Pisa Pierluigi Paggiaro GINA International Executive Committee, Chairman GINA ITaly Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department,
Titrating Steroids on Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Asthma A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Titrating Steroids on Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Asthma A Randomized Controlled Trial Mariëlle W. Pijnenburg, E. Marije Bakker, Wim C. Hop, and Johan C. De Jongste Departments of Pediatrics/Pediatric
Titrating Steroids on Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children with Asthma A Randomized Controlled Trial Mariëlle W. Pijnenburg, E. Marije Bakker, Wim C. Hop, and Johan C. De Jongste Departments of Pediatrics/Pediatric
Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association
 Measurement of Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Page 1 of 18 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Measurement of Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Exhaled Breath Condensate
Measurement of Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Page 1 of 18 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Measurement of Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Exhaled Breath Condensate
Asthma and obesity, implications for airway inflammation and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness
 Asthma and obesity, implications for airway inflammation and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness Fernando Holguin MD MPH Asthma Institute University of Pittsburgh Obesity Trends* Among U.S. Adults BRFSS, 1990,
Asthma and obesity, implications for airway inflammation and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness Fernando Holguin MD MPH Asthma Institute University of Pittsburgh Obesity Trends* Among U.S. Adults BRFSS, 1990,
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention
 Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Asthma Therapy 2017 JOSHUA S. JACOBS, M.D.
 Asthma Therapy 2017 JOSHUA S. JACOBS, M.D. BACKGROUND-PREVALENCE Asthma is one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide with an estimated 300 million affected individuals Prevalence is increasing
Asthma Therapy 2017 JOSHUA S. JACOBS, M.D. BACKGROUND-PREVALENCE Asthma is one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide with an estimated 300 million affected individuals Prevalence is increasing
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring
 Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Michael S. Blaiss, MD
 Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine Division of Clinical Immunology and Allergy University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca,
Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine Division of Clinical Immunology and Allergy University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca,
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Clinical Study Report SLO-AD-1 Final Version DATE: 09 December 2013
 1. Clinical Study Report RANDOMIZED, OPEN, PARALLEL GROUP, PHASE IIIB STUDY ON THE EVALUATION OF EFFICACY OF SPECIFIC SUBLINGUAL IMMUNOTHERAPY IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH ATOPIC DERMATITIS, WITH OR WITHOUT
1. Clinical Study Report RANDOMIZED, OPEN, PARALLEL GROUP, PHASE IIIB STUDY ON THE EVALUATION OF EFFICACY OF SPECIFIC SUBLINGUAL IMMUNOTHERAPY IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH ATOPIC DERMATITIS, WITH OR WITHOUT
INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY. Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim
 INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim Definition Involves Administration of gradually increasing quantities of specific allergens to patients with IgE-mediated
INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim Definition Involves Administration of gradually increasing quantities of specific allergens to patients with IgE-mediated
SLIT: Review and Update
 SLIT: Review and Update Disclosure Speaker: ISTA Pharmaceuticals Speaker: GlaxoSmithKline Allergen IT - Evidence Based Evaluation: Rescue Medications Meta-analysis Disease IT # of Patients Rescue Medication
SLIT: Review and Update Disclosure Speaker: ISTA Pharmaceuticals Speaker: GlaxoSmithKline Allergen IT - Evidence Based Evaluation: Rescue Medications Meta-analysis Disease IT # of Patients Rescue Medication
Allergy, Asthma and the Athlete Sergio Bonini
 Allergy, Asthma and the Athlete Sergio Bonini Professor of Medicine Second University of Naples Institute of Translational Pharmacology Italian National Research,Rome se.bonini@gmail.com Cancun December
Allergy, Asthma and the Athlete Sergio Bonini Professor of Medicine Second University of Naples Institute of Translational Pharmacology Italian National Research,Rome se.bonini@gmail.com Cancun December
Distinction and Overlap. Allergy Dpt, 2 nd Pediatric Clinic, University of Athens
 Asthma Phenotypes: Distinction and Overlap Nikos Papadopoulos Allergy Dpt, 2 nd Pediatric Clinic, University of Athens Asthma as a syndrome From the Iliad to ADAM 33 and back again Bronchoconstriction,
Asthma Phenotypes: Distinction and Overlap Nikos Papadopoulos Allergy Dpt, 2 nd Pediatric Clinic, University of Athens Asthma as a syndrome From the Iliad to ADAM 33 and back again Bronchoconstriction,
Hypersensitivity diseases
 Hypersensitivity diseases Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 18 July 2006 11:40 AM) 2005 Elsevier Type-I Hypersensitivity Basic terms Type-I = Early= IgE-mediated = Atopic = Anaphylactic type of hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity diseases Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 18 July 2006 11:40 AM) 2005 Elsevier Type-I Hypersensitivity Basic terms Type-I = Early= IgE-mediated = Atopic = Anaphylactic type of hypersensitivity
Maternal food consumption during pregnancy and the longitudinal development of childhood asthma
 Maternal food consumption during pregnancy and the longitudinal development of childhood asthma Saskia M. Willers, Alet H. Wijga, Bert Brunekreef, Marjan Kerkhof, Jorrit Gerritsen, Maarten O. Hoekstra,
Maternal food consumption during pregnancy and the longitudinal development of childhood asthma Saskia M. Willers, Alet H. Wijga, Bert Brunekreef, Marjan Kerkhof, Jorrit Gerritsen, Maarten O. Hoekstra,
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide measurements are most closely associated with allergic sensitization in school-age children
 Original article Fractional exhaled nitric oxide measurements are most closely associated with allergic sensitization in school-age children Daniel J. Jackson, MD, a,b Christine M. Virnig, MD, a,b Ronald
Original article Fractional exhaled nitric oxide measurements are most closely associated with allergic sensitization in school-age children Daniel J. Jackson, MD, a,b Christine M. Virnig, MD, a,b Ronald
The FDA Critical Path Initiative
 The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
EFFECTIVE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE Severity Assessment, Guidelines, and New Therapeutic Options
 Educational Objectives EFFECTIVE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE Bradley E. Chipps, MD, FAAP, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FCCP President-Elect, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Medical Director,
Educational Objectives EFFECTIVE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE Bradley E. Chipps, MD, FAAP, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FCCP President-Elect, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Medical Director,
Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes:
 Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
From Chronic Lung Disease of Infancy to Asthma
 From Chronic Lung Disease of Infancy to Asthma Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP Certified Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Pediatric Lung Care Bon Secours Medical Group St. Mary s Hospital 1 Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP
From Chronic Lung Disease of Infancy to Asthma Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP Certified Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Pediatric Lung Care Bon Secours Medical Group St. Mary s Hospital 1 Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP
PFT s / 2017 Pulmonary Update. Eric S. Papierniak, DO University of Florida NF/SG VHA
 PFT s / 2017 Pulmonary Update Eric S. Papierniak, DO University of Florida NF/SG VHA Outline Overview of pulmonary function testing Uses/indications/limitations Technical aspects Basics of interpretation
PFT s / 2017 Pulmonary Update Eric S. Papierniak, DO University of Florida NF/SG VHA Outline Overview of pulmonary function testing Uses/indications/limitations Technical aspects Basics of interpretation
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide ASTHMA
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
