Asthma. Definition. Symptoms
|
|
|
- Clinton McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some people, asthma is a minor nuisance. For others, it can be a major problem that interferes with daily activities and may lead to a life-threatening asthma attack. Asthma can't be cured, but its symptoms can be controlled. Because asthma often changes over time, it's important that you work with your doctor to track your signs and symptoms and adjust treatment as needed. Symptoms Asthma symptoms vary from person to person. You may have infrequent asthma attacks, have symptoms only at certain times such as when exercising or have symptoms all the time. Asthma signs and symptoms include: Shortness of breath Chest tightness or pain Trouble sleeping caused by shortness of breath, coughing or wheezing A whistling or wheezing sound when exhaling (wheezing is a common sign of asthma in children) Coughing or wheezing attacks that are worsened by a respiratory virus, such as a cold or the flu Signs that your asthma is probably worsening include: Asthma signs and symptoms that are more frequent and bothersome Increasing difficulty breathing (measurable with a peak flow meter, a device used to check how well your lungs are working) The need to use a quick-relief inhaler more often For some people, asthma signs and symptoms flare up in certain situations: Exercise-induced asthma, which may be worse when the air is cold and dry
2 Occupational asthma, triggered by workplace irritants such as chemical fumes, gases or dust Allergy-induced asthma, triggered by particular allergens, such as pet dander, cockroaches or pollen When to see a doctor Seek emergency treatment Severe asthma attacks can be life-threatening. Work with your doctor to determine what to do when your signs and symptoms worsen and when you need emergency treatment. Signs of an asthma emergency include: Rapid worsening of shortness of breath or wheezing No improvement even after using a quick-relief inhaler, such as albuterol Shortness of breath when you are doing minimal physical activity Contact your doctor See your doctor: If you think you have asthma. If you have frequent coughing or wheezing that lasts more than a few days or any other signs or symptoms of asthma, see your doctor. Treating asthma early may prevent long-term lung damage and help keep the condition from worsening over time. To monitor your asthma after diagnosis. If you know you have asthma, work with your doctor to keep it under control. Good long-term control helps you feel better from day to day and can prevent a life-threatening asthma attack. If your asthma symptoms get worse. Contact your doctor right away if your medication doesn't seem to ease your symptoms or if you need to use your quickrelief inhaler more often. Don't try to solve the problem by taking more medication without consulting your doctor. Overusing asthma medication can cause side effects and may make your asthma worse. To review your treatment. Asthma often changes over time. Meet with your doctor regularly to discuss your symptoms and make any needed treatment adjustments.
3 Causes It isn't clear why some people get asthma and others don't, but it's probably due to a combination of environmental and genetic (inherited) factors. Asthma triggers Exposure to various irritants and substances that trigger allergies (allergens) can trigger signs and symptoms of asthma. Asthma triggers are different from person to person and can include: Airborne allergens, such as pollen, animal dander, mold, cockroaches and dust mites Respiratory infections, such as the common cold Physical activity (exercise-induced asthma) Cold air Air pollutants and irritants, such as smoke Certain medications, including beta blockers, aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen (Aleve) Strong emotions and stress Sulfites and preservatives added to some types of foods and beverages, including shrimp, dried fruit, processed potatoes, beer and wine Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a condition in which stomach acids back up into your throat Treatments and drugs Prevention and long-term control are key in stopping asthma attacks before they start. Treatment usually involves learning to recognize your triggers, taking steps to avoid them and tracking your breathing to make sure your daily asthma medications are keeping symptoms under control. In case of an asthma flare-up, you may need to use a quick-relief inhaler, such as albuterol. Medications The right medications for you depend on a number of things your age, symptoms, asthma triggers and what works best to keep your asthma under control. Preventive, long-term control medications reduce the inflammation in your airways that leads to symptoms. Quick-relief inhalers (bronchodilators) quickly open swollen airways that are limiting breathing. In some cases, allergy medications are necessary.
4 Long-term asthma control medications, generally taken daily, are the cornerstone of asthma treatment. These medications keep asthma under control on a day-to-day basis and make it less likely you'll have an asthma attack. Types of long-term control medications include: Inhaled corticosteroids. These anti-inflammatory drugs include fluticasone (Flonase, Flovent HFA), budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler, Rhinocort), flunisolide (Aerospan HFA), ciclesonide (Alvesco, Omnaris, Zetonna), beclomethasone (Qnasl, Qvar), mometasone (Asmanex) and fluticasone furoate (Arnuity Ellipta). You may need to use these medications for several days to weeks before they reach their maximum benefit. Unlike oral corticosteroids, these corticosteroid medications have a relatively low risk of side effects and are generally safe for long-term use. Leukotriene modifiers. These oral medications including montelukast (Singulair), zafirlukast (Accolate) and zileuton (Zyflo) help relieve asthma symptoms for up to 24 hours. In rare cases, these medications have been linked to psychological reactions, such as agitation, aggression, hallucinations, depression and suicidal thinking. Seek medical advice right away for any unusual reaction. Long-acting beta agonists. These inhaled medications, which include salmeterol (Serevent) and formoterol (Foradil, Perforomist), open the airways. Some research shows that they may increase the risk of a severe asthma attack, so take them only in combination with an inhaled corticosteroid. And because these drugs can mask asthma deterioration, don't use them for an acute asthma attack. Combination inhalers. These medications such as fluticasone-salmeterol (Advair Diskus), budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort) and formoterol-mometasone (Dulera) contain a long-acting beta agonist along with a corticosteroid. Because these combination inhalers contain long-acting beta agonists, they may increase your risk of having a severe asthma attack. Theophylline. Theophylline (Theo-24, Elixophyllin, others) is a daily pill that helps keep the airways open (bronchodilator) by relaxing the muscles around the airways. It's not used as often now as in past years. Quick-relief (rescue) medications are used as needed for rapid, short-term symptom relief during an asthma attack or before exercise if your doctor recommends it. Types of quick-relief medications include:
5 Short-acting beta agonists. These inhaled, quick-relief bronchodilators act within minutes to rapidly ease symptoms during an asthma attack. They include albuterol (ProAir HFA, Ventolin HFA, others) and levalbuterol (Xopenex). Short-acting beta agonists can be taken using a portable, hand-held inhaler or a nebulizer a machine that converts asthma medications to a fine mist so that they can be inhaled through a face mask or a mouthpiece. Ipratropium (Atrovent). Like other bronchodilators, ipratropium acts quickly to immediately relax your airways, making it easier to breathe. Ipratropium is mostly used for emphysema and chronic bronchitis, but it's sometimes used to treat asthma attacks. Oral and intravenous corticosteroids. These medications which include prednisone and methylprednisolone relieve airway inflammation caused by severe asthma. They can cause serious side effects when used long term, so they're used only on a short-term basis to treat severe asthma symptoms. If you have an asthma flare-up, a quick-relief inhaler can ease your symptoms right away. But if your long-term control medications are working properly, you shouldn't need to use your quick-relief inhaler very often. Keep a record of how many puffs you use each week. If you need to use your quickrelief inhaler more often than your doctor recommends, see your doctor. You probably need to adjust your long-term control medication. Allergy medications may help if your asthma is triggered or worsened by allergies. These include: Allergy shots (immunotherapy). Over time, allergy shots gradually reduce your immune system reaction to specific allergens. You generally receive shots once a week for a few months, then once a month for a period of three to five years. Omalizumab (Xolair). This medication, given as an injection every two to four weeks, is specifically for people who have allergies and severe asthma. It acts by altering the immune system. Bronchial thermoplasty This treatment which isn't widely available nor right for everyone is used for severe asthma that doesn't improve with inhaled corticosteroids or other long-term asthma medications.
6 Generally, over the span of three outpatient visits, bronchial thermoplasty heats the insides of the airways in the lungs with an electrode, reducing the smooth muscle inside the airways. This limits the ability of the airways to tighten, making breathing easier and possibly reducing asthma attacks. Treat by severity for better control: A stepwise approach Your treatment should be flexible and based on changes in your symptoms, which should be assessed thoroughly each time you see your doctor. Then your doctor can adjust your treatment accordingly. For example, if your asthma is well-controlled, your doctor may prescribe less medicine. If your asthma isn't well-controlled or is getting worse, your doctor may increase your medication and recommend more-frequent visits. Asthma action plan Work with your doctor to create an asthma action plan that outlines in writing when to take certain medications or when to increase or decrease the dose of your medications based on your symptoms. Also include a list of your triggers and the steps you need to take to avoid them. Your doctor may also recommend tracking your asthma symptoms or using a peak flow meter on a regular basis to monitor how well your treatment is controlling your asthma. Prevention While there's no way to prevent asthma, by working together, you and your doctor can design a step-by-step plan for living with your condition and preventing asthma attacks. Follow your asthma action plan. With your doctor and health care team, write a detailed plan for taking medications and managing an asthma attack. Then be sure to follow your plan. Asthma is an ongoing condition that needs regular monitoring and treatment. Taking control of your treatment can make you feel more in control of your life in general. Get vaccinated for influenza and pneumonia. Staying current with vaccinations can prevent flu and pneumonia from triggering asthma flare-ups. Identify and avoid asthma triggers. A number of outdoor allergens and irritants ranging from pollen and mold to cold air and air pollution can trigger asthma
7 attacks. Find out what causes or worsens your asthma, and take steps to avoid those triggers. Monitor your breathing. You may learn to recognize warning signs of an impending attack, such as slight coughing, wheezing or shortness of breath. But because your lung function may decrease before you notice any signs or symptoms, regularly measure and record your peak airflow with a home peak flow meter. Identify and treat attacks early. If you act quickly, you're less likely to have a severe attack. You also won't need as much medication to control your symptoms. When your peak flow measurements decrease and alert you to an oncoming attack, take your medication as instructed and immediately stop any activity that may have triggered the attack. If your symptoms don't improve, get medical help as directed in your action plan. Take your medication as prescribed. Just because your asthma seems to be improving, don't change anything without first talking to your doctor. It's a good idea to bring your medications with you to each doctor visit, so your doctor can doublecheck that you're using your medications correctly and taking the right dose. Pay attention to increasing quick-relief inhaler use. If you find yourself relying on your quick-relief inhaler, such as albuterol, your asthma isn't under control. See your doctor about adjusting your treatment.
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Asthma medications: Know your options - MayoClinic.com. Asthma medications: Know your options
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Some Facts About Asthma
 Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide ASTHMA
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
Asthma 101. Introduction
 TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
Respiratory Health. Asthma and COPD
 Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Get Healthy Stay Healthy
 Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Breathe Easy. Living with Asthma
 Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath.
 Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath. AccuNeb inhalation 0.021% solution: 0.63mg/3mL 3-4 times solution
Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath. AccuNeb inhalation 0.021% solution: 0.63mg/3mL 3-4 times solution
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
LivingWith Asthma. A Guide to Understanding Asthma...
 A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
Allergies and Asthma 5/21/2013. Objectives. Allergic Rhinitis (AR): Risk Factor for ASTHMA. Rhinitis and Asthma
 Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA
 Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
Breathe Easy ACTIVITIES. A Family Guide to Living with Asthma F O R T H E K ! I D S
 Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Staying Healthy. with Asthma. Illustrations by paulsharp.com
 Staying Healthy with Asthma Illustrations by paulsharp.com Lungs & Asthma What is Asthma? Inflammation or swelling of airways that leads to: 1) Mucous production deep inside the airways. 2) Temporary difficulty
Staying Healthy with Asthma Illustrations by paulsharp.com Lungs & Asthma What is Asthma? Inflammation or swelling of airways that leads to: 1) Mucous production deep inside the airways. 2) Temporary difficulty
Asthma Management. Photo from
 Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Provider Respiratory Inservice
 Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Asthma Education. The Keys to Asthma Prevention and Control. what to do when one s asthma is flared! Lucile Packard Children s Hospital.
 Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
ASTHMA CONTROL. Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms.
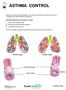 ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
Home Management Plan. Cover Page
 Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
Asthma. What Is Asthma? Overview. Asthma
 Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness,
Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness,
Key features and changes to these four components of asthma care include:
 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Adults Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions regarding
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Adults Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions regarding
MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING Presented by:
 MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
Sources. Taking Charge of Your Asthma. Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company
 Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) Green Zone: (80 to 00% of my personal best) Peak Flow between and (00% = personal best) You can do all the things you usually do. Your asthma medicine
Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) Green Zone: (80 to 00% of my personal best) Peak Flow between and (00% = personal best) You can do all the things you usually do. Your asthma medicine
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather
 Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Breath of Fresh Air. nniversary 20th. New National Asthma Survey: How Does Your Asthma Compare? Long-Acting Bronchodilators: Why All the Fuss?
 Information, news and advice for improving asthma well-being Volume 12, No. 1 Summer 2010 New National Asthma Survey: How Does Your Asthma Compare? nniversary 20th Sometimes if one has to live with a chronic
Information, news and advice for improving asthma well-being Volume 12, No. 1 Summer 2010 New National Asthma Survey: How Does Your Asthma Compare? nniversary 20th Sometimes if one has to live with a chronic
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Supporting Evidence: Diagnosis and Management of Asthma The subdivision of this section is: Appendix B Tables Copyright 2016 by 1 Eleventh Edition/December 2016 Appendix B Asthma Summary Tables Class:
Supporting Evidence: Diagnosis and Management of Asthma The subdivision of this section is: Appendix B Tables Copyright 2016 by 1 Eleventh Edition/December 2016 Appendix B Asthma Summary Tables Class:
Kickin Asthma. Workbook for Children with Asthma. Name:
 Kickin Asthma Workbook for Children with Asthma Name: Why Have You Been Invited to Kickin Asthma? You have been invited to Kickin Asthma because you have asthma. Asthma is a disease of your air tubes that
Kickin Asthma Workbook for Children with Asthma Name: Why Have You Been Invited to Kickin Asthma? You have been invited to Kickin Asthma because you have asthma. Asthma is a disease of your air tubes that
Foundations of Pharmacology
 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
COPD. Definitionn. make. when (bronchioles) in. the lungs. Wheezing Chest tightness. your lungs. greenish. Lack of energy
 COPD Definitionn Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two most common conditions thatt make up COPD. Chronic bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which carry air to
COPD Definitionn Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two most common conditions thatt make up COPD. Chronic bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which carry air to
Web E-Mial Registration Form. Med practitioner s name. Med practitioner s phone. Name/location of the clinic
 AsthmaCare Program Buteyko Clinic USA, LLC Web www.asthmacare.us E-Mial info@asthmacare.us Workshop Date Workshop location Registration Form The purpose of this form is to assist AsthmaCare practitioner
AsthmaCare Program Buteyko Clinic USA, LLC Web www.asthmacare.us E-Mial info@asthmacare.us Workshop Date Workshop location Registration Form The purpose of this form is to assist AsthmaCare practitioner
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
How can I benefit most from my COPD medications?
 Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
TRELEGY ELLIPTA (fluticasone-umeclidinium-vilanterol) aerosol powder
 TRELEGY ELLIPTA (fluticasone-umeclidinium-vilanterol) aerosol powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
TRELEGY ELLIPTA (fluticasone-umeclidinium-vilanterol) aerosol powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
SAMPLE. mg by mouth every day for day(s) Prednisolone. Other Medicine: Medicine Dose How long Directions
 Pediatric Asthma Discharge Prescription and Short-Term Plan The doctor will fill out this form before your child is discharged. Please follow this plan until you see your usual doctor in 3 to 7 days. Hospital
Pediatric Asthma Discharge Prescription and Short-Term Plan The doctor will fill out this form before your child is discharged. Please follow this plan until you see your usual doctor in 3 to 7 days. Hospital
MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINES ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE DATE: 07/05/18 SECTION: DRUGS LAST REVIEW DATE: LAST CRITERIA REVISION DATE: ARCHIVE DATE:
 CINQAIR (reslizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
CINQAIR (reslizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
Understanding. Asthma. National Jewish Health. An educational health series from
 Understanding Asthma An educational health series from National Jewish Health National Jewish Health Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution.
Understanding Asthma An educational health series from National Jewish Health National Jewish Health Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution.
Welcome to our Asthma Program
 Welcome to our Asthma Program We re here to help you be your healthiest through information, education and support for your asthma. We ll work with you by: Partnering with your health care team to make
Welcome to our Asthma Program We re here to help you be your healthiest through information, education and support for your asthma. We ll work with you by: Partnering with your health care team to make
Because the more you know, the better you ll feel.
 ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma and the things you can do every day to help control symptoms. As always, talk to your
ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma and the things you can do every day to help control symptoms. As always, talk to your
Asthma. Basic Information About Asthma. What is asthma? Who is at risk? What are the most common triggers for asthma symptoms?
 In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
How to Manage Asthma
 How to Manage Asthma Table of Contents I. What is Asthma? Page 2 II. How Do Your Lungs Work Page 2 III. What Triggers an Asthma Attack? Page 3 IV. How to Control Asthma Triggers Page 3 V. Your Peak Flow
How to Manage Asthma Table of Contents I. What is Asthma? Page 2 II. How Do Your Lungs Work Page 2 III. What Triggers an Asthma Attack? Page 3 IV. How to Control Asthma Triggers Page 3 V. Your Peak Flow
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD
 How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
How To Treat And Control Asthma
 How To Treat And Control Asthma 314 Great Tips For Getting Quick Relief From Asthma By Adam Colton Published by Bizmove Free Health Books Copyright by Liraz Publishing. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
How To Treat And Control Asthma 314 Great Tips For Getting Quick Relief From Asthma By Adam Colton Published by Bizmove Free Health Books Copyright by Liraz Publishing. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
Asthma. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing worldwide, but why this is happening is not known.
 Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Bronchiectasis. Examples include: Viral infections (measles, adenovirus, influenza)
 Bronchiectasis What is Bronchiectasis? Bronchiectasis (pronounced bron-kee-ek'-tas-is) is a condition of the airways in the lungs. These airways (bronchial tubes) are tubelike structures that branch from
Bronchiectasis What is Bronchiectasis? Bronchiectasis (pronounced bron-kee-ek'-tas-is) is a condition of the airways in the lungs. These airways (bronchial tubes) are tubelike structures that branch from
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017
 Protocol Title: Adult Asthma Protocol Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based
Protocol Title: Adult Asthma Protocol Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based
Asthma. January 2011
 Asthma January 2011 What is Asthma? Asthma is a lung disease that affects the breathing tubes (airways) that allow air to go in and out of the lungs. Normal airways are wide open, so air can go in and
Asthma January 2011 What is Asthma? Asthma is a lung disease that affects the breathing tubes (airways) that allow air to go in and out of the lungs. Normal airways are wide open, so air can go in and
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES. School Nurses November 2015
 ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
MY ASTHMA BOOKLET. Name: Date: / /
 MY ASTHMA BOOKLET Name: Date: / / 1 2 WHAT IS ASTHMA? WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma is a lung disease. The airways in the lungs get very small. It is hard for air to move through very small airways. It is hard
MY ASTHMA BOOKLET Name: Date: / / 1 2 WHAT IS ASTHMA? WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma is a lung disease. The airways in the lungs get very small. It is hard for air to move through very small airways. It is hard
The Right Medicines Can Help You Get Control of Asthma. BlueCare SM TennCareSelect
 The Right Medicines Can Help You Get Control of Asthma BlueCare SM TennCareSelect Wheezing. COUGHING. Shortness of breath. CHEST TIGHTNESS. If you or a family member has asthma, you know these symptoms
The Right Medicines Can Help You Get Control of Asthma BlueCare SM TennCareSelect Wheezing. COUGHING. Shortness of breath. CHEST TIGHTNESS. If you or a family member has asthma, you know these symptoms
FASENRA (benralizumab)
 FASENRA (benralizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
FASENRA (benralizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
Because the more you know, the better you ll feel.
 ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. What You ll Find Attitudes and Beliefs Asthma What Is It? Where You ll Find It Page 4-5 This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma
ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. What You ll Find Attitudes and Beliefs Asthma What Is It? Where You ll Find It Page 4-5 This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma
A cough can be acute, subacute, or chronic, depending on how long it lasts.
 What Is? A cough is a natural reflex that protects your lungs. ing helps clear your airways of lung irritants, such as smoke and mucus (a slimy substance). This helps prevent infections. A cough also can
What Is? A cough is a natural reflex that protects your lungs. ing helps clear your airways of lung irritants, such as smoke and mucus (a slimy substance). This helps prevent infections. A cough also can
PATIENT INFORMATION FORM
 PATIENT INFORMATION FORM "I am going to ask you a number of questions about your asthma. The set of questions is somewhat long, but I will try to move through it fairly quickly so that we can complete
PATIENT INFORMATION FORM "I am going to ask you a number of questions about your asthma. The set of questions is somewhat long, but I will try to move through it fairly quickly so that we can complete
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA. A guide for parents. childrensmn.org
 CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA A guide for parents childrensmn.org Content Your child has asthma a chronic lung disease. To best control the symptoms of asthma, it is important that you learn all you can about asthma.
CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA A guide for parents childrensmn.org Content Your child has asthma a chronic lung disease. To best control the symptoms of asthma, it is important that you learn all you can about asthma.
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
II: Moderate Worsening airflow limitations Dyspnea on exertion, cough, and sputum production; patient usually seeks medical
 Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
REVISED RESPIRATORY MEDICATION USE QUESTIONNAIRE
 REVISED RESPIRATORY MEDICATION USE QUESTIONNAIRE ID NUMBER: 0a) Date of Collection / / 0b) Staff Code Instructions: This form should be completed during the participant s clinic visit. 1) Are you regularly
REVISED RESPIRATORY MEDICATION USE QUESTIONNAIRE ID NUMBER: 0a) Date of Collection / / 0b) Staff Code Instructions: This form should be completed during the participant s clinic visit. 1) Are you regularly
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING
 UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
What You Need to Know about Metered-Dose Inhalers and the HFA Propellant
 What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
Asthma. doh.sd.gov/statistics/2009brfss/asthma.pdf
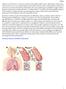 is an obstructive or restrictive condition which inhibits airflow due to inflammation of the airway. This obstruction occurs via increased edema in the small bronchioles walls as well as greater production
is an obstructive or restrictive condition which inhibits airflow due to inflammation of the airway. This obstruction occurs via increased edema in the small bronchioles walls as well as greater production
A patient educational resource provided by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Asthma and Travel to Beijing By Dr. Fiona Newton BMBS (Hons) Family Medicine Physician at Beijing United Family Hospital and Clinics
 Asthma and Travel to Beijing By Dr. Fiona Newton BMBS (Hons) Family Medicine Physician at Beijing United Family Hospital and Clinics So you have asthma? Is travel to Beijing out of the question? Asthma
Asthma and Travel to Beijing By Dr. Fiona Newton BMBS (Hons) Family Medicine Physician at Beijing United Family Hospital and Clinics So you have asthma? Is travel to Beijing out of the question? Asthma
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
COPD. The goals of COPD. about. you quit. If you. efforts to quit. Heart
 How Is COPD Treated? COPD has no cure yet. However, lifestyle changes and treatments can help you feel better, stay more active, and slow the progress of the disease. The goals of COPD treatment include:
How Is COPD Treated? COPD has no cure yet. However, lifestyle changes and treatments can help you feel better, stay more active, and slow the progress of the disease. The goals of COPD treatment include:
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Washington Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Washington Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Asthma Action Plan and Education
 Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Breathe Easy. Tips for controlling your Asthma
 Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
your breathing problems worsen quickly. you use your rescue inhaler, but it does not relieve your breathing problems.
 MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR DISKUS [ad vair disk us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is the most important information I should know about ADVAIR DISKUS?
MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR DISKUS [ad vair disk us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is the most important information I should know about ADVAIR DISKUS?
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
10/18/2012. Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C
 Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens
 A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP 3 Main Categories Inhaled Respiratory Drugs Binds to beta-2 receptors Relaxation of smooth muscles in the lung
A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP 3 Main Categories Inhaled Respiratory Drugs Binds to beta-2 receptors Relaxation of smooth muscles in the lung
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Washington Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Washington Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians
 Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Asthma in Adults Melissa Ngai, Pharm.D Candidate Peter J. Hughes, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham,
Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Asthma in Adults Melissa Ngai, Pharm.D Candidate Peter J. Hughes, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham,
Cough Associated with Bronchitis
 Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUGS CHAPTER 21. Antineoplastic drugs - designed to treat malignancies, now also used to treat diseases with inflammatory component
 ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUGS CHAPTER 21 Antineoplastic drugs - designed to treat malignancies, now also used to treat diseases with inflammatory component Tx of malignancies Antineoplastic drugs: methotrexate
ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUGS CHAPTER 21 Antineoplastic drugs - designed to treat malignancies, now also used to treat diseases with inflammatory component Tx of malignancies Antineoplastic drugs: methotrexate
Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide
 Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S A N D T H E C H E S T F O U N D A T I O N Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide
Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S A N D T H E C H E S T F O U N D A T I O N Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide
CMS Asthma Education Program
 CMS Asthma Education Program ASTHMA IS Common Chronic Treatable Distressing Misunderstood Potentially Dangerous CMS Prevalence Number one chronic disease Leading cause of Absences 6481 CMS students (2003-04)
CMS Asthma Education Program ASTHMA IS Common Chronic Treatable Distressing Misunderstood Potentially Dangerous CMS Prevalence Number one chronic disease Leading cause of Absences 6481 CMS students (2003-04)
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
ESSENTIAL STANDARD. 6.PCH.1 Understand wellness, disease prevention, and recognition of symptoms.
 PRE-TEST 1.What are the basic functions of the respiratory system? 2.Describe five symptoms of asthma. 3.How can asthma be controlled? 4.What are some common asthma triggers? ESSENTIAL STANDARD 6.PCH.1
PRE-TEST 1.What are the basic functions of the respiratory system? 2.Describe five symptoms of asthma. 3.How can asthma be controlled? 4.What are some common asthma triggers? ESSENTIAL STANDARD 6.PCH.1
Breath of Fresh Air. Information, news and advice for improving asthma well-being. National Asthma Guidelines: A Stepped Approach to Asthma Therapy
 Information, news and advice for improving asthma well-being Volume 11, No. 1 Summer 2008 National Asthma Guidelines: A ped Approach to Asthma Therapy In the last issue of Breath of Fresh Air, we discussed
Information, news and advice for improving asthma well-being Volume 11, No. 1 Summer 2008 National Asthma Guidelines: A ped Approach to Asthma Therapy In the last issue of Breath of Fresh Air, we discussed
Asthma. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know
 1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Inhaled Corticosteroids Drugs: Aerospan (flunisolide), Advair Diskus, Advair HFA (fluticasone/salmeterol), Alvesco (ciclesonide), Arnuity Ellipta (fluticasone furoate), Asmanex
Drug Class Monograph Class: Inhaled Corticosteroids Drugs: Aerospan (flunisolide), Advair Diskus, Advair HFA (fluticasone/salmeterol), Alvesco (ciclesonide), Arnuity Ellipta (fluticasone furoate), Asmanex
COPD. Helen Suen & Lexi Smith
 COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD. Diseases and Conditions
 Diseases and Conditions COPD By Mayo Clinic Staff Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing
Diseases and Conditions COPD By Mayo Clinic Staff Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Texas Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the Provider
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Texas Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the Provider
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation
![PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation](/thumbs/74/71128680.jpg) PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
Alberta Childhood Asthma Pathway for Primary Care
 Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
