Focus on Upper and Lower Respiratory Diseases
|
|
|
- Colin Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting Focus on Upper and Lower Respiratory Diseases Salt Lake City, UT, USA 2010 Next Focus Meetings: July 24-26, Focus on Colic Indianapolis, IN, USA September 18-20, 2011 Focus on Dentistry Location TBD Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the AAEP
2 Rational Treatment of Inflammatory Airway Disease Environment and Drugs Melissa R. Mazan, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM Author s address: Tufts University, School of Veterinary Medicine, Department of Clinical Sciences, North Grafton, MA 01536; melissa.mazan@tufts.edu. Recurrent airway obstruction (RAO, or heaves) and inflammatory airway disease (IAD) are highly prevalent in stabled horses, and require treatment with corticosteroids and bronchodilators in addition to environmental modification. Topical application of bronchodilators and glucocorticoid drugs can help in avoiding the side effects and even toxicities associated with the systemic delivery of these drugs. Treatment Strategy The goals of treatment must be clear in order for there to be client, patient, and veterinarian satisfaction this entails a team approach and an acceptance that this may be a life-long problem that may be modified but is unlikely to go away. Goals in treating RAO should include: 1) immediate relief of the bronchospasm that causes cough and dyspnea, 2) reduction of lower airway inflammation (neutrophils, mast cells, or both), 3) long-term prevention of episodes of heaves by control of lower airway inflammation and airway obstruction, and 4) return to limited or even full athletic potential. The goals for treatment of non-septic IAD are similar: 1) eliminate cough and bronchoconstriction that impair performance, 2) reduce mucus production and airway plugging, 3) reduce airway reactivity and 4) prevent recurrences. There is a place for aerosolized therapy in each one of these goals, although systemic corticosteroids are usually necessary for initial reduction of airway inflammation, and environmental control is paramount in long-term control of RAO. In order to achieve success, the veterinarian and client should plan for regular check-ups and be prepared for changes in treatment strategy that might be necessary. Owner education is critical in achieving compliance. Establishment of a reasonable definition of return to athletic use is critical to client satisfaction. It is reasonable to look forward to returning a mildly affected, young racehorse to full racing potential. A reasonable goal for a horse with RAO might be a much more modest return to light pleasure riding. When available, lung function testing and response to bronchodilator can be very useful for identifying the horse that is less likely to respond to conventional therapy. Monitoring Therapy It is important to have a baseline assessment of the horse prior to initiating therapy. Ideally, this would include auscultation with and without a rebreathing bag, careful physical examination, observation during exercise, and baseline pulmonary function testing and measure of airway reactivity (IAD), or in the case of horses with RAO, the effect of bronchodilation, and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cytology in either case. Although pulmonary function testing is currently available only at a few specialized veterinary pulmonology clinics, it is likely that userfriendly systems for field-testing will soon be available, making objective baseline assessments 107
3 available to practitioners. The goal of a thorough baseline assessment is to facilitate a treatment regimen tailored to the individual horse, and to monitor response to therapy. At our pulmonary clinic, we offer free lung function testing one month after initiation of therapy to assess response to therapy and fine tune therapy for the upcoming months. We also encourage telephone and communication with owners and referring veterinarians in order to facilitate this process. Environment The first and most important treatment environmental remediation is also the most long lasting and free of side effects, but many owners are reluctant to fully pursue this path. The following evidence may serve as greater impetus to do so. Multiple studies have shown that environmental remediation, usually meaning pasture with pelleted complete feed and complete cessation of hay feeding, results in almost complete remission from RAO. If pasture is not available, then cardboard bedding accompanied by complete pelleted feed is a suitable alternative. A randomized controlled study demonstrated that a combination of complete pelleted feed and outdoor living resulted in remission in heavey horses, using PFTs and BAL to confirm. Only in severe cases was the addition of inhaled fluticasone propionate necessary. Subsequently, this group has shown that RAO horses kept in low dust environments with no medical management for up to 5-6 years are indistinguishable from a control group without probing the lower airways via measurements of FEV. We commonly recommend that horses be removed from the barn when stall-cleaning or any other barn cleaning is done, as this is a time when airborne particulates are very high. Likewise, we recommend that when possible, horses eat outside, as eating is also associated with a high respirable particulate load. There are, however, some horses not just those in the South, with Summer Pasture Associated Recurrent Airway Obstruction (SPARAO) that seem to have the worst exacerbations of airway obstruction during warm, humid summer weather. This may be because airborne endotoxin loads are highest outside during the summer. It may also be due to mold blooms on unthatched pastures. We encourage owners to keep a diary of disease exacerbations and possible exposures in order to gain a more balanced view of the best environment for each horse. Short-Term Drugs: Beta 2-Agonists Beta 2 agonists work by increasing the production of adenylate cyclase; they thereby increase intracellular camp levels with subsequent relaxation of airway smooth muscle. Short-acting β 2 agonists such as albuterol and fenoterol, are of vital importance in treatment of acute exacerbations of RAO. The horse that is laboring to breath and has paroxysmal coughing will experience rapid relief with the use of β 2 agonists. However, these are correctly termed rescue drugs, and should not be used on a regular basis. It is important to remember that the inflammatory condition will persist despite apparent improvement due to transient bronchodilation, and the disease will worsen. Regular use of β 2 agonists in the absence of antiinflammatory medication may mask symptoms that would otherwise indicate progressive worsening of the disease in particular, further airway obstruction with mucus. Short-acting β 2 agonists are not performance enhancing in humans, and increasing evidence supports this finding in horses. Nonetheless, albuterol and similar drugs remain proscribed by all 108
4 equine sporting events, and due care should be taken to stop drug administration before competition. Short-acting β 2 agonists can be useful in horses with IAD and underlying airway obstruction to improve the return to training. Administration of albuterol may also increase the peripheral lung deposition of other concurrently used drugs. Short-acting bronchodilators are also useful during lung function testing to assess the reversibility of airway obstruction in horses with RAO. No more than 450mg of albuterol by inhalation is necessary to bronchodilate most horses, irrespective of the delivery device chosen. Although aerosolized β 2 agonists have a relatively low incidence of side effects, excessive use or sensitive individuals may experience systemic effects such as trembling, anxiety and cardiac arrhythmias. The author has noted all these in individuals treated with 900 micrograms of albuterol, whereas other individuals show no signs of intolerance. Repeated use of the drug tends to decrease side effects as the body down regulates receptors. Very occasionally, horses may exhibit signs of bronchoconstriction to β 2 agonists. This paradoxical response is likely due to the effects of the drug vehicle on airways and is transient. Short-Term Benefits: Anticholinergics Both cough and bronchoconstriction are vagally mediated, thus parasympatholytic drugs (such as ipratropium bromide) are effective in mitigating these. As with any parasympatholytic drug, there is a potential for tachycardia, thickened mucous, decreased ciliary beat frequency, and decreased mucociliary clearance, however, studies in horses have showed no such side effects with doses up to 1200 micrograms. The index of safety is considerably greater than systemically administered atropine. Ipratropium has a slower onset of action than albuterol, and its actions seem to be confined primarily to the central (larger) airways rather than bronchioles. Studies in horses suggest that pulmonary function begins to improve 15 minutes after administration, and although duration of action has only been verified through one hour, clinical evidence suggests that horses experience relief for up to 4 to 6 hours. Although ipratropium may act as a useful adjunct to β 2 agonists for a rescue treatment during exacerbations of RAO, it is not the primary treatment of choice due to its slower onset of action. In horses with adverse responses to β 2 agonists, ipratropium bromide may be preferred. Long-Term Control: Corticosteroids Corticosteroids remain the cornerstone of successful treatment for both IAD and RAO. The use of inhaled corticosteroids has truly revolutionized the treatment of RAO and IAD. While initial systemic tapered corticosteroid therapy is often necessary with all but very mild IAD, regular inhaled therapy is essential for long-term success in most cases. Inflammation underlies remodeling of the airways with accompanying airway hyperreactivity, or increased twitchiness of the airways, and consequent coughing and expiratory dyspnea. Bronchodilator drugs will help to relieve acute, debilitating bronchospasm, but only consistent anti-inflammatory therapy, in conjunction with avoidance of environmental triggers, will break the vicious cycle of inflammation, airway hyperreactivity, and bronchoconstriction. The most important factor in limiting regular use of inhaled corticosteroids is cost: drugs such as fluticasone (Flovent ) and beclomethasone (QVAR ) are very expensive. 109
5 The anti-inflammatory effect of corticosteroids in both RAO and IAD is impressive. Corticosteroids activate glucocorticoid receptors, thus putting into motion a profound inhibition of the arachadonic acid cascade and limiting production of leukotrienes and other inflammatory molecules. Response to steroids can vary considerably from horse to horse. RAO horses treated with beclomethasone dipropionate have shown both objective and subjective evidence of decreased airway obstruction, as well as a decrease in pulmonary neutrophilia within 24 hours of initiation of therapy. Doses range from 500 micrograms to 1200 micrograms when using the HFA formulation. Although there is evidence of adrenal (HPA)- hypopituitary (i.e., reduced serum cortisol levels) suppression with all doses 500mg, this does not pose a risk of chronic HPA suppression or rebound Addisonian crisis. Fluticasone propionate decreases pulmonary neutrophilia, improves pulmonary function, and reduces airway hyperreactivity in RAO-affected horses. Fluticasone propionate is the most potent of the inhaled corticosteroids, has the longest pulmonary residence time, and causes the least adrenal suppression. Newer formulations of beclomethasone dipropionate that incorporate HPA as the propellant have more uniform particle size, and are more uniformly mixed, requiring little to no agitation or waiting before actuation of the inhaler. The general strategy pursued at the pulmonary clinic at Tufts University School of Veterinary Medicine is to treat in a stepwise manner, starting with a high dose given frequently, with a gradual reduction in therapy until the lowest effective dose can be found. If owners are vigilant in environmental control and are compliant with treatment recommendations, many horses can eventually be treated successfully on an every other day basis to prevent recurrences. Some owners have been successful in documenting seasonal exacerbations: in this case we recommend beginning treatment with inhaled corticosteroids and, occasionally, mast-cell inhibitors, at least two weeks before the anticipated allergen season. It is important to remember, though, that unless all stimuli for pulmonary inflammation is removed, the effect of inhaled corticosteroids is transient, and symptoms will return when the horse is exposed to organic dust and other allergens. Corticosteroids should not be used for quick-relief, or rescue therapy, as the onset of action is at least 24 hours, and several months of regular use may be necessary for optimum results. With severe inflammation, systemic corticosteroids are usually necessary to achieve break-through before initiating inhaled therapy. Most horses with RAO and RAD will require loading doses for 2-4 weeks of systemic steroids before reliance on aerosol medications although trials are lacking that demonstrate the effective preventative dose. Mast Cell Inhibitors Mast cells are important mediators of inflammation in horses with IAD or RAO, with studies linking mast cells with airway reactivity, environment, and levels of inflammatory mediators in lavage (ie BAL) fluid. These drugs stabilize the mast cell membrane, thus blocking degranulation and inhibiting the allergic response at an early stage. These drugs have a tendency to cause cough and aversion (perhaps due to a bad taste) in horses. There is anecdotal evidence that pre-treatment with albuterol may attenuate some of the cough response. Their greatest therapeutic effect is seen when given a long-term therapy and prior to exposure to allergen such as before allergy season or before transporting a horse to a new environment. There is, understandably, less customer satisfaction and, consequently poorer compliance, with drugs 110
6 that do not have a visibly dramatic effect, such as the β 2 agonists and even the potent corticosteroids. Long-Acting Beta 2-Agonists We treat selected cases of RAO and moderate IAD with long-acting β 2 agonist (LABA) therapy in addition to inhaled corticosteroids, with the initial impression of enhanced performance and quality of life. It cannot be emphasized enough, however, that regular use of long acting β 2 agonists must be accompanied with regular use of inhaled corticosteroids. The most commonly used LABAs are salmeterol and formoterol, whose basic mechanism of action is the familiar camp pathway. Their duration of action in horses is 6-8 hours. When the Patient Does not Respond to Therapy If there is poor response to therapy, it is important to do some detective work to determine why treatment has been unsuccessful. It is essential to check the client s technique for using the drug delivery device. Failure to modify the environment may, in some horses, negate any attempts at drug therapy. Some horses with chronic, severe pathology may be resistant to corticosteroids or may have irreversible changes in the lungs that prevent response to bronchodilators. Finally, lack of response to therapy may be due to underlying infectious disease and may indicate the need for further diagnostics and perhaps an entirely different approach or concomitant antibiotic use. 111
Respiratory Health - Managing the Racehorse s Environment By Heather Smith Thomas
 Respiratory Health - Managing the Racehorse s Environment By Heather Smith Thomas If a horse can t breathe optimally, he can t run as fast or as far. Respiratory health is important for any racehorse,
Respiratory Health - Managing the Racehorse s Environment By Heather Smith Thomas If a horse can t breathe optimally, he can t run as fast or as far. Respiratory health is important for any racehorse,
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Proceedings of the 57th Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - AAEP -
 http://www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 57th Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - AAEP - November 18-22, 2011 San Antonio, Texas, USA Next Meeting : Dec. 1-5, 2012 - Anaheim,
http://www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 57th Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - AAEP - November 18-22, 2011 San Antonio, Texas, USA Next Meeting : Dec. 1-5, 2012 - Anaheim,
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Dr. R. Leguilette - Upper airways (throat) and lung problems in Alberta horses: Latest developments.
 Renaud Léguillette started at the UCVM in 2006 as an assistant professor in equine internal medicine. He graduated in Paris, France, was trained in equine internal medicine at the Université de Montréal
Renaud Léguillette started at the UCVM in 2006 as an assistant professor in equine internal medicine. He graduated in Paris, France, was trained in equine internal medicine at the Université de Montréal
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE INCIDENCE UP TO 380,000 PEOPLE IN IRELAND HSE FIGURES 110,000 DIAGNOSED AND 200,000 UNDIAGNOSED. AFFECTS MORE MEN THAN WOMEN BUT RATES ARE RISING 1500 DEATHS PER YEAR
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE INCIDENCE UP TO 380,000 PEOPLE IN IRELAND HSE FIGURES 110,000 DIAGNOSED AND 200,000 UNDIAGNOSED. AFFECTS MORE MEN THAN WOMEN BUT RATES ARE RISING 1500 DEATHS PER YEAR
Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS
 Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS Asthma Usually acquire before the age of 10 These patients exhibit hyper-reactive airways Spasm Constriction Swelling Secretions are
Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS Asthma Usually acquire before the age of 10 These patients exhibit hyper-reactive airways Spasm Constriction Swelling Secretions are
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II
 Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists
 Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
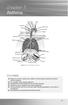 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Asthma. Definition. Symptoms
 Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
National Asthma Educator Certification Board Detailed Content Outline
 I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
Proceedings of the 18th Annual Meeting of the. Italian Association of Equine Veterinarians SIVE
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 18th Annual Meeting of the Italian Association of Equine Veterinarians SIVE Feb. 3-5, 2012 - Bologna, Italy Next SIVE Meeting: Feb. 1-3,
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 18th Annual Meeting of the Italian Association of Equine Veterinarians SIVE Feb. 3-5, 2012 - Bologna, Italy Next SIVE Meeting: Feb. 1-3,
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
II: Moderate Worsening airflow limitations Dyspnea on exertion, cough, and sputum production; patient usually seeks medical
 Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management
 Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Asthma medications: Know your options - MayoClinic.com. Asthma medications: Know your options
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Public Dissemination
 1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
31 - Respiratory System
 31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract
 Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES. School Nurses November 2015
 ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention
 Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
10/18/2012. Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C
 Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Asthma. doh.sd.gov/statistics/2009brfss/asthma.pdf
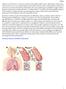 is an obstructive or restrictive condition which inhibits airflow due to inflammation of the airway. This obstruction occurs via increased edema in the small bronchioles walls as well as greater production
is an obstructive or restrictive condition which inhibits airflow due to inflammation of the airway. This obstruction occurs via increased edema in the small bronchioles walls as well as greater production
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Respiratory Health. Asthma and COPD
 Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
Asthma in Day to Day Practice
 Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Recurrent Airway Obstruction (Heaves) (Last Updated: 30-Nov-2001)
 1 van 9 2-12-2009 10:03 In: Equine Respiratory Diseases, Lekeux P. (Ed.) International Veterinary Information Service, Ithaca NY (www.ivis.org), 2001; B0317.1101 Recurrent Airway Obstruction (Heaves) (Last
1 van 9 2-12-2009 10:03 In: Equine Respiratory Diseases, Lekeux P. (Ed.) International Veterinary Information Service, Ithaca NY (www.ivis.org), 2001; B0317.1101 Recurrent Airway Obstruction (Heaves) (Last
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 13 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema Multimedia Directory Slide 7 Slide 12 Slide 60 COPD Video Passive
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 13 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma, Chronic Bronchitis, and Emphysema Multimedia Directory Slide 7 Slide 12 Slide 60 COPD Video Passive
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Asthma. Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital. Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence,
 Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Comparison of Airway Response in Recurrent Airway Obstruction-Affected Horses Fed Steamed versus Non-steamed Hay. Celeste Ann Blumerich
 Comparison of Airway Response in Recurrent Airway Obstruction-Affected Horses Fed Steamed versus Non-steamed Hay Celeste Ann Blumerich Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute
Comparison of Airway Response in Recurrent Airway Obstruction-Affected Horses Fed Steamed versus Non-steamed Hay Celeste Ann Blumerich Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
 Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Decramer 2014 a &b [21]
![Decramer 2014 a &b [21] Decramer 2014 a &b [21]](/thumbs/90/101390504.jpg) Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA
 Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Learning Objective. Asthma. Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Asthma 2/22/2017
 Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
New Therapies for Asthma
 New Therapies for Asthma Tracy Bridges, MD Speaker Disclosure: Dr. Bridges participates in speaker bureaus for Teva, Genetech & Astra Zeneca. Objectives: Discuss the use of LAMA s for Asthma Detail the
New Therapies for Asthma Tracy Bridges, MD Speaker Disclosure: Dr. Bridges participates in speaker bureaus for Teva, Genetech & Astra Zeneca. Objectives: Discuss the use of LAMA s for Asthma Detail the
The FDA Critical Path Initiative
 The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES
 AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease CareOregon Pharmacy Abridged sample of presentation content Home Equipment Pathophysiology Exacerbations Guidelines Lifestyle Modification Medication Management Sample
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease CareOregon Pharmacy Abridged sample of presentation content Home Equipment Pathophysiology Exacerbations Guidelines Lifestyle Modification Medication Management Sample
Foundations of Pharmacology
 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO
 ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide
 Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
You ve come a long way, baby.
 COPD Dr Badri Paudel Dept of Medicine GMC/CHRC 4/22/12 badri@gmc 2 You ve come a long way, baby. Wayne McLaren Former Marlboro Man 4/22/12 badri@gmc 3 Age 30 a robust young man Age 51 riding into the sunset
COPD Dr Badri Paudel Dept of Medicine GMC/CHRC 4/22/12 badri@gmc 2 You ve come a long way, baby. Wayne McLaren Former Marlboro Man 4/22/12 badri@gmc 3 Age 30 a robust young man Age 51 riding into the sunset
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness. treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years
 The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
Focus on Upper and Lower Respiratory Diseases
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting Focus on Upper and Lower Respiratory Diseases Salt Lake City, UT, USA 2010 Next Focus Meetings: July 24-26,
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting Focus on Upper and Lower Respiratory Diseases Salt Lake City, UT, USA 2010 Next Focus Meetings: July 24-26,
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD
 Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
COPD in primary care: reminder and update
 COPD in primary care: reminder and update Managing COPD continues to be a major feature of primary care, particularly in practices with a high proportion of M ori and Pacific peoples. COPDX clinical practice
COPD in primary care: reminder and update Managing COPD continues to be a major feature of primary care, particularly in practices with a high proportion of M ori and Pacific peoples. COPDX clinical practice
Childhood Asthma. The pathophysiology of asthma is an interplay. CME Case Study. Case Study. By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC
 CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Catherine Whittaker (BPharm, MRPharmS) Abstract Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease affects millions of people, has a major impact on quality of life and has become
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Catherine Whittaker (BPharm, MRPharmS) Abstract Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease affects millions of people, has a major impact on quality of life and has become
Asthma: Chronic Management. Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015
 Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
JANUARY Guide to the WADA Prohibited List and Therapeutic Use Exemptions
 JANUARY 2018 Guide to the WADA Prohibited List and Therapeutic Use Exemptions Contents The WADA Prohibited List 3 Therapeutic Use Exemptions (TUEs) 5 Requirements for asthma TUEs 9 2 The WADA Prohibited
JANUARY 2018 Guide to the WADA Prohibited List and Therapeutic Use Exemptions Contents The WADA Prohibited List 3 Therapeutic Use Exemptions (TUEs) 5 Requirements for asthma TUEs 9 2 The WADA Prohibited
Barn Air Quality and Transmissible Disease Protection
 Barn Air Quality and Transmissible Disease Protection Kara Lascola DVM, MS, DACVIM University of Illinois Horseman s clinic February 6 th 2016 Why do we care about the barn environment? Protection from
Barn Air Quality and Transmissible Disease Protection Kara Lascola DVM, MS, DACVIM University of Illinois Horseman s clinic February 6 th 2016 Why do we care about the barn environment? Protection from
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP?
 THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
MEDICATION GUIDE. ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol
![MEDICATION GUIDE. ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol MEDICATION GUIDE. ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol](/thumbs/78/76835983.jpg) MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol ADVAIR HFA 115/21 (fluticasone propionate 115 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation
MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol ADVAIR HFA 115/21 (fluticasone propionate 115 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation
I have no perceived conflicts of interest or commercial relationships to disclose.
 ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis. Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine
 Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
3. Identify the importance in the prehospital setting for the administration of nebulized bronchodilator.
 TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
Allergies and Asthma 5/21/2013. Objectives. Allergic Rhinitis (AR): Risk Factor for ASTHMA. Rhinitis and Asthma
 Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017
 Protocol Title: Adult Asthma Protocol Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based
Protocol Title: Adult Asthma Protocol Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based
