Altered Ventilation and Diffusion
|
|
|
- Allyson Norton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
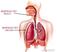
1 Respiratory Structures Altered Ventilation and Diffusion Alveolar type 1: provide structure and air exchange Alveolar type 2: lubricant that coats the inner portion of the alveolus, promotes easy expansion, repels fluid accumulation ** inflation would be impossible w/out it Rate and volume of ventilation is regulated by: 1. Functioning respiratory control center (RCC): responds to chemical messages in the body. Composed of neurons in the pons/medulla. It sends impulses to diaphragm, muscles to contract/relax. (Constriction= Para, Dilation = Symp) 2. Lung receptors: Located in the epithelium/smooth muscle airways. 3. Chemoreceptors: detect gas exchange needs based on PaO2, PaCo2, ph levels. Central chemoreceptors: near RCC, respond to ph changes in the CSF. Detects CO2 levels in the blood. ( CO2 = ventilation to expel CO2) Peripheral chemorecepotrs: sensitive to O2 levels, located in aorta/carotid arteries. ( O2 = ventilation)
2 Ventilation: Process of moving air in/out of lungs Involves both acquiring oxygen (inspiration) and removing carbon dioxide (expiration) from the blood Neuronal impulses are directed by lung receptors, which map the current state of breathing and lung function Uses the intercostal muscles, diaphragm, and sternocleidomastoid muscles Inspiration Breathing in to acquire oxygen Unidirectional from high pressure to low pressure. Chest cavity size changes to alter the pressure gradient Neuronal stimulation/movement moves diaphragm down and out (reduces pressure inside lungs to pull air in) Expiration Removing carbon dioxide out of the body through the lungs The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles relax Lungs compress and increase the pressure inside the airways Chest wall moves in and diaphragm moves upwards. Inside pressure is more than atm pressure (so air moves OUT) Measurement of Ventilation 1. Tidal volume (TV): the amount of air exhaled after passive inspiration (air in and out at rest) ** 500 ml 2. Vital capacity (VC): max amount of air in/out of lungs with forced inhale/exhale 3. Forced capacity (FVC): amount exhaled during forced exhale 4. Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1): amount exhaled from lungs in 1 sec 5. Residual volume (RV): volume of air left in lungs after maximal expiration 6. Total lung capacity: total air in lungs when they are maximally expanded (VC+ RV) Diffusion: Process of moving/exchanging O2/Co2 through membranes Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged at alveolar capillary junctions Two major process occur: Oxygen is trying to get to all the cells Carbon dioxide is trying to escape the body through the lungs Effectiveness depends on: Pressure (Co2, O2 in blood), Solubility (Co2 more soluble), and Membranes (thickness/sa)
3 Partial Pressure The collision of oxygen and carbon dioxide creates pressure PaO2 PaCO2 Perfusion: Process of supplying oxygenated blood to lungs and organ systems via blood vessels Respiration: Process in which cells in the body use O2 to make energy Oxygen Diffusion and Transport Oxyhemoglobin (HbO2): As PaCO2 oxygen dissociates from the plasma and connects with hemoglobin molecules on RBC s. Based on attraction to iron. When it is attached to hemoglobin, it is not available to the cell. Oxygen Saturation (SaO2): Attraction of hemoglobin continutes until the hemoglobin molecules are completely saturated. It is NOT affected by blood volume. Once saturation occurs, oxygen continues to diffuse and dissolve in the plasma, until the partial pressures in arteries = that in the alveoli Carbon Dioxide Diffusion and Transport Dissolved in the plasma (10%) Bound to hemoglobin (20%) Diffused into the red blood cell as bicarbonate (70%): converted to either carbonic acid, bicarbonate ions (which helps regulate ph) Diffusing Capacity The measurement of carbon monoxide, oxygen, or nitric oxide transfer from inspired gas to pulmonary capillary blood and is reflective of the volume of a gas that diffuses through the alveolar capillary membrane each minute.
4 Impaired Ventilation A problem of blocking airflow in and out of the lungs Two major mechanisms implicated: Compression or narrowing of the airways ( airway resistance, leading to difficulties with airway clearance, ie. Edema, exudates or inflammation) Disruption of the neuronal transmissions needed to stimulate the mechanics of the airways (ignores messages sent by chemoreceptors/lung receptors, ie. Drug overdose) Impaired Ventilation-Perfusion Matching Two possible scenarios: Lung are ventilated, but not perfused Lung is perfused, but not ventilated Impaired ventilation: inadequate o2 comes from lungs even though the blood flow is ready and able to carry oz. Impaired perfusion: the blood flow to the lungs is restricted in one or more areas. Oxygen might be coming in, but have no blood flow to carry it to the body. Altered Ventilation and Perfusion
5 Impaired Diffusion Restricted transfer of oxygen or carbon dioxide across the alveolar capillary junction Dependent upon: solubility and partial pressure of the gas: partial pressure is increased when molecules are packed in a space, temp increases, when barometric pressure increases. Decreased oxygen pp can occur in o2 deprevation, hypothermia. CO2 increases with metabolism increase/ exercise. surface area and thickness of the membrane The Effects of Impaired Ventilation and Diffusion 1. Hypoxemia: is decreased oxygen in the arterial blood leading to a decrease in the PaO2. (caused by o2 deprivation, hypoventilation) 2. Hypoxia: When cells are deprived of adequate oxygen. (widespread hypoxemia) 3. Hypercapnia: a state of CO2 in the blood (CO2 is more easily diffused, so it only really happens when there is severe alveolar hypoventilation followed by hypoxia). General Manifestations of Impaired Ventilation and Diffusion Local manifestations: usually due to inflammatory processes Cough (common, protective), mucus, hemoptysis Dyspnea (feeling of SOB), orthopnea (the physical need to sit in an upright/standing position) Adventitious lung sounds (altered) (ie. Wheezing= constricted airway) Use of accessory muscles (retractions= the pulling in of accessory muscles to promote more effective inspiration) Chest pain (can originate in the visceral/pleural/airway/chest wall. Pleural pain increases with deep inspiration and often described as sharp/stabbing pain) Barrel chest: due to chronic dilation and distention of the alveoli (i.e emphysema) Systemic manifestations: due to hypoxemia/ hypercapnia Fever, malaise, leukocytosis plasma proteins Dusky/cyanotic mucus membrane color Changes in arterial blood gases Mental status changes Finger clubbing (painless enlargement/flattening of tips of fingers/toes, caused by chronic hypoxia)
6 Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests History and physical examination Visualization (bronchoscopy, x-ray, CT, MRI, nuclear medicine, etc.) Pulmonary function tests Pulse oximetry Laboratory studies Treating Impaired Ventilation and Diffusion Remove obstruction and restore physical integrity of airways, lung tissues Decrease inflammation and mucus; treat infection Supplemental oxygen Mechanical ventilation
7 Pneumonia Pathophysiology: Acute infectious process on ventilation/diffusion (caused by miccrorganism, community acquired: strep/staph/influenza; nosocomial: pseudo/staph) Respiratory droplet spread Causes inflammation of the lungs Occurs commonly in the bronchioles, interstitial lung tissue and/or the alveoli Products of inflammation accumulate and cause consolidation (products of inflammation accumulate as a solid mass) 3 stages: 1. Recent infection shows rapid filling of alveolar capillaries with purulent fluid, 2. Red hepatization: fills with fibrinous exudates, appear as dry red lung tissue, 3. Gray hepatization: WBC s pack into alveoli as RBC s degenerate. Pneumococcal bacteria release toxins that contribute to cell death (forming yellow exudates which are absorbed and resolution begins). Clinical Manifestations: Oxygen diffusion is impaired, hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, dehydration Sudden onset of fever Dyspnea (SOB) Chills Tachypnea (rapid breathing) Cough Tachycardia Sputum production Pleuritic pain Fatigue Crackles in lungs Loss of appetite Diagnostic Criteria: History and physical examination Complete blood cell count ( WBC s) Chest X-ray Thoracic CT scan (to see areas of consolidation) Examine sputum: pneumococcal= bloody/rust color, pseudomonas = green, anaerobic= foul smelling Treatment: Restore optimal ventilation and diffusion Identify pathogen and target with appropriate pharmacologic treatment (with C&S, and gram stain) Supplemental oxygen
8 COPD Refers to all chronic obstructive lung problems: Emphysema, Chronic Bronchitis and Asthma Usually used to denote E+ CB Inflammatory processes in both bronchi/ bronchioles Progressive, unremitting diseases Pathophysiology: Emphysema Irreversible enlargement of the air spaces beyond terminal bronchioles destruction of the alveolar walls obstruction of airflow Chronic smoking most often implicated Loss of elastic recoil in alveoli leads to airflow obstruction Vascular changes: The inner lining of arteries/arterioles become thicker and fibrotic Clinical Manifestations: Persistent cough Dyspnea Wheezing Barrel chest Pursed lip breathing Diagnostic Criteria: History and physical examination Pulmonary function tests ( AAT) Chest x-ray (signs of hyperinflation) Hypoxemia (early)/ Hypercapnia (later stages) FEV1 is most common test, 6+ seconds is bad Treatment: Maintain optimal lung function in order to allow the individual to perform the desired activities of daily life Smoking cessation Pharmacologic therapy (bronchodilators, steroids) Lung volume reduction or transplant
9 Smoking: impairs alveolar function: 1. Inhalation of smoke triggers an inflammatory response 2. Neutrophils/ macrophages are activated and retain in lung tissue 3. They release proteolytic enzymes (proteinases/elastases), that destroy components of ECM (i.e. elastin) 4. The elasticity of the lung is significantly reduced leading to inability of the alveoli to recoil and release CO2 into atm. ** Elasticity is key! If the alveoli wall collapses, air gets trapped (which decreases O2 intake and CO2 release). Hyperinflation results, which makes them get further stretched and continue to lose elasticity. CO2 retained and ph is reduced.
10 Chronic Bronchitis Pathophysiology: Persistent, productive cough lasting three months or greater, for two or more consecutive years Result of changes in bronchi/bronchioles: 1. Chronic inflammation and edema of the airways 2. Hyperplasia of the bronchial mucous glands and smooth muscles 3. Destruction of cilia 4. Squamous cell metaplasia 5. Bronchial wall thickening and development of fibrosis Clinical Manifestations: Cough Purulent sputum Dyspnea Adventitious lung sounds Hypoxemia, hypercapnia and cyanosis (more common than emphysema, b/c excess mucous/obstructed ventilation) Diagnostic Criteria: History and physical examination (recurrent upper/lower resp infections) Arterial blood gases Pulmonary function tests Pulse oximetry Sputum analysis Treatment: Smoking cessation Pulmonary rehabilitation Pharmacologic therapy Supplemental oxygen
11 Asthma Pathophysiology: Intermittent or persistent airway obstruction due to: 1. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness (IgE mediators cause edema, bronchoconstriction, release histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, forms mucous in airways) 2. Chronic inflammation 3. Bronchoconstriction 4. Excess mucous production
12 Clinical Manifestations: Wheezing and tachypnea, use of accessory muscles Dyspnea and coughing Chest tightness Excessive sputum production Anxiety Hyperventilation can lead to respiratory alkalosis Diagnostic Criteria: History and physical examination Evidence of respiratory distress Pulsus paradoxus: exaggerated decrease in systolic BP during inspiration Wheezing Prolong expiratory phase Atopic dermatitis: eczema, hypersensitivity reactions on skin. Pulmonary function tests Laboratory studies Chest x-ray Treatment: 1. Monitor lung function 2. Control environmental triggers 3. Pharmacologic therapy 4. Patient and family education; action plan
13 Cystic Fibrosis Pathophysiology: Autosomal recessive disorder of electrolyte and water transport affecting certain epithelial cells (respiratory, digestive, and reproductive lining) Mutation of the CF gene (both parents have to have it); inability of epithelial cells to conduct Cl; and therefore transport water across mucosal surfaces leads to thick secretions and obstructions in the resp tract Associated with mucus plugging, inflammation, and infection in the lungs; also affects other body systems Respiratory failure is most common cause of death Clinical Manifestations: 1. Reproductive: Men get infertile (clogs vas deferens), but the women get altered menses 2. Respiratory: respiratory infections, chronic cough, sputum, vomiting, tachypnea, wheezing, crackles, chest pain, respiratory distress, cyanosis, barrel chest, recurrent sinusitis, nasal polyps 3. Gastrointestinal: Cl secretions, get large, greasy BM s. Get inflammation/scars which increase bowel obstructions, poor fat absorption, weight loss Diagnostic Criteria: History and physical examination Sweat test (Since there are problems with the Cl channels, get salty deposits on the skin) Genetic testing Chest x-ray (see how much secretions) Sputum analysis Treatment: Respiratory Chest physiotherapy (press on back) Pharmacologic treatment (aerosol to thin secretions) Lung transplant (extensive scarring/cysts on the lungs) Gastrointestinal Optimal nutrition Pancreatic enzymes Mucous plugging: (result of) 1. Greater mucus production 2. Airway dehydration, due to thickened mucus caused by impaired cl secretion, excess Na absorption, decreased water 3. Adherence of mucus to epithelium with impaired cilia
14 Pathophysiology: Sepsis is most common cause Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: ARDS Lung injury to respiratory distress within hours Severe acute inflammation and pulmonary edema without evidence of fluid overload or impaired cardiac function pulm edema, damages alveolar capillary junction, damage to type II cells, increased protein, disruption of surfactant = atelectasis, alveolar collapse) Mortality rate 30%-40% from multi-system organ failure in those untreated Clinical Manifestations: Tachypnea Dyspnea Retractions Crackles due to fluid accumulation Restlessness, anxiety Diagnostic Criteria: History and physical examination (lung injury) Arterial blood gases: depict hypoxemia/hypercapnia resp. alkylosis Laboratory studies (blood cultures to detect sepsis) Imaging studies Treatment Remove causative factors Administration of 100% oxygen Mechanical ventilation
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Chronic obstructive lung disease. Dr/Rehab F.Gwada
 Chronic obstructive lung disease Dr/Rehab F.Gwada Obstructive lung diseases Problem is in the expiratory phase Lung disease Restrictive lung disease Restriction may be with, or within the chest wall Problem
Chronic obstructive lung disease Dr/Rehab F.Gwada Obstructive lung diseases Problem is in the expiratory phase Lung disease Restrictive lung disease Restriction may be with, or within the chest wall Problem
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Acute respiratory failure
 Rita Williams, NP-C, PA PeaceHealth Medical Group Pulmonary & Critical Care Acute respiratory failure Ventilation/perfusion mismatching Most common cause of hypoxemia Normal is 1:1 ratio or 1 Ventilation
Rita Williams, NP-C, PA PeaceHealth Medical Group Pulmonary & Critical Care Acute respiratory failure Ventilation/perfusion mismatching Most common cause of hypoxemia Normal is 1:1 ratio or 1 Ventilation
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Respiratory Disease. Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician
 Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
CPAP. Pre-Hospital Treatment Using The Respironics Whisperflow CPAP Device. Charlottesville Albemarle Rescue Squad - CPAP
 CPAP Pre-Hospital Treatment Using The Respironics Whisperflow CPAP Device CPAP What Is It? C ontinuous P ositive A irway P ressure Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Alveoli Anatomy Review Chest
CPAP Pre-Hospital Treatment Using The Respironics Whisperflow CPAP Device CPAP What Is It? C ontinuous P ositive A irway P ressure Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Alveoli Anatomy Review Chest
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Gas exchange Regulate blood ph Voice production Olfaction Innate immunity
 Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
The Respiratory System
 Elaine N. Marieb Katja Hoehn Human Anatomy & Physiology SEVENTH EDITION C H A P T E R PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, Bluegrass Technical and Community College 22P A R T B The Respiratory
Elaine N. Marieb Katja Hoehn Human Anatomy & Physiology SEVENTH EDITION C H A P T E R PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, Bluegrass Technical and Community College 22P A R T B The Respiratory
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology
 Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Oxygenation. Chapter 45. Re'eda Almashagba 1
 Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP QUIT ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System 2007 Ontario Base Hospital Group ADVANCED ASSESSMENT Respiratory System AUTHOR(S) Mike Muir AEMCA, ACP, BHSc Paramedic Program Manager
GAS EXCHANGE IB TOPIC 6.4 CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM. Terminal bronchiole Nasal cavity. Pharynx Left lung Alveoli.
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
Lecture Notes. Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
Respiratory System Mechanics
 M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 3: CHRONIC BRNCHITIS AND BRONCHIECTASIS
 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 3: CHRONIC BRNCHITIS AND BRONCHIECTASIS INTRDUCTION In the last lecture we discussed the difference between restrictive and obstructive lung
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 3: CHRONIC BRNCHITIS AND BRONCHIECTASIS INTRDUCTION In the last lecture we discussed the difference between restrictive and obstructive lung
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Respiration. Functions Anatomy
 Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
Respiration Functions Anatomy Major Functions Gas exchange: absorb O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
COPD Management in LTC: Presented By: Jessica Denney RRT
 COPD Management in LTC: Presented By: Jessica Denney RRT Sponsored by Z & D Medical Services, Diamond Sponsor Seizing Opportunities to Provide Individualized Treatment and Device Selection for your COPD
COPD Management in LTC: Presented By: Jessica Denney RRT Sponsored by Z & D Medical Services, Diamond Sponsor Seizing Opportunities to Provide Individualized Treatment and Device Selection for your COPD
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 136 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 24 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bernice Betweiler is a 73-year-old retired seamstress who has never been married. She worked in the alterations department
136 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 24 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bernice Betweiler is a 73-year-old retired seamstress who has never been married. She worked in the alterations department
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
Contents. In this lecture, we will discuss: Tuberculosis. Asthma. Cystic fibrosis. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Miss.kamlah
 1 Contents In this lecture, we will discuss: Tuberculosis. Asthma. Cystic fibrosis. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 2 Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is transmitted
1 Contents In this lecture, we will discuss: Tuberculosis. Asthma. Cystic fibrosis. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 2 Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is transmitted
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases
 Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
Respiratory Pathophysiology
 Respiratory Pathophysiology Objectives: Respiratory infections and lung cancer. Pleural effusion & edema, pleuritis, pneumothorax and atelectasis. Obstructive airway disease and chronic interstitial lung
Respiratory Pathophysiology Objectives: Respiratory infections and lung cancer. Pleural effusion & edema, pleuritis, pneumothorax and atelectasis. Obstructive airway disease and chronic interstitial lung
Respiratory Emergencies. Chapter 11
 Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Asthma. - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness.
 Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
3. Which statement is false about anatomical dead space?
 Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Collin County Community College
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 10 Respiratory System Carbon Dioxide Transport Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in three forms Dissolved in plasma 7 to 10%
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 10 Respiratory System Carbon Dioxide Transport Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in three forms Dissolved in plasma 7 to 10%
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
The Goal of the Respiratory Assessment. Two Parts of the Respiratory Assessment
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Assessment of the Adult Patient Mary Douglas, MSN, RN Nurse Educator Minneapolis VA Health Care System Respiratory system: moves oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System Respiratory Assessment of the Adult Patient Mary Douglas, MSN, RN Nurse Educator Minneapolis VA Health Care System Respiratory system: moves oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Respiration Lesson 3. Respiration Lesson 3
 Respiration Lesson 3 and Airway Resistance (key factors affecting air flow) 1) What is the arterial blood pressure in a healthy 18 year old male? 2) What would his venous blood pressure be? 3) What is
Respiration Lesson 3 and Airway Resistance (key factors affecting air flow) 1) What is the arterial blood pressure in a healthy 18 year old male? 2) What would his venous blood pressure be? 3) What is
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Pulmonary Emergencies. Lower Airway Structures Trachea Bronchial tree Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Lungs
 Pulmonary Emergencies Lower Airway Structures Trachea Bronchial tree Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Lungs Pulmonary Surfactant Thin film that coats alveoli Prevents alveoli from
Pulmonary Emergencies Lower Airway Structures Trachea Bronchial tree Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Lungs Pulmonary Surfactant Thin film that coats alveoli Prevents alveoli from
Coexistence of confirmed obstruction in spirometry and restriction in body plethysmography, e.g.: COPD + pulmonary fibrosis
 Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
Volumes: IRV inspiratory reserve volume Vt tidal volume ERV expiratory reserve volume RV residual volume Marcin Grabicki Department of Pulmonology, Allergology and Respiratory Oncology Poznań University
How does COPD really work?
 How does COPD really work? by Alex Goodell View online Where does COPD fit in the mix of respiratory diseases? I ve made a map of the major pathologies outlined in Robbins and First Aid (obviously these
How does COPD really work? by Alex Goodell View online Where does COPD fit in the mix of respiratory diseases? I ve made a map of the major pathologies outlined in Robbins and First Aid (obviously these
CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY
 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY Section 1: Respiratory System (65 points) 1) It provides CO 2 and O 2 exchange, enables vocalization, provides the sense of smell, helps control the
CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY Section 1: Respiratory System (65 points) 1) It provides CO 2 and O 2 exchange, enables vocalization, provides the sense of smell, helps control the
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
COPD. Dr.O.Paknejad Pulmonologist Shariati Hospital TUMS
 IN THE NAME OF GOD COPD Dr.O.Paknejad Pulmonologist Shariati Hospital TUMS Definition of COPD* COPD is a preventable and treatable chronic lung disease characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully
IN THE NAME OF GOD COPD Dr.O.Paknejad Pulmonologist Shariati Hospital TUMS Definition of COPD* COPD is a preventable and treatable chronic lung disease characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully
Ch 16 A and P Lecture Notes.notebook May 03, 2017
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Respiratory Distress Respiratory distress is a broad medical term that applies to any type of breathing difficulty and the associated
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Respiratory Distress Respiratory distress is a broad medical term that applies to any type of breathing difficulty and the associated
Focus on Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic Fibrosis
 Focus on (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Autosomal recessive, multisystem
Focus on (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Autosomal recessive, multisystem
RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN TGESBIOLOGY ISC 11
 RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN Difference between dry and wet cough Irritation of respiratory tract Due to dust or smoke Accumulation of mucus Due to infections The respiratory tract Tracheal epithelium
RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN Difference between dry and wet cough Irritation of respiratory tract Due to dust or smoke Accumulation of mucus Due to infections The respiratory tract Tracheal epithelium
COMPREHENSIVE RESPIROMETRY
 INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
Respiratory Emergencies. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Respiratory Emergencies Lesson Goal Assess and provide timely treatment & transport to patients experiencing respiratory emergencies Lesson Objectives List parts of respiratory system and how they work
Respiratory Emergencies Lesson Goal Assess and provide timely treatment & transport to patients experiencing respiratory emergencies Lesson Objectives List parts of respiratory system and how they work
Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
 Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES. Michael Waters MD April 2004
 RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES Michael Waters MD April 2004 ASTHMA Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways with variable or reversible airway obstruction Characterized by increased sensitivity
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES Michael Waters MD April 2004 ASTHMA Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways with variable or reversible airway obstruction Characterized by increased sensitivity
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Anatomy Review. Anatomy Review. Respiratory Emergencies CHAPTER 16
 CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review 1 Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons
CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review 1 Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons
ALCO Regulations. Protocol pg. 47
 For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
Care of the Patient with a Respiratory Disorder
 Care of the Patient with a Respiratory Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology External respiration Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lung and the environment Internal respiration
Care of the Patient with a Respiratory Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology External respiration Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lung and the environment Internal respiration
Respiratory Emergencies
 CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons for
CHAPTER 16 Respiratory Emergencies Anatomy Review Anatomy Review Pediatric Anatomy Airway structure differences Proportionally larger tongue Smaller, more flexible trachea Abdominal breathers Reasons for
