Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
|
|
|
- Clarissa Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
2 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 10 Respiratory System 1 Anatomy & Physiology Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
3 Session plan o Functions of the respiratory system o Respiratory System Anatomy: Nose Pharynx Larynx Vocal Cords Trachea Bronchi Lungs o Blood Supply to the Lungs Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 3
4 Functions of the Respiratory System Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 4
5 The Respiratory System o The respiratory system: contributes to homeostasis Provides for gas exchange intake of O2 and elimination of CO2 Helps adjust the ph of body fluids o Respiration: the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells. o Three basic steps: Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 5
6 The Respiratory System o Functions of the respiratory system Gas exchange: intake of O 2 2 for delivery to body cells and removal of CO 2 2 produced by body cells Helps regulate blood ph Contains receptors for sense of smell Filters inspired air Produces vocal sounds (phonation) Excretes small amounts of water and heat Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 6
7 Respiratory System Anatomy Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 7
8 The Respiratory System Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 8
9 Respiratory System Anatomy Structural divisions: o The upper respiratory system: consist of Nose Nasal cavity Pharynx (throat), and associated structures. o The lower respiratory system: consists of Larynx (voice box) Trachea (windpipe) Bronchi (airways) Lungs Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 9
10 Respiratory System Anatomy Functional divisions: o The conducting zone: consists of a series of interconnecting cavities and tubes both outside and within the lungs. the nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles o Function: to filter, warm, and moisten air and conduct it into the lungs. o The respiratory zone: consists of tubes and tissues within the lungs the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli o Function: the main sites of gas exchange between air and blood. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 10
11 Nose o The nose: A specialized organ at the entrance of the respiratory system o Two parts: External nose: External portion Nasal cavity: Internal portion Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 11
12 Nasal cavity o The nasal cavity: A large space in the anterior aspect of the skull that lies inferior to the nasal bone and superior to the oral cavity. o Duct openings: Duct from the paranasal sinuses (which drain mucus) and the nasolacrimal ducts (which drain tears) open in nasal cavity. o Regions: Superior olfactory region: smaller, olfactory function Inferior respiratory region: larger, respiratory function lined with the respiratory epithelium-pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with numerous goblet cells. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 12
13 Nasal cavity Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 13
14 Airway Epithelium o Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells produce a moving mass of mucus. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 14
15 Functions of the Nasal Structures o Ciliated pseudostratified columnar with goblet cells: Lines the nasal cavity Warms air due to high vascularity Mucous moistens air and traps dust Cilia move mucous towards pharynx o Olfactory epithelium: Detecting olfactory stimuli o Paranasal sinuses: Modifying speech vibrations as they pass through the large, hollow resonating chambers. Resonance refers to prolonging, amplifying, or modifying a sound by vibration. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 15
16 Pharynx Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 16
17 Pharynx o Structure: a funnel-shaped tube about 13 cm (5 in.) long that starts at the internal nares and extends to the level of the cricoid cartilage, the most inferior cartilage of the o Functions: Passageway for food and air Resonating chamber for speech production Tonsils (lymphatic tissue) in the walls protects entryway into body o Distinct regions: nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 17
18 Pharynx Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 18
19 Larynx o The larynx (voice box): A passageway that connects the laryngopharynx with the trachea. o Structure: Contains nine pieces of cartilage: Three single cartilages: thyroid cartilage, epiglottis, and cricoid cartilage Three paired cartilages: arytenoid, cuneiform, and corniculate cartilages o Function: Voice production o Vocal folds (true vocal cords): produce sound. o Taunt vocal folds produce high pitches, and relaxed vocal folds produce low pitches. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 19
20 Larynx Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 20
21 Trachea o The trachea (windpipe): o Location: anterior to the oesophagus, extends from the larynx to the primary bronchi level of T5 o Size: 12 cm long and 2.5 cm diameter o Layers of the tracheal wall: Mucosa Submucosa Hyaline cartilage Adventitia Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 21
22 Trachea o Mucosa: consists of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Protects from dust and foreign particles. o Submucosa: Consists of areolar connective tissue that contains seromucous glands and their ducts. o Hyaline cartilage:16 to 20 incomplete C shaped cartilage rings Provide a semirigid support to maintain patency so that the tracheal wall does not collapse inward (especially during inhalation) and obstruct the air passageway. o The Adventitia: consists of areolar connective tissue joins the trachea to surrounding tissues. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 22
23 Trachea and Bronchial Tree o The bronchial tree begins at the trachea and ends at the terminal bronchioles. o Full extent of airways is visible starting at the larynx and trachea Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 23
24 Bronchi o Primary bronchi: the trachea divides into a right primary bronchus and a left primary bronchus supply each lung The right primary bronchus is more vertical, shorter, and wider than the left. an aspirated object is more likely to enter and lodge in the right primary bronchus than the left o Carina: An internal ridge formed by a posterior and inferior projection of the last tracheal cartilage, at the point where the trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi Significance: One of the most sensitive areas of the entire larynx and trachea for triggering a cough reflex. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 24
25 Bronchi o Secondary bronchi: Supply each lobe of the lungs (3 right + 2 left) o Tertiary bronchi: Supply each bronchopulmonary segment (10 in each lung) Divide into bronchioles which in turn branch repeatedly, divide into smaller tubes called terminal bronchioles Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 25
26 Bronchial Tree Structural changes as the branching becomes more extensive: o The mucous membrane: Gradually changes from pseudostratified ciliated to cuboidal nonciliated o Rings of cartilage: Gradually replaced by rings of smooth muscle and then connective tissue Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 26
27 Bronchial Tree o Sympathetic nervous system: stimulates adrenal glands to release epinephrine that relaxes smooth muscle. dilates airways and improves lung ventilation o Parasympathetic nervous system: cause contraction of bronchiolar smooth muscle constricts of distal bronchiole o Mediators of allergic reactions such as histamine: Released during asthma attacks or allergic reactions constrict distal bronchiole smooth muscle o Nebulization therapy = inhale mist with chemicals that relax muscles and reduce thickness of mucous Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 27
28 Pleural Membranes and Pleural Cavity o Pleural membrane: A double-layered serous membrane that enclose and protect each lung Visceral pleura covers lungs Parietal pleura lines thoracic cavity o Pleural cavity: A potential space between the visceral and parietal pleurae Contains a pleural fluid secreted by the membranes. Reduces friction between the membranes, allowing them to slide easily over one another during breathing. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 28
29 Pleural Membranes and Pleural Cavity Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 29
30 Lungs o Shape: Paired cone shaped organs o Location: in the thoracic cavity; extend from the diaphragm to just slightly superior to the clavicles and lie against the ribs anteriorly and posteriorly. o Enclosed and protected by the pleural membrane. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 30
31 Lungs o Shape: Paired cone shaped organs o Location: in the thoracic cavity; extend from the diaphragm to just slightly superior to the clavicles and lie against the ribs anteriorly and posteriorly. o Enclosed and protected by the pleural membrane. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 31
32 Gross Anatomy of Lungs o Base, apex (cupula), costal surface, cardiac notch o Lobes: The right lung: three lobes separated by two fissures- Oblique and horizontal fissure The left lung: two lobes separated by one fissure- Oblique fissure Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 32
33 Mediastinal Surface of Lungs o Blood vessels and airways enter lungs at hilus o Forms root of lungs o Covered with pleura (parietal becomes visceral) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 33
34 Microscopic Anatomy of Lungs o Bronchopulmonary segment: The segment of lung tissue that each tertiary bronchus supplies o Lobules: Small compartments of bronchopulmonary segment Wrapped in elastic connective tissue Each contains an arteriole, a venule, and a branch from a terminal bronchiole Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 34
35 Microscopic Anatomy of Lungs o Respiratory bronchioles: microscopic sub branches from terminal bronchioles o Alveolar ducts: Respiratory bronchioles in turn subdivide into several (2 11) alveolar ducts, o Alveoli: A cup-shaped outpouching around the circumference of the alveolar ducts (150 million/lung) o Alveolar sacs: Two or more alveoli that share a common opening Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 35
36 Cells Types of the Alveoli o Type I alveolar cells: Form a continuous lining of the alveolar wall. Site for gas exchange. Are the most prevalent alveolar cells o Type II alveolar cells (septal cells): Found between type I alveolar cells Secrete alveolar fluid containing surfactant Surfactant lowers the surface tension of alveolar fluid, preventing the collapse of alveoli with each expiration Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 36
37 Other cells types of the Alveoli o Alveolar dust cells Wandering macrophages that remove debris o Fibroblasts: Produce reticular and elastic fibers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 37
38 Alveolar-Capillary Membrane o Alveolar-capillary membrane/ Respiratory membrane: Formed by alveolar and capillary walls where the alveoli are in close proximity to the capillaries 0.5 micron thick Site for exchange of gases Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 38
39 Blood Supply to the Lungs o Arterial supply: Pulmonary arteries: carry deoxygenated blood from the right heart to the lungs for oxygenation Bronchial arteries: branch from the aorta and deliver oxygenated blood to the lungs primarily perfusing the muscular walls of the bronchi and bronchioles o Venous drainage: Four pulmonary veins: Drain into the left atrium o Ventilation perfusion coupling: Vasoconstriction in response to hypoxia diverts pulmonary blood from poorly ventilated areas of the lungs to well-ventilated regions for more efficient gas exchange. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 39
40 Readings and Resources o Tortora, GJ & Derrickson, B Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 14th edn, Wiley. o Harris, P, Nagy, S & Vardaxis, N 2010, Mosby s Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing and Health Professions, 2nd edn, Mosby Elsevier. o Guyton, AC & Hall, JE 2011, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th edn, Saunders Elsevier. o Marieb, EN & Hoehn, K 2010, Human Anatomy and Physiology, 8th edn, Benjamin Cummings Pearson. o Moore, KL, Dalley, AF & Agur, AMR 2010, Clinically Orientated Anatomy, 6th edn, Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 40
41 Copyright COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the Endeavour College of Natural Health pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 41
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Karachi King s College of Nursing
 Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
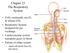 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
The RESPIRATORY System
 The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
The RESPIRATORY System Respira5on The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ven5la5on - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary) Respira5on
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
The Respiratory System:
 The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
The Respiratory System. Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration
 C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
C H A P T E R 22 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Supplies body with oxygen Disposes of carbon dioxide Four processes in respiration Pulmonary ventilation External respiration Transport of
The Respiratory System
 C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
CHAPTER 24. Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
Chapter 24 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed.
 Chapter 24 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p.731) 1. The cardiovascular system and the respiratory system cooperate in order to: i. supply oxygen which is required by cells
Chapter 24 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p.731) 1. The cardiovascular system and the respiratory system cooperate in order to: i. supply oxygen which is required by cells
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity.
 Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
NAME PER DATE. membrane
 NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
Chapter 11. The respiratory system. Glossary. Anthony Wheeldon
 Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
Bio 104 Respiratory System 81
 81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
81 Lecture Outline: Respiratory System Hole s HAP [Chapter 19] I. Introduction Respiration is the process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells. Respiration consists of: Ventilation
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23
 The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
RESPIRATORY LAB. Introduction: trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
 RESPIRATORY LAB Danil Hammoudi.MD Introduction: a) system includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
RESPIRATORY LAB Danil Hammoudi.MD Introduction: a) system includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, extrapulmonary bronchi, and lungs b) passage for and conditioning of air (moisten, warm, and filtering)
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Read Me. We are the Learning Lab. to look
 Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Respiratory System (Chapter 23) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Respiratory System (Chapter 23) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Respiratory System (Chapter 23) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy & Physiology
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th & 12 th Eds.)
 PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
otorhinolaryngology -the study of the structure, function, and disorders of the ears, nose, and throat
 89 Chapter 6 Respiratory System Overview -The respiratory system consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and the lungs (Figure 6.1, Derrickson). -The purpose of the respiratory system
89 Chapter 6 Respiratory System Overview -The respiratory system consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and the lungs (Figure 6.1, Derrickson). -The purpose of the respiratory system
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 22 Part 1 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system Supplies
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 22 Part 1 The Respiratory System The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system Supplies
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
SCPA602 Respiratory System
 SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Overview Oxygen is important to our body. The cardiovascular and respiratory system share responsibility for supplying the body with oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide. Functional
The Respiratory System Overview Oxygen is important to our body. The cardiovascular and respiratory system share responsibility for supplying the body with oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide. Functional
Respiratory System. Ling Shucai
 Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Hyoid Bone. Lower Airway. Aspiration. Larynx. Cartilages of the Larynx. Larynx Tracheobronchial Tree (TB Tree) Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles
 Lower Airway Larynx Tracheobronchial Tree (TB Tree) Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Respiratory Terminal Hyoid Bone Not part of the larynx. The Hyoid bone is an anchor for the anterior muscles of the neck
Lower Airway Larynx Tracheobronchial Tree (TB Tree) Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Respiratory Terminal Hyoid Bone Not part of the larynx. The Hyoid bone is an anchor for the anterior muscles of the neck
The Respiratory System. Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb
 The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Respiratory System Structures and Gas Exchange
 A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
A. Respiratory medium the oxygen source 1. Air 2. Water Respiratory Medium Organism Cellular Respiration O 2 CO 2 B. Respiratory surface the structure where exchange of gases with the surrounding environment
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
