Drugs acting on the respiratory tract
|
|
|
- Britton Tate
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Drugs acting on the respiratory tract
2 Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness; inflammation may lead to irreversible obstruction in a few patients. A classification based on severity before the start of treatment and disease progression is of importance when decisions have to be made about management. It can be divided by severity into intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent and severe persistent. These are useful in the management of the disease since therapy has a stepwise approach which must be discussed with the patient before commencing therapy. The level of therapy is increased as the severity of the asthma increases with stepping-down if control is sustained (see tables on treatment below). INHALATION Medications for asthma can be administered in several different ways, including inhaled, oral and parenteral (subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous). The main advantage of delivering drugs directly into the airways via inhalation is that high concentrations can be delivered more effectively and rapidly to the airways, and systemic adverse effects avoided or minimized. It is important that patients receive careful instruction in the use of pressurized (aerosol) inhalation (using a metered-dose inhaler) to obtain optimum results. Before use, the inhaler should be shaken well. After exhaling as completely as possible, the mouthpiece of the inhaler should be placed well into the mouth and the lips firmly closed around it. The patient should inhale deeply through the mouth while actuating the inhaler. After holding the breath for 10 seconds or as long as is comfortable, the mouthpiece should be removed and the patient should exhale slowly. It is important to check that patients continue to use their inhalers correctly as inadequate technique may be mistaken for drug failure. Spacing devices provide a space between the inhaler and the mouth. They may be of benefit for patients such as the elderly, small children and the asthmatic who find inhalers difficult to use or for those who have difficulty synchronizing their breathing with administration of the aerosol. A large volume spacing device is also recommended for inhalation of high doses of corticosteroids to reduce oropharyngeal deposition which can cause candidosis. The use of metered-dose inhalers with spacers is less expensive and may be as effective as use of nebulizers, although drug delivery may be affected by choice of spacing device. Breath-actuated devices including dry powder inhalers are also available. Solutions for nebulization are available for use in acute severe asthma. They are administered over a period of 5 10 minutes from a nebulizer, usually driven by oxygen in hospital. ORAL
3 The oral route is used when administration by inhalation is not possible. Systemic adverse effects occur more frequently when a drug is given orally rather than by inhalation. Drugs given by mouth for the treatment of asthma include beta 2 -agonists, corticosteroids, and theophylline. PARENTERAL Drugs such as beta 2 -agonists, corticosteroids, and aminophylline may be given by injection in acute severe asthma when administration by nebulization is inadequate or inappropriate. If the patient is being treated in the community, urgent transfer to hospital should be arranged. PREGNANCY Poorly controlled asthma in pregnant women can have an adverse effect on the fetus, resulting in perinatal mortality, increased prematurity and low birth-weight. For this reason using medications to obtain optimal control of asthma is justified. Administration of drugs by inhalation during pregnancy has the advantage that plasma drug concentrations are not likely to be high enough to have an effect on the fetus. Acute exacerbations should be treated aggressively in order to avoid fetal hypoxia. Acute exacerbation of asthma Severe asthma can be fatal and must be treated promptly and energetically. Acute severe asthma attacks require hospital admission where resuscitation facilities are immediately available. Severe asthma is characterized by persistent dyspnoea poorly relieved by bronchodilators, exhaustion, a high pulse rate (usually more than 110/minute) and a very low peak expiratory flow. As asthma becomes more severe, wheezing may be absent. Patients should be given oxygen 40 60% (if available) (see also section 1.1.3). Patients should also be given salbutamol or terbutaline via a nebulizer. In emergencies where a nebulizer is not available, salbutamol 100 micrograms by aerosol inhalation can be repeated times preferably using a large-volume spacing device. Patients should also be given a corticosteroid ; for adults, prednisolone mg by mouth or hydrocortisone 200 mg (preferably as sodium succinate) intravenously; for children, prednisolone 1 2 mg/kg by mouth (1 4 years, maximum 20 mg, 5 15 years, maximum 40 mg) or hydrocortisone 100 mg (preferably as sodium succinate) intravenously; if the patient experiences vomiting the parenteral route may be preferred for the first dose. If response is inadequate, ipratropium by nebulizer should be considered. Most patients do not benefit from the addition of intravenous aminophylline or a parenteral beta 2 -agonist; both cause more adverse effects than nebulized beta 2 -agonists. Nevertheless, an occasional patient who has not been taking theophylline, may benefit from a slow intravenous infusion of aminophylline. The use of epinephrine (adrenaline) (see section 3.1) in asthma has generally been superseded by beta 2 -selective adrenoceptor agonists.
4 Treatment should never be delayed for investigations, patients should never be sedated and the possibility of pneumothorax should be considered. Patients who deteriorate further despite treatment may need intermittent positive pressure ventilation. STEP 4 Severe Persistent TREATMENT OF CHRONIC ASTHMA: INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN UNDER 5 YEARS OLD Preferred treatments are in bold print Long-term Preventive Quick Relief Daily medications Inhaled corticosteroid, beclometasone dipropionate MDI with spacer and face mask > 1 mg daily or nebulized beclometasone > 1 mg twice daily Consider short course of soluble prednisolone tablets, regular inhaled long-acting beta 2 -agonist or modifiedrelease theophyllinealso, nebulized beta 2 -agonist Inhaled short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist or ipratropium bromide as needed for symptoms, not to exceed 3 4 times daily STEP 3 Moderate Persistent STEP 2 Mild Persistent STEP 1 Intermittent Daily medications Inhaled corticosteroid, beclometasone dipropionate MDI with spacer and face mask micrograms daily or nebulized beclometasone <= 1 mg twice dailyconsider short course of soluble prednisolone tablets, regular inhaled long-acting beta 2 -agonist or modifiedrelease theophylline Daily medications Either inhaled corticosteroid, beclometasone dipropionate, micrograms, or cromoglicate (use MDI with a spacer and face mask or use a nebulizer) None needed Step down Review treatment every 3 to 6 months. If control is sustained for at least 3 months, a gradual stepwise reduction in treatment may be possible. Inhaled short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist or ipratropium bromide as needed for symptoms, not to exceed 3 4 times daily Inhaled short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist or ipratropium bromide as needed for symptoms, not to exceed 3 4 times daily Inhaled short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist or ipratropium bromide as needed for symptoms, but not more than once daily Intensity of treatment will depend on severity of attack Step up If control is not achieved, consider step up. But first: review patient medication
5 STEP 4 Severe Persistent STEP 3 Moderate Persistent STEP 2 Mild Persistent STEP 1 Intermittent technique, compliance and environmental control. TREATMENT OF CHRONIC ASTHMA: ADULTS AND CHILDREN OVER 5 YEARS OLD Preferred treatments are in bold print Long-term Preventive Quick Relief Daily medications Inhaled corticosteroid, beclometasone dipropionate mg + Longacting bronchodilator: either longacting inhaled beta2-agonist, and/or modified-release theophylline, and/or long-acting beta 2 -agonist tablets or syrup + corticosteroid tablets or syrup long term Daily medications Inhaled corticosteroid, beclometasone diproprionate mg daily in divided doses + if needed Longacting bronchodilator: either longacting inhaled beta2-agonist, modified-release theophylline, or long-acting beta 2 -agonist tablets or syrup Daily medications Either inhaled corticosteroid, beclometasone dipropionate micrograms twice daily, sodium cromoglicate or modified-release theophylline None needed Step down Review treatment every 3 to 6 months. If control is sustained for at least 3 months, a gradual stepwise reduction in treatment may be possible. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist as needed for symptoms Short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist as needed for symptoms, not to exceed 3 4 times daily Short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist as needed for symptoms, not to exceed 3 4 times daily Short-acting bronchodilator: inhaled beta2-agonist as needed for symptoms (up to once daily) Intensity of treatment will depend on severity of attack Inhaled beta 2 -agonist or sodium cromoglicate before exercise or exposure to allergen Step up If control is not achieved, consider step up. But first: review patient medication technique, compliance and environmental control. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (chronic bronchitis and emphysema) may be helped by an inhaled short-acting beta2-adrenoceptor agonist used as required or
6 when the airways obstruction is more severe, by an inhaled anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) bronchodilator or both if necessary. Although many patients are treated with an inhaled corticosteroid its role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is not clear at present. A limited trial of high-dose inhaled corticosteroid or an oral corticosteroid is recommended for patients with moderate airflow obstruction to determine the extent of the airway reversibility and to ensure that asthma has not been overlooked. Long-term oxygen therapy prolongs survival in some patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Beta2-adrenoceptor agonists (beta2-adrenoceptor stimulants) The adrenoreceptors in bronchi are mainly beta 2 type and their stimulation causes bronchial muscles to relax. The beta 2 -adrenoceptor agonists include salbutamol, terbutaline, and fenoterol. When salbutamol is given by inhalation ( micrograms) the effect can last as long as 4 hours thus making it suitable for both the treatment (see Tables) and prevention of asthma. Salbutamol can also be taken orally in a dose of 2 4 mg up to 4 times daily but is less effective and causes more adverse effects. It can also be given by injection for severe bronchospasm. ADVERSE EFFECTS Cardiovascular adverse effects (arrhythmias, palpitations and tachycardia) may occur with salbutamol, but are infrequent with inhaled preparations. Hypokalaemia may result from beta 2 -adrenoceptor agonist therapy. Particular caution is required in severe asthma because this effect may be potentiated by concomitant treatment with xanthines (for example theophylline), corticosteroids, diuretics and hypoxia. Plasma potassium concentrations should be monitored in severe asthma. Xanthines Xanthines include theophylline and aminophylline. They relax bronchial smooth muscle relieving bronchospasm and also stimulate respiration. Absorption of theophylline from the gastrointestinal tract is usually rapid and complete. It is metabolized by the liver but its half-life can vary considerably in certain diseases including hepatic impairment and cardiac failure, with some coadministered drugs (see Appendix 1) as well as by factors such as age, smoking and alcohol intake. The half-life variation can be important because theophylline has a narrow margin between therapeutic and toxic effects. At therapeutic doses some patients experience nausea and diarrhoea and when plasma concentrations exceed the recommended range of mg/litre ( micromol/litre) arrhythmias and convulsions which may be fatal can occur. Monitoring of plasma concentrations is therefore recommended. Theophylline is used to treat chronic asthma, usually in the form of modified-release preparations which produce adequate plasma concentrations for up to 12 hours. It is used as an adjunct to beta 2 -agonist or corticosteroid therapy when additional bronchodilation is required but there is an increased risk of adverse effects with beta 2 -agonists (see above). When given as a single dose at night, modified-release
7 preparations may be useful in controlling nocturnal asthma and early morning wheezing. The absorption characteristics of modified-release theophylline peparations vary considerably and therefore it is important to keep the patient on the same brand-name formulation. Theophylline is given by injection as aminophylline (a mixture of theophylline with ethylenediamine) which is 20 times more soluble in water than theophylline alone. It is administered by slow intravenous injection in severe asthma attacks. Corticosteroids INHALED CORTICOSTEROIDS Inhaled corticosteroids, such as beclometasone, are the most effective antiinflammatory medications for the treatment of asthma. They are recommended for the long-term control of asthma in patients using a beta 2 -adrenoceptor agonist more than once a day. Regular use of inhaled corticosteroids reduces the risk of exacerbations of asthma. Corticosteroids must be used regularly to obtain maximum benefit. Symptom control is usually effective after 3 to 7 days treatment. Long-term high-dose regimens of inhaled corticosteroids are useful for the treatment of severe persistent asthma because they both reduce the need for the long-term use of oral corticosteroids and have fewer systemic adverse effects. Local adverse effects from inhaled corticosteroids include oropharyngeal candidosis, dysphonia and occasional coughing from upper airway irritation. The use of spacing devices reduces oropharyngeal deposition and thus reduces the incidence of candidosis. The risk for systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids is small and is dependent upon the dose and potency of the corticosteroid as well as its bioavailability and the plasma half-life of its systemically absorbed fraction. Systemic effects are rare and include skin thinning and easy bruising, a small increased risk of glaucoma and cataracts, adrenal suppression, decrease of bone metabolism and growth retardation in children. SYSTEMIC CORTICOSTEROIDS Oral corticosteroids (sections 3.1 and 18.1) may be used as maximum therapy to achieve control of a patient s asthma. This may be useful either when initiating longterm therapy for a patient with uncontrolled asthma or as a short rescue course at any stage for acute exacerbation. Long-term oral corticosteroid therapy may be required to control severe persistent asthma, but its use is limited by the risk of significant adverse effects. In these cases high-dose inhaled corticosteroids should be continued so that oral requirements are reduced to a minimum. Oral doses should be given as a single dose in the morning to reduce the disturbance to the circadian cortisol secretion. Dosage should always be adjusted to the lowest dose which controls symptoms.
8 Sodium cromoglicate Sodium cromoglicate prevents the asthmatic response to certain allergic and nonallergic stimuli. It may be used as long-term therapy early in the course of asthma. It reduces symptoms and the frequency of exacerbations and allows dosage reduction of bronchodilators and oral corticosteroids. Prophylaxis with sodium cromoglicate is generally less effective in adults than prophylaxis with inhaled corticosteroids, but long-tem use of inhaled corticosteroids may be associated with more adverse effects. Sodium cromoglicate is of value in the prevention of exercise-induced asthma, a single dose being inhaled 30 minutes beforehand. Sodium cromoglicate is of no value for the treatment of acute attacks of asthma. In general, sodium cromoglicate produces only minimal adverse effects such as occasional coughing upon inhalation of the powder formulation. Anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) bronchodilators Ipratropium can provide short-term relief in chronic asthma, but short-acting beta 2 - agonists work more quickly. Ipratropium is also used as a bronchodilator in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Salbutamol Salbutamol is a representative beta 2 -adrenoceptor agonist. Various drugs can serve as alternatives Tablets, salbutamol (as sulfate) 2 mg, 4 mg Syrup, salbutamol (as sulfate) 2 mg/5 ml Injection (Solution for injection), salbutamol (as sulfate) 50 micrograms/ml, 5-ml ampoule Aerosol inhalation (Pressurized inhalation), salbutamol (as sulfate) 100 micrograms/metered inhalation Nebulizer solution, salbutamol (as sulfate) 5 mg/ml, 20-ml ampoules Uses: prophylaxis and treatment of asthma; premature labour (section 22.1) Precautions: hyperthyroidism, myocardial insufficiency, arrhythmias, susceptibility to QT-interval prolongation, hypertension, pregnancy (but appropriate to use; see also notes above); breastfeeding (Appendix 3); diabetes mellitus especially intravenous administration (monitor blood glucose; ketoacidosis reported); interactions: Appendix 1 Dosage:
9 Chronic asthma (when inhalation is ineffective), by mouth, ADULT 2 4 mg 3 or 4 times daily; in some patients up to maximum of 8 mg 3 or 4 times daily; CHILD under 2 years, 100 micrograms/kg 4 times daily, 2 6 years, 1 2 mg 3 4 times daily, 6 12 years, 2 mg 3 4 times daily Severe acute bronchospasm, by slow intravenous injection, ADULT 250 micrograms, repeated if necessary Relief of acute bronchospasm, by aerosol inhalation, ADULT micrograms (1 2 puffs); CHILD 100 micrograms (1 puff) increased to 200 micrograms (2 puffs) if necessary; by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, ADULT 500 micrograms repeated every 4 hours if necessary Prophylaxis of exercise-induced bronchospasm, by aerosol inhalation, ADULT 200 micrograms (2 puffs); CHILD 100 micrograms (1 puff) increased to 200 micrograms (2 puffs) if required Chronic asthma (as adjunct in stepped treatment), by aerosol inhalation, ADULT micrograms (1 2 puffs) up to 3 4 times daily; CHILD 100 micrograms (1 puff) 3 4 times daily, increased to 200 micrograms (2 puffs) 3 4 times daily if necessary Severe acute asthma or chronic bronchospasm unresponsive to conventional treatment, by inhalation of nebulized solution, ADULT and CHILD over 18 months, 2.5 mg repeated up to 4 times daily; may be increased to 5 mg if necessary medical assessment should be considered since alternative therapy may be indicated; CHILD under 18 months, clinical efficacy uncertain (transient hypoxaemia may occur consider oxygen supplementation) Adverse effects: hypokalaemia after high doses (see notes above); arrhythmias, tachycardia, palpitations, peripheral vasodilation, fine tremor (usually hands), muscle cramps, headache, insomnia, behavioural disturbances in children; hypersensitivity reactions including paradoxical bronchospasm, urticaria and angioedema; slight pain on intramuscular injection Beclometasone dipropionate Beclometasone dipropionate is a representative corticosteroid. Various drugs can serve as alternatives Aerosol inhalation (Pressurized inhalation), beclometasone dipropionate 50 micrograms/metered inhalation (standard dose inhaler), 250 micrograms/metered inhalation (high dose inhaler) Uses: chronic asthma not controlled by short-acting beta 2 -adrenoceptor agonists
10 Precautions: see notes above; active or quiescent tuberculosis; systemic therapy may be required during periods of stress or when airway obstruction or mucus prevent drug access to smaller airways; not for relief of acute symptoms; monitor height of children receiving prolonged treatment if growth slowed, review therapy Dosage: Chronic asthma, by aerosol inhalation (standard dose inhaler), ADULT 200 micrograms twice daily or 100 micrograms 3 4 times daily (in more severe cases, initially micrograms daily); CHILD micrograms 2 4 times daily or micrograms twice daily Chronic asthma, by aerosol inhalation (high dose inhaler), ADULT 500 micrograms twice daily or 250 micrograms 4 times daily; if necessary may be increased to 500 micrograms 4 times daily; CHILD not recommended Adverse effects: oropharyngeal candidosis, cough and dysphonia (usually only with high doses); adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, impaired bone metabolism, glaucoma and cataract (with high doses, but less frequent than with systemic corticosteroids); paradoxical bronchospasm requires discontinuation and alternative therapy (if mild, may be prevented by inhalation of beta 2 -adrenoceptor agonist or by transfer from aerosol to powder inhalation); rarely, urticaria, rash, angioedema Candidosis. Candidosis can be reduced by use of a spacing device (see notes above); rinsing the mouth with water after inhalation may help to prevent candidosis Theophylline and Aminophylline Aminophylline is a representative xanthine bronchodilator. Various drugs including theophylline can serve as alternatives Tablets, theophylline 100 mg Modified-release tablets, theophylline 200 mg, 300 mg Injection (Solution for injection), aminophylline 25 mg/ml, 10-ml ampoule Uses: chronic asthma including nocturnal asthma; acute severe asthma Contraindications: porphyria; known hypersensitivity to ethylenediamine (for aminophylline)
11 Precautions: cardiac disease, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, peptic ulcer, epilepsy, hepatic impairment (Appendix 5), pregnancy (Appendix 2), breastfeeding (Appendix 3), elderly, fever; smokers may require larger or more frequent doses; interactions: Appendix 1 Dosage: Chronic asthma, by mouth (as tablets), ADULT and CHILD over 12 years, mg 3 4 times daily after food; by mouth (as modified-release tablets) ADULT mg every 12 hours Nocturnal asthma, by mouth (as modified-release tablets), ADULT total daily requirement as single evening dose Note. Plasma theophylline concentration for optimum response mg/litre ( micromol/litre); narrow margin between therapeutic and toxic dose; see notes above; a range of 5 15 mg/litre ( micromol/litre) may be effective and associated with fewer adverse effects Acute severe asthma (not previously treated with theophylline), by slow intravenous injection (over at least 20 minutes), ADULT and CHILD 5 mg/kg; maintenance, by intravenous infusion, ADULT 500 micrograms/kg/hour; CHILD 6 months 9 years, 1 mg/kg/hour, years, 800 micrograms/kg/hour, adjusted according to plasmatheophylline concentration Note. Patients taking oral theophylline (or aminophylline) should not normally receive intravenous aminophylline unless plasma-theophylline concentration is available to guide dosage Adverse effects: nausea and other gastrointestinal disturbances, restlessness, anxiety, tremor, palpitations, headache, insomnia, dizziness; convulsions, arrhythmias and hypotension especially if given by rapid injection; urticaria, erythema and exfoliative dermatitis resulting from hypersensitivity to ethylenediamine component of aminophylline Sodium cromoglicate Sodium cromoglicate is a representative antiasthma drug. Various drugs can serve as alternatives Sodium cromoglicate is a complementary drug Aerosol inhalation (Pressurized inhalation), sodium cromoglicate 5 mg/metered inhalation Uses:
12 prophylaxis of asthma; prevention of exercise-induced asthma Precautions: pregnancy (appropriate to use; see notes above and Appendix 2); breastfeeding (Appendix 3) Dosage: Prophylaxis of asthma and exercise-induced asthma, by aerosol inhalation, ADULT and CHILD 10 mg 4 times daily, increased in severe cases or during periods of risk to 6 8 times daily; additional doses may be taken before exercise; when stabilized, may be possible to reduce to maintenance of 5 mg 4 times daily Adverse effects: coughing, transient bronchospasm Ipratropium bromide Aerosol inhalation (Pressurized inhalation), ipratropium bromide 20 micrograms/metered dose Uses: chronic asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Precautions: prostatic hypertrophy; pregnancy; glaucoma (standard doses unlikely to be harmful; reported with nebulized drug, particularly in association with nebulized salbutamol) Dosage: Chronic asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, by aerosol inhalation, ADULT micrograms, in early treatment up to 80 micrograms at a time, 3 4 times daily; CHILD up to 6 years, 20 micrograms 3 times daily, 6 12 years, micrograms 3 times daily Adverse effects: occasionally, dry mouth; rarely, urinary retention, constipation
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis
 Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION
 VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENTOLIN Respirator Solution contains 5mg salbutamol, as sulphate, per ml of solution and is supplied in 10 ml bottles.
VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENTOLIN Respirator Solution contains 5mg salbutamol, as sulphate, per ml of solution and is supplied in 10 ml bottles.
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP
 PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
REVIEW AMINOPHYLLINE. Background
 REVIEW AMINOPHYLLINE Background The current 13 th edition of the WHO Model Essential Medicines List (dated April 2003) includes aminophylline on the Complementary List. The listing is as shown below (together
REVIEW AMINOPHYLLINE Background The current 13 th edition of the WHO Model Essential Medicines List (dated April 2003) includes aminophylline on the Complementary List. The listing is as shown below (together
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
ASTHALIN Respirator Solution (Salbutamol sulphate)
 Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respirator Solution (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 1 ml contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP.. 5 mg Dosage Form Solution for inhalation
Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respirator Solution (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 1 ml contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP.. 5 mg Dosage Form Solution for inhalation
Drugs used in obstetrics
 Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs used in obstetrics Drugs may be used to modify uterine contractions. These include oxytocic drugs used to stimulate uterine contractions both in induction of labour and to
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
IPRAVENT Respules/Respirator solution (Ipratropium bromide)
 Published on: 19 Sep 2014 IPRAVENT Respules/Respirator solution (Ipratropium bromide) Composition IPRAVENT Respules Each 2 ml contains: Ipratropium Bromide BP equivalent to Ipratropium Bromide (anhydrous)
Published on: 19 Sep 2014 IPRAVENT Respules/Respirator solution (Ipratropium bromide) Composition IPRAVENT Respules Each 2 ml contains: Ipratropium Bromide BP equivalent to Ipratropium Bromide (anhydrous)
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Salapin: Salbutamol BP 2mg as sulphate in each 5mL of a raspberry cola flavoured, sugar free syrup.
 Salapin Salbutamol Syrup 2mg/5mL Qualitative and quantitative composition Salapin: Salbutamol BP 2mg as sulphate in each 5mL of a raspberry cola flavoured, sugar free syrup. Clinical particulars Therapeutic
Salapin Salbutamol Syrup 2mg/5mL Qualitative and quantitative composition Salapin: Salbutamol BP 2mg as sulphate in each 5mL of a raspberry cola flavoured, sugar free syrup. Clinical particulars Therapeutic
BRICANYL INJECTION. terbutaline sulfate PRODUCT INFORMATION
 BRICANYL INJECTION terbutaline sulfate PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Terbutaline sulfate, 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl) ethanol sulfate, a sympathomimetic bronchodilator with a
BRICANYL INJECTION terbutaline sulfate PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Terbutaline sulfate, 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl) ethanol sulfate, a sympathomimetic bronchodilator with a
patient group direction
 SALBUTAMOL v01 1/12 SALBUTAMOL PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
SALBUTAMOL v01 1/12 SALBUTAMOL PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
Utibron Neohaler. (indacaterol, glycopyrrolate) New Product Slideshow
 Utibron Neohaler (indacaterol, glycopyrrolate) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Utibron Neohaler Generic name: Indacaterol, glycopyrrolate Pharmacological class: Long-acting beta2- agonist
Utibron Neohaler (indacaterol, glycopyrrolate) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Utibron Neohaler Generic name: Indacaterol, glycopyrrolate Pharmacological class: Long-acting beta2- agonist
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
ASTHALIN Respules (Salbutamol sulphate)
 Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respules (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 2.5 ml respule contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP. 2.5 mg Normal saline solution.q.s. Dosage
Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respules (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 2.5 ml respule contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP. 2.5 mg Normal saline solution.q.s. Dosage
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN DISKS
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN DISKS APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol sulphate B.P. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder. It is soluble in 4 parts
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN DISKS APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol sulphate B.P. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder. It is soluble in 4 parts
NEW ZEALAND CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION. Salbutamol (as sulfate) 100 micrograms per actuation inhalation aerosol
 NEW ZEALAND CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION RESPIGEN TM Salbutamol (as sulfate) 100 micrograms per actuation inhalation aerosol Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. Keep
NEW ZEALAND CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION RESPIGEN TM Salbutamol (as sulfate) 100 micrograms per actuation inhalation aerosol Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. Keep
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION AND NEBULES
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION AND NEBULES APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol Sulphate BP PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder.
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION AND NEBULES APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol Sulphate BP PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder.
Core Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Dry Powder Inhaler, Nebuliser Suspension, pressurised Metered Dose Inhaler (pmdi)
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Budesonide Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Dry Powder Inhaler, Nebuliser Suspension, pressurised Metered Dose Inhaler (pmdi) P - RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0041/001 Date of FAR:
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Budesonide Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Dry Powder Inhaler, Nebuliser Suspension, pressurised Metered Dose Inhaler (pmdi) P - RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0041/001 Date of FAR:
PRODUCT INFORMATION INTAL CFC-FREE INHALER AND INTAL FORTE CFC-FREE INHALER
 PRODUCT INFORMATION INTAL CFC-FREE INHALER AND INTAL FORTE CFC-FREE INHALER NAME OF MEDICINE Sodium Cromoglycate for Oral Inhalation. C 23 H 14 Na 2 O 11 Mol Wt. 512.3 CAS No. [15826-37-6] Sodium cromoglycate
PRODUCT INFORMATION INTAL CFC-FREE INHALER AND INTAL FORTE CFC-FREE INHALER NAME OF MEDICINE Sodium Cromoglycate for Oral Inhalation. C 23 H 14 Na 2 O 11 Mol Wt. 512.3 CAS No. [15826-37-6] Sodium cromoglycate
SEROBID Inhaler (Salmeterol xinafoate)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 SEROBID Inhaler (Salmeterol xinafoate) Composition Each actuation delivers: Salmeterol (as Salmeterol Xinafoate IP) 25 mcg Suspended in propellant HFA 134a.....q.s. Dosage Form
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 SEROBID Inhaler (Salmeterol xinafoate) Composition Each actuation delivers: Salmeterol (as Salmeterol Xinafoate IP) 25 mcg Suspended in propellant HFA 134a.....q.s. Dosage Form
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Atrovent Administration
 Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET SEREVENT Accuhaler
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET SEREVENT Accuhaler Salmeterol xinafoate (50 mcg per inhalation) Presentation SEREVENT Accuhaler is a moulded plastic device containing a foil strip with 60 regularly placed blisters
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET SEREVENT Accuhaler Salmeterol xinafoate (50 mcg per inhalation) Presentation SEREVENT Accuhaler is a moulded plastic device containing a foil strip with 60 regularly placed blisters
Asmol uni-dose Salbutamol (sulfate) PRODUCT INFORMATION
 Asmol uni-dose Salbutamol (sulfate) PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF MEDICINE The active ingredient of Asmol uni-dose is salbutamol (as sulfate). The chemical name for salbutamol sulfate is: 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol
Asmol uni-dose Salbutamol (sulfate) PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF MEDICINE The active ingredient of Asmol uni-dose is salbutamol (as sulfate). The chemical name for salbutamol sulfate is: 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET NAME OF MEDICINE OXIS TURBUHALER Eformoterol fumarate dihydrate (6 µg per inhalation) PRESENTATION OXIS TURBUHALER is a multidose, inspiratory flow driven, metered dose, dry powder
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET NAME OF MEDICINE OXIS TURBUHALER Eformoterol fumarate dihydrate (6 µg per inhalation) PRESENTATION OXIS TURBUHALER is a multidose, inspiratory flow driven, metered dose, dry powder
PRODUCT INFORMATION. 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol Sulphate.
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION AND NEBULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE: Salbutamol Sulphate BP Chemical Name: 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol Sulphate. Structure:
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION AND NEBULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE: Salbutamol Sulphate BP Chemical Name: 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol Sulphate. Structure:
Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol)
 Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol) For inhalation use Important: Read instructions carefully Wash your inhaler once a week and allow to dry What you need
Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol) For inhalation use Important: Read instructions carefully Wash your inhaler once a week and allow to dry What you need
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD
 Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Salmeterol (Serevent)
 Prior to administration: Assess for presence/history of chronic asthma, exercise induced asthma, acute asthma attacks, and acute upper airway obstruction. Assess respiratory rate and lung sounds, pulse
Prior to administration: Assess for presence/history of chronic asthma, exercise induced asthma, acute asthma attacks, and acute upper airway obstruction. Assess respiratory rate and lung sounds, pulse
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/126654/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax, which details the measures
EMA/126654/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for DuoResp Spiromax, which details the measures
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Patient Group Direction for SALBUTAMOL INHALER (Version 02) Valid From 1 October September 2019
 Version Control This PGD has been agreed by the following organisations FCMS PDS Medical Doncaster CCG Lancashire CCGs including East Lancashire, Fylde and Wyre and North Lancashire CCGs Change history
Version Control This PGD has been agreed by the following organisations FCMS PDS Medical Doncaster CCG Lancashire CCGs including East Lancashire, Fylde and Wyre and North Lancashire CCGs Change history
7.2 Part VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary
 7.2 Part VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary 7.2.1 Part VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by persistent airflow limitation that is usually
7.2 Part VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary 7.2.1 Part VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by persistent airflow limitation that is usually
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/639304/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva, which
EMA/639304/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Budesonide/Formoterol Teva, which
New Zealand Datasheet
 New Zealand Datasheet 1 PRODUCT NAME Asthalin 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Salbultamol respiratory solution 3 PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Asthalin is a plastic ampoule presentation containing a sterile,
New Zealand Datasheet 1 PRODUCT NAME Asthalin 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Salbultamol respiratory solution 3 PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Asthalin is a plastic ampoule presentation containing a sterile,
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
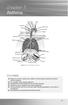 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol)
 EMA/675937/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax, which details the measures
EMA/675937/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax (budesonide / formoterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Vylaer Spiromax, which details the measures
Chapter 55. Changes in the Airway With COPD. Manifestations of Severe COPD. Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders
 Chapter 55 Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders Changes in the Airway With COPD Manifestations of Severe COPD Air is trapped in the lower respiratory tract The alveoli degenerate and fuse
Chapter 55 Drugs Used to Treat Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders Changes in the Airway With COPD Manifestations of Severe COPD Air is trapped in the lower respiratory tract The alveoli degenerate and fuse
A COPD medication delivery device option: an overview of the NEOHALER
 A COPD medication delivery device option: an overview of the NEOHALER 2017 Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved 9/17 RESP019-17 Indication and Boxed Warning INDICATION ARCAPTA NEOHALER (indacaterol)
A COPD medication delivery device option: an overview of the NEOHALER 2017 Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved 9/17 RESP019-17 Indication and Boxed Warning INDICATION ARCAPTA NEOHALER (indacaterol)
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN ROTACAPS
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN ROTACAPS APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol sulphate B.P. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder. It is soluble in 4
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN ROTACAPS APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol sulphate B.P. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder. It is soluble in 4
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Summary of Product Characteristics
 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Salbuvent 5 mg/2.5 ml Nebuliser Solution Summary of Product Characteristics 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ampoule contains 5mg salbutamol (as sulphate).
1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Salbuvent 5 mg/2.5 ml Nebuliser Solution Summary of Product Characteristics 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ampoule contains 5mg salbutamol (as sulphate).
OXIS TURBUHALER 4.5 µg/dose and 9 µg/dose ASTRAZENECA
 10-14 OXIS TURBUHALER 4.5 µg/dose and 9 µg/dose ASTRAZENECA formoterol fumarate dihydrate Inhalation powder Composition Each delivered dose (i.e. the dose leaving the mouthpiece) from Oxis Turbuhaler contains
10-14 OXIS TURBUHALER 4.5 µg/dose and 9 µg/dose ASTRAZENECA formoterol fumarate dihydrate Inhalation powder Composition Each delivered dose (i.e. the dose leaving the mouthpiece) from Oxis Turbuhaler contains
INTERNAL ONLY STANDING ORDER EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS SALBUTAMOL SULFATE Administration by Accredited Emergency Nurses for symptom relief of asthma
 POLICY STATEMENT This order may only be activated under the specific circumstances set out in the section Indications and provided there are no contraindications present. The administering nurse must be
POLICY STATEMENT This order may only be activated under the specific circumstances set out in the section Indications and provided there are no contraindications present. The administering nurse must be
Document Details. Patient Group Direction
 Document Details Title Patient Group Direction (PGD) Salbutamol Aerosol Inhaler and salbutamol Nebulised Solution Trust Ref No 1569-34313 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document Treatment of acute
Document Details Title Patient Group Direction (PGD) Salbutamol Aerosol Inhaler and salbutamol Nebulised Solution Trust Ref No 1569-34313 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document Treatment of acute
Chemical name: di[(rs)-2-(1,1-dimethyl)ethylamino-1-[4-hydroxy-3- (hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethanol] sulphate
![Chemical name: di[(rs)-2-(1,1-dimethyl)ethylamino-1-[4-hydroxy-3- (hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethanol] sulphate Chemical name: di[(rs)-2-(1,1-dimethyl)ethylamino-1-[4-hydroxy-3- (hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethanol] sulphate](/thumbs/78/76910401.jpg) Product Information Page 1 PRODUCT INFORMATION SALBUTAMOL SANDOZ 2.5MG/2.5ML, 5MG/2.5ML INHALATION AMPOULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE Generic name: Salbutamol sulphate BP Chemical name: di[(rs)-2-(1,1-dimethyl)ethylamino-1-[4-hydroxy-3-
Product Information Page 1 PRODUCT INFORMATION SALBUTAMOL SANDOZ 2.5MG/2.5ML, 5MG/2.5ML INHALATION AMPOULES NAME OF THE MEDICINE Generic name: Salbutamol sulphate BP Chemical name: di[(rs)-2-(1,1-dimethyl)ethylamino-1-[4-hydroxy-3-
PRODUCT INFOMATION APO-IPRATROPIUM SOLUTION
 PRODUCT INFOMATION APO-IPRATROPIUM SOLUTION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Ipratropium bromide. Chemical Name: (1R,3r,5S,8r)-3-[[(2RS)-3-Hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-8-methyl-8-(1- methylethyl)-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane
PRODUCT INFOMATION APO-IPRATROPIUM SOLUTION NAME OF THE MEDICINE Ipratropium bromide. Chemical Name: (1R,3r,5S,8r)-3-[[(2RS)-3-Hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoyl]oxy]-8-methyl-8-(1- methylethyl)-8-azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Duaklir Genuair (aclidinium / formoterol fumarate dihydrate)
 EMA/605453/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Duaklir Genuair (aclidinium / formoterol fumarate dihydrate) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Duaklir Genuair, which
EMA/605453/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Duaklir Genuair (aclidinium / formoterol fumarate dihydrate) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Duaklir Genuair, which
Smoking and Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) Lec:5
 Smoking and Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) Lec:5 Tobacco use remains the single largest preventable cause of mortality. Cigarette smoke is a complex mixture of an estimated 4800 compounds. Approximately
Smoking and Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) Lec:5 Tobacco use remains the single largest preventable cause of mortality. Cigarette smoke is a complex mixture of an estimated 4800 compounds. Approximately
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
VENTOLIN EVOHALER. Salbutamol
 VENTOLIN EVOHALER CFC FREE Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENTOLIN EVOHALER is a pressurised metered-dose inhaler which delivers 100 mcg salbutamol (as sulphate) per actuation, into
VENTOLIN EVOHALER CFC FREE Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENTOLIN EVOHALER is a pressurised metered-dose inhaler which delivers 100 mcg salbutamol (as sulphate) per actuation, into
Pharmacology Drugs of Respiratory system. Drugs acting on respiratory system. Dr. Ahmad Al-Zohyri Lec. 11
 Drugs acting on respiratory system Dr. Ahmad Al-Zohyri Lec. 11 Respiratory system is subjected to a lot of injurers and harms because it is nearly the only system which is in continuous contact with the
Drugs acting on respiratory system Dr. Ahmad Al-Zohyri Lec. 11 Respiratory system is subjected to a lot of injurers and harms because it is nearly the only system which is in continuous contact with the
Core Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% Date of FAR:
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Carteolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% P - RMS: SK/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 16.03.2012 4.1 THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS Ocular hypertension
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Carteolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% P - RMS: SK/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 16.03.2012 4.1 THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS Ocular hypertension
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Salamol CFC-Free Inhaler Salbutamol sulphate Ph.Eur., equivalent to Salbutamol 100 micrograms per actuation, Metered Dose Inhaler Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Salamol
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET Salamol CFC-Free Inhaler Salbutamol sulphate Ph.Eur., equivalent to Salbutamol 100 micrograms per actuation, Metered Dose Inhaler Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Salamol
COMBIVENT Metered Aerosol Boehringer
 COMBIVENT Metered Aerosol Boehringer Composition 1 metered dose contains: (8r)-3*-Hydroxy-8-isopropyl-1*,5*-tropanium bromide (±)-tropate monohydrate (= ipratropium bromide monohydrate) 21 mcg equivalent
COMBIVENT Metered Aerosol Boehringer Composition 1 metered dose contains: (8r)-3*-Hydroxy-8-isopropyl-1*,5*-tropanium bromide (±)-tropate monohydrate (= ipratropium bromide monohydrate) 21 mcg equivalent
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Asthma Medications: Information for Children and Families. What You Need to Know about Medicines for Asthma
 Page 1 of 8 PED-ALL-005-1992 Asthma Medications: Information for Children and Families What You Need to Know about Medicines for Asthma What Medicines Are used to Treat Asthma? There are two kinds of medicines:
Page 1 of 8 PED-ALL-005-1992 Asthma Medications: Information for Children and Families What You Need to Know about Medicines for Asthma What Medicines Are used to Treat Asthma? There are two kinds of medicines:
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET. Each pressurised metered-dose aerosol inhaler contains 100 micrograms of salbutamol (as sulfate)
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET RESPIGEN TM 1. Product Name Respigen TM 100 micrograms per actuation inhalation aerosol 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Each pressurised metered-dose aerosol inhaler
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET RESPIGEN TM 1. Product Name Respigen TM 100 micrograms per actuation inhalation aerosol 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Each pressurised metered-dose aerosol inhaler
GenRx SALBUTAMOL INHALATION AMPOULE
 GenRx SALBUTAMOL INHALATION AMPOULE NAME OF THE MEDICINE Salbutamol sulfate. Chemical Name: di[(rs)-2-(1,1-dimethyl)ethylamino-1-[4-hydroxy-3- (hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethanol] sulfate. Structural Formula:
GenRx SALBUTAMOL INHALATION AMPOULE NAME OF THE MEDICINE Salbutamol sulfate. Chemical Name: di[(rs)-2-(1,1-dimethyl)ethylamino-1-[4-hydroxy-3- (hydroxymethyl)phenyl]ethanol] sulfate. Structural Formula:
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Ventolin Inhaler (CFC-Free) 100 micrograms 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Ventolin Inhaler (CFC-Free) is a pressurised metered-dose inhaler which delivers
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Ventolin Inhaler (CFC-Free) 100 micrograms 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Ventolin Inhaler (CFC-Free) is a pressurised metered-dose inhaler which delivers
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet
 1 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE PAEDIATRIC ASTHMA Purpose of Procedure/
1 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE PAEDIATRIC ASTHMA Purpose of Procedure/
3. Identify the importance in the prehospital setting for the administration of nebulized bronchodilator.
 TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN ROTACAPS. The chemical name of salbutamol sulfate is 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(tertbutylamino)ethanol
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN ROTACAPS NAME OF THE MEDICINE: Ventolin Rotacaps Ventolin Rotacaps contain salbutamol (as sulfate) B.P. The chemical name of salbutamol sulfate is 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(tertbutylamino)ethanol
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN ROTACAPS NAME OF THE MEDICINE: Ventolin Rotacaps Ventolin Rotacaps contain salbutamol (as sulfate) B.P. The chemical name of salbutamol sulfate is 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(tertbutylamino)ethanol
Do not use Easyhaler Salbutamol if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to: Salbutamol lactose
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient user Easyhaler Salbutamol Sulphate 100 and 200 micrograms/dose inhalation powder Salbutamol sulphate (salbutamol) Read all of this leaflet carefully before
Package leaflet: Information for the patient user Easyhaler Salbutamol Sulphate 100 and 200 micrograms/dose inhalation powder Salbutamol sulphate (salbutamol) Read all of this leaflet carefully before
500 micrograms/dose Turbohaler dry powder device 500 micrograms/ml injection. 12 micrograms/dose Turbohaler dry powder device
 3.1 BRONCHODILATORS 3.1.1.1 SELECTIVE BETA 2 -AGONISTS Short acting Salbutamol Terbutaline 100 micrograms/actuation aerosol inhaler 100 micrograms/actuation breath-actuated e.g. Easi-Breathe 200 micrograms/dose
3.1 BRONCHODILATORS 3.1.1.1 SELECTIVE BETA 2 -AGONISTS Short acting Salbutamol Terbutaline 100 micrograms/actuation aerosol inhaler 100 micrograms/actuation breath-actuated e.g. Easi-Breathe 200 micrograms/dose
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Administration of Short-Acting Beta-agonists for Acute Episodes of Moderate or Severe Asthma by Practice Nurses
 1. Clinical Condition or situation to which this Patient Group Direction applies Definition of clinical condition/situation Adults and children aged 2 years and above presenting with increasing symptoms
1. Clinical Condition or situation to which this Patient Group Direction applies Definition of clinical condition/situation Adults and children aged 2 years and above presenting with increasing symptoms
Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Betaxolol eyedrops Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS: HU/H/PSUR/0010/002 Date of FAR: 20.03.2013 4.2 Posology
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Betaxolol eyedrops Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS: HU/H/PSUR/0010/002 Date of FAR: 20.03.2013 4.2 Posology
IPRAVENT Rotacaps (Ipratropium bromide)
 Published on: 10 Jul 2014 IPRAVENT Rotacaps (Ipratropium bromide) Composition IPRAVENT Rotacaps Each capsule contains: Ipratropium Bromide BP, equivalent to Ipratropium Bromide (anhydrous) 40 mcg Excipient..q.s.
Published on: 10 Jul 2014 IPRAVENT Rotacaps (Ipratropium bromide) Composition IPRAVENT Rotacaps Each capsule contains: Ipratropium Bromide BP, equivalent to Ipratropium Bromide (anhydrous) 40 mcg Excipient..q.s.
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
BNF CHAPTER 3: RESPIRATORY
 3.1 BRONCHODILATORS BNF CHAPTER 3: RESPIRATORY 3.1.1.1 SELECTIVE BETA 2 -AGONISTS Short acting Salbutamol 100 micrograms/actuation aerosol inhaler 100 micrograms/actuation breath-actuated (e.g., Easi-Breathe
3.1 BRONCHODILATORS BNF CHAPTER 3: RESPIRATORY 3.1.1.1 SELECTIVE BETA 2 -AGONISTS Short acting Salbutamol 100 micrograms/actuation aerosol inhaler 100 micrograms/actuation breath-actuated (e.g., Easi-Breathe
New Zealand Data Sheet
 New Zealand Data Sheet 1 PRODUCT NAME Salair 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Pressurised metered-dose inhaler (pmdi) containing Salbutamol sulphate (equivalent to 100mcg salbutamol base per
New Zealand Data Sheet 1 PRODUCT NAME Salair 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Pressurised metered-dose inhaler (pmdi) containing Salbutamol sulphate (equivalent to 100mcg salbutamol base per
patient group direction
 CYCLIZINE v01 1/7 CYCLIZINE PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner (Nurse)
CYCLIZINE v01 1/7 CYCLIZINE PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner (Nurse)
1 actuation (delivered dose from the mouthpiece) contains 160 micrograms of ciclesonide.
 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Alvesco 160 Inhaler 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 actuation (delivered dose from the mouthpiece) contains 160 micrograms of ciclesonide. For a full list
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Alvesco 160 Inhaler 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 actuation (delivered dose from the mouthpiece) contains 160 micrograms of ciclesonide. For a full list
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN. SUGAR FREE SYRUP and INJECTION. 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol Sulphate.
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN SUGAR FREE SYRUP and INJECTION NAME OF THE MEDICINE: Salbutamol Sulphate BP Chemical Name 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol Sulphate. Structure HOH
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN SUGAR FREE SYRUP and INJECTION NAME OF THE MEDICINE: Salbutamol Sulphate BP Chemical Name 1-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethylphenyl)-2-(t-butylamino)ethanol Sulphate. Structure HOH
Nausicalm solution for injection is a clear colourless solution, presented in 1 ml ampoules.
 Nausicalm Cyclizine lactate 50 mg/ml solution for injection Presentation Nausicalm solution for injection is a clear colourless solution, presented in 1 ml ampoules. Uses Actions Cyclizine is a piperazine
Nausicalm Cyclizine lactate 50 mg/ml solution for injection Presentation Nausicalm solution for injection is a clear colourless solution, presented in 1 ml ampoules. Uses Actions Cyclizine is a piperazine
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide
 Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
Better Living with Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide Second Edition November 2012 Queensland Health a Better Living with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A Patient Guide is a joint project
Children Enteric coated tablet : 1-3 mg/kg per day in divided doses.
 Ultrafen Tablet/SR Tablet/Suppository/Gel Description Ultrafen is a preparation of Diclofenac is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent with marked analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
Ultrafen Tablet/SR Tablet/Suppository/Gel Description Ultrafen is a preparation of Diclofenac is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent with marked analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
Ventolin Injection 500 micrograms (0.5mg), salbutamol, as sulphate, in 1ml (500 micrograms/ml).
 Ventolin parenteral preparations Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Ventolin Injection 500 micrograms (0.5mg), salbutamol, as sulphate, in 1ml (500 micrograms/ml). Ventolin Solution for
Ventolin parenteral preparations Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Ventolin Injection 500 micrograms (0.5mg), salbutamol, as sulphate, in 1ml (500 micrograms/ml). Ventolin Solution for
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation
![PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation](/thumbs/74/71128680.jpg) PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
It is recommended that a mask and protective eyewear be worn when providing care to a patient with a cough
 UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
Agreed Core Safety Profile for Budesonide nasal spray suspension and Budesonide nasal powder
 CSP Drug Budesonide Substance Date 13 Oct 2011 rev 11Nov Supersedes 18 Aug 2011 Agreed Core Safety Profile for DK/H/PSUR/0041/001 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE TITLE PAGE... 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 Introduction...
CSP Drug Budesonide Substance Date 13 Oct 2011 rev 11Nov Supersedes 18 Aug 2011 Agreed Core Safety Profile for DK/H/PSUR/0041/001 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE TITLE PAGE... 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 Introduction...
PM-03 PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS. Protocol SECTION: PM-03 PROTOCOL TITLE: PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS REVISED: 01MAY2018
 SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
