What Will You Learn From This Module?
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Robert Shepherd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What Is This Module About? Have you ever wondered what it would be like not being able to breathe? Not being able to smell the sweet-smelling flowers in your garden or your mom s delicious cooking? Can a person stay alive without breathing? Humans, like other animals, are able to breathe because of a special system that allows oxygen to be taken into the body. This is called the respiratory system. The respiratory system also releases carbon dioxide. It never stops working even when a person is asleep. This module will tell you all about the respiratory system. You will discover the parts that make up this system and their functions. You will also learn how to take proper care of your respiratory system and the diseases that can affect it. This module is composed of four lessons: Lesson 1 How the Respiratory System Works Lesson 2 The Parts of The Respiratory System Lesson 3 Diseases That Can Affect the Respiratory System Lesson 4 Taking Care of the Respiratory System What Will You Learn From This Module? After studying this module, you should be able to: describe the functions of the human respiratory system; identify the parts that make up the human respiratory system; describe how the human respiratory system works; name diseases that can affect the human respiratory system; identify recent inventions that enable defective parts of the respiratory system to function normally; and cite ways of taking care of the human respiratory system. 1
2 Let s See What You Already Know Before you proceed on studying this module, let s find out what you already know about the topics to be discussed. Write your answers in the blanks. 1. Name the function of the respiratory system. 2. State three parts of the respiratory system. a. b. c. 3. Give three diseases that can affect the respiratory system. a. b. c. 4. Cite two ways of taking care of the respiratory system. a. b. Well, how was it? Do you think you fared well? Compare your answers with those in the Answer Key on page 28. If all your answers are correct, very good! This shows that you already know much about the topics in this module. You may still study the module to review what you already know. Who knows, you might learn some more new things. If you got a low score, don t feel bad. This module is for you and it will help you understand some important concepts that you can apply in your daily life. If you study this module carefully, you will learn the answers to all the items in the test and a lot more! Are you ready? You may go now to the next page to begin Lesson 1. 2
3 LESSON 1 How the Respiratory System Works All animals breathe in oxygen. Oxygen is needed by the body in order to function properly. However, not all animals breathe the way humans do. Fishes, for example, use gills instead of noses since they live underwater. The special structures that allow oxygen to be used by the cells of the body make up the respiratory system. To respire means to inhale and exhale air. This lesson will tell you about the many functions of the respiratory system. Are you ready to know more about this wonderful system in your body? Let s Think About This Do you know why people breathe? Why does your respiratory system work tirelessly to bring oxygen into your body? Why is breathing important? Reflect on this before proceeding to the next part of the module. 3
4 Let s Learn The respiratory system is made up of organs through which air flows during pulmonary ventilation. What most of us call breathing, doctors call pulmonary ventilation. This term simply means that air is drawn into the body through several structures of the respiratory system. These are the same structures that carbon dioxide would need to pass through on its way out of the body. The term respiration, from the word respire refers to the act of the respiratory system which allows respiration to occur. Respiration takes place as soon as oxygen enters the body. Oxygen helps release the energy contained in food for use by cells in the body. In the process, a by-product or waste called carbon dioxide is produced. Carbon dioxide is released from the body because it can harm the cells. Let s Think About This Plants produce food through a process called photosynthesis. Oxygen is then released into the air as a product of this process. Carbon dioxide Oxygen The Carbon Dioxide Cycle People take in oxygen into their bodies and release carbon dioxide in a process called respiration. The organisms in an environment participate in a mutually beneficial relationship called the carbon dioxide cycle. 4
5 Let s Think About This How can you tell if a person is alive? The two observable functions that indicate life are the beating of the heart and the ability to breathe. When these functions stop, so does life. Do you see now how important breathing is for humans? Let s See What You Have Learned Fill in the blanks with the correct word or words. 1. is the gas needed by the cells of the body. 2. The respiratory system is important for the process of. 3. is the gas expelled from the body. 4. The word respiration means. 5. Pulmonary ventilation refers to the process of. After answering this exercise, check your answers with the Answer Key on page 28. If your score is 5, well done! You learned a lot from this lesson. You may proceed to the next lesson. If your score is 4 or below, it s okay. But you need to study this lesson again before proceeding to the next. Let s Remember The respiratory system is important for life and life functions, because it helps oxygen enter your body and helps carbon dioxide come out; and enables respiration to occur. 5
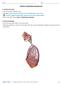
6 LESSON 2 The Parts of the Respiratory System In Lesson 1, you learned what the respiratory system is. It is a group of structures that allow oxygen to enter the body and carbon dioxide to come out. The respiratory system helps keep you alive. But how does it work? To understand how the respiratory system is able to carry out its function, you need to learn the structures of which it is made up. In this lesson, you will learn about the parts of the respiratory system. You will also know how these structures work together to bring oxygen to the cells of the body in the process called respiration. Let s Try This Sit comfortably on a chair. Breathe in and out. Inhale deeply and exhale very slowly. As you do so, close your eyes and imagine the structures the air is passing through. Where are these structures located? Let s Study And Analyze The respiratory system is composed of organs through which air that contains oxygen flows through during pulmonary ventilation. These organs include the nasal cavity (or nose), pharynx (or throat), larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs. Study the structures of the respiratory system in the figure below. Epiglottis Larynx Pharynx Trachea Left primary bronchus Secondary bronchus Terminal bronchiole Bronchiole Alveolar duct Alveoli 6
7 The respiratory system is a group of organs that supply oxygen needed by the cells of the body. The organs are arranged in such a way that the maximum amount of air is supplied to the body and is utilized well. The first of these organs, where air passes, is the nose. The nose is the first station where air enters. The nose has two external openings called the nostrils. The nostrils are also called external nares. The nose is not just a simple passageway. It acts like an airconditioning system that filters, humidifies and warms air as it passes through. The nose has hairs which are called vibrissae, that filter air. These hairs make sure that dust and other particles from the air are trapped so that they cannot enter the interior of the respiratory system. Dust and other small particles in the air might be harmful to the more delicate organs of the body. The nose also humidifies air. This means that it provides some moisture to the air because dry air is bad for the body. It irritates the linings of the internal organs of the respiratory system. You can feel this when you stay inside an airconditioned room for a long time and start to feel your nose is drying up. The nose also warms the air entering the body. The ideal temperature of air needs to be maintained to prevent the formation of ice crystals inside the organs of the respiratory system when you stay in a very cold environment. This also means that the nose preserves moisture. When dry air enters the nose, the air is first moistened by the mucus membranes that line the nose. In this sense, the wetness of the membranes of the other organs of the respiratory system is maintained. Nasal cavity External naris Nasapharynx Oropharynx Epiglottis Laryngopharynx Esophagus Internal naris Oral cavity Tongue Ventricular fold (false vocal cord) Thyroid cartilage Vocal fold (true vocal cord) Trachea Larynx 7
8 Let s Think About This Have you ever had a cold? A cold is caused by a virus, a very small but harmful particle that causes the nose to produce a lot of mucus. Mucus is the syrupy fluid that comes out of your nose. When this fluid accumulates, the nerve endings of the nose used for smelling are covered up. What do you think happens to your sense of smell when you have colds? The Pharynx The pharynx is commonly known as the throat. It is the second area where air passes through as it goes inside the body. The pharynx technically belongs to both the digestive and the respiratory systems because food also passes through this area. How is food prevented from going to the respiratory system? The pharynx divides into two distinct structures. The trachea brings air to the respiratory system while the esophagus brings food to the digestive system. Food is prevented from entering the airway because of the presence of a special structure called the epiglottis which automatically closes when one swallows. Swallowing is accomplished only when the mouth is closed. Larynx Upper trachea Epiglottis Thyroid cartilage Vestibular folds (false vocal cords) Vocal cords Glottis (passageway) Cricoid cartilage Cartilage 8
9 Let s Try This Try swallowing with your mouth open. Were you able to do it? Swallowing with the mouth open is impossible to do. This is because the mouth must first be closed to allow the epiglottis to close the airway. In this manner, food goes to the esophagus and not the trachea. This is an amazing function, because if large particles like food enter your respiratory system, you could die! The Layrnx The larynx or voice box is atop the trachea. It is a rigid box of cartilage, similar to the soft white bones of chicken. The larynx has the capability to contract. In adult males, the area of the larynx is marked by a bump in the throat called the Adam s apple. When air passes from the lungs through the larynx, the membranes of the voice box, which are called vocal cords, vibrate. This is what produces speech. Hold your throat as you speak and feel the vibrations produced by your vocal cords. To understand how the vocal cords work, try pushing out air through closed lips. You would notice that your lips would flap or vibrate when air is forced out from the respiratory system. This is how vocal sounds are produced. The Trachea If you recall, you found out that the pharynx opens out into two structures, the esophagus and the trachea. Food and liquids force open the usually compressed esophagus during swallowing. Between swallows, the esophagus closes. The trachea, on the other hand, never closes because air is needed by the body. Air is never pushed into this tube, it is sucked in by the action of your lungs. The trachea is kept open because it is surrounded by C-shaped rings of cartilage. A cartilage is like a very soft bone. Hold your earlobes. Your earlobes are made of cartilage. The trachea is kept open by cartilage, hence, everything that you breathe in will reach the other parts of your respiratory system. Be careful what you inhale! It may cause damage to the respiratory system. 9
10 The figure on the left shows you the C- shaped series of cartilages that surround the trachea. These keep your trachea always open. Cartilages Before you proceed to the next topic, study again the structure of the respiratory system below. Nasal Cavity Oral Cavity Pharynx Larynx Ribs (cut away) Esophagus Trachea Right primary bronchus Secondary bronchi Bronchioles Left lung covered by pleura The Bronchi and Bronchioles The trachea extends from the larynx to just above the level of the heart where it separates into two structures, the left and right bronchi. The right bronchus goes toward the right lung and the left bronchus goes toward the left lung. Inside the lungs, the bronchi again divide into smaller branches called the bronchioles. In this way, the respiratory system is like a tree that has a main trunk and then divides into branches, on which the leaves of the tree are found. Interestingly, the passage of the respiratory system, where air travels, is called the tracheobronchial tree. Trachea Bronchioles Bronchi 10
11 The Lungs As a tree divides into more and more branches, you can not see the branches anymore, because they are hidden among the leaves of the tree. In the human body, the foliage or the leaves of the tracheobronchial tree are referred to as the lungs. Like the leaves of a tree, the lungs contain the sites of gas exchange. The lungs are two masses of sponge-like tissue on the left and right sides of the heart inside the chest. The ribcage of the chest protects the lungs and the heart. Epiglottis Larynx Pharynx Trachea Left primary bronchus Secondary bronchus Terminal bronchiole Bronchiole Alveolar duct Alveoli Inside the lungs, the bronchioles divide into the respiratory bronchioles, which divide further into alveolar ducts. These ducts feed into the air chambers of the lungs, which are called the alveolar sacs. The air that enters the respiratory system, ultimately reaches the alveolar sacs. Here, oxygen is delivered for use by the body. Gas exchanges between the lungs and the blood occur in the alveolar sac, which resembles a bunch of tiny grapes or a cluster of bubbles. The sac is made up of alveoli. Gas transfer takes place in the walls of each alveolus. The alveolus has a very thin lining that allows oxygen to mix with the blood entering the lungs. This oxygenated blood is then delivered to the cells of the body by the circulatory system. Let s Think About This The lungs contain about 300 million alveoli. If you combine their surface areas, the alveoli would cover 70 square meters or 750 square feet. That s roughly the size of 2 tennis courts! The process of gas exchange must really be important for the body to provide a very big surface area just for that purpose. Without gas exchange, life would not be possible! 11
12 Let s Learn The Process of Gas Exchange Gases are exchanged in the alveoli. The oxygen from the air is exchanged for the carbon dioxide from the blood. Oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide enters the alveoli from where it is ultimately exhaled into the environment. The ultimate task of the respiratory system is to allow respiration to occur. Respiration is not just breathing. In the human body, respiration is achieved in three levels: 1. External respiration takes place when oxygen from the air moves through the alveoli toward the blood and carbon dioxide passes from the blood toward the alveoli. This is also known as gas exchange. 2. Internal respiration refers to the movement of the blood from the circulatory system toward the cells and tissues of the body. 3. Cellular respiration refers to the use of oxygen inside the cells to obtain energy from food. Breathing PULMONARY VENTILATION CO 2 CO 2 Tissues CO 2 Blood Sugar Usable Energy Lungs O O 2 2 Cardiovascular system and blood O 2 CO 2 O 2 CELLULAR RESPIRATION O2 O 2 O O2 2 CO 2 CO 2 EXTERNAL RESPIRATION INTERNAL RESPIRATION Without the respiratory system, air that contains oxygen cannot enter the body; gas exchange will not occur and the cells cannot produce energy for the body to use. Life would not be possible without the tireless respiratory system working to supply life-giving oxygen to the body. 12
13 Let s See What You Have Learned Fill in the blanks with the correct word or words based on what you have learned from the previous lesson. 1. is the primary task of the respiratory system. 2. The respiratory system is also called the tree. 3. is needed by the cells of the body to produce energy from food. 4. The closes to prevent food from getting into the trachea. 5. The C shaped rings of the trachea are composed of. 6. Voice is produced through the vibrations of the. 7. The lungs contain the in which gas exchange takes place. 8. The trachea divides into two. 9. The bronchi divide into. 10. The exchange of carbon dioxide from the blood with oxygen from the alveoli is called respiration. After answering this exercise, check your answers with the Answer Key found on page 29. If your score is 7 and above, well done! You now know more about the respiratory system. You may proceed to the next lesson. If your score is 6 or below, it s okay. But you need to study this lesson again before proceeding to the next. 13
14 Let s Remember The respiratory system is the organ system that allows respiration to occur. Respiration occurs in three levels: external respiration, internal respiration, and cellular respiration. The respiratory system is composed of air passages that ultimately lead to the lungs where gas exchange takes place. The first of the air passages is the nose, which filters, warms and humidifies the air entering the body. The pharynx opens towards the trachea and the esophagus. Food is prevented from entering the respiratory system through the closure of the epiglottis. The trachea is the trunk of the tracheobronchial tree. Atop the trachea is the larynx. It contains the vocal cords that vibrate when air is expired to produce sound. The trachea divides into two bronchi, each of which divides into bronchioles. The branching continues from the bronchi to the respiratory bronchioles to alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs. Individual alveoli make up the alveoli sacs. The alveolus is the site of gas exchange. Without the respiratory system, life would not be possible. 14
15 LESSON 3 Diseases that Can Affect the Respiratory System By this time, you have already learned about the function and parts of the respiratory system. You have discovered how important it is to your life. The respiratory system is vulnerable because it allows air into its passages. When air enters the passages of the respiratory system, it brings with it things that might cause more harm than good. Find out what happened to a boy named Jose. Jose s classmate had a cough and a runny nose. He had colds too. But Jose still played with him. The following day, Jose woke up with a fever and cold. He was coughing, too. Because of this, he was unable to go to school. Jose was brought to a hospital after two days because he found it very difficult to breathe. The doctor told his mother that Jose had pneumonia. He stayed in the hospital for several days. He was forced to miss school. The doctors gave him a lot of medicine to make him feel better. He also had to wear an oxygen mask for a while. Jose was lucky because he was able to recover from his illness. Nevertheless, he had to miss school for several days. His doctors suspect that he got the bacteria that causes pneumonia from his classmate. 15
16 Let s Think About This Imagine that you are Jose. Would you like to stay in a hospital, too? What are the fun things that you would miss if you got sick? The respiratory system s work is very important. To prove this, try holding your breath for as long as you can. How long were you able to do it? Let s Learn Disorders of the Respiratory System The disorders of the respiratory system are usually manifested as coughing or difficulty in breathing. These are the symptoms of a disease. Below are some conditions and their symptoms. 1. Pneumonia Pneumonia is a disease in which the bronchioles and the alveolar sacs become inflamed due to infection. Bacteria that cause pneumonia are present even in healthy throats. When the body s defenses are weakened, the bacteria multiply and cause damage. They work their way into the lungs and get stuck in the alveolar sacs, which then get inflamed. Viruses and chemical irritants can also cause pneumonia. A person who has pneumonia usually has a fever and cough and has difficulty breathing. The difficulty in breathing is caused by the excessive mucus secretion that prevents gas exchange. Pneumonia is cured with antibiotics that kill the bacteria inside the lungs. Other areas of the tracheobronchial tree can also suffer from bacterial or viral infection. The suffix -itis (which means disease or inflammation) is attached to the name of the affected part to indicate that that part has inflammation and infection. Hence, you could have pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis and bronchiolitis. These diseases are not as severe as pneumonia, but they can all cause a person to have difficulty breathing. 16
17 2. Asthma John is 12 years old. He occasionally finds himself gasping for air. Whenever he breathes, a wheezing sound is heard coming from his chest. What does John have? Asthma is a condition characterized by hypersensivity of the lungs. The passages of the respiratory system are sensitive to allergens, which are substances that can cause irritation. This sensitiveness of the air passages serves to protect the respiratory system. However, some people s respiratory system are much too sensitive that they often suffer allergic reaction, manifested as wheezing and difficulty in breathing. Asthma still has no cure. Drugs are either inhaled or taken to relax the constricting hyper-reactive airways. But these are just temporary measures. Asthma attacks usually occur again after a while. 3. Emphysema Diana was 14 years old when she started smoking. Her habit got to the point where she would smoke 2 to 3 packs a day. Recently, she has found it very difficult to breathe. She can not walk ten steps without stopping for rest. She also finds it very hard to climb stairs. Her doctor told her she has emphysema, and that she needs to quit smoking. 17
18 Smoking is bad for the respiratory system. It destroys the delicate structures of the lungs and the tracheobronchial tree. It also deposits harmful substances inside the lungs. A person who smokes is 4 to 25 times more likely to develop emphysema than nonsmokers. Smoking cut short a person s life span. Diana was diagnosed to have emphysema. Emphysema is characterized by abnormal permanent enlargements of the alveoli, caused by the destruction of the alveolar walls. This destruction is usually due to the chemical irritants found in tobacco smoke. There is no cure for emphysema. The alveolar walls cannot be repaired, hence smoking must be stopped to prevent further damage. 4. Lung Cancer Buboy started smoking 12 years ago. He smokes two packs a day. For two years, he has had severe coughing episodes especially in the morning. The cough has worsened, but he still continued smoking. Later on, he began to have chest pains and difficulty in breathing. He consulted a physician, who said that he has lung cancer. Buboy felt devastated. He knows that cancer can kill. He wished he never started smoking at all but it s all too late. Smoking destroys the respiratory system, since harmful substances like tar and nicotine from cigarettes are deposited in the lungs. This affects the natural capacity of the lung to rid themselves of waste materials, hence more of these wastes accumulate. When the damage from chemicals becomes too much, the bronchial cells become malignant. This causes lung cancer, a fatal condition. Lung cancer can be prevented by quitting tobacco smoking. Even with active medical treatment, people with lung cancer usually die within a few years after the onset of the disease. 5. Rhinitis Ronald usually wakes up with a runny nose. He finds it difficult to breathe because of too much mucus secretion inside his nose. His mucus membranes are often inflamed. He has had this condition for years. Because of his sickness, he is often late or absent from work. Medicines given to him by his doctors work only for some time. What does Ronald have? 18
19 Rhinitis is an inflammation of the nasal cavity. In the example, Ronald has allergic rhinitis. Like asthma, rhinitis is an allergic reaction to dust and pollutants. This allergic reaction causes the mucus membranes of the nose to secrete too much fluid. Allergic rhinitis is very difficult to treat because it is a recurring condition. The best way to control it is to avoid the substances that can cause allergic reactions. 6. Tuberculosis Mr. Cruz is 50 years old. For the past year, he has noticed himself losing much weight; coughing constantly; suffering from fever in the afternoons or evenings and sweating at night. One day, he noticed that there was blood where he spat on the ground. He consulted a doctor, who told him he has pulmonary tuberculosis. Pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) is a common infection of the lungs that occurs especially among people living in developing countries. It is caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis which are transmitted between persons in crowded places. The bacteria stay inside the lungs and are very hard to eliminate. However, an anti-tb drug regimen is available, which the patients usually have to take for months. If left untreated, TB can destroy the lungs and spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones and intestines. 19
20 Let s Try This Do you know anybody who has tuberculosis? How does he or she look? You can go to a hospital and visit a patient with tuberculosis. Don t stay too close because PTB disease is communicable or easily transmitted. Think how lucky you are that you have a respiratory system that functions very well. Because of the many diseases that can affect the respiratory system, new technological advances in the field of pulmonology (the study of the respiratory system) have been developed. These advances help to develop better the understanding of the structures of the respiratory system and the diseases that affect it. Recent Advances in Pulmonology New instruments are currently available for the study, diagnosis and treatment of diseases and injuries that can affect the respiratory system. These technological advances enable doctors to discover new and better ways of helping patients. A very important technology developed to understand diseases is the X ray machine, which can show pictures of the lungs and the ribcage. It is quite old but is still very useful. Nowadays, doctors can use computed tomography scan or CT scan. A CT scanner is a machine that functions like an X ray machine. However, a CT scan gives a more detailed picture of the lungs and other parts of the respiratory system. It passes small amounts of harmless radiation into the body to create images of even non-bony structures, such as the lungs. An X ray, on the other hand, is like a picture of the body. It is limited, however, because it is best used only for bony structures that show up as white patterns on X-ray films. A more sensitive machine is the MRI or magnetic resonance imaging machine. Instead of passing radiation, it passes sound waves through the body. Computers then create images out of these bouncing sound waves to show what the inside of the body looks like. An MRI can detect tumors inside the lungs. Nowadays, doctors can also pass tubes into the tracheobronchial tree to visualize it. These tubes are called endoscopes and are used to assess the condition of the passages of the respiratory system. Lung transplants are now also possible. Segments of lungs are transferred from one person to another to replace damaged parts. 20
21 Drugs used for the treatment of respiratory system infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, laryngitis and tuberculosis are currently available. More powerful drugs are being developed, and some of them are currently being used to help patients recover. People are, indeed, learning more and more about the respiratory system because of these new technological developments. How about you, are you learning more about your respiratory system, too? Breathe deeply before you proceed. Let s See What You Have Learned Write True on the line before each correct statement and False before each incorect statement. 1. Pulmonology is the study of the lungs. 2. Asthma is characterized by hypersensitivity of the lungs. 3. Rhinitis and asthma are similar. 4. Smoking is good for the body. 5. Pneumonia is an infection of the nose. 6. Smoking deposits are harmful substances in the alveoli. 7. A CT scan makes detailed study of the lungs possible. 8. Lung cancer is caused by smoking. 9. Tuberculosis is easy to cure. 10. PTB is common among people in developing countries. Check your answers in the Answer Key on page 29. If your score is 8 and above, congratulations! You have learned about the respiratory system well. You may proceed to the next lesson. If your score is 6 or below, you need to review this lesson before proceeding to the next page. 21
22 Let s Remember The respiratory system is prone to diseases that can affect its functions. Coughing and difficulty in breathing are the primary symptoms of most respiratory disorders. Some respiratory diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis, laryngitis and pharyngitis are infections. Antibiotics are available to fight bacteria and viruses that cause infections. The diseases often associated with smoking are emphysema and lung cancer. Diseases caused by allergic reactions include asthma and rhinitis. Recent technological advances in pulmonology are the CT scan and the MRI. Aside from these, more sophisticated medical procedures such as transplants and pulmonary endoscopy are now quite common. New drugs are also being developed to cure respiratory disorders. 22
23 LESSON 4 Taking Care of the Respiratory System In the previous lesson, you learned about some of the disorders that can affect the human respiratory system. You also discovered some recent advances in technology and treatment procedures that are used to correct the disorders of the respiratory system. In this lesson, you will learn how to take care of your respiratory system, a very important system without which life would not exist. It is easy to take care of your respiratory system. Observe the following practices to make sure that your respiratory system remains healthy and functioning well. Avoid smoking Eat fruits and vegetables that contain substances that fight cancer. Avoid people with cough or colds. Bacteria and viruses can easily enter your body and cause respiratory infections. Always wear protective equipments, especially face masks when working in an environment with a lot of dust or smoke which can irritate the lungs. 23
24 Cover your nose when you sneeze. Do not share personal items such as handkerchiefs especially when you have colds. Maintain good hygiene to prevent infections. Take a vacation every now and then to get fresh air into your body. Keep your surroundings clean to minimize dust that aggravates asthma. Be sensitive to changes in your body. Consult a doctor when you feel something is wrong. Rest when you are tired. 24
25 Let s See What You Have Learned Check the numbers that best illustrates the proper care for the respiratory system. 1. taking a bath regularly to avoid infections 2. smoking 3. getting enough sleep and rest 4. consulting a doctor only when really needed 5. covering the mouth and nose when sneezing 6. wearing a mask in construction sites 7. avoiding dust and smoke 8. eating nutritious foods 9. relaxing when feeling stressed 10. cleaning the nose regularly and properly After answering, compare your answers with those in the Answer Key on page 30. A score of 8 or higher means that you have learned the lesson well. If your score is 7 or lower, review the items you missed. Let s Remember Taking care of the respiratory system involves the observation of some very simple habits. Avoid people with cough and colds. Do not share personal items such as handkerchiefs. Cover your nose while sneezing. Use a protective mask when working in environments that have a lot of smoke and dust. Avoid smoking. Rest and avoid stress. Get fresh air every now and then. Eat nutritious foods, especially those rich in vitamin B. Consult a doctor if you notice something is wrong with your body. You have now reached the end of the module. Congratulations! Did you enjoy studying this module? Did you learn a lot from it? The following is a summary of the module s main points to help you remember them better. 25
26 Let s Sum Up This module tells us that: The respiratory system takes in air that contains oxygen needed to maintain life. The respiratory system is composed of air passages that allow pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange to occur. The nose warms, moistens and filters air before it enters the phraynx. The epiglottis prevents food from entering the trachea. The trachea is the trunk of the tracheobronchial tree. It branches into the bronchi, bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles and the alveolar sacs. The alveoli that make up the sacs are the site of gas exchange or external respiration. Internal respiration and cellular respiration take place afterwards. What Have You Learned? A. Fill in the blanks with the correct word or words. Choose your answers from the words in the box. Lungs Internal respiration Tuberculosis Trachea Emphysema Olfaction Valsalva Pulmonary ventilation Epiglottis CT Scan 1. The exchange of gases between the blood and the cells is called. 2. The contain the alveoli needed for gas exchange. 3. Smoking results in a condition called. 4. The trunk of the tracheobronchial tree is the. 5. Breathing is technically called. 6. is a technological advance used to study the structure of the lungs. 7. is a common disease caused by a Mycobacterium. 8. The trachea is closed by the during swallowing. 26
27 B. Label the parts of the respiratory system in the figure below. Compare your answers with those in the Answer Key on page 30. If your score is 0 5 You need to study the whole module again more carefully You should review the parts of the module you did not understand very well Well done! Just review the items you missed Congratulations! You learned a lot from this module. You are now ready for the next one. 27
28 Answer Key A. Let s See What You Already Know (page 2) 1. Helps oxygen enter the body and carbon dioxide to come out 2. a. nose b. trachea c. phraynx (other possible answers: bronchi, lungs, brochioles and alveoli) 3. a. pneumonia b. lung cancer c. rhinitis (Other possible answers: tuberculosis, asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, bronchiolitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis). 4. a. avoiding smoking b. covering nose when sneezing (Other possible answers: eating nutritious foods, observing proper hygiene, wearing masks, undergoing regular medical checkups) B. Lesson 1 Let s See What You Have Learned (page 5) 1. Oxygen 2. respiration 3. Carbon dioxide 4. exchange of gases 5. breathing or taking in air from the environment 28
29 C. Lesson 2 Let s See What You Have Learned (page 13) 1. Respiration 2. tracheobronchial tree 3. Oxygen 4. epiglottis 5. cartilage 6. vocal cords 7. alveoli 8. bronchi 9. bronchioles 10. external D. Lesson 3 Let s See What You Have Learned (page 21) 1. True 2. True 3. True 4. False. Smoking increases the chances of developing emphysema and lung cancer. 5. False. Pneumonia is an infection of the alveoli. 6. True 7. True 8. True 9. False. The Mycobacterium that causes tuberculosis is quite resistant to drugs. 10. True 29
30 E. Lesson 4 Let s See What Have You Learned (page 25) The following should be underlined. 1. taking a bath regularly to avoid infections 3. getting enough sleep and rest 5. covering the mouth and nose when sneezing 6. wearing a mask in construction sites 7. avoiding dust and smoke 8. eating nutritious foods 9. relaxing when feeling stressed 10. cleaning the nose regularly and properly F. What Have You Learned (pages 26 27) A. 1. internal respiration 2. lungs 3. emphysema 4. trachea 5. pulmonary ventilation 6. CT Scan 7. Tuberculosis 8. epiglottis B. Epiglottis Larynx Pharynx Trachea Left primary bronchus Secondary bronchus Terminal bronchiole Bronchiole Alveolar duct Alveoli 30
31 Glossary Adam s apple A prominent cartilage in the layrnx of males Alveolar sacs Saclike structures where alveoli are found Alveoli Site of gas exchange in the lungs Asthma A disease that affects the respiratory system, characterized by wheezing due to the constriction of hypersensitive airways Bronchi The first pair of branches into which the trachea divides Bronchioles Smaller branches of the bronchi Carbon dioxide Waste product of respiration; exhaled gas Carbon dioxide cycle Refers to the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between plants and animals CT scan Stands for computed tomography scan, a recent development in diagnosing diseases of the respiratory system that uses radioactive waves Cellular respiration The process of utilization of oxygen by the cells of the body Emphysema A disease characterized by a difficulty in breathing; usually prevalent among smokers Endoscopy A diagnostic technique, wherein a tube is passed down the structures of the respiratory system for visualization Epiglottis Protects the airway by closing during the act of swallowing; this prevents food from entering the trachea. External nares Nostrils External respiration The process of taking in oxygen from the environment to the respiratory system Gas exchange The process of exchange of carbon dioxide for oxygen or vice versa Internal respiration Happens in the alveoli where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide Laryngitis Inflammation of the larynx Larynx Voice box Lungs A pair of spongy organs in the chest; main site of gas exchange in the respiratory system 31
32 Lung cancer A disease common among smokers, characterized by the presence and multipication of malignant growths in the lungs Oral cavity Interior of the mouth Pharynx The throat Oxygen Gas needed by the cells to extract energy from food MRI Stands for magnetic resonance imaging; a technological advance that uses sound waves to visualize the respiratory system Nasal cavity Interior of the nose where air first passes through Pharyngitis Inflammation of the pharynx Photosynthesis The process of food production by plants using radiant energy from sunlight Pneumonia Infection of the alveoli in the lungs Pulmonary ventilation The medical term for breathing Pulmonology The study of the respiratory system Pulmonologist A medical doctor, who specializes in the diseases of the respiratory system Respiration The process of production and utilization of energy Respiratory system A system of organs that functions for gas exchange Trachea Also known as windpipe; the area below the pharynx where air passes through Tracheobronchial tree The part of the respiratory system composed of branching structures from the trachea to the alveoli Tuberculosis A lung infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis; hard to treat and common among people in crowded areas Vibrissae Medical term for nose hair; trap larger particles to prevent them from entering the airway X ray A means for examining the lungs 32
33 References Campbell, N. Biology. 4 th ed. USA: The Benjamin and Cummings Publishing Company, Inc., Rischer, C. and T. Easton. Focus on Human Biology. 2 nd ed. Harper Collins College Publishers, 1995 Van de Graaff, K. and Stuart I.F. Forx. Concepts of Human Anatomy and Physiology. 2 nd ed. Iowa: WM Brown Publishers, Iowa, Vellocott. Jane and S. Side. Understanding Advanced Human Biology. Hodden and Stoughton,
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
What Is This Module About? What Will You Learn From This Module?
 What Is This Module About? Breathing is very important and natural to man. Every breath means life. Do you know what system of the human body helps us breathe? What elements in air does man need to live?
What Is This Module About? Breathing is very important and natural to man. Every breath means life. Do you know what system of the human body helps us breathe? What elements in air does man need to live?
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Emphysema. Lungs The lungs help us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Everyone is born with 2 lungs: a right lung and a left lung.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects millions of people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This makes
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects millions of people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This makes
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Write It! Station Directions
 Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from?
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
ESSENTIAL STANDARD. 6.PCH.1 Understand wellness, disease prevention, and recognition of symptoms.
 PRE-TEST 1.What are the basic functions of the respiratory system? 2.Describe five symptoms of asthma. 3.How can asthma be controlled? 4.What are some common asthma triggers? ESSENTIAL STANDARD 6.PCH.1
PRE-TEST 1.What are the basic functions of the respiratory system? 2.Describe five symptoms of asthma. 3.How can asthma be controlled? 4.What are some common asthma triggers? ESSENTIAL STANDARD 6.PCH.1
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
Reference Guide for Group Education
 A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 1 Introduction to Living Well with COPD Education Program Participants Expectations Towards the Program Health in COPD
A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 1 Introduction to Living Well with COPD Education Program Participants Expectations Towards the Program Health in COPD
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE. Learning Objectives. Pronunciation Guide Click on the megaphone icon before each item to hear the pronunciation.
 ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
