Tiotropium Bromide as an Adjunct Therapy to Inhaled Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Adults With Chronic Asthma
|
|
|
- Betty Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Winter Tiotropium Bromide as an Adjunct Therapy to Inhaled Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Adults With Chronic Asthma Kevin M. Dennis Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Medicine and Health Sciences Commons Recommended Citation Dennis, Kevin M., "Tiotropium Bromide as an Adjunct Therapy to Inhaled Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Adults With Chronic Asthma" (2011). School of Physician Assistant Studies. Paper 260. This Capstone Project is brought to you for free and open access by the Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects at CommonKnowledge. It has been accepted for inclusion in School of Physician Assistant Studies by an authorized administrator of CommonKnowledge. For more information, please contact
2 Tiotropium Bromide as an Adjunct Therapy to Inhaled Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Adults With Chronic Asthma Abstract Background: Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease effecting 24.6 million children and adults in the United States. Current treatment guidelines recommend the use of inhaled corticosteroids and both short and long acting beta agonists. Several systematic reviews have evaluated the use of anticholinergics with mixed results. Tiotropium bromide became available in the United States in 2004, yet there have been few studies utilizing this long acting anticholinergic for the treatment of asthma patients. Purpose: This paper evaluates the current literature on the improvements in pulmonary function in asthmatics with the use of tiotropium in addition to an ICS. GRADE was used to rate the quality of evidence. Method: An exhaustive search of the available literature using Medline, Pubmed, Web of Science, Cochrane Systematic Reviews and CINHAL. The keywords used included tiotropium, asthma and adults individually and in combination. Results: Four articles were found to be relevant to the topic of this paper. Two randomized clinical trials showed statistically improved lung function with the addition of tiotropium to an ICS. One observational study showed that 33% of patients demonstrated a response of 15% improvement in FEV1 with the addition of tiotropium. A case report also demonstrated improvements in PEF and a decrease in oral steroid use in a chronic asthma patient. Conclusion: Tiotropium bromide in conjunction with an ICS provides statistically significant improvement in lung function for adult patients with chronic asthma. This conclusion is based on a moderate grade of evidence using the GRADE analysis. Degree Type Capstone Project Degree Name Master of Science in Physician Assistant Studies Keywords tiotropium, asthma, inhaled corticosteroid, adult asthma Subject Categories Medicine and Health Sciences Rights Terms of use for work posted in CommonKnowledge. This capstone project is available at CommonKnowledge:
3 Copyright and terms of use If you have downloaded this document directly from the web or from CommonKnowledge, see the Rights section on the previous page for the terms of use. If you have received this document through an interlibrary loan/document delivery service, the following terms of use apply: Copyright in this work is held by the author(s). You may download or print any portion of this document for personal use only, or for any use that is allowed by fair use (Title 17, 107 U.S.C.). Except for personal or fair use, you or your borrowing library may not reproduce, remix, republish, post, transmit, or distribute this document, or any portion thereof, without the permission of the copyright owner. [Note: If this document is licensed under a Creative Commons license (see Rights on the previous page) which allows broader usage rights, your use is governed by the terms of that license.] Inquiries regarding further use of these materials should be addressed to: CommonKnowledge Rights, Pacific University Library, 2043 College Way, Forest Grove, OR 97116, (503) inquiries may be directed to:. copyright@pacificu.edu This capstone project is available at CommonKnowledge:
4 NOTICE TO READERS This work is not a peer-reviewed publication. The Master s Candidate author of this work has made every effort to provide accurate information and to rely on authoritative sources in the completion of this work. However, neither the author nor the faculty advisor(s) warrants the completeness, accuracy or usefulness of the information provided in this work. This work should not be considered authoritative or comprehensive in and of itself and the author and advisor(s) disclaim all responsibility for the results obtained from use of the information contained in this work. Knowledge and practice change constantly, and readers are advised to confirm the information found in this work with other more current and/or comprehensive sources. The student author attests that this work is completely his/her original authorship and that no material in this work has been plagiarized, fabricated or incorrectly attributed.
5 Tiotropium Bromide as an Adjunct Therapy to Inhaled Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Adults With Chronic Asthma Kevin Michael Dennis A course paper presented to the College of Health Professions in partial fulfillment of the requirements of the degree of Master of Science Pacific University School of Physician Assistant Studies March, 2011 Faculty Advisor: Mark Pedemonte, MD Clinical Graduate Project Instructors: Torry Cobb, DHSc, MPH, PA-C & Annjanette Sommers MS, PAC
6 Biography [Redacted for privacy] Acknowledgements To my family: Thank you for all of the support that you have provided over the years. To Charles Bentz, MD: Thank you for encouraging me to follow my passion for healthcare and to apply to PA school.
7 ABSTRACT Background: Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease effecting 24.6 million children and adults in the United States. Current treatment guidelines recommend the use of inhaled corticosteroids and both short and long acting beta agonists. Several systematic reviews have evaluated the use of anticholinergics with mixed results. Tiotropium bromide became available in the United States in 2004, yet there have been few studies utilizing this long acting anticholinergic for the treatment of asthma patients. Purpose: This paper evaluates the current literature on the improvements in pulmonary function in asthmatics with the use of tiotropium in addition to an ICS. GRADE was used to rate the quality of evidence. Method: An exhaustive search of the available literature using Medline, Pubmed, Web of Science, Cochrane Systematic Reviews and CINHAL. The keywords used included tiotropium, asthma and adults individually and in combination. Results: Four articles were found to be relevant to the topic of this paper. Two randomized clinical trials showed statistically improved lung function with the addition of tiotropium to an ICS. One observational study showed that 33% of patients demonstrated a response of 15% improvement in FEV1 with the addition of tiotropium. A case report also demonstrated improvements in PEF and a decrease in oral steroid use in a chronic asthma patient. Conclusion: Tiotropium bromide in conjunction with an ICS provides statistically significant improvement in lung function for adult patients with chronic asthma. This conclusion is based on a moderate grade of evidence using the GRADE analysis. Keywords: Tiotropium, inhaled corticosteroid, asthma, adult asthma.
8 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 5 Background... 5 Purpose of the Study... 7 METHOD... 7 Inclusion Criteria... 8 Exclusion Criteria... 8 RESULTS... 8 DISCUSSION REFERENCES APPENDIXES Table 1: GRADE... 22
9 INTRODUCTION Background Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease effecting both children and adults with significant morbidity and mortality. It contributes to significantly personal, social and economic burdens. Asthma is characterized by recurring bronchial inflammation, airway obstruction and airway hyper-responsiveness. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), as of 2009, 24.6 million children and adults in the United States (8.2% of the population) currently have asthma. In 2008 there were 10.5 million missed school days and 14.2 million missed workdays due to asthma. For million asthmatics required emergency department visits and 456,000 required hospitalizations for exacerbations of their condition. Health statistics from 2007 determined that there were 3,447 deaths due to asthma in that year. The prevalence of asthma has increased by an average 1.2% annually between 2001 and (Akinbami, Moorman and Liu, 2011). Current treatment guidelines published in 2007 by the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (National Heart, Lung and Blood Intstitute, 2007) were developed to provide a best practices approach for clinicians to diagnose and treat patients with asthma. The guidelines provide a step-wise approach based on asthma severity to monitor and control patient symptoms. Patients with intermittent asthma are managed with short acting beta agonists (SABA), such as albuterol, on an as needed basis. As the severity increases the preferred treatment is a low dose inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). If the patient has
10 moderate to severe asthma the recommendation is to add a long acting beta agonist (LABA) to the ICS or to increase the dose of the ICS. However, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2010) now requires manufacturers to include a warning for LABAs due to potential increases in asthma exacerbations and deaths in asthma patients. This possible safety issue has lead researchers to study the use of long-acting anticholinergics such as tiotropium bromide in the treatment of moderate to severe asthmatics. (Peters, et al, 2010). Tiotropium is currently indicated for the treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), however it is not indicated for the treatment of asthma. The efficacy of tiotropium in COPD has been demonstrated in multiple randomized clinical trials including a long-term use trial by Tashkin, Celli, Kesten, Lystig and Decremer (2010). Based on recently published studies, tiotropium may prove to be an effective treatment option in conjunction with an ICS. Previous systematic reviews have evaluated the use of anticholinergics in the treatment of asthma with mixed results. A systematic review by Westby, Benson and Gibson (2004) did not find enough adequate data at the time to determine the specific role that long-acting anticholinergics have in the treatment of chronic asthma. In the review by Flynn, Glynn and Kennedy (2009), the authors concluded that there was not enough current data to support the use of anticholinergics in chronic asthma. The review by Donahue (2004) found that anticholinergic agents provide more benefit to patients with COPD than patients with asthma. However, he concluded that some asthmatics, especially the
11 elderly patients with a history of smoking or with concurrent beta-blocker use might benefit from the addition of an anticholinergic. Most studies of anticholinergic use in asthma patients in the past have evaluated the effects of ipratropium on the improvement of lung function in both acute and chronic asthma. Ipratropium is a short acting anticholinergic that requires dosing every 6 hours. In 2004, tiotropium became available in the United states as a once-daily anticholinergic agent for the treatment of patients with COPD. Recently, there has been interest to continue to evaluate the use of anticholinergics in asthma patients with the availability of the longer acting tiotropium. Purpose of the Study The purpose of this paper is to perform a systematic review of the literature on the use of tiotropium bromide as an adjunct to inhaled corticosteroids for patients suffering from moderate to severe asthma using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) tool developed by the GRADE Working Group. METHODS An extensive literature search was performed using Medline, Pubmed, Web of Science, Cochrane Systematic Reviews and CINHAL. These databases were accessed through the Pacific University Library system. The keywords searched included tiotropium, asthma and adults individually and in combination. The search was limited to human subjects and the English
12 language. The initial results included 37 articles. Articles older than January 2000 and duplicates were excluded. Articles with COPD as the main topic were also excluded. Four articles were chosen for this review based on their relevance to the topic. RESULTS The first study reviewed was conducted by Peters et al. (2010) and was funded by the National Heart, Blood and Lung Institute who published their results in an article entitled Tiotropium Bromide as an Alternative to Increased Inhaled Glucocorticoid in Patients Inadequately Controlled on a Lower Dose of Inhaled Corticosteroid (TALC) Study. The study was a randomized, doubleblind, triple crossover study that compared the outcomes of the addition of tiotropium, salmeterol or increased dose of beclamethasone (Qvar) in patients that were not controlled with a lower dose of ICS. Patients were enrolled in the study if they were over the age of 18, had a history of asthma, a forced expiratory volume greater than 40%, and less than a 10 pack year history of smoking. Each participant was subjected to a common four week run-in period that included treatment with 80 µg beclamethasone meter dosed inhaler (Qvar) twice daily. Patients that at the end of the four week run-in period had less than 70% predicted FEV1 and no contraindication for tiotropium were then randomized into one of three treatment arms. One arm consisted of 160 µg beclamethasone twice daily and placebo for tiotropium and salmeterol. The second arm was treated with 80 µg beclamethsone twice daily and 18 µg tiotropium bromide once daily and placebo in place of salmeterol. The third arm was treated with 80 µg of
13 beclamethasone twice daily, salmeterol xinafoate 50 µg inhaler (Serevent) twice daily and a tiotropium placebo. Each arm was treated for 14 weeks and then washed-out for two weeks on just 80 µg beclamethasone inhaler twice daily. They were then crossed over to another treatment arm for an additional 14 weeks. This was followed by an additional two week wash-out period and another crossover in treatment arms. The primary outcome in the study was the difference in the morning peak expiratory flow (PEF) compared to baseline. Secondary outcomes included; evening PEF, albuterol rescue inhaler use, mean daily symptom score, proportion of asthma-control days, prebronchodilator FEV1, Asthma Symptom Utility Index Score, Asthma-Control Questionnaire score, Asthma Quality-Of-Life Questionnaire score and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) after four puffs of albuterol. The mean difference in change from baseline of the morning PEF for the tiotropium versus double-dose beclamethasone was 25.8L per minute, 95% confidence interval ( ), p- value < The tiotropium versus double-dose beclamethasone analysis had a mean difference change from baseline for the evening PEF of 35.3L per minute, 95% CI ( ), p-value < The tiotropium versus salmeterol analysis had a mean difference change from baseline for morning and evening PEF of 6.4L per minute, 95% CI ( ), p-value 0.26 and 10.6L per minute, 95% CI ( ), p-value 0.05, respectively. The salmeterol versus doubledose beclamethasone analysis had morning and evening PEF differences of 19.4L per minute, 95% CI ( ), p-value <0.001 and 24.7L per minute, 95% CI ( ), p-value <0.001, respectively. The authors determined that
14 tiotropium in addition to an ICS provided statistically better PEF when compared to twice the dose of ICS. They also reported that the addition of tiotropium to an ICS was not inferior to the use of salmeterol and an ICS. The next study reviewed was conducted by Park et al. (2009) and evaluated the response of severe asthmatics to the addition of tiotropium to highdose ICS and an inhaled LABA. They enrolled 160 patients diagnosed with severe persistent asthma determined by lung function testing and medication usage records. The patients also had to have 10 pack year history of smoking, a change in FEV1 of less than 5% over eight consecutive weeks prior to study enrollment, and no abnormalities detected on chest radiograph. The patients in this study were being treated with a high-dose corticosteroid (equivalent dose to µg of budesonide inhaler) and a LABA. Tiotropium bromide 18 µg inhaler was added to their treatment regimen for 12 weeks and they were evaluated with spirometry every four weeks. The patients were then categorized as responders or non-responders to tiotropium based on a finding of 15% improvement in FEV1 for at least 8 consecutive weeks. Of the 160 patients, 138 (86%) enrollees completed the study. Reasons for drop-out were five exacerbations, 11 patients noncompliant with treatment, and withdrawal of six patients from enrollment. Out of the 138 patients that completed the study, 46 (33.3%) were categorized as responders to tiotropium. Of the remaining nonresponders, 15 had improvements in FEV1 15 but did not maintain that improvement for the full 8 week period. The authors of this study concluded that
15 tiotropium provided benefit to 33% of severe asthmatic patients with decreased lung function on standard therapy. The next article reviewed was authored by Kapoor et al. (2009) and is a case report on a 43-year old man with severe asthma requiring 20mg of oral prednisone, 500µg inhaled fluticasone and 50mg salmeterol as the Advair discus formulation, montelukast 10 mg daily and salbutemol rescue inhaler used several times a week. His initial pulmonary function tests demonstrated his severe airflow restriction that was reversible with salbutemol. Tiotropium 18µg daily was added to his treatment regimen for one year. Initially, he had a PEF of 450L per minute. After 3 months on tiotropium his oral prednisone was decreased to 15mg daily and he had a PEF of 490L per minute. Between 6 months and a year the patient s oral prednisone dose was decreased to 2mg daily and he was able to maintain a PEF between L per minute. The patient also reported improvements in his quality of life and exercise capacity. The conclusion of this case report was that tiotropium may provide patients a steroid sparing benefit on high doses of oral glucocorticosteroids. The final study reviewed was conducted by Fardon, Haggart, Lee and Lipworth (2007) and was a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, crossover study evaluating the benefit of halving the dose of ICS and adding either salmeterol and placebo or salmeterol and tiotropium. Patients were included in the trial if they were over 18 years of age, with no history of an upper respiratory tract infection or use of oral corticosteroids in the past 3 months and they had an FEV1 65% and FVC of less than 80% of the predictive values v for
16 both respectively. 26 patients were enrolled in the trial. The patients stopped all first and second line asthma treatments and were treated with 1000 µg fluticasone inhaler dosed as 250 µg two puffs twice daily for a four week run-in period. The patients were then reevaluated using FEV1 and forced vital capacity (FVC) measurements as a baseline after the run-in period. They were then randomly assigned to receive a total of 500 µg fluticasone and 100 µg salmeterol (125 µg fluticasone and 25 µg salmeterol 2 puffs twice daily) daily plus placebo tiotropium or the 500/100 dosing plus 18 µg tiotropium bromide inhaler. Each study arm was treated for 4 weeks with cross-over after 4 weeks of treatment. The improvements from baseline (1000µg fluticasone) as measured by morning PEF were 41.6L per minute, 95% CI ( ), p-value < 0.01 and 55.3l per minute, 95% CI ( ), p-value < 0.01 for the fluticasone, salmeterol, placebo (F,S,P) group and the fluticasone, salmeterol and tiotropium (F,S,T) group respectively. The change from baseline for the evening PEF was 37L per minute, 95% CI (12-63), p-value < 0.01 for the F,S,P group and 44L per minute, 95% CI (26-62), p-value <0.01 for the F,S,T group. The authors concluded that the addition of salmeterol and tiotropium to half the dose of fluticasone provided patients with a small amount of improvement in lung function compared with twice the dose of fluticasone. DISCUSSION All four articles included in this review reported significant improvements in pulmonary function with the use of tiotropium in those with moderate to severe asthma. The articles by Peters et al. (2010) and Fardon et al, (2006)
17 demonstrated the improvement in both PEF and FEV1. The study conducted by Park et al. (2010) only reported the improvement in FEV1. The case report by Kapoor et al. (2009) evaluated the improvements in lung function by PEF. The improvements noted in PEF and FEV1 by Fardon et al. (2006) were small but still statistically significant. A limitation of their study is the small study population of 26 patients with only 18 (69%) completing the study. An additional limitation to this crossover study was that there was no apparent wash out period between study arms. The measurements of PEF and FEV1 were conducted during the study visits before and after the crossover with no wash-out period to return to the baseline line comparator of double-dose fluticasone. Each segment of the trial was only four weeks in length. This may have had an effect on the results of the crossover. The patients in the first half of the study were stepped down to half the dose of fluticasone. At the time of the crossover, the patients had already been on half the dose of fluticasone for four weeks. Additionally, in the article by Park et al. (2010), they determined in a preliminary study that a treatment of eight weeks was necessary to note improvements in the FEV1 with tiotropium. The short treatment length of each arm could lead to an underestimation of the true effect of tiotropium on lung function. The study by Peters et al. (2010) demonstrated a significant improvement in both morning PEF and FEV1 in patients that were given tiotropium in addition to an ICS. This was compared to doubling the dose of the ICS. They also found that the addition of tioptropium to an ICS was not inferior to the use of an ICS and salmeterol. This study provided a longer treatment arm of 14 weeks and a
18 four-week washout period between crossovers. The potential limitations of this study include the moderate sized population of 210 patients and the reported compliance with treatment. As part of the study oversight, treatment compliance was monitored. Compliance percentages were reported as 84.1%±16.2%, 92.6%±12.3%, and 93.0%±12.2% (p.1719) for beclamethasone, salmeterol and tiotropium, respectively. The difference in treatment compliance between beclamethasone and salmeterol or tiotropium may have an effect on the pulmonary function measurements in this study. The article by Park, et al. (2009) demonstrates the response that severe asthmatic patients have with the addition of tiotropium. Responders to tiotropium did have significant improvements in their FEV1 showing an improvement in one measure of their lung function. However, there are several limitations to this article. The primary weakness of this study is that it was an observational study with no comparator group. Nor did the authors mention the time of day that the pulmonary function testing was completed. This is significant since patients with asthma may have considerable differences in their FEV1 depending on the time of day. It is not disclosed in the paper whether the patients were given the doses of tiotropium in the morning or the evening. Without this information it is difficult to evaluate the true effect of tiotropium on lung function. Timing of medication dosing can add several confounders to the analysis. Patients can have a lower pre-dose trough FEV1 than a post-dose FEV1. The time of day is also important in asthmatic patients with significant atopy. The authors noted that the responders to tiotropium had higher rates of atopy determined by skin prick. This
19 can effect the lung function results based on exposure to potential allergens. An additional limitation to the results is that only 86% of the patients completed the study. Patients were dropped from the study due to exacerbations of their asthma, noncompliance or because they withdrew from enrollment. This can provide a significant variation in the data in a study with 138 patients at the beginning of enrollment. According to the guidelines, oral corticosteroids should be considered in patients who are still unable to control their asthma symptoms despite the use of a high dose ICS and LABA. The case report by Kapoor et al. (2010) demonstrates the benefit to lung function that tiotropium conferred on a patient still symptomatic despite using a high dose ICS, LABA, leukotriene modifier and oral corticosteroids. Over a one-year period the patient had significant improvements in his PEF while slowly reducing his oral steroid dose from 20mg prednisone to 2mg daily. This article has many limitations however. First, it is a case report which means that the information is anecdotal instead of statistically relevant. This patient also had a 15 pack-year smoking history. This is a significant confounder because the worsening of symptoms since his first diagnosis at age 26 could be partially due to a COPD component of his airway disease. The authors did note that the patient maintained some fixed airflow obstruction after bronchodilator use when measuring his initial FEV1. The evidence supporting the improvements in pulmonary function with tiotropium as an adjunct therapy to inhaled corticosteroids for adult patients with asthma we be evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment,
20 Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach. (Guyatt et al. 2008). The GRADE approach was developed to evaluate the quality of clinical evidence in regards to patient management. Levels of evidence include very low, low, moderate, and high. The GRADE working group defines these levels of evidence as: High Quality Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect Moderate quality Further research is likely to have an important impact on the confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate Low quality Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimates Very low quality Any estimate of effect is very uncertain (Guyatt et al. 2008, p. 926) The outcomes evaluated in this review are the improvement in lung function, improvement in PEF and improvement in FEV1. The evidence for these outcomes is listed in the GRADE table in the appendix. The two randomized clinical trials provided a moderate level of evidence to support the use of tiotropium to improve pulmonary function, PEF and FEV1. Their GRADE begins as a high level of evidence because they are RCTs. Both studies did provide consistent evidence that tiotropium did improve pulmonary function, PEF and FEV1. The overall evidence that they provide is decreased however because they are indirect comparisons of tiotropium. Peters et al.
21 (2010) and Fardon et al. (2006) had different treatment arms in their clinical trials and cannot be directly compared. Overall, the two RCTs provided a moderate level of evidence. The case report article by Kapoor et al. (2010) demonstrated the improvements in pulmonary function and PEF. This level of evidence begins as low quality due to it being a case report of a single patient. It gains strength to a moderate level because of the significant dose response seen with the addition tiotropium as measured by the PEF and the decrease in use of oral glucosteroids OGS. The authors were primarily reporting on the decrease in OGS versus the use of tiotropium with an ICS. This causes this article to have the greatest indirectness with the other articles in terms of the authors outcomes but the improvements in PEF were directly related to the outcomes in this review. The study by Park et al. (2009) also showed in improvements in pulmonary function and FEV1 with the use of tiotropium. Because it is an observational study the initial level of evidence is low. The dose-response noted in this study increases its strength. However, the obvious confounders mentioned above decrease the strength of the evidence. This study provided a low quality of evidence for the outcomes evaluated in this review. The four articles reviewed here provide an overall moderate level of evidence of the improvement of pulmonary function, PEF and FEV1 seen with the use of tiotropium along with an ICS in the treatment of adults with asthma. Based on the GRADE assessment of the evidence, tiotropium appears to provide benefit to adult patients with asthma. Further large-scale RCTs need to
22 be conducted in order to recommend tiotropium be added to the asthma treatment guidelines. Longer studies could adequately evaluate other outcomes such as decreases in exacerbations, decreases in rescue inhaler use, and improvements in quality of life. Longer studies can also evaluate potential risks of long term use of tiotropium in asthma patients. In conclusion, the available data to date demonstrates that tiotropium in conjunction with an ICS provides statistically improved lung function in patients with moderate to severe asthma. Tiotropium should be considered as a treatment option when patients are not well controlled on the currently recommended treatment regimens.
23 REFERENCES Akinbami, L., Moorman, J., Liu, X. (2011). Asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality: United Sates, National Health Statistics Reports, Donohue, J. (2004). Therapeutic responses in asthma and COPD: Bronchodilators. Chest, 126 (2), 125s-137s. Fardon, T., Haggart, K., Lee, D. & Lipworth, B. (2007). A proof of concept study to evaluate stepping down the dose of fluticasone in the combination with salmeterol and tiotropium in severe persistent asthma. Respiratory Medicine, 101, Flynn, R., Glynn, D., Kennedy, M. (2009). Anticholinergic treatment in airways diseases. Adv Ther 26 (10), Global Initiative for Asthma (2009). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. Retrieved from Guyatt, G.H., Oxman, A.D., Vist, G., Kunz, R., Falck-Ytter, Y., Alonso-Coello, P., Schunemann, H.J. (2008). Rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. British Medical Journal, 336, Kapoor, AS., Olsen, SR., O Hara, C., Puttagunta, L.& Vethanayagam, D. (2009). The efficacy of tiotropium as a steroid-sparing agent in severe asthma. Canadian Respiratory Journal, 16 (3), National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. (2007) Expert panel report 3 (EPR3): Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma. Retrieved from Park, H-W., Yang, M-S., Park, Kim, T-B., Moon, K-U., Min, K-U., Kim, Y-Y., & Cho, S-H. (2009). Additive role of tiotropium in severe asthmatics and Arg16Gly in ADRB2 as a potential marker to predict response. Allergy, 64, Peters, SP., Kunselman, SJ., Icitovic, N., Moore, W., Pascual, R., Ameredes, B.,... Bleecker, E. (2010). Tiotropium bromide step-up therapy for adults with uncontrolled asthma. New England Journal of Medicine, 363,
24 Rodrigo, G., Rodrigo, C. (2002). The role of anticholinergics in acute asthma treatments: An evidence based evaluation. Chest, 121, Tashkin, D., Bartolome, C., Kesten, S., Lystig, T., Decramer, M. (2010). Effect of tiotropium in men and women with COPD: Results of the 4-year UPLIFT trial. Respiratory Medicine, 104, U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2010). FDA drug safety Communication: Drug labels now contain updated recommendations for the appropriate use of long-acting inhaled asthma medications called long-acting betaagonists (LABAs). Retrieved from PatientsandProviders/ucm htm Westby, M., Benson, M., Gibson, P. (2004). Anticholinergics agents for chronic asthma in adults (review). The Cochrane Collaboration, 3.
25 APPENDIX A Table 1: GRADE Table Outcome Quantity and type of evidence Findings Starting grade Decrease GRADE Study Quality Consistency Directness Precision Publication Bias Increase GRADE Large Magnitude Dose-Response Confounders Grade of Evidence by article type Tiotropium vs increased doses of Inhaled Corticosteroids in asthma Pulmonary Function (based on all measurement types) Peak Expiratory Flow 2 RCT Improved High Mod pulmonary function 1 Case Report 1 Obs Low Mod 2 RCT Increased High Mod PEF 1 Case Report Low Mod FEV1 2 RCT Increased FEV1 High Mod
26 1 Obs Low Mod
Postoperative Analgesic Effects of Favorite Music After Cesarean Delivery Under General Anesthesia
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 5-15-2011 Postoperative Analgesic Effects of Favorite Music After Cesarean Delivery
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 5-15-2011 Postoperative Analgesic Effects of Favorite Music After Cesarean Delivery
Allergies to Staple Foods and the Financial Burden on Households
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-13-2016 Allergies to Staple Foods and the Financial Burden on Households Ashley
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-13-2016 Allergies to Staple Foods and the Financial Burden on Households Ashley
The Effect of the Clinical Digital Rectal Exam on the Complexed Prostate-Specific Antigen Versus the Total Prostate-Specific Antigen
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 2-15-2011 The Effect of the Clinical Digital Rectal Exam on the Complexed Prostate-Specific
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 2-15-2011 The Effect of the Clinical Digital Rectal Exam on the Complexed Prostate-Specific
DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES:
 TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
Is reslizumab effective in improving quality of life and asthma control in adolescent and adult patients with poorly controlled eosinophilic asthma?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Long Term Care Formulary RS -29
 RESTRICTED USE Asthma/COPD Management 1 of 6 PROTOCOL: Asthma Glossary of Medication Acronyms: SABA: short-acting beta agonist (e.g. salbutamol) SABD: short-acting bronchodilator (e.g. ipratropium or SABA)
RESTRICTED USE Asthma/COPD Management 1 of 6 PROTOCOL: Asthma Glossary of Medication Acronyms: SABA: short-acting beta agonist (e.g. salbutamol) SABD: short-acting bronchodilator (e.g. ipratropium or SABA)
Treatment Responses. Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
 Asthma and COPD: Are They a Spectrum Treatment Responses Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Pharmacological Treatments Bronchodilators Inhaled short-acting β -Agonist (rescue) Inhaled short-acting
Asthma and COPD: Are They a Spectrum Treatment Responses Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Pharmacological Treatments Bronchodilators Inhaled short-acting β -Agonist (rescue) Inhaled short-acting
Decramer 2014 a &b [21]
![Decramer 2014 a &b [21] Decramer 2014 a &b [21]](/thumbs/90/101390504.jpg) Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
This is the publisher s version. This version is defined in the NISO recommended practice RP
 Journal Article Version This is the publisher s version. This version is defined in the NISO recommended practice RP-8-2008 http://www.niso.org/publications/rp/ Suggested Reference Chong, J., Karner, C.,
Journal Article Version This is the publisher s version. This version is defined in the NISO recommended practice RP-8-2008 http://www.niso.org/publications/rp/ Suggested Reference Chong, J., Karner, C.,
Efficacy of inhaled Technosphere insulin: a comparative review to injectable insulin
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-9-2014 Efficacy of inhaled Technosphere insulin: a comparative review to injectable
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-9-2014 Efficacy of inhaled Technosphere insulin: a comparative review to injectable
II: Moderate Worsening airflow limitations Dyspnea on exertion, cough, and sputum production; patient usually seeks medical
 Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
The Effect of Nitric Oxide on Pain From Acute Vascular Occlusion Crisis in Sickle Cell Disease: A Systematic Review
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 4-2011 The Effect of Nitric Oxide on Pain From Acute Vascular Occlusion Crisis
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 4-2011 The Effect of Nitric Oxide on Pain From Acute Vascular Occlusion Crisis
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing Fracture Occurrence in Children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A.
 aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Association Between Sedentary Lifestyle, Television-Watching and Asthma
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies College of Health Professions Summer 8-11-2018 Association Between Sedentary Lifestyle, Television-Watching and Asthma Nathan Bliss
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies College of Health Professions Summer 8-11-2018 Association Between Sedentary Lifestyle, Television-Watching and Asthma Nathan Bliss
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo,
 Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo, BRONCHODILATORS: Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists Actions Adrenoreceptor agonists have many of the same actions as epinephrine/adrenaline,
Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo, BRONCHODILATORS: Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists Actions Adrenoreceptor agonists have many of the same actions as epinephrine/adrenaline,
The Rheos System, a Baroreflex Activation Device for use in a Resistant Hypertension Population: a Systematic Review
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-11-2012 The Rheos System, a Baroreflex Activation Device for use in a Resistant
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-11-2012 The Rheos System, a Baroreflex Activation Device for use in a Resistant
Pharmacological Management of Obstructive Airways in Humans. Introduction to Scientific Research. Submitted: 12/4/08
 Pharmacological Management of Obstructive Airways in Humans Introduction to Scientific Research Submitted: 12/4/08 Introduction: Obstructive airways can be characterized as inflammation or structural changes
Pharmacological Management of Obstructive Airways in Humans Introduction to Scientific Research Submitted: 12/4/08 Introduction: Obstructive airways can be characterized as inflammation or structural changes
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Consumption of Wine for Prevention of Colorectal Cancer
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 3-2011 Consumption of Wine for Prevention of Colorectal Cancer Sean Naylor Follow
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Spring 3-2011 Consumption of Wine for Prevention of Colorectal Cancer Sean Naylor Follow
TORCH: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate and Survival in COPD
 TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
Efficacy of Opioid Antagonist in the Treatment of Pathological Gambling
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Fall 8-9-2014 Efficacy of Opioid Antagonist in the Treatment of Pathological Gambling
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Fall 8-9-2014 Efficacy of Opioid Antagonist in the Treatment of Pathological Gambling
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): Α A REVIEW
 Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
#1 cause of school absenteeism in children 13 million missed days annually
 Asthma Update 2013 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures None 2 Objectives Review burden
Asthma Update 2013 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures None 2 Objectives Review burden
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized
 DANIEL E. HILLEMAN, PharmD ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To review the role of long-acting bronchodilators in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including the importance of treatment
DANIEL E. HILLEMAN, PharmD ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To review the role of long-acting bronchodilators in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including the importance of treatment
Late Gadolinium Enhancement by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Major Adverse Coronary Events
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies College of Health Professions Summer 8-12-2017 Late Gadolinium Enhancement by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Major Adverse
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies College of Health Professions Summer 8-12-2017 Late Gadolinium Enhancement by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Major Adverse
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION (FLUTICASONE FUROATE/VILANTEROL) (Breo Ellipta GlaxoSmithKline) Indication: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION (FLUTICASONE FUROATE/VILANTEROL) (Breo Ellipta GlaxoSmithKline) Indication: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
glycopyrronium 44 micrograms hard capsules of inhalation powder (Seebri Breezhaler ) SMC No. (829/12) Novartis Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
 glycopyrronium 44 micrograms hard capsules of inhalation powder (Seebri Breezhaler ) SMC No. (829/12) Novartis Pharmaceuticals Ltd. 07 December 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
glycopyrronium 44 micrograms hard capsules of inhalation powder (Seebri Breezhaler ) SMC No. (829/12) Novartis Pharmaceuticals Ltd. 07 December 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed
Type of intervention Treatment. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Cost-effectiveness of salmeterol/fluticasone propionate combination product 50/250 micro g twice daily and budesonide 800 micro g twice daily in the treatment of adults and adolescents with asthma Lundback
Cost-effectiveness of salmeterol/fluticasone propionate combination product 50/250 micro g twice daily and budesonide 800 micro g twice daily in the treatment of adults and adolescents with asthma Lundback
roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd
 roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd 06 August 2010 (Issued 10 September 2010) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd 06 August 2010 (Issued 10 September 2010) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Asthma: Chronic Management. Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015
 Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Nonfasting LDL-C as a Predictor of Cardiovascular Event Risk
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-13-2016 Nonfasting LDL-C as a Predictor of Cardiovascular Event Risk Richard
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-13-2016 Nonfasting LDL-C as a Predictor of Cardiovascular Event Risk Richard
umeclidinium, 55 micrograms, powder for inhalation (Incruse ) SMC No. (1004/14) GlaxoSmithKline
 umeclidinium, 55 micrograms, powder for inhalation (Incruse ) SMC No. (1004/14) GlaxoSmithKline 07 November 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
umeclidinium, 55 micrograms, powder for inhalation (Incruse ) SMC No. (1004/14) GlaxoSmithKline 07 November 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
 Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Asthma Management in Pregnancy HEATHER HOWE, MD UNIVERSITY OF UTAH PULMONARY DIVISION
 Asthma Management in Pregnancy HEATHER HOWE, MD UNIVERSITY OF UTAH PULMONARY DIVISION Asthma Management in Pregnancy Effects of asthma on pregnancy outcomes Effects of pregnancy on asthma control Management
Asthma Management in Pregnancy HEATHER HOWE, MD UNIVERSITY OF UTAH PULMONARY DIVISION Asthma Management in Pregnancy Effects of asthma on pregnancy outcomes Effects of pregnancy on asthma control Management
Asthma Upate 2018: What s New Since the 2007 Asthma Guidelines of NAEPP?
 10:50-11:50am Asthma Update 2018: What s New Since the 2007 National Asthma Guidelines? SPEAKER Christopher H. Fanta, MD Disclosures The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher
10:50-11:50am Asthma Update 2018: What s New Since the 2007 National Asthma Guidelines? SPEAKER Christopher H. Fanta, MD Disclosures The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher
Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction as an Adjunct Treatment to Diabetes
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction as an Adjunct Treatment to Diabetes
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction as an Adjunct Treatment to Diabetes
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
The use of Levetiracetam and Phenytoin for Seizure Prophylaxis in the Setting of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-11-2012 The use of Levetiracetam and Phenytoin for Seizure Prophylaxis in the
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-11-2012 The use of Levetiracetam and Phenytoin for Seizure Prophylaxis in the
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Temple, TX October
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Temple, TX October
Aclidinium bromide/ formoterol Benefit assessment according to 35a Social Code Book V 1
 IQWiG Reports Commission No. A15-06 Aclidinium bromide/ formoterol Benefit assessment according to 35a Social Code Book V 1 Extract 1 Translation of Sections 2.1 to 2.6 of the dossier assessment Aclidiniumbromid/Formoterol
IQWiG Reports Commission No. A15-06 Aclidinium bromide/ formoterol Benefit assessment according to 35a Social Code Book V 1 Extract 1 Translation of Sections 2.1 to 2.6 of the dossier assessment Aclidiniumbromid/Formoterol
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Co-Primary Outcomes/Efficacy Variables:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies
 Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
Case-Compare Impact Report
 Case-Compare Impact Report October 8, 20 For CME Activity: Developed through an independent educational grant from Genentech: Moderate to Severe Persistent Asthma: A Case-Based Panel Discussion (March
Case-Compare Impact Report October 8, 20 For CME Activity: Developed through an independent educational grant from Genentech: Moderate to Severe Persistent Asthma: A Case-Based Panel Discussion (March
MEDICAL ASSISTANCE BULLETIN
 ISSUE DATE January 6, 2016 SUBJECT EFFECTIVE DATE January 20, 2016 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE BULLETIN NUMBER *See below BY Prior Authorization of COPD Agents Pharmacy Service Leesa M. Allen, Deputy Secretary
ISSUE DATE January 6, 2016 SUBJECT EFFECTIVE DATE January 20, 2016 MEDICAL ASSISTANCE BULLETIN NUMBER *See below BY Prior Authorization of COPD Agents Pharmacy Service Leesa M. Allen, Deputy Secretary
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Change in Illness Perception to Improve Quality of Life for Chronic Pain Patients
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 Change in Illness Perception to Improve Quality of Life for Chronic
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 Change in Illness Perception to Improve Quality of Life for Chronic
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Calverley P M A, Anzueto A R, Carter K, et
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Calverley P M A, Anzueto A R, Carter K, et
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN. Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department
 TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
Bronchial Thermoplasty
 Bronchial Thermoplasty Policy Number: 7.01.127 Last Review: 9/2014 Origination: 11/2010 Next Review: 3/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for bronchial
Bronchial Thermoplasty Policy Number: 7.01.127 Last Review: 9/2014 Origination: 11/2010 Next Review: 3/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for bronchial
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management. Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018
 Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest 2 Objectives Summarize
Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest 2 Objectives Summarize
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness. treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years
 The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma
 Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Meeting the Challenges of Asthma
 Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
COPD: A Renewed Focus. Disclosures
 COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984]
![Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984]](/thumbs/85/91889043.jpg) Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background & Clinical Effectiveness John McMurray 11 th January 2016 For
Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background & Clinical Effectiveness John McMurray 11 th January 2016 For
Inhaled corticosteroids versus long-acting beta 2 -agonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Review)
 Inhaled corticosteroids versus long-acting beta 2 -agonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Review) Spencer S, Evans DJ, Karner C, Cates CJ This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and
Inhaled corticosteroids versus long-acting beta 2 -agonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Review) Spencer S, Evans DJ, Karner C, Cates CJ This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and
SUMMARY THIS IS A PRINTED COPY OF AN ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT. PLEASE CHECK ITS VALIDITY BEFORE USE.
 i SUMMARY ZENECA PHARMACEUTICALS FINISHED PRODUCT: ACTIVE INGREDIENT: ACCOLATE zafirlukast (ZD9188) Trial title (number): A Dose-ranging, Safety and Efficacy Trial with Zafirlukast (ACCOLATE ) in the Treatment
i SUMMARY ZENECA PHARMACEUTICALS FINISHED PRODUCT: ACTIVE INGREDIENT: ACCOLATE zafirlukast (ZD9188) Trial title (number): A Dose-ranging, Safety and Efficacy Trial with Zafirlukast (ACCOLATE ) in the Treatment
Clinical Policy: Roflumilast (Daliresp) Reference Number: CP.PMN.46 Effective Date: Last Review Date: 08.18
 Clinical Policy: (Daliresp) Reference Number: CP.PMN.46 Effective Date: 11.01.11 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: (Daliresp) Reference Number: CP.PMN.46 Effective Date: 11.01.11 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Data Behind Mandatory Flu Vaccinations for Health Care Workers in Tertiary Care Hospitals is Inconclusive
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-10-2013 Data Behind Mandatory Flu Vaccinations for Health Care Workers in Tertiary
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-10-2013 Data Behind Mandatory Flu Vaccinations for Health Care Workers in Tertiary
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma
 Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
SYNOPSIS THIS IS A PRINTED COPY OF AN ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT. PLEASE CHECK ITS VALIDITY BEFORE USE.
 Drug product: Drug substance(s): Document No.: Edition No.: 1 Study code: Accolate Zafirlukast (ZD9188) 9188IL/0138 Date: 02 May 2007 SYNOPSIS A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, -controlled, Parallel
Drug product: Drug substance(s): Document No.: Edition No.: 1 Study code: Accolate Zafirlukast (ZD9188) 9188IL/0138 Date: 02 May 2007 SYNOPSIS A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, -controlled, Parallel
รศ. นพ. ว ชรา บ ญสว สด M.D., Ph.D. ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น
 รศ. นพ. ว ชรา บ ญสว สด M.D., Ph.D. ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น COPD Guideline Changing concept in COPD management Evidences that we can offer COPD patients better life COPD Guidelines
รศ. นพ. ว ชรา บ ญสว สด M.D., Ph.D. ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น COPD Guideline Changing concept in COPD management Evidences that we can offer COPD patients better life COPD Guidelines
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
The Effectiveness of Dexamethasone as Adjunctive Therapy to Racemic Epinephrine for a Pediatric Patient With Bronchiolitis
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 The Effectiveness of Dexamethasone as Adjunctive Therapy to Racemic Epinephrine
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 The Effectiveness of Dexamethasone as Adjunctive Therapy to Racemic Epinephrine
Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice. Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital
 Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital Therapy at each stage of COPD I: Mild II: Moderate III: Severe IV: Very severe
Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital Therapy at each stage of COPD I: Mild II: Moderate III: Severe IV: Very severe
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD
 Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1014 1020 Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD J.F. Donohue a, *, S. Menjoge b, S. Kesten b a University of North Carolina School of Medicine, 130
Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1014 1020 Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD J.F. Donohue a, *, S. Menjoge b, S. Kesten b a University of North Carolina School of Medicine, 130
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline. MedStar Health
 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk. NICE All rights reserved.
 Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Provider Respiratory Inservice
 Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007
 Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Version Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Version Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
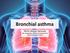 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Loading Dose of Rosuvastatin Before PCI and its Beneficial Post-Procedural Effects: A Systematic Review
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-9-2014 Loading Dose of Rosuvastatin Before PCI and its Beneficial Post-Procedural
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-9-2014 Loading Dose of Rosuvastatin Before PCI and its Beneficial Post-Procedural
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek
 Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
PDE-5 Inhibitors and the Increase Risk of Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy in Males with Erectile Dysfunction
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies College of Health Professions Summer 8-12-2017 PDE-5 Inhibitors and the Increase Risk of Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies College of Health Professions Summer 8-12-2017 PDE-5 Inhibitors and the Increase Risk of Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management?
 Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
The use of Seprafilm Adhesion Barrier in Adult Patients Undergoing Laparotomy to Reduce the Incidence of Post-Operative Small Bowel Obstruction
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-11-2012 The use of Seprafilm Adhesion Barrier in Adult Patients Undergoing Laparotomy
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-11-2012 The use of Seprafilm Adhesion Barrier in Adult Patients Undergoing Laparotomy
CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS
 CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS Controlling Asthma Severity: Identifying Unmet Needs and Optimizing Therapeutic Options There are no fees for participating in and receiving continuing medical education
CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS Controlling Asthma Severity: Identifying Unmet Needs and Optimizing Therapeutic Options There are no fees for participating in and receiving continuing medical education
Bronchial Thermoplasty
 Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 178 Bronchial Thermoplasty Next Review: September 2018 Last Review: October 2017 Effective: November 1, 2017 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies are developed
Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 178 Bronchial Thermoplasty Next Review: September 2018 Last Review: October 2017 Effective: November 1, 2017 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies are developed
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C
 MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
