Impact of humidification and gas warming systems on ventilatorassociated
|
|
|
- Hugh Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Online Data Supplement Impact of humidification and gas warming systems on ventilatorassociated pneumonia. Jean-Claude Lacherade, M.D. 1, Marc Auburtin, M.D. 2, Charles Cerf, M.D. 3, Andry Van de Louw, M.D. 3, Lilia Soufir, M.D. 1, Yves Rebuffat, M.D. 4, Saïda Rezaiguia, M.D. 3, Jean-Damien Ricard, M.D. 2, François Lellouche, M.D. 1, Christian Brun- Buisson, M.D. 1, Laurent Brochard, M.D. 1 1 Medical ICU, Créteil (France); 3 Surgical ICU, 4 Neuro-surgical ICU, Henri Mondor Hospital, Words: (text only)
2 MATERIALS and METHODS Study Design The study was conducted in five intensive care units (ICUs) located in two French university-affiliated teaching hospitals (Hôpital Henri Mondor, Creteil and Hôpital Bichat-Claude Bernard, Paris). Three of these were surgical ICUs and two were medical ICUs. During the study period, all patients hospitalized in these ICUs, aged more than 18 years and expected to require mechanical ventilation (via a nasotracheal, orotracheal, or tracheostomy tube) for more than 48 hours were eligible to be randomly assigned to receive airway humidification via either a heat and moisture exchanger (HMEF) or a heated water humidifier (HH). Patients already ventilated for more than 24 hours, patients having contraindications to the use of a HMEF (hemoptysis, severe hypothermia), or of a HH (active tuberculosis), patients admitted after cardiac arrest, patients already enrolled in another clinical trial and patients with early decision to limit active therapy, were not included. A randomization list in blocks of six, stratified by participating ICU, was generated from a computer, and treatment allocation was concealed using sequentially numbered opaque sealed envelopes. The HMEF was the hygroscopic DAR-Hygrobac (DAR SpA, Mirandola, Italy) device. The HH was the Fisher-Paykel MR 730 device (Fisher and Paykel Ltd, Auckland, New Zealand), including warming of the inspiratory and expiratory circuits; the reservoir was filled with sterile irrigation water. 1
3 Heat moisture exchanger devices (placed between the y-connector of the ventilator tubing and the tracheal tube) were routinely changed at 48 hours interval. The ventilator circuits were not changed in any group of randomization during the duration of ventilation for a given patient, as recommended (E1, E2). For all patients requiring a transport out of the ICU, a HMEF system was placed on the ventilator circuit for the time of transportation, irrespective of the randomization group. The protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the French Society of Intensive Care Medicine (SRLF). Because both systems were already routinely used without clear guidelines in these ICUs, consent was waived. Information about the study was provided to patients or family. Diagnosis of Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) Included patients were screened daily for the occurrence of VAP. Episodes of pneumonia diagnosed within 48 hours of ventilation were not considered as ventilatorassociated. Screening for VAP was maintained until the first episode of VAP, or 48 h after weaning from the ventilator, death, or the 28 th day of mechanical ventilation, whichever occurred first. In the event of unsuccessful weaning (ventilatory support needed again less than 48 h after extubation), patients were kept in the study as described above. A clinical suspicion of VAP was based on the presence of a recent and persistent infiltrate on chest X-ray and two of the following criteria: fever (>38.3 C) or hypothermia (<36.5 C), leucocytosis (> /l) or leucopenia (< /l), and purulent tracheal secretions. Confirmation of pneumonia required a positive quantitative culture of either a protected telescoping catheter (PTC) or of broncho- 2
4 alveolar lavage. Protected telescoping catheters samplings were obtained blindly via the endotracheal tube, or via bronchoscopy as previously described (E3); bronchoalveolar lavage were obtained via bronchoscopy using a standard lavage with successive instillation of three aliquots of 50 ml warmed isotonic saline and reaspiration (E4); the second sample was used for culture. Samples were obtained before any change or introduction of new antibiotics. The diagnosis of VAP was confirmed when the quantitative culture of a protected distal sample or of a bronchoalveolar lavage respectively grew >10 3 colony-forming units (CFU/ml) or >10 4 CFU/ml of at least one microorganism. Microbiologists were unaware of the randomization arm during the trial. VAP occurring between the 3 rd and 7 th day of mechanical ventilation was considered as early-onset pneumonia, and those occurring later as late-onset pneumonia. The incidence density of VAP in each group (per 1000 mechanical ventilation-days) was calculated as the ratio between the number of VAP and the sum of days exposed to mechanical ventilation (i.e., the whole duration of ventilation for patients without VAP or the duration of ventilation until the first episode of VAP). Microorganisms causing VAP were recorded. Data collection and definitions The following parameters were recorded prospectively for each patient: age, sex, organ failure at admission, diagnostic category (medical, planned post-operative admission, emergency post-operative admission), Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II) (E5) at the 24 th hour after admission, major comorbidities (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hemopathy, other malignancy, immunosuppressive 3
5 treatment, HIV infection), parameters at initiation of the mechanical ventilation (PaO2/FiO2 ratio and Logistic Organ Dysfunction score) (E6). During the course of ventilation, the following was recorded : maximal inspired oxygen fraction (for at least 6 consecutive hours), need for positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), highest level of PEEP required, duration of mechanical ventilation prior to pneumonia, total duration of mechanical ventilation (until death or weaning), need for tracheostomy, duration of ICU stay and outcome at ICU discharge. Other potential risk factors for VAP were recorded daily during the follow-up: intravenous sedation, paralytic agents, stress ulcer prophylaxis, enteral feeding, ability to maintain semirecumbent position of the trunk above 30 degrees, position of endotracheal tube (nasal or oral), position of gastric tube (nasal or oral), need for reintubation, transport out of ICU, antibiotic therapy, use of corticosteroids. The safety of the humidification systems was assessed by recording episodes of endotracheal tube occlusion. Outcome measures The primary end-point was the comparison of the VAP rate between the two groups of randomization (HME and HH). Secondary outcome variables included the duration of mechanical ventilation before the occurrence of VAP, the ICU mortality rate, the duration of mechanical ventilation, the duration of ICU stay, and the tracheostomy rate. 4
6 Statistical Analysis For the main end-point, we estimated the sample size necessary to provide a 80% chance to detect a relative reduction of 40% in the VAP rate between the two study groups, based on a previous report by Kirton et al. (E7). A 25 % incidence of VAP was expected to occur in the HH group. Based on these assumptions, 250 patients were needed in each group. An interim analysis was performed after 250 patients to examine the overall rate of VAP; because this rate was higher than expected, the sample size was recalculated to include 185 patients per group. Comparisons between groups were done using Student s t-test for continuous variables and the chi-square statistic for categorical variables. A multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed including VAP as the dependent variable, and group of randomization and other pertinent variables which differed between the groups (with p value below 0.20 in the univariate analysis) as potentially independent variables. The time to occurrence of VAP was also analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method and tested with a log-rank test. RESULTS Flow diagram of the study: A flow diagram of the study protocol is presented in Figure E1.During the study period, 1147 patients received mechanical ventilation in the five participating ICUs patients were expected to require mechanical ventilation less than 48 hours. Among the 589 remaining patients, 219 patients were not included: 99 patients 5
7 already under mechanical ventilation for more than 24 hours, 20 patients admitted after cardiac arrest (asystole or pulseless electrical activity), 2 patients already enrolled in another clinical trial, early decision to limited active therapy done for 6 patients, 1 patient with bacillary tuberculosis and 91 patients because of an unavailability of HH systems or of investigators. Finally, 370 patients could be included, 186 in the HMEF arm and 184 in the HH arm. One patient in the HMEF group was secondary excluded because of early decision to limit active therapy including the lack of specific diagnostic procedure for pneumonia. The mean number of included patients per center participating to the trial was Number and type of samples obtained. A clinical suspicion of pneumonia occurred in 74 (40%) and 77 (42%) patients in the HMEF and HH group, respectively, and a similar number of samples (106 and 112) were obtained in each group. There was no difference in the type of sample (bronchoscopic or non-bronchoscopic) obtained in each group (Table E1), although a slight majority of samples were obtained non-bronchoscopically in both groups. Among bronchoscopic samples, there was a trend to more BAL being used in the HH group compared to the HEMF group (30 vs. 18, P=0.1) and to more BAL being positive in the former (15/30 vs. 5/18, P=0.25). The proportion of non-bronchoscopic samples positive for pneumonia (58/125; 46%) was however similar to that of bronchoscopic samples (42/93; 45%). Reintubation Reintubation occurred mostly in patients with unsuccessful weaning (ventilatory support needed again within 48 hours after extubation). These patients were kept in the study until the first episode of VAP, or 48 h after weaning from the ventilator, 6
8 death, or the 28 th day of mechanical ventilation, whichever occurred first. Twenty-one of the 58 patients (36.2%) reintubated during the follow-up developed VAP, as compared 25.4% VAP rate in patients not reintubated. REFERENCES E1. Kollef, M. H The prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia. N Engl J Med 340(8): E2. Cook, D., J. D. Ricard, B. Reeve, J. Randall, M. Wigg, L. Brochard, and D. Dreyfuss Ventilator circuit and secretion management strategies: a Franco- Canadian survey [In Process Citation]. Crit Care Med 28(10): E3. Pham, L. H., C. Brun-Buisson, P. Legrand, A. Rauss, F. Verra, L. Brochard, and F. Lemaire Diagnosis of nosocomial pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. Comparison of a plugged telescoping catheter with the protected specimen brush. Am Rev Respir Dis 143(5 Pt 1): E4. Fartoukh, M., B. Maitre, S. Honore, C. Cerf, J. R. Zahar, and C. Brun-Buisson Diagnosing pneumonia during mechanical ventilation: the clinical pulmonary infection score revisited. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168(2): E5. Le Gall, J. R., S. Lemeshow, and F. Saulnier A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. Jama 270(24): E6. Le Gall, J. R., J. Klar, S. Lemeshow, F. Saulnier, C. Alberti, A. Artigas, and D. Teres The Logistic Organ Dysfunction system. A new way to assess organ dysfunction in the intensive care unit. ICU Scoring Group. Jama 276(10): E7. Kirton, O. C., B. DeHaven, J. Morgan, O. Morejon, and J. Civetta A prospective, randomized comparison of an in-line heat moisture exchange filter and heated wire humidifiers: rates of ventilator- associated early-onset (communityacquired) or late-onset (hospital- acquired) pneumonia and incidence of endotracheal tube occlusion. Chest 112(4):
9 Table E1 Samples obtained and positivity rates in the two groups HMEF HH p value Number of patients Patients with clinically suspected pneumonia No. samples obtained Non-bronchoscopic samples Protected telescoping catheter 66 (30) 59 (28) 0.17 Bronchoscopic samples Protected telescoping catheter 22 (12) 23 (10) 1.0 8
10 Broncho-alveolar lavage 18 (5) 30 (15) 0.1 *p value for comparison between HMEF and HH groups. Numbers in brackets indicate number of positive samples 9
11 Figure E1: Flow chart of the study 1147 patients requiring mechanical ventilation Duration of mechanical ventilation suspected < 48 hours n=558 Duration MV really < 48 hours n= 481 Duration MV < 72 hours n= 44 Duration MV < 96 hours n= 33 Patients already ventilated for more than 24 hours n= 99 Cardiac arrest n= 20 Early decision of withdrawal n=6 Inclusion in another clinical study n=2 Active tuberculosis n=1 Unavailability of HH systems or of investigators n= patients included in the trial Secondary withdrawal n=1 369 patients included in the data analysis 10
Trial protocol - NIVAS Study
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
Diagnosing Pneumonia during Mechanical Ventilation The Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score Revisited
 Diagnosing Pneumonia during Mechanical Ventilation The Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score Revisited Muriel Fartoukh, Bernard Maître, Stéphanie Honoré, Charles Cerf, Jean-Ralph Zahar, and Christian Brun-Buisson
Diagnosing Pneumonia during Mechanical Ventilation The Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score Revisited Muriel Fartoukh, Bernard Maître, Stéphanie Honoré, Charles Cerf, Jean-Ralph Zahar, and Christian Brun-Buisson
ANWICU knowledge
 ANWICU knowledge www.anwicu.org.uk This presenta=on is provided by ANWICU We are a collabora=ve associa=on of ICUs in the North West of England. Permission to provide this presenta=on has been granted
ANWICU knowledge www.anwicu.org.uk This presenta=on is provided by ANWICU We are a collabora=ve associa=on of ICUs in the North West of England. Permission to provide this presenta=on has been granted
FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME
 FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME Guillaume CARTEAUX, Teresa MILLÁN-GUILARTE, Nicolas DE PROST, Keyvan RAZAZI, Shariq ABID, Arnaud
FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME Guillaume CARTEAUX, Teresa MILLÁN-GUILARTE, Nicolas DE PROST, Keyvan RAZAZI, Shariq ABID, Arnaud
Extubation Failure & Delay in Brain-Injured Patients
 Extubation Failure & Delay in Brain-Injured Patients Niall D. Ferguson, MD, FRCPC, MSc Director, Critical Care Medicine University Health Network & Mount Sinai Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine
Extubation Failure & Delay in Brain-Injured Patients Niall D. Ferguson, MD, FRCPC, MSc Director, Critical Care Medicine University Health Network & Mount Sinai Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine
AJRCCM Articles. Published on February 23, 2012
 Fever Control Using External Cooling in Septic Shock: A Randomized Controlled Trial Frédérique Schortgen, Karine Clabault, Sandrine Katsahian, Jerome Devaquet, Alain Mercat, Nicolas Deye, Jean Dellamonica,
Fever Control Using External Cooling in Septic Shock: A Randomized Controlled Trial Frédérique Schortgen, Karine Clabault, Sandrine Katsahian, Jerome Devaquet, Alain Mercat, Nicolas Deye, Jean Dellamonica,
During mechanical ventilation
 Heat and moisture exchangers in mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients: A plea for an independent assessment of their performance Guillaume Thiéry, MD; Alexandre Boyer, MD; Etienne Pigné,
Heat and moisture exchangers in mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients: A plea for an independent assessment of their performance Guillaume Thiéry, MD; Alexandre Boyer, MD; Etienne Pigné,
VAP Prevention bundles
 VAP Prevention bundles Dr. Shafiq A.Alimad MD Head of medical department at USTH YICID workshop, 15-12-2014 Care Bundles What are they & why use them? What are Care Bundles? Types of Care Bundles available
VAP Prevention bundles Dr. Shafiq A.Alimad MD Head of medical department at USTH YICID workshop, 15-12-2014 Care Bundles What are they & why use them? What are Care Bundles? Types of Care Bundles available
High Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure. Laurent Brochard Toronto
 High Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure Laurent Brochard Toronto Conflicts of interest Our clinical research laboratory has received research grants for clinical research projects from the
High Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure Laurent Brochard Toronto Conflicts of interest Our clinical research laboratory has received research grants for clinical research projects from the
Day-to-day management of Tracheostomies & Laryngectomies
 Humidification It is mandatory that a method of artificial humidification is utilised when a tracheostomy tube is in situ, for people requiring oxygen therapy dry oxygen should never be given to someone
Humidification It is mandatory that a method of artificial humidification is utilised when a tracheostomy tube is in situ, for people requiring oxygen therapy dry oxygen should never be given to someone
Journal Club American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Zhang Junyi
 Journal Club 2018 American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Zhang Junyi 2018.11.23 Background Mechanical Ventilation A life-saving technique used worldwide 15 million patients annually
Journal Club 2018 American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Zhang Junyi 2018.11.23 Background Mechanical Ventilation A life-saving technique used worldwide 15 million patients annually
Humidification of inspired gases in the mechanically ventilated patient
 Humidification of inspired gases in the mechanically ventilated patient Dr Liesel Bösenberg Specialist Physician and Fellow in Critical Care Kalafong Hospital University of Pretoria Points to ponder: Basic
Humidification of inspired gases in the mechanically ventilated patient Dr Liesel Bösenberg Specialist Physician and Fellow in Critical Care Kalafong Hospital University of Pretoria Points to ponder: Basic
American College of Surgeons Critical Care Review Course 2012: Infection Control
 American College of Surgeons Critical Care Review Course 2012: Infection Control Overview: I. Central line associated blood stream infection (CLABSI) II. Ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP) I. Central
American College of Surgeons Critical Care Review Course 2012: Infection Control Overview: I. Central line associated blood stream infection (CLABSI) II. Ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP) I. Central
Exclusion Criteria 1. Operator or supervisor feels specific intra- procedural laryngoscopy device will be required.
 FELLOW Study Data Analysis Plan Direct Laryngoscopy vs Video Laryngoscopy Background Respiratory failure requiring endotracheal intubation occurs in as many as 40% of critically ill patients. Procedural
FELLOW Study Data Analysis Plan Direct Laryngoscopy vs Video Laryngoscopy Background Respiratory failure requiring endotracheal intubation occurs in as many as 40% of critically ill patients. Procedural
Facilitating EndotracheaL Intubation by Laryngoscopy technique and Apneic Oxygenation Within the Intensive Care Unit (FELLOW)
 Facilitating EndotracheaL Intubation by Laryngoscopy technique and Apneic Oxygenation Within the Intensive Data Analysis Plan: Apneic Oxygenation vs. No Apneic Oxygenation Background Critically ill patients
Facilitating EndotracheaL Intubation by Laryngoscopy technique and Apneic Oxygenation Within the Intensive Data Analysis Plan: Apneic Oxygenation vs. No Apneic Oxygenation Background Critically ill patients
Surviving Sepsis Campaign. Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock. An Overview
 Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock An Overview Mechanical Ventilation of Sepsis-Induced ALI/ARDS ARDSnet Mechanical Ventilation Protocol Results: Mortality
Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis/Septic Shock An Overview Mechanical Ventilation of Sepsis-Induced ALI/ARDS ARDSnet Mechanical Ventilation Protocol Results: Mortality
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Torres A, Sibila O, Ferrer M, et al. Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory
Supplementary Online Content Torres A, Sibila O, Ferrer M, et al. Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory
VAP Definitions. CDC New Approach to VAP Surveillance. Conflict of Interest Disclosure Robert M Kacmarek. Artificial Airways, Cuffs, Bioflim and VAP
 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Robert M Kacmarek Artificial Airways, Cuffs, Bioflim and VAP Bob Kacmarek PhD, RRT Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 9-14-18
Conflict of Interest Disclosure Robert M Kacmarek Artificial Airways, Cuffs, Bioflim and VAP Bob Kacmarek PhD, RRT Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 9-14-18
Clinical Practice Management Guideline for Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Diagnosis, Treatment & Prevention
 Clinical for Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Diagnosis, Treatment & Prevention Background Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), a pneumonia that develops 48hrs after initiation of mechanical ventilation,
Clinical for Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Diagnosis, Treatment & Prevention Background Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), a pneumonia that develops 48hrs after initiation of mechanical ventilation,
Jean-Yves Fagon,* Jean Chastre, Yves Domart, Jean-Louis Trnuillet, and Claude Gibert
 538 Mortality Due to Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia or Colonization with Pseudomonas or Acinetobacter Species: Assessment by Quantitative Culture of Samples Obtained by a Protected Specimen Brush Jean-Yves
538 Mortality Due to Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia or Colonization with Pseudomonas or Acinetobacter Species: Assessment by Quantitative Culture of Samples Obtained by a Protected Specimen Brush Jean-Yves
Benefits and risks of success or failure of noninvasive ventilation
 Intensive Care Med (2006) 32:1756 1765 DOI 10.1007/s00134-006-0324-1 ORIGINAL Alexandre Demoule Emmanuelle Girou Jean-Christophe Richard Solenne Taille Laurent Brochard Benefits and risks of success or
Intensive Care Med (2006) 32:1756 1765 DOI 10.1007/s00134-006-0324-1 ORIGINAL Alexandre Demoule Emmanuelle Girou Jean-Christophe Richard Solenne Taille Laurent Brochard Benefits and risks of success or
Lâcher les VAP pour les VAC, les IVAC?...(CDC) INTRODUCTION
 Lâcher les VAP pour les VAC, les IVAC?...(CDC) lila.bouadma@bch.aphp.fr INTRODUCTION VAP surveillance is needed to measure incidence and to gauge the success of prevention efforts. However, VAP diagnosis
Lâcher les VAP pour les VAC, les IVAC?...(CDC) lila.bouadma@bch.aphp.fr INTRODUCTION VAP surveillance is needed to measure incidence and to gauge the success of prevention efforts. However, VAP diagnosis
New Surveillance Definitions for VAP
 New Surveillance Definitions for VAP 2012 Critical Care Canada Forum Toronto Dr. John Muscedere Associate Professor of Medicine, Queen s University Kingston, Ontario Presenter Disclosure Dr. J. G. Muscedere
New Surveillance Definitions for VAP 2012 Critical Care Canada Forum Toronto Dr. John Muscedere Associate Professor of Medicine, Queen s University Kingston, Ontario Presenter Disclosure Dr. J. G. Muscedere
Section 2.1 Daily checks Humidification
 Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 2.1 Daily checks Humidification This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative. The GTC
Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 2.1 Daily checks Humidification This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative. The GTC
HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA: DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT & PREVENTION
 HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA: DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT & PREVENTION David Jay Weber, M.D., M.P.H. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, & Epidemiology Associate Chief Medical Officer, UNC Health Care Medical
HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA: DIAGNOSIS, TREATMENT & PREVENTION David Jay Weber, M.D., M.P.H. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, & Epidemiology Associate Chief Medical Officer, UNC Health Care Medical
Incidence and outcome of weaning from mechanical ventilation according to new categories
 Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 88 94 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00056909 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2010 Incidence and outcome of from mechanical ventilation according to new categories G-C. Funk*, S. Anders*, M-K.
Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 88 94 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00056909 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2010 Incidence and outcome of from mechanical ventilation according to new categories G-C. Funk*, S. Anders*, M-K.
Predictors and Outcome of Early-Onset Pneumonia After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 Predictors and Outcome of Early-Onset Pneumonia After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Dirk Pabst MD, Sonja Römer MD, Alexander Samol MD, Philipp Kümpers MD, Johannes Waltenberger MD, and Pia Lebiedz MD
Predictors and Outcome of Early-Onset Pneumonia After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Dirk Pabst MD, Sonja Römer MD, Alexander Samol MD, Philipp Kümpers MD, Johannes Waltenberger MD, and Pia Lebiedz MD
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement
 CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
Diagnosis of Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia: Where are we now?
 Diagnosis of Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia: Where are we now? Gary French Guy s & St. Thomas Hospital & King s College, London BSAC Guideline 2008 Masterton R, Galloway A, French G, Street M, Armstrong
Diagnosis of Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia: Where are we now? Gary French Guy s & St. Thomas Hospital & King s College, London BSAC Guideline 2008 Masterton R, Galloway A, French G, Street M, Armstrong
MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway
 Case report Crit Care Shock (2016) 19:54-58 MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway Ann Tsung, Brian T. Wessman An 80-year-old female with a past medical history of chronic obstructive
Case report Crit Care Shock (2016) 19:54-58 MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway Ann Tsung, Brian T. Wessman An 80-year-old female with a past medical history of chronic obstructive
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
WEANING READINESS & SPONTANEOUS BREATHING TRIAL MONITORING
 CLINICAL EVIDENCE GUIDE WEANING READINESS & SPONTANEOUS BREATHING TRIAL MONITORING Weaning readiness and spontaneous breathing trial monitoring protocols can help you make the right weaning decisions at
CLINICAL EVIDENCE GUIDE WEANING READINESS & SPONTANEOUS BREATHING TRIAL MONITORING Weaning readiness and spontaneous breathing trial monitoring protocols can help you make the right weaning decisions at
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
 The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) with surfactant in pediatric ARDS
 Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) with surfactant in pediatric ARDS M. Luchetti, E. M. Galassini, A. Galbiati, C. Pagani,, F. Silla and G. A. Marraro gmarraro@picu.it www.picu.it Anesthesia and Intensive Care
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) with surfactant in pediatric ARDS M. Luchetti, E. M. Galassini, A. Galbiati, C. Pagani,, F. Silla and G. A. Marraro gmarraro@picu.it www.picu.it Anesthesia and Intensive Care
PREVALENCE PATTERN OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN VENTILATION ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA (VAP) PATIENTS OF INTENSIVE CARE UNIT (ICU) IN MAHARASHTRA REGION.
 Original research article International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208 PREVALENCE PATTERN OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN VENTILATION ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA (VAP)
Original research article International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208 PREVALENCE PATTERN OF MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY IN VENTILATION ASSOCIATED PNEUMONIA (VAP)
Prone Positioning in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
 Prone Positioning in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Claude Guérin, M.D., Ph.D., Jean Reignier, M.D., Ph.D., Jean-Christophe Richard, M.D., Ph.D., Pascal Beuret, M.D., Arnaud Gacouin, M.D.,
Prone Positioning in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Claude Guérin, M.D., Ph.D., Jean Reignier, M.D., Ph.D., Jean-Christophe Richard, M.D., Ph.D., Pascal Beuret, M.D., Arnaud Gacouin, M.D.,
Intracheal antibiotics administration
 Intracheal antibiotics administration Jean Chastre, M.D. www.reamedpitie.com Disclosure Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Bayer, Pfizer, Cubist/Merck, Basilea, Kenta/Aridis, Roche, AstraZeneca/Medimmune
Intracheal antibiotics administration Jean Chastre, M.D. www.reamedpitie.com Disclosure Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Bayer, Pfizer, Cubist/Merck, Basilea, Kenta/Aridis, Roche, AstraZeneca/Medimmune
Landmark articles on ventilation
 Landmark articles on ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity ARDS AECC DEFINITION-1994 ALI Acute onset Bilateral chest infiltrates PCWP
Landmark articles on ventilation Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity ARDS AECC DEFINITION-1994 ALI Acute onset Bilateral chest infiltrates PCWP
DAILY SCREENING FORM
 DAILY SCREENING FORM Patient s initials: Date of admission: Time of admission: Gender: M F Year of Birth: Type of admission: Medical/Surgical/Postoperative (elective) Days Date Mechanical ventilation Lung
DAILY SCREENING FORM Patient s initials: Date of admission: Time of admission: Gender: M F Year of Birth: Type of admission: Medical/Surgical/Postoperative (elective) Days Date Mechanical ventilation Lung
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Randomized controlled trial of interrupted versus continuous sedative infusions in ventilated children
 Feature Articles Randomized controlled trial of interrupted versus continuous sedative infusions in ventilated children Kunal Gupta, MD; Vipul K. Gupta, MD, DNB; Jayashree Muralindharan, MD; Sunit Singhi,
Feature Articles Randomized controlled trial of interrupted versus continuous sedative infusions in ventilated children Kunal Gupta, MD; Vipul K. Gupta, MD, DNB; Jayashree Muralindharan, MD; Sunit Singhi,
Invasive mechanical ventilation is
 A randomized, controlled trial of the role of weaning predictors in clinical decision making* Maged A. Tanios, MD, MPH; Michael L. Nevins, MD; Katherine P. Hendra, MD; Pierre Cardinal, MD; Jill E. Allan,
A randomized, controlled trial of the role of weaning predictors in clinical decision making* Maged A. Tanios, MD, MPH; Michael L. Nevins, MD; Katherine P. Hendra, MD; Pierre Cardinal, MD; Jill E. Allan,
Effectiveness of heat and moisture exchangers in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients: a meta-analysis
 Menegueti et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2014, 14:115 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effectiveness of heat and moisture exchangers in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients: a meta-analysis
Menegueti et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2014, 14:115 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effectiveness of heat and moisture exchangers in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients: a meta-analysis
Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality?
 Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality? Clinical problem and domain I selected this case because although this was the second patient we had proned in our unit within a week,
Does proning patients with refractory hypoxaemia improve mortality? Clinical problem and domain I selected this case because although this was the second patient we had proned in our unit within a week,
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes. Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center
 Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION FOR RESPIRATORY CARE TMC DETAILED CONTENT OUTLINE COMPARISON
 A. Evaluate Data in the Patient Record I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Patient history e.g., admission data orders medications progress notes DNR status / advance directives social history
A. Evaluate Data in the Patient Record I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Patient history e.g., admission data orders medications progress notes DNR status / advance directives social history
Diagnosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Pilot, Exploratory Analysis of a New Score Based on Procalcitonin and Chest Echography
 CHEST 2014; 146(6): 1578-1585 文献精读 Diagnosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Pilot, Exploratory Analysis of a New Score Based on Procalcitonin and Chest Echography Giovanni Zagli, MD, PhD ; Morena
CHEST 2014; 146(6): 1578-1585 文献精读 Diagnosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Pilot, Exploratory Analysis of a New Score Based on Procalcitonin and Chest Echography Giovanni Zagli, MD, PhD ; Morena
r e s s R Y u r e i r w a v e i t i I R A T O P o s S P u s R E u o i n n t C o Boussignac CPAP Just breathe
 S P I R A T O u s P o s R Y i t i v e A i r w a y P r e s s u r e R E u o i n n t C o Boussignac CPAP Just breathe What is Boussignac CPAP? Boussignac CPAP is a Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) device generating
S P I R A T O u s P o s R Y i t i v e A i r w a y P r e s s u r e R E u o i n n t C o Boussignac CPAP Just breathe What is Boussignac CPAP? Boussignac CPAP is a Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) device generating
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities
 Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
Critical care resources are often provided to the too well and as well as. to the too sick. The former include the patients admitted to an ICU
 Literature Review Critical care resources are often provided to the too well and as well as to the too sick. The former include the patients admitted to an ICU following major elective surgery for overnight
Literature Review Critical care resources are often provided to the too well and as well as to the too sick. The former include the patients admitted to an ICU following major elective surgery for overnight
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Bronchoscopy SICU Protocol
 Bronchoscopy SICU Protocol Updated January 2013 Outline Clinical indications Considerations Preparation Bronchoscopy technique Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) Post-procedure Purpose Bronchoscopy is a procedure
Bronchoscopy SICU Protocol Updated January 2013 Outline Clinical indications Considerations Preparation Bronchoscopy technique Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) Post-procedure Purpose Bronchoscopy is a procedure
Ventilator-Associated Event (VAE) For use in adult locations only
 Ventilator-Associated Event () For use in adult locations only Table of Contents: Introduction 1 Settings 3 Definitions 3 Reporting Instructions 16 Figures 1-4, Algorithm 18 Numerator Data 23 Denominator
Ventilator-Associated Event () For use in adult locations only Table of Contents: Introduction 1 Settings 3 Definitions 3 Reporting Instructions 16 Figures 1-4, Algorithm 18 Numerator Data 23 Denominator
Efficiency and Safety of Mechanical Ventilation with a Heat and Moisture Exchanger Changed Only Once a Week
 Efficiency and Safety of Mechanical Ventilation with a Heat and Moisture Exchanger Changed Only Once a Week JEAN-DAMIEN RICARD, ERIC LE MIÈRE, PHILIPPE MARKOWICZ, SERGE LASRY, GEORGES SAUMON, KAMEL DJEDAÏNI,
Efficiency and Safety of Mechanical Ventilation with a Heat and Moisture Exchanger Changed Only Once a Week JEAN-DAMIEN RICARD, ERIC LE MIÈRE, PHILIPPE MARKOWICZ, SERGE LASRY, GEORGES SAUMON, KAMEL DJEDAÏNI,
What s New About Proning?
 1 What s New About Proning? J. Brady Scott, MSc, RRT-ACCS, AE-C, FAARC Director of Clinical Education and Assistant Professor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences Division of Respiratory Care Rush University
1 What s New About Proning? J. Brady Scott, MSc, RRT-ACCS, AE-C, FAARC Director of Clinical Education and Assistant Professor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences Division of Respiratory Care Rush University
Noninvasive pressure support ventilation in COPD patients with postextubation hypercapnic respiratory insufficiency
 Eur Respir J 1998; 11: 1349 1353 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.98.11061349 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Noninvasive pressure support
Eur Respir J 1998; 11: 1349 1353 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.98.11061349 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Noninvasive pressure support
NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Use of NIV 1998-2010 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1998
NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Use of NIV 1998-2010 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1998
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither?
 Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Effect of Ventilation Equipment on Imposed Work of Breathing
 Original articles Effect of Ventilation Equipment on Imposed Work of Breathing C. J. FRENCH*, R. BELLOMO, J. BUCKMASTER *Department of Intensive Care, Western Hospital, Footscray, VICTORIA Department of
Original articles Effect of Ventilation Equipment on Imposed Work of Breathing C. J. FRENCH*, R. BELLOMO, J. BUCKMASTER *Department of Intensive Care, Western Hospital, Footscray, VICTORIA Department of
Therapist Written RRT Examination Detailed Content Outline
 I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 4 7 17 28 A. Review Data in the Patient Record 1 4 0 5 1. Patient history e.g., present illness admission notes respiratory care orders medication history
I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 4 7 17 28 A. Review Data in the Patient Record 1 4 0 5 1. Patient history e.g., present illness admission notes respiratory care orders medication history
NIV and Aerosoltherapy
 NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim
 Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Nosocomial Pneumonia. <5 Days: Non-Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
 Nosocomial Pneumonia Meredith Deutscher, MD Troy Schaffernocker, MD Ohio State University Burden of Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia Second most common nosocomial infection in the U.S. 5-10 episodes per 1000
Nosocomial Pneumonia Meredith Deutscher, MD Troy Schaffernocker, MD Ohio State University Burden of Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia Second most common nosocomial infection in the U.S. 5-10 episodes per 1000
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia
 1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Does ICU-acquired paresis lengthen weaning from mechanical ventilation?
 Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:1117 1121 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2174-z O R I G I N A L Bernard De Jonghe Sylvie Bastuji-Garin Tarek Sharshar HervØ Outin Laurent Brochard Does ICU-acquired paresis lengthen
Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:1117 1121 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2174-z O R I G I N A L Bernard De Jonghe Sylvie Bastuji-Garin Tarek Sharshar HervØ Outin Laurent Brochard Does ICU-acquired paresis lengthen
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU
 High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
Oxygenation Failure. Increase FiO2. Titrate end-expiratory pressure. Adjust duty cycle to increase MAP. Patient Positioning. Inhaled Vasodilators
 Oxygenation Failure Increase FiO2 Titrate end-expiratory pressure Adjust duty cycle to increase MAP Patient Positioning Inhaled Vasodilators Extracorporeal Circulation ARDS Radiology Increasing Intensity
Oxygenation Failure Increase FiO2 Titrate end-expiratory pressure Adjust duty cycle to increase MAP Patient Positioning Inhaled Vasodilators Extracorporeal Circulation ARDS Radiology Increasing Intensity
Factors Affecting Invasive Management after Unplanned Extubation in an Intensive Care Unit
 Korean J Crit Care Med 2015 August 30(3):164-170 / ISSN 2383-4870 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2383-4889 (Online) Original Article Factors Affecting Invasive Management after Unplanned Extubation in an Intensive Care
Korean J Crit Care Med 2015 August 30(3):164-170 / ISSN 2383-4870 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2383-4889 (Online) Original Article Factors Affecting Invasive Management after Unplanned Extubation in an Intensive Care
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Ventilator Associated Pneumonia ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Attributable mortality VAP Meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomized prevention studies Attributable mortality mainly results
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Attributable mortality VAP Meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomized prevention studies Attributable mortality mainly results
Evaluation of Outcome for Intubated Patients with Pneumonia Due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 973 Evaluation of Outcome for Intubated Patients with Pneumonia Due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Jordi Rello, Paola Jubert, Jordi Valles, Antonio Artigas, Montse Rue, and Michael S. Niederman From the Department
973 Evaluation of Outcome for Intubated Patients with Pneumonia Due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Jordi Rello, Paola Jubert, Jordi Valles, Antonio Artigas, Montse Rue, and Michael S. Niederman From the Department
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Ventilator Associated Pneumonia ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Attributable mortality VAP Meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomized prevention studies Attributable mortality mainly results
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Attributable mortality VAP Meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomized prevention studies Attributable mortality mainly results
Concerns and Controversial Issues in NPPV. Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation
 : Common Therapy in Daily Practice Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Rongchang Chen Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease as the first choice of mechanical
: Common Therapy in Daily Practice Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Rongchang Chen Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease as the first choice of mechanical
NIV in acute hypoxic respiratory failure
 All course materials, including the original lecture, are available as webcasts/podcasts at www.ers-education. org/niv2009.htm NIV in acute hypoxic respiratory failure Educational aims This presentation
All course materials, including the original lecture, are available as webcasts/podcasts at www.ers-education. org/niv2009.htm NIV in acute hypoxic respiratory failure Educational aims This presentation
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU
 High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
Ventilator Associated
 Ventilator Associated Pneumonia: Key and Controversial Issues Christopher P. Michetti, MD, FACS Inova Fairfax Hospital, Falls Church, VA Forrest Dell Moore, MD, FACS Banner Healthcare System, Phoenix,
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia: Key and Controversial Issues Christopher P. Michetti, MD, FACS Inova Fairfax Hospital, Falls Church, VA Forrest Dell Moore, MD, FACS Banner Healthcare System, Phoenix,
Difficult weaning from mechanical ventilation
 Difficult weaning from mechanical ventilation Paolo Biban, MD Director, Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit Division of Paediatrics, Major City Hospital Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata
Difficult weaning from mechanical ventilation Paolo Biban, MD Director, Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit Division of Paediatrics, Major City Hospital Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata
IICU Staff Meeting Minutes May 15 and 16, 2013 IICU Conference Room
 IICU Staff Meeting Minutes May 15 and 16, 2013 IICU Conference Room 1) Decreasing Telemetry Alarms Janice Marlett, BSN, RN, Nursing Staff Educator To decrease tele alarms: Properly prep the skin Shave
IICU Staff Meeting Minutes May 15 and 16, 2013 IICU Conference Room 1) Decreasing Telemetry Alarms Janice Marlett, BSN, RN, Nursing Staff Educator To decrease tele alarms: Properly prep the skin Shave
GE Healthcare. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator. Relief, Relax, Recovery
 GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
Gram staining of protected pulmonary specimens in the early diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 85 (5): 735±9 (2000) Gram staining of protected pulmonary specimens in the early diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia O. Mimoz *, A. Karim, J. X. Mazoit, A. Edouard,
British Journal of Anaesthesia 85 (5): 735±9 (2000) Gram staining of protected pulmonary specimens in the early diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia O. Mimoz *, A. Karim, J. X. Mazoit, A. Edouard,
Multivariate Analysis of the Factors Associated With the Risk of Pneumonia in Intensive Care Units
 BJID 2007; 11 (June) 339 Multivariate Analysis of the Factors Associated With the Risk of Pneumonia in Intensive Care Units Cláudia Maria Dantas de Maio Carrilho 1, Cintia Magalhães Carvalho Grion 1, Ana
BJID 2007; 11 (June) 339 Multivariate Analysis of the Factors Associated With the Risk of Pneumonia in Intensive Care Units Cláudia Maria Dantas de Maio Carrilho 1, Cintia Magalhães Carvalho Grion 1, Ana
Research & Reviews of. Pneumonia
 Chapter Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of VAP in Adult ICU Patients Priyam Batra * ; Purva Mathur Research & Reviews of Department of Laboratory Medicine, AIIMS, Trauma Centre, New Delhi, India. *
Chapter Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of VAP in Adult ICU Patients Priyam Batra * ; Purva Mathur Research & Reviews of Department of Laboratory Medicine, AIIMS, Trauma Centre, New Delhi, India. *
Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management. Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS
 Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS Objectives How it works COPD Management today The role of NHFC Evidence Research/Case Studies Types
Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS Objectives How it works COPD Management today The role of NHFC Evidence Research/Case Studies Types
infection control and hospital epidemiology january 2008, vol. 29, no. 1 original article
 infection control and hospital epidemiology january 2008, vol. 29, no. 1 original article Development of an Algorithm for Surveillance of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia With Electronic Data and Comparison
infection control and hospital epidemiology january 2008, vol. 29, no. 1 original article Development of an Algorithm for Surveillance of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia With Electronic Data and Comparison
Removal of Endotracheal Tube Obstruction With a Secretion Clearance Device
 Removal of Endotracheal Tube Obstruction With a Secretion Clearance Device Cristina Mietto MD, Kevin Foley RRT, Lindsay Salerno RRT, Jenna Oleksak RRT, Riccardo Pinciroli MD, Jeremy Goverman MD, and Lorenzo
Removal of Endotracheal Tube Obstruction With a Secretion Clearance Device Cristina Mietto MD, Kevin Foley RRT, Lindsay Salerno RRT, Jenna Oleksak RRT, Riccardo Pinciroli MD, Jeremy Goverman MD, and Lorenzo
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT Rev. 2/2011 These
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT Rev. 2/2011 These
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia: New for 2008
 Ventilator Associated Pneumonia: New for 2008 Jeanine P. Wiener-Kronish, MD Henry Isaiah Dorr Professor of Research and Teaching in Anaesthetics and Anaesthesia Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care
Ventilator Associated Pneumonia: New for 2008 Jeanine P. Wiener-Kronish, MD Henry Isaiah Dorr Professor of Research and Teaching in Anaesthetics and Anaesthesia Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care
Challenges in Diagnosis, Surveillance and Prevention of Ventilator-associated pneumonia
 Challenges in Diagnosis, Surveillance and Prevention of Ventilator-associated pneumonia Massachusetts Coalition for the Prevention of Errors November 6, 2008 Michael Klompas MD, MPH, FRCPC Brigham and
Challenges in Diagnosis, Surveillance and Prevention of Ventilator-associated pneumonia Massachusetts Coalition for the Prevention of Errors November 6, 2008 Michael Klompas MD, MPH, FRCPC Brigham and
Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care
 Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care Date Revised: January 2015 Course Description Student Learning Objectives:
Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care Date Revised: January 2015 Course Description Student Learning Objectives:
Web Appendix 1: Literature search strategy. BTS Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure (AHRF) write-up. Sources to be searched for the guidelines;
 Web Appendix 1: Literature search strategy BTS Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure (AHRF) write-up Sources to be searched for the guidelines; Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) Database of
Web Appendix 1: Literature search strategy BTS Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure (AHRF) write-up Sources to be searched for the guidelines; Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) Database of
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Early-goal-directed therapy and protocolised treatment in septic shock
 CAT reviews Early-goal-directed therapy and protocolised treatment in septic shock Journal of the Intensive Care Society 2015, Vol. 16(2) 164 168! The Intensive Care Society 2014 Reprints and permissions:
CAT reviews Early-goal-directed therapy and protocolised treatment in septic shock Journal of the Intensive Care Society 2015, Vol. 16(2) 164 168! The Intensive Care Society 2014 Reprints and permissions:
Noninvasive Ventilation: Non-COPD Applications
 Noninvasive Ventilation: Non-COPD Applications NONINVASIVE MECHANICAL VENTILATION Why Noninvasive Ventilation? Avoids upper A respiratory airway trauma system lacerations, protective hemorrhage strategy
Noninvasive Ventilation: Non-COPD Applications NONINVASIVE MECHANICAL VENTILATION Why Noninvasive Ventilation? Avoids upper A respiratory airway trauma system lacerations, protective hemorrhage strategy
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
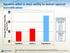 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
New Curriculum Content Map NBRC Exam Content Outline
 New Curriculum Content Map NBRC Exam Content Outline Patient Data Evaluation and Recommendations Review Existing Data in the Patient Record Including: 1 Patient history [e.g., present illness, admission
New Curriculum Content Map NBRC Exam Content Outline Patient Data Evaluation and Recommendations Review Existing Data in the Patient Record Including: 1 Patient history [e.g., present illness, admission
Mechanical Ventilation
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 33: Mechanical Ventilation Authors C. Landelle, PharmD, PhD D. Pittet, MD, MS Chapter Editor Gonzalo Bearman, MD, MPH, FACP, FSHEA, FIDSA Topic Outline
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 33: Mechanical Ventilation Authors C. Landelle, PharmD, PhD D. Pittet, MD, MS Chapter Editor Gonzalo Bearman, MD, MPH, FACP, FSHEA, FIDSA Topic Outline
Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data
 Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data David Ebler, MD David Skarupa, MD Andrew J. Kerwin, MD, FACS Jhun de Villa, MD Michael S. Nussbaum, MD, FACS J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS
Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data David Ebler, MD David Skarupa, MD Andrew J. Kerwin, MD, FACS Jhun de Villa, MD Michael S. Nussbaum, MD, FACS J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS
