Example of features used to assess asthma (not complete, please see link)
|
|
|
- Charla Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Asthma: diagnosis in adults The 2008 British Thoracic Society guidelinesmarked a subtle change in the approach to diagnosing asthma. This approach is supported in the updated 2011 guidelines. It suggests dividing patients into a high, intermediate and low probability of having asthma based on the presence or absence of typical symptoms. A list can be found in the external link but include typical symptoms such as wheeze, nocturnal cough etc Example of features used to assess asthma (not complete, please see link) Increase possibility of asthma Wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness and cough, worse at night/early morning History of atopic disorder Wheeze heard on auscultation Unexplained peripheral blood eosinophilia Decrease possibility of asthma Prominent dizziness, light-headedness, peripheral tingling Chronic productive cough in the absence of wheeze or breathlessness Repeatedly normal physical examination Significant smoking history (i.e. > 20 packyears) Normal PEF or spirometry when symptomatic Management is based on this assessment: high probability: trial of treatment intermediate probability: see below low probability: investigate/treat other condition For patients with an intermediate probability of asthma further investigations are suggested. The guidelines state that spirometry is the preferred initial test: FEV1/FVC < 0.7: trial of treatment FEV1/FVC > 0.7: further investigation/consider referral Recent studies have shown the limited value of other 'objective' tests. It is now recognised that in patients with normal or near-normal pre-treatment lung function there is little room for measurable improvement in FEV1 or peak flow. A > 400 ml improvement in FEV1 is considered significant before and after 400 mcg inhaled salbutamol in patients with diagnostic uncertainty and airflow obstruction present at the time of assessment if there is an incomplete response to inhaled salbutamol, after either inhaled corticosteroids (200 mcg twice daily beclometasone equivalent for 6-8 weeks) or oral prednisolone (30 mg once daily for 14 days) It is now advised to interpret peak flow variability with caution due to the poor sensitivity of the test diurnal variation % = [(Highest - Lowest PEFR) / Highest PEFR] x 100 assessment should be made over 2 weeks 1
2 greater than 20% diurnal variation is considered significant COPD: stable management NICE updated it's guidelines on the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in General management smoking cessation advice annual influenza vaccination one-off pneumococcal vaccination Bronchodilator therapy a short-acting beta2-agonist (SABA) or short-acting muscarinic antagonist (SAMA) is firstline treatment for patients who remain breathless or have exacerbations despite using short-acting bronchodilators the next step is determined by the FEV1 FEV1 > 50% long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA), for example salmeterol, or: long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), for example tiotropium FEV1 < 50% LABA + inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) in a combination inhaler, or: LAMA For patients with persistent exacerbations or breathlessness if taking a LABA then switch to a LABA + ICS combination inhaler otherwise give a LAMA and a LABA + ICS combination inhaler Oral theophylline NICE only recommends theophylline after trials of short an long-acting bronchodilators or to people who cannot used inhaled therapy the dose should be reduced if macrolide or fluoroquinolone antibiotics are co-prescribed Mucolytics should be 'considered' in patients with a chronic productive cough and continued if symptoms improve Cor pulmonale features include peripheral oedema, raised jugular venous pressure, systolic parasternal heave, loud P2 2
3 use a loop diuretic for oedema, consider long-term oxygen therapy ACE-inhibitors, calcium channel blockers and alpha blockers are not recommended by NICE Factors which may improve survival in patients with stable COPD smoking cessation - the single most important intervention in patients who are still smoking long term oxygen therapy in patients who fit criteria lung volume reduction surgery in selected patients Asthma: stepwise management in adults The management of stable asthma is now well established with a step-wise approach: Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Inhaled short-acting B2 agonist as required Add inhaled steroid at mcg/day* 400 mcg is an appropriate starting dose for many patients. Start at dose of inhaled steroid appropriate to severity of disease 1. Add inhaled long-acting B2 agonist (LABA) 2. Assess control of asthma: good response to LABA - continue LABA benefit from LABA but control still inadequate: continue LABA and increase inhaled steroid dose to 800 mcg/day* (if not already on this dose) no response to LABA: stop LABA and increase inhaled steroid to 800 mcg/ day.* If control still inadequate, institute trial of other therapies, leukotriene receptor antagonist or SR theophylline Step 4 Consider trials of: increasing inhaled steroid up to 2000 mcg/day* addition of a fourth drug e.g. Leukotriene receptor antagonist, SR theophylline, B2 agonist tablet Step 5 Use daily steroid tablet in lowest dose providing adequate control. Consider other treatments to minimise the use of steroid tablets Maintain high dose inhaled steroid at 2000 mcg/day* Refer patient for specialist care *beclometasone dipropionate or equivalent Additional notes 3
4 Leukotriene receptor antagonists e.g. Montelukast, zafirlukast have both anti-inflammatory and bronchodilatory properties should be used when patients are poorly controlled on high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and a long-acting b2-agonist particularly useful in aspirin-induced asthma associated with the development of Churg-Strauss syndrome Fluticasone is more lipophilic and has a longer duration of action than beclometasone Hydrofluoroalkane is now replacing chlorofluorocarbon as the propellant of choice. Only half the usually dose is needed with hydrofluoroalkane due to the smaller size of the particles Long acting B2-agonists acts as bronchodilators but also inhibit mediator release from mast cells. Recent meta-analysis showed adding salmeterol improved symptoms compared to doubling the inhaled steroid dose Respiratory pathogens The table below lists the more common respiratory pathogens: Pathogen Associated condition Respiratory syncytial Bronchiolitis virus Parainfluenza virus Croup Rhinovirus Common cold Influenza virus Flu Streptococcus The most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia pneumoniae Haemophilus Community-acquired pneumonia influenzae Most common cause of bronchiectasis exacerbations Staphylococcus Pneumonia, particularly following influenza aureus Mycoplasma Atypical pneumonia pneumoniae Flu-like symptoms classically precede a dry cough. Complications include haemolytic anaemia and erythema multiforme Legionella Atypical pneumonia pneumophilia Classically spread by air-conditioning systems, causes dry cough. Lymphopenia, deranged liver function tests and hyponatraemia may be seen Pneumocystis Common cause of pneumonia in HIV patients. Typically patients have few jiroveci chest signs and develop exertional dyspnoea Mycobacterium Causes tuberculosis. A wide range of presentations from asymptomatic to 4
5 tuberculosis disseminated disease are possible. Cough, night sweats and weight loss may be seen COPD: investigation and diagnosis NICE recommend considering a diagnosis of COPD in patients over 35 years of age who are smokers or ex-smokers and have symptoms such as exertional breathlessness, chronic cough or regular sputum production. The following investigations are recommended in patients with suspected COPD: post-bronchodilator spirometry to demonstrate airflow obstruction: FEV1/FVC ratio less than 70% chest x-ray: hyperinflation, bullae, flat hemidiaphragm. Also important to exclude lung cancer full blood count: exclude secondary polycythaemia body mass index (BMI) calculation The severity of COPD is categorised using the FEV1*: Post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC FEV1 (of predicted) Severity < 0.7 > 80% Stage 1 - Mild** < % Stage 2 - Moderate < % Stage 3 - Severe < 0.7 < 30% Stage 4 - Very severe Measuring peak expiratory flow is of limited value in COPD, as it may underestimate the degree of airflow obstruction. *note that the grading system has changed following the 2010 NICE guidelines. If the FEV1 is greater than 80% predicted but the post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC is < 0.7 then this is classified as Stage 1 - mild **symptoms should be present to diagnose COPD in these patients Haemoptysis The table below lists the main characteristics of the most important causes of haemoptysis: Lung cancer Pulmonary oedema Tuberculosis Pulmonary embolism History of smoking Symptoms of malignancy: weight loss, anorexia Dyspnoea Bibasal crackles and S3 are the most reliable signs Fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss Pleuritic chest pain Tachycardia, tachypnoea 5
6 Lower respiratory tract infection Bronchiectasis Mitral stenosis Aspergilloma Wegener's granulomatosis Goodpasture's syndrome Usually acute history of purulent cough Usually long history of cough and daily purulent sputum production Dyspnoea Atrial fibrillation Malar flush on cheeks Mid-diastolic murmur Often past history of tuberculosis. Haemoptysis may be severe Chest x-ray shows rounded opacity Upper respiratory tract: epistaxis, sinusitis, nasal crusting Lower respiratory tract: dyspnoea, haemoptysis Glomerulonephritis Saddle-shape nose deformity Haemoptysis Systemically unwell: fever, nausea Glomerulonephritis COPD: long-term oxygen therapy The 2010 NICE guidelines on COPD clearly define which patients should be assessed for and offered long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT). Patients who receive LTOT should breathe supplementary oxygen for at least 15 hours a day. Oxygen concentrators are used to provide a fixed supply for LTOT. Assess patients if any of the following: very severe airflow obstruction (FEV1 < 30% predicted). Assessment should be 'considered' for patients with severe airflow obstruction (FEV % predicted) cyanosis polycythaemia peripheral oedema raised jugular venous pressure oxygen saturations less than or equal to 92% on room air Assessment is done by measuring arterial blood gases on 2 occasions at least 3 weeks apart in patients with stable COPD on optimal management. Offer LTOT to patients with a po2 of < 7.3 kpa or to those with a po2 of kpa and one of the following: secondary polycythaemia nocturnal hypoxaemia peripheral oedema pulmonary hypertension 6
7 Bronchiectasis: management Bronchiectasis describes a permanent dilatation of the airways secondary to chronic infection or inflammation. After assessing for treatable causes (e.g. immune deficiency) management is as follows: physical training (e.g. inspiratory muscle training) - has a good evidence base for patients with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis postural drainage antibiotics for exacerbations + long-term rotating antibiotics in severe cases bronchodilators in selected cases immunisations surgery in selected cases (e.g. Localised disease) Most common organisms isolated from patients with bronchiectasis: Haemophilus influenzae (most common) Pseudomonas aeruginosa Klebsiella spp. Streptococcus pneumonia Asthma: diagnosis in adults The 2008 British Thoracic Society guidelinesmarked a subtle change in the approach to diagnosing asthma. This approach is supported in the updated 2011 guidelines. It suggests dividing patients into a high, intermediate and low probability of having asthma based on the presence or absence of typical symptoms. A list can be found in the external link but include typical symptoms such as wheeze, nocturnal cough etc Example of features used to assess asthma (not complete, please see link) Increase possibility of asthma Wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness and cough, worse at night/early morning History of atopic disorder Wheeze heard on auscultation Unexplained peripheral blood eosinophilia Decrease possibility of asthma Prominent dizziness, light-headedness, peripheral tingling Chronic productive cough in the absence of wheeze or breathlessness Repeatedly normal physical examination Significant smoking history (i.e. > 20 pack-years) Normal PEF or spirometry when symptomatic 7
8 Management is based on this assessment: high probability: trial of treatment intermediate probability: see below low probability: investigate/treat other condition For patients with an intermediate probability of asthma further investigations are suggested. The guidelines state that spirometry is the preferred initial test: FEV1/FVC < 0.7: trial of treatment FEV1/FVC > 0.7: further investigation/consider referral Recent studies have shown the limited value of other 'objective' tests. It is now recognised that in patients with normal or near-normal pre-treatment lung function there is little room for measurable improvement in FEV1 or peak flow. A > 400 ml improvement in FEV1 is considered significant before and after 400 mcg inhaled salbutamol in patients with diagnostic uncertainty and airflow obstruction present at the time of assessment if there is an incomplete response to inhaled salbutamol, after either inhaled corticosteroids (200 mcg twice daily beclometasone equivalent for 6-8 weeks) or oral prednisolone (30 mg once daily for 14 days) It is now advised to interpret peak flow variability with caution due to the poor sensitivity of the test diurnal variation % = [(Highest - Lowest PEFR) / Highest PEFR] x 100 assessment should be made over 2 weeks greater than 20% diurnal variation is considered significant COPD: long-term oxygen therapy The 2010 NICE guidelines on COPD clearly define which patients should be assessed for and offered long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT). Patients who receive LTOT should breathe supplementary oxygen for at least 15 hours a day. Oxygen concentrators are used to provide a fixed 8
9 supply for LTOT. Interestingly, NICE do not view smoking as an absolute contraindication to LTOT, despite the obvious safety issues. It states 'If they smoke, warn them about the risk of fire and explosion'. Assess patients if any of the following: very severe airflow obstruction (FEV1 < 30% predicted). Assessment should be 'considered' for patients with severe airflow obstruction (FEV % predicted) cyanosis polycythaemia peripheral oedema raised jugular venous pressure oxygen saturations less than or equal to 92% on room air Assessment is done by measuring arterial blood gases on 2 occasions at least 3 weeks apart in patients with stable COPD on optimal management. Offer LTOT to patients with a po2 of < 7.3 kpa or to those with a po2 of kpa and one of the following: secondary polycythaemia nocturnal hypoxaemia peripheral oedema pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary embolism: management The NICE guidelines of 2012 provided some clarity on how long patients should be anticoagulated for after a pulmonary embolism (PE). Selected points are listed below. Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) or fondaparinux should be given initially after a PE is diagnosed. An exception to this is for patients with a massive PE where thrombolysis is being considered. In such a situation unfractionated heparin should be used. a vitamin K antagonist (i.e. warfarin) should be given within 24 hours of the diagnosis the LMWH or fondaparinux should be continued for at least 5 days or until the international normalised ratio (INR) is 2.0 or above for at least 24 hours, whichever is longer, i.e. LMWH or fondaparinux is given at the same time as warfarin until the INR is in the therapeutic range warfarin should be continued for at least 3 months. At 3 months, NICE advise that clinicians should 'assess the risks and benefits of extending treatment' NICE advise extending warfarin beyond 3 months for patients with unprovoked PE. This essentially means that if there was no obvious cause or provoking factor (surgery, trauma, 9
10 significant immobility) it may imply the patient has a tendency to thrombosis and should be given treatment longer than the norm of 3 months for patients with active cancer NICE recommend using LMWH for 6 months Thrombolysis thrombolysis is now recommended as the first-line treatment for massive PE where there is circulatory failure (e.g. hypotension). Other invasive approaches should be considered where appropriate facilities exist Cystic fibrosis Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disorder causing increased viscosity of secretions (e.g. lungs and pancreas). It is due to a defect in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene (CFTR), which codes a camp-regulated chloride channel In the UK 80% of CF cases are due to delta F508 on the long arm of chromosome 7. Cystic fibrosis affects 1 per 2500 births, and the carrier rate is c. 1 in 25 Organisms which may colonise CF patients Staph aureus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Burkholderia cepacia* Aspergillus *previously known as Pseudomonas cepacia 10
JOINT CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES
 JOINT CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES Authors Dr Ian Benton Respiratory Consultant COCH Penny Rideal Respiratory Nurse COCH Kirti Burgul Respiratory Pharmacist COCH Pam
JOINT CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES Authors Dr Ian Benton Respiratory Consultant COCH Penny Rideal Respiratory Nurse COCH Kirti Burgul Respiratory Pharmacist COCH Pam
COPD/ Asthma. Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer
 COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Treatment Guidelines
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Treatment Guidelines Where appropriate the following should be offered before commencing inhaled treatment: Offer treatment and support to stop smoking. Smoking
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Treatment Guidelines Where appropriate the following should be offered before commencing inhaled treatment: Offer treatment and support to stop smoking. Smoking
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Asthma - Chronic. Presentations of asthma Cough Wheeze Breathlessness Chest tightness
 Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
Asthma - Chronic Definition of asthma Chronic inflammatory disease of the airways 3 components: o Reversible and variable airflow obstruction o Airway hyper-responsiveness to stimuli o Inflammation of
Defining COPD. Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist
 Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Prescribing guidelines: Management of COPD in Primary Care
 Prescribing guidelines: Management of COPD in Primary Care Establish diagnosis of COPD in patients 35 years with appropriate symptoms with history, examination and spirometry (FEV1/FVC ratio < 70%) Establish
Prescribing guidelines: Management of COPD in Primary Care Establish diagnosis of COPD in patients 35 years with appropriate symptoms with history, examination and spirometry (FEV1/FVC ratio < 70%) Establish
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
SABA: VENTOLIN EVOHALER (SALBUTAMOL) SAMA: ATROVENT IPRATROPIUM. Offer LAMA (discontinue SAMA) OR LABA
 COPD GUIDELINES DIAGNOSIS >35 years of age Symptoms of cough, breathlessness, sputum, wheeze, Risk factor (SMOKING) Spirometry (post bronchodilator) FEV1/FVC = 0.7 ENCOURAGE PATIENTS TO BRING INHALERS
COPD GUIDELINES DIAGNOSIS >35 years of age Symptoms of cough, breathlessness, sputum, wheeze, Risk factor (SMOKING) Spirometry (post bronchodilator) FEV1/FVC = 0.7 ENCOURAGE PATIENTS TO BRING INHALERS
COPD in primary care: reminder and update
 COPD in primary care: reminder and update Managing COPD continues to be a major feature of primary care, particularly in practices with a high proportion of M ori and Pacific peoples. COPDX clinical practice
COPD in primary care: reminder and update Managing COPD continues to be a major feature of primary care, particularly in practices with a high proportion of M ori and Pacific peoples. COPDX clinical practice
COPD GOLD Guidelines & Barnet inhaler choices. Dr Dean Creer, Respiratory Consultant, Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust
 COPD GOLD Guidelines & Barnet inhaler choices Dr Dean Creer, Respiratory Consultant, Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust GOLD 2017 Report: Chapters 1. Definition and Overview 2. Diagnosis and Initial
COPD GOLD Guidelines & Barnet inhaler choices Dr Dean Creer, Respiratory Consultant, Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust GOLD 2017 Report: Chapters 1. Definition and Overview 2. Diagnosis and Initial
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition of COPD Airflow obstruction that is: o Not fully reversible o Progressive o Does not change markedly over several months Combination of airway and
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Definition of COPD Airflow obstruction that is: o Not fully reversible o Progressive o Does not change markedly over several months Combination of airway and
If you require this document in another format such as Braille, large print, audio or another language please contact the Trusts Communications Team
 MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) IN ADULTS Summary statement: How does the document support patient care? Staff/stakeholders involved in development: Job titles only Division:
MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) IN ADULTS Summary statement: How does the document support patient care? Staff/stakeholders involved in development: Job titles only Division:
62 year old man with a cough! Dr. Aflah Sadikeen Consultant Respiratory Physician Colombo
 62 year old man with a cough! Dr. Aflah Sadikeen Consultant Respiratory Physician Colombo History Mr.KS, a 62 year-old, has been feeling unwell - Worsening cough for the last 5 days - Feels out of breath
62 year old man with a cough! Dr. Aflah Sadikeen Consultant Respiratory Physician Colombo History Mr.KS, a 62 year-old, has been feeling unwell - Worsening cough for the last 5 days - Feels out of breath
Chronic obstructive lung disease. Dr/Rehab F.Gwada
 Chronic obstructive lung disease Dr/Rehab F.Gwada Obstructive lung diseases Problem is in the expiratory phase Lung disease Restrictive lung disease Restriction may be with, or within the chest wall Problem
Chronic obstructive lung disease Dr/Rehab F.Gwada Obstructive lung diseases Problem is in the expiratory phase Lung disease Restrictive lung disease Restriction may be with, or within the chest wall Problem
COPD is a syndrome of chronic limitation in expiratory airflow encompassing emphysema or chronic bronchitis.
 1 Definition of COPD: COPD is a syndrome of chronic limitation in expiratory airflow encompassing emphysema or chronic bronchitis. Airflow obstruction may be accompanied by airway hyper-responsiveness
1 Definition of COPD: COPD is a syndrome of chronic limitation in expiratory airflow encompassing emphysema or chronic bronchitis. Airflow obstruction may be accompanied by airway hyper-responsiveness
REFERRAL GUIDELINES RESPIRATORY
 REFERRAL GUIDELINES RESPIRATORY Referral Form: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tool (previously known as the Victorian Statewide Referral Form) GP Referral Template This tool is housed
REFERRAL GUIDELINES RESPIRATORY Referral Form: The GP Referral Template is the preferred referral tool (previously known as the Victorian Statewide Referral Form) GP Referral Template This tool is housed
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Guidelines and updates
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Guidelines and updates October 20, 2018 Saratoga Springs, NY COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity in the United
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Guidelines and updates October 20, 2018 Saratoga Springs, NY COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity in the United
Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of COPD
 Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of COPD Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a respiratory disorder largely caused by smoking. It is characterized by progressive, partially
Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of COPD Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a respiratory disorder largely caused by smoking. It is characterized by progressive, partially
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected
 Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Bronchiectasis in Adults - Suspected Clinical symptoms which may indicate bronchiectasis for patients Take full respiratory history including presenting symptoms, past medical & family history Factors
Pulmonary Pearls. Medical Pearls. Case 1: Case 1 (cont.): Case 1: What is the Most Likely Diagnosis? Case 1 (cont.):
 Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
Pulmonary Pearls Christopher H. Fanta, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Medical Pearls Definition: Medical fact that is
Guideline on the Management of Asthma in adults SHSCT
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Management of Asthma in adults Dr A John, Dr J Lindsay Respiratory Medicine/ MUSC Medicine Date Uploaded: 23/11/15 Review Date
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Management of Asthma in adults Dr A John, Dr J Lindsay Respiratory Medicine/ MUSC Medicine Date Uploaded: 23/11/15 Review Date
Decramer 2014 a &b [21]
![Decramer 2014 a &b [21] Decramer 2014 a &b [21]](/thumbs/90/101390504.jpg) Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk. NICE All rights reserved.
 Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Asthma Assessment & Review
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 National Institute for Clinical Excellence Issue date: February 2004 Quick reference guide Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults in primary
National Institute for Clinical Excellence Issue date: February 2004 Quick reference guide Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults in primary
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3. Chronic Cough Guidelines
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
COPD/Asthma. Prudence Twigg, AGNP
 COPD/Asthma Prudence Twigg, AGNP COPD/Asthma Qualifying Diagnosis Known diagnosis of COPD/asthma or CXR showing COPD with hyperinflated lungs and no infiltrates + two or more: Wheezing, SOB, increased
COPD/Asthma Prudence Twigg, AGNP COPD/Asthma Qualifying Diagnosis Known diagnosis of COPD/asthma or CXR showing COPD with hyperinflated lungs and no infiltrates + two or more: Wheezing, SOB, increased
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update) Issued: June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg101
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update) Issued: June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 guidance.nice.org.uk/cg101
Interpreting Spirometry. Vikki Knowles BSc(Hons) RGN Respiratory Nurse Consultant G & W`CCG
 Interpreting Spirometry Vikki Knowles BSc(Hons) RGN Respiratory Nurse Consultant G & W`CCG Why Spirometry? supports diagnosis classifies defect - obstructive/restrictive assesses -severity of defect -
Interpreting Spirometry Vikki Knowles BSc(Hons) RGN Respiratory Nurse Consultant G & W`CCG Why Spirometry? supports diagnosis classifies defect - obstructive/restrictive assesses -severity of defect -
Provider Respiratory Inservice
 Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Version Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Version Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma
Quality Care Innovation lead clinician for integrated respiratory service georges ng* man kwong
 Working in partnership Quality Care Innovation lead clinician for integrated respiratory service georges ng* man kwong chest physician pronounced ning qualified 1990 chief clinical information officer
Working in partnership Quality Care Innovation lead clinician for integrated respiratory service georges ng* man kwong chest physician pronounced ning qualified 1990 chief clinical information officer
Managing Exacerbations of COPD (Version 3.0)
 Managing Exacerbations of COPD (Version 3.0) Guideline Readership This guideline is intended for use in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation.
Managing Exacerbations of COPD (Version 3.0) Guideline Readership This guideline is intended for use in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation.
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Page 1 of 5 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is an 'umbrella' term for people with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. With COPD the airflow to the
Page 1 of 5 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is an 'umbrella' term for people with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both. With COPD the airflow to the
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Address Comorbidities
 Greater Manchester COPD Management Plan Non-pharmacological management for ALL patients Smoking Cessation Annual Flu Vaccination Pulmonary Rehabilitation Increase daily activity Inhaler Technique Measure
Greater Manchester COPD Management Plan Non-pharmacological management for ALL patients Smoking Cessation Annual Flu Vaccination Pulmonary Rehabilitation Increase daily activity Inhaler Technique Measure
GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES
 October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
COPD and Asthma Update. April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute
 COPD and Asthma Update April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute What we ll be talking about COPD: diagnosis, management of stable COPD, COPD exacerbations Asthma: diagnosis,
COPD and Asthma Update April 29 th, 2017 Rachel M Taliercio, DO Staff, Respiratory Institute What we ll be talking about COPD: diagnosis, management of stable COPD, COPD exacerbations Asthma: diagnosis,
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma
 Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
Community COPD Service Protocol
 Community COPD Service Protocol Acknowledgements This protocol is based on the following documents: 1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults
Community COPD Service Protocol Acknowledgements This protocol is based on the following documents: 1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults
ASTHMA. Dr Liz Gamble BRI
 ASTHMA Dr Liz Gamble BRI Diagnosis Clinical: wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness, cough Variable airflow obstruction: peak flow chart, spirometry with reversibility to bronchodilators Airways hyper-responsiveness
ASTHMA Dr Liz Gamble BRI Diagnosis Clinical: wheeze, breathlessness, chest tightness, cough Variable airflow obstruction: peak flow chart, spirometry with reversibility to bronchodilators Airways hyper-responsiveness
COPD: Current Medical Therapy
 COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
Exacerbations of COPD. Dr J Cullen
 Exacerbations of COPD Dr J Cullen Definition An AECOPD is a sustained worsening of the patient s clinical condition from their stable state that is beyond their usual day-to-day variation is acute in onset
Exacerbations of COPD Dr J Cullen Definition An AECOPD is a sustained worsening of the patient s clinical condition from their stable state that is beyond their usual day-to-day variation is acute in onset
Guideline Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over s: diagnosis and management Draft for consultation, July 0 This guideline covers diagnosing and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over s: diagnosis and management Draft for consultation, July 0 This guideline covers diagnosing and
Salford COPD Treatment Pathway
 Salford COPD Treatment Pathway Development led by Helen Pyne with Salford Asthma and Respiratory Team (SART) Department Respiratory Medicine Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust Hope Hospital, Stott Lane,
Salford COPD Treatment Pathway Development led by Helen Pyne with Salford Asthma and Respiratory Team (SART) Department Respiratory Medicine Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust Hope Hospital, Stott Lane,
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Pneumonia. Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine
 Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Spirometry in primary care
 Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Guideline
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Medicines Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Medicines Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (Chronic & Acute) Guidelines for Primary Care Guideline Authors: Shaneez Dhanji (Wandsworth CCG) Samantha Prigmore (St George s Hospital)
Medicines Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (Chronic & Acute) Guidelines for Primary Care Guideline Authors: Shaneez Dhanji (Wandsworth CCG) Samantha Prigmore (St George s Hospital)
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
Cystic Fibrosis. Jennifer McDaniel, BS, RRT-NPS
 Cystic Fibrosis Jennifer McDaniel, BS, RRT-NPS Overview Cystic fibrosis is the most common fatal, inherited disease in the U. S. CF results from a defective autosomal recessive gene One copy of gene =
Cystic Fibrosis Jennifer McDaniel, BS, RRT-NPS Overview Cystic fibrosis is the most common fatal, inherited disease in the U. S. CF results from a defective autosomal recessive gene One copy of gene =
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
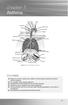 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM
 HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM ID NUMBER: VERSION: A 10/23/2015 0a. Form Completion Date... / / 0b. Staff Code... 0c. Event ID: 0d. Event Date: / / Instructions: Answers are derived from the medical
HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM ID NUMBER: VERSION: A 10/23/2015 0a. Form Completion Date... / / 0b. Staff Code... 0c. Event ID: 0d. Event Date: / / Instructions: Answers are derived from the medical
Algorithm for the use of inhaled therapies in COPD Version 2 May 2017
 Algorithm for the use of inhaled therapies in COPD This document has been revised by the Berkshire West Respiratory Network to support clinicians in selecting the most appropriate, cost effective treatments
Algorithm for the use of inhaled therapies in COPD This document has been revised by the Berkshire West Respiratory Network to support clinicians in selecting the most appropriate, cost effective treatments
COPD Update. Muhammad Talha Khan MD. COPD Exacerbations. COPD Clinical Importance. COPD Pathophysiology. Overview/Objectives
 Overview/Objectives COPD Update Muhammad Talha Khan MD Pulmonologist St Croix Regional Medical Center, St Croix Falls, WI. Overview of COPD and disease impact Classification of COPD Severity Treatment
Overview/Objectives COPD Update Muhammad Talha Khan MD Pulmonologist St Croix Regional Medical Center, St Croix Falls, WI. Overview of COPD and disease impact Classification of COPD Severity Treatment
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE (COPD), BRONCHIAL ASTHMA
 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE (COPD), BRONCHIAL ASTHMA GOLD GINA Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world.1 COPD is projected to
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE (COPD), BRONCHIAL ASTHMA GOLD GINA Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world.1 COPD is projected to
Referring for specialist respiratory input. Dr Melissa Heightman Consultant respiratory physician, UCLH,WH, CNWL
 Referring for specialist respiratory input Dr Melissa Heightman Consultant respiratory physician, UCLH,WH, CNWL Respiratory Specialist- who? GPSI Community Team Secondary Care Respiratory physician and
Referring for specialist respiratory input Dr Melissa Heightman Consultant respiratory physician, UCLH,WH, CNWL Respiratory Specialist- who? GPSI Community Team Secondary Care Respiratory physician and
Clinical guideline Published: 23 June 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg101
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 June 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg101 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 23 June 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg101 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights
COPD: A Renewed Focus. Disclosures
 COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
Guideline Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over s: diagnosis and management Draft for consultation, February 0 This guideline covers diagnosing
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over s: diagnosis and management Draft for consultation, February 0 This guideline covers diagnosing
COPD. Helen Suen & Lexi Smith
 COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
Bronchial asthma. E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics. Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013
 Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek
 Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
(Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Over the last several years various national and
 Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
 Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
ASTHMA & RESPIRATORY FOUNDATION NZ ADULT ASTHMA GUIDELINES: A QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 1
 ASTHMA & RESPIRATORY FOUNDATION NZ ADULT ASTHMA GUIDELINES: A QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 1 1. Richard Beasley, Bob Hancox, Matire Harwood, Kyle Perrin, Betty Poot, Janine Pilcher, Jim Reid, Api Talemaitoga,
ASTHMA & RESPIRATORY FOUNDATION NZ ADULT ASTHMA GUIDELINES: A QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 1 1. Richard Beasley, Bob Hancox, Matire Harwood, Kyle Perrin, Betty Poot, Janine Pilcher, Jim Reid, Api Talemaitoga,
NICE guideline Published: 5 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng115
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management NICE guideline Published: 5 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng115 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management NICE guideline Published: 5 December 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng115 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Co. Durham & Darlington Respiratory Network COPD Treatment Guide
 Co. Durham & Darlington Respiratory Network COPD Treatment Guide Age > 35, Productive cough, Breathless, Smoking Hx Spirometry (post-bronchodilator) COPD Advice Intensive smoking cessation support Vaccination
Co. Durham & Darlington Respiratory Network COPD Treatment Guide Age > 35, Productive cough, Breathless, Smoking Hx Spirometry (post-bronchodilator) COPD Advice Intensive smoking cessation support Vaccination
Assessing wheeze in pre-school children
 Assessing wheeze in pre-school children 8 Wheeze in children aged less than five years has many potential causes. Often it is regarded as the first sign of asthma, however, a substantial proportion of
Assessing wheeze in pre-school children 8 Wheeze in children aged less than five years has many potential causes. Often it is regarded as the first sign of asthma, however, a substantial proportion of
Asthma ASTHMA. Current Strategies for Asthma and COPD
 Current Strategies for Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor of Medicine Chair, Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco (UCSF) San Francisco,
Current Strategies for Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor of Medicine Chair, Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco (UCSF) San Francisco,
Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center
 Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center dtaylor@ochsner.org Observations from Yesterday EPIC is epidemic No EMR No Way!!! Accountability/Benchmarking
Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center dtaylor@ochsner.org Observations from Yesterday EPIC is epidemic No EMR No Way!!! Accountability/Benchmarking
Medical Directive. Activation Date: April 24, 2013 Review due by: December 1, Medical Director: Date: December 1, 2017
 Medical Directive Pre and Post Bronchodilator Spirometry Testing and Treatment Initiation Assigned Number: Activation Date: April 24, 2013 Review due by: December 1, 2019 23 Approval Signature & Date Medical
Medical Directive Pre and Post Bronchodilator Spirometry Testing and Treatment Initiation Assigned Number: Activation Date: April 24, 2013 Review due by: December 1, 2019 23 Approval Signature & Date Medical
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
COPD. Dr.O.Paknejad Pulmonologist Shariati Hospital TUMS
 IN THE NAME OF GOD COPD Dr.O.Paknejad Pulmonologist Shariati Hospital TUMS Definition of COPD* COPD is a preventable and treatable chronic lung disease characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully
IN THE NAME OF GOD COPD Dr.O.Paknejad Pulmonologist Shariati Hospital TUMS Definition of COPD* COPD is a preventable and treatable chronic lung disease characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
You ve come a long way, baby.
 COPD Dr Badri Paudel Dept of Medicine GMC/CHRC 4/22/12 badri@gmc 2 You ve come a long way, baby. Wayne McLaren Former Marlboro Man 4/22/12 badri@gmc 3 Age 30 a robust young man Age 51 riding into the sunset
COPD Dr Badri Paudel Dept of Medicine GMC/CHRC 4/22/12 badri@gmc 2 You ve come a long way, baby. Wayne McLaren Former Marlboro Man 4/22/12 badri@gmc 3 Age 30 a robust young man Age 51 riding into the sunset
Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD
 Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor
Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor
Quality Improvement Tool Instruction Guide GRASP-COPD
 PRIMIS: Quality Improvement Tool Instructional Guide Quality Improvement Tool Instruction Guide GRASP-COPD The GRASP-COPD quality improvement tool has been developed by PRIMIS and delivered in partnership
PRIMIS: Quality Improvement Tool Instructional Guide Quality Improvement Tool Instruction Guide GRASP-COPD The GRASP-COPD quality improvement tool has been developed by PRIMIS and delivered in partnership
COPD Treatable. Preventable.
 My COPD Action Plan Patient s Copy (Patient s Name) Date Canadian Respiratory COPD Treatable. Preventable. This is to tell me how I will take care of myself when I have a COPD flare-up. My goals are My
My COPD Action Plan Patient s Copy (Patient s Name) Date Canadian Respiratory COPD Treatable. Preventable. This is to tell me how I will take care of myself when I have a COPD flare-up. My goals are My
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable: Secondary Outcome/Efficacy Variable(s): Statistical Methods:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Abstract Whittaker C, BPharm, MRPharmS Amayeza Info Centre Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease affects millions of people, has a major impact on quality of life
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Abstract Whittaker C, BPharm, MRPharmS Amayeza Info Centre Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease affects millions of people, has a major impact on quality of life
