In 1956, the world's first pressurized MDI was introduced. Invented by Charles Thiel and two colleagues at Riker Laboratories.
|
|
|
- Jeffery Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEVICE
2 In 1956, the world's first pressurized MDI was introduced. Invented by Charles Thiel and two colleagues at Riker Laboratories. The idea was born after the daughter of a Riker president asked "Why can't they put my asthma medicine in a spray can, like they do hair spray?"
3 SPACER SYSTEMS Maison GL, inventor; Riker Laboratories, Inc., assignee: Aerosol Dispensing Apparatus. United States patent US 3,001,524. Priority date March 21, 1956; filed March 5,1957; issued September 26, Medihaler pmdi: The original pmdi was equipped with an elongated mouthpiece, arguably making it the first tube spacer. Maison 1956
4 Charles Thiel
5 SPACER SYSTEMS I soon tired of gluing my fingers together and the following year a plastics company manufactured the device Beclomethasone Aerosol by Reservoir Bottle (BARB). Spacer system comprised a 1.2-L vinegar bottle and facemask with one-way valve. Freigang 1977
6 Spacers (no valves) Valved holding Chambers VHC
7 PRIMARY OBJECTIVE OF VHC Minimize the need for coordination between actuation of pmdi and inhalation hand-lung coordination (present the aerosol as a standing cloud of particles) Ensure that the aerosol particles trail the inspiratory flow Reduce the proportion of the dose contained in large particles and increase the proportion contained in small particles
8 Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical that is used to enhance the clarity and durability of some clear, plastic products. The Government of Canada has taken steps to ban the use of BPA in baby bottles to reduce newborn and infant exposure.
9 Sources of aerosol loss within the spacer Impaction Electrostatic attraction time dependent Dead space Leaking Leaking Valve insufficiency Sedimentation time dependent
10
11 Mean net fine-particle-dose electrical charge of aerosols from commercially available metered-dose inhalers
12 Barry 1999
13 Rau 2006
14 ELECTROSTATIC CHARGE new detergent-coated Kwok 2006
15 ELECTROSTATIC CHARGE Dose delivered to filter during 100 consecutive acutations of BUD- Nebuchamber (nonelectrostatic) and FP-Babyhaler (electrostatic) Nebuchamber Babyhaler Increase 0.8% in day Berg 1998
16 dead space Shah 2006
17 TV 18 mon TV 6 mon Shah 2006
18
19
20 CHALLENGES OF INHALED THERAPIES FOR YOUNG CHILDREN Small tidal volume Small airways Rapid respiration Inability to hold breath with inhaled medication Nose breathing Aversion to masks Cognitive ability Fussiness and crying Everard 2003
21 Pattern respiratorio nel bambino
22 Obligate nasal breathing in the newborn Intranarial position of the larynx, secure a continuous airway from the nose to the bronchi, therefore decreases the risk of pulmonary contamination by swallowed matter.
23 GROWTH OF NASAL-LARYNGEAL AIRWAYS IN CHILDREN Xi 2013
24 GROWTH OF NASAL-LARYNGEAL AIRWAYS IN CHILDREN Inhalation airflow under quiet breathing conditions Xi 2013
25 PULMONARY OBSTRUCTION Lung volumes and ventilation distribution in healthy and obstructive disease. Tidal Volume, Total Lung Capacity Functional Residual Capacity Lannefores 2006
26 INHALATION Changes in FEV1 for three different routes of administration with terbutaline. Greater clinical effect was seen with drug delivered as inhaled aerosol from a metered-dose inhaler, compared to similar or larger doses delivered orally or by subcutaneous injection.
27 Adults Normal (n=10) FEV1 110 % FEF % Mean dose SAL mg 3.28 ( ) Lower plasma concentration 1.31 vs 2,4 and 2.45 ng/ml Mild (n=10) FEV1 102 % FEF % Mean dose SAL mg 3.13 ( ) Severe (n=10) FEV1 49 % FEF % Mean dose SAL mg 3.11 ( ) 40ug/Kg Salbutamol Ventstream Neb-mouthpiece plasma SAL peak (Cmax) average (Cav) levels Lipworth 1997
28 EFFECT OF ph ON ALBUTEROL TRASPORT Effect of ph on overall albuterol transport in human bronchial epithelial cells. A decrease in ph is known to change the proton acceptor sites in tight junctions and decrease the paracellular permeability of cations. Unwalla 2012
29 SALBUTAMOL Blake 2008
30 SALBUTAMOL Salbutamol is a selective β2-adrenoreceptor agonist which relaxes airway wall smooth muscle (ASM) irrespective of the mechanism leading to contraction. When inhaled, salbutamol is absorbed into the pulmonary circulation via the alveolar epithelium. There is also evidence to suggest that epithelial cells of conducting airways transport drug from luminal to basal surfaces, that is, into the walls of conducting airways. This suggests that inhaled drug delivery should achieve higher ASM tissue salbutamol concentrations than the intravenous route, on a dose-for-dose basis Starkey 2014
31 SALBUTAMOL IN AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION Acute airflow obstruction due to airway wall oedema and/or mucus plugging, as might occur in acute bronchiolitis, is not relieved by salbutamol. There is no convincing data to show that infants with recurrent/persistent wheeze benefit from salbutamol Either. Physiological measures of airway obstruction show that salbutamol does reduce airway obstruction in some with recurrent/persistent wheeze. However, most have no response to salbutamol or respond paradoxically. These findings support the presence of functional β2 adrenoreceptors and ASM in the very young. The lack of clinical benefit implies that airflow obstruction in this group of patients is not predominantly due to ASM-induced bronchoconstriction. Starkey 2014
32 SALBUTAMOL The bronchodilator action of salbutamol in stable asthma is associated with blood concentrations between 5 and 20 ng/ml for children and adults. Concentration of salbutamol associated with adverse reactions in children is not known. In adults, salbutamol toxicity is associated with blood concentrations greater than 30 ng/ml with a putative lethal level of >160 ng/ml. Very high blood salbutamol concentrations ( ng/ml) have been recorded inchildren receiving intravenous salbutamol and mechanical ventilation for severe asthma. Starkey 2014
33 BIGGER MAY BE BETTER: TARGETED Β2-AGONIST THERAPY? Placebo Δ 15 µg of 6µm pmdi 200µg 15 µg of 3 µm 15 µg of 1.5µm 30µg of 6µm pmdi 200µg 30µg of 3 µm 30µg of 1.5µm Placebo Usmani 2005
34 SALBUTAMOL SYSTEMIC EFFECTS Glucose (rapid dose related) & insulin (inadequate) BSL liver muscle ß 2 glycogenolysis, hyperinsulinaemia potassium K + (rapid dose related) Na/K-ATPase intracellular shift lactate lactic acidosis(dose related) anaerobic glycolysis in muscle, increased vent demand cardiovascular BP HR vasodilation skeletal muscle beds + reflex tachycardia, vasodilation pulmonary bed uncouples VQ match tachycardia cardiac ß 1, direct inotrope, prolongs QT c interval, cardiac ß 2 exacerbated by low K + low Mg increases minute ventilation metabolic rate oxygen consumption CO 2 production Imbalance fast- and slow-twitch muscle groups of extremities Tremor development of tolerance (reduced ß receptor sensitivity) Sears 2002 Tobin 2005
35 SIDE EFFECTS SALBUTAMOL Intravenous (IV) albuterol (250 ug) causes Decreases in serum potassium (mean 0.6 ±0.3 meq/l) Glucose increases (mean 25±15 mg/dl) Heart rate increases (mean 11±6 beats/mm) Rohr 1986
36 Tremor,Hypo-K - Direct stimulation skeletal muscle β 2 -adrenoceptors Tachicardia - Direct stimulation cardiac β 2 - adrenoceptors - Indirect activation periphral R (vasodilatation) and consequent reflex vagal withdrawal Fowler 2001
37 SIDE EFFECTS SALBUTAMOL p = (p < 0.001) 26 patients; age >16 years Nebulized salbutamol (2.5 mg) x3 times at every hour. Sahan 2012
38 SALBUTAMOL KINTEICS INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION Simulations for children ( =3 year old,δ=7 year old, =12 year old) were developed on 15 mcg/kg (max 250 mcg) bolus dose over 10 min followed by continuous infusion (CI)=1 mcg/kg/min for 3 hours. Simulations for adults ( ) Starkey 2014
39 INTRAVENOUS SALBUTAMOL DOSING RECOMMENDATIONS BRITISH NATIONAL FORMULARIES FOR CHILDREN AND ADULTS ADULTS CHILDREN Bolus dose 250 mcg slow intravenous injection Less than 2 years age 5 mcg/kg Over 2 years age 15 mcg/kg; maximum 250 mcg All doses over 5 min Continuous infusion 3 20 mcg/min 1 5 mcg/kg/min
40 INTRAVENOUS SALBUTAMOL Bolus + CI Bolus=15 mcg/kg (max 250 mcg) CI=1 mcg/kg/min or 3 mcg/min Cmax (ng/ml) maximum plasma concentration AUC (hr.ng/ml) area under curve (total systemic exposure) Adult (70 kg) Child 3 years (14 kg) Child 7 years (23 kg) Child 12 years (39 kg) Starkey 2014
41 L/min SABUTAMOL: NEBULIZED VS I.V. mm Hg Neb superior in hypercapnic acute asthma 200 PEF ** Pa CO2 Clinical Index * 100 * ** ** N = hr 0 1 hr 0 NEB Group IV Group salbutamol NEB : 5mg x 2 IV : 0.5mg in 1h *p 0.05 **p hr Salmeron 1994
42 ASTHMATICS: TOO DRUNK Time response curve for breath alcohol level using Ethylometer (679T) after Salamol, inhalation for 16 normal volunteers O Conell 2006
43 Holding chambers (spacers) versus nebulisers for beta-agonist treatment of acute asthma 2295 children and 614 adults included in 27 trials from emergency room and community settings. Method of delivery of ß2-agonist did not appear to affect hospital admission rates. In adults, the relative risk of admission for spacer versus nebuliser was 0.97 (95% CI 0.63 to 1.49). The relative risk for children was 0.72 (95% CI: 0.47 to 1.09). In children, length of stay in the emergency department was significantly shorter when the spacer was used, with a mean difference of hours (95% CI: to hours). Length of stay in the emergency department for adults was similar for the two delivery methods. PEF and FEV1 were also similar for the two delivery methods. Pulse rate was lower for spacer in children, mean difference -6.27% baseline (95% CI: to -4.25% baseline). Authors conclusions : MDIwith spacer produced outcomes that were at least equivalent to nebuliser delivery. Spacers may have some advantages compared to nebulisers for children with acute asthma Updated January 2008 Cates 2008
44 Aeroch Aeroch Babyhaler Aeroch Babyhaler Bayhaer/Vol Volumetic Aeroch/ACE Acorn Unkown Ratio Nevoni Ratio S/N 1/ 4-10 Pulmo-Aide Ratio S/N 1/3.5 Marquest Ratio S/N 1 /4 Ultrasonic Ratio S/N 1/3 Airve 5 Ratio S/N 1/3-1/5 Neb not stated Ratio S/N 1.3/1 Pari Unkown Ratio Forest plot of comparison 1 Spacer (chamber) versus Nebuliser (Multiple treatment studies) outcome: 1.1 Hospital admission Cates 2008
45 Aeroch Water bott Babyhal/Vol Nevoni Ratio S/N 1/ 4-10 Fleam Unkown Ratio Airve 5 Ratio S/N 1/3-1/5 Forest plot of comparison 1 Spacer (chamber) versus Nebuliser (Multiple treatment studies) outcome: 1.3 Duration in emergency department (hours) Cates 2008
46 Volumetic Aeroch Aeroch Water bott. Babyhaler Aeroch Bayhaer/Vol Volumetic Neb not stated Acorn Unkown Ratio Nevoni Ratio S/N 1/ 4-10 Fleam Unkown Ratio Pulmo-Aide Ratio S/N 1/3.5 Marquest Ratio S/N 1/4 Airve 5 Ratio S/N 1/3-1/5 Neb not stated Ratio S/N 1.3/1 Forest plot of comparison 1 Spacer (chamber) versus Nebuliser (Multiple treatment studies) outcome: 1.9 Rise in pulse rate (% baseline). Cates 2008
47 19 asthmatics (12 ) mean (SD) age 53.7 (17.1) 2-4 days after exacerbation SAL urine 30, SAL urine 24 (HPLC); lung function MDI + VHC Volumetic- treated 5x100 µg SAL NEB Sidestream-Respironics 5000 µg in 4 ml I vitro emittted dose (µg) (8.8) (49.1) % fine particle fraction 44.0 (2.4) 80.1 (2.0) Fine particle dose (3.9) (39.3) MMAD (µm) 2.8 (0.1) 2.2 (0.4) Geometric standard deviation 1.7 (0.1) 3.45 (1.1) Mazhar 2006
48 Nebulizers VS Inhalers: And the Winner Is? MDI + VHC NEB USAL 0.5 (µg) 14.7 (7.2) 14.1 (7.6) USAL 0.5 (% nominal) 2.94 (1.45) 0.28 (0.15)* USAL 24 (µg) (53.4) (55.1)* SAL left i the device (µg) (47.6) 3117(414)* SAL dose emitted (µg) (47.6) 1883(413.5)* USAL 0.5 (% dose emitted) 5.74(2.99) 0.79 (0.51)* FEV1 pre (% predicted) 42.2 (15.6) 46.9 (18.2) Δ FEV1 in 60 min 9.6 (12.4) 6.5 (7.7) Mazhar 2006
49 Pediatric breathing Simulator Nominal dose 5 mg Salbutamol LC Star+Turboboy LC Plus+Turboboy LC Star+air Sidestream+Portaneb Ventstream+air Ventstream+Portaneb Cirrus+Novair II Bary 1999
50 Inhaled drug % Drug lost to ambient % Drug lost in nebulizer % Time min Misty-Neb SideStream Pari LCD Circulaire AeroEclipse mg in 3 ml of albuterol sulfate and powred by O2 at 8L/min Rau 2004
51 INITIAL TREATMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN >2 YRS There is good evidence supporting recommendations for the initial treatment of acute asthma presenting to primary and secondary healthcare resources. There is less evidence to guide the use of second line therapies to treat the small number of severe cases poorly responsive to first line measures. β2 agonists should be given as first line treatment. Increase β2 agonist dose by two puffs every two minutes according to response up to ten puffs. Children with acute asthma at home and symptoms not controlled by up to 10 puffs of salbutamol via pmdi and spacer, or mg of nebulised salbutamol, should seek urgent medical attention. Additional doses of bronchodilator should be given as needed whilst awaiting medical attention if symptoms are severe. Paramedics attending to children with acute asthma should administer nebulised salbutamol driven by oxygen if symptoms are severe whilst transferring the child to the emergency department. Children with severe or life threatening asthma should be transferred to hospital urgently. British Guideline 2012
52 INHALED β2 agonists 2-4 puffs of a salbutamol 100 ug repeated every minutes according to clinical response might be sufficient for mild attacks although up to 10 puffs might be needed for more severe asthma. Single puffs should be given one at a time and inhaled separately with five tidal breaths. If hourly doses of bronchodilators are needed for more than 4-6 hours, the patient should be switched to nebulised bronchodilators. Children with severe or life threatening asthma (SpO2 <92%) should receive frequent doses of nebulised bronchodilators driven by oxygen (2.5-5 mg salbutamol or 5-10 mg terbutaline). Doses can be repeated every min. Continuous nebulised β2 agonists are of no greater benefit than the use of frequent intermittent doses in the same total hourly dosage. If there is poor response to the initial dose of β2 agonists, subsequent doses should be given in combination with nebulised ipratropium bromide. British Guideline 2012
53 TREATMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA: SABA A SABA is recommended for all patients The repetitive or continuous administration of SABAs is the most effective means of reversing airflow obstruction. Continuous administration of SABA may be more effective in severely obstructed patients. Because of the risk of cardiotoxicity, use only selective SABA (albuterol, levabuterol) in high doses. In mild or moderate exacerbation, equivalent bronchodilation can be achieved either by high doses (4-12 puffs) of SABA by MDI + chamber under supervision of trained personnel or by nebulizer therapy. Nebulized therapy may be preferred for patients who are unable to cooperate. The onset of action of SABAs is less than 5 minutes; repetitive administration produces incremental bronchodilation. Duration of action of brochodilation from SABAs in severe asthma exacerbation is not known (can be significantly shorter than that in stable asthma) NHLBI-NAEPP 2007
54 Recommended dosages of inhaled β2 agonists BRITISH GL MDI via spacer Salbutamol or Terbutaline 10 puffs given singly at second intervals (repeat after15-30 minutes if necessary) Nebulised (Repeat after minutes if necessary) salbutamol Terbutaline > 5 yrs: 5 mg < 5 yrs: 2.5 mg > 5 yrs: 10 mg < 5 yrs: 5 mg LG SIP 2008 Nebulizzazione Spary predosato Nebulizzazione continua 0,15 mg/kg/dose (1 goccia 0,25 mg), (10 Kg. 6 gocce) ripetere ogni minuti (max 5 mg) (33Kg...20 gocce) 2-4 ( mcg) spruzzi, fino a 10 spruzzi nelle forme più gravi, ripetuti se necessario ogni min nella prima ora, poi ogni 1-4 ore secondo la necessità. 0,5-5 mg/kg/ora
55 Kantar 2015
Perceptual reasons for resistance to change in the emergency department use of holding chambers for children with asthma
 Perceptual reasons for resistance to change in the emergency department use of holding chambers for children with asthma The need for sufficient human resources and deal with the perceived increase in
Perceptual reasons for resistance to change in the emergency department use of holding chambers for children with asthma The need for sufficient human resources and deal with the perceived increase in
Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience
 Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience 8th Annual North Regional Respiratory Care Conference Minnesota & Wisconsin Societies for Respiratory Care Mayo Civic
Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience 8th Annual North Regional Respiratory Care Conference Minnesota & Wisconsin Societies for Respiratory Care Mayo Civic
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline
 Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Acute Severe Asthma Document Control Information Author E Randle Author Position CATS Consultant Document Owner E Polke Document Owner Position Co-ordinator
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Acute Severe Asthma Document Control Information Author E Randle Author Position CATS Consultant Document Owner E Polke Document Owner Position Co-ordinator
It is recommended that a mask and protective eyewear be worn when providing care to a patient with a cough
 UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
Management of acute asthma in children in emergency department. Moderate asthma
 152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
PEDIATRIC ACUTE ASTHMA SCORE (P.A.A.S.) GUIDELINES. >97% 94% to 96% 91%-93% <90% Moderate to severe expiratory wheeze
 Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update. Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch
 Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch Acknowledgements BTS/SIGN guidelines GINA guidelines NAEPP guidelines
Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch Acknowledgements BTS/SIGN guidelines GINA guidelines NAEPP guidelines
patient group direction
 SALBUTAMOL v01 1/12 SALBUTAMOL PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
SALBUTAMOL v01 1/12 SALBUTAMOL PGD Details Version 1.0 Legal category Staff grades Approved by POM Paramedic (Non-ECP) Nurse (Non-ECP) Emergency Care Practitioner (Paramedic) Emergency Care Practitioner
Paediatric pulmonary drug delivery: considerations in asthma treatment
 Review Paediatric pulmonary drug delivery: considerations in asthma treatment 1. Introduction 2. Guideline recommendations 3. Factors affecting drug delivery to the lung 4. Nebulisers 5. Metered-dose inhalers
Review Paediatric pulmonary drug delivery: considerations in asthma treatment 1. Introduction 2. Guideline recommendations 3. Factors affecting drug delivery to the lung 4. Nebulisers 5. Metered-dose inhalers
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS. Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK
 THE PRESS-AND-BREATHE pmdi ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK steve.newman@physics.org Compact, portable, convenient Asthma
THE PRESS-AND-BREATHE pmdi ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK steve.newman@physics.org Compact, portable, convenient Asthma
Recurrent wheezing illnesses 24.9% Similar to Australia Above global averages
 Prof Mike South Department of General Medicine Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Australia www.mikesouth.org.au Asthma is very common in Australia Approx 25% children have recurrent wheezing illnesses
Prof Mike South Department of General Medicine Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Australia www.mikesouth.org.au Asthma is very common in Australia Approx 25% children have recurrent wheezing illnesses
Asthma/wheeze management plan
 Asthma/wheeze management plan Name of Patient Date of Birth NHS Number GP surgery Telephone Next appointment Children s Assessment unit/ward telephone Out of hours call 111 Open access Y/N Until date Some
Asthma/wheeze management plan Name of Patient Date of Birth NHS Number GP surgery Telephone Next appointment Children s Assessment unit/ward telephone Out of hours call 111 Open access Y/N Until date Some
Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health.
 Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health Background: These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and
Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health Background: These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and
10/6/2014. Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement. Disclosure. Objectives for this talk.
 Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Pediatrics in mechanical ventilation
 Pediatrics Optimization Intitulé du cours of aerosol therapy in mechanical ventilation Thèmes donnés Ermindo Di Paolo, PhD Departments of Pharmacy and Pediatrics Lausanne University Hospital Switzerland
Pediatrics Optimization Intitulé du cours of aerosol therapy in mechanical ventilation Thèmes donnés Ermindo Di Paolo, PhD Departments of Pharmacy and Pediatrics Lausanne University Hospital Switzerland
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract
 Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Nguyen Tien Dung A/Prof. PhD. MD Head of Pediatric Department - Bach Mai Hospital
 Nguyen Tien Dung A/Prof. PhD. MD Head of Pediatric Department - Bach Mai Hospital A girl patient 11 years old admitted to Bach mai Hospital at 4h15, 12nd November because of difficult breathing She has
Nguyen Tien Dung A/Prof. PhD. MD Head of Pediatric Department - Bach Mai Hospital A girl patient 11 years old admitted to Bach mai Hospital at 4h15, 12nd November because of difficult breathing She has
An update on inhalation devices
 OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma
 Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma Talk Outline Case Delivery of bronchodilators Meter-dose inhalers and spacers Continuous nebulization
Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma Talk Outline Case Delivery of bronchodilators Meter-dose inhalers and spacers Continuous nebulization
Latex Free. An affordable, easy to use, high density, small volume nebulizer with a breath enhanced design! Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer
 Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients alike. This
Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients alike. This
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
SCVMC RESPIRATORY CARE PROCEDURE
 Page 1 of 8 Rev. - 11/99, 11/05, 4/11 R-NC - 08/99,08/00, 04/03,10/08,04/09, 07/11, 6/12 B7180-43 OBJECTIVE Continuous Nebulization allows for continuous, controlled drug delivery to the lung, avoiding
Page 1 of 8 Rev. - 11/99, 11/05, 4/11 R-NC - 08/99,08/00, 04/03,10/08,04/09, 07/11, 6/12 B7180-43 OBJECTIVE Continuous Nebulization allows for continuous, controlled drug delivery to the lung, avoiding
Patricia KP Burnell Inhalation Product Development
 Patricia KP Burnell Inhalation Product Development Inhaled products: types, development The critical parameters In-vitro testing Ex-vivo testing What dose? Product Development: drug medicine Safety and
Patricia KP Burnell Inhalation Product Development Inhaled products: types, development The critical parameters In-vitro testing Ex-vivo testing What dose? Product Development: drug medicine Safety and
Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test
 powder for solution, for inhalation Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test Provocholine is a registered trademark of Methapharm Inc. Copyright Methapharm Inc. 2016. All rights reserved. Healthcare professionals
powder for solution, for inhalation Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test Provocholine is a registered trademark of Methapharm Inc. Copyright Methapharm Inc. 2016. All rights reserved. Healthcare professionals
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU
 Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
CLINICAL RELEVANCE OF IN VITRO PARTICLE SIZING DATA. Steve Newman, PhD Nottingham, UK November 2006
 IPAC-RS Conference 6-8 November 2006 CLINICAL RELEVANCE OF IN VITRO PARTICLE SIZING DATA Steve Newman, PhD Nottingham, UK November 2006 IPAC-RS Conference 6-8 November 2006 1 EFFECT OF PARTICLE SIZE ON
IPAC-RS Conference 6-8 November 2006 CLINICAL RELEVANCE OF IN VITRO PARTICLE SIZING DATA Steve Newman, PhD Nottingham, UK November 2006 IPAC-RS Conference 6-8 November 2006 1 EFFECT OF PARTICLE SIZE ON
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and the delivery of pediatric bronchodilator therapy
 Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and the delivery of pediatric bronchodilator therapy David P. Skoner, MD Pittsburgh, Pa β 2 -adrenergic receptor agonists have long been used for the amelioration of
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and the delivery of pediatric bronchodilator therapy David P. Skoner, MD Pittsburgh, Pa β 2 -adrenergic receptor agonists have long been used for the amelioration of
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators
 I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
AT TRIAGE. Alberta Acute Childhood Asthma Pathway: Evidence based* recommendations For Emergency / Urgent Care
 1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION
 VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENTOLIN Respirator Solution contains 5mg salbutamol, as sulphate, per ml of solution and is supplied in 10 ml bottles.
VENTOLIN RESPIRATOR SOLUTION Salbutamol QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENTOLIN Respirator Solution contains 5mg salbutamol, as sulphate, per ml of solution and is supplied in 10 ml bottles.
Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Cardiac chest pain or suspected Myocardial Infarction.
 s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
University of Groningen. Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne
 University of Groningen Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): Α A REVIEW
 Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
Medical Emergencies at Moderate and High Altitude
 Medical Emergencies at Moderate and High Altitude Annalisa Cogo Clinica Pneumologica e Centro Studi Biomedici Applicati allo Sport Università di Ferrara Payer Hutte, Ortler Mountain Environment Barometric
Medical Emergencies at Moderate and High Altitude Annalisa Cogo Clinica Pneumologica e Centro Studi Biomedici Applicati allo Sport Università di Ferrara Payer Hutte, Ortler Mountain Environment Barometric
NIV and Aerosoltherapy
 NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
Respiratory Therapy. Medical/Scientific/General Background
 Respiratory Therapy Medical/Scientific/General Background Marketing Europe Dr. Rainer Jakobs PMM Europe 1 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM Europe RT Medical/Scientific/General Background 2 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM
Respiratory Therapy Medical/Scientific/General Background Marketing Europe Dr. Rainer Jakobs PMM Europe 1 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM Europe RT Medical/Scientific/General Background 2 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM
Bronchodilator Delivery and Nebuliser Trials in Adults
 Bronchodilator Delivery and Nebuliser Trials in Adults Acute Management Favour the use of MDI (+/- Spacer) If considering nebuliser Short term treatment Approx. < 3 weeks See optimisation of inhaled bronchodilators
Bronchodilator Delivery and Nebuliser Trials in Adults Acute Management Favour the use of MDI (+/- Spacer) If considering nebuliser Short term treatment Approx. < 3 weeks See optimisation of inhaled bronchodilators
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations. Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa
 Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION. A Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication in the community setting
 NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION A Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication in the community setting Aim This guide has been developed from the generic guidance circulated in April 2014.
NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION A Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication in the community setting Aim This guide has been developed from the generic guidance circulated in April 2014.
LRI Children s Hospital
 LRI Children s Hospital Asthma Management in Children On-going Care after Admission to Ward Staff relevant to: Medical & Nursing staff providing asthma management care to Children within UHL Children s
LRI Children s Hospital Asthma Management in Children On-going Care after Admission to Ward Staff relevant to: Medical & Nursing staff providing asthma management care to Children within UHL Children s
Emergency Department Protocol Initiative
 Emergency Department Protocol Initiative ACUTE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT TOOLKIT March 2006 Provincial Emergency Services Project PHYSICIAN ORDER TEMPLATE FOR CTAS LEVEL 1 ASTHMA ADULT PEDIATRIC Date: Site: Arrival
Emergency Department Protocol Initiative ACUTE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT TOOLKIT March 2006 Provincial Emergency Services Project PHYSICIAN ORDER TEMPLATE FOR CTAS LEVEL 1 ASTHMA ADULT PEDIATRIC Date: Site: Arrival
Simone Gambazza, PT Cystic Fibrosis Centre, Milan Fondazione I.R.C.C.S. Cà Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico
 Simone Gambazza, PT Cystic Fibrosis Centre, Milan Fondazione I.R.C.C.S. Cà Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Aerosol Deposition and Particles Sizes þ Inertial impaction It occurs with larger (>3µm)
Simone Gambazza, PT Cystic Fibrosis Centre, Milan Fondazione I.R.C.C.S. Cà Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Aerosol Deposition and Particles Sizes þ Inertial impaction It occurs with larger (>3µm)
Your Inhaler Devices & You
 1 Your Inhaler Devices & You COUNSEL ON THE APPROPRIATE USE OF A: METERED DOSE INHALER (MDI) DRY POWDER INHALER (DPI) DISCUSS THE APPROPRIATE USAGE OF A PEAK FLOW METER AND SPACER/HOLDING CHAMBER DEVICE
1 Your Inhaler Devices & You COUNSEL ON THE APPROPRIATE USE OF A: METERED DOSE INHALER (MDI) DRY POWDER INHALER (DPI) DISCUSS THE APPROPRIATE USAGE OF A PEAK FLOW METER AND SPACER/HOLDING CHAMBER DEVICE
Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients
 Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Latex Free. An affordable, easy to use, high density, small volume nebulizer with a revolutionary breath enhanced design!
 Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a revolutionary breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients
Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a revolutionary breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients
(PLACE PATIENT LABEL HERE) Date: Time: Assessment nurse: Sign: STOP!
 ASTHMA BEST CARE BUNDLE P A T H W A Y ADULT ASTHMA Date: Time: Assessment nurse: Sign: INCLUSION CRITERIA Known asthmatic Shortness of breath and / or wheeze EXCLUSION CRITERIA Chronic lung disease other
ASTHMA BEST CARE BUNDLE P A T H W A Y ADULT ASTHMA Date: Time: Assessment nurse: Sign: INCLUSION CRITERIA Known asthmatic Shortness of breath and / or wheeze EXCLUSION CRITERIA Chronic lung disease other
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Important Principles of Aerosol Therapy for Your Patients
 Important Principles of Aerosol Therapy for Your Patients Disclaimer Appendix 3 Declaration of Vested Interest Form Name of presenter: David Henry RRT Name of employer: DeVilbiss Healthcare Inc. Definition:
Important Principles of Aerosol Therapy for Your Patients Disclaimer Appendix 3 Declaration of Vested Interest Form Name of presenter: David Henry RRT Name of employer: DeVilbiss Healthcare Inc. Definition:
IPRAVENT Respules/Respirator solution (Ipratropium bromide)
 Published on: 19 Sep 2014 IPRAVENT Respules/Respirator solution (Ipratropium bromide) Composition IPRAVENT Respules Each 2 ml contains: Ipratropium Bromide BP equivalent to Ipratropium Bromide (anhydrous)
Published on: 19 Sep 2014 IPRAVENT Respules/Respirator solution (Ipratropium bromide) Composition IPRAVENT Respules Each 2 ml contains: Ipratropium Bromide BP equivalent to Ipratropium Bromide (anhydrous)
Holding chambers (spacers) versus nebulisers for beta-agonist treatment of acute asthma (Review)
 EVIDENCE-BASED CHILD HEALTH: A COCHRANE REVIEW JOURNAL Evid.-Based Child Health 1: 948 1017 (2006) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/ebch.67 Holding chambers
EVIDENCE-BASED CHILD HEALTH: A COCHRANE REVIEW JOURNAL Evid.-Based Child Health 1: 948 1017 (2006) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/ebch.67 Holding chambers
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
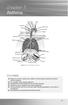 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Position within the Organisation
 ASTHMA TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma Version 4.0 Ratification date September
ASTHMA TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma Version 4.0 Ratification date September
Current Challenges and Opportunities in Demonstrating Bioequivalence
 Current Challenges and Opportunities in Demonstrating Bioequivalence Gur Jai Pal Singh, Ph.D. Watson Laboratories, Inc. Corona, California, USA Demonstrating Bioequivalence of Locally Acting Orally Inhaled
Current Challenges and Opportunities in Demonstrating Bioequivalence Gur Jai Pal Singh, Ph.D. Watson Laboratories, Inc. Corona, California, USA Demonstrating Bioequivalence of Locally Acting Orally Inhaled
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Type: Clinical Guideline Register No: Status: Public MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN MORE THAN 2 YEARS IN HOSPITAL
 MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN MORE THAN 2 YEARS IN HOSPITAL Type: Clinical Guideline Register No: 09055 Status: Public Developed in Response to: Best practice CQC Fundamental Standard: 9, 12,
MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN MORE THAN 2 YEARS IN HOSPITAL Type: Clinical Guideline Register No: 09055 Status: Public Developed in Response to: Best practice CQC Fundamental Standard: 9, 12,
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET SEREVENT Accuhaler
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET SEREVENT Accuhaler Salmeterol xinafoate (50 mcg per inhalation) Presentation SEREVENT Accuhaler is a moulded plastic device containing a foil strip with 60 regularly placed blisters
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET SEREVENT Accuhaler Salmeterol xinafoate (50 mcg per inhalation) Presentation SEREVENT Accuhaler is a moulded plastic device containing a foil strip with 60 regularly placed blisters
ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN BASKET OF CARE SUBCOMMITTEE Report to: Minnesota Department of Health. June 22, 2009
 This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
beclometasone 100 MDI 2 puffs twice a day (recently changed to non CFC (Clenil Modulite))
 Case 1 Mr Thomson, a 32 year old asthmatic who is well known to you comes into your pharmacy. He is known to have a best peak flow of 640 L/min. He tells you that over the last few weeks he has been wakening
Case 1 Mr Thomson, a 32 year old asthmatic who is well known to you comes into your pharmacy. He is known to have a best peak flow of 640 L/min. He tells you that over the last few weeks he has been wakening
This letter is to notify you of recent changes to the PULMOZYME product monograph. Please note, additions/changes have been highlighted in yellow.
 April 9, 2015 Subject: Revised Product Monograph - PULMOZYME (dornase alfa) Dear Drug Information / Poison Control Centres, This letter is to notify you of recent changes to the PULMOZYME product monograph.
April 9, 2015 Subject: Revised Product Monograph - PULMOZYME (dornase alfa) Dear Drug Information / Poison Control Centres, This letter is to notify you of recent changes to the PULMOZYME product monograph.
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness. treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years
 The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
Respiratory Care in PICU Aerosol Therapy ส พ ชชา ชา แสงโขต โรงพยาบาลสมเด จพระป นเกล า
 Respiratory Care in PICU Aerosol Therapy น.อ.หญ ง ส พ ชชา ชา แสงโขต โรงพยาบาลสมเด จพระป นเกล า Aerosol liquid droplets or solid particles suspended in a gas(air) visible like fog Aerosol vs Humidity Humidity
Respiratory Care in PICU Aerosol Therapy น.อ.หญ ง ส พ ชชา ชา แสงโขต โรงพยาบาลสมเด จพระป นเกล า Aerosol liquid droplets or solid particles suspended in a gas(air) visible like fog Aerosol vs Humidity Humidity
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet
 1 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE PAEDIATRIC ASTHMA Purpose of Procedure/
1 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE PAEDIATRIC ASTHMA Purpose of Procedure/
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
NebuTech nebulizer from Salter. Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION. To help you and your patients. easy. breathe
 nebulizer from Salter To help you and your patients breathe easy Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION nebulizer from Salter Let go to work for you and your patients today. Performance Versatility
nebulizer from Salter To help you and your patients breathe easy Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION nebulizer from Salter Let go to work for you and your patients today. Performance Versatility
Valved holding chamber drug delivery is dependent on breathing pattern and device design
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE PAEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY Valved holding chamber drug delivery is dependent on breathing pattern and device design Péter Csonka 1,2 and Lauri Lehtimäki 3,4 Affiliations: 1 Centre for Child
ORIGINAL ARTICLE PAEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY Valved holding chamber drug delivery is dependent on breathing pattern and device design Péter Csonka 1,2 and Lauri Lehtimäki 3,4 Affiliations: 1 Centre for Child
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER
 MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS
 NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
Care and Use of Nebulisers
 For further information visit: www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk www.lhch.nhs.uk www.dipex.org If you require a copy of this leaflet in any other format or language please contact us quoting the leaflet code and the
For further information visit: www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk www.lhch.nhs.uk www.dipex.org If you require a copy of this leaflet in any other format or language please contact us quoting the leaflet code and the
Anticholinergic therapy for acute asthma in children(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Anticholinergic therapy for acute asthma in children(review) TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Anticholinergic therapy for acute asthma in children(review) TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB.
The FDA Critical Path Initiative
 The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Delay Between Actuation and Shaking of a Hydrofluoroalkane Fluticasone Pressurized Metered-Dose Inhaler
 Delay Between Actuation and Shaking of a Hydrofluoroalkane Fluticasone Pressurized Metered-Dose Inhaler Ariel Berlinski MD, Dirk von Hollen, John N Pritchard PhD, and Ross HM Hatley PhD BACKGROUND: Inhaled
Delay Between Actuation and Shaking of a Hydrofluoroalkane Fluticasone Pressurized Metered-Dose Inhaler Ariel Berlinski MD, Dirk von Hollen, John N Pritchard PhD, and Ross HM Hatley PhD BACKGROUND: Inhaled
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
 Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
The Collapsible Chamber
 NEW The Collapsible Chamber DESIGNED FOR PERFORMANCE AND CONVENIENCE INDICATIONS FOR USE Flexichamber is an anti-static valved collapsible holding chamber intended to be used by patients under the care
NEW The Collapsible Chamber DESIGNED FOR PERFORMANCE AND CONVENIENCE INDICATIONS FOR USE Flexichamber is an anti-static valved collapsible holding chamber intended to be used by patients under the care
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE
 BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE December 2014 Review Date: December 2017 Bulletin 206 : DuoResp Spiromax 160 / 4.5 and 320 / 9 budesonide & formoterol dry powder inhaler JPC Recommendations
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE December 2014 Review Date: December 2017 Bulletin 206 : DuoResp Spiromax 160 / 4.5 and 320 / 9 budesonide & formoterol dry powder inhaler JPC Recommendations
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
A NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION. Generic Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication
 A NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION Generic Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication Aim The aim of this guide is to provide a template for those who wish to develop their own nebuliser
A NEBULISERS AND NEBULISED MEDICATION Generic Guide for the use of nebulisers and nebulised medication Aim The aim of this guide is to provide a template for those who wish to develop their own nebuliser
