Morphological and Dermatoglyphic Perculiarities in a Family with Autosomal Dominant Inherited Syndactyly
|
|
|
- Meghan Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kamla-Raj 2001 IJHG 1(4): (2001) Morphological and Dermatoglyphic Perculiarities in a Family with Autosomal Dominant Inherited Syndactyly B. Busert Institut für Humangenetik der Universität Bonn, Germany, Wilhelmstr.31, Bonn, Germany, Phone (0) , Fax (0) , barbarabusert@gmx.de KEY WORDS Syndactyly Type I; dermatoglyphic perculiarities; autosomal inheritance; variable expressivity of symptoms; family investigation ABSTRACT A family with isolated, autosomal dominant syndactyly of the hands is presented. 40 persons from 5 generations are included in the study. Morphological and dermatoglyphic investigations were carried out on 10 probands, only 1 of whom showed solely the characteristic changes of the dermatoglyphics. Syndactyly of the fingers 3-5 occured with reduced penetrance and variable expressivity. 8 persons exhibited bilateral osseous or cutaneous changes. Analysis of the pattern on fingertips revealed an increased number of whorls in probands in comparison to their relatives and the middleeuropean population (65.6 % :28.6 % :25.4%). A parallel course of ridges without pattern formation was observed on 5 fingers of 4 probands. The c-triradius was absent in 14 hands of 9 persons, fusions bc were found in 3 hands and fusions cd in 8 hands. In 3 cases the C-line was reduced. The number of palmar interdigital patterns was reduced in probands. The ridge structure was aberrant in the regions of syndactyly in 8 of 9 probands. A chromosome rearrangement was excluded as the cause of the syndactyly. An assignment to Syndactyly Ia, II and III was excluded by the molecular investigations. A morphologic correspondence to Type I seems obvious. INTRODUCTION Syndactyly is a specific type of extremity malformation, a developmental abnormality caused by the inhibition of the transversal differentiation of the extremity bud in the 6 th to 7 th week of pregnancy. Exogeneous syndactyly is caused by mechanical influences during embryogenesis. Endogeneous syndactyly can either be a symptom of a syndrome, such as Apert- or Oculo- Dento-Digital-Syndrome, or of an isolated malformation. As the latter it has a frequency of 1:2000 in the population (de Smet et al. 1994). Three types and one subtype of syndactyly which show the best correspondence to the family whom we investigated are described in detail. 1. Syndactyly Type I or Zygodactyly (MIM #185900) It is the most frequent type. Temtamy and McKusick describe investigations carried out on 169 males and 142 females and on 32 pedigrees (1978). Morphology: Mainly the 3 rd and 4 th fingers and the 2 nd and 3 rd toes are involved; in some cases the 5 th finger and the 4 th toe can be affected, also. This type of syndrome shows high variability of symptoms and can include the nails or be restricted to the basic phalanges. The syndactyly can be cutaneous or osseous. It may be restricted to hands or feet. The feet are involved four times more frequently than the hands and about 50 % of the patients show a bilateral involvement (Lenz and Majewski 1981; Winter et al. 1993). 2. Type I a- Syndactyly Type Lueken. Subgroup of Zygodactyly. In 1938 Lueken presented 5 generations of a family with 29 female and 18 male probands. Morphology: They showed variable syndactyly of the fingers 2-5. The second and third toes were mainly involved. Genetics: Type I and Ia are inherited in an autosomal-dominant manner with variable expressivity and reduced penetrance. Men are carriers as often as females. Bosse et al. (2000) reinvestigated Type Ia and localized the responsable gene on chromosome 2q34-q Synpolydactyly Type II (MIM#18600) The cases of 16 families were published. Thomsen (1928) investigated the largest family with 31 male and 11 female carriers in 7 generations. Morphology: The 3 rd and 4 th fingers are often completely fused, including synostosis. Duplications of these fingers are frequently observed. The 5 th finger is sometimes included; additionally, contractions and clinodactyly can occur. In 50 % of the cases the 4 th and 5 th toes show complete syndactyly. The 5 th toe additionally may have partial and complete
2 276 B. BUSERT polydactyly (Temtamy and McKusick 1978; Lenz and Majewski 1981; Winter et al. 1993). Genetics: Autosomal-dominant inheritance and variable expressivity. Some families exhibited reduced penetrance. The phenotype is caused by a mutation of the HOXD-13 gene, localized in 2q31. A 27 bp duplication occurs in the region coding for polyalanine. The expressivity of the disorder is about 97 % (Akarsu et al. 1996; McKusick 1998). 4. Syndactyly of fingers 4 and 5, Type III (MIM#186100) This type was observed in 4 families, the largest with 7 men and 7 women in 5 generations. Morphology: The 4 th and the 5 th fingers are involved, the middle phalanx of the 5 th finger is reduced or missing. In cases of complete syndactyly, the 4 th finger shows contractions. The nails can be fused as well as the end-phalanx. The toes do not exhibit syndactyly (Temtamy and McKusick 1978; Lenz and Majewski 1981; de Smet 1994). Genetics: The mutation follows an autosomaldominant inheritance with complete penetrance in all but one family. The gene is localized in 6q22- q23, the region of the Oculo-Dento-Digital- Syndrome (Gladwin et al. 1997; Boyadjiev et al. 1999). FAMILY INVESTIGATED In this paper we present a family with an autosomal-dominant syndactyly of the hands (Fig.1). Clinical, cytogenetic and molecular investigations were carried out. Special emphasis was placed on the analysis of the dermatoglyphics. INVESTGATION METHODS Clinical Examinations: Hands and feet of the probands were investigated and photographs taken, X-ray-pictures and operation reports were included in the analysis of symptoms (Fig. 2). 8 of 10 persons were bilaterally affected (III:5; III:8; IV:11; IV:12; IV:17; V:6; V:8; V:10) and 2 only unilaterally (IV:7; IV:10) (including one proband (IV:10) with microsymptoms who is not taken into consideration in the following description). In 7 of 9 probands there are 3 fingers involved (III:5; IV:11; IV:12; IV:17; V:6; V:8; V:10) and 2 persons have two phalanges affected, namely the 3 rd and 4 th finger (III:8; IV:7). In 5 cases there were osseous fusions (III:5; IV:11; IV:12; IV:17; V:10) and in 4 cases there were cutaneous fusions (III:8; IV:7; V:6; V:8). 7 of 9 probands have a complete syndactyly (III:5; IV:11; IV:12; IV:17; V:6; V:10), one person has only fusions of the proximal phalanx (III:8) and another proband has the proximal and middle phalanx included (IV:7). Dermatoglyphics: Prints from fingers and palms were taken by the graphite-cling- and filmmethod. The analyses were performed according to Cummins and Midlo (1961) and Schaumann Fig. 1. Family with dominant inheritance of isolated syndactyly of the hands in 5 generations
3 MORPHOLOGICAL AND DERMATOGLYPHIC PERCULIARITIES 277 Fig. 2a Fig. 2b Fig. 2c Fig. 2. Proband IV:17: a) X-ray preoperative (1974) b) preoperative (1974) c) postoperative (2000)
4 278 B. BUSERT and Alter (1976). Chromosome Diagnostics: In one test person (IV/17) a chromosome analysis was performed to exclude a balanced rearrangement in carriers as a cause of syndactyly. A lymphocyte culture was set up and chromosomes were analysed after GTG-banding. Moleculargenetic Investigations: Microsatellite investigations were performed for regions 2q34-q36, 2q31 and 6q22-q23 which show mutations in syndactyly type Ia to III. These investigations proved that there was no linkage between the trades examined here and the above metioned chromosome regions. Family investigation RESULTS It was possible to obtain data from 40 persons out of 5 generations, 12 of whom were affected (7 men and 5 women; Fig. 1). In all cases the syndactyly was restricted to the hands and showed a significant variability of symptoms that was sex-independent. There was no progression in the severity of the expression of clinical syndactyly from generation to generation. The inheritance of the syndactyly was thus autosomal-dominant with variable expressivity. There were no additional teratogenic agents involved in the pregnancies. Personal investigations were performed on 10 carriers and 8 healthy first-degree relatives from 3 generations (pedigree, Fig. 1, generations III, IV, V). Dermatoglyphics In the investigated family the dermatoglyphics of 16 persons were analysed; 7 of these were non-affected relatives of the probands. Seven probands were severely affected; 5 of them (III:5, IV:11, IV:12, IV;17;V:6) were investigated postoperatively and one proband (V:8) preoperatively. Three further probands showed a very mild expression of the syndrome, making an operation unnecessary (III:8, IV:7, IV:10). Patterns on the Fingertips The patterns of 6 probands and 7 non-affected relatives were analysed. Two probands (IV:12, V:8) did not have a pattern on the fourth finger of the left hand and one did not have one on the fourth finger of the right hand. Proband IV:17 showed a pattern-free area on both 4 th fingers. The abnormality is caused by the syndactyly. The pattern-analysis on the fingertips showed a large number of whorls in the probands (65.6 %); the non-affected relatives and the average population have this pattern in 28.6 % and 25.4 %, respectively. The probands had a frequency of 21.1 % ulnar loops while their relatives showed 67.1 % and the general population recorded 69.7 % ulnar loops respectively. Radial loops showed up more frequently in the probands (7.8 %) than in the relatives and the average of the population (Table 1). The bimanual differences were not significant among the probands, their relatives and the general population. A comparison of the Total Finger Ridge Count (TFRC) of the probands (average: females=172; males = 178) with that of their relatives (average: females = 149; males = 152) reveals that the index group had a higher TFRC than the relatives, due to the higher frequency of whorls. Sex-specific differences occured in both groups: men had a higher average value than women. Formulation of Configurational Areas Hypothenar, thenar and interdigital areas II to IV of 9 probands and 7 non-affected relatives were analysed: three of the probands show a loop-pattern on the hypothenar on one hand (III:5, III:8 and IV:12) while V:8 has an ulnar loop on both hands. The pattern-frequency in the hands of the probands was 28.0 %. In the relatives it was 21.0 % and in the general population 32.9 % (Cummins and Midlo 1961). The thenar was always patternless in the Table 1: Pattern frequency of the fingertips in the affected probands, their relatives and the average of the population (n= 5000 (Cummins und Midlo 1961)) W L u L r Probands 65.6 % 21.1 % 7.8 % (TL 6.0 %) Relatives 28.6 % 67.1 % 4.3 % (TL 5.7 %) Average population 25.4 % 69.7 % 5.7 % (TL 3.1 %) (W = whorl; L u = ulnar loop; L r = radial loop, TL = twinloop)
5 MORPHOLOGICAL AND DERMATOGLYPHIC PERCULIARITIES 279 proband group (0 %). One of the relatives (V:7) had a proximal loop and a vestige (7.0 %). By contrast, 17.0 % of the general population show a pattern on the thenar (Schade 1954). The interdigital area II was patternless in all probands (0 %). One relative had distal loops on both hands (14.0 %). According to Schade, 6.0 % of the average population showed patterns (1954). Two probands had digital loops in the interdigital area III on one hand (11.0 %). IV:7 and V:6 showed a vestige bilaterally, IV:11 unilaterally. 4 relatives had bilateral patterns in this region of the palm (7 distal loops and one vestige). The pattern-frequency was 11.0 % for probands, 50.0 % for relatives and 53.6 % for the general population (Cummins and Midlo 1961). Vestiges were not counted as patterns. Only proband V:8 showed a pattern in the interdigital area IV; she had a distal loop on the right hand. The relatives showed 5 distal loops on both hands in addition to one vestige. The pattern-frequency of the probands was 5.5 % as compared to 71.4 % among the relatives and 55.8 % in the general population (Cummins and Midlo 1961). We found that the probands had a lower pattern-frequency than their relatives, especially in the interdigital areas III and IV, the main regions of alterations caused by the syndactyly. The degree of severity of the syndactyly did not influence this distribution. Analysis of the Digital Triradii The formation and position of the triradii a -d were examined. Probands and relatives possesed a well-expressed triradius a in central proximal position of the second finger on both hands. The second finger was not involved in the syndactyly in any of the probands. In 7 cases two of the triradii b, c and d were fused and they were shifted into the interdigital area. One fusion bc and 6 fusions cd were found. In three cases the digital triradius was displaced into the interdigital space. Despite a digital triradius d an interdigital triradius cd was found. The average number of triradii in probands was 2.4 on the left hand and 2.7 on the right hand. All relatives showed the normal number of 4 triradii (a, b, c, d). One proband (III:8) and 3 relatives (III:7, IV:9, IV:14) showed additional triradii a, ab, bc and cd ; they were caused by the patterns of the interdigital areas. Position of the Axial Triradii and size of the atd-angle In the probands it was possible to analyse the atd-angle in only 4 of 18 hands, as the triradius d was missing in all the others. The atdangle of the probands was between 31 and 54, which is the same rage as in the average population. Additional triradii were found in 2 probands and 2 relatives, the maximum being 2 triradii in the axial part of the palm. The additional triradii appeared in combination with a pattern on the hypothenar and in proband V:7 on the thenar. Identification of the Main Lines on the Palms Due to the missing d-triradius, 72.0 % of the patients showed a loss of the D-line. None of the probands had a D-line on the left hand and, on the right hand it was missing in 5 of 9 persons. The C-lines were missing in 78.0 %, with both hands equally affected. The line was rudimentary in 3 cases. The B-line was missing in 50.0 %. When present it was equally frequent on both hands. The A-line was normal in all patients. The relatives did not show any missing or rudimentary main-lines (Table 2). Comparison of the Fingers Affected by the Syndactyly and the Development of the Main Lines of the Patients. The findings showed that the alteration of the main lines did not occur only under those fingers which were involved in the syndactyly. They were also a phenotypic expression of the hereditary disease. Patient III:8 showed this phenomenon on the right hand and patient IV:7 on both hands. The dermatoglyphic changes thus were not exclusively a result of the fusions of fingers. The end areas of the main lines were comparable only for the A-line % of the patients lines terminate in the areas 4 and 5 as compared to 71.0 % of the relatives lines. This is known to be the characteristic diagonal course of the middle-european population (Cummins and Midlo 1961). Ridge Formation The structure of the ridges showed alterations in the probands in the distal parts of the palmae.
6 280 B. BUSERT Table 2: The ending areas of the main lines on the palms of the probands and their relatives (X = rudimentory main line) The distance between them was partially increased in 6 patients (III:5, IV:7, IV:11, IV:12, V:6, V:10). Patient V:6 exhibited a meandering course of the ridges and probands IV:10 and V:6 had an increased number of minutiae. The diameter of the ridges varied in 2 cases (IV:11, IV:17). Two patients showed a disruption of the ridges (III:5, IV:12). None of these alterations was observed in the non-affected relatives. The course of the palmar flexion creases was normal in the probands. Chromosome Findings The proband IV:17 showed a normal female karyotype (46,XX,GTG, bands/genome). Thus a balanced translocation or inversion was excluded as the cause of the syndactyly in the family. Molecular Investigations D-line C-line B-line A-line D-line C-line B-line A-line Probands Left hand Right hand III: III: IV:7 - X IV:10 - X X 5 4 IV: IV: IV: V: V: Relative Left hand Right hand III: III: IV: IV: IV: IV: L r V: Investigations were performed by microsatellite-fragment analysis. There was no evidence of linkage for the marker on chromosome 2q34-q36 (Type Ia), 2q31 (Type II) and 6q22- q23 (Type III). Further investigations are intended. DISCUSSION In 1923 Cummins and Midlo pointed out that clinical investigations in patients with zygodactyly remain incomplete or may lead to false conclusions if only cutaneous or osseous changes on fingers and toes of probands are considered as symptoms for carrier determination. Alterations of the dermatoglyphics must always be taken into consideration. Wolff-Quenot and Clavert (1983) investigated the dermatoglyphics in syndactyly patients and found various alterations. Watanabe et al. (1949) found a fusion or aplasia of digital triradii under the fused fingers as the main symptom of dermatoglyphic changes in their patients. In some carriers of the mutation the only symptom was a reduction of an interdigital area and a shift of the digital triradius. In patients with syndactyly Type I Matton et al. (1982) found an increased reduction of the C-line. In our study, the c-triradius was absent in 14 hands of 9 probands. In 3 hands there were fusions of bc and in 8 of cd. In 3 cases the C-line was reduced. One carrier (IV/10) showed dermatoglyphic changes as the only symptom of the syndrome. Her child (V:8) had a complete syndactyly of fingers 3-5 on both hands. According to Matton et al. the pattern on fingertips revealed an increase in whorls in carriers as compared to their relatives and the general population (1981). The same peculiarity was found in our family. The frequency of whorls was 65.6 % compared to 28.6 % in relatives and 25.4 % in the general population. The fingertip ridges may show a parallel
7 MORPHOLOGICAL AND DERMATOGLYPHIC PERCULIARITIES 281 course without formation of pattern (Matton et al. 1981). In the family investigated here we observed this abnormality on 5 fingers of 4 persons. The analysis of the palmar pattern showed a reduced occurrence of loops and whorls in the interdigital areas II-IV in probands as compared to their relatives and the general population. Hypothenar and thenar patterns showed no differences for the 3 groups who were coq1mpared. The structure of the ridges showed peculiarities in 8 of the 9 probands in the regions of the syndactyly. The distance of the ridges varied and was significantly increased in some cases. The ridges were interrupted, the number of minutiae was increased and the course of ridges appeared wavy. Comparable findings have not been published by other investigators. Embryological investigations of Matton showed an increased bud formation in the 7 th week of development in probands with syndactyly (1981). It is known that large buds lead to more complex dermatoglyphic patterns. The authors assumed a common mechanism for the bud formation of the fingers and the development of the syndactyly, but further investigations are necessary to obtain detailed insight into the differentiation mechanisms. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I would like to thank Prof. Dr. Gesa Schwanitz for her support and her continuing fruitful discussions. REFERENCES Akarsu AN, Stoilov I, Yilmaz E, Sayli BS, Sarfarazi, M (1996). Genomic structure of HOXD-13 gene: a nine polyalanine duplication causes synpolydactyly in two unrelated families. Hum Mol Genet, 5: Bosse K, Betz RC, Lee YA, Wienker TF, Reis A, Kleen H, Propping P, Cichon S, Nöthen MM Localization of a gene for syndaktyly type 1 to chromosome 2q34-q36. Am J Hum Genet, 67 (2): Boyadjiev SA, Jabs EW, LaBusa M, Jamal JE, Torbergsen T, Ptácek LJ, Rogers LC, Nyberg-Hansen, R, Opjordsmoen S, Zeller CB, Stine OC, Stalker HJ, Zori RT, Shapiro RE Linkage analysis narrows the critical region for the oculodentodigital dysplasia to chromosome 6q22-q23. Genomics, 58: Cummins H, Midlo C Finger Prints, Palms and Soles An Introduction to Dermatoglyphics. New York: Dover Publications. Gladwin A, Donnaqi D, Metcalfe K, Schrader-Stumpel C, Brueton L, Verloes A, Aylsworth A, Toriello H, Winter R, Dixon M Localization of a gene for oculodentodigital syndrome to human chromo-some 6q22-q24. Hum Mol Genet, 6/1: Lenz W, Majewski F Fehlbildungen der Gliedmaßen. In: Schinz HR, Baensch WE, Frommhold W, Glauner R, Uehlinger W, Wellauer J (Ed.): Lehrbuch der Röntgendiagnostik in 5 Bänden Bd II, Teil 2: Skelett, Weichteile und Gefäße. 6. Aufl Stuttgart, New York: Thieme, Matton M, De Bie S, Anseeuw A Familial dermatoglyphic analysis in syndactyly type I. J Hand Surg, 6/6: McKusick V Mendelian Inheritance in Man. A Catalog of Human Genes and Genetic Disorders. 12. Ed. Vol II. London: The Johns Hopkins University Press. Schade H Vaterschaftsbegutachtung. Grundlagen und Methoden der anthropologisch-erbbiologischen Vaterschaftsfeststellung. Stuttgart: Schweizerbart s-che Verlag-sbuchhandlung. Smet, L de, Mulier T, Fabry G Syndactyly of the ring and small finger. Genetic Counseling, 5/1: Temtamy SA, McKusick V The genetics of hand malformations. Birth Defects, 14/3: i - xviii, Watanabe K, Nakamura R, Miura T Palmar dermatoglyphics in congenital hand anomalies. J Hand Surg, 19 A/6: Winter R M, Trickle C Syndactylies and polydactylies: embryological overviews in suggested classification. EJHG, 1/93: Wolff-Quenot, MJ Clavert JM Les dermatoglyphes de mains malformées. Chir Pédiatr, 24:
Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
Educational Items Section
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Embryology, Semiology, Dysmorphology Jean-Loup Huret Genetics, Dept Medical Information,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Embryology, Semiology, Dysmorphology Jean-Loup Huret Genetics, Dept Medical Information,
Mesoaxial complete syndactyly and synostosis
 8686 Med Genet 1998;35:868-874 Department of Medical Biology and Genetics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical Faculty, Sivas, Turkey E F Percin I Sezgin Department of Orthopaedics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical
8686 Med Genet 1998;35:868-874 Department of Medical Biology and Genetics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical Faculty, Sivas, Turkey E F Percin I Sezgin Department of Orthopaedics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical
LESS COMMON DERMATOGLYPHIC PATTERNS ON THE PALM IN MORAVIAN POPULATION
 ACTA UNIVERSITATIS PALACKIANAE OLOMUCENSIS FACULTAS RERUM NATURALIUM (2001 2002) BIOLOGICA 39 40 LESS COMMON DERMATOGLYPHIC PATTERNS ON THE PALM IN MORAVIAN POPULATION Václav Hajn Department of Zoology
ACTA UNIVERSITATIS PALACKIANAE OLOMUCENSIS FACULTAS RERUM NATURALIUM (2001 2002) BIOLOGICA 39 40 LESS COMMON DERMATOGLYPHIC PATTERNS ON THE PALM IN MORAVIAN POPULATION Václav Hajn Department of Zoology
Plantar and digital dermatoglyphic patterns in Malawian patients with diabetes, hypertension and diabetes with hypertension
 Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2001) : 24-31 24 Plantar and digital dermatoglyphic patterns in Malawian patients with diabetes, hypertension and diabetes with hypertension PS Igbigbi, BC Msamati, TM Ng ambi
Int J Diabetes & Metabolism (2001) : 24-31 24 Plantar and digital dermatoglyphic patterns in Malawian patients with diabetes, hypertension and diabetes with hypertension PS Igbigbi, BC Msamati, TM Ng ambi
STUDY OF PALMAR DERMATOGLYPHICS IN CARCINOMA
 IJCRR Vol 05 issue 04 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 05/01/13 Revised on: 26/01/13 Accepted on: 18/02/13 STUDY OF PALMAR DERMATOGLYPHICS IN CARCINOMA OF CERVIX Balsurkar Smita Kashinathappa
IJCRR Vol 05 issue 04 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 05/01/13 Revised on: 26/01/13 Accepted on: 18/02/13 STUDY OF PALMAR DERMATOGLYPHICS IN CARCINOMA OF CERVIX Balsurkar Smita Kashinathappa
An Investigation of the Linkage Relationships of the Blood Groups and Types with Hand Patterns and Handedness
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 43, Issue 4 (July, 1943) 1943-07 An Investigation of the Linkage Relationships
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 43, Issue 4 (July, 1943) 1943-07 An Investigation of the Linkage Relationships
BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY 1
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2001), 54, 34-38 9 2001 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10,1054/bjps.2000.3453 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY 1 Polydactyly of the feet in children:
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2001), 54, 34-38 9 2001 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10,1054/bjps.2000.3453 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY 1 Polydactyly of the feet in children:
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Finger and Palm Prints in Chromatin-positive Males*
 J. med. Genet. (1968). 5, 112. Finger and Palm Prints in Chromatin-positive Males* H. HUNTER From Balderton Hospital, Balderton, Nr. Newark, Notts. Holt in 1955 provided evidence that total finger ridge
J. med. Genet. (1968). 5, 112. Finger and Palm Prints in Chromatin-positive Males* H. HUNTER From Balderton Hospital, Balderton, Nr. Newark, Notts. Holt in 1955 provided evidence that total finger ridge
SWGFAST Glossary - Anatomy
 SWGFAST Glossary - Anatomy BALL AREA The large cushion area below the base of the big toe. BRACHYDACTYLY Abnormal shortness of fingers or toes. BULB OF FINGERS (THUMBS, TOES) The portion of the friction
SWGFAST Glossary - Anatomy BALL AREA The large cushion area below the base of the big toe. BRACHYDACTYLY Abnormal shortness of fingers or toes. BULB OF FINGERS (THUMBS, TOES) The portion of the friction
(synpolydactyly). 2 Homozygous phenotype?
 J Med Genet 1995;32:435-441 A large Turkish kindred with syndactyly type II (synpolydactyly). 2 Homozygous phenotype? 435 Department of Medical Biology and Genetics, University of Ankara, Faculty of Medicine,
J Med Genet 1995;32:435-441 A large Turkish kindred with syndactyly type II (synpolydactyly). 2 Homozygous phenotype? 435 Department of Medical Biology and Genetics, University of Ankara, Faculty of Medicine,
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY
 Ypn. J. Human Genet. 33, 487-492, 1988 APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY Yoshinori [ZUMIKAWA, Kenji NARITOMI, Shoko [KEMA, Yoshinobu
Ypn. J. Human Genet. 33, 487-492, 1988 APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY Yoshinori [ZUMIKAWA, Kenji NARITOMI, Shoko [KEMA, Yoshinobu
I handedness are in general agreement in finding slight but nevertheless 'real
 GENETIC INTERRELATIONSHIPS OF DERMATOGLYPHICS AND FUNCTIONAL HANDEDNESS' DAVID C. RIFE Ohio Stale University Received July 18, 1942 NVESTIGATORS of the relationships of dermatoglyphics and functional I
GENETIC INTERRELATIONSHIPS OF DERMATOGLYPHICS AND FUNCTIONAL HANDEDNESS' DAVID C. RIFE Ohio Stale University Received July 18, 1942 NVESTIGATORS of the relationships of dermatoglyphics and functional I
The Study of Dermatoglyphic in Simian Crease Group (The Human Masukake- Gata) at Minangkabau Ethnic, West Sumatra, Indonesia
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2199 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (1): 9-14 (2016) Research Article The Study of Dermatoglyphic in Simian Crease
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2199 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 4 (1): 9-14 (2016) Research Article The Study of Dermatoglyphic in Simian Crease
Symphalangism. Symphalangism usually involves the proximal, interphalangeal
 Case Reports 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 285. A Pedigree from South India GEMMA SAVARINATHAN and WILLARD R. CENTERWALL From the Department of Paediatrics, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore,
Case Reports 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 285. A Pedigree from South India GEMMA SAVARINATHAN and WILLARD R. CENTERWALL From the Department of Paediatrics, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore,
Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2010, 51(12) 965
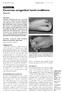 Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2010, 51(12) 965 CME Article Common congenital hand conditions Chong A K S ABSTRACT Congenital hand deformities are common but most of these conditions are minor. Polydactyly
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2010, 51(12) 965 CME Article Common congenital hand conditions Chong A K S ABSTRACT Congenital hand deformities are common but most of these conditions are minor. Polydactyly
Finger and Palmar Ridge Pattern in NIDDM Patients and Controls
 Human Biology Review (ISSN 2277 4424) 5 (1) 2016 Human Biology Review Brief Report (Ghosh et al. pp.86-91) www.humanbiologyjournal.com Revised and Accepted on November 3, 2015 Finger and Palmar Ridge Pattern
Human Biology Review (ISSN 2277 4424) 5 (1) 2016 Human Biology Review Brief Report (Ghosh et al. pp.86-91) www.humanbiologyjournal.com Revised and Accepted on November 3, 2015 Finger and Palmar Ridge Pattern
Study of Palamar Dermatoglyphic Pattern in the Intersex of Selected Bengaluru Population
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Priyadarshini et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 9- () ISSN: DOI: http://dx.doi.org/.88/-. ISSN: Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 9- () Research Article Study of Palamar
Available online at www.ijpab.com Priyadarshini et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 9- () ISSN: DOI: http://dx.doi.org/.88/-. ISSN: Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. (): 9- () Research Article Study of Palamar
Palmar Dermatoglyphics in Essential Hypertension Amongst Rivers Indigenes
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(12): 6300-6305, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Palmar Dermatoglyphics in Essential Hypertension Amongst Rivers Indigenes 1 Oladipo,G.S (PhD); 1 Osogba,I.G(BSc);
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(12): 6300-6305, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Palmar Dermatoglyphics in Essential Hypertension Amongst Rivers Indigenes 1 Oladipo,G.S (PhD); 1 Osogba,I.G(BSc);
Ethnic Groups in Israel
 J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, ii6. A Genetic Study of Stub Thumbs among Various Ethnic Groups in Israel RICHARD M. GOODMAN*, AVINOAM ADAM, and CHAIM SHEBA From the Institute for Human Genetics, Tel Hashomer
J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, ii6. A Genetic Study of Stub Thumbs among Various Ethnic Groups in Israel RICHARD M. GOODMAN*, AVINOAM ADAM, and CHAIM SHEBA From the Institute for Human Genetics, Tel Hashomer
Pattern Intensity index, Dankmeijer Index, Main line formula, Main line index.
 Course Name: PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY Paper No. & Title: B.A. / B.Sc. (Honours) 5 th Semester (Practical) Topic No. & Title: (7/17) Pattern Intensity index, Dankmeijer Index, Main line formula, Main line
Course Name: PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY Paper No. & Title: B.A. / B.Sc. (Honours) 5 th Semester (Practical) Topic No. & Title: (7/17) Pattern Intensity index, Dankmeijer Index, Main line formula, Main line
DERMATOGLYPHIC ANALYSIS OF NON-SYNDROMIC ORAL CLEFTS CASES, UNAFFECTED FAMILY MEMBERS AND CONTROLS. Shwetha Shri Rajagopalan
 DERMATOGLYPHIC ANALYSIS OF NON-SYNDROMIC ORAL CLEFTS CASES, UNAFFECTED FAMILY MEMBERS AND CONTROLS by Shwetha Shri Rajagopalan B.D.S, DR. MGR MADRAS MEDICAL UNIVERSITY, 2010 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty
DERMATOGLYPHIC ANALYSIS OF NON-SYNDROMIC ORAL CLEFTS CASES, UNAFFECTED FAMILY MEMBERS AND CONTROLS by Shwetha Shri Rajagopalan B.D.S, DR. MGR MADRAS MEDICAL UNIVERSITY, 2010 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty
Original Article Dermatoglyphics: a study of finger tip patterns in bronchial asthma and its genetic disposition.
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2003) Vol. 1, No. 4, Issue 4, 267-271 Original Article Dermatoglyphics: a study of finger tip patterns in bronchial asthma and its genetic disposition. Gupta UK 1
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2003) Vol. 1, No. 4, Issue 4, 267-271 Original Article Dermatoglyphics: a study of finger tip patterns in bronchial asthma and its genetic disposition. Gupta UK 1
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know
 Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
A New Vocabulary. Secreted Factors. Three Axes of Limb Development 11/9/15. Proteins released from a cell into surrounding area Examples
 Congenital Hand Update Terry R. Light, MD Tampa, FL November 7, 2015 Terminology n Difference rather than Deformity n Cleft Hand rather than Lobster Claw Embryonic period - Events Day 26 - arm bud appears
Congenital Hand Update Terry R. Light, MD Tampa, FL November 7, 2015 Terminology n Difference rather than Deformity n Cleft Hand rather than Lobster Claw Embryonic period - Events Day 26 - arm bud appears
CONGENITAL HAND DIFFERENCES
 CONGENITAL HAND DIFFERENCES Lisa Lattanza, MD Chief Division of Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery UCSF Medical Center Amy L Ladd MD, Chief, Chase Hand Center Stanford University CONGENITAL DEFORMITIES Upper
CONGENITAL HAND DIFFERENCES Lisa Lattanza, MD Chief Division of Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery UCSF Medical Center Amy L Ladd MD, Chief, Chase Hand Center Stanford University CONGENITAL DEFORMITIES Upper
Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite grafts
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1995), 48. 396-400 1995 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons BRITISH JOURNAL OF / PLASTIC SURGERY I Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1995), 48. 396-400 1995 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons BRITISH JOURNAL OF / PLASTIC SURGERY I Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite
Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum?
 JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
Case A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI.
 Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
DERMATOGLYPHICS STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH MENTAL RETARDATION
 Original Research Article DERMATOGLYPHICS STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH MENTAL RETARDATION Esther Yamuna N * 1, Dhanalakshmi V 2. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2017, Vol
Original Research Article DERMATOGLYPHICS STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH MENTAL RETARDATION Esther Yamuna N * 1, Dhanalakshmi V 2. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2017, Vol
Congenital Hand Anomalies - An Overview. Occupational Therapy Department The Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne, 2014
 Congenital Hand Anomalies - An Overview Occupational Therapy Department The Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne, 2014 Presentation outline Incidence Embryology Classification of Congenital Hand Anomalies
Congenital Hand Anomalies - An Overview Occupational Therapy Department The Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne, 2014 Presentation outline Incidence Embryology Classification of Congenital Hand Anomalies
A Study of Dermatoglyphics in Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Dr.K.Sumangala Devi*, Dr.Mohammed Meraj Ahmed*
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-83, p-issn: 79-8.Volume, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. ), PP -9 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Dermatoglyphics in Insulin Dependent Diabetes
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-83, p-issn: 79-8.Volume, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. ), PP -9 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Dermatoglyphics in Insulin Dependent Diabetes
and duodenal atresia. Two other families reported may have had the same syndrome. Case reports CASE 1 (III.8, FAMILY 1)
 JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
Dermatoglyphic s in Congenital Cardiac Disease
 Dermatoglyphic s in Congenital Cardiac Disease ORIGINAL ARTICLE Singh Brijendra 1, Gupta Renu 1, Agrawal Dushyant 1, Garg Rajneesh 2, and Katri Sunil 3 1 Department of Anatomy, Jodhpur Medical College,
Dermatoglyphic s in Congenital Cardiac Disease ORIGINAL ARTICLE Singh Brijendra 1, Gupta Renu 1, Agrawal Dushyant 1, Garg Rajneesh 2, and Katri Sunil 3 1 Department of Anatomy, Jodhpur Medical College,
Comparison of Dermatoglyphic Pattern among Cleft and Noncleft Children: A Cross-sectional Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Dermatoglyphic Pattern 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1444 among Cleft and Noncleft Children Comparison of Dermatoglyphic Pattern among Cleft and Noncleft Children: A Cross-sectional
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Dermatoglyphic Pattern 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1444 among Cleft and Noncleft Children Comparison of Dermatoglyphic Pattern among Cleft and Noncleft Children: A Cross-sectional
SURGICAL REPAIR OF CONGENITALLY SYNDACTYLIZED TOES
 SURGICAL REPAIR OF CONGENITALLY SYNDACTYLIZED TOES Bradley D. Castellano, D.P.M. Congenital syndactyly of the toes is a relatively common deformity. lts incidence has been estimated at between 1 in 2,000
SURGICAL REPAIR OF CONGENITALLY SYNDACTYLIZED TOES Bradley D. Castellano, D.P.M. Congenital syndactyly of the toes is a relatively common deformity. lts incidence has been estimated at between 1 in 2,000
Role Of Dermatoglyphics As A Potential Diagnostic Marker For Periodontitis: A Clinical Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver.VII (September). 2016), PP 99-103 www.iosrjournals.org Role Of Dermatoglyphics As A Potential
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver.VII (September). 2016), PP 99-103 www.iosrjournals.org Role Of Dermatoglyphics As A Potential
Skin Carvings: Predictive Diagnosis in Modern Era
 Review Article DOI: 10.17354/cr/2015/55 Skin Carvings: Predictive Diagnosis in Modern Era M Parvathi Devi 1, Sumeet Shah 2, S V Ravindra 3, Nivedita Bajantri 3, Dharamveer Singh 4 1 Professor and Head,
Review Article DOI: 10.17354/cr/2015/55 Skin Carvings: Predictive Diagnosis in Modern Era M Parvathi Devi 1, Sumeet Shah 2, S V Ravindra 3, Nivedita Bajantri 3, Dharamveer Singh 4 1 Professor and Head,
Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
Brachydactyly, Macrodactyly, Amniotic band syndrome
 Brachydactyly, Macrodactyly, Amniotic band syndrome Brachydactyly Brachydactyly Short finger where all the elements of digital skeleton are present but one or more reduced in size Brachydactyly Brachytelophalangy
Brachydactyly, Macrodactyly, Amniotic band syndrome Brachydactyly Brachydactyly Short finger where all the elements of digital skeleton are present but one or more reduced in size Brachydactyly Brachytelophalangy
Clinical assessment of the relative lengths of the fingers of the human hand
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 1, May, 2009. pp. 31-35 Clinical assessment of the relative lengths of the fingers of the human hand Dawood Jafari 1,MD.,
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 1, May, 2009. pp. 31-35 Clinical assessment of the relative lengths of the fingers of the human hand Dawood Jafari 1,MD.,
STUDY OF ATD ANGLE, FINGER RIDGE COUNT IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS PATIENTS
 Original Research Article STUDY OF ATD ANGLE, FINGER RIDGE COUNT IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS PATIENTS Jagdish S. Chaudhari * 1, Bharat J. Sarvaiya 2, S.M. Patel 3, S.V. Patel 4. India. ABSTRACT Objective:
Original Research Article STUDY OF ATD ANGLE, FINGER RIDGE COUNT IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS PATIENTS Jagdish S. Chaudhari * 1, Bharat J. Sarvaiya 2, S.M. Patel 3, S.V. Patel 4. India. ABSTRACT Objective:
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res. 2014; 5(1): 3850-3854 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
Int J Biol Med Res. 2014; 5(1): 3850-3854 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
Presidency General Hospital, Calcutta
 CONGENITAL ANOMALY OF HAND: " MIRROR HAND " By M. MUKERJI, F.R.C.S. Presidency General Hospital, Calcutta Case Report.--S. B., aged 4 months, was born with eight fingers and no thumb on the left hand and
CONGENITAL ANOMALY OF HAND: " MIRROR HAND " By M. MUKERJI, F.R.C.S. Presidency General Hospital, Calcutta Case Report.--S. B., aged 4 months, was born with eight fingers and no thumb on the left hand and
Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal
 Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism
 J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 159. XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism also Showing Features of Klinefelter's Syndrome D. A. SPENCER, JULIE W. EYLES, and M. K. MASON From Westwood Hospital, Bradford 6, and
J. med. Genet. (1969). 6, 159. XYY Syndrome, and XYY/XXYY Mosaicism also Showing Features of Klinefelter's Syndrome D. A. SPENCER, JULIE W. EYLES, and M. K. MASON From Westwood Hospital, Bradford 6, and
GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP
 GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP University of New Mexico 1. General Description: UNM MFM fellows rotate through genetics during their PGY5 and PGY7 years. The PGY5 fellow
GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVES MATERNAL-FETAL MEDICINE FELLOWSHIP University of New Mexico 1. General Description: UNM MFM fellows rotate through genetics during their PGY5 and PGY7 years. The PGY5 fellow
Dermatoglyphics and Cheiloscopy in the Inheritance of Cleft Lip and Palate: Unraveling the Mystery
 Original article Dermatoglyphics and Cheiloscopy in the Inheritance of Cleft Lip 10.5005/jp-journals-10021-1240 and Palate: Unraveling the Mystery Dermatoglyphics and Cheiloscopy in the Inheritance of
Original article Dermatoglyphics and Cheiloscopy in the Inheritance of Cleft Lip 10.5005/jp-journals-10021-1240 and Palate: Unraveling the Mystery Dermatoglyphics and Cheiloscopy in the Inheritance of
Dermatoglyphic Study in Oral Cancer and Precancerous Patients
 Original Research Article Dermatoglyphic Study in Oral Cancer and Precancerous Patients Dr. Daya Shankar 1, Dr. Shivendra Choudhary 2, Dr. Sobhana Chandra 3, Dr. Medha Nanda 4, Dr. Gayatri Bharti 5 1 Senior
Original Research Article Dermatoglyphic Study in Oral Cancer and Precancerous Patients Dr. Daya Shankar 1, Dr. Shivendra Choudhary 2, Dr. Sobhana Chandra 3, Dr. Medha Nanda 4, Dr. Gayatri Bharti 5 1 Senior
Dermatoglyphic patterns in subjects with potentially malignant disorders and oral carcinoma
 Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2015), 2, 7 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dermatoglyphic patterns in subjects with potentially malignant disorders and oral carcinoma Maria Priscilla David 1, Pooja
Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2015), 2, 7 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dermatoglyphic patterns in subjects with potentially malignant disorders and oral carcinoma Maria Priscilla David 1, Pooja
Aneuploidy: Dermatoglyphs, Parental Ages,
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1970). 7, 345. Comments on Patients with Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy: Dermatoglyphs, Parental Ages, Xga Blood Group DIGAMBER S. BORGAONKAR and EMILIE MULES From the Division
Journal of Medical Genetics (1970). 7, 345. Comments on Patients with Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy: Dermatoglyphs, Parental Ages, Xga Blood Group DIGAMBER S. BORGAONKAR and EMILIE MULES From the Division
Dermatoglyphic pattern in patients with bronchial asthma : A qualitative and quantitative study
 Dermatoglyphic pattern in patients with bronchial asthma : A qualitative and quantitative study Dr.Sahana B N 1, Dr. B M Bannur 2, Dr.B G Patil 3, Mr. G A Hadimani 4, Dr.Arun P Jose 5 1-4 Department of
Dermatoglyphic pattern in patients with bronchial asthma : A qualitative and quantitative study Dr.Sahana B N 1, Dr. B M Bannur 2, Dr.B G Patil 3, Mr. G A Hadimani 4, Dr.Arun P Jose 5 1-4 Department of
Comparison of Dermatoglyphic Patterns Between Healthy and Hypertensive People
 Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 5(1): 19-5, 1 ISSN: 4-8765; e-issn: 4-877 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 1 Submitted: August 4, 1 Accepted: October 19, 1 ublished: February 5, 1 Comparison of Dermatoglyphic
Asian Journal of Medical Sciences 5(1): 19-5, 1 ISSN: 4-8765; e-issn: 4-877 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 1 Submitted: August 4, 1 Accepted: October 19, 1 ublished: February 5, 1 Comparison of Dermatoglyphic
The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1968, 43, 94. The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome C. J. PADFIELD, M. W. PARTINGTON*, and N. E. SIMPSON* From the Departments of Paediatrics and Biology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario,
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1968, 43, 94. The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome C. J. PADFIELD, M. W. PARTINGTON*, and N. E. SIMPSON* From the Departments of Paediatrics and Biology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario,
Thumbs Up! A Novel Use of the Acutrak Screw Fixation System for the Management of Triphalangeal Thumb
 Thumbs Up! A Novel Use of the Acutrak Screw Fixation System for the Management of Triphalangeal Thumb Z. Ahmad, BSc(Hons), MBBS, MRCS, and C. N. McGuiness, MBBS, FRCS(Plast) Odstock Centre for Burns and
Thumbs Up! A Novel Use of the Acutrak Screw Fixation System for the Management of Triphalangeal Thumb Z. Ahmad, BSc(Hons), MBBS, MRCS, and C. N. McGuiness, MBBS, FRCS(Plast) Odstock Centre for Burns and
Medical Significance of Finger-prints and Related Phenomena*
 11 May 1968 BRITISH 321 Papers and Originals Medical Significance of Finger-prints and Related Phenomena* Brit. med. 7., 1968, 2, 321-325 History L. S. PENROSE,t M.D., D.SC., F.R.C.P., F.R.S. In 1684 a
11 May 1968 BRITISH 321 Papers and Originals Medical Significance of Finger-prints and Related Phenomena* Brit. med. 7., 1968, 2, 321-325 History L. S. PENROSE,t M.D., D.SC., F.R.C.P., F.R.S. In 1684 a
Gender variation in finger prints of Esan ethnic group of Edo state, Nigeria
 International Research on Medical Sciences Vol.4(5), pp. 071-075, June, 2016 Available online at http://www.apexjournal.org ISSN 2315-8845 2016 Apex Journal International Full Length Research Gender variation
International Research on Medical Sciences Vol.4(5), pp. 071-075, June, 2016 Available online at http://www.apexjournal.org ISSN 2315-8845 2016 Apex Journal International Full Length Research Gender variation
Congenital upper limb malformations : pictorial review
 Congenital upper limb malformations : pictorial review Poster No.: C-2085 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Aucourt, J.-F. Budzik, S. Manouvrier, A. Mezel, M. 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 1 3 Cagneaux,
Congenital upper limb malformations : pictorial review Poster No.: C-2085 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Aucourt, J.-F. Budzik, S. Manouvrier, A. Mezel, M. 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 1 3 Cagneaux,
Structural Chromosome Aberrations
 Structural Chromosome Aberrations 2 Structural chromosome aberrations or chromosome mutations represent apart from aneuploidies the most frequent pathologic findings in applied chromosome diagnostics.
Structural Chromosome Aberrations 2 Structural chromosome aberrations or chromosome mutations represent apart from aneuploidies the most frequent pathologic findings in applied chromosome diagnostics.
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL. Denise LM Goh
 APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
Alzheimer type: a case-control study
 INSERM U360, Epidemiological Research in Neurology and Psychopathology, 16 av P V Couturier, 94807 Villejuif Cedex, France C Berr A Alperovitch Hopital Charles Richet, Villiers Le Bel, France N Okra-Podrabinek
INSERM U360, Epidemiological Research in Neurology and Psychopathology, 16 av P V Couturier, 94807 Villejuif Cedex, France C Berr A Alperovitch Hopital Charles Richet, Villiers Le Bel, France N Okra-Podrabinek
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism
 Kamla-Raj 2006 Int J Hum Genet, 6(4): 291-295 (2006) Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism Cyril Cyrus 1, Teena K. 2, Solomon F.D.Paul 2, Chandra N.
Kamla-Raj 2006 Int J Hum Genet, 6(4): 291-295 (2006) Familial Robertsonian Translocation 13;21 in a Down Syndrome Patient with XYY/XY Mosaicism Cyril Cyrus 1, Teena K. 2, Solomon F.D.Paul 2, Chandra N.
Qualitative analysis fingertip patterns in ABO blood group
 GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND PUBLIC HEALTH Qualitative analysis fingertip patterns in ABO blood group S. V. KShirsagar 1*, S. P. Fulari 2 ABSTRACT The inheritance of the dermatoglyphic patterns is polygenic.
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND PUBLIC HEALTH Qualitative analysis fingertip patterns in ABO blood group S. V. KShirsagar 1*, S. P. Fulari 2 ABSTRACT The inheritance of the dermatoglyphic patterns is polygenic.
SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY.
 SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: GAIN,
SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: GAIN,
The Inheritance of Fingerprint Patterns
 Am J Hum Genet 28:280-289, 1976 The Inheritance of Fingerprint Patterns HERMAN M. SLATIS,1 MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON,2 AND BATSHEVA BONNE-TAMIR3 Although there have been a few reports on the inheritance
Am J Hum Genet 28:280-289, 1976 The Inheritance of Fingerprint Patterns HERMAN M. SLATIS,1 MARIASSA BAT-MIRIAM KATZNELSON,2 AND BATSHEVA BONNE-TAMIR3 Although there have been a few reports on the inheritance
SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY.
 SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: LOSS,
SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: LOSS,
Congenital upper limb malformations : pictorial review
 Congenital upper limb malformations : pictorial review Poster No.: C-2085 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Aucourt, J.-F. BUDZIK, S. Manouvrier, A. Mezel, M. 1 4 2 3 1 3 2 3 3 Cagneaux,
Congenital upper limb malformations : pictorial review Poster No.: C-2085 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Aucourt, J.-F. BUDZIK, S. Manouvrier, A. Mezel, M. 1 4 2 3 1 3 2 3 3 Cagneaux,
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: BASIC CONCEPTS OF PRAKRUTI IN AYURVEDA IN RELATION TO THE DERMATOGLYPHICS
 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 BASIC CONCEPTS OF PRAKRUTI IN AYURVEDA IN RELATION TO THE DERMATOGLYPHICS Sulgante Suharini 1 1 Lecturer, Dept of Shareera Rachana,SHES
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 BASIC CONCEPTS OF PRAKRUTI IN AYURVEDA IN RELATION TO THE DERMATOGLYPHICS Sulgante Suharini 1 1 Lecturer, Dept of Shareera Rachana,SHES
Role of Dermatoglyphic Fingertip Patterns in the prediction of Maturity Onset Diabetes Mellitus (Type II)
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 8, Issue 1 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 01-05 Role of Dermatoglyphic Fingertip Patterns in the prediction of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 8, Issue 1 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 01-05 Role of Dermatoglyphic Fingertip Patterns in the prediction of
AMERICAN BOARD OF MEDICAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS
 AMERICAN BOARD OF MEDICAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS Logbook Guidelines for Certification in Clinical Genetics and Genomics for the 2017 Examination as of 10/5/2015 Purpose: The purpose of the logbook is to
AMERICAN BOARD OF MEDICAL GENETICS AND GENOMICS Logbook Guidelines for Certification in Clinical Genetics and Genomics for the 2017 Examination as of 10/5/2015 Purpose: The purpose of the logbook is to
Association between Finger Patterns of Digit II and Intelligence Quotient Level in Adolescents
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:277-284 Association between Finger Patterns of Digit II and Intelligence Quotient Level in Adolescents Mostaf Najafi, MD Department of Psychiatry,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:277-284 Association between Finger Patterns of Digit II and Intelligence Quotient Level in Adolescents Mostaf Najafi, MD Department of Psychiatry,
Congenital malformations of human dermatoglyphs
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1973, 48, 191. Congenital malformations of human dermatoglyphs T. J. DAVID From the General Hospital, Bristol David, T. J. (1973). Archives of Disease in Childhood, 48,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1973, 48, 191. Congenital malformations of human dermatoglyphs T. J. DAVID From the General Hospital, Bristol David, T. J. (1973). Archives of Disease in Childhood, 48,
Congenital Differences of the Upper Extremity: Classification and Treatment Principles
 Review Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:172-177 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.3.172 Congenital Differences of the Upper Extremity: Classification and Treatment Principles Moon Sang
Review Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:172-177 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.3.172 Congenital Differences of the Upper Extremity: Classification and Treatment Principles Moon Sang
The carpal bones in Poland syndrome
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:585 591 DOI 10.1007/s00256-008-0638-x SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE The carpal bones in Poland syndrome Talia Friedman & Martin Reed & Alison M. Elliott Received: 28 October 2008 / Revised:
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:585 591 DOI 10.1007/s00256-008-0638-x SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE The carpal bones in Poland syndrome Talia Friedman & Martin Reed & Alison M. Elliott Received: 28 October 2008 / Revised:
Integra. SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE SafeGuard Mini Carpal Release System Contents Surgical Technique...2 Description...2 The SafeGuard System...2 Indications...2 Contraindications...2
SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE SafeGuard Mini Carpal Release System Contents Surgical Technique...2 Description...2 The SafeGuard System...2 Indications...2 Contraindications...2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Characterization of Congenital Anomalies in Individuals With Choanal Atresia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characterization of Congenital Anomalies in Individuals With Choanal Atresia T. Andrew Burrow, MD; Howard M. Saal, MD; Alessandro de Alarcon, MD; Lisa J. Martin, PhD; Robin T. Cotton,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characterization of Congenital Anomalies in Individuals With Choanal Atresia T. Andrew Burrow, MD; Howard M. Saal, MD; Alessandro de Alarcon, MD; Lisa J. Martin, PhD; Robin T. Cotton,
Challenges of CGH array testing in children with developmental delay. Dr Sally Davies 17 th September 2014
 Challenges of CGH array testing in children with developmental delay Dr Sally Davies 17 th September 2014 CGH array What is CGH array? Understanding the test Benefits Results to expect Consent issues Ethical
Challenges of CGH array testing in children with developmental delay Dr Sally Davies 17 th September 2014 CGH array What is CGH array? Understanding the test Benefits Results to expect Consent issues Ethical
B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and relate that theory to Gregor Mendel s principles of genetics
 B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and relate that theory to Gregor Mendel s principles of genetics The Chromosome theory of inheritance is a basic principle in biology that states genes
B-4.7 Summarize the chromosome theory of inheritance and relate that theory to Gregor Mendel s principles of genetics The Chromosome theory of inheritance is a basic principle in biology that states genes
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle
 CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
CYTOGENETICS Dr. Mary Ann Perle I) Mitosis and metaphase chromosomes A) Chromosomes are most fully condensed and clearly distinguishable during mitosis. B) Mitosis (M phase) takes 1 to 2 hrs and is divided
N. M. Scott. S. M. Weinberg. K. Neiswanger. College of Nursing Publications
 College of Nursing Publications 4-1-2005 Dermatoglyphic fingerprint heterogeneity among individuals with nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate and their unaffected relatives in China and
College of Nursing Publications 4-1-2005 Dermatoglyphic fingerprint heterogeneity among individuals with nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate and their unaffected relatives in China and
Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Multiple Copy Number Variations in a Patient with Developmental Delay ASCLS- March 31, 2016
 Multiple Copy Number Variations in a Patient with Developmental Delay ASCLS- March 31, 2016 Marwan Tayeh, PhD, FACMG Director, MMGL Molecular Genetics Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Department of Pediatrics
Multiple Copy Number Variations in a Patient with Developmental Delay ASCLS- March 31, 2016 Marwan Tayeh, PhD, FACMG Director, MMGL Molecular Genetics Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Department of Pediatrics
MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES. MG L-10 July 7 th 2014
 MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES MG L-10 July 7 th 2014 Genetic Diseases Unifactorial Chromosomal Multifactorial AD Numerical AR Structural X-linked Microdeletions Mitochondrial Spectrum of Alterations in DNA Sequence
MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASES MG L-10 July 7 th 2014 Genetic Diseases Unifactorial Chromosomal Multifactorial AD Numerical AR Structural X-linked Microdeletions Mitochondrial Spectrum of Alterations in DNA Sequence
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Syndactyly. What is syndactyly? Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
The unique find of male skeleton from Kalisz-Zawodzie with multiple pathological changes
 Studies in Historical Anthropology, vol. 4:2004[2006], pp. 207 212 The unique find of male skeleton from Kalisz-Zawodzie with multiple pathological changes Alina Wierciñska Laboratory of Anthropology State
Studies in Historical Anthropology, vol. 4:2004[2006], pp. 207 212 The unique find of male skeleton from Kalisz-Zawodzie with multiple pathological changes Alina Wierciñska Laboratory of Anthropology State
Patterns in Inheritance. Chapter 10
 Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
Patterns in Inheritance Chapter 10 What you absolutely need to know Punnett Square with monohybrid and dihybrid cross Heterozygous, homozygous, alleles, locus, gene Test cross, P, F1, F2 Mendel and his
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities. Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD. Pediatric Genetics Team
 Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Literature databases OMIM
 Literature databases OMIM Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man OMIM OMIM is a database that catalogues all the known diseases with a genetic component, and when possible links them to the relevant genes
Literature databases OMIM Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man OMIM OMIM is a database that catalogues all the known diseases with a genetic component, and when possible links them to the relevant genes
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs. Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
A PROPOSED INTERNATIONAL TERMINOLOGY FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL LIMB DEFICIENCIES*
 A PROPOSED INTERNATIONAL TERMINOLOGY FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL LIMB DEFICIENCIES* The Recommendations of a Working Group of the International Society for Prosthetics and Orthotics Hector W.
A PROPOSED INTERNATIONAL TERMINOLOGY FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF CONGENITAL LIMB DEFICIENCIES* The Recommendations of a Working Group of the International Society for Prosthetics and Orthotics Hector W.
