Theories of Schizophrenia. Dr Bharat Shah
|
|
|
- Jasmine Jessica Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theories of Schizophrenia Dr Bharat Shah
2 History Benedict Morel ( ) a French psychiatrist, used the term demence precoce to describe deteriorated patients whose illness began in adolescence. Emil Kraepelin ( ) translated Morels demence precoce into dementia precox. Patients with dementia precox were described as having a long-term deteriorating course and the clinical symptoms of hallucinations and delusions. Kraepelin distinguished these patients from manic-depressive psychosis and paranoia, which was characterized by persistent persecutory delusions and lacked the deteriorating course of dementia precox.
3 History A. Alzheimer ( ) made detailed observations of the cerebral pathology of psychotic patients. Consequently, he found that patients with psychotic symptoms exhibited no gliosis. As an expression describing this prolonged era, it was said that schizophrenia is a graveyard for neuropathologists. At the 1st International Congress of Neuropathology in 1952 (in Rome), the conclusion that there is no neuropathology of schizophrenia
4 Bleuler s theory Eugene Bleuler ( ) coined the term schizophrenia, which replaced dementia precox. He chose the term to express the presence of schisms between thought, emotion, and behavior in patients with the disorder. Fundamental (or primary) symptoms of schizophrenia: Associational disturbances of thought, especially looseness, Affective disturbances, Autism, and Ambivalence. Accessory (secondary) symptoms: hallucinations and delusions. They have encased themselves with their desires and wishes, have cut themselves off as much as possible from any contact with the external world. This detachment from reality with the relative and absolute predominance of the inner life is autism
5 Psychoanalytical theory Schizophrenia is a regression to the oral stage when the ego has not emerged from the id. As there is no distinct ego, by regressing to the primary narcissistic stage, schizophrenics lose contact with the world. There is heightening of id impulses specially of sexual nature during adolescence. Lack of interpersonal relations and libidinal attachment are attributed to pt s heightened sensitivity to criticism. By trying to adapt with the demands of the id impulses and to have contact with some stimulus, symptoms of delusions, hallucination and thought disorders are found.
6 Psychoanalytical theory Freud named the illness as narcissistic neuroses. In his view, positive symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions were restitutional. His famous quote is - A delusion is like a patch applied over the tear between the ego and external world
7 Psychosocial theory Harry Sullivan viewed SCZ as disturbance in interpersonal relatedness. Severe anxiety that threatens sense of self and unrelatedness is rescued by distortions which lead to paranoia.
8 Family Systems An early, but since discredited theory, focused on the role of the schizophrenogenic mother. In what some feminists view as historic psychiatric sexism, the schizophrenogenic mother was described as cold, aloof, overprotective, and domineering. She was characterized as stripping her children of self-esteem, stifling their independence, and forcing them into dependency on her. Children reared by such mothers were believed to be at special risk for developing schizophrenia if their fathers were passive and failed to counteract the mother s pathogenic influences.
9 Family Systems Theory Origins in: The psychoanalytical tradition (the influence of the family on abnormal behaviour) Systems thinking (idea that things are best understood by looking at the relationships between a set of entities)
10 Family System M F A family can be seen as a set of entities, each interacting with all the others. C 1 C 2 C 3 The behaviour of each entity can only be understood by looking at its relationships with the others
11 Family System M F If one person starts to behave abnormally the problem might not lie within that person C 1 C 2 C 3 Their behaviour may be a manifestation of a problem occurring within the wider family system
12 Double Bind Theory In a double bind situation a person is given mutually contradictory signals by another person This places them in an impossible situation, causing internal conflict Schizophrenic symptoms represent an attempt to escape from the double bind The patient is a symptom of a family-wide problem They become ill to protect the stability of the family system
13 Family System-EE Some evidence that family processes play a role in relapse of schizophrenia patients following stabilisation Relapse more likely (58% vs. 10%) where family is high in expressed emotion Families high in criticism, hostility over-involvement
14 Punishment LEARNING THEORY Withdrawal Labelled as odd Reinforced by attention Conforming to label
15 Neuropathology Subsequently, in the 1980s, with progress in brain imaging technology such as CT, morphological abnormalities of schizophrenia were reported, and moreover, with MRI, PET, SPECT, and the like, detailed brain images including the functions of schizophrenia cases were examined. Neuropathological techniques such as image analysis with a computer, and immunohistological special staining and post 1990, genetic research added to the view of brain damage
16 Neuropathology in SCZ,
17 Brain volume loss in SCZ
18 Two hit theory
19 Neuro developmental dysfunction hypothesis
20 Environmental risk factors in schizophrenia From: Sullivan, The Genetics of Schizophrenia. PloS Medicine
21 The influence of adolescent-onset cannabis use on adult psychosis is moderated by variations in the COMT gene Caspi et al, 2005.
22 Good idea to genotype yourself before you fly to Amsterdam. 13% of individuals carrying the Val/Val genotype and using cannabis had schizophreniform disoder
23 Immunological theories in SCZ 13% of individuals carrying the Val/Val genotype and using cannabis had schizophreniform disoder Good idea to genotype yourself before you fly to Amsterdam.
24 The familial risk of schizophrenia A graph to show the genetic risk of developing schizophrenia.
25 Genetics Generally speaking, the more closely one is related to people who have developed schizophrenia, the greater the risk of developing schizophrenia for oneself. Monozygotic (MZ) twins, whose genetic heritages are identical, are much more likely than dizygotic (DZ) twins, whose genes overlap by 50%, to be concordant for schizophrenia.
26 Genetics: The Copenhagen High-Risk Study Kety and collegues (1962) identified 207 offspring of mothers diagnosed with schizophrenia (high risk) along with a matched control of 104 children with healthy mothers (low risk) Children aged between years at start of study and matched on age, gender, parental socio-economic status and urban/rural residence.
27 Follow-up studies conducted in 1974 and 1989 Results: Schizophrenia diagnosed in 16.2% of high risk group compared to 1.9% in low risk group Schizotypal personality disorder diagnosed in 18.8% of high risk group vs 5% of low risk group
28 Genetics: Twin Studies Compare concordance rates for identical (MZ) and dizygotic (DZ) twins Both share the same environment but only MZ twins have identical genetics Many studies conducted all show much higher concordance rate in MZ than DZ twins To separate environment from genetic influences, researchers have sought out MZ twins reared apart where at least 1 has been diagnosed with schizophrenia
29 Genetics: Twin Studies Gottesman & Shields (1982) used the Maudsley twin register and found 58% (7/12 MZ) twins reared apart were concordant for schizophrenia. If the genetic hypothesis is correct, then the offspring of a non-affected discordant MZ twin should still be highrisk A study found that 9.4% of such offspring developed schizophrenia, which is a much higher incidence than in the general population (1%)
30 Genetics: Adoption Studies More effective in separating effects of genetic and environmental factors Look at adopted children who later develop schizophrenia and compare to biological parents
31 The Finish Adoption Study (1969) identified adopted offspring of biological mothers with schizophrenia (112 cases) Matched control group (135 adopted offspring of nonschizophrenic biological mothers) Adoptees ranged from 5-7 yrs at the start of the study, and separated from mothers before 4 Study checked children again in 1987 Reported 7% of high risk group developed schizophrenia compared to 1.5% of controls. The Danish Adoption Study (1994) took a national sample across Denmark Found high rates of diagnosis for chronic schizophrenia in adoptees whose biological parents had the same diagnosis, despite living with healthy parents
32 Genetics Strategies to find specific genes that cause SCZ: Linkage studies Association studies Single nucleotide polymorphism(snp) genotyping Copy number variants
33
34
35
36 Candidate genes in schizophrenia
37
38
39 Neurophysiological Evidence : Auditory P300 Abnormalities One of the most consistently replicated neurophysiological abnormalities observed in schizophrenia. Auditory P300 amplitude is reduced, often delayed Observed in chronic patients, first episode patients, schizophrenia spectrum patients, and first degree relatives of schizophrenic patients. Good Endophenotype ( A possible marker of genetic vulnerability and/or neurodevelopmental insult) Another abnormality is N100. Interpretation is Pts are highly sensitive to incoming stimuli and compensate by blunting the processing at a higher cortical level.
40 PPI and MMN Inability to filter irrelevant sensory information is cognitive defect. A neuro physiological correlate of this deficit is evaluated by a preattentive paradigm called paired pulse inhibition (PPI). Subjects are presented a startling (test) stimulus with or without a preceding non-startling (conditioning) stimulus. In control subjects, the response to the test stimulus is suppressed by the conditioned stimulus, but this suppression is reduced in SCZ subjects Another ERP is MisMatch Negativity(MMN). An evoked potential generated in the supra-granular layer of primary auditory cortex called mismatch negativity is reduced in schizophrenia.
41 Dopaminergic theory:history How did chlorpromazine work? Role of dopamine. The relation between the clinical effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs and their affinity for dopamine receptors..
42
43
44
45 Revised dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: Prefrontal deficit and subcortical hyperdopaminergia Mesocortical DA projections to the prefrontal cortex might be hypoactive -> hypostimulation of D1 receptors -> negative symptoms and cognitive impairment Subcortical mesolimbic DA projections might be hyperactive-> hyperstimulation of D2 receptors -> productive symptoms Frontal cortex hypoactivity Limbic system hyperactivity Negative symptoms Davis KL, Kahn RS, Am J Psychiatry.1991;148: Positive symptoms
46 Dopamine in schizophrenia Patients with schizophrenia have elevated synthesis and storage of dopamine in presynaptic dopaminergic nerve terminals in striatum. This is the most consistent finding. The increased levels are linked with increase in psychosis. Increased dopamine release at synapses and baseline increased occupancy of D2 receptors by dopamine. There is some evidence of D1 receptor levels in PFC and that reflects chronic low dopamine levels in PFC and relates with negative and cognitive defects. Moore RY, Brain Res. 2003;982: Abi-Dargham A, J Neurosci. 2002;22:
47 Aberrant Salience Salience refers to the motivational properties of a stimulus, which can cause it to attract attention and drive behavior. Aberrant salience refers to the tendency for irrelevant stimuli to be attributed motivational salience and thus to attract attention and influence behavior inappropriately Roiser JP, Schizophrenia Bulletin, 2013,vol. 39 no. 6:
48 Aberrant Salience Increasing evidence of dopamine s role in motivational incentive salience. Abnormal firing of dopamine neurons and the abnormal release of dopamine leads to an aberrant assignment of salience to innocuous stimuli. Over time the individual s own explanation of the experience of aberrant salience leads to formation of delusions and hallucinations Kapur S, Mizrahi R, Li M. Schizophr Res. 2005;79:59 68.
49 Environmental factors and Dopamine Late environmental markers of adversity such as migration, unemployment, urban upbringing, lack of close friends, and childhood abuse are all associated with a well-established increased risk for schizophrenia Animal Studies of social isolations and subordination find that these factors lead to dopaminergic overactivity.
50 Dopamine model of psychosis Oliver D. Howes and Shitij Kapur Schizophr Bull. May 2009; 35(3):
51 Glutamate hypothesis Phencyclidine (PCP): dissociative anesthetic: Noncompetitive NMDA antagonist (blocks Ca2+ channel) 2 weeks PCP in monkeys schizophrenia-like symptoms Including poor performance on frontal lobe-sensitive task Ketamine (NMDA antag) similar effects In Schizophrenia is there a pathology that is causing NMDA hypofunction?
52 Glutamate system and schizophrenia (1) NMDA Receptors Hypofunction Hypothesis of Schizophrenia (The Glutamate theory vs the Dopamine theory in schizophrenia) (2) The Glutamate Excitotoxicity as part of the Neurodevelopmental Theory of Schizophrenia The excessive pruning theory 52
53 Gluamate Glu is an aminoacid involved in building proteins, and in energy metabolism. It is aslo a NT Glu is the workhorse transmitter for excitatory signaling in the nervous system > 60% receptors in brain Involved in many behavioral and physiological functions, but perhaps the most important is synaptic plasticity Changes in the strength of connections Learning and memory
54
55
56
57 NMDA receptors NMDA receptors require two different neurotransmitters to open the channel 1) Glutamate 2) Glycine or D-serine Glycine (or D-serine) has its own binding site. Thus glycine (or D-serine) is considered to be a co-agonist. Usually the co-agonist binding site is occupied though, so the presence or absence of glutamate determines channel opening
58 GABA receptors
59 GABA interneurons Most Gabaergic cortical interneurons can be divided into three distinct subgroups based on several neurochemical markers: parvalbumin- (PV+), somatostatin- (Sst+), or calretininexpressing(cr+) interneurons. PV+ are fast-spiking (FS) and comprise two major subtypes: basket and chandelier cells.
60
61 Evidence: Neuropatholgy in GABA cells There is decreased expression of GABA synthesizing enzyme- Glutamic acid decaroxylase (GAD)esp its isoform GAD67 in paravalbumin containing GABAergic chandelier and basket cells in DLPC, hippocampus. These cells innervate Glutamatergic Pyramidal cells and inhibit them.
62 GABA and Epigenetics GAD67 levels are tightly controlled by neural activity via transcriptional regulation of GAD1, the gene encoding GAD67. Different levels of GAD1 transcription maybe linked to genetic variability, and polymorphisms in the 5 region of GAD1 have been associated with schizophrenia and decreased GAD67 transcription. In the cortex of a subset of schizophrenia patients, methylation of histones (the core proteins of chromatin) near the promoter region of GAD1 shows a shift from transcription-open to transcription repressive chromatin structure, which is accompanied by a reduction in GAD67 mrna in the same individuals.
63 GABA and cortical oscillations GABA-mediated inhibition may play roles in addition to oscillatory synchronization of neuronal activity. GABA mediated inhibition are important to maintain and terminate persistent activity. Persistent activity is viewed as the cellular basis of working memory, a form of memory that is altered in schizophrenia and is essential for cognitive function.
64 GABA and cortical oscillations Mice were genetically engineered to express light-sensitive ion channels exclusively in pyramidal cells or PV neurons in order to selectively drive cell activity by means of light flashes. Selective activation of PV cells in these mice produced γ band oscillations, whereas inhibiting PV neurons suppressed them. Moreover, nonrhythmic stimulation of pyramidal neurons drives PV cells to produce feedback inhibition generated a γ rhythm. These and other elegant optogenetics experiments show that PV cell activity, possibly driven by pyramidal cells via AMPARs, generates γ oscillations.
65
66
67
68 Ketamine & Sigma receptor Ketamine has mild sigma R blocking action. The sigma receptor is a nonopioid receptor found in the endoplasmic reticulum. The sigma-1 receptor is involved in mitochondrial Ca2+ signaling, neuroprotection, neuroplasticity, and neurite outgrowth, thus leading to the hypothesis that it is also necessary for optimal cognition and cerebral metabolism. Sigma receptor ligands can protect dopaminergic cells from the excitotoxic effects of NMDA. Mice that are repeatedly administered PCP show frontocortical reductions of the sigma-1 receptor.
69 Ketamine & Kappa opioid receptor Ketamine to be an agonist of the kappa opioid receptor. Salvinorin A is a kappa receptor agonist and the most potent naturally occurring hallucinogen. Many studies report a positive correlation between levels of dynorphins, endogenous kappa receptor ligands, in the cerebrospinal fluid of schizophrenia patients and psychotic symptoms. An abnormal laminar distribution of kappa receptors in the hippocampus has also been reported for schizophrenia patients. Finally, kappa receptor agonists administered to rats have varied effects on prepulse inhibition, which is reduced in schizophrenia.
70
71 THANK YOU
Outline. Outline. Background Literature and Slides 10/23/2013. The Schizophrenia Research Forum online: Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior
 Background Literature and Slides Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior Roberto Fernández Galán, PhD Assistant Professor of Neurosciences Mt. Sinai Health Care Foundation Scholar Alfred P. Sloan Research
Background Literature and Slides Molecules, Neural Networks and Behavior Roberto Fernández Galán, PhD Assistant Professor of Neurosciences Mt. Sinai Health Care Foundation Scholar Alfred P. Sloan Research
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal
 ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia
 Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders
 The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
Computational Neuropharmacology
 Computational Neuropharmacology Schizophrenia: Symptoms & Pathologies Computational Models of Mental Illness: Neurons, synapses and modulators Example: Working Memory Model Pharmaceutical Industry: Progress
Computational Neuropharmacology Schizophrenia: Symptoms & Pathologies Computational Models of Mental Illness: Neurons, synapses and modulators Example: Working Memory Model Pharmaceutical Industry: Progress
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health
 Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Schizophrenia: What Do We Know? Where Do We Go From Here? Tracey G. Skale, MD Chief Medical Officer Greater Cincinnati Behavioral Health Objectives Participants will be able to: Understand the clinical
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs
 Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION. Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre
 1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
Dr. Fred Rose. Schizophrenia. Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview. Prevalence of Schizophrenia 10/20/10. Schizophrenia vs.
 Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses
 Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Genetics of Behavior (Learning Objectives)
 Genetics of Behavior (Learning Objectives) Recognize that behavior is multi-factorial with genetic components Understand how multi-factorial traits are studied. Explain the terms: prevalence, incidence,
Genetics of Behavior (Learning Objectives) Recognize that behavior is multi-factorial with genetic components Understand how multi-factorial traits are studied. Explain the terms: prevalence, incidence,
Schizophrenia What is schizophrenia? Definition, pros and cons Core symptoms, other features
 Schizophrenia What is schizophrenia? Definition, pros and cons Core symptoms, other features Kraepelin s dementia praecox Early 1800 s, not much of a language for describing mental illness, odd behaviour
Schizophrenia What is schizophrenia? Definition, pros and cons Core symptoms, other features Kraepelin s dementia praecox Early 1800 s, not much of a language for describing mental illness, odd behaviour
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00
 Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders
 and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Schizophrenia. Positive Symptoms. Course of Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders?
 Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Genes and environment: The complex etiology of psychiatric disorders
 Genes and environment: The complex etiology of psychiatric disorders János Réthelyi, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy Semmelweis University September 18th 2013 Outline The issue of
Genes and environment: The complex etiology of psychiatric disorders János Réthelyi, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy Semmelweis University September 18th 2013 Outline The issue of
DOPAMINERGIC AND GLUTAMATERGIC DYSFUNCTIONS IN
 Chapter DOPAMINERGIC AND GLUTAMATERGIC DYSFUNCTIONS IN THE NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Wen-Jun Gao * Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia,
Chapter DOPAMINERGIC AND GLUTAMATERGIC DYSFUNCTIONS IN THE NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Wen-Jun Gao * Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia,
Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Age Distribution of Onset 2/24/2009. Schizophrenia. Hallmark trait is psychosis
 Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Genetics of Behavior (Learning Objectives)
 Genetics of Behavior (Learning Objectives) Recognize that behavior is multi-factorial with genetic components Understand how multi-factorial traits are studied. Explain the terms: incidence, prevalence,
Genetics of Behavior (Learning Objectives) Recognize that behavior is multi-factorial with genetic components Understand how multi-factorial traits are studied. Explain the terms: incidence, prevalence,
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 Similar observations in all subsets of the disorder. Personality Disorders. General Symptoms. Chapter 9
 Slide 1 Personality Disorders Chapter 9 Slide 2 General Symptoms Problems must be part of an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates significantly from the expectations of the individual
Slide 1 Personality Disorders Chapter 9 Slide 2 General Symptoms Problems must be part of an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates significantly from the expectations of the individual
Schizophrenic twin. Normal twin
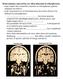 Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
serotonin in learning and plasticity
 serotonin in learning and plasticity pt.1 immediate action L P H N NRX N N R X N CDH RhoA/ROCK RAC1 DAG [Ca2+] camp GIRK2 P11 Gq CASK PICK1 VELI MINT-1 CaMK Ca2+ channel AC Gi mglur7 mglur5 Glutamate NMDAR
serotonin in learning and plasticity pt.1 immediate action L P H N NRX N N R X N CDH RhoA/ROCK RAC1 DAG [Ca2+] camp GIRK2 P11 Gq CASK PICK1 VELI MINT-1 CaMK Ca2+ channel AC Gi mglur7 mglur5 Glutamate NMDAR
WEEK 1 - Application of the stress-vulnerability model in the context of schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder:
 WEEK 1 - Application of the stress-vulnerability model in the context of schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder: Aetiological models Theories relating to the aetiology of the mental illness can be
WEEK 1 - Application of the stress-vulnerability model in the context of schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder: Aetiological models Theories relating to the aetiology of the mental illness can be
PERCEPTION: Gain Control & Integration. Mark A. Geyer, Ph.D. Departments of Psychiatry & Neurosciences University of California, San Diego
 PERCEPTION: Gain Control & Integration Mark A. Geyer, Ph.D. Departments of Psychiatry & Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Perception Integration Integration: The processes linking the output
PERCEPTION: Gain Control & Integration Mark A. Geyer, Ph.D. Departments of Psychiatry & Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Perception Integration Integration: The processes linking the output
marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD
 marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD in this talk what is marijuana? the brain on marijuana is the teen brain special? current research what is marijuana?
marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD in this talk what is marijuana? the brain on marijuana is the teen brain special? current research what is marijuana?
Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
4. General overview Definition
 4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
4. General overview 4.1. Definition Schizophrenia is a severe psychotic mental disorder characterized by significant disturbances of mental functioning. It has also been called early dementia, intrapsychic
How have developments in molecular imaging techniques furthered schizophrenia research?
 REVIEW How have developments in molecular imaging techniques furthered schizophrenia research? Molecular imaging techniques have led to significant advances in understanding the pathophysiology of schizophrenia
REVIEW How have developments in molecular imaging techniques furthered schizophrenia research? Molecular imaging techniques have led to significant advances in understanding the pathophysiology of schizophrenia
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003
 Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP
 Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP Disclosures This speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Define drug abuse and addiction Identify the
Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP Disclosures This speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Define drug abuse and addiction Identify the
LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS
 LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS Dolores Malaspina, MD, MS, MSPH Anita & Joseph Steckler Professor of Psychiatry & Child Psychiatry - NYU Langone Medical Center
LO S I N G TO U C H W I T H R E A L I T Y SEARCHING FOR THE SEEDS OF PSYCHOSIS Dolores Malaspina, MD, MS, MSPH Anita & Joseph Steckler Professor of Psychiatry & Child Psychiatry - NYU Langone Medical Center
Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders
 1 6 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders 16 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders The Toll of Psychiatric Disorders Is Huge Schizophrenia is the major neurobiological
1 6 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders 16 Psychopathology: Biological Basis of Behavioral Disorders The Toll of Psychiatric Disorders Is Huge Schizophrenia is the major neurobiological
Reversing the Effects of Fragile X Syndrome
 CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF BASIC RESEARCH Paul J. Lombroso, M.D., Marilee P. Ogren, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Reversing the Effects of Fragile X Syndrome MARILEE P. OGREN, PH.D., AND PAUL J. LOMBROSO, M.D.
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF BASIC RESEARCH Paul J. Lombroso, M.D., Marilee P. Ogren, Ph.D. Assistant Editors Reversing the Effects of Fragile X Syndrome MARILEE P. OGREN, PH.D., AND PAUL J. LOMBROSO, M.D.
marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD
 marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD in this talk what is marijuana? the brain on marijuana is the teen brain special? current research what is marijuana?
marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD in this talk what is marijuana? the brain on marijuana is the teen brain special? current research what is marijuana?
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development. John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University
 Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University Four problems We don t know the disorders sufficiently The biology is complex and heterogeneous We have animal
Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University Four problems We don t know the disorders sufficiently The biology is complex and heterogeneous We have animal
SCHIZOPHRENIA IS COGNITION IMPAIRED IN SCHIZOPHRENIA?
 CHAPTER 10: DISTURBED COGNITION IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Traditionally, functioning of the mind is described under four headings: perception, emotion, cognition, and conation. Perception refers to awareness of
CHAPTER 10: DISTURBED COGNITION IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Traditionally, functioning of the mind is described under four headings: perception, emotion, cognition, and conation. Perception refers to awareness of
Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues. ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland
 Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland Need for a New Treatment Paradigm in Schizophrenia Sixty years after approval for the
Disease Modification in Schizophrenia: Overview of the Issues ISCTM February 18 th 2014 Ravi Anand, MD Switzerland Need for a New Treatment Paradigm in Schizophrenia Sixty years after approval for the
Animal Models of Psychosis: Current State and Future Directions
 Curr Behav Neurosci Rep (2014) 1:100 116 DOI 10.1007/s40473-014-0013-2 PSYCHOSIS (R GUR AND B CLEMENTZ, SECTION EDITORS) Animal Models of Psychosis: Current State and Future Directions Alexandra D. Forrest
Curr Behav Neurosci Rep (2014) 1:100 116 DOI 10.1007/s40473-014-0013-2 PSYCHOSIS (R GUR AND B CLEMENTZ, SECTION EDITORS) Animal Models of Psychosis: Current State and Future Directions Alexandra D. Forrest
The Role of Smoking in Cocaine. Addiction
 The Role of Smoking in Cocaine Addiction Luca Colnaghi Eric Kandel Laboratory Columbia University in the City of New York Department of Neuroscience Index 1- The Brain, memory, metaplasticity 2- Cocaine
The Role of Smoking in Cocaine Addiction Luca Colnaghi Eric Kandel Laboratory Columbia University in the City of New York Department of Neuroscience Index 1- The Brain, memory, metaplasticity 2- Cocaine
Neuropsychiatry. I. Schizophrenia II. Mood Disorders III. Substance-Related Disorders
 Neuropsychiatry I. Schizophrenia II. Mood Disorders III. Substance-Related Disorders I. Schizophrenia Important Initial Contributors Emil Kraepelin Dementia praecox Eugene Bleuler Schizophrenia Positive
Neuropsychiatry I. Schizophrenia II. Mood Disorders III. Substance-Related Disorders I. Schizophrenia Important Initial Contributors Emil Kraepelin Dementia praecox Eugene Bleuler Schizophrenia Positive
NEUROBIOLOGY ALCOHOLISM
 NEUROBIOLOGY ALCOHOLISM THERE HAS BEEN A MAJOR THEORETICAL SHIFT IN MEDICATION DEVELOPMENT IN ALCOHOLISM Driven by animal models of intermittent ethanol administration followed by termination, then access
NEUROBIOLOGY ALCOHOLISM THERE HAS BEEN A MAJOR THEORETICAL SHIFT IN MEDICATION DEVELOPMENT IN ALCOHOLISM Driven by animal models of intermittent ethanol administration followed by termination, then access
Genetics of psychiatric disorders Dr Radwan Banimustafa
 Genetics of psychiatric disorders Dr Radwan Banimustafa Schizophrenia Is a chronic relapsing psychotic disorder which affects young population and interfere with: - Thoughts - Perception - Volition - Behavior
Genetics of psychiatric disorders Dr Radwan Banimustafa Schizophrenia Is a chronic relapsing psychotic disorder which affects young population and interfere with: - Thoughts - Perception - Volition - Behavior
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com
 Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis
 Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture. Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu
 Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture Speaker: Title: What Anthony is the title Berger/Angela of this lecture? Williams Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu Chapter
Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture Speaker: Title: What Anthony is the title Berger/Angela of this lecture? Williams Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu Chapter
590,000 deaths can be attributed to an addictive substance in some way
 Mortality and morbidity attributable to use of addictive substances in the United States. The Association of American Physicians from 1999 60 million tobacco smokers in the U.S. 14 million dependent on
Mortality and morbidity attributable to use of addictive substances in the United States. The Association of American Physicians from 1999 60 million tobacco smokers in the U.S. 14 million dependent on
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTS, PARADIGMS AND STIGMA KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTS, PARADIGMS AND STIGMA KEY TERMS American Psychiatric Association (APA) A scientific and professional organization that represents psychiatry in the United States Amygdala The region
CHAPTER 1: CONCEPTS, PARADIGMS AND STIGMA KEY TERMS American Psychiatric Association (APA) A scientific and professional organization that represents psychiatry in the United States Amygdala The region
Index. Index. More information
 ability dysfunctional beliefs affecting 91 92 motivation and negative symptoms 90 91 acetylcholine 269 270 acetylcholinesterase inhibitors 272 adolescents, relevance of performance-based measures 262 affect
ability dysfunctional beliefs affecting 91 92 motivation and negative symptoms 90 91 acetylcholine 269 270 acetylcholinesterase inhibitors 272 adolescents, relevance of performance-based measures 262 affect
IMPLICATIONS OF GENE- ENVIRONMENT INTERPLAY FOR APPROACHES TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND COMORBIDITY
 Ppt. Oslo 3 th Nov 9 IMPLICATIONS OF GENE- ENVIRONMENT INTERPLAY FOR APPROACHES TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND COMORBIDITY By Michael Rutter PERCENTAGE OF GENETIC INFLUENCE REPORTED IN BEHAVIORAL GENETIC STUDIES
Ppt. Oslo 3 th Nov 9 IMPLICATIONS OF GENE- ENVIRONMENT INTERPLAY FOR APPROACHES TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND COMORBIDITY By Michael Rutter PERCENTAGE OF GENETIC INFLUENCE REPORTED IN BEHAVIORAL GENETIC STUDIES
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION
 BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
CORTICAL INHIBITORY NEURONS AND SCHIZOPHRENIA
 CORTICAL INHIBITORY NEURONS AND SCHIZOPHRENIA David A. Lewis*,Takanori Hashimoto* and David W. Volk* Abstract Impairments in certain cognitive functions, such as working memory, are core features of schizophrenia.
CORTICAL INHIBITORY NEURONS AND SCHIZOPHRENIA David A. Lewis*,Takanori Hashimoto* and David W. Volk* Abstract Impairments in certain cognitive functions, such as working memory, are core features of schizophrenia.
Neurobiology of Addiction. Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago
 Neurobiology of Addiction Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Disclosure Information I have the following financial relationships to disclose: My research is supported by NIDA, AFSP,
Neurobiology of Addiction Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Disclosure Information I have the following financial relationships to disclose: My research is supported by NIDA, AFSP,
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
The Biological Perspective. Jørg Mørland Senior researcher, Norwegian Institute of Public Health Professor em of Medicine University of Oslo
 The Biological Perspective Jørg Mørland Senior researcher, Norwegian Institute of Public Health Professor em of Medicine University of Oslo The Biological Perspective What is it? More than «the» one biological
The Biological Perspective Jørg Mørland Senior researcher, Norwegian Institute of Public Health Professor em of Medicine University of Oslo The Biological Perspective What is it? More than «the» one biological
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 15 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 15 Alphabetical antipsychotic drugs antipsychotic drugs Neuroleptic drugs. Used to treat schizophrenia. Primarily block dopamine receptors. atypical
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 15 Alphabetical antipsychotic drugs antipsychotic drugs Neuroleptic drugs. Used to treat schizophrenia. Primarily block dopamine receptors. atypical
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia - continued
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder
 Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago, IL 6/8/2016 Disclosure Information My research is
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago, IL 6/8/2016 Disclosure Information My research is
CASE 49. What type of memory is available for conscious retrieval? Which part of the brain stores semantic (factual) memories?
 CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
A NEW APPROACH FOR BORDERLINE PERSONALITY DISORDER
 A NEW APPROACH FOR BORDERLINE PERSONALITY DISORDER WPA Melbourne Feb 2018 Professor Jayashri Kulkarni Monash Alfred Psychiatry Research Centre. Melbourne Funding disclosure NHMRC grant : A Randomised Controlled
A NEW APPROACH FOR BORDERLINE PERSONALITY DISORDER WPA Melbourne Feb 2018 Professor Jayashri Kulkarni Monash Alfred Psychiatry Research Centre. Melbourne Funding disclosure NHMRC grant : A Randomised Controlled
Announcements. Grade Query Tool+ PsychPortal. Final Exam Wed May 9, 1-3 pm
 Grade Query Tool+ Announcements This tool is the definitive source for your final grade! Now includes Grade Estimator Tool PsychPortal Technical glitches in Learning Curves for Chapters 5, 14, and 15 are
Grade Query Tool+ Announcements This tool is the definitive source for your final grade! Now includes Grade Estimator Tool PsychPortal Technical glitches in Learning Curves for Chapters 5, 14, and 15 are
Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
 Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia In other information sheets we have discussed the two major types of symptoms traditionally thought to characterise schizophrenia: first of all the positive symptoms
Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia In other information sheets we have discussed the two major types of symptoms traditionally thought to characterise schizophrenia: first of all the positive symptoms
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Computational Psychiatry: Tasmia Rahman Tumpa
 Computational Psychiatry: Tasmia Rahman Tumpa Computational Psychiatry: Existing psychiatric diagnostic system and treatments for mental or psychiatric disorder lacks biological foundation [1]. Complexity
Computational Psychiatry: Tasmia Rahman Tumpa Computational Psychiatry: Existing psychiatric diagnostic system and treatments for mental or psychiatric disorder lacks biological foundation [1]. Complexity
ES.S10: Drugs and the Brain Syllabus Spring 2013 Zak Fallows
 ES.S10: Drugs and the Brain Syllabus Spring 2013 Zak Fallows About the Class: One-Sentence Description: This class is a multidisciplinary introduction to pharmacology, neurotransmitters, drug mechanisms,
ES.S10: Drugs and the Brain Syllabus Spring 2013 Zak Fallows About the Class: One-Sentence Description: This class is a multidisciplinary introduction to pharmacology, neurotransmitters, drug mechanisms,
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders
 PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
PSYCH 335 Psychological Disorders Chapter 10 Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders Outline/Overview Schizophrenia Statistics/Impact/History Criteria Prognostic indicators/ suicide Epidemiology/correlates
The Neurobiology of Mood and Psychotic Disorders
 The Neurobiology of Mood and Psychotic Disorders Daphne J. Holt, MD, PhD Co-Director, Schizophrenia Clinical and Research Program Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor,
The Neurobiology of Mood and Psychotic Disorders Daphne J. Holt, MD, PhD Co-Director, Schizophrenia Clinical and Research Program Department of Psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor,
Final Exam PSYC2022. Fall (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication with cannabis.
 Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions
 The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions Lobes in a lateral view of left hemisphere Atlas Fig.2-11 The Insula The Hidden Lobe Atlas Fig. 2-11 Atlas Fig. 2-39 Lobes in a lateral view of left
The Cerebral Cortex and Higher Intellectual Functions Lobes in a lateral view of left hemisphere Atlas Fig.2-11 The Insula The Hidden Lobe Atlas Fig. 2-11 Atlas Fig. 2-39 Lobes in a lateral view of left
Potential Treatment and Current Research in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome. 11/16/2016 Frambu Center for Rare Disorders
 Potential Treatment and Current Research in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome 11/16/2016 Frambu Center for Rare Disorders Genetics is Complicated! Deletion 22q13: Therapies Under Investigation Intranasal insulin
Potential Treatment and Current Research in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome 11/16/2016 Frambu Center for Rare Disorders Genetics is Complicated! Deletion 22q13: Therapies Under Investigation Intranasal insulin
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
vglu-t ~ metabotropic ~ ./ AMPA \ kainate Receptors receptor
 Glutamate Receptors vglu-t ~ \ metabotropic ~ receptor @\presynaptic EAAT./ AMPA receptor \ kainate receptor FIGURE 9-36 Glutamate receptors. Shown here are receptors for glutamate that regulate its neurotransmission.
Glutamate Receptors vglu-t ~ \ metabotropic ~ receptor @\presynaptic EAAT./ AMPA receptor \ kainate receptor FIGURE 9-36 Glutamate receptors. Shown here are receptors for glutamate that regulate its neurotransmission.
Neurons have cell membranes that separate them from the environment outside the neuron.
 Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
PHARMACOLOGY Vol. I - Neuropsychopharmacology - Mirjam A.F.M. Gerrits and Jan M. van Ree
 NEUROPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY Mirjam A.F.M. Gerrits and Jan M. van Ree Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, Department of Neuroscience and Pharmacology, Universiteitsweg 100, 3584 CG Utrecht, The Netherlands
NEUROPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY Mirjam A.F.M. Gerrits and Jan M. van Ree Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, Department of Neuroscience and Pharmacology, Universiteitsweg 100, 3584 CG Utrecht, The Netherlands
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain -
 - Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
Topography and significance of the dopaminergic dysfunction in schizophrenia
 Topography and significance of the dopaminergic dysfunction in schizophrenia Anissa Abi-Dargham MD Professor of Psychiatry and Vice Chair for Research Department of Psychiatry Stony Brook University Professor
Topography and significance of the dopaminergic dysfunction in schizophrenia Anissa Abi-Dargham MD Professor of Psychiatry and Vice Chair for Research Department of Psychiatry Stony Brook University Professor
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Clinical Genetics & Dementia
 Clinical Genetics & Dementia Dr Nayana Lahiri Consultant in Clinical Genetics & Honorary Senior Lecturer Nayana.lahiri@nhs.net Aims of the Session To appreciate the potential utility of family history
Clinical Genetics & Dementia Dr Nayana Lahiri Consultant in Clinical Genetics & Honorary Senior Lecturer Nayana.lahiri@nhs.net Aims of the Session To appreciate the potential utility of family history
Chapter 14. Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition
 Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition Abnormal Behavior Historical aspects of mental disorders F 14.1 The medical model What is abnormal behavior? 3 criteria F 14.2 Deviant Maladaptive Causing
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders 8 th Edition Abnormal Behavior Historical aspects of mental disorders F 14.1 The medical model What is abnormal behavior? 3 criteria F 14.2 Deviant Maladaptive Causing
Sensory Gating Measures. Auditory P50 Response Prepulse Inhibition of Startle (PPI) Bruce Turetsky, M.D. IOM Workshop June 22, 2010
 Sensory Gating Measures Auditory P50 Response Prepulse Inhibition of Startle (PPI) Bruce Turetsky, M.D. IOM Workshop June 22, 2010 Heuristically, sensory gating denotes the ability to filter out irrelevant
Sensory Gating Measures Auditory P50 Response Prepulse Inhibition of Startle (PPI) Bruce Turetsky, M.D. IOM Workshop June 22, 2010 Heuristically, sensory gating denotes the ability to filter out irrelevant
