Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6
|
|
|
- Janel Bailey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 Genotype Abbreviation Expression patterns Ubi-Gal4 Ubi Ubiquitous dome-gal4;elav-gal80 dome MZ Progenitor-specific in the lymph gland; not expressed in the brain (see S1G,H) ((Ghiglione et al., 2002) Tep4 MZ Progenitor-specific in the lymph gland; not expressed in the brain (see S1I,P) (Avet-Rochex et al., 2010) Antp-Gal4 Antp PSC-specific in the lymph gland (Emerald and Cohen, 2004) Elav-Gal4 Elav Pan-neuronal (Luo et al., 1994) Kurs6-Gal4 Kurs6 Majority of neurosecretory cells in the brain including Kurs6 + GABA + cells; not expressed in the Dilp2 + cells (Siegmund and Korge, 2001) TepIV-Gal4;elavgal80 Hand-Gal4, Hml - HHLT Blood-specific expression including the Gal4 UAS-FLP; lymph gland, circulating hemocytes, and A5C-FRT-STOP- heart (Shim et al., 2012) FRT-Gal4 Hand-Gal4; UAS- HandLT Lymph gland including the PSC and FLP; A5C-FRT- progenitors, and heart (Evans et al., 2009) STOP-FRT-Gal4 Hml-Gal4 Hml Mature blood cell-specific expression in the lymph gland and in circulation (Sinenko and Mathey-Prevot, 2004) Dilp2-Gal4 Dilp2 Insulin-producing neurosecretory cells (Rulifson et al., 2002) Orco-Gal4 Orco Olfactory receptor neuron (ORN) (Larsson et al., 2004) GH146-Gal4 GH146 Projection neuron (PN) (Stocker et al., 1997) GH298-Gal4 GH298 Inhibitory interneuron (iln) (Stocker et al., 1997) OR42a-Gal4 OR42a OR42a (Goldman et al., 2005)
2 Table S2. Constituents and Concentration of Minimum Odor Media, Related to 6 Nutrient *Sucrose (Fisher Scientific) *Trehalose (Sigma T3663) Glucose solution (Sigma G8644) Amount added per 50ml 0.1 g 0.15 g 0.5 ml 10X Grace s amino acid solution (Sigma G0273) 5 ml (Final 1X) 1 Nitrogen base without amino acids (Sigma Y0626) 0.5 g 2 Cholesterol (Sigma C8667) 2 Phosphatidylcholine (Sigma P3556) 3 Antibiotic-, antimycotic solution (Invitrogen) 10 mg 5 mg Final 1X *Agarose (Invitrogen) 0.5 g (0.1 % w.v) 1 added from 10X stock made in water 2 added from 100X stock made in ethanol 3 added from 100X stock * mix with water and autoclave before adding solutions
3 Table S3. Quantitation of Phenotypes in s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, and S2 Genotype Percentages Phenotype 1 F dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP 60.7 ± 6.5 Progenitors G dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 7.5 H dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 10.8 RyR RNAi I dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 9.5 Orai RNAi J dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 13 IP3R K dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 15 SERCA DN L dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 12.1 CaMKII RNAi M dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 12.1 CaM B34Q N dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 7.9 CaMKII WT 2 A TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP (Early) 55 ± 12 GCaMP B TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP (Late) 32 ± 6 C TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 34 ± 10 D TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 14 ± 4 E TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 68 ± 9 Serca DN F TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 50 ± 10 Serca DN G TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 16 ± 10 GBR1 RNAi H TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 14 ± 9 GBR1 RNAi I TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 22 ± 7 GBR2 RNAi J TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- GBR2 RNAi 9 ± 4 Control dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP 60.8 ± 6.5 Progenitors K dome MZ -gal4; UAS-GABA B R1 RNAi 45.7 ± 7.9 L dome MZ -gal4; UAS ± 17.2 M dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS ± 16 GABA B R1 RNAi ; UAS-CaMKII N dome MZ -gal4, UAS-2xEYFP; UAS- GABA B R2 RNA ; UAS-CaMKII 60.2 ± 5.3
4 S1 0.5 ± ± ± ± 5 Q Antp-gal4, UAS-GFP 1± 0.48 Lymph R Antp-gal4, UAS-GFP; UAS- GABA B R1 RNAi size S Antp-gal4, UAS-GFP; UAS- A elav-gal ± 6 P1+ cells B elav-gal4; UAS-Gad1 RNAi 74.2 ± 5.3 Control Kurs6-gal4, UAS-mCD8GFP 37 ± 15 I Kurs6-gal4, UAS-mCD8GFP; UAS- Gad1 RNAi J Kurs6-gal4, UAS-mCD8GFP; UAS- VGAT RNAi A orco 2 /+ 36 ± 11 Pxn+ cells B orco 2 /Df[orco] 68 ± 16 C Orco-gal4; UAS-hid, UAS-rpr 70 ± 8 D Orco-gal4; UAS-orco RNAi 70 ± 9 E Orco-gal4; UAS- Shi ts1 71 ± 18 Control Kurs6-gal4, UAS-mCD8GFP 32.3 ± 10.3 Pxn+ cells Control GH298-gal ± 10 F GH146-gal ± 8 H GH146-gal4; UAS-Shi ts 74 ± 15 J GH298-gal4; UAS-NaChBac 65.2 ± 8 K Kurs6-gal4, UAS-VGAT; GH % ± 11 QF, QUAS-Shi ts Control Kurs6-gal4 32 ± 9.3 Pxn+ cells P Kurs6-gal4; UAS-GABA B R1 RNAi 66 ± 13 O Kurs6-gal4; UAS- 67 ± 16 A Or42a-gal ± 7.5 Pxn+ cells B Or42a-gal4, UAS-Shi ts 67.2 ± 12.9 C Or42a f04305 /Df[Or42a] 70 ± 18 Control GH146-gal normal food 32.3 ± 10.3 Pxn+ cells K GH146-gal4 odorless food 73.2 ± 11.9 P GH146-gal4 odor rescue 37.2 ± 13.5 J HHLT-gal4 57 ± 11 Pxn- cells K HHLT-gal4; UAS- 19 ± 13.3 L HHLT-gal4; UAS-RyR RNAi 24.2 ± 8.7 M HHLT-gal4; UAS-PLC RNAi 26 ± 13 N HHLT-gal4; UAS-CaM B34Q 16.6 ± 11.2 P TepIV MZ -gal ± 7.8 TepIV+ cell Q TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS ± 9 R TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-RyR RNAi 21.9 ± 10.9 S TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-IP3R 59.2 ± 6.1 T TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-SERCA DN 53.8 ± 9 U TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-CaMKII RNAi 17.7 ± 11.5 V TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-CaMKII WT 49.2 ± 12.5
5 S2 S2V S2W 0.5 ± ± ± ± 0.26 A TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP 39 ± 7.2 GCaMP B TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 16 ± 9 GABA B R1 RNAi C TepIV MZ -gal4; UAS-GCaMP; UAS- 13 ± 5.2 I HandLT-gal4; UAS-GABA B R1 RNAi 11.5 ± 9.8 Pxn- cells O HandLT-gal4; UAS-GABA B R1 RNAi ; 37.8 ± 17.5 UAS-Orai R HandLT-gal4; UAS-GABA B R1 RNAi ; 75.5 ± 11.5 UAS-CaMKII WT J HandLT-gal4; UAS- 18 ± 13.1 P HandLT-gal4; UAS- ; 48.7 ± 13.7 UAS-Orai S HandLT-gal4; UAS- ; 66 ± 14.3 UAS-CaMKII Early Antp-gal4; UAS-GFP 1 ± 0.48 Size instars Antp-gal4; UAS-GFP; UAS- (Fold) GABA B R1 RNAi Antp-gal4; UAS-GFP; UAS- Late Antp-gal4; gal80 ts 1 ± 0.16 instars Antp-gal4; UAS-GABA B R1 RNAi ; gal80 ts Antp-gal4; UAS- ; gal80 ts
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
G-TRACE: rapid Gal4-based cell lineage analysis in Drosophila
 nature methods G-TRACE: rapid Gal4-based cell lineage analysis in Drosophila Cory J Evans, John M Olson, Kathy T Ngo, Eunha Kim, Noemi E Lee, Edward Kuoy, Alexander N Patananan, Daniel Sitz, PhuongThao
nature methods G-TRACE: rapid Gal4-based cell lineage analysis in Drosophila Cory J Evans, John M Olson, Kathy T Ngo, Eunha Kim, Noemi E Lee, Edward Kuoy, Alexander N Patananan, Daniel Sitz, PhuongThao
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of escargot (esg) and genetic approach for achieving IPC-specific knockdown. (a) esg MH766 -Gal4 UAS-cd8GFP (green) and esg-lacz B7-2-22 (red) show similar expression
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of escargot (esg) and genetic approach for achieving IPC-specific knockdown. (a) esg MH766 -Gal4 UAS-cd8GFP (green) and esg-lacz B7-2-22 (red) show similar expression
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
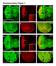 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
50mM D-Glucose. Percentage PI. L-Glucose
 Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
doi: /nature09554
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supplemental Information. Proprioceptive Opsin Functions. in Drosophila Larval Locomotion
 Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Supplementary Figures
 J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
GABAergic Projection Neurons Route Selective Olfactory Inputs to Specific Higher-Order Neurons
 Article GABAergic Projection s Route Selective Olfactory Inputs to Specific Higher-Order s Liang Liang, 1,2 Yulong Li, 3,5 Christopher J. Potter, 1,6 Ofer Yizhar, 4,7 Karl Deisseroth, 4 Richard W. Tsien,
Article GABAergic Projection s Route Selective Olfactory Inputs to Specific Higher-Order s Liang Liang, 1,2 Yulong Li, 3,5 Christopher J. Potter, 1,6 Ofer Yizhar, 4,7 Karl Deisseroth, 4 Richard W. Tsien,
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
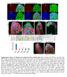 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
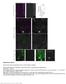 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states.
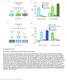 Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson
 Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson Supplementary Tale 1: Genotypes The genotypes used y figure are as follows: Figure 1a Figure
Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson Supplementary Tale 1: Genotypes The genotypes used y figure are as follows: Figure 1a Figure
100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
Drosophila Cytokine Unpaired 2 Regulates Physiological Homeostasis by Remotely Controlling Insulin Secretion
 Drosophila Cytokine Unpaired 2 Regulates Physiological Homeostasis by Remotely Controlling Insulin Secretion Akhila Rajan 1, * and Norbert Perrimon 1,2, * 1 Department of Genetics 2 Howard Hughes Medical
Drosophila Cytokine Unpaired 2 Regulates Physiological Homeostasis by Remotely Controlling Insulin Secretion Akhila Rajan 1, * and Norbert Perrimon 1,2, * 1 Department of Genetics 2 Howard Hughes Medical
Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation
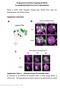 Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation Sayaka U. Sekine, Shuka Haraguchi, Kinhong Chao, Tomoko Kato, Liqun Luo, Masayuki Miura, and Takahiro Chihara
Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation Sayaka U. Sekine, Shuka Haraguchi, Kinhong Chao, Tomoko Kato, Liqun Luo, Masayuki Miura, and Takahiro Chihara
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0450 TITLE: The role of NF1 in memory retrieval PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yi Zhong, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0450 TITLE: The role of NF1 in memory retrieval PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yi Zhong, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila
 Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila Angelique Lamaze 1, Arzu Öztürk-Çolak 2, Robin Fischer 3, Nicolai Peschel 3, Kyunghee Koh 2 and James E.C. Jepson 1* 1 UCL Institute
Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila Angelique Lamaze 1, Arzu Öztürk-Çolak 2, Robin Fischer 3, Nicolai Peschel 3, Kyunghee Koh 2 and James E.C. Jepson 1* 1 UCL Institute
Supplementary Figure 1: Electrophysiological recordings from Drosophila olfactory receptor neurons and projection neurons.
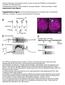 Sensory Processing in the Drosophila Antennal Lobe Increases the Reliability and Separability of Ensemble Odor Representations Vikas Bhandawat, Shawn R. Olsen, Nathan W. Gouwens, Michelle L. Schlief, and
Sensory Processing in the Drosophila Antennal Lobe Increases the Reliability and Separability of Ensemble Odor Representations Vikas Bhandawat, Shawn R. Olsen, Nathan W. Gouwens, Michelle L. Schlief, and
Remote Control of Insulin Secretion by Fat Cells in Drosophila
 Article Remote Control of Insulin Secretion by Fat Cells in Drosophila Charles Géminard, Eric J. Rulifson, and Pierre Léopold, * Institute for Developmental Biology and Cancer, CNRS/University of Nice-Sophia
Article Remote Control of Insulin Secretion by Fat Cells in Drosophila Charles Géminard, Eric J. Rulifson, and Pierre Léopold, * Institute for Developmental Biology and Cancer, CNRS/University of Nice-Sophia
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
Transgenic Expression of the Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor CagA Promotes Apoptosis or Tumorigenesis through JNK Activation in Drosophila
 Transgenic Expression of the Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor CagA Promotes Apoptosis or Tumorigenesis through JNK Activation in Drosophila Anica M. Wandler, Karen Guillemin* Institute of Molecular
Transgenic Expression of the Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor CagA Promotes Apoptosis or Tumorigenesis through JNK Activation in Drosophila Anica M. Wandler, Karen Guillemin* Institute of Molecular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
Insulin Signaling, Lifespan and Stress Resistance Are Modulated by Metabotropic GABA Receptors on Insulin Producing Cells in the Brain of Drosophila
 Insulin Signaling, Lifespan and Stress Resistance Are Modulated by Metabotropic GABA Receptors on Insulin Producing Cells in the Brain of Drosophila Lina E. Enell., Neval Kapan., Jeannette A. E. Söderberg,
Insulin Signaling, Lifespan and Stress Resistance Are Modulated by Metabotropic GABA Receptors on Insulin Producing Cells in the Brain of Drosophila Lina E. Enell., Neval Kapan., Jeannette A. E. Söderberg,
The microrna bantam Functions in Epithelial Cells to Regulate Scaling Growth of Dendrite Arbors in Drosophila Sensory Neurons
 Article The microrna bantam Functions in Epithelial Cells to Regulate Scaling Growth of Dendrite Arbors in Drosophila Sensory Neurons Jay Z. Parrish, 1,2 Peizhang Xu, 1,2 Charles C. Kim, 1 Lily Yeh Jan,
Article The microrna bantam Functions in Epithelial Cells to Regulate Scaling Growth of Dendrite Arbors in Drosophila Sensory Neurons Jay Z. Parrish, 1,2 Peizhang Xu, 1,2 Charles C. Kim, 1 Lily Yeh Jan,
A Drosophila model for alcohol reward. Supplemental Material
 Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH TITLE: Sleep Homeostasis and Synaptic Plasticity. PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ravi Allada
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0169 TITLE: Sleep Homeostasis and Synaptic Plasticity PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ravi Allada CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60201 REPORT DATE: June
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0169 TITLE: Sleep Homeostasis and Synaptic Plasticity PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ravi Allada CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60201 REPORT DATE: June
The Serotonergic Central Nervous System of the Drosophila Larva: Anatomy and Behavioral Function
 The Serotonergic Central Nervous System of the Drosophila Larva: Anatomy and Behavioral Function Annina Huser 1., Astrid Rohwedder 1,5., Anthi A. Apostolopoulou 1,5, Annekathrin Widmann 1,5, Johanna E.
The Serotonergic Central Nervous System of the Drosophila Larva: Anatomy and Behavioral Function Annina Huser 1., Astrid Rohwedder 1,5., Anthi A. Apostolopoulou 1,5, Annekathrin Widmann 1,5, Johanna E.
Drosophila model for fetal alcohol syndrome disorders: Role for the insulin pathway
 San Jose State University SJSU ScholarWorks Faculty Publications Biological Sciences 5-1-2011 Drosophila model for fetal alcohol syndrome disorders: Role for the insulin pathway Rachael L. French San Jose
San Jose State University SJSU ScholarWorks Faculty Publications Biological Sciences 5-1-2011 Drosophila model for fetal alcohol syndrome disorders: Role for the insulin pathway Rachael L. French San Jose
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal
 glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
Control of Metabolic Homeostasis by Stress Signaling Is Mediated by the Lipocalin NLaz
 Control of Metabolic Homeostasis by Stress Signaling Is Mediated by the Lipocalin NLaz Julie Hull-Thompson 1., Julien Muffat 2., Diego Sanchez 3, David W. Walker 2, Seymour Benzer 2, Maria D. Ganfornina
Control of Metabolic Homeostasis by Stress Signaling Is Mediated by the Lipocalin NLaz Julie Hull-Thompson 1., Julien Muffat 2., Diego Sanchez 3, David W. Walker 2, Seymour Benzer 2, Maria D. Ganfornina
Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain
 Article Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain Highlights d d d d Gustatory projection neurons (sgpns) are involved in sweet taste behaviors sgpn dendrites
Article Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain Highlights d d d d Gustatory projection neurons (sgpns) are involved in sweet taste behaviors sgpn dendrites
PEER REVIEW FILE. Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this manuscript entitled "Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila", the authors
PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this manuscript entitled "Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila", the authors
Manipulation of components that control feeding behavior in Drosophila melanogaster increases sensitivity to amino acid starvation
 Manipulation of components that control feeding behavior in Drosophila melanogaster increases sensitivity to amino acid starvation J.D. Slade and B.E. Staveley Department of Biology, Elizabeth Avenue,
Manipulation of components that control feeding behavior in Drosophila melanogaster increases sensitivity to amino acid starvation J.D. Slade and B.E. Staveley Department of Biology, Elizabeth Avenue,
NAME: OPTION GROUP: WJEC
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: WJEC MATHS FOR AS BIOLOGY MAKING SOLUTIONS MATHS COVERED IN THIS BOOKLET ARE: 1. Revision of scientific notation. 2. Molar solutions. 3. Concentrations. 4. Volumes of liquids. 5. Dilutions.
NAME: OPTION GROUP: WJEC MATHS FOR AS BIOLOGY MAKING SOLUTIONS MATHS COVERED IN THIS BOOKLET ARE: 1. Revision of scientific notation. 2. Molar solutions. 3. Concentrations. 4. Volumes of liquids. 5. Dilutions.
This is a repository copy of Sparse, decorrelated odor coding in the mushroom body enhances learned odor discrimination.
 This is a repository copy of Sparse, decorrelated odor coding in the mushroom body enhances learned odor discrimination. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/89890/
This is a repository copy of Sparse, decorrelated odor coding in the mushroom body enhances learned odor discrimination. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/89890/
Shocking revelations and saccharin sweetness in the study of Drosophila olfactory memory
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms University of Massachusetts Medical School Faculty Publications 9-9-2013 Shocking revelations and saccharin sweetness in the study of Drosophila
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms University of Massachusetts Medical School Faculty Publications 9-9-2013 Shocking revelations and saccharin sweetness in the study of Drosophila
Dunce Phosphodiesterase Acts as a Checkpoint for Drosophila Long-Term Memory in a Pair of Serotonergic Neurons
 Article Dunce Phosphodiesterase Acts as a Checkpoint for Drosophila Long-Term Memory in a Pair of Serotonergic Neurons Highlights d Dunce phosphodiesterase is a default inhibitor of long-term memory (LTM)
Article Dunce Phosphodiesterase Acts as a Checkpoint for Drosophila Long-Term Memory in a Pair of Serotonergic Neurons Highlights d Dunce phosphodiesterase is a default inhibitor of long-term memory (LTM)
Pre- and Postsynaptic Role of Dopamine D2 Receptor DD2R in Drosophila Olfactory Associative Learning
 Biology 2014, 3, 831-845; doi:10.3390/biology3040831 Article OPEN ACCESS biology ISSN 2079-7737 www.mdpi.com/journal/biology Pre- and Postsynaptic Role of Dopamine D2 Receptor DD2R in Drosophila Olfactory
Biology 2014, 3, 831-845; doi:10.3390/biology3040831 Article OPEN ACCESS biology ISSN 2079-7737 www.mdpi.com/journal/biology Pre- and Postsynaptic Role of Dopamine D2 Receptor DD2R in Drosophila Olfactory
Supplemental Information. Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body. Output Synapses Are Cholinergic
 Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Mir-184 affects lifespan via regulating the Activin pathway in Drosophila
 1 Mir-184 affects lifespan via regulating the Activin pathway in Drosophila Senior Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the School of Arts and Sciences Brandeis University Undergraduate Program in the Department
1 Mir-184 affects lifespan via regulating the Activin pathway in Drosophila Senior Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the School of Arts and Sciences Brandeis University Undergraduate Program in the Department
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012
 Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation.
 ` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
A GABAergic Inhibitory Neural Circuit Regulates Visual Reversal Learning in Drosophila
 11524 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 22, 2012 32(34):11524 11538 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive A GABAergic Inhibitory Neural Circuit Regulates Visual Reversal Learning in Drosophila Qingzhong Ren,
11524 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 22, 2012 32(34):11524 11538 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive A GABAergic Inhibitory Neural Circuit Regulates Visual Reversal Learning in Drosophila Qingzhong Ren,
Midgut-Derived Activin Regulates Glucagon-like Action in the Fat Body and Glycemic Control
 Article Midgut-Derived Activin Regulates Glucagon-like Action in the Fat Body and Glycemic Control Graphical Abstract Authors Wei Song, Daojun Cheng, Shangyu Hong,..., Michael B. O Connor, Pavlos Pissios,
Article Midgut-Derived Activin Regulates Glucagon-like Action in the Fat Body and Glycemic Control Graphical Abstract Authors Wei Song, Daojun Cheng, Shangyu Hong,..., Michael B. O Connor, Pavlos Pissios,
Molecular Genetic Analysis of Sexual Rejection: Roles of Octopamine and Its Receptor OAMB in Drosophila Courtship Conditioning
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October, 32(4):428 4287 428 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Molecular Genetic Analysis of Sexual Rejection: Roles of Octopamine and Its Receptor OAMB in Drosophila Courtship Conditioning
The Journal of Neuroscience, October, 32(4):428 4287 428 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Molecular Genetic Analysis of Sexual Rejection: Roles of Octopamine and Its Receptor OAMB in Drosophila Courtship Conditioning
SLOB, a SLOWPOKE channel binding protein, regulates insulin pathway signaling and metabolism in Drosophila.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neuroscience Sidney Kimmel Medical College 8-5-2011 SLOB, a SLOWPOKE channel binding protein, regulates insulin pathway signaling and
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neuroscience Sidney Kimmel Medical College 8-5-2011 SLOB, a SLOWPOKE channel binding protein, regulates insulin pathway signaling and
Diet-induced plasticity in the adult Drosophila melanogaster midgut
 Diet-induced plasticity in the adult Drosophila melanogaster midgut Honors Thesis Presented to the College of Arts and Sciences, Cornell University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Biological
Diet-induced plasticity in the adult Drosophila melanogaster midgut Honors Thesis Presented to the College of Arts and Sciences, Cornell University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Biological
The hector G-Protein Coupled Receptor Is Required in a Subset of fruitless Neurons for Male Courtship Behavior
 The hector G-Protein Coupled Receptor Is Required in a Subset of fruitless Neurons for Male Courtship Behavior Yuanli Li, Valbona Hoxha, Chamala Lama, Bich Hien Dinh, Christina N. Vo, Brigitte Dauwalder*
The hector G-Protein Coupled Receptor Is Required in a Subset of fruitless Neurons for Male Courtship Behavior Yuanli Li, Valbona Hoxha, Chamala Lama, Bich Hien Dinh, Christina N. Vo, Brigitte Dauwalder*
A post-ingestive amino acid sensor promotes food consumption in Drosophila
 www.nature.com/cr www.cell-research.com ARTICLE OPEN A post-ingestive amino acid sensor promotes food consumption in Drosophila Zhe Yang 1,2, Rui Huang 3,4, Xin Fu 5,6,7, Gaohang Wang 1,2, Wei Qi 1,2,
www.nature.com/cr www.cell-research.com ARTICLE OPEN A post-ingestive amino acid sensor promotes food consumption in Drosophila Zhe Yang 1,2, Rui Huang 3,4, Xin Fu 5,6,7, Gaohang Wang 1,2, Wei Qi 1,2,
What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?!
 Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Gustatory habituation in Drosophila relies on rutabaga (adenylate cyclase)-dependent plasticity of GABAergic inhibitory neurons
 Research Gustatory habituation in Drosophila relies on rutabaga (adenylate cyclase)-dependent plasticity of GABAergic inhibitory neurons Pushkar Paranjpe, 1,5 Veronica Rodrigues, 1,2,4 K. VijayRaghavan,
Research Gustatory habituation in Drosophila relies on rutabaga (adenylate cyclase)-dependent plasticity of GABAergic inhibitory neurons Pushkar Paranjpe, 1,5 Veronica Rodrigues, 1,2,4 K. VijayRaghavan,
p53-and ERK7-Dependent Ribosome Surveillance Response Regulates Drosophila Insulin-Like Peptide Secretion
 https://helda.helsinki.fi p53-and ERK7-Dependent Ribosome Surveillance Response Regulates Drosophila Insulin-Like Peptide Secretion Hasygar, Kiran 2014 Hasygar, K & Hietakangas, V 2014, ' p53-and ERK7-Dependent
https://helda.helsinki.fi p53-and ERK7-Dependent Ribosome Surveillance Response Regulates Drosophila Insulin-Like Peptide Secretion Hasygar, Kiran 2014 Hasygar, K & Hietakangas, V 2014, ' p53-and ERK7-Dependent
Drosophila PTEN Regulates Cell Growth and Proliferation through PI3K-Dependent and -Independent Pathways
 Developmental Biology 221, 404 418 (2000) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9680, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Drosophila PTEN Regulates Cell Growth and Proliferation through PI3K-Dependent and
Developmental Biology 221, 404 418 (2000) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9680, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Drosophila PTEN Regulates Cell Growth and Proliferation through PI3K-Dependent and
Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult Drosophila Brain
 4768 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2009 29(15):4768 4781 Cellular/Molecular Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult Drosophila Brain Johnna Doherty,* Mary A. Logan,* Özge E. Taşdemir,
4768 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2009 29(15):4768 4781 Cellular/Molecular Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult Drosophila Brain Johnna Doherty,* Mary A. Logan,* Özge E. Taşdemir,
Loss of IP 3 receptor function in neuropeptide secreting neurons leads to obesity in adult Drosophila
 Subramanian et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:157 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Loss of IP 3 receptor function in neuropeptide secreting neurons leads to obesity in adult Drosophila Manivannan Subramanian
Subramanian et al. BMC Neuroscience 2013, 14:157 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Loss of IP 3 receptor function in neuropeptide secreting neurons leads to obesity in adult Drosophila Manivannan Subramanian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Control of Growth within Drosophila Peripheral Nerves by Ras and Protein Kinase A
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0272 TITLE: Control of Growth within Drosophila Peripheral Nerves by Ras and Protein Kinase A PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Stern, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Rice University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0272 TITLE: Control of Growth within Drosophila Peripheral Nerves by Ras and Protein Kinase A PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Stern, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Rice University
Odour-intensity learning in fruit flies
 BOCKSTALLER Marie Joint Master in Neuroscience M1 2011-2012 Summer Project Report Odour-intensity learning in fruit flies Supervisor : Ayse Yarali Institution : Max Planck Institut for Neurobiology, Martinsried
BOCKSTALLER Marie Joint Master in Neuroscience M1 2011-2012 Summer Project Report Odour-intensity learning in fruit flies Supervisor : Ayse Yarali Institution : Max Planck Institut for Neurobiology, Martinsried
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014
 HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
Synaptic Protein Synthesis Associated with Memory Is Regulated by the RISC Pathway in Drosophila
 Synaptic Protein Synthesis Associated with Memory Is Regulated by the RISC Pathway in Drosophila Shovon I. Ashraf, 1 Anna L. McLoon, 1,2 Sarah M. Sclarsic, 1,2 and Sam Kunes 1, * 1 Department of Molecular
Synaptic Protein Synthesis Associated with Memory Is Regulated by the RISC Pathway in Drosophila Shovon I. Ashraf, 1 Anna L. McLoon, 1,2 Sarah M. Sclarsic, 1,2 and Sam Kunes 1, * 1 Department of Molecular
AD (Leave blank) TITLE: Control of Growth Within Drosophila Peripheral Nerves by Ras and Protein Kinase A
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0272 TITLE: Control of Growth Within Drosophila Peripheral Nerves by Ras and Protein Kinase A PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Stern, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0272 TITLE: Control of Growth Within Drosophila Peripheral Nerves by Ras and Protein Kinase A PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Stern, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
The ADAR RNA editing enzyme controls neuronal excitability in Drosophila melanogaster
 Published online 16 October 2013 Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, Vol. 42, No. 2 1139 1151 doi:10.1093/nar/gkt909 The ADAR RNA editing enzyme controls neuronal excitability in Drosophila melanogaster Xianghua
Published online 16 October 2013 Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, Vol. 42, No. 2 1139 1151 doi:10.1093/nar/gkt909 The ADAR RNA editing enzyme controls neuronal excitability in Drosophila melanogaster Xianghua
Modeling Excitatory and Inhibitory Chemical Synapses
 In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
In review, a synapse is the place where signals are transmitted from a neuron, the presynaptic neuron, to another cell. This second cell may be another neuron, muscle cell or glandular cell. If the second
Biology 12 January 2002 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 January 2002 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I,
Biology 12 January 2002 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I,
Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh
 Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila
 Article Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila Chuan Zhou, 1 Yufeng Pan, 1 Carmen C. Robinett, 1 Geoffrey W. Meissner, 1 and Bruce S. Baker 1, 1 Janelia Farm
Article Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila Chuan Zhou, 1 Yufeng Pan, 1 Carmen C. Robinett, 1 Geoffrey W. Meissner, 1 and Bruce S. Baker 1, 1 Janelia Farm
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Supplemental Information. Sleep Drive Is Encoded by Neural. Plastic Changes in a Dedicated Circuit. Sha Liu, Qili Liu, Masashi Tabuchi, and Mark N.
 Cell, Volume 165 Supplemental Information Sleep Drive Is Encoded by Neural Plastic Changes in a Dedicated Circuit Sha Liu, Qili Liu, Masashi Tabuchi, and Mark N. Wu Supplemental Experimental Procedures
Cell, Volume 165 Supplemental Information Sleep Drive Is Encoded by Neural Plastic Changes in a Dedicated Circuit Sha Liu, Qili Liu, Masashi Tabuchi, and Mark N. Wu Supplemental Experimental Procedures
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
ns ns hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1
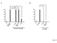 A ns ns B 100 100 80 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 0 0% 0 0% hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1 A 100 80 15 o C 22 o C 25 o C % Dauers 60 40 20 0 0% 0% * 0% 0% 0% Class I alleles Class II alleles daf-2(lf;ts)
A ns ns B 100 100 80 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 0 0% 0 0% hp761(lf); daf-28(lf) daf-28(gf) Figure S1 A 100 80 15 o C 22 o C 25 o C % Dauers 60 40 20 0 0% 0% * 0% 0% 0% Class I alleles Class II alleles daf-2(lf;ts)
Università degli Studi di Torino. Ruolo del fattore trascrizionale FoxO-3 nei progenitori CD34+ Ph positivi nella leucemia mieloide cronica (LMC)
 Università degli Studi di Torino Ruolo del fattore trascrizionale FoxO-3 nei progenitori CD34+ Ph positivi nella leucemia mieloide cronica (LMC) Francesca Messa Forkhead family CBP?? Ub Ub CBP Ub Ac Ac
Università degli Studi di Torino Ruolo del fattore trascrizionale FoxO-3 nei progenitori CD34+ Ph positivi nella leucemia mieloide cronica (LMC) Francesca Messa Forkhead family CBP?? Ub Ub CBP Ub Ac Ac
Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A
 Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A 157 (2010) 398 404 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cbpa
Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A 157 (2010) 398 404 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cbpa
Miniature Neurotransmission Regulates Drosophila Synaptic Structural Maturation
 Article Miniature Neurotransmission Regulates Drosophila Synaptic Structural Maturation Ben Jiwon Choi, 1,2,3 Wendy L. Imlach, 1,2,4 Wei Jiao, 1,2,4 Verena Wolfram, 5 Ying Wu, 6 Mark Grbic, 1,2 Carolina
Article Miniature Neurotransmission Regulates Drosophila Synaptic Structural Maturation Ben Jiwon Choi, 1,2,3 Wendy L. Imlach, 1,2,4 Wei Jiao, 1,2,4 Verena Wolfram, 5 Ying Wu, 6 Mark Grbic, 1,2 Carolina
Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila
 Received 2 Jun 216 Accepted 3 Mar 217 Published 15 May 217 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1523 OPEN Neural circuits for long-term water-reward processing in thirsty Drosophila Wei-Huan Shyu 1, Tai-Hsiang Chiu 1, Meng-Hsuan
Received 2 Jun 216 Accepted 3 Mar 217 Published 15 May 217 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1523 OPEN Neural circuits for long-term water-reward processing in thirsty Drosophila Wei-Huan Shyu 1, Tai-Hsiang Chiu 1, Meng-Hsuan
Understanding the impact of. during vinification. George van der Merwe Associate Professor
 Understanding the impact of fermentation stresses on yeast during vinification George van der Merwe Associate Professor CCOVI May 20100 Wine yeast: Saccharomyces What do yeast do? Nutrients Plasma membrane
Understanding the impact of fermentation stresses on yeast during vinification George van der Merwe Associate Professor CCOVI May 20100 Wine yeast: Saccharomyces What do yeast do? Nutrients Plasma membrane
Diagnosis and prevention of metabolic diseases in Drosophila melanogaster
 Southern Methodist University SMU Scholar Engaged Learning Collection Engaged Learning Spring 2013 Diagnosis and prevention of metabolic diseases in Drosophila melanogaster Claire Marie Coogan Southern
Southern Methodist University SMU Scholar Engaged Learning Collection Engaged Learning Spring 2013 Diagnosis and prevention of metabolic diseases in Drosophila melanogaster Claire Marie Coogan Southern
Three Dopamine Pathways Induce Aversive Odor Memories with Different Stability
 Three Dopamine Pathays Induce Aversive Odor Memories ith Different Stability Yoshinori Aso 1 a *, Andrea Herb 2, Maite Ogueta 2 b, Igor Sianoicz 1 a, Thomas Templier 1, Anja B. Friedrich 1, Kei Ito 3,
Three Dopamine Pathays Induce Aversive Odor Memories ith Different Stability Yoshinori Aso 1 a *, Andrea Herb 2, Maite Ogueta 2 b, Igor Sianoicz 1 a, Thomas Templier 1, Anja B. Friedrich 1, Kei Ito 3,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks
 How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
Drosophila DPM Neurons Form a Delayed and Branch-Specific Memory Trace after Olfactory Classical Conditioning
 Drosophila DPM Neurons Form a Delayed and Branch-Specific Memory Trace after Olfactory Classical Conditioning Dinghui Yu, 1 Alex C. Keene, 4 Anjana Srivatsan, 2 Scott Waddell, 4 and Ronald L. Davis 1,3,
Drosophila DPM Neurons Form a Delayed and Branch-Specific Memory Trace after Olfactory Classical Conditioning Dinghui Yu, 1 Alex C. Keene, 4 Anjana Srivatsan, 2 Scott Waddell, 4 and Ronald L. Davis 1,3,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
AGGRESSION is an important behavioral trait enabling
 INVESTIGATION HIGHLIGHTED ARTICLE Regulation of Aggression by Obesity-Linked Genes TfAP-2 and Twz Through Octopamine Signaling in Drosophila Michael J. Williams, 1 Philip Goergen, Jayasimman Rajendran,
INVESTIGATION HIGHLIGHTED ARTICLE Regulation of Aggression by Obesity-Linked Genes TfAP-2 and Twz Through Octopamine Signaling in Drosophila Michael J. Williams, 1 Philip Goergen, Jayasimman Rajendran,
Macromolecules Cut & Paste
 Macromolecules Cut & Paste Adapted from http://mrswords.weebly.com/uploads/1/5/2/4/15244382/ch_6-3_life_molecules_cut-out_lab.pdf INTRODUCTION Many of the molecules in living cells are so large that they
Macromolecules Cut & Paste Adapted from http://mrswords.weebly.com/uploads/1/5/2/4/15244382/ch_6-3_life_molecules_cut-out_lab.pdf INTRODUCTION Many of the molecules in living cells are so large that they
Article. Regulation of Gustatory Physiology and Appetitive Behavior by the Drosophila Circadian Clock
 Current Biology 20, 300 309, February 23, 2010 ª2010 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2009.12.055 Regulation of Gustatory Physiology and Appetitive Behavior by the Drosophila Circadian
Current Biology 20, 300 309, February 23, 2010 ª2010 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2009.12.055 Regulation of Gustatory Physiology and Appetitive Behavior by the Drosophila Circadian
The genetic basis of phenotypic diversity. Virginie Orgogozo Institut Jacques Monod Paris
 The genetic basis of phenotypic diversity Virginie Orgogozo Institut Jacques Monod Paris What makes us different? between individuals between species? How do genotypes map onto phenotypes? Phenotype =
The genetic basis of phenotypic diversity Virginie Orgogozo Institut Jacques Monod Paris What makes us different? between individuals between species? How do genotypes map onto phenotypes? Phenotype =
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons
 5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
Supplemental Data SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
 Temporal transcription factors and their targets schedule the end of neural proliferation in Drosophila. Cédric Maurange, Louise Cheng and Alex P. Gould Supplemental Data SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Temporal transcription factors and their targets schedule the end of neural proliferation in Drosophila. Cédric Maurange, Louise Cheng and Alex P. Gould Supplemental Data SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Interglomerular communication in olfactory processing
 Commentary Cellscience Reviews Vol 5 No 1 ISSN 1742-8130 Interglomerular communication in olfactory processing John P. McGann 1 & Matt Wachowiak 2 1 Psychology Department & 2 Biology Department, Boston
Commentary Cellscience Reviews Vol 5 No 1 ISSN 1742-8130 Interglomerular communication in olfactory processing John P. McGann 1 & Matt Wachowiak 2 1 Psychology Department & 2 Biology Department, Boston
A subset of octopaminergic neurons are important for Drosophila aggression
 28 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureneuroscience A subset of octopaminergic neurons are important for Drosophila aggression Chuan Zhou 1,2, Yong Rao 1 & Yi Rao 1,3 Aggression is an innate
28 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureneuroscience A subset of octopaminergic neurons are important for Drosophila aggression Chuan Zhou 1,2, Yong Rao 1 & Yi Rao 1,3 Aggression is an innate
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Science. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 April 28.
 Interaction Between Notch and Hif-α in Development and Survival of Drosophila Blood Cells Tina Mukherjee 1, William Sang Kim 1, Lolitika Mandal 1,*, and Utpal Banerjee 1,2, 1 Department of Molecular, Cell
Interaction Between Notch and Hif-α in Development and Survival of Drosophila Blood Cells Tina Mukherjee 1, William Sang Kim 1, Lolitika Mandal 1,*, and Utpal Banerjee 1,2, 1 Department of Molecular, Cell
Carbon Compounds (2.3) (Part 1 - Carbohydrates)
 Carbon Compounds (2.3) (Part 1 - Carbohydrates) The Chemistry of Carbon (Organic Chemistry) Organic Chemistry: The study of compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon can bond with many
Carbon Compounds (2.3) (Part 1 - Carbohydrates) The Chemistry of Carbon (Organic Chemistry) Organic Chemistry: The study of compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon can bond with many
The Drosophila melanogaster life cycle
 The Drosophila melanogaster life cycle Eclosion The first phenotype described in Drosophila as an endogenous rhythm (1954): Number of eclosed flies Hamblen et al., Gene3cs 1998 rhythm with a periodicity
The Drosophila melanogaster life cycle Eclosion The first phenotype described in Drosophila as an endogenous rhythm (1954): Number of eclosed flies Hamblen et al., Gene3cs 1998 rhythm with a periodicity
