Utility of the WHO Ten Questions Screen for Disability Detection in a Rural Community the North Indian Experience
|
|
|
- Eugene Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Utility of the WHO Ten Questions Screen for Disability Detection in a Rural Community the North Indian Experience by Pratibha Singhi, a Munish Kumar, b Prabhjot Malhi, c and Rajesh Kumar d a Department of Pediatrics b Department of Pediatrics c Department of Pediatrics d Department of Community Medicine Summary The utility of the WHO Ten Questions Screen (TQS) was studied in a rural community of North India. The study was done in three villages, in two phases. In phase 1, the TQS was administered to parents of aged between 2 and 9 years, during a house-to-house survey. In phase 2, all screened positive and a random sample of 110 screened negative were clinically evaluated in detail. The total population of the three villages was 5830 with 1763 aged between 2 and 9 years. Seventy-six were positive on the TQS, of these, 38 were found to have significant disability, 18 had protein energy malnutrition and 19 were found normal on clinical evaluation. All the 110 screen-negative were normal. Significantly larger numbers of boys were positive on TQS as compared to girls [Odd Ratio (OR) 1.5]. The sensitivity of the TQS for significant disability was 100%; the positive predictive value was 50% and was higher for boys than for girls. Of the 50% classified as false positive 23% had mild delays due to malnutrition. The estimated prevalence of disability was 16/1000. The TQS was found to be a sensitive tool for detection of significant disabilities among 2 9 years of age. The low-positive predictive value would lead to over referrals but a large number of these would benefit from medical attention. Introduction Childhood disability is a major problem in developing countries. There is paucity of data on prevalence rates mainly because of the lack of systems for data collection. Detection of disabilities in communities is difficult; lack of public awareness about disabilities and rehabilitation, lack of trained professionals and lack of screening tools are some of the causes. To be used on a large population, with limited resources, any screening tool should be simple, inexpensive, and at the same time, sensitive and specific. The WHO Ten Questions Screen (TQS) was devised as a simple questionnaire for the detection of common disabilities (physical, mental, speech, hearing, visual and epilepsy) among 2 9 years of age, at the Correspondence: Pratibha Singhi, Advanced Pediatric Center, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Sector 12, Chandigarh , India. Tel.: <psinghi@glide.net.in>. community level. It contains 10 questions and probe questions that follow each of the questions, and is intended to be used across cultures. The validity of the questionnaire has been reported from some countries such as Bangladesh, Jamaica and Pakistan, [1 3] with variable results. There is little information on its use in the Indian population. We therefore used the screen in a rural setting in North India to study its utility in the detection of disabilities. Method The TQS was first translated into the two commonly used local languages Hindi as well as Punjabi and was pilot tested on 30 each. The study was done in three selected villages around Chandigarh, which were already being visited by workers from the community medicine department of our institute and where a good rapport had already been established. The study was conducted in two phases. In phase 1, a house-to-house survey was done and the WHO 10-point questionnaire was administered as a personal interview to parents/guardians of between the ages of 2 and 9 completed years. ß The Author [2007]. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org 383 doi: /tropej/fmm047 Advance Access Published on 7 June 2007
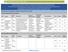
2 TABLE 1 Age and sex distribution of the sample and percent positive on the Ten Questions (TQ) Age (years) Boys Girls Total Total no. No. (and% TQþve) Total no. No. (and% TQþve) Total no. No. (and% TQþve) (6.6) (3.6) (6.6) 91 7 (7.6) (7.1) (5.5) (3.8) (3.4) (2.4) (1.7) (2.5) (5.7) 93 3 (3.2) (4.5) (3.9) (2.3) (3.1) (6.0) 85 6 (7.0) (6.5) (7.2) (1.9) (4.6) Total (5.1) (3.4) (4.3) In phase 2, all with a positive-screening result as well as a random sample of 110 screennegative, were evaluated clinically. Clinical examinations were done by a team of a pediatrician and a psychologist, who were blinded to the screening results. A detailed pre-structured Medical and Neurodevelopment Assessment Form was used to record the results of the physical examination and developmental assessment of included in phase 2 of the study. Hearing assessment by age appropriate methods was done. IQ assessment was done by the psychologist using the Malin s adaptation of the Weschler Intelligence scale for school [4], for between 6 and 9 years of age and the WPSS1 [5] for aged between 2 and 5 years. Definitions Used Disability Inability to carry out certain activities considered normal for one s age, sex etc. Standard procedures and criteria were used to diagnose and assess the level of disability (mild, moderate and severe) in five areas: cognitive (mental retardation), motor, vision, hearing and seizures. Mental retardation Significantly sub average general intellectual functioning (IQ standard score of less than 70) in association with deficits in two or more of the following ten adaptive skill areas: communication, self care, home living, social skills, community use, self direction, health and safety, functional, academics, leisure and work. Hearing loss Moderate (32 35 db), severe (50 70 db) or profound (70 db or greater). Delayed speech No use of single word by 1.5 years or single word vocabulary of 10 words by 2 years of age; The Expressive Language Milestone Scale [6] was used for older. Impaired vision Visual acuity <3/60 (Snellen) or its equivalent. Seizure disorder Diagnosis was made on the basis of medical history and EEG other investigations were done if needed. Children diagnosed to have a disability of any kind were referred to the existing community-based rehabilitation programmes. The data were analyzed using the SPSS 10 statistical package. Results The total population of the three villages was 5830; there were 1763 aged between 2 and 9 completed years. The age and sex distribution of the screened as well as the rates of positive responses on the TQS are shown in Table 1. The percent positive on the TQS was lower for 5- and 7-year-old as compared to other ages. A larger percentage of boys had a positive screening as compared to girls [5.1% vs. 3.4%]. A total of 76 were found to be positive on any one of the 10 questions. On analysis of the individual responses to the 10 questions (Table 2), it was found that the maximum numbers of positive responses were related to learning, and the minimum to vision. Significantly larger numbers of boys screened positive for problems of delayed milestones, no speech or unclear speech and slowness (p-values 0.01, 0.007, 0.04, respectively Table 2). For the TQS as a whole, the odds ratio was 1.5 for boys vs. girls, indicating that parents were about 1.5 times more likely to report a problem for sons than for daughters. The problems of comprehension and 384 Journal of Tropical Pediatrics Vol. 53, No. 6
3 TABLE 2 Frequencies and odds ratio (ORs) of individual question (rows 1 10) on TQ in boys and girls Question Related disability Total no. (% positive) No. of positive Boys vs. girls Boys Girls OR 95% CL 1 Developmental Milestones 33 (1.8) , Vision 5 (0.2) , Hearing 10 (0.5) , Comprehension 7 (0.4) , Movements 9 (0.5) , Seizures 7 (0.4) , Learning 60 (3.4) , No speech 15 (0.8) , Unclear speech 20 (1.1) , Slowness 18 (1.0) , 21.4 TABLE 3 Results of clinical evaluation of positive on the TQS Age (years) Total screen positive Significant disability PEM Normal Total a a One child had stuttering. learning were significantly more common in older as compared to younger (p-values 0.01 and 0.02, respectively). The age wise results of clinical evaluation for screen-positive are shown in Table 3. Thirty-eight of 76 evaluated had significant (comprehension, vision, hearing, seizures and motor disorder) disabilities, 18 had mild delays with protein energy malnutrition (PEM) and 19 were found to be normal. One child was found to have mild stuttering. Of the 110 screen-negative clinically evaluated, none had significant disability. A total of 79 disabilities were identified in the 38, many of whom had multiple disabilities. Of the 79, there were 32 cognitive, 29 motor, 7 seizures, 2 vision and 9 hearing disabilities. The estimated prevalence was calculated as the weighted average of prevalence estimated in those screened positive and those screened negative. These estimates were based upon a sample of 186 clinically evaluated and were adjusted for the fact that with positive-screening results were over represented within this sample. Based on the numbers of true and TABLE 4 Distribution of parameters in 186 clinically evaluated Parameter Boys Girls Younger Older All Trueþve (a) Falseþve (b) False ve (c) True ve (d) false positives and negatives (Table 4), the validity of the TQS for screening significant disability was calculated (Table 5). The sensitivity and negative predictive value were found to be 100%, indicating that all 38 found to have significant disabilities were positive on the TQS. The positive predictive value of the screen for significant disabilities was 50%. The overall estimated prevalence of disabilities was about 16/1000 and was significantly (p < 0.05) higher for boys (16.4/1000) than girls (5.1/1000), but not significantly different among older vs. younger. A total of 38 were classified as false positives on the TQS. Although none of them had significant disability, 50% had mild delays with malnutrition or a minor speech problems. If these milder conditions are also included, the positive predictive value of the screen goes up to 75%. Discussion The TQS was found to be a sensitive tool for detection of significant disabilities in aged between 2 and 9 years. The positive-predictive value of the screen was only 50% implying that if used as a case finding tool for epidemiological purposes, it would lead to a number of over referrals. However, of those classified as false positives for significant disability, 23% had mild delays due to malnutrition Journal of Tropical Pediatrics Vol. 53, No
4 TABLE 5 Estimates of the validity of the TQs for screening serious disabilities, and estimates of prevalence of serious disability in rural areas around Chandigarh based on the sub-sample of 186 clinically evaluated All Boys Girls Older (5 9) years Younger (2 4) years Sensitivity ¼ a/a þ c x Specificity ¼ d/b þ d Positive predictive value ¼ a/a þ b Negative predictive value ¼ d/c þ d and 25% were normal. This observation suggests that referring all with positive results will not necessarily result in an inefficient use of professional resources, since early identification and treatment of malnutrition and other health problems is also important and helps in prevention of further significant disabilities. The TQS has been used in other developing countries. The overall screen positive percentages were 15.6, 14.7 and 6.9 in Jamaica, Pakistan and Bangladesh, respectively. [1 3] An analysis of the validity of the TQS, [7] found an acceptable (80 100%) sensitivity for serious cognitive, motor and seizure disabilities but not for vision and hearing disabilities. The positive predictive value of the TQS has been found to be low, and was 22% in the Bangladesh study [1], but 70% of classified as false positive had mild disabilities or conditions for which early detection and intervention could be beneficial. In a study from Kenya [8], the overall sensitivity of the TQS was found to be 98.6% while the positive predictive value was only 29% and was highest (55.6%) for seizures and low for speech and learning difficulty. Although the positive-predictive value of the TQS is low, it must be remembered that the TQS is a low-cost-quick screening tool that can be used by community workers, and not an assessment tool. As such, false positivity is not unexpected particularly if it is validated against a detailed clinical examination. Interestingly, in our study, the positive-predictive value was found to be higher for boys (61%) as compared to girls (31%). This is consistent with the observed tendency for parents in India to display more concern for the health of sons than for daughters. The higher number of false positives in older may be due to the fact that parents become more aware of the child s problems as the age of the child advances. In the present study, question 7 (related to hearing) elicited a much larger positive response than any other question whereas in the studies from Jamaica and Pakistan, a higher-positive response rate was reported for question 10 (retardation) and for questions 1, 5, 6 and 9 (delayed milestones, movement, fits, learning and unclear speech), respectively. In our study, the frequency of positive responses to questions 8 and 9, related to speech and question 10 related to slowness was somewhat different between boys and girls which is similar to that reported in the Bangladesh study. Problems in comprehension and learning (questions 4 and 7) were expectedly reported more frequently in older than in younger. However, there were no significant age or gender differences in the probability of being positive on the TQS on any one or more questions. Thus, the screen does not appear to grossly over identify or under identify any one or the other of these groups. None of the who screened positive or screened negative and randomly evaluated, had autism or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The TQS is not specifically designed to detect these disabilities, although with speech delays and motor problems associated with these disabilities could theoretically be detected with this screen. Only 8% of parents/guardians were aware about rehabilitation programmes for disabled being run in their area. A population-based survey of childhood disability in Eastern Jeddah using the TQS and further information found a prevalence rate of 36.7/1000 and the families reported lack of services for their disabled [9]. We found that the TQS is an effective screening tool for detection of significant disabilities in our culture. This is in accordance with the reported crosscultural reliability of the screen [10]. Minor variations in culturally divergent population are acceptable for questionnaires designed for large-scale epidemiological research. The over-referrals associated with the screen could perhaps be minimized by the use of further specific probe questions. A couple of questions related to screening for autism and ADHD could perhaps increase the scope and completeness of the questionnaire. References 1. Zaman S, Khan N, Islam S, et al. Validity of the ten questions for screening serious childhood 386 Journal of Tropical Pediatrics Vol. 53, No. 6
5 disabilities: result from urban Bangladesh. Int J Epidemiol 1990;19: Thorburn M, Desai P, Paul TJ, et al. Identification of childhood disability in Jamaica: evaluation of the ten-question screen. Int J Rehabil Res 1992;15: Durkin MS, Hasan ZM, Hasan KZ. The ten questions screen for childhood disabilities: it uses and limitations in Pakistan. J Epidemiol Commun H 1995;49: Malin AJ. Malin s Intelligence Scale for Indian Children Manual Nagpur. Child Guidance Centre, Wecholer D. Wechster Preschoel and Primary Scale of Intelligence. 3rd edn. San Antonio, Texas, Psychological Corperation, Leptan J. The Early Language Milestone Scale. Autism. Pro-ed inc. Austin, Texas, USA, Durkin MS, Davidson LL, Hasan ZM, et al. Validity of ten question screen for childhood disability: results from population based studies in Bangladesh, Jamaica and Pakistan. Epidemiology 1994;5: Muga E. Screening for disability in a community: ten questions screen for, in Bondo, Kenya. Afr Health Sci 2003;3: Milaat WA, Ghabrah TM, Al-Bar HM, et al. Population-based survey of childhood disability in eastern Jeddah using the ten-question tool. Disabil Rehabil 2001;23: Durkin MS, Wang W, Shrout PE, et al. Evaluation of the Ten Questions screen for childhood disability: reliability and internal structure in different cultures. J Clin Epidemiol 1995;48: Journal of Tropical Pediatrics Vol. 53, No
Prevalence and Correlates of Mental Retardation among Children in Karachi, Pakistan
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Prevalence and Correlates of Mental
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Prevalence and Correlates of Mental
Guidelines for the Care of Children and Adolescents with a Seizure Disorder
 Guidelines for the Care of Children and Adolescents with a Seizure Disorder Basic Team The special care needs of children with a seizure disorder can be met by an experienced primary care physician working
Guidelines for the Care of Children and Adolescents with a Seizure Disorder Basic Team The special care needs of children with a seizure disorder can be met by an experienced primary care physician working
Early identification and screening
 Early identification and screening Vibha Krishnamurthy, MD, FAAP Medical Director, Ummeed Child Development Center, Staff Physician, Children s Hospital, Boston Golu s Story Golu is a 7 year old from a
Early identification and screening Vibha Krishnamurthy, MD, FAAP Medical Director, Ummeed Child Development Center, Staff Physician, Children s Hospital, Boston Golu s Story Golu is a 7 year old from a
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
 Neurodevelopmental Disorders Intellectual Disability Disorder Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Motor Disorders/Tourette s Disorder Intellectual Disability
Neurodevelopmental Disorders Intellectual Disability Disorder Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Motor Disorders/Tourette s Disorder Intellectual Disability
Prevalence and risk factors of neurological disability and impairment in children living in rural Kenya
 Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Epidemiological Association International Journal of Epidemiology 2006;35:683 688 Ó The Author 2006; all rights reserved. Advance Access
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Epidemiological Association International Journal of Epidemiology 2006;35:683 688 Ó The Author 2006; all rights reserved. Advance Access
Report of Children with Disabilities (IDEA) Ages 6 through 21 by Disability, Educational Environment, and Age Group (OSEP010)
 Disability Category class 80% or more of the class 40% through 79% of class less than 40% of 6-11 12-17 18-21 6-11 12-17 18-21 6-11 12-17 18-21 Intellectual disability 818 1,624 462 1,005 1,830 483 3,036
Disability Category class 80% or more of the class 40% through 79% of class less than 40% of 6-11 12-17 18-21 6-11 12-17 18-21 6-11 12-17 18-21 Intellectual disability 818 1,624 462 1,005 1,830 483 3,036
Medical Advisory Council: Verified
 What is White Sutton Syndrome? White Sutton Syndrome (WHSUS) is a condition characterized by autism and developmental delay and/or intellectual disability, as well as a characteristic facial profile. Children
What is White Sutton Syndrome? White Sutton Syndrome (WHSUS) is a condition characterized by autism and developmental delay and/or intellectual disability, as well as a characteristic facial profile. Children
MENTAL DISORDERS. Department of Pediatrics Soochow University Affiliated Children s Hospital
 MENTAL DISORDERS Department of Pediatrics Soochow University Affiliated Children s Hospital CLASSIFICATION OF CHILDHOOD MENTAL DISORDERS The American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical
MENTAL DISORDERS Department of Pediatrics Soochow University Affiliated Children s Hospital CLASSIFICATION OF CHILDHOOD MENTAL DISORDERS The American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice 1 Guideline title SCOPE Autism: the management and support of children and young people on the autism spectrum 1.1 Short
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice 1 Guideline title SCOPE Autism: the management and support of children and young people on the autism spectrum 1.1 Short
Perinatal Risk Factors for Mental Retardation Durkin et al. Prenatal and Postnatal Risk Factors for Mental Retardation among Children in Bangladesh
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 152, No. 11 Printed in U.S.A. Perinatal Risk Factors for Mental
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 152, No. 11 Printed in U.S.A. Perinatal Risk Factors for Mental
S N A P S H OT Report 1 Data from December May 2017
 SNAPSHOT Report 1 Data from December 2015 - May 2017 Did you know that 18,089 people with autism are participating in SPARK? Welcome to the first SPARK Snapshot a window into the autism journey of SPARK
SNAPSHOT Report 1 Data from December 2015 - May 2017 Did you know that 18,089 people with autism are participating in SPARK? Welcome to the first SPARK Snapshot a window into the autism journey of SPARK
Education Options for Children with Autism
 Empowering children with Autism and their families through knowledge and support Education Options for Children with Autism Starting school is a major milestone in a child s life, and a big step for all
Empowering children with Autism and their families through knowledge and support Education Options for Children with Autism Starting school is a major milestone in a child s life, and a big step for all
Fragile CLINIC. Expert Help for Children with Fragile X Syndrome
 x Fragile CLINIC Expert Help for Children with Fragile X Syndrome Fragile X syndrome is the most common inherited cause of intellectual disabilities in children. It is also one of the leading known causes
x Fragile CLINIC Expert Help for Children with Fragile X Syndrome Fragile X syndrome is the most common inherited cause of intellectual disabilities in children. It is also one of the leading known causes
Municipal Employee Guide to Autism Awareness
 RISK Winter 2014 Municipal Employee Guide to Autism Awareness A D M M R M A V I S O A D M R Y C I N O I S T R A T M M I T T I V E E Michigan Municipal Risk Management Authority Administrative Advisory
RISK Winter 2014 Municipal Employee Guide to Autism Awareness A D M M R M A V I S O A D M R Y C I N O I S T R A T M M I T T I V E E Michigan Municipal Risk Management Authority Administrative Advisory
ASHA Comments* (ASHA Recommendations Compared to DSM-5 Criteria) Austism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
 DSM-5 (Criteria and Major Changes for SLP-Related Conditions) Individuals meeting the criteria will be given a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder with three levels of severity based on degree of support
DSM-5 (Criteria and Major Changes for SLP-Related Conditions) Individuals meeting the criteria will be given a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder with three levels of severity based on degree of support
Developmental Disabilities. Medical and Psychosocial Aspects Presented by: Dr. Anna Lamikanra
 Developmental Disabilities Medical and Psychosocial Aspects Presented by: Dr. Anna Lamikanra Themes Decreased Independence Social Barriers Communication Difficulties Sexual Issues Limited Vocational Opportunities
Developmental Disabilities Medical and Psychosocial Aspects Presented by: Dr. Anna Lamikanra Themes Decreased Independence Social Barriers Communication Difficulties Sexual Issues Limited Vocational Opportunities
INTRODUCTION. 9 March Hartford, Connecticut New England s s Rising Star. Connecticut Children s s Medical Center
 EARLY DETECTION OF DEVELOPMENTAL PROBLEMS Evolution of the Concept and Current Practice-A A US Perspective Early Detection of Health and Developmental Problems in Young Children Centre for Community Child
EARLY DETECTION OF DEVELOPMENTAL PROBLEMS Evolution of the Concept and Current Practice-A A US Perspective Early Detection of Health and Developmental Problems in Young Children Centre for Community Child
Research Article JIACAM Vol. 1, No. 3, Article 6
 Research Article JIACAM Vol. 1, No. 3, Article 6 Clinical Profile of Childhood Onset Schizophrenia in India* I. Sharma 1, D. Giri 2, Anna Dutta 3, P. Mazumder 4 & Mrs Anuradha 5 Department of Psychiatry
Research Article JIACAM Vol. 1, No. 3, Article 6 Clinical Profile of Childhood Onset Schizophrenia in India* I. Sharma 1, D. Giri 2, Anna Dutta 3, P. Mazumder 4 & Mrs Anuradha 5 Department of Psychiatry
October 31, 2018 RE: Annie M. Farnsworth SSN: DOB: 1/1/2012
 PLACE ON AGENCY LETTERHEAD SAMPLE: MSR for Annie Farnsworth- child SSI applicant October 31, 2018 RE: Annie M. Farnsworth SSN: 111-11-1111 DOB: 1/1/2012 DDS Adjudicator- Unit 22 Disability Determination
PLACE ON AGENCY LETTERHEAD SAMPLE: MSR for Annie Farnsworth- child SSI applicant October 31, 2018 RE: Annie M. Farnsworth SSN: 111-11-1111 DOB: 1/1/2012 DDS Adjudicator- Unit 22 Disability Determination
Clinical evaluation of children testing positive in screening tests for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A preliminary report
 Eur. J. Psychiat. Vol. 23, N. 2, (115-120) 2009 Keywords: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; Diagnosis; Psychiatric assessment; Screening tests. Clinical evaluation of children testing positive
Eur. J. Psychiat. Vol. 23, N. 2, (115-120) 2009 Keywords: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; Diagnosis; Psychiatric assessment; Screening tests. Clinical evaluation of children testing positive
This is autism. Autism in different diagnostic manuals 1(6)
 1(6) This is autism Original title: Det här är autism Eric Zander Översättning: Semantix Autism is a functional impairment. People who have autism have difficulty interacting and communicating with others
1(6) This is autism Original title: Det här är autism Eric Zander Översättning: Semantix Autism is a functional impairment. People who have autism have difficulty interacting and communicating with others
1/30/2018. Adaptive Behavior Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Disclosures. Learning Objectives
 Adaptive Behavior Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorders Celine A. Saulnier, PhD Associate Professor Emory University School of Medicine Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, Third Edition 1 Disclosures As
Adaptive Behavior Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorders Celine A. Saulnier, PhD Associate Professor Emory University School of Medicine Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, Third Edition 1 Disclosures As
CHARACTERISTICS OF NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS IN THE CLINICAL POPULATION OF A MENTAL HEALTH CENTER
 ANTON et al. ORIGINAL PAPERS CHARACTERISTICS OF NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS IN THE CLINICAL POPULATION OF A MENTAL HEALTH CENTER Miruna RĂDAN 1, Mihaela GĂIȘTEANU 1 1 Alessandrescu-Rusescu National Institute
ANTON et al. ORIGINAL PAPERS CHARACTERISTICS OF NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS IN THE CLINICAL POPULATION OF A MENTAL HEALTH CENTER Miruna RĂDAN 1, Mihaela GĂIȘTEANU 1 1 Alessandrescu-Rusescu National Institute
Critical Evaluation of the Beach Center Family Quality of Life Scale (FQOL-Scale)
 Critical Evaluation of the Beach Center Family Quality of Life Scale (FQOL-Scale) Alyssa Van Beurden M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
Critical Evaluation of the Beach Center Family Quality of Life Scale (FQOL-Scale) Alyssa Van Beurden M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
Introduction to Abnormal Psychology
 Introduction to Abnormal Psychology Truth or Fiction? In the Middle Ages, innocent people were drowned as a way of proving that they were not possessed by the Devil. People with schizophrenia may see and
Introduction to Abnormal Psychology Truth or Fiction? In the Middle Ages, innocent people were drowned as a way of proving that they were not possessed by the Devil. People with schizophrenia may see and
Original Articles. Child Psychiatric Disorders Presenting to a Tertiary Multidisciplinary Child Development Service in Bangladesh
 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (3): 84-89 Original Articles Child Psychiatric Disorders Presenting to a Tertiary Multidisciplinary Child Development Service in Bangladesh FARZANA ISLAM 1, MONOWARA
BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (3): 84-89 Original Articles Child Psychiatric Disorders Presenting to a Tertiary Multidisciplinary Child Development Service in Bangladesh FARZANA ISLAM 1, MONOWARA
Invisible handicap = Invisible people
 Invisible handicap = Invisible people Mentally disabled are about 15% of all disabled folks in India (by census data) 40 lakh mentally disabled in India Seeing, Hearing, Speech, Movement, & Mental Mentally
Invisible handicap = Invisible people Mentally disabled are about 15% of all disabled folks in India (by census data) 40 lakh mentally disabled in India Seeing, Hearing, Speech, Movement, & Mental Mentally
DEVELOPMENTAL BEHAVIOURAL REFERRAL
 Date DEVELOPMENTAL BEHAVIOURAL REFERRAL Completed By Role: Paediatrician/GP How long Other professionals involved with the child (e.g. psychologist, OT, speech therapist) Reason for this referral List
Date DEVELOPMENTAL BEHAVIOURAL REFERRAL Completed By Role: Paediatrician/GP How long Other professionals involved with the child (e.g. psychologist, OT, speech therapist) Reason for this referral List
Table 1 Results of the 12-item General Health Questionnaire among caregivers who were or were not evacuated Not evacuated (N=46)
 Table 1 Results of the 12-item General Health Questionnaire among caregivers who were or were not evacuated Not evacuated (N=46) Evacuated (N=46) Item N % N % 2a p Unable to concentrate 4 4 20 22 14.4
Table 1 Results of the 12-item General Health Questionnaire among caregivers who were or were not evacuated Not evacuated (N=46) Evacuated (N=46) Item N % N % 2a p Unable to concentrate 4 4 20 22 14.4
J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2016; 12(4): Original Article
 291 J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2016; 12(4):291-308 Original Article To study the age of recognition of symptoms and their correlates in children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders:
291 J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2016; 12(4):291-308 Original Article To study the age of recognition of symptoms and their correlates in children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders:
PREVALENCE OF CONDUCT DISORDER IN PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF RURAL AREA Nimisha Mishra 1, Ambrish Mishra 2, Rajeev Dwivedi 3
 PREVALENCE OF CONDUCT DISORDER IN PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF RURAL AREA Nimisha Mishra 1, Ambrish Mishra 2, Rajeev Dwivedi 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Nimisha Mishra, Ambrish Mishra, Rajeev Dwivedi. Prevalence
PREVALENCE OF CONDUCT DISORDER IN PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF RURAL AREA Nimisha Mishra 1, Ambrish Mishra 2, Rajeev Dwivedi 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Nimisha Mishra, Ambrish Mishra, Rajeev Dwivedi. Prevalence
Eligibility Criteria for Children with ASD
 AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER SERIES Eligibility Criteria for Children with ASD Review the Characteristics of Children with ASD* The following are the most common signs and symptoms of a child with ASD: The
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER SERIES Eligibility Criteria for Children with ASD Review the Characteristics of Children with ASD* The following are the most common signs and symptoms of a child with ASD: The
PREVALENCE OF EPILEPSY IN CHILDREN (A POPULATION SURVEY REPORT)
 PREVALENCE OF EPILEPSY IN CHILDREN (A POPULATION SURVEY REPORT) Pages with reference to book, From 134 To 136 Hasan Aziz, Mehr Hasan, K. Zaki Hasan ( Department of Neurology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical
PREVALENCE OF EPILEPSY IN CHILDREN (A POPULATION SURVEY REPORT) Pages with reference to book, From 134 To 136 Hasan Aziz, Mehr Hasan, K. Zaki Hasan ( Department of Neurology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical
Adaptive Behavior Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorders
 Adaptive Behavior Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorders Celine A. Saulnier, PhD Associate Professor Emory University School of Medicine Director of Research Operations Marcus Autism Center Vineland Adaptive
Adaptive Behavior Profiles in Autism Spectrum Disorders Celine A. Saulnier, PhD Associate Professor Emory University School of Medicine Director of Research Operations Marcus Autism Center Vineland Adaptive
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Kim, E. S., Berkovits, L. D., Bernier, E. P., Leyzberg, D., Shic, F., Paul, R., & Scassellati, B. (2013). Social robots as embedded reinforcers of social behavior in children
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Kim, E. S., Berkovits, L. D., Bernier, E. P., Leyzberg, D., Shic, F., Paul, R., & Scassellati, B. (2013). Social robots as embedded reinforcers of social behavior in children
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19149 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Maljaars, Janne Pieternella Wilhelmina Title: Communication problems in children
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19149 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Maljaars, Janne Pieternella Wilhelmina Title: Communication problems in children
SYLLABUS FOR POST-GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN GUIDANCE AND COUNSELING. Personality and Adjustment M. Marks: 100
 SYLLABUS FOR POST-GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN GUIDANCE AND COUNSELING Duration of the programme: : : Two semesters July to December January to June (Vocation and holidays shall be as per university calendar) Paper
SYLLABUS FOR POST-GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN GUIDANCE AND COUNSELING Duration of the programme: : : Two semesters July to December January to June (Vocation and holidays shall be as per university calendar) Paper
BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex M F Address: Home Number: Work Number: Cell Number: Email: SSN: Name and Address of Employer: Date of Birth: Age: Ethnicity: Referred By: Referral Question or
BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex M F Address: Home Number: Work Number: Cell Number: Email: SSN: Name and Address of Employer: Date of Birth: Age: Ethnicity: Referred By: Referral Question or
SURVEY OF SCREENING FOR DEVELOPMENT DELAYS IN CHILDREN A CANADIAN PRIMARY CARE PERSPECTIVE
 SURVEY OF SCREENING FOR DEVELOPMENT DELAYS IN CHILDREN A CANADIAN PRIMARY CARE PERSPECTIVE A. PARTICIPANT PRESCREENING Please complete this questionnaire if one or more of the following apply to your current
SURVEY OF SCREENING FOR DEVELOPMENT DELAYS IN CHILDREN A CANADIAN PRIMARY CARE PERSPECTIVE A. PARTICIPANT PRESCREENING Please complete this questionnaire if one or more of the following apply to your current
The prevalence of psychiatric illness among the informants of psychiatric patients
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 25-29 www.iosrjournals.org The prevalence of psychiatric illness
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2015), PP 25-29 www.iosrjournals.org The prevalence of psychiatric illness
Prevalence and Pattern of Psychiatric Disorders in School Going Adolescents
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 3, No. 100, DIP 18.01.074/20170403 ISBN: 978-1-387-00243-6 http://www.ijip.in April-June, 2017 Prevalence
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 3, No. 100, DIP 18.01.074/20170403 ISBN: 978-1-387-00243-6 http://www.ijip.in April-June, 2017 Prevalence
An Autism Primer for the PCP: What to Expect, When to Refer
 An Autism Primer for the PCP: What to Expect, When to Refer Webinar November 9, 2016 John P. Pelegano MD Chief of Pediatrics Hospital for Special Care Disclosures None I will not be discussing any treatments,
An Autism Primer for the PCP: What to Expect, When to Refer Webinar November 9, 2016 John P. Pelegano MD Chief of Pediatrics Hospital for Special Care Disclosures None I will not be discussing any treatments,
DISABILITY IN PERVASIVE DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY WITH MENTAL RETARDATION IN INDIA
 ISSN: 0973-5755 DISABILITY IN PERVASIVE DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY WITH MENTAL RETARDATION IN INDIA Krishan Kumar*, V. K. Sinha**, B.L. Kotia*** and Sushil Kumar**** ABSTRACT Pervasive
ISSN: 0973-5755 DISABILITY IN PERVASIVE DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY WITH MENTAL RETARDATION IN INDIA Krishan Kumar*, V. K. Sinha**, B.L. Kotia*** and Sushil Kumar**** ABSTRACT Pervasive
One or more genetic anomalies that affect brain development, such as Down syndrome
 Intellectual disability Hearing Definition Characteristics Causes Prevalence Potential Impact on Learning Formerly known as mental retardation, it is defined as an individual with an IQ lower than 70-75
Intellectual disability Hearing Definition Characteristics Causes Prevalence Potential Impact on Learning Formerly known as mental retardation, it is defined as an individual with an IQ lower than 70-75
Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Autism Spectrum Disorder 1) Approximately 1 out of every children in the United States will have an ASD. a) 44 b) 88 c) 122 d) 244 2) Asperger s syndrome presents more frequently in boys than it does in
Autism Spectrum Disorder 1) Approximately 1 out of every children in the United States will have an ASD. a) 44 b) 88 c) 122 d) 244 2) Asperger s syndrome presents more frequently in boys than it does in
Prematurity as a Risk Factor for ASD. Disclaimer
 Prematurity as a Risk Factor for ASD Angela M. Montgomery, MD, MSEd Assistant Professor of Pediatrics (Neonatology) Director, Yale NICU GRAD Program Suzanne L. Macari, PhD Research Scientist, Child Study
Prematurity as a Risk Factor for ASD Angela M. Montgomery, MD, MSEd Assistant Professor of Pediatrics (Neonatology) Director, Yale NICU GRAD Program Suzanne L. Macari, PhD Research Scientist, Child Study
CDC s Public Health Research on Autism
 CDC s Public Health Research on Autism José F. Cordero, MD, MPH Assistant Surgeon General Director, NCBDDD Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental
CDC s Public Health Research on Autism José F. Cordero, MD, MPH Assistant Surgeon General Director, NCBDDD Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental
Oklahoma Psychological Association DSM-5 Panel November 8-9, 2013 Jennifer L. Morris, Ph.D.
 Oklahoma Psychological Association DSM-5 Panel November 8-9, 2013 Jennifer L. Morris, Ph.D. DSM-5 continues developmental progression, starting with disorders that are observed in early life. Disorders
Oklahoma Psychological Association DSM-5 Panel November 8-9, 2013 Jennifer L. Morris, Ph.D. DSM-5 continues developmental progression, starting with disorders that are observed in early life. Disorders
What Do We Know: Autism Screening and Diagnosis and Supporting Families of Young Children
 What Do We Know: Autism Screening and Diagnosis and Supporting Families of Young Children militaryfamilieslearningnetwork.org/event/30358/ This material is based upon work supported by the National Institute
What Do We Know: Autism Screening and Diagnosis and Supporting Families of Young Children militaryfamilieslearningnetwork.org/event/30358/ This material is based upon work supported by the National Institute
Background Information on ADHD
 Get to know ADHD Background Information on ADHD condition, which affects those parts of the brain which control attention, impulses and concentration (a neurobiological condition). It is thought to affect
Get to know ADHD Background Information on ADHD condition, which affects those parts of the brain which control attention, impulses and concentration (a neurobiological condition). It is thought to affect
Developmental Screening in Wisconsin
 Developmental Screening in Wisconsin Community of Practice on Autism February 10, 2010 Christine M. Breunig, Program Administrator, NE Regional Center - CYSHCN Mala Mathur, MD, Group Health Cooperative
Developmental Screening in Wisconsin Community of Practice on Autism February 10, 2010 Christine M. Breunig, Program Administrator, NE Regional Center - CYSHCN Mala Mathur, MD, Group Health Cooperative
Feil & Oppenheimer Psychological Services
 Feil & Oppenheimer Psychological Services 260 Waseca Ave. Barrington, RI 02806 401-245-4040 Fax: 401-245-1240 feiloppenheimer@gmail.com Adult Patient Questionnaire Name: Today's Date: Address: Home Phone:
Feil & Oppenheimer Psychological Services 260 Waseca Ave. Barrington, RI 02806 401-245-4040 Fax: 401-245-1240 feiloppenheimer@gmail.com Adult Patient Questionnaire Name: Today's Date: Address: Home Phone:
The following professionals have been involved in developing this guidance:
 Guidelines for the Identification and Referral of School Placed Children and Young People In Neath Port Talbot County Borough Council with suspected Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) An Autism Spectrum Disorder
Guidelines for the Identification and Referral of School Placed Children and Young People In Neath Port Talbot County Borough Council with suspected Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) An Autism Spectrum Disorder
Implementing NICE guidance
 Implementing NICE guidance Penny Williams Speech and Language Therapist NICE clinical guideline 128 September 2011 What this presentation covers Background Development Scope of the Guideline Key Recommendations
Implementing NICE guidance Penny Williams Speech and Language Therapist NICE clinical guideline 128 September 2011 What this presentation covers Background Development Scope of the Guideline Key Recommendations
Shristi Special Academy
 Shristi Special Academy Evaluation/Tracking over 2009-10 and 2010-11 Updates from 2011 Budget for 2011-12 Presented at Asha SV and Asha Austin, Jun/Jul 2011 Invisible handicap = Invisible people Mentally
Shristi Special Academy Evaluation/Tracking over 2009-10 and 2010-11 Updates from 2011 Budget for 2011-12 Presented at Asha SV and Asha Austin, Jun/Jul 2011 Invisible handicap = Invisible people Mentally
The key findings are presented in the sections of: Literature Review, Survey Questionnaire and Focus Groups.
 Autism Spectrum Disorders in the European Union ASDEU. Summary of Final Report WP2. Current Best Practices on Early Detection and Intervention in EU Member States taking into account Gender Difference
Autism Spectrum Disorders in the European Union ASDEU. Summary of Final Report WP2. Current Best Practices on Early Detection and Intervention in EU Member States taking into account Gender Difference
Dr Keith Ganasen Department of Psychiatry UCT
 Dr Keith Ganasen Department of Psychiatry UCT A. Significantly subaverage intellectual functioning: an IQ of approximately 70 or below on an individually administered IQ test B. Concurrent deficits or
Dr Keith Ganasen Department of Psychiatry UCT A. Significantly subaverage intellectual functioning: an IQ of approximately 70 or below on an individually administered IQ test B. Concurrent deficits or
Impact of Comorbidities on Self-Esteem of Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 3, No.1, DIP: 18.01.011/20160303 ISBN: 978-1-365-03416-9 http://www.ijip.in April - June, 2016 Impact
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 3, No.1, DIP: 18.01.011/20160303 ISBN: 978-1-365-03416-9 http://www.ijip.in April - June, 2016 Impact
Juvenile-onset Huntington s disease
 Juvenile-onset Huntington s disease Presenter Disclosures Martha A. Nance MD The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation existed during the past
Juvenile-onset Huntington s disease Presenter Disclosures Martha A. Nance MD The following personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation existed during the past
MCPAP Clinical Conversations: Screening for Developmental and Behavioral Problems in Young Children
 MCPAP Clinical Conversations: Screening for Developmental and Behavioral Problems in Young Children Michael Tang, MD Ellen C. Perrin, MD R. Christopher Sheldrick, PhD April 25, 2017 What is screening?
MCPAP Clinical Conversations: Screening for Developmental and Behavioral Problems in Young Children Michael Tang, MD Ellen C. Perrin, MD R. Christopher Sheldrick, PhD April 25, 2017 What is screening?
Psychological Testing
 Psychological Testing Lyssa Haase, Psy.D. Licensed Psychologist Primary Children s Center for Counseling Primary Children s Hospital Salt Lake City, Utah Objectives Obtain an overview of psychological
Psychological Testing Lyssa Haase, Psy.D. Licensed Psychologist Primary Children s Center for Counseling Primary Children s Hospital Salt Lake City, Utah Objectives Obtain an overview of psychological
Gohel Aniruddha et al: Assessment of ophthalmic morbidities in school children
 Original Article Assessment of ophthalmic morbidities in school children (6-14 years) in rural community Gohel Aniruddha*, Bundela Chintan*, Rathod Mittal*, Solanki iren**, Shah Viral***, Makwana Naresh****,
Original Article Assessment of ophthalmic morbidities in school children (6-14 years) in rural community Gohel Aniruddha*, Bundela Chintan*, Rathod Mittal*, Solanki iren**, Shah Viral***, Makwana Naresh****,
The 14 th International Fragile X Conference, Garden Grove, CA, Friday, July 18 th, 2014
 Presenters: Sharon Kidd, MPH, PhD; Ave Lachiewicz, MD; Deborah Barbouth, MD; Robin Blitz, MD; Carol Delahunty, MD; Dianne McBrien, MD; Elizabeth Berry-Kravis, MD, PhD The 14 th International Fragile X
Presenters: Sharon Kidd, MPH, PhD; Ave Lachiewicz, MD; Deborah Barbouth, MD; Robin Blitz, MD; Carol Delahunty, MD; Dianne McBrien, MD; Elizabeth Berry-Kravis, MD, PhD The 14 th International Fragile X
Developmental Delay In Children. Special Focus on Autism and Foster Children
 Developmental Delay In Children Special Focus on Autism and Foster Children Objectives Statistics Definitions Causes BiopsychosocialStreams and Red Flags Autism/DD First Signs DSM-5 Early Intervention/Screening
Developmental Delay In Children Special Focus on Autism and Foster Children Objectives Statistics Definitions Causes BiopsychosocialStreams and Red Flags Autism/DD First Signs DSM-5 Early Intervention/Screening
AUTISM SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS PEARLS FOR PEDIATRICS. Catherine Riley, MD Developmental Behavioral Pediatrician
 AUTISM SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS PEARLS FOR PEDIATRICS Catherine Riley, MD Developmental Behavioral Pediatrician Disclosure I do not have any financial relationships to disclose I do not plan to discuss
AUTISM SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS PEARLS FOR PEDIATRICS Catherine Riley, MD Developmental Behavioral Pediatrician Disclosure I do not have any financial relationships to disclose I do not plan to discuss
The child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy thinking beyond the motor impairment. Dr Paul Eunson Edinburgh
 The child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy thinking beyond the motor impairment Dr Paul Eunson Edinburgh Content Coming to a diagnosis The importance of understanding the injury MRI scans Role of epilepsy
The child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy thinking beyond the motor impairment Dr Paul Eunson Edinburgh Content Coming to a diagnosis The importance of understanding the injury MRI scans Role of epilepsy
ATTENTION AND EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONS OF CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER
 Research Report ATTENTION AND EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONS OF CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER P.A. Fazal Ghafoor 1, Firoz Kazhungil 2*, Liji Premlal 3, Suni Muraleedharan 4, G Manoj Kumar
Research Report ATTENTION AND EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONS OF CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER P.A. Fazal Ghafoor 1, Firoz Kazhungil 2*, Liji Premlal 3, Suni Muraleedharan 4, G Manoj Kumar
Appendix A California Longitudinal Pupil Achievement Data System Disability Codes
 Appendices Appendix A California Longitudinal Pupil Achievement Data System Disability Codes Intellectual Disability (ID) Hard of hearing (HH) Deafness (DEAF)/Hearing impairment (HI) Speech or language
Appendices Appendix A California Longitudinal Pupil Achievement Data System Disability Codes Intellectual Disability (ID) Hard of hearing (HH) Deafness (DEAF)/Hearing impairment (HI) Speech or language
Autism. Recognition, referral and diagnosis of children and young people on the autism spectrum
 Issue date: September 2011 Autism Recognition, referral and diagnosis of children and young people on the autism spectrum NICE clinical guideline 128 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for
Issue date: September 2011 Autism Recognition, referral and diagnosis of children and young people on the autism spectrum NICE clinical guideline 128 Developed by the National Collaborating Centre for
Assessment of Nutritional Status among Children less than 5 years old in Hilla City
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016 276 Assessment of Nutritional Status among Children less than 5 years old in Hilla City * Ismael Hasan Jawad,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 8, August 2016 276 Assessment of Nutritional Status among Children less than 5 years old in Hilla City * Ismael Hasan Jawad,
History Form for Adult Client
 History Form for Adult Client Referral Date: Who referred you to our office (please circle one)? Self Other, please specify: Reason for Referral: Require a Diagnostic Evaluation for Autism Spectrum Disorder
History Form for Adult Client Referral Date: Who referred you to our office (please circle one)? Self Other, please specify: Reason for Referral: Require a Diagnostic Evaluation for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Intellectual Disability
 Intellectual Disability Tara Anne Matthews, MD Fellow Kapila Seshadri, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ Robert Wood Johnson Medical Wednesday November 14, 2012 Intellectual Disability (Mental
Intellectual Disability Tara Anne Matthews, MD Fellow Kapila Seshadri, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ Robert Wood Johnson Medical Wednesday November 14, 2012 Intellectual Disability (Mental
FRAGILE X 101. A guide for the newly-diagnosed and those already living with Fragile X. fragilex.org
 FRAGILE X 101 A guide for the newly-diagnosed and those already living with Fragile X. fragilex.org Introduction Most people first hear about Fragile X disorders when someone in their family is unexpectedly
FRAGILE X 101 A guide for the newly-diagnosed and those already living with Fragile X. fragilex.org Introduction Most people first hear about Fragile X disorders when someone in their family is unexpectedly
Choose the Right Word
 Choose the Right Word Instead of Please use Afflicted by cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, arthritis, etc. Person who has cerebral palsy. Person who has multiple sclerosis. Person who has arthritis,
Choose the Right Word Instead of Please use Afflicted by cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, arthritis, etc. Person who has cerebral palsy. Person who has multiple sclerosis. Person who has arthritis,
Attention Deficit Disorder. Evaluation Scale-Home Version 16. The Attention Deficit Disorders. Evaluation Scale-School Version 17
 The Development of an Educational and Screening Instrument for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in a Pediatric Residency Program Stephen P. Amos, Ph.D., Robert Wittler, M.D., Corrie Nevil, M.D.,
The Development of an Educational and Screening Instrument for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in a Pediatric Residency Program Stephen P. Amos, Ph.D., Robert Wittler, M.D., Corrie Nevil, M.D.,
The Nuts and Bolts of Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorders In Young Children. Overview
 The Nuts and Bolts of Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorders In Young Children Jessica Greenson, Ph.D. Autism Center University of Washington Overview Diagnostic Criteria Current: Diagnostic & Statistical
The Nuts and Bolts of Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorders In Young Children Jessica Greenson, Ph.D. Autism Center University of Washington Overview Diagnostic Criteria Current: Diagnostic & Statistical
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS for X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY
 MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS for X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY WHAT IS X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY? Intellectual disability (ID), sometimes called mental retardation (MR) or developmental delay (DD), is
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS for X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY WHAT IS X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY? Intellectual disability (ID), sometimes called mental retardation (MR) or developmental delay (DD), is
AAA. Report #9 Study Update. - Principal Investigators Marsha Mailick Seltzer, Ph.D.
 AAA Adolescents & Adults with Autism A Study of Family Caregiving Report #9 Study Update - Principal Investigators Marsha Mailick Seltzer, Ph.D. Jan S. Greenberg, Ph.D. Waisman Center University of Wisconsin
AAA Adolescents & Adults with Autism A Study of Family Caregiving Report #9 Study Update - Principal Investigators Marsha Mailick Seltzer, Ph.D. Jan S. Greenberg, Ph.D. Waisman Center University of Wisconsin
EAC-AZ Webinar #7 November 18 th & 25 th. Today s Objectives 11/17/2015. Month 4 Related Medical/Behavioral Issues
 EAC-AZ Webinar #7 November 18 th & 25 th Robin Blitz, MD Sara Bode, MD Amber Wright, CPNP Today s Objectives Month 4 Article Review STAT Reliability Testing ADOS Interpretation AzEIP / School Testing M-CHAT-R
EAC-AZ Webinar #7 November 18 th & 25 th Robin Blitz, MD Sara Bode, MD Amber Wright, CPNP Today s Objectives Month 4 Article Review STAT Reliability Testing ADOS Interpretation AzEIP / School Testing M-CHAT-R
Center for. Our Mission. Autism and Related Disorders. Helping children with autism through patient care, research, and education.
 707 North Broadway Baltimore, Maryland 21205 www.kennedykrieger.org Our Mission We at the Kennedy Krieger Institute dedicate ourselves to helping children and adolescents with disorders of the brain, spinal
707 North Broadway Baltimore, Maryland 21205 www.kennedykrieger.org Our Mission We at the Kennedy Krieger Institute dedicate ourselves to helping children and adolescents with disorders of the brain, spinal
Handbook Of Autism And Pervasive Developmental Disorders Assessment Interventions And Policy
 Handbook Of Autism And Pervasive Developmental Disorders Assessment Interventions And Policy Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 19, 87-94. Motivation Assessment Scale. Cohen D. (Eds.),
Handbook Of Autism And Pervasive Developmental Disorders Assessment Interventions And Policy Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 19, 87-94. Motivation Assessment Scale. Cohen D. (Eds.),
The Effect of Brain Gym Exercises on Self- Esteem and Sensory Processing Speed on High School Hearing Impaired Students
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 2, No. 93, DIP: 18.01.136/20170402 ISBN: 978-1-365-78193-3 http://www.ijip.in January-March, 2017 The
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 2, No. 93, DIP: 18.01.136/20170402 ISBN: 978-1-365-78193-3 http://www.ijip.in January-March, 2017 The
Behavioral Health Clinician in Primary Care Billing & Coding Guidance (Created September 2017)
 Behavioral Health Clinician in Primary Care Billing & Coding Guidance (Created September 2017) This information was drafted by behavioral leaders interested in supporting optimal billing for behavioral
Behavioral Health Clinician in Primary Care Billing & Coding Guidance (Created September 2017) This information was drafted by behavioral leaders interested in supporting optimal billing for behavioral
Mental Retardation in Early Intervention Perspective
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. II, Issue 6/ September 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.1 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Mental Retardation in Early Intervention Perspective Dr. SMITA
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. II, Issue 6/ September 2014 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.1 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Mental Retardation in Early Intervention Perspective Dr. SMITA
Risk factors associated with Borderline Intelligence in Schoolchildren: A Case-Control Study
 Original Article Risk factors associated with Borderline Intelligence in Schoolchildren: A Case-Control Study Farhadifar F 1, Ghotbi N 2, Yari A 3, Haydarpur M 4, Mohammadzadeh H 5, Afkhamzadeh A 6, Delpisheh
Original Article Risk factors associated with Borderline Intelligence in Schoolchildren: A Case-Control Study Farhadifar F 1, Ghotbi N 2, Yari A 3, Haydarpur M 4, Mohammadzadeh H 5, Afkhamzadeh A 6, Delpisheh
CHILD AND TEEN CHECKUPS PERIODICITY SCHEDULE UPDATES FOR OCTOBER 1, 2017
 Slide notes CHILD AND TEEN CHECKUPS PERIODICITY SCHEDULE UPDATES FOR OCTOBER 1, 2017 These notes are an accessible version of the slide notes embedded in the PowerPoint presentation of the same title.
Slide notes CHILD AND TEEN CHECKUPS PERIODICITY SCHEDULE UPDATES FOR OCTOBER 1, 2017 These notes are an accessible version of the slide notes embedded in the PowerPoint presentation of the same title.
2017 Gatlinburg Conference Symposium Submission SS-1
 Symposium Title: Outcomes for Young Children with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities: A Discussion of Behavioral Phenotypes, Differential Responses and Outcome Measures Chair: Jena McDaniel 1
Symposium Title: Outcomes for Young Children with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities: A Discussion of Behavioral Phenotypes, Differential Responses and Outcome Measures Chair: Jena McDaniel 1
Clinical Neuropsychology Residency Program. Department of Health Psychology in the School of Health Professions
 Clinical Neuropsychology Residency Program Department of Health Psychology in the School of Health Professions Last Updated: 11/16/2017 1 Program description: The post-doctoral residency program in neuropsychology
Clinical Neuropsychology Residency Program Department of Health Psychology in the School of Health Professions Last Updated: 11/16/2017 1 Program description: The post-doctoral residency program in neuropsychology
Ana Apolónio (ARSA)& Vítor Franco (U. Évora)
 1 ᶳᶵ International Early Childhood Conference Eurlyaid Annual Conference 2012 Braga, 14.09.2012 Ana Apolónio (ARSA)& Vítor Franco (U. Évora) Projecto PTDC/CPE-CED/115276/2009 Fragile X Syndrome Most common
1 ᶳᶵ International Early Childhood Conference Eurlyaid Annual Conference 2012 Braga, 14.09.2012 Ana Apolónio (ARSA)& Vítor Franco (U. Évora) Projecto PTDC/CPE-CED/115276/2009 Fragile X Syndrome Most common
topic : Co-Morbid Conditions by Cindy Ring, MSW, LSW and Michele LaMarche, BCBA
 ABA Literature Summary e-newsletter OCTOBER 2011 ISSUE 5 topic : Co-Morbid Conditions by Cindy Ring, MSW, LSW and Michele LaMarche, BCBA 1. Co-Morbidity Rates and Types in Individuals with Autism............
ABA Literature Summary e-newsletter OCTOBER 2011 ISSUE 5 topic : Co-Morbid Conditions by Cindy Ring, MSW, LSW and Michele LaMarche, BCBA 1. Co-Morbidity Rates and Types in Individuals with Autism............
RISK APPROACH FOR REDUCING MALNUTRITION IN CHILDREN FROM A PRIVILEGED COMMUNITY
 RISK APPROACH FOR REDUCING MALNUTRITION IN CHILDREN FROM A PRIVILEGED COMMUNITY Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 59 To 61 Inayat Hussain Thaver ( Department of Community Health Sciences, Aga
RISK APPROACH FOR REDUCING MALNUTRITION IN CHILDREN FROM A PRIVILEGED COMMUNITY Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 59 To 61 Inayat Hussain Thaver ( Department of Community Health Sciences, Aga
Diagnostic tests for autism may miss many girls
 NEWS Diagnostic tests for autism may miss many girls BY DEBORAH RUDACILLE 27 JUNE 2011 1 / 8 2 / 8 3 / 8 4 / 8 Lonely child: Girls with Asperger syndrome show an interest in socializing, but have difficulty
NEWS Diagnostic tests for autism may miss many girls BY DEBORAH RUDACILLE 27 JUNE 2011 1 / 8 2 / 8 3 / 8 4 / 8 Lonely child: Girls with Asperger syndrome show an interest in socializing, but have difficulty
SOCIO-ECONOMIC BURDEN OF CHILDHOOD ASTHMA
 SOCIO-ECONOMIC BURDEN OF CHILDHOOD ASTHMA A. Lal L. Kumar S. Malhotra ABSTRACT The socio-economic burden of childhood asthma has not been assessed in India. We interviewed parents of asthmatic 85 children
SOCIO-ECONOMIC BURDEN OF CHILDHOOD ASTHMA A. Lal L. Kumar S. Malhotra ABSTRACT The socio-economic burden of childhood asthma has not been assessed in India. We interviewed parents of asthmatic 85 children
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder. By: Nicole Tyminski
 Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder By: Nicole Tyminski What is Autism? Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and autism are both general terms for a group of complex disorders of brain development. These
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder By: Nicole Tyminski What is Autism? Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and autism are both general terms for a group of complex disorders of brain development. These
Simons VIP Phenotyping: What we ve learned so far. Ellen Hanson, Ph.D. and Raphael Bernier, Ph.D. Family Meeting Summer, 2015
 Simons VIP Phenotyping: What we ve learned so far Ellen Hanson, Ph.D. and Raphael Bernier, Ph.D. Family Meeting Summer, 2015 Outline Brief review of data collection procedures Discussion of Neurodevelopmental
Simons VIP Phenotyping: What we ve learned so far Ellen Hanson, Ph.D. and Raphael Bernier, Ph.D. Family Meeting Summer, 2015 Outline Brief review of data collection procedures Discussion of Neurodevelopmental
With additional support from Florida International University and The Children s Trust.
 The Society for Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology (SCCAP): Initiative for Dissemination of Evidence-based Treatments for Childhood and Adolescent Mental Health Problems With additional support from
The Society for Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology (SCCAP): Initiative for Dissemination of Evidence-based Treatments for Childhood and Adolescent Mental Health Problems With additional support from
Page24. Indexed in: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Sunny Agarwal Founder / Digital Marketing Specialist at Code- LIT. September 2018; 5(3):24-28
 Page24 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Sunny Agarwal Founder / Digital Marketing Specialist at Code- LIT Email: agarwalsunny68@gmail.com KEY WORDS: Autism, Sign/symptoms of ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorder),
Page24 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Sunny Agarwal Founder / Digital Marketing Specialist at Code- LIT Email: agarwalsunny68@gmail.com KEY WORDS: Autism, Sign/symptoms of ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorder),
Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury. Seth Warschausky, PhD Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation University of Michigan
 Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury Seth Warschausky, PhD Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation University of Michigan Modules Module 1: Overview Module 2: Cognitive and Academic Needs Module
Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury Seth Warschausky, PhD Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation University of Michigan Modules Module 1: Overview Module 2: Cognitive and Academic Needs Module
Developmental delay Poor School Progress. I Smuts Department of Paediatrics
 Developmental delay Poor School Progress I Smuts Department of Paediatrics References Normal development: Handbook of Neurology: Paediatric clinical examination guideline How do children present Children
Developmental delay Poor School Progress I Smuts Department of Paediatrics References Normal development: Handbook of Neurology: Paediatric clinical examination guideline How do children present Children
AUTISM STRATEGY FOR ADULTS IN BIRMINGHAM
 CONSULTATION DOCUMENT AUTISM STRATEGY FOR ADULTS IN BIRMINGHAM 2013 2016 HELPING ADULTS WITH AUTISM TO ACHIEVE FULFILLING AND REWARDING LIVES RAISING AWARENESS TO INFORM, IMPLEMENT AND IMPROVE Strategy
CONSULTATION DOCUMENT AUTISM STRATEGY FOR ADULTS IN BIRMINGHAM 2013 2016 HELPING ADULTS WITH AUTISM TO ACHIEVE FULFILLING AND REWARDING LIVES RAISING AWARENESS TO INFORM, IMPLEMENT AND IMPROVE Strategy
