Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression
|
|
|
- Paula Lewis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression Depression causes low mood or sadness that can last for weeks or months. People with depression often feel hopeless and lose interest in things they used to enjoy. Other symptoms include sleeping badly, and having no appetite or sex drive. Transcranial magnetic stimulation is a possible treatment for depression that uses a powerful electromagnet, placed on the scalp, to produce electric currents in the brain. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is examining repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression and will publish guidance on its safety and efficacy to the NHS. NICE s Interventional Procedures Advisory Committee has considered the available evidence and the views of specialist advisers, who are consultants with knowledge of the procedure. The Advisory Committee has made provisional recommendations about repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression. This document summarises the procedure and sets out the provisional recommendations made by the Advisory Committee. It has been prepared for public consultation. The Advisory Committee particularly welcomes: comments on the provisional recommendations the identification of factual inaccuracies additional relevant evidence, with bibliographic references where possible. Note that this document is not NICE s formal guidance on this procedure. The recommendations are provisional and may change after consultation. The process that NICE will follow after the consultation period ends is as follows. The Advisory Committee will meet again to consider the original evidence and its provisional recommendations in the light of the comments received during consultation. Page 1 of 10
2 The Advisory Committee will then prepare draft guidance which will be the basis for NICE s guidance on the use of the procedure in the NHS. For further details, see the Interventional Procedures Programme process guide, which is available from the NICE website. Through its guidance NICE is committed to promoting race and disability equality, equality between men and women, and to eliminating all forms of discrimination. One of the ways we do this is by trying to involve as wide a range of people and interest groups as possible in the development of our interventional procedures guidance. In particular, we aim to encourage people and organisations from groups who might not normally comment on our guidance to do so. In order to help us promote equality through our guidance, we should be grateful if you would consider the following question: Are there any issues that require special attention in light of NICE s duties to have due regard to the need to eliminate unlawful discrimination, advance equality of opportunity, and foster good relations between people with a characteristic protected by the equalities legislation and others? Please note that NICE reserves the right to summarise and edit comments received during consultations or not to publish them at all where in the reasonable opinion of NICE, the comments are voluminous, publication would be unlawful or publication would otherwise be inappropriate. Closing date for comments: 23 July 2015 Target date for publication of guidance: November Provisional recommendations 1.1 The evidence on repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression shows no major safety concerns. The evidence on its efficacy in the short term is adequate, although the clinical response is variable and some patients may not benefit. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression may be used with normal arrangements for clinical governance and audit, provided that patients are informed, during the consent process, about the other treatment options available and they understand the Page 2 of 10
3 possibility that they may derive little or no benefit from the procedure. 1.2 NICE encourages publication of further evidence on patient selection, the use of maintenance treatment and long-term outcomes. 2 Indications and current treatments 2.1 Depression is a common disorder. It is characterised by persistent sadness, loss of interest or pleasure, feelings of guilt or low selfworth, disturbed sleep, appetite and libido, tiredness and poor concentration. It is also often accompanied by feelings of hopelessness and suicidal thoughts. Depression can last from weeks to years, and can be recurrent. It can substantially impair an individual s ability to function at work or cope with daily life. Treatments for depression include a range of psychological therapies and antidepressant medications. In severe depression, electroconvulsive therapy or transcranial direct current stimulation are sometimes used. 3 The procedure 3.1 Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms) does not need anaesthesia and can be done on an outpatient basis. A purposemade electromagnetic coil is held against the scalp with the intention of inducing electric currents in the cerebral cortex. Imaging may be used to help target specific areas of the brain. Treatment is usually considered for patients with depression that has not responded to antidepressant medication. Page 3 of 10
4 3.2 In rtms, repetitive pulses of electromagnetic energy are delivered at various frequencies or stimulus intensities. Conventional rtms uses continuous pulses of electromagnetic energy whereas thetaburst rtms uses intermittent pulses. Stimulation can either be delivered unilaterally, over the left or right dorso-lateral prefrontal cortex, or bilaterally over both cortices. Bilateral stimulation may be done sequentially or simultaneously. Treatment with rtms usually comprises daily sessions lasting about 30 minutes, typically for 2 to 6 weeks. 4 Efficacy This section describes efficacy outcomes from the published literature that the Committee considered as part of the evidence about this procedure. For more detailed information on the evidence, see the interventional procedure overview. 4.1 In a systematic review of 40 randomised controlled trials including 1592 patients with depression (type unspecified) treated by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms, n=751) or sham stimulation (n=632), meta-analysis of mean changes in unspecified depression rating scales showed a significant effect in favour of rtms (Hedges g value of 0.55, p<0.001). 4.2 In a non-randomised comparative study of 185 patients with treatment-resistant depression treated by conventional rtms (n=98) or theta-burst rtms (n=87), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) scores (lower scores indicate less depression) decreased from 22.1±6.9 to 12.3±8.9 and from 21.1±5.1 to 12.7±7.9 respectively at 1- month follow-up (p value within groups <0.001, p value between groups not significant). In the same study, Beck Depressive Inventory scores (scores range from 0 to 63, with Page 4 of 10
5 lower scores indicating less depression) decreased from 35.4±10.8 to 22.4±15.5 in the conventional rtms group and from 35.9±9.9 to 20.2±13.3 in the theta-burst rtms group at 1-month follow-up (p value within groups <0.001, p value between groups not significant). 4.3 In a systematic review of 63 studies including 3236 patients treated by rtms (n=2330), sham stimulation (n=806) or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT; n=100), percentage changes in HDRS scores (lower scores indicate less depression) were pooled and converted to Clinical Global Impression - Improvement scale (CGI-I) scores (scores range from 1 to 7, with lower scores indicating greater improvements in a patient s mental illness). For patients with any type of depression, the mean percentage reduction in HDRS scores was 37% (CGI-I equivalent, 2.8) in the rtms group and 22% (CGI-I 3.4) in the sham stimulation group (p<0.05). For patients with treatment-resistant depression, the mean percentage reduction in HDRS scores was 48% (CGI-I 2.4) in the rtms group and 23% (CGI-I 3.4) in the sham stimulation group (p<0.05). When rtms was compared against ECT in patients with any type of depression, the mean percentage reduction in HDRS scores was 34% (CGI-I equivalent not reported) in the rtms group and 46% (CGI-I 2.45) in the ECT group (p<0.05). 4.4 In a systematic review of 10 randomised controlled trials including 634 patients with treatment-resistant depression treated by bilateral rtms, unilateral rtms or sham simulation, clinical response (defined as more than a 50% improvement in HDRS or Montgomery Åsberg Depression Rating Scale scores) was compared between groups. Meta-analysis of clinical response rates in patients treated by bilateral rtms or sham stimulation revealed a Page 5 of 10
6 risk ratio of 3.29 in favour of bilateral rtms (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.69 to 6.38, p=0.0004). In the same study, metaanalysis of remission (classified according to predefined criteria in each included study) revealed no significant difference between patients treated by bilateral rtms or sham stimulation (risk ratio 0.5; 95% CI 0.19 to 1.31, p=0.16). 4.5 In a systematic review of 10 randomised controlled trials including 429 patients with a primary major depressive episode treated by rtms (n=217) or ECT (n=212), meta-analysis of clinical response (defined as more than a 50% improvement in HDRS scores) revealed a risk ratio of 1.52, in favour of ECT (95% CI 1.18 to 1.95, p=0.001). Meta-analysis of remission (classified according to predefined criteria in each included study) revealed a risk ratio of 1.42 in favour of ECT (95% CI 1.16 to 1.75, p=0.0007). 4.6 A case series evaluated 120 patients who had at least a partial response (that is, at least a 25% improvement in HDRS scores); 99 patients were recruited from the active rtms arm of a randomised sham-controlled trial, while 21 patients initially had sham stimulation and subsequently received active rtms. For patients originally in the active rtms arm of the trial, the mean HDRS score was 9.1±6.2 at the end of rtms therapy and 9.0±7.1 at 6-month follow-up (p=0.537), indicating a maintained treatment effect. No pre-treatment scores were reported. No mean HDRS scores were reported for patients who initially had sham stimulation and subsequently received active rtms. In the same study, the relapse rate (Kaplan-Meier estimate) at 6-month follow-up was 13% in patients who were originally in the active rtms arm of the trial and 16% in patients who initially had sham stimulation and subsequently received active rtms (No p value reported). Page 6 of 10
7 4.7 Specialist advisers listed improvements in depressive symptoms, and health-related quality of life as efficacy outcomes. 5 Safety This section describes safety outcomes from the published literature that the Committee considered as part of the evidence about this procedure. For more detailed information on the evidence, see the interventional procedure overview. 5.1 A self-limiting complex partial seizure was reported in 1 patient who had unilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms), at a frequency of 20 Hz and at 110% of the motor threshold. The patient was awake after 8 seconds; she was alert with no postictal confusion and had no memory of what happened. No subsequent physical sequelae were reported. 5.2 A hypomanic episode was reported in 1 patient, soon after completion of therapy, in a randomised controlled trial of 130 patients treated by 1 Hz or 2 Hz rtms. The exact timing of occurrence was not reported. 5.3 Headache was reported in 10% (46/472) of patients treated by high-frequency rtms, 4% (4/109) treated by low-frequency rtms and 3% (12/461) given sham stimulation in a systematic review of 40 randomised controlled trials that included 1592 patients with depression (type unspecified). 5.4 Scalp discomfort was reported in 9% (45/472) of patients treated by high-frequency rtms, 2% (2/109) treated by low-frequency rtms and 2% (9/461) given sham stimulation in the systematic review of Page 7 of 10
8 40 randomised controlled trials that included 1592 patients with depression (type unspecified). 5.5 Pain at the rtms application site was reported in 6% (6/99) of patients in a case series of 120 patients with major depressive disorder treated by rtms. 5.6 Facial twitching was reported in 2% (9/472) of patients treated by high-frequency rtms, none treated by low-frequency rtms (n=109) and none given sham stimulation (n=461) in the systematic review of 40 randomised controlled trials that included 1592 patients with depression (type unspecified). 5.7 Local erythema was reported in 1% (6/472) of patients treated by high-frequency rtms, none treated by low-frequency rtms (n=109) and none given sham stimulation (n=461) in the systematic review of 40 randomised controlled trials that included 1592 patients with depression (type unspecified). 5.8 Drowsiness was reported in 3% (12/472) of patients treated by high-frequency rtms, none treated by low-frequency rtms (n=109) and none given sham stimulation (n=461) in the systematic review of 40 randomised controlled trials that included 1592 patients with depression (type unspecified). 5.9 Vertigo was reported in no patients in the conventional rtms (n=98) group and 1 patient in the theta-burst TMS group (n=87) in a non-randomised comparative study of 185 patients with treatment resistant depression Increasingly hostile thoughts were reported in no patients in the conventional rtms group (n=98) and 1 patient in the theta-burst Page 8 of 10
9 rtms group (n=85) in the non-randomised comparative study of 185 patients with treatment-resistant depression. The timing of occurrence was not reported Device-related insomnia was reported in 1 patient in the case series of 120 patients with major depressive disorder treated by rtms Device-related arthralgia was reported in 1 patient in the case series of 120 patients with major depressive disorder treated by rtms In addition to safety outcomes reported in the literature, specialist advisers are asked about anecdotal adverse events (events which they have heard about) and about theoretical adverse events (events which they think might possibly occur, even if they have never done so). For this procedure, specialist advisers listed the following anecdotal adverse events: discomfort, unpleasant twitching, worsening psychomotor agitation in patients with mixed affective disorder, transient confusion, transient problems with concentration and/or working memory, and transient hearing loss. They did not suggest any theoretical adverse events. 6 Committee comments 6.1 The Committee recognised the difficulties in conducting research on repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms) for depression, in the context of the variable natural history of depression, the challenges of providing sham treatment, and a variable and often small response. Despite large numbers of patients in the published studies there were difficulties in assessing the effect size. Nevertheless, the Committee noted consistently Page 9 of 10
10 positive outcomes in many studies and a good safety profile. These considerations underpinned the recommendation for use with normal arrangements, provided that patients are properly informed about alternative treatment options, about the risk that they may derive little or no benefit from rtms and about the possible need for repeated treatments. 6.2 The Committee noted that commentary from patients was positive and described significant benefits to their quality of life, including the advantages, for some patients, of being able to stop the use of oral antidepressant medications. Page 10 of 10
Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine Cluster
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine Cluster
Implantation of a sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation device for chronic cluster headache
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation device for chronic cluster headache Cluster headaches
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation device for chronic cluster headache Cluster headaches
Implanting a baroreceptor stimulation device for resistant hypertension
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implanting a baroreceptor stimulation device for resistant hypertension Hypertension (or high blood pressure)
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implanting a baroreceptor stimulation device for resistant hypertension Hypertension (or high blood pressure)
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator insertion for preventing sudden cardiac death
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator insertion for preventing sudden cardiac death A subcutaneous
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator insertion for preventing sudden cardiac death A subcutaneous
Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator cuff is a group of muscles
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator cuff is a group of muscles
Statement on Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression. Position statement CERT03/17
 Statement on Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression Position statement CERT03/17 Approved by the Royal College of Psychiatrists, Committee on ECT and Related Treatments: February 2017
Statement on Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression Position statement CERT03/17 Approved by the Royal College of Psychiatrists, Committee on ECT and Related Treatments: February 2017
Processed nerve allografts to repair peripheral nerve discontinuities
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Processed nerve allografts to repair peripheral nerve discontinuities Accidents or major surgery can damage
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Processed nerve allografts to repair peripheral nerve discontinuities Accidents or major surgery can damage
Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema Chronic lymphoedema is the swelling and build-up of body fluid and fat,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema Chronic lymphoedema is the swelling and build-up of body fluid and fat,
Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
Extracranial to intracranial bypass for intracranial atherosclerosis
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Extracranial to intracranial bypass for intracranial atherosclerosis In cerebrovascular disease, blood vessels
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Extracranial to intracranial bypass for intracranial atherosclerosis In cerebrovascular disease, blood vessels
Neuromodulation Approaches to Treatment Resistant Depression
 1 Alternative Treatments: Neuromodulation Approaches to Treatment Resistant Depression Audrey R. Tyrka, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Brown University Department of Psychiatry Associate Chief, Mood Disorders
1 Alternative Treatments: Neuromodulation Approaches to Treatment Resistant Depression Audrey R. Tyrka, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Brown University Department of Psychiatry Associate Chief, Mood Disorders
Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
Insertion of an epiretinal prosthesis for retinitis pigmentosa
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Insertion of an epiretinal prosthesis for retinitis pigmentosa Retinitis pigmentosa is a disease that affects
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Insertion of an epiretinal prosthesis for retinitis pigmentosa Retinitis pigmentosa is a disease that affects
Patient Manual Brainsway Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder
 Dr. Zahida Tayyib www.mvptms.com Patient Manual Brainsway Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder If you are considering Brainsway Deep treatment
Dr. Zahida Tayyib www.mvptms.com Patient Manual Brainsway Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder If you are considering Brainsway Deep treatment
rtms Versus ECT The Future of Neuromodulation & Brain Stimulation Therapies
 rtms Versus ECT The Future of Neuromodulation & Brain Stimulation Therapies rtms Treatment Equipment rtms Equipment Positioning of coil ECT & rtms Innovative Treatment Options for Patients Only a fraction
rtms Versus ECT The Future of Neuromodulation & Brain Stimulation Therapies rtms Treatment Equipment rtms Equipment Positioning of coil ECT & rtms Innovative Treatment Options for Patients Only a fraction
Some newer, investigational approaches to treating refractory major depression are being used.
 CREATED EXCLUSIVELY FOR FINANCIAL PROFESSIONALS Rx FOR SUCCESS Depression and Anxiety Disorders Mood and anxiety disorders are common, and the mortality risk is due primarily to suicide, cardiovascular
CREATED EXCLUSIVELY FOR FINANCIAL PROFESSIONALS Rx FOR SUCCESS Depression and Anxiety Disorders Mood and anxiety disorders are common, and the mortality risk is due primarily to suicide, cardiovascular
Patient Education Brief. NeuroStar TMS Therapies
 Patient Education Brief NeuroStar TMS Therapies Provided by Dr Terrence A. Boyadjis MD 790 E Market Street Suite 245 West Chester, PA 19382 610.738.9576 About Depression Depression is a serious medical
Patient Education Brief NeuroStar TMS Therapies Provided by Dr Terrence A. Boyadjis MD 790 E Market Street Suite 245 West Chester, PA 19382 610.738.9576 About Depression Depression is a serious medical
Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Biodegradable spacer insertion to reduce rectal toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer Radiotherapy
FDA CLEARS NEUROSTAR TMS THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE FDA CLEARS NEUROSTAR TMS THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION First and Only Non-systemic and Non-invasive Treatment Cleared for Patients Who Have Not Benefited From Prior Antidepressant
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE FDA CLEARS NEUROSTAR TMS THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION First and Only Non-systemic and Non-invasive Treatment Cleared for Patients Who Have Not Benefited From Prior Antidepressant
Implantation of a corneal graft keratoprosthesis for severe corneal opacity in wet blinking eyes
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a corneal graft keratoprosthesis for severe corneal opacity in wet blinking eyes The cornea
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a corneal graft keratoprosthesis for severe corneal opacity in wet blinking eyes The cornea
Original Effective Date: 8/28/2013. Subject: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Major Depression
 Subject: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Major Depression Guidance Number: MCG-104 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 8/28/2013 Medical Coverage Guidance Approval Date: 8/28/2013
Subject: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Major Depression Guidance Number: MCG-104 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 8/28/2013 Medical Coverage Guidance Approval Date: 8/28/2013
What is Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation?
 rtms for Refractory Depression: Findings and Future Jonathan Downar, MD PhD Asst Professor, Dept of Psychiatry University of Toronto, Canada Co-Director, rtms Clinic Toronto Western Hospital University
rtms for Refractory Depression: Findings and Future Jonathan Downar, MD PhD Asst Professor, Dept of Psychiatry University of Toronto, Canada Co-Director, rtms Clinic Toronto Western Hospital University
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation for aortic stenosis
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcatheter aortic valve implantation for aortic stenosis Aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcatheter aortic valve implantation for aortic stenosis Aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve
Treatment of Depression: A Brief History
 2500 82nd Place Urbandale, Ia Treatment of Depression: A Brief History 1960 s to Present Community Based Services SSRI Antidepressants SNRI Antidepressants 1970 s to present 20% of patients do not respond
2500 82nd Place Urbandale, Ia Treatment of Depression: A Brief History 1960 s to Present Community Based Services SSRI Antidepressants SNRI Antidepressants 1970 s to present 20% of patients do not respond
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600
 Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600 Your responsibility This guidance represents
Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600 Your responsibility This guidance represents
DEEP TMS TREATMENT CONSENT FORM
 DEEP TMS TREATMENT CONSENT FORM My doctor has recommended that I receive treatment with Brainsway Deep TMS. The nature of this treatment, including the benefits and risks that I may experience, has been
DEEP TMS TREATMENT CONSENT FORM My doctor has recommended that I receive treatment with Brainsway Deep TMS. The nature of this treatment, including the benefits and risks that I may experience, has been
Case 2:15-cv MWF-JPR Document Filed 03/20/17 Page 1 of 36 Page ID #:388 EXHIBIT 1
 Case 2:15-cv-07074-MWF-JPR Document 65-10 Filed 03/20/17 Page 1 of 36 Page ID #:388 EXHIBIT 1 Case 2:15-cv-07074-MWF-JPR Document 65-10 Filed 03/20/17 Page 2 of 36 Page ID #:389 Cigna Medical Coverage
Case 2:15-cv-07074-MWF-JPR Document 65-10 Filed 03/20/17 Page 1 of 36 Page ID #:388 EXHIBIT 1 Case 2:15-cv-07074-MWF-JPR Document 65-10 Filed 03/20/17 Page 2 of 36 Page ID #:389 Cigna Medical Coverage
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Depression
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Depression Paul E. Holtzheimer, MD Associate Professor Departments of Psychiatry and Surgery Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Dartmouth-Hitchcock
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Depression Paul E. Holtzheimer, MD Associate Professor Departments of Psychiatry and Surgery Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Dartmouth-Hitchcock
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
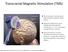 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) The treatment coil produces MRI-strength magnetic field pulses. Magnetic field pulses pass unimpeded through the cranium for 2-3 cm. and induce a small electric
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) The treatment coil produces MRI-strength magnetic field pulses. Magnetic field pulses pass unimpeded through the cranium for 2-3 cm. and induce a small electric
Post-Stroke Depression
 Research Reviews Post-Stroke Depression John Kevin Keeley, LCSW August 8, 2018 Towfighi, A. MD, Ovbiagele, B. MD et al Poststroke Depression. A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the
Research Reviews Post-Stroke Depression John Kevin Keeley, LCSW August 8, 2018 Towfighi, A. MD, Ovbiagele, B. MD et al Poststroke Depression. A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy
 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583
 Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Remission From Depression Is Possible
 Remission From Depression Is Possible About Depression Over 350 million people worldwide suffer from depression 1 While medications may help manage symptoms of depression, many patients are not satisfied
Remission From Depression Is Possible About Depression Over 350 million people worldwide suffer from depression 1 While medications may help manage symptoms of depression, many patients are not satisfied
Uterine artery embolisation for treating adenomyosis
 Uterine artery embolisation for treating Issued: December 2013 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional procedures
Uterine artery embolisation for treating Issued: December 2013 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional procedures
Frequently Asked Questions FAQS. NeuroStar TMS Therapies
 Frequently Asked Questions FAQS NeuroStar TMS Therapies Provided by Dr Terrence A. Boyadjis MD 790 E Market Street Suite 245 West Chester, PA 19382 610.738.9576 FAQS About TMS Therapies Page 1 NeuroStar
Frequently Asked Questions FAQS NeuroStar TMS Therapies Provided by Dr Terrence A. Boyadjis MD 790 E Market Street Suite 245 West Chester, PA 19382 610.738.9576 FAQS About TMS Therapies Page 1 NeuroStar
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation:
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: What has experience told us? Jonathan Downar MD PhD FRCPC MRI-Guided rtms Clinic University Health Network www.rtmsclinic.ca Disclosures Research funding: Canadian Institutes
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: What has experience told us? Jonathan Downar MD PhD FRCPC MRI-Guided rtms Clinic University Health Network www.rtmsclinic.ca Disclosures Research funding: Canadian Institutes
Administration of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms)
 Professional Practice Guideline 16 Administration of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms) November 2018 Authorising Body: Responsible Committee/Department: Responsible Department: Document
Professional Practice Guideline 16 Administration of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rtms) November 2018 Authorising Body: Responsible Committee/Department: Responsible Department: Document
Depressive and Bipolar Disorders
 Depressive and Bipolar Disorders Symptoms Associated with Depressive and Bipolar Disorders Characteristics of mood symptoms Affects a person s well being, school, work, or social functioning Continues
Depressive and Bipolar Disorders Symptoms Associated with Depressive and Bipolar Disorders Characteristics of mood symptoms Affects a person s well being, school, work, or social functioning Continues
Biological treatments: Electroconvulsive Therapy, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Light therapy
 Biological treatments: Electroconvulsive Therapy, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Light therapy Basic trainee talk 23 May 2007 ECT When is ECT used. Depression. Severe, melancholic. Resistant to treatment.
Biological treatments: Electroconvulsive Therapy, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Light therapy Basic trainee talk 23 May 2007 ECT When is ECT used. Depression. Severe, melancholic. Resistant to treatment.
Information for patients, families and caregivers
 Depression Information for patients, families and caregivers Read this booklet to learn: what depression is what causes it the signs or symptoms of depression what treatments can help Please visit the
Depression Information for patients, families and caregivers Read this booklet to learn: what depression is what causes it the signs or symptoms of depression what treatments can help Please visit the
Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine prolapse repair
 Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine Issued: January 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg280 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Infracoccygeal sacropexy using mesh for uterine Issued: January 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg280 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Patient Information Leaflet
 Further information about the content, reference sources or production of this leaflet can be obtained from the Patient Information Centre. This information can be made available in a range of formats
Further information about the content, reference sources or production of this leaflet can be obtained from the Patient Information Centre. This information can be made available in a range of formats
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Date of Origin: 7/24/2018 Last Review Date: 7/24/2018 Effective Date: 08/01/18 Dates Reviewed: 7/24/2018 Developed By: Medical Necessity Criteria Committee I. Description
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Date of Origin: 7/24/2018 Last Review Date: 7/24/2018 Effective Date: 08/01/18 Dates Reviewed: 7/24/2018 Developed By: Medical Necessity Criteria Committee I. Description
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
 Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Seasonal affective disorder (SAD), also known as winter depression, winter blues, summer depression, summer blues, or seasonal depression, is considered a mood disorder
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Seasonal affective disorder (SAD), also known as winter depression, winter blues, summer depression, summer blues, or seasonal depression, is considered a mood disorder
Are you not responding to antidepressants?
 PATIENTS & RELATIVES Are you not responding to antidepressants? TMS therapy might be the solution for you. Does not affect cognitive function No anesthesia Covered by most private providers Outpatient
PATIENTS & RELATIVES Are you not responding to antidepressants? TMS therapy might be the solution for you. Does not affect cognitive function No anesthesia Covered by most private providers Outpatient
BRAINSWAY DEEP TMS SYSTEM
 510(K) SUMMARY JAN 0 72013 BRAINSWAY DEEP TMS SYSTEM Applicant Name: Company Name: Address: 510(k) Number K122288 Brainsway Ltd. 19 Hartumn St. (Bynet Bldg) Har Hotzvim, Jerusalem, ISRAEL 91451 Tel: +972-2-5813
510(K) SUMMARY JAN 0 72013 BRAINSWAY DEEP TMS SYSTEM Applicant Name: Company Name: Address: 510(k) Number K122288 Brainsway Ltd. 19 Hartumn St. (Bynet Bldg) Har Hotzvim, Jerusalem, ISRAEL 91451 Tel: +972-2-5813
Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s NICE quality standard
 March 2017 Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s NICE quality standard Draft for consultation This quality standard covers the assessment and management of non-specific low back pain and sciatica in young
March 2017 Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s NICE quality standard Draft for consultation This quality standard covers the assessment and management of non-specific low back pain and sciatica in young
Your journal: how can it help you?
 Journal Your journal: how can it help you? By monitoring your mood along with other symptoms like sleep, you and your treatment team will be better able to follow the evolution of your symptoms and therefore
Journal Your journal: how can it help you? By monitoring your mood along with other symptoms like sleep, you and your treatment team will be better able to follow the evolution of your symptoms and therefore
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation as a for Treatment of Refractory Depression and other Psychiatric/Neurologic Disorders
 Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation as a for Treatment of Refractory Depression and other Psychiatric/Neurologic Disorders Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.12.015 08/01/2014 Line(s)
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation as a for Treatment of Refractory Depression and other Psychiatric/Neurologic Disorders Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.12.015 08/01/2014 Line(s)
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Patient Information Leaflet
 Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Patient Information Leaflet Contents Page Introduction 3 What is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)? 3 Why has ECT been recommended? 3 What will happen if I have ECT? 3-4 How
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Patient Information Leaflet Contents Page Introduction 3 What is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)? 3 Why has ECT been recommended? 3 What will happen if I have ECT? 3-4 How
Depression. Content. Depression is common. Depression Facts. Depression kills. Depression attacks young people
 Content Depression Dr. Anna Lam Associate Consultant Department of Psychiatry, Queen Mary Hospital Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong 1.
Content Depression Dr. Anna Lam Associate Consultant Department of Psychiatry, Queen Mary Hospital Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong 1.
Review Paper. Introduction
 Review Paper Unilateral and bilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials over decades Shayan Sehatzadeh, MD,
Review Paper Unilateral and bilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials over decades Shayan Sehatzadeh, MD,
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Patient Information Leaflet
 Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Patient Information Leaflet 2 Contents Page Introduction 3 What is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)? 3 Why has ECT been recommended? 3 What will happen if I have ECT? 3-4
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Patient Information Leaflet 2 Contents Page Introduction 3 What is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)? 3 Why has ECT been recommended? 3 What will happen if I have ECT? 3-4
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Page 1 of 24 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See also: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Vagus Nerve
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Page 1 of 24 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See also: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Vagus Nerve
5 Diagnosis. Timely diagnosis. Back to contents
 5 5 Diagnosis Back to contents Study Advisory Group questions: Are there delays in diagnosis? Is there variation in how the cerebral palsies are described? signs can fluctuate, to avoid over-diagnosis
5 5 Diagnosis Back to contents Study Advisory Group questions: Are there delays in diagnosis? Is there variation in how the cerebral palsies are described? signs can fluctuate, to avoid over-diagnosis
Interventions for Relapsing Depression: TMS, ECT, and Ketamine
 Interventions for Relapsing Depression: TMS, ECT, and Ketamine MDD top cause of disability; suicide only top-10 cause of death currently increasing. 10-15% lifetime prevalence A third of patients do not
Interventions for Relapsing Depression: TMS, ECT, and Ketamine MDD top cause of disability; suicide only top-10 cause of death currently increasing. 10-15% lifetime prevalence A third of patients do not
Interventions for Relapsing Depression: TMS, ECT, and Ketamine
 Interventions for Relapsing Depression: TMS, ECT, and Ketamine MDD top cause of disability; suicide only top-10 cause of death currently increasing. 10-15% lifetime prevalence A third of patients do not
Interventions for Relapsing Depression: TMS, ECT, and Ketamine MDD top cause of disability; suicide only top-10 cause of death currently increasing. 10-15% lifetime prevalence A third of patients do not
AN OVERVIEW OF ANXIETY
 AN OVERVIEW OF ANXIETY Fear and anxiety are a normal part of life. Normal anxiety keeps us alert. Intervention is required when fear and anxiety becomes overwhelming intruding on a persons quality of life.
AN OVERVIEW OF ANXIETY Fear and anxiety are a normal part of life. Normal anxiety keeps us alert. Intervention is required when fear and anxiety becomes overwhelming intruding on a persons quality of life.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Cranial Electrical Stimulation (CES) as a Treatment of Depression and Other Psychiatric/Neurologic Disorders
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Cranial Electrical Stimulation (CES) as a Treatment of Depression and Other Psychiatric/Neurologic Disorders Policy Number: 2.01.50 Last Review: 10/2017 Origination:
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Cranial Electrical Stimulation (CES) as a Treatment of Depression and Other Psychiatric/Neurologic Disorders Policy Number: 2.01.50 Last Review: 10/2017 Origination:
Family Medicine Forum November 10, 2017 Montreal., Quebec. Jon Davine, CCFP, FRCP(C) Associate Professor, McMaster University
 APPROACH TO DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE Family Medicine Forum November 10, 2017 Montreal., Quebec. Jon Davine, CCFP, FRCP(C) Associate Professor, McMaster University DISCLOSURE Speaker/Presenter Disclosure
APPROACH TO DEPRESSION IN PRIMARY CARE Family Medicine Forum November 10, 2017 Montreal., Quebec. Jon Davine, CCFP, FRCP(C) Associate Professor, McMaster University DISCLOSURE Speaker/Presenter Disclosure
Ixekizumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID904]
![Ixekizumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID904] Ixekizumab for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [ID904]](/thumbs/86/94899473.jpg) Thank you for agreeing to make a submission on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can provide a unique perspective on the technology
Thank you for agreeing to make a submission on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can provide a unique perspective on the technology
The use of electroconvulsive therapy
 NHS National Institute for Clinical Excellence The use of electroconvulsive therapy Understanding NICE guidance information for service users, their advocates and carers, and the public April 2003 The
NHS National Institute for Clinical Excellence The use of electroconvulsive therapy Understanding NICE guidance information for service users, their advocates and carers, and the public April 2003 The
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 24 July 2013 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta292
 Aripiprazole for treating moderate to severe ere manic episodes in adolescents with bipolar I disorder Technology appraisal guidance Published: 24 July 2013 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta292 NICE 2018. All rights
Aripiprazole for treating moderate to severe ere manic episodes in adolescents with bipolar I disorder Technology appraisal guidance Published: 24 July 2013 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta292 NICE 2018. All rights
The Next Chapter in Brain Stimulation Therapy
 The Next Chapter in Brain Stimulation Therapy Outline I. Depression and Treatment Resistant Depression Barriers to Treatment Treatment Options Cost and Impact of Depression II. Electroconvulsive Therapy
The Next Chapter in Brain Stimulation Therapy Outline I. Depression and Treatment Resistant Depression Barriers to Treatment Treatment Options Cost and Impact of Depression II. Electroconvulsive Therapy
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Scientific evidence in major depression and schizophrenia C.W. Slotema Parnassia Bavo Group The Hague, the Netherlands Faraday s law (1831) Electrical current magnetic
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Scientific evidence in major depression and schizophrenia C.W. Slotema Parnassia Bavo Group The Hague, the Netherlands Faraday s law (1831) Electrical current magnetic
DEPRESSION. Men and women of all ages, races, and economic levels can have depression. It occurs more often in women.
 DEPRESSION The exact cause of depression is not known. Many researchers believe it is caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, which may be hereditary or caused by events in a person's life. Some types
DEPRESSION The exact cause of depression is not known. Many researchers believe it is caused by chemical imbalances in the brain, which may be hereditary or caused by events in a person's life. Some types
Medical technologies guidance Published: 23 January 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg41
 Senza spinal cord stimulation system for delivering ering HF10 therapy to treat chronic neuropathic pain Medical technologies guidance Published: 23 January 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg41 NICE 2019. All
Senza spinal cord stimulation system for delivering ering HF10 therapy to treat chronic neuropathic pain Medical technologies guidance Published: 23 January 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg41 NICE 2019. All
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rtms)
 Page 1 of 33 Medical Policies - Mental Health Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rtms) Print Number: PSY301.015 Effective Date: 07-01-2014 Coverage: Initial rtms Treatment Repetitive transcranial
Page 1 of 33 Medical Policies - Mental Health Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rtms) Print Number: PSY301.015 Effective Date: 07-01-2014 Coverage: Initial rtms Treatment Repetitive transcranial
Bright Nights: Understanding Depression
 Bright Nights: Understanding Depression KEVIN SETHI, MD MARCH 18 TH, 2019 Objectives Features of Depression Facts and Myths Treatment Options Medications Neuromodulation Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Mindfulness
Bright Nights: Understanding Depression KEVIN SETHI, MD MARCH 18 TH, 2019 Objectives Features of Depression Facts and Myths Treatment Options Medications Neuromodulation Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Mindfulness
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Page 1 of 21 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See also: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Vagus Nerve
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Page 1 of 21 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See also: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Vagus Nerve
HCT Medical Policy. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) for Major Depression Policy # 121 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016.
 HCT Medical Policy Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) for Major Depression Policy # 121 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan
HCT Medical Policy Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) for Major Depression Policy # 121 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan
Depression: Assessment and Treatment For Older Adults
 Tool on Depression: Assessment and Treatment For Older Adults Based on: National Guidelines for Seniors Mental Health: the Assessment and Treatment of Depression Available on line: www.ccsmh.ca www.nicenet.ca
Tool on Depression: Assessment and Treatment For Older Adults Based on: National Guidelines for Seniors Mental Health: the Assessment and Treatment of Depression Available on line: www.ccsmh.ca www.nicenet.ca
Prosthetic intervertebral disc replacement in the cervical spine: Cost-effectiveness compared with cervical discectomy with or without vertebral
 Prosthetic intervertebral disc replacement in the cervical spine: Cost-effectiveness compared with cervical discectomy with or without vertebral fusion Author: William Horsley NHS North East Treatment
Prosthetic intervertebral disc replacement in the cervical spine: Cost-effectiveness compared with cervical discectomy with or without vertebral fusion Author: William Horsley NHS North East Treatment
Medical technologies guidance Published: 2 October 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg39
 ifuse for treating chronic sacroiliac joint pain Medical technologies guidance Published: 2 October 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg39 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
ifuse for treating chronic sacroiliac joint pain Medical technologies guidance Published: 2 October 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg39 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
BRAIN STIMULATION AN ALTERNATIVE TO DRUG THERAPY IN MATERNAL DEPRESSION?
 BRAIN STIMULATION AN ALTERNATIVE TO DRUG THERAPY IN MATERNAL DEPRESSION? Kira Stein, MD Medical Director West Coast Life Center Sherman Oaks, California CA Maternal Mental Health Initiative - 2013 2013
BRAIN STIMULATION AN ALTERNATIVE TO DRUG THERAPY IN MATERNAL DEPRESSION? Kira Stein, MD Medical Director West Coast Life Center Sherman Oaks, California CA Maternal Mental Health Initiative - 2013 2013
The Evidence Base for rtms Reimbursement
 The Evidence Base for rtms Reimbursement Bradley N. Gaynes, MD, MPH Professor of Psychiatry Associate Chair of Research Training and Education Institute of Medicine Workshop March 3, 2015 What do we know,
The Evidence Base for rtms Reimbursement Bradley N. Gaynes, MD, MPH Professor of Psychiatry Associate Chair of Research Training and Education Institute of Medicine Workshop March 3, 2015 What do we know,
A70.4 Insertion of neurostimulator electrodes into peripheral nerve Z12.2 Posterior tibial nerve R15.X Faecal incontinence
 The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 28 March 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta516
 Cabozantinib for treating medullary thyroid cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 28 March 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta516 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Cabozantinib for treating medullary thyroid cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 28 March 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta516 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Major Depression Major Depression
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Major Depression Major Depression Characterized by a change in several aspects of a person s life and emotional state
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Major Depression Major Depression Characterized by a change in several aspects of a person s life and emotional state
The treatment of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents
 DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION The treatment of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents The paragraphs in the draft are numbered for the purposes of consultation. The final version will not contain
DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION The treatment of bipolar disorder in adults, children and adolescents The paragraphs in the draft are numbered for the purposes of consultation. The final version will not contain
Nonpharmacologic Interventions for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Public Meeting December 9, 2011
 Nonpharmacologic Interventions for Treatment-Resistant Depression Public Meeting December 9, 2011 New England CEPAC Goal: To improve the application of evidence to guide practice and policy in New England
Nonpharmacologic Interventions for Treatment-Resistant Depression Public Meeting December 9, 2011 New England CEPAC Goal: To improve the application of evidence to guide practice and policy in New England
GREATER MANCHESTER INTERFACE PRESCRIBING GROUP
 GREATER MANCHESTER INTERFACE PRESCRIBING GROUP On behalf of the GREATER MANCHESTER MEDICINES MANAGEMENT GROUP SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF SELECTIVE SEROTONIN REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SSRIs)
GREATER MANCHESTER INTERFACE PRESCRIBING GROUP On behalf of the GREATER MANCHESTER MEDICINES MANAGEMENT GROUP SHARED CARE GUIDELINE FOR THE PRESCRIBING OF SELECTIVE SEROTONIN REUPTAKE INHIBITORS (SSRIs)
Jonathan Haverkampf BIPOLAR DISORDR BIPOLAR DISORDER. Dr. Jonathan Haverkampf, M.D.
 BIPOLAR DISORDER Dr., M.D. Abstract - Bipolar disorder is a condition affecting an individual s affective states (mood). The different flavors of bipolar disorder have in common that there are alterations
BIPOLAR DISORDER Dr., M.D. Abstract - Bipolar disorder is a condition affecting an individual s affective states (mood). The different flavors of bipolar disorder have in common that there are alterations
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia
 Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
Condensed Clinical Practice Guideline Treatment Of Patients With Schizophrenia I. Key Points a. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness affecting all aspects of person s life i. Treatment Planning Goals 1.
ª The Author(s) The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry / La Revue Canadienne de Psychiatrie 1-15
 Canadian Psychiatric Association Association des psychiatres du Canada Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) 2016 Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Major Depressive
Canadian Psychiatric Association Association des psychiatres du Canada Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) 2016 Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Major Depressive
Aiming for recovery for patients with severe or persistent depression a view from secondary care. Chrisvan Koen
 Aiming for recovery for patients with severe or persistent depression a view from secondary care Chrisvan Koen Kent and Medway NHS and Social care Partnership trust Persistent depressive disorder F34 Persistent
Aiming for recovery for patients with severe or persistent depression a view from secondary care Chrisvan Koen Kent and Medway NHS and Social care Partnership trust Persistent depressive disorder F34 Persistent
Primary Care Tool for Assessment of Depression during Pregnancy and Postpartum
 HRSA-UIC Assessment of Depression Perinatal during Pregnancy Project: and Postpartum Primary Care Tool for Assessment of Depression during Pregnancy and Postpartum te to health care provider: This tool
HRSA-UIC Assessment of Depression Perinatal during Pregnancy Project: and Postpartum Primary Care Tool for Assessment of Depression during Pregnancy and Postpartum te to health care provider: This tool
(U) USSOCOM. (U) Magnetic qeeg guided Resonance Therapy (MeRT)
 United States Special Operations Command (U) USSOCOM MeRT Clinical Trial for Treatment of TBI COL Mark Baggett, Ph.D., US Army USSOCOM Command Psychologist Date: 14 Feb 2018 1 (U) Magnetic qeeg guided
United States Special Operations Command (U) USSOCOM MeRT Clinical Trial for Treatment of TBI COL Mark Baggett, Ph.D., US Army USSOCOM Command Psychologist Date: 14 Feb 2018 1 (U) Magnetic qeeg guided
Functional Assessment of Depression and Anxiety Disorders Relevant to Work Requirements
 Functional Assessment of Depression and Anxiety Disorders Relevant to Work Requirements Paul S. Appelbaum, MD Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine & Law Columbia University Overview Depression and
Functional Assessment of Depression and Anxiety Disorders Relevant to Work Requirements Paul S. Appelbaum, MD Dollard Professor of Psychiatry, Medicine & Law Columbia University Overview Depression and
Geriatric Depression; Not a Normal Part of Growing Older. Cherie Warriner, LCSW
 1 Geriatric Depression; Not a Normal Part of Growing Older Cherie Warriner, LCSW What is Depression? While it is normal to feel sad or blue on occasion, these feelings are often transient. Depression is
1 Geriatric Depression; Not a Normal Part of Growing Older Cherie Warriner, LCSW What is Depression? While it is normal to feel sad or blue on occasion, these feelings are often transient. Depression is
Depression in adults: treatment and management
 Depression in adults: treatment and management NICE guideline: short version Draft for consultation, July 0 This guideline covers identifying, treating and managing depression in people aged and over.
Depression in adults: treatment and management NICE guideline: short version Draft for consultation, July 0 This guideline covers identifying, treating and managing depression in people aged and over.
Introduction to TMS Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
 Introduction to TMS Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Lisa Koski, PhD, Clin Psy TMS Neurorehabilitation Lab Royal Victoria Hospital 2009-12-14 BIC Seminar, MNI Overview History, basic principles, instrumentation
Introduction to TMS Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Lisa Koski, PhD, Clin Psy TMS Neurorehabilitation Lab Royal Victoria Hospital 2009-12-14 BIC Seminar, MNI Overview History, basic principles, instrumentation
Delirium. Quick reference guide. Issue date: July Diagnosis, prevention and management
 Issue date: July 2010 Delirium Diagnosis, prevention and management Developed by the National Clinical Guideline Centre for Acute and Chronic Conditions About this booklet This is a quick reference guide
Issue date: July 2010 Delirium Diagnosis, prevention and management Developed by the National Clinical Guideline Centre for Acute and Chronic Conditions About this booklet This is a quick reference guide
Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis
 Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis Issued: August 2007 www.nice.org.uk/ipg230 Copyright NICE 2007 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 The procedure... 4
Arthroscopic knee washout, with or without debridement, for the treatment of osteoarthritis Issued: August 2007 www.nice.org.uk/ipg230 Copyright NICE 2007 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 The procedure... 4
