Schizophrenia. Introduction. Overview and Facts
|
|
|
- Merryl Cunningham
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It is characterized by fundamental distortions in thinking and perception, and by inappropriate emotions. The disturbance in volves many of the most basic functions that give the normal person a feeling of individuality, self-direction, and independence in functioning. The first signs of often appear as confusing or even shocking changes in behavior. The onset of can either be sudden, with severe psychotic symptoms such as delusions and hallucina tions, or progressive, that is less obvious, with symptoms such as social withdrawal or isolation, unusual speech, thinking or behavior that may precede the psychotic symptoms. Overview and Facts occurs in as much as 1% of all adults, with onset typically in late adolescence or early adult hood. It is uncommon in pre-pubertal children and it is hard to recognize in its early phases in this age group. The behavior of children and early adolescents with may differ from that of adults with this illness. Children and adolescents may for example, have trouble telling dreams from reality, confusing televi sion with reality, seeing things and hearing voices which are not real. They may also have confused thinking, vivid and bizarre thoughts and ideas, as well as paranoid thoughts like people are out to get them. They might suffer from severe anxiety and fearfulness, resulting in a severe problem making and keeping friends. Children who used to normally enjoy relationships with others may start to become more shy or withdrawn and seem to be in their own world. They may also start to cling to their parents. People with may attempt suicide at some time during the course of their illness. Studies show that 30% of patients diagnosed with this disorder had attempted suicide at least once during their lifetime. About 10% of persons with die through suicide. In the 1990 s, a major international study was undertaken by the World Bank, the World Health Organiza tion (WHO), and the Harvard School of Public Health, called the Global Burden of Disease (GBD). GBD measured how diseases affect people s capacity to function by calculating the years lost to disability or pre mature death due to a certain illnesses. This unit of measurement of the burden of disease is called a DALY (Disability Adjusted Life Years). The Global Burden of Disease analysis showed that places an enormous burden on societies everywhere in the world, and is ranked as the eighth leading cause of burden among all diseases for the population between 15 and 44 years of age. was also reported to be the seventh leading cause of the years of life lived with disability (YLD s) in the year 2000 for all age groups. For the population between 15 and 44 years of age, was reported to be the third leading cause of YLD s. It exceeds HIV/AIDS and pulmonary diseases in the amount of disability associated with it.
3 Symptoms The types of symptoms present in are generally divided into 3 categories: positive, negative, and disorganized symptoms. Positive symptoms (symptoms added to the personality) include: - Delusions are false personal beliefs that are not subject to reason or contradictory evidence and are not explained by one s usual cultural concepts. They may have different themes. For example, delusions of persecution are false and irrational beliefs that the person is being cheated, harassed, poisoned or conspired against. Some other delusions are quite bizarre, for instance that a neighbor is controlling their behavior and/or their thoughts with magnetic waves, that people on television are directing messages to them, or that their thoughts are being broadcast aloud to others. - Hallucinations are disturbances of perception that are common in people suffering from. They can occur in any sensory form: auditory (sound), visual (sight), tactile (touch), gustatory (taste), or olfactory (smell). Auditory hallucinations (hearing voices that other people do not hear) are the most common type of hallucinations in. Voices may describe the person s activities, carry on a conversation, warn of dangers, or even issue orders to the individual. Negative symptoms (symptoms lost from the personality ) include: - Emotional flatness or lack of expression, - Speech that is brief and lacking content, - Lack of interest in life and an inability to follow through with activities. - Low motivation for work, as well as for interest or enjoyment of life. Disorganized symptoms refer to: - Cognitive deficits that might lead to a certain disorganized behavior. For example, the person may not be able to concentrate on one thought or on one simple task for very long and may be easily distracted. - Difficulties connecting thoughts into logical sequences occur, thus thoughts become disorganized and fragmented. This lack of logical continuity of thoughts, called thought disorder, can make conversation very difficult and may contribute to further social isolation. Also, people with schizophrenia might have Disorders of Movement. People with schizophrenia can be clumsy and uncoordinated. They may also exhibit involuntary movements and may grimace or exhibit unusual mannerisms. They may repeat certain motions over and over or, in extreme cases, may become catatonic. Catatonia is a state of immobility and unresponsiveness. It was more common when treatment for schizophrenia was not available; fortunately, it is now rare. Causes and Risk Factors Experts do not know what causes schizophrenia. It may have different causes for different people. In some people, brain chemistry (involving the neurotransmitters dopamine and glutamate) and brain structure aren't normal. For example, the brains of schizophrenics
4 appear to have less gray matter, and some areas of the brain may have less or more activity. This can be due to problems in brain development before birth. The reason behind schizophrenia showing after puberty is due to the fact that the brain undergoes major changes during puberty, and these changes could trigger psychotic symptoms. Family history plays a role, in fact schizophrenia occurs in 10% of people who have a firstdegree relative with the disorder, (parent, brother, or sister). People who have second-degree relatives (aunts, uncles, grandparents, or cousins) with schizophrenia also develop the disorder more often than the general population. The risk is highest for an identical twin of a person with schizophrenia. He or she has a 40 to 65 % chance of developing the disorder. Scientists also found that some genes and genetic mutations are associated with an increased risk of schizophrenia. Genes are not sufficient to develop schizophrenia as environmental factors play a role such as exposure to viruses and malnutrition that harm a baby's brain during pregnancy. Tests and Diagnosis To diagnose schizophrenia, a person should consult a mental health professional who rely on scientific criteria to check whether he/she has the disorder. The doctor will examine you and ask about your symptoms. At least one of the symptoms must be delusions, hallucinations or disorganized speech. He or she may ask other questions to see how you are doing emotionally. This is called a mental health assessment. The doctor may also do blood or urine tests to rule out other conditions, that can cause similar symptoms such as substance abuse, medications or a medical condition. The doctor may also request imaging studies, such as an MRI or CT scan. Tests and Diagnosis Well-established and effective treatment procedures for are available. With treatment, there can be complete symptomatic and social recovery in many cases. On the other hand, could follow a chronic or recurrent course, with residual symptoms and incomplete social recovery. Residual symptoms include lack of interest and initiative in daily activities and work, social incompetence, and inability to take interest in pleasurable activities. During times of severe symptoms, hospitalization may be required. requires lifelong treatment, even when symptoms have stopped. Treatment is composed of medications and psychotherapy: 1- Medications Medications are very important for schizophrenia treatment. However, medications for schizophrenia can cause side effects which make some people hesitant to take them. a. Antipsychotic medications are mostly used to control symptoms by affecting the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin. In general, antipsychotic medications are used to control signs and symptoms at the lowest possible dosage. The psychiatrist may try different medications, dosages or combinations over time to achieve the best result. i. Atypical antipsychotics: these are second-generation medications and have a lower risk of side effects than conventional medications. They include:
5 Aripiprazole Asenapine Clozapine Iloperidone Lurasidone Olanzapine Paliperidone Quetiapine Risperidone ii. Ziprasidone Conventional, or typical antipsychotics: these first-generation medications have frequent side effects, including the possibility of developing a movement disorder (tardive dyskinesia) that may or may not be reversible. These medications are cheaper than the second generation, this is why they are considered for long term treatment. This group of medications includes: Chlorpromazine Fluphenazine Haloperidol Perphenazine It is important to know that it can take several weeks after starting a medication to notice an improvement in symptoms. b. Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications can be used as well in some cases. 2- Psychotherapy Psychotherapy helps the person to cope with stress and identify signs of relapse. Family therapy is also a way to help families support their relatives who are dealing with schizophrenia. A lot of people also benefit from social skills training which focuses on improving communication and social interactions. Sources and Links
The National Institute of Mental Health:
 The National Institute of Mental Health: http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia/index.shtml Schizophrenia What Is Schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain disorder
The National Institute of Mental Health: http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia/index.shtml Schizophrenia What Is Schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain disorder
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Psychotic Disorders. There is a loss of contact with and difficulty in recognizing reality.
 Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
Schizophrenia: an inside view. Nepean High School, November 2016 Introduction to Psychology class.
 Schizophrenia: an inside view Nepean High School, November 2016 Introduction to Psychology class. Schizophrenia: basic definition Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how
Schizophrenia: an inside view Nepean High School, November 2016 Introduction to Psychology class. Schizophrenia: basic definition Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
Who has Schizophrenia? What is Schizophrenia? 11/20/2013. Module 33. It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders!
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man walks the streets of New York with aluminum foil under
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness
 Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS
 1 SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS OBJECTIVES 2 Know and understand: How to evaluate a person with psychotic symptoms The epidemiology and clinical characteristics of lateonset schizophrenia
1 SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS OBJECTIVES 2 Know and understand: How to evaluate a person with psychotic symptoms The epidemiology and clinical characteristics of lateonset schizophrenia
Schizophrenia. Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior.
 Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia. This factsheet covers -
 Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
The cancer of mental illness
 The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications
 Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
Crisis Management. Crisis Management Goals. Emotionally Disturbed Persons 10/29/2009
 Crisis Management Crisis Management Goals try to ensure safety for yourself, other officers, subjects, and other citizens establish and maintain control resolve the situation positively when appropriate,
Crisis Management Crisis Management Goals try to ensure safety for yourself, other officers, subjects, and other citizens establish and maintain control resolve the situation positively when appropriate,
CHAPTER 3. Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment
 CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 What symptoms would you expect this person to display? It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! 1 Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man
What is Schizophrenia? Module 33 What symptoms would you expect this person to display? It is also one of the most misunderstood of all psychological disorders! 1 Who has Schizophrenia? A middle-aged man
Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Age Distribution of Onset 2/24/2009. Schizophrenia. Hallmark trait is psychosis
 Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide MENTAL HEALTH
 The following Evidence Base Guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: MCG Behavioral Health Guidelines and National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). Documented Health Conditions: Depression
The following Evidence Base Guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: MCG Behavioral Health Guidelines and National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). Documented Health Conditions: Depression
Abnormal Psychology Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS Introduction Schizophrenia and delusional disorder are distinct disorders that may share certain features, such as paranoia, suspiciousness, and unrealistic thinking.
SCHIZOPHRENIA AND DELUSIONAL DISORDERS Introduction Schizophrenia and delusional disorder are distinct disorders that may share certain features, such as paranoia, suspiciousness, and unrealistic thinking.
Biological Psych Schizophrenia
 Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
Biological Psych Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Slightly more common in men Earlier onset, more severe Originally: dementia
9/3/2014. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Autism. Childhood Autism and Schizophrenia. Autism, Part 1 Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-IV-TR) Behavioral Characteristics of Autism
 Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
3/9/2017. A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course. Our purpose
 A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com
 Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis
 Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects
 Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects a person s thoughts, feelings and behaviours. Whilst it is serious, schizophrenia is both treatable and manageable, and we
25 Things To Know. disorders
 Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
Biological Psych 25 Things To Know Schizo phrenia disorders Schizophrenia Psychotic disorders The Schizophrenias 1% incidence More likely in US & Europe 10 to 100 times Schizophrenia Demographic Data Slightly
The alternate reality of schizophrenia
 The alternate reality of schizophrenia MICHAEL TRINSEY SCHIZOPHRENIA IS A GROUP of chronic, disabling psychiatric disorders characterized by disturbed thinking and disorganized speech. Patients with schizophrenia
The alternate reality of schizophrenia MICHAEL TRINSEY SCHIZOPHRENIA IS A GROUP of chronic, disabling psychiatric disorders characterized by disturbed thinking and disorganized speech. Patients with schizophrenia
CE-CREDIT.com "Your Continuing Education Resource"
 Schizophrenia DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICE NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The Schizophrenia Bulletin features art done by current and former mental hospital patients. The
Schizophrenia DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICE NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH The Schizophrenia Bulletin features art done by current and former mental hospital patients. The
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception
 Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders
 and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Roseanna Parkhurst-Gatewood MSN FNP-BC, PMHNP-BC DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder 3 A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive
Roseanna Parkhurst-Gatewood MSN FNP-BC, PMHNP-BC DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for schizoaffective disorder 3 A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (major depressive
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental illness with a number of symptoms, including confused or unclear thinking and speech,
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental illness with a number of symptoms, including confused or unclear thinking and speech,
Schizophrenia. This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available.
 This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
This factsheet provides a basic description of schizophrenia, its symptoms and the treatments and support options available. What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a severe mental health condition. However,
SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Psychiatry 2 Practical # 2
 Psychiatrická klinika LFUK a UNB, Bratislava SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Psychiatry 2 Practical # 2 Author: MUDr. Ľubomíra Izáková, PhD. Supervisor: doc. MUDr. Ján Pečeňák, CSc. Podporené grantom
Psychiatrická klinika LFUK a UNB, Bratislava SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM DISORDERS Psychiatry 2 Practical # 2 Author: MUDr. Ľubomíra Izáková, PhD. Supervisor: doc. MUDr. Ján Pečeňák, CSc. Podporené grantom
Schizophrenia. Positive Symptoms. Course of Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
 Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Antidepressants. Dr Malek Zihlif
 Antidepressants The optimal use of antidepressant required a clear understanding of their mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, potential drug interaction and the deferential diagnosis of psychiatric
Antidepressants The optimal use of antidepressant required a clear understanding of their mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, potential drug interaction and the deferential diagnosis of psychiatric
SCHIZOPHRENIA. What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3. By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin
 Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
Schizophrenia. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 11/30/2008. Name that Psychotic Disorder! Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Name that Psychotic Disorder! Chris has started spending large amounts of time guarding his home. They have bugged his phone and are sending cars past
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents
 Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
SCHIZOPHRENIA IS COGNITION IMPAIRED IN SCHIZOPHRENIA?
 CHAPTER 10: DISTURBED COGNITION IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Traditionally, functioning of the mind is described under four headings: perception, emotion, cognition, and conation. Perception refers to awareness of
CHAPTER 10: DISTURBED COGNITION IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Traditionally, functioning of the mind is described under four headings: perception, emotion, cognition, and conation. Perception refers to awareness of
Schizoaffective Disorder
 Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Schizoaffective Disorder combination of schizophrenia symptoms (hallucinations or delusions) and mood disorder symptoms (such as mania or depression.) Controversial Requires presence of delusions for 2
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network
 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart
VI.2 Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Incidence and prevalence of target indication Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a breakdown of thought processes
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Incidence and prevalence of target indication Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a breakdown of thought processes
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 5. Schizophrenia Schizophrenia- a group of severe psychotic disorders characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotion, & behavior Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 5. Schizophrenia Schizophrenia- a group of severe psychotic disorders characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotion, & behavior Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia
A-Z of Mental Health Problems
 Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA
 Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS
 MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
Psych 120. General Psychology. Today s class. Anxiety Disorders 7/26/2010
 Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the final three lecture sections of the course, we ll be discussing
Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the final three lecture sections of the course, we ll be discussing
First Episode Psychosis: Identification and Treatment. Monica McConkey MA, LPC Prairie St. John s
 First Episode Psychosis: Identification and Treatment Monica McConkey MA, LPC Prairie St. John s Objectives 1. Attendees will learn to identify common signs and symptoms of early onset psychosis 2. Attendees
First Episode Psychosis: Identification and Treatment Monica McConkey MA, LPC Prairie St. John s Objectives 1. Attendees will learn to identify common signs and symptoms of early onset psychosis 2. Attendees
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY
 Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders
 Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like disorders Dr: Weibo Liu E-mail:liuweibo1020@163.com The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University College of Medicine Category of psychotic disorders Schizophrenia
What percentage of the population would you guess have a psychological disorder?
 What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What are Mood Disorders? What is Schizophrenia? What percentage
What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What are Mood Disorders? What is Schizophrenia? What percentage
Elements for a Public Summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder often characterized by abnormal social behaviour and failure to recognize what
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder often characterized by abnormal social behaviour and failure to recognize what
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC
 Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Psychosis. Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah
 Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses
 Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Behavioral Issues in Dementia. March 27, 2014 Dylan Wint, M.D.
 Behavioral Issues in Dementia March 27, 2014 Dylan Wint, M.D. OVERVIEW Key points Depression Definitions and detection Treatment Psychosis Definitions and detection Treatment Agitation SOME KEY POINTS
Behavioral Issues in Dementia March 27, 2014 Dylan Wint, M.D. OVERVIEW Key points Depression Definitions and detection Treatment Psychosis Definitions and detection Treatment Agitation SOME KEY POINTS
What Team Members Other Than Prescribers Need To Know About Antipsychotics
 What Team Members Other Than Prescribers Need To Know About Antipsychotics The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State
What Team Members Other Than Prescribers Need To Know About Antipsychotics The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Early Warning Signs of Psychotic Disorders and the Importance of Early Intervention
 Early Warning Signs of Psychotic Disorders and the Importance of Early Intervention Margaret Migliorati, MA, LPCC The University of New Mexico mmigliorati@salud.unm.edu Mental Health As a Public Health
Early Warning Signs of Psychotic Disorders and the Importance of Early Intervention Margaret Migliorati, MA, LPCC The University of New Mexico mmigliorati@salud.unm.edu Mental Health As a Public Health
What is Abnormal anyway?
 What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What Is Abnormal Behavior? Abnormal behavior is characterized
What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What Is Abnormal Behavior? Abnormal behavior is characterized
Mental Health and Stress
 Mental Health and Stress Learning Objectives Ø Define mental health and discuss the characteristics of mentally healthy and selfactualized people Ø Describe the various mental disorders and appropriate
Mental Health and Stress Learning Objectives Ø Define mental health and discuss the characteristics of mentally healthy and selfactualized people Ø Describe the various mental disorders and appropriate
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia - continued
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
CHILDHOOD SCHIZOPHRENIA (2 CE HOURS)
 CHILDHOOD SCHIZOPHRENIA (2 CE HOURS) Learning objectives To understand the history of childhood schizophrenia and psychosis. To understand the significant definitions related to childhood schizophrenia
CHILDHOOD SCHIZOPHRENIA (2 CE HOURS) Learning objectives To understand the history of childhood schizophrenia and psychosis. To understand the significant definitions related to childhood schizophrenia
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA FAMILY ASSESSMENT AND INTERVENTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA FAMILY ASSESSMENT AND INTERVENTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 treatment of schizophrenia family assessment and intervention treatment of schizophrenia
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA FAMILY ASSESSMENT AND INTERVENTION PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 treatment of schizophrenia family assessment and intervention treatment of schizophrenia
Average? Anyone at the extremes is? Violating social norms? Cultural Norms? Experiencing subjective discomfort? Maladaptive Behavior?
 Psychopathology: scientific study of abnormal behavior Historically, things haven t always gone well Trepanning in ancient times (frees demons) Hippocrates: humors out of balance Middle Ages: demonic possession
Psychopathology: scientific study of abnormal behavior Historically, things haven t always gone well Trepanning in ancient times (frees demons) Hippocrates: humors out of balance Middle Ages: demonic possession
Bi-polar MDD. Repeated episodes of mania and depression
 MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
Disorders. Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality.
 Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
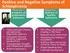 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents
 Keeping Your Balance Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents Medication Treatment for Bipolar Disorder 2 Page Medication Record 5 Psychosocial Treatments for Bipolar Disorder 6 Module Summary 8
Keeping Your Balance Treatment Options for Bipolar Disorder Contents Medication Treatment for Bipolar Disorder 2 Page Medication Record 5 Psychosocial Treatments for Bipolar Disorder 6 Module Summary 8
10. Psychological Disorders & Health
 10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
Antipsychotics. Neuroleptics/ Major Tranquilizers. Hiwa K. Saaed, PhD Pharmacology & Toxicology /5/18 1
 Antipsychotics Neuroleptics/ Major Tranquilizers Hiwa K. Saaed, PhD Pharmacology & Toxicology hiwa.saaed@univsul.edu.iq 2018-2019 12/5/18 1 Learning objectives Pharmacy students should: be familiar with
Antipsychotics Neuroleptics/ Major Tranquilizers Hiwa K. Saaed, PhD Pharmacology & Toxicology hiwa.saaed@univsul.edu.iq 2018-2019 12/5/18 1 Learning objectives Pharmacy students should: be familiar with
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders
 AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
 Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia In other information sheets we have discussed the two major types of symptoms traditionally thought to characterise schizophrenia: first of all the positive symptoms
Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia In other information sheets we have discussed the two major types of symptoms traditionally thought to characterise schizophrenia: first of all the positive symptoms
SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Atypical (2
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Atypical (2
8/23/2016. Chapter 34. Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric Disorder. Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric Disorder
 Chapter 34 Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric
Chapter 34 Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric
Antipsychotic Medications
 TRAIL: Team Review of EVIDENCE REVIEW & RECOMMENDATIONS FOR LTC Behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) refer to the non-cognitive symptoms of disturbed perception, thought content, mood
TRAIL: Team Review of EVIDENCE REVIEW & RECOMMENDATIONS FOR LTC Behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) refer to the non-cognitive symptoms of disturbed perception, thought content, mood
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Abnormal Psychology Exam Notes Psychotic Disorders- Week 7- Chapter 4 Narrow definitions of psychosis only require the presence of hallucinations and delusions, whereas broad definitions of psychosis incorporate
Is Lurasidone more safe and effective in the treatment ofschizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia than other commonanti-psychotic medications?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Lurasidone more safe and effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Lurasidone more safe and effective
Paranoid Schizophrenia. Prepared by : Noor Al-Hakami pharm-d candidate KSU
 Paranoid Schizophrenia Prepared by : Noor Al-Hakami pharm-d candidate KSU Paranoid schizophrenia is one of several types of schizophrenia which affect around 40 % of people with schizophrenia It tends
Paranoid Schizophrenia Prepared by : Noor Al-Hakami pharm-d candidate KSU Paranoid schizophrenia is one of several types of schizophrenia which affect around 40 % of people with schizophrenia It tends
Schizophrenia Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE -NURSING PROGRAM
 Schizophrenia Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE -NURSING PROGRAM NURS 203 GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY DANITA NARCISO PHARM D Learning Objectives Understand the result of dopamine binding to D2 receptors
Schizophrenia Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE -NURSING PROGRAM NURS 203 GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY DANITA NARCISO PHARM D Learning Objectives Understand the result of dopamine binding to D2 receptors
Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care
 Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care Stephanie Saur & Christina Pacheco Acute Care Behavioural Consultants Alzheimer Society Peel What is Mental Health? Mental health includes our
Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care Stephanie Saur & Christina Pacheco Acute Care Behavioural Consultants Alzheimer Society Peel What is Mental Health? Mental health includes our
Schizophrenia. Brooke Jones Charity Payne Alyssa Stewart
 Schizophrenia Brooke Jones Charity Payne Alyssa Stewart Brogan s Story Definition Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally. Schizophrenia may result in some
Schizophrenia Brooke Jones Charity Payne Alyssa Stewart Brogan s Story Definition Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally. Schizophrenia may result in some
D. Exclusion of schizoaffective disorder and mood disorder with psychotic features.
 65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
Chapter Sixteen. Psychological Disorders
 Chapter Sixteen Psychological Disorders Prevalence of Psychological Disorders? Approximately 25% of the Adult Population here in the U.S. of A. Higher percentages in areas / countries with high poverty
Chapter Sixteen Psychological Disorders Prevalence of Psychological Disorders? Approximately 25% of the Adult Population here in the U.S. of A. Higher percentages in areas / countries with high poverty
Schizophrenia. Class Objectives. Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia? 12/7/2011. Other psychotic disorders and causes
 Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders and causes Class Objectives What are Delusional Disorders? What causes Schizophrenia? How can Schizophrenia be treated? Can someone be psychotic without having schizophrenia?
