PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
|
|
|
- Duane McCarthy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
2 5. Schizophrenia Schizophrenia- a group of severe psychotic disorders characterized by distortions in thinking, perception, emotion, & behavior
3 Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia - characterized by delusions or auditory hallucinations relating to delusions of grandeur, persecution, or jealousy. - Intact cognitive skills - A Beautiful Mind, 1/3 show - partial recovery like Nash
4 Schizophrenia cont. Paranoid Schizophrenia - characterized by delusions or auditory hallucinations relating to delusions of grandeur, persecution, or jealousy. - Intact cognitive skills - A Beautiful Mind, 1/3 show - partial recovery like Nash
5 Schizophrenia cont. Disorganized Schizophrenia disintegration of personality including erratic speech, childish mannerisms & bizarre behavior - Cognitive slippage Illogical speech, word salad - mimic speech of others - meaningless rhyming of words - Neologism made-up words
6 Schizophrenia cont. Catatonic Schizophrenia characterized by a tendency to remain in a fixed stuporous state for long periods; may be short periods of extreme excitement - imitate speech & imitate movement - Complete catatonia tends to be severe & quite rare
7 Schizophrenia cont. What type os schizophrenia? Why?
8 Causes of Schizophrenia Causes Psychodynamic - regression to early childhood, an extreme reaction to anxiety. Family that is extremely critical & pushy, can be a factor causing schizo.
9 Causes cont. Biological Views - Genetic factors play a role in developing schizophrenia(twins Stds).
10 Causes cont. Multifactorial Model All factors, environment & biological are an influence in schizophrenia a. The Role of Stress May activate Schizo b. Family Interactions High emotion w/criticism & emotional overinvolvement, & hostility c. Cultural variation Highest in Caucasian Complications during pregnancy & birth Genetic Factors Viral infections Stress Schizophrenia Quality of Parenting Multifactorial Model
11 Causes cont. Schizophrenia Note Questions Name Date Period 1. What are the main characteristics of someone who has schizophrenia? Multifactorial Model All factors, environment & biological are an influence in schizophrenia 2. What are three types of Schizophrenia? Complications 4. How does paranoid schizophrenia during differ from disorganized schizophrenia? pregnancy & birth 5. Some victims of schizophrenia lapse into a motionless states that can last for hours. This state is called a. The Role of Stress May activate Schizo b. Family Interactions High emotion w/criticism & emotional overinvolvement, & hostility c. Cultural variation Highest in Caucasian Genetic Factors 3. A delusion is a belief in something that is not true? Which type of schizophrenia is most characterized by delusions Schizophrenia 6. How did Freud s explanation for the cause Viral of Schizophrenia? infections 7. According to the Multifactorial Model of Schizophrenia, what are the five factors that interact which may be the cause of the development of Schizophrenia? Stress Quality of Parenting Multifactorial Model
12 Schizophrenia Note Questions Name Date Period 1. What are the main characteristics of someone who has schizophrenia? 2. What are three types of Schizophrenia? 3. A delusion is a belief in something that is not true? Which type of schizophrenia is most characterized by delusions 4. How does paranoid schizophrenia differ from disorganized schizophrenia? 5. Some victims of schizophrenia lapse into a motionless states that can last for hours. This state is called 6. How did Freud s explanation for the cause of Schizophrenia? 7. According to the Multifactorial Model of Schizophrenia, what are the five factors that interact which may be the cause of the development of Schizophrenia? Schizophrenia
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception
 Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Goal: To recognize and differentiate different forms of psychopathology that involve disordered thinking and reasoning and distorted perception Psychotic disorders, or psychoses, are among the most serious
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Chapter 12. Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders. PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders PSY 440: Abnormal Psychology Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University psychotic disorders disorders so severe that the person has essentially lost
Psychotic Disorders. There is a loss of contact with and difficulty in recognizing reality.
 Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
Psychotic Disorders A psychosis or psychotic disorder, involves a major disorganization of thought processes, confused and extreme emotional responses, and distorted perceptions of the world. There is
The psychological disorders
 The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
The psychological disorders Defining abnormal Statistical infrequency Normal distribution; the normal curve Violation of norms Culture bound syndromes Personal distress Some disorders do not involve distress
Chapter 14. Psychological Disorders
 Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders We ve Come a Long Way Trepanning Ancient priests or medicine men cut holes into the skills of living persons, to release the demons. What is Abnormality Psychopathology
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders We ve Come a Long Way Trepanning Ancient priests or medicine men cut holes into the skills of living persons, to release the demons. What is Abnormality Psychopathology
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3. By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin
 Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
Phycology and Sociology Review: Unit 3 By:Owen Krahwinkel and Luke Lajcin ADHD: DSM-IV DSM-IV Codes are the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders This is primary
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders
 Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia & Psychotic Disorders The Misunderstood Disorder Speak the word schizophrenia and you ll likely receive reactions ranging from misunderstanding to fear. The disorder is largely shrouded in
Schizophrenia. Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior.
 Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Schizophrenia Severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking, emotion, perception and behavior. Nearly 1 in a 100 suffer from schizophrenia. World- 24 million people suffer from the disorder Strikes
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis
 Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Week #1 Classification & Diagnosis 3 Categories in the Conceptualisation of Abnormality Psychological Dysfunction: Refers to a breakdown in cognitive, emotional or behavioural functioning. Knowing where
Schizophrenia. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Psychological Disorders. Module 51. Schizophrenia
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Schizophrenia Module 51 2 Psychological Disorders Schizophrenia Symptoms
Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications
 Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
Reality Non-reality VS. Psychosis & Antipsychotic Medications Disorganized thinking, hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behaviors What is Psychosis? Psychosis is mental disorganization to such a degree
Psychosis. Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah
 Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Psychosis Paula Gibbs, MD Department of Psychiatry University of Utah Psychotic Symptoms Psychosis in a broad sense, signifies impaired reality testing ability Symptoms include: hallucinations, delusions,
Schizophrenia. Introduction. Overview and Facts
 Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Introduction is a chronic, severe and disabling brain disease that typically shows its first clear symptoms in late adolescence or early adulthood. It is one of several types of Psychotic Disorders. It
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
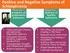 Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Positive and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive + presence of problematic behaviors Negative - absence of healthy behaviors Hallucinations (illusory perceptions), especially auditory Delusions
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Dr. Fred Rose. Schizophrenia. Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview. Prevalence of Schizophrenia 10/20/10. Schizophrenia vs.
 Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Dr. Fred Rose Nature of Schizophrenia and Psychosis: An Overview Schizophrenia vs. Psychosis Psychosis Cluster of disorders; hallucinations and/or loss of contact with reality Schizophrenia
How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders
 How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders What are psychological disorders? Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts,
How to Win Friends and Influence People Lesson 6 Psychological Patterns and Disorders What are psychological disorders? Mental health workers view psychological disorders as ongoing patterns of thoughts,
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW
 SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
SCHIZOPHRENIA AN OVERVIEW Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your physician,
Average? Anyone at the extremes is? Violating social norms? Cultural Norms? Experiencing subjective discomfort? Maladaptive Behavior?
 Psychopathology: scientific study of abnormal behavior Historically, things haven t always gone well Trepanning in ancient times (frees demons) Hippocrates: humors out of balance Middle Ages: demonic possession
Psychopathology: scientific study of abnormal behavior Historically, things haven t always gone well Trepanning in ancient times (frees demons) Hippocrates: humors out of balance Middle Ages: demonic possession
9/3/2014. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness
 Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Handout 2: Understanding Psychotic Illness A Psychosis refers to a state where a person loses contact with reality. The word is derived from the Latin words "psyche" meaning mind and "osis" meaning illness.
Anxiety Disorders are characterized by excessive fear and anxiety in the absence of true danger. 1. Anxiety Disorders
 ANXIETY DISORDERS Anxiety Disorders are characterized by excessive fear and anxiety in the absence of true danger. 1 These are a class of disorders. Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic
ANXIETY DISORDERS Anxiety Disorders are characterized by excessive fear and anxiety in the absence of true danger. 1 These are a class of disorders. Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic
Chapter 18 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
 Chapter 18 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 1 Section 1: What Are Psychological Disorders? Section 2: Anxiety Disorders Section 3: Dissociative Disorders Section 4: Somatoform Disorders Section 5: Mood Disorders
Chapter 18 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS 1 Section 1: What Are Psychological Disorders? Section 2: Anxiety Disorders Section 3: Dissociative Disorders Section 4: Somatoform Disorders Section 5: Mood Disorders
Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Age Distribution of Onset 2/24/2009. Schizophrenia. Hallmark trait is psychosis
 Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Affects people from all walks of life Is about as prevalent as epilepsy Usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood Hallmark trait is psychosis
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com
 Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychotic disorders Dr. Sarah DeLeon, MD PGYIV, Psychiatry ConceptsInPsychiatry.com Introduction Psychotic spectrum disorders include schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, brief psychotic
Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2
 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 3 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 4 Phobic Disorders A phobia is an intense and irrational fear of a particular object or situation;
Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 2 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 3 Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, 4 Phobic Disorders A phobia is an intense and irrational fear of a particular object or situation;
Schizophrenia. Nikita Verma 2017 Page 1
 Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
Schizophrenia It is a severe psychiatric disorder with symptoms of emotional instability, detachment from reality and withdrawal into self. It is an umbrella term used to outline a range of different psychiatric
SCHIZOPHRENIA. What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
SCHIZOPHRENIA What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are there different types of Schizophrenia Yes there are Paranoid Schizophrenia: In this version of the disease, hallucinations
Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by:
 Schizophrenia Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by: Gross distortions in reality Withdrawal from relationships Disorganization and fragmentation of perception, thought, emotion
Schizophrenia Ultimate in psychological breakdown The Mad Characterized by: Gross distortions in reality Withdrawal from relationships Disorganization and fragmentation of perception, thought, emotion
CHAPTER 12 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS YOU KNOW YOU ARE READY FOR THE TEST IF YOU ARE ABLE TO! Define abnormality and briefly discuss the historical and cultural impact on defining psychological disorders.! Present the
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS YOU KNOW YOU ARE READY FOR THE TEST IF YOU ARE ABLE TO! Define abnormality and briefly discuss the historical and cultural impact on defining psychological disorders.! Present the
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
Schizophrenia A psychotic Disorder Schizophrenia A TYPE OF PSYCHOSIS: Psychosis: mental disorders characterized by major departures from reality Schizophrenia: a psychosis marked by disturbances of thought,
True or False? Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders. What is Abnormal Behavior? 12/9/10. Characteristics of Abnormal Behavior
 Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormality Classifying Psychological Disorders Origins of Psychological Disorders True or False? Abnormal behaviors are always bizarre. A clear distinction
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormality Classifying Psychological Disorders Origins of Psychological Disorders True or False? Abnormal behaviors are always bizarre. A clear distinction
Disorders. Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality.
 Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
Disorders Perspectives Anxiety Mood Schizophrenia Personality http://dove.ccs.fau.edu/~dawei/psy Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be:
General Psychology. Chapter Outline. Psychological Disorders 4/28/2013. Psychological Disorders: Maladaptive patterns of behavior that cause distress
 General Psychology Jeffrey D. Leitzel, Ph.D. Chapter 1: Behavioral (Psychological) Disorders 1 Chapter Outline Defining abnormality Historical perspectives on abnormality Classifying/identifying disorders
General Psychology Jeffrey D. Leitzel, Ph.D. Chapter 1: Behavioral (Psychological) Disorders 1 Chapter Outline Defining abnormality Historical perspectives on abnormality Classifying/identifying disorders
Schizophrenia The artwork of Louis Wain ( )
 Schizophrenia The artwork of Louis Wain (1860-1939) onset of schizophrenia Nearly 1% of the population suffers from schizophrenia Schizophrenia strikes young people as they mature into adults. (18-24 years
Schizophrenia The artwork of Louis Wain (1860-1939) onset of schizophrenia Nearly 1% of the population suffers from schizophrenia Schizophrenia strikes young people as they mature into adults. (18-24 years
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS
 MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
MENTAL HEALTH DISEASE CLASSIFICATIONS DIAGNOSIS OF MENTAL DISORDERS DSM-IV-TR Published by APA ( 2000 ) Multiaxial system 5 categories called axes Facilitate holistic assessment for care Is a great resource
Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar Disorder. Theory of Depression. Explaining Mood Disorders. Theory of Depression. Suicide
 Bipolar Disorder Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms Manic Symptoms Bipolar Disorder Many great writers,
Bipolar Disorder Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms Manic Symptoms Bipolar Disorder Many great writers,
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders
 AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
AP PSYCH Unit 12.3 Schizophrenia & Personality Disorders 1. If a criminal claimed that voices in their head told them to commit a murder, should they be found guilty or innocent? Why? 2. Describe interactions
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Chapter 12 PART II V. What Are Dissociative Disorders? Sudden but temporary alteration in consciousness, identity, sensorimotor behavior, or memory Relatively rare, but very dramatic
Psychological Disorders Chapter 12 PART II V. What Are Dissociative Disorders? Sudden but temporary alteration in consciousness, identity, sensorimotor behavior, or memory Relatively rare, but very dramatic
Announcements. Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class)
 Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
5) Which of he following is not one of the main clinical symptoms of Schizophrenia? a) Delusions b) Hallucinations c) Apathy d) Narcolepsy (A)
 Chapter 7.teachers 1 In Schizophrenia, the phenomenon known as downward drift means? a) Falling to the bottom of the social ladder b) Become homeless c) Inability to hold down a job 2) Which of the following
Chapter 7.teachers 1 In Schizophrenia, the phenomenon known as downward drift means? a) Falling to the bottom of the social ladder b) Become homeless c) Inability to hold down a job 2) Which of the following
Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorders. Schizophrenia. Chapter 13
 Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Schizophrenia Chapter 13 Psychotic Disorders Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective
Announcements. Abnormal Psychology. I. Introduction. Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional. Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional 4/30/2014
 Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Announcements The final Aplia gauntlet: Chapter 12 Aplia due next Monday Chapter 13 Aplia due next Wednesday (final day of class) Final Exam is May 14, 3:30 pm More experiments going up daily! Enhanced
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders I felt the need to clean my room spent 4 to 5 hours at it At the time I loved it but then didn't want to do it any more, but could not stop The clothes hung two fingers apart I
Psychological Disorders I felt the need to clean my room spent 4 to 5 hours at it At the time I loved it but then didn't want to do it any more, but could not stop The clothes hung two fingers apart I
D. Exclusion of schizoaffective disorder and mood disorder with psychotic features.
 65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
65 CHAPTER 8: APPENDIX. ADDENDUM A DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia A. Characteristic symptoms: Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of time during a one-month
Psychological Disorders
 1 2 3 4 5 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological Disorders Societal Does the behavior conform to existing social norms? Individual Personal sense of well-being Happy, satisfied, peaceful
1 2 3 4 5 Psychological Disorders Perspectives on Psychological Disorders Societal Does the behavior conform to existing social norms? Individual Personal sense of well-being Happy, satisfied, peaceful
Abnormal Psychology Notes
 Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Abnormal Psychology Notes Abnormal Behaviors Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be: atypical not enough in itself disturbing varies with time/culture maladaptive
Agoraphobia. An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible.
 Agoraphobia An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible. (See page 634) Antisocial personality disorder (APD) A personality disorder marked
Agoraphobia An anxiety disorder marked by fear of being in situations in which escape may be difficult or impossible. (See page 634) Antisocial personality disorder (APD) A personality disorder marked
Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment
 Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment This is an example structure of a case study assignment given by the Practice Educator whilst on placement. ABOUT THIS SERVICE 1. Describe the role of
Orientation to Mental Health - Student Assignment This is an example structure of a case study assignment given by the Practice Educator whilst on placement. ABOUT THIS SERVICE 1. Describe the role of
Autism. Childhood Autism and Schizophrenia. Autism, Part 1 Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-IV-TR) Behavioral Characteristics of Autism
 Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Autism Childhood Autism and Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Autism comes from the Latin within oneself Autism: Severe developmental disorder characterized by abnormalities in: Social functioning Language
Abnormal Psychology. Defining Abnormality
 Abnormal Psychology Defining Abnormality Statistical Approach abnormality = infrequency but this is not sufficient on its own Valuative Approach abnormality = social deviance unacceptable or doesn t conform
Abnormal Psychology Defining Abnormality Statistical Approach abnormality = infrequency but this is not sufficient on its own Valuative Approach abnormality = social deviance unacceptable or doesn t conform
Paranoid Schizophrenia. Prepared by : Noor Al-Hakami pharm-d candidate KSU
 Paranoid Schizophrenia Prepared by : Noor Al-Hakami pharm-d candidate KSU Paranoid schizophrenia is one of several types of schizophrenia which affect around 40 % of people with schizophrenia It tends
Paranoid Schizophrenia Prepared by : Noor Al-Hakami pharm-d candidate KSU Paranoid schizophrenia is one of several types of schizophrenia which affect around 40 % of people with schizophrenia It tends
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC
 Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Hope FIRST: An Innovative Treatment for First Episode Psychosis PRESENTATION BY REBECCA FLATTERY, LCSW AND BRIAN ROHLOFF, LPC What is a first episode of psychosis? The word psychosis is used to describe
Cours 6 : Mental Illness and Mental Health Care, Part II
 UE1-Anglais Pr. Bernier Le 14/12/2017 à 8H 30 Ronéotypeur : Roxane BIDAUD Cours 6 : Mental Illness and Mental Health Care, Part II 1 /8 Sommaire I) Chapter I: Mood Disorders, depression and Bipolar Disorder
UE1-Anglais Pr. Bernier Le 14/12/2017 à 8H 30 Ronéotypeur : Roxane BIDAUD Cours 6 : Mental Illness and Mental Health Care, Part II 1 /8 Sommaire I) Chapter I: Mood Disorders, depression and Bipolar Disorder
CHAPTER 3. Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment
 CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
SMI and SED Qualifying Diagnoses Table
 295.00 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Unspecified State 295.01 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Subchronic State 295.02 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Chronic State 295.03 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Subchronic State
295.00 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Unspecified State 295.01 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Subchronic State 295.02 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Chronic State 295.03 Simple Type Schizophrenia, Subchronic State
10/14/2008. History. Abnormal Behavior. Deviant? Deviant? Maladaptive?
 History Historically, individuals who suffered from Psychological Disorders were thought to be crazy or possessed by evil spirits. Abnormal Behavior Deviant? Deviant Distressful Maladaptive Deviant? Maladaptive?
History Historically, individuals who suffered from Psychological Disorders were thought to be crazy or possessed by evil spirits. Abnormal Behavior Deviant? Deviant Distressful Maladaptive Deviant? Maladaptive?
Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 /
 Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 / Psychological Disorder(p.630) The presence of a constellation of symptoms that create significant distress; impair work, school, family, relationships,
Psychological Disorders: More Than Everyday Problems 14 / Psychological Disorder(p.630) The presence of a constellation of symptoms that create significant distress; impair work, school, family, relationships,
10. Psychological Disorders & Health
 10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
10. Psychological Disorders & Health We will now study different psychological disorders and theories for treating psychopathology. We will also cover health, stress and how to cope with them. The sections
22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome Fact Sheet - Treatable Psychiatric Illnesses in Adults
 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome Fact Sheet - Treatable Psychiatric Illnesses in Adults Anne S. Bassett (MD, FRCPC) Professor of Psychiatry, University of Toronto Director, Clinical Genetics Research Program,
22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome Fact Sheet - Treatable Psychiatric Illnesses in Adults Anne S. Bassett (MD, FRCPC) Professor of Psychiatry, University of Toronto Director, Clinical Genetics Research Program,
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
 Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders Psychosis, schizophrenia What does psychosis mean? What does schizophrenia mean? Is there any difference between them? Psychosis, schizophrenia Psychosis: -
Disorganized Symptoms of Psychosis
 Disorganized Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart Technologies
Disorganized Symptoms of Psychosis The Care Transitions Network National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office of Mental Health Netsmart Technologies
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited
 SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
SCHIZOPRHENIA - 1 II. A. Early description/diagnosis of schizophrenia 1. Emil Kraepelin: a. Combined catatonic (i.e., alternating immobility and excited agitation), hebephrenia (i.e., silly and immature
Treatment of Psychological Disorders
 Chapter 11 Treatment of Psychological Disorders McGraw-Hill 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Psychotherapy: Psychodynamic, Behavioral, and Cognitive Approaches Learning Outcomes
Chapter 11 Treatment of Psychological Disorders McGraw-Hill 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Psychotherapy: Psychodynamic, Behavioral, and Cognitive Approaches Learning Outcomes
Abnormal Psychology. A.K.A. Psychological Disorders
 Abnormal Psychology A.K.A. Psychological Disorders A harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive and unjustifiable. Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil
Abnormal Psychology A.K.A. Psychological Disorders A harmful dysfunction in which behavior is judged to be atypical, disturbing, maladaptive and unjustifiable. Early Theories Abnormal behavior was evil
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
CHAPTER 8: EXPERIENCING PSYCHOSIS: SCHIZOPHRENIA SPECTRUM PROBLEMS KEY TERMS Abnormal attribution processes The view that paranoid delusions may be the result of a bias towards attributing negative life
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses
 Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
Schizophrenia and the Psychoses Taking leave of one s senses Students of schizophrenia need to study and understand: Clinical presentation via case studies Terms and Definitions Biological features Prognosis
The alternate reality of schizophrenia
 The alternate reality of schizophrenia MICHAEL TRINSEY SCHIZOPHRENIA IS A GROUP of chronic, disabling psychiatric disorders characterized by disturbed thinking and disorganized speech. Patients with schizophrenia
The alternate reality of schizophrenia MICHAEL TRINSEY SCHIZOPHRENIA IS A GROUP of chronic, disabling psychiatric disorders characterized by disturbed thinking and disorganized speech. Patients with schizophrenia
Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated?
 Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated? 1 Video Examples of Delusional Type Schizophrenia 1) Subjective symptoms Somebody threatens
Schizophrenia 1. Symptoms What are the symptoms? 2. Causes What is the mechanism? 3. Treatment How is it treated? 1 Video Examples of Delusional Type Schizophrenia 1) Subjective symptoms Somebody threatens
PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives
 Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Too much dopamine can be bad for you: 1I. Latent inhibition and schizophrenia PSY/NEU338: Animal learning and decision making: Psychological, computational and neural perspectives thanks to Ina Weiner
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents
 Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
Psychotic Disorders in Children and Adolescents Dr. Marcelo Rodriguez-Chevres, M.D. Emergence Health Network Learning Objectives Audience will be able to: 1. Distinguish developmentally normal experiences
Psychological Disorders
 Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
Psychological Disorders Chapter 15 Class Objectives What are Mood Disorders? Depression, Mania and Bipolar What are Psychotic Disorders? Schizophrenia Moods THINK on your own What are some everyday moods
What is Abnormal anyway?
 What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What Is Abnormal Behavior? Abnormal behavior is characterized
What is Abnormal anyway? Chapter 13-Psychological Disorders CLASS OBJECTIVES: How do we define abnormal behavior? What are Anxiety Disorders? What Is Abnormal Behavior? Abnormal behavior is characterized
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Delusions and Paranoia. Dennis Combs, Ph.D. University of Tulsa
 Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Delusions and Paranoia Dennis Combs, Ph.D. University of Tulsa Brief Background Many persons consider that the only effective treatments for schizophrenia are antipsychotic
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Delusions and Paranoia Dennis Combs, Ph.D. University of Tulsa Brief Background Many persons consider that the only effective treatments for schizophrenia are antipsychotic
Schizophrenia. Positive Symptoms. Course of Schizophrenia. Psychotic Disorder
 Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline What is Schizophrenia? Positive Symptoms Negative Symptoms Subtypes Phases Development Causes Treatment What Is
9/5/2016 PsychPortal: Myers, Psychology 10e Prologue Summative Quiz
 1. Compared with the structuralists, early behaviorists were much LESS likely to focus on the study of: a. thinking. b. smiling. c. fighting. d. screaming. 2. You begin seeing a therapist to cope with
1. Compared with the structuralists, early behaviorists were much LESS likely to focus on the study of: a. thinking. b. smiling. c. fighting. d. screaming. 2. You begin seeing a therapist to cope with
Psych 120. General Psychology. Today s class. Anxiety Disorders 7/26/2010
 Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the final three lecture sections of the course, we ll be discussing
Psych 120 General Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 1030A Office hours: MW 4:30-5:30 Email: gadecj@gmail.com Class MW 1:30-4:30 Room 2240 In the final three lecture sections of the course, we ll be discussing
Unit 6: Psychopathology and Psychotherapy (chapters 11-12)
 Unit 6: Psychopathology and Psychotherapy (chapters 11-12) Learning Objective 1 (pp. 381-382): Conceptions of Mental Illness Biological Dysfunction 1. What is psychopathology? 2. What criteria are used
Unit 6: Psychopathology and Psychotherapy (chapters 11-12) Learning Objective 1 (pp. 381-382): Conceptions of Mental Illness Biological Dysfunction 1. What is psychopathology? 2. What criteria are used
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders?
 Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
Psychological Disorders (mental illnesses): A Little History What are psychological disorders? What are some major classes of psychological disorders? Through the ages, people suffering from psychological
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA
 Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Entitlement Eligibility Guideline SCHIZOPHRENIA Page 1 of 8 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINE SCHIZOPHRENIA MPC 00607 ICD-9 295 ICD-10 F20 DEFINITION SCHIZOPHRENIA Characteristic symptoms of Schizophrenia
Active listening. drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antianxiety drugs
 Active listening empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy. Antianxiety drugs drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antidepressant
Active listening empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy. Antianxiety drugs drugs used to control anxiety and agitation. Antidepressant
Personality Disorders Explained
 Personality Disorders Explained Personality Disorders Note: This information was taken pre-dsm-v. There are ten basically defined personality disorders. These are defined below in alphabetical order. Note:
Personality Disorders Explained Personality Disorders Note: This information was taken pre-dsm-v. There are ten basically defined personality disorders. These are defined below in alphabetical order. Note:
The cancer of mental illness
 The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
The cancer of mental illness KWL Chart and Hearing Voices Simulations De-brief on activity What is schizophrenia? Recognition of Schizophrenia Symptoms Anderson Cooper Simulation Diagnosis and Treatment
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
Three Minute Review. Test Yourself. and Dissociative Identity Disorder
 and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
and Dissociative Identity Disorder paintings by artist, Louis Wain, during his worsening schizophrenia Three Minute Review Personality Disorders Axis II of DSM controversial 3 clusters Dramatic/Impulsive,
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 16 Schizophrenia Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties, but can be as
Classifying Psychological Disorders
 Classifying Psychological Disorders Classification of psychological disorders requires that symptoms be identified; sets of symptoms form a syndrome. Several of the most prevalent of the DSM IV's 16 categories
Classifying Psychological Disorders Classification of psychological disorders requires that symptoms be identified; sets of symptoms form a syndrome. Several of the most prevalent of the DSM IV's 16 categories
Psychological Disorders
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 16 Psychological Disorders James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorder a harmful dysfunction in which behavior
Schizophrenia. This factsheet covers -
 Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
Schizophrenia There are many misconceptions about schizophrenia. It is an illness that can be treated. One in a hundred people will experience schizophrenia during their lifetime 1 and the majority of
Department of Public Welfare PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENT REPORT
 Department of Public Welfare PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENT REPORT The purpose of this report is to outline the information needed to make a disability determination. This is not a required format; however,
Department of Public Welfare PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENT REPORT The purpose of this report is to outline the information needed to make a disability determination. This is not a required format; however,
Index 1. The Author(s) 2018 L. Bortolotti (ed.), Delusions in Context,
 Index 1 A Abductive inferences, 42 Abuse, 3, 14, 15, 101, 105 Action, 2, 3, 10, 20, 39, 48, 50, 54, 75, 79, 87, 100, 108, 112, 113 Adaptiveness, 48, 53, 76, 83, 98,,, n8, 110 Adjustment heuristic, 45,
Index 1 A Abductive inferences, 42 Abuse, 3, 14, 15, 101, 105 Action, 2, 3, 10, 20, 39, 48, 50, 54, 75, 79, 87, 100, 108, 112, 113 Adaptiveness, 48, 53, 76, 83, 98,,, n8, 110 Adjustment heuristic, 45,
What is Schizophrenia?
 What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
What is Schizophrenia? What is schizophrenia? Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects one person in every hundred. Schizophrenia interferes with the mental functioning of a person and, in the long
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing. Features of Schizophrenia. Features of Schizophrenia - continued
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Chapter 16 Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders Features of Schizophrenia Prevalence in U.S. is 1.1%. Average onset is late teens to early twenties,
Chapter 12 1/29/2018. Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders. Epidemiology. Comorbidity. Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1%
 Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Epidemiology Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1% No difference related to 2 Comorbidity Substance abuse disorders Anxiety, depression,
Chapter 12 Schizophrenia and Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Epidemiology Lifetime prevalence of schizophrenia is 1% No difference related to 2 Comorbidity Substance abuse disorders Anxiety, depression,
A-Level Abnormal- Schizophrenia AICE Psychology Syllabus Seth M. Alper, Ph.D. Schizophrenic & Psychotic Disorders
 A-Level Abnormal- Schizophrenia AICE Psychology- 9990 Syllabus Seth M. Alper, Ph.D. Schizophrenic & Psychotic Disorders Syllabus Content Topic 1: Characteristics of Schizophrenia Spectrum & Psychotic Disorders
A-Level Abnormal- Schizophrenia AICE Psychology- 9990 Syllabus Seth M. Alper, Ph.D. Schizophrenic & Psychotic Disorders Syllabus Content Topic 1: Characteristics of Schizophrenia Spectrum & Psychotic Disorders
3/9/2017. A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course. Our purpose
 A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
A module within the 8 hour Responding to Crisis Course Our purpose 1 What is mental Illness Definition of Mental Illness A syndrome characterized by clinically significant disturbance in an individual
A-Z of Mental Health Problems
 Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Mental health problems can cover a broad range of disorders, but the common characteristic is that they all affect the affected person s personality, thought processes or social interactions. They can
Chapter 17 Psychological Disorders
 Chapter 17 Psychological Disorders What is Normal? Psychopathology: Scientific study of mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders; also studies maladaptive and abnormal behavior Subjective Discomfort:
Chapter 17 Psychological Disorders What is Normal? Psychopathology: Scientific study of mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders; also studies maladaptive and abnormal behavior Subjective Discomfort:
Bi-polar MDD. Repeated episodes of mania and depression
 MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
MDD Long-lasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life. Bi-polar Repeated episodes of mania and depression Biology of Depression: The
