Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation
|
|
|
- Ashlie Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail. Nilsen TW, Graveley BR. Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature Jan 28;463(7280):
2 38% 18% 8% 3% Remaining 33% Cell 126:37 (2006) Nature Reviews: Genetics 5:773 (2004)
3 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation facilitating splice site recognition inhibiting splice site recognition direct interference multimerization and looping out model position dependent splicing regulation some splicing factors act as activators or repressor depending on the location of their binding sites, the CLIP assay (NOVA, FOX and PTB) transcription coupled alternative splicing regulation and the kinetic model
4 Splicing and spliceosomal assembly Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation: insights from molecular and genomics approaches Mo Chen and James L. Manley NATURE REVIEwS Molecular cell Biology VOLUME 10 NOVEMBER
5 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation facilitating splice site recognition Exonic elements :SR proteins binds ESE and facilitate recruitment of U2 at the 3 ss recruitment of U1 at the 5 ss recruitment of cofactors (Tra2 or SRm160) Intronic ISE (AU rich seq) binds TIA1 and facilitate recruitment of U1snRNP
6 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation inhibiting splice site recognition direct interference Direct steric interference blocking the access of the snrnp or of a positive splicing factor Polypyrimidine Tract Binding proteins directly binds to polyy and blocks U2AF hnrnpa1 binds to an ISS near U2 site (HIV) the tissue specific splicing factors FOX1 and FOX2 interfere with the Branch Point or with an ESE
7 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation inhibiting splice site recognition multimerization and looping out models
8 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation position dependent splicing regulation some splicing factors act as activators or repressor depending on their location on their binding sites the CLIP example (NOVA, FOX and PTB) Anna Corrionero and Juan Valcarcel Molecular Cell 36, December 24, 2009
9 Cross Linking ImmunoPrecipitation (CLIP) A method to identify protein binding site on RNA in living cells. After UV irradiation, cells are lysed and the crosslinked RNA protein complexes immunoprecipitated. Treatment with RNase digests away the RNA molecules except for those fragments protected by their interaction with the protein. Sequencing of these RNA tags not only identifies target transcripts, but also informs about the location of protein binding within the transcript. When combined with high throughput sequencing technologies, the method allows one to exhaustively characterize binding sites in whole transcriptomes, thus providing a panoramic view of targets and possible functions of the RNA binding protein.
10 How it works? Cells or tissues are treated with UV irradiation that generates a covalent bond between RNA and protein that are in close contact within the complex cell UV RNA proteins
11 Cell lysate preparation Collection of cells and centrifugation Cell lysis Sonication and centrifugation Supernatant with RNAprotein complexes Partial RNase digestion (size of cross linked RNA is reduced to approximately 50 nucleotides) RNA RNase digestion proteins
12 Antibody and beads preparation Beads containing Antibody coupling Antibodies protein A/G to the beads beads Immunoprecipitation (purification of RNA protein complexes) Antibodies coupled to beads mixed with cell lysate + Centrifuge Protein A/G beads with Ab RNA-protein complex Beads/Ab/RNAprotein complex Purified RNAprotein complex
13 RNA labelling, SDS PAGE and protein degradation 32 P 32 P 32 P labelling SDS-PAGE Band excision Proteinase K treatment 32 P 32 P RNA isolation and purification RT PCR and sequencing of RNA tags (HITS CLIP Gene alignment and in vivo validation
14 Cross Linking ImmunoPrecipitation summary
15 Ule, J., Jensen, K.B., Ruggiu, M., Mele, A., Ule, A., and Darnell, R.B. (2003). Science 302,
16 1) NOVA proteins RNA binding proteins studied by CLIP Neuron specific antigens Regulate neuronal pre mrna splicing Ule, J., Jensen, K.B., Ruggiu, M., Mele, A., Ule, A., and Darnell, R.B. (2003). Science 302, Target transcripts encode for proteins that function at the neuronal synapse Genomic location of the tags YCAY tetramer abundance in NOVA tags
17 NOVA dependent regulation of alternative splicing Splicing enhancers Splicing silencers RNA map predicts NOVA-dependent splicing regulation
18 2) Fox 2 protein tissue specific expression in muscle and neuronal cells Regulates alternative splicing through binding to UGCAUG sequence stem cells Yeo et al Nat Struct Mol Biol (2):
19 2) Fox 2 protein
20 3) PTB RNA-binding protein Generally considered as a splicing repressor HeLa cells Molecular Cell 36,
21 Anna Corrionero and Juan Valcarcel Molecular Cell 36, December 24, 2009
22 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation transcription coupled alternative splicing regulation recruitment model kinetic model
23 Coupling of pre mrna processing and transcription Bentley experiments bacterial Polymerases do not support RNA processing use amanitin resistant PolII with different length of the tail reducing the PolII tail reduces RNA processing (capping, splicing and polyadenilation) promoter and alternative splicing the promoter architecture modulate alternative splicing speed of the the polymerase PolII processivity influences alternative splicing
24 RNA Processing is Coupled with Tx
25 The CTD of the large subunit co ordinates transcription and RNA processing in protein coding genes CTD YSPTSPS X 52 (human) Pol II McCracken et al. Nature 1997
26 α Amanitin resistant pol II Cell 1 52 Nucleus Pol II CTD 1 25 Pol II Gene RNA 1 5 Rpb1 CTD complementation system
27 α Amanitin resistant pol II Cell α Amanitin 1 52 Nucleus Pol II 1 25 Gene X X Pol II RNA 1 5
28 α Amanitin resistant pol II Cell α Amanitin 1 52 Nucleus 1 25 Pol II 1 5 Pol II Gene RNA
29 The C terminal domain of PolII couples RNA processing to transcription Bentley Nature 1997
30 The promoter architecture modulates alternative splicing
31 A human PolII carrying a mutation (R749H) is less processive in vivo and affects alternative splicing
32 Kinetic coupling model for the regulation of alternative splicing by pol II elongation
33 Kinetic coupling model for the regulation of alternative splicing by pol II elongation Slow elongation is caused by the CTD hyperphosphorylation (yellow circles) that follows for example UV triggered DNA damage. The 3 splice site by the alternative cassette exon (blue) is weaker than the 3 splice site of the downstream intron (red). High elongation rates (a) favor skipping, whereas low transcriptional elongation rates (b) and (c) favor exon inclusion. (b) and (c) depict two alternative pathways for the first come, first served mechanism of splice site selection leading to higher exon inclusion. (b) Slow elongation causes preferential excision of the upstream intron (first served = first excised). (c) Slow elongation causes commitment to inclusion of the alternative exon via recruitment of splicing factors (first served = first committed) independent of the relative order of intron removal
34 Mean exon size corresponds to nucleosome accommodation on DNA Nucleosomes (broken circles) are preferentially bound to exons, whereas introns are mostly devoid of nucleosomes. Exons are therefore marked at the DNA level by nucleosome positioning, which may act as 'speed bumps' for RNA polymerase II, helping in the co-transcriptional recruitment of splicing factors to the nascent premrna and improving exon definition. As nucleosomes accommodate DNA stretches of approximately 147 nt, their preferential location on exons (mean size 145bp) may act as the selective pressure factor for the conservation in exon length. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 16, (2009) When chromatin meets splicing Kornblihtt A. et al
35 exon skipping exon inclusion H3K6me3 Alt spliced exon
36 Alternative splicing and tissue specificity AS regulation by constitutive splicing factors subtle changes in the concentration of antagonistic splicing factors (hnrnps and SR proteins) AS regulation by post translational modification of splicing factors (phosphorylation) AS regulation by tissue specific splicing factors
37 Alternative splicing and tissue specificity AS regulation by tissue specific splicing factors
38 Readings MMo Chen and James L. Manley. Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation: insights from molecular and genomics approaches NATURE REVIEwS,Molecular cell Biology, 10, 2009, 741. Nilsen TW, Graveley BR. Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature Jan 28;463(7280): Ule J, Jensen KB, Ruggiu M, Mele A, Ule A, Darnell RB. CLIP identifies Nova regulated RNA networks in the brain. Science Nov 14;302(5648): Anna Corrionero and Juan Valcarcel Molecular. Cell 36, December 24, 2009 (News and Views on CLIP assays) Alberto Kornblihtt. Promoter usage and alternative splicing. Current Opinion Cell Biol : Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 16, (2009) When chromatin meets splicing Kornblihtt A. et al Nature Nov 27;456(7221):464 9 HITS CLIP yields genome wide insights into brain alternative RNA processing. Licatalosi DD, et al (The CLIP identify NOVA as regulator of Alterantive PolyAdenilation) In red those papers that are part of the exam (i.e. one question will be to comment a figure)
Alternative splicing control 2. The most significant 4 slides from last lecture:
 Alternative splicing control 2 The most significant 4 slides from last lecture: 1 2 Regulatory sequences are found primarily close to the 5 -ss and 3 -ss i.e. around exons. 3 Figure 1 Elementary alternative
Alternative splicing control 2 The most significant 4 slides from last lecture: 1 2 Regulatory sequences are found primarily close to the 5 -ss and 3 -ss i.e. around exons. 3 Figure 1 Elementary alternative
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription. 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra
 Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER
 REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
REGULATED SPLICING AND THE UNSOLVED MYSTERY OF SPLICEOSOME MUTATIONS IN CANCER RNA Splicing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, H. Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING
 REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
REGULATED AND NONCANONICAL SPLICING RNA Processing Lecture 3, Biological Regulatory Mechanisms, Hiten Madhani Dept. of Biochemistry and Biophysics MAJOR MESSAGES Splice site consensus sequences do have
Mechanism of splicing
 Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics
 1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics to gain mechanistic insight! 4. Return to step 2, as
1. Identify and characterize interesting phenomena! 2. Characterization should stimulate some questions/models! 3. Combine biochemistry and genetics to gain mechanistic insight! 4. Return to step 2, as
Accessing and Using ENCODE Data Dr. Peggy J. Farnham
 1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
iclip Predicts the Dual Splicing Effects of TIA-RNA Interactions
 iclip Predicts the Dual Splicing Effects of TIA-RNA Interactions Zhen Wang 1., Melis Kayikci 1., Michael Briese 1, Kathi Zarnack 2, Nicholas M. Luscombe 2,3, Gregor Rot 4, Blaž Zupan 4, Tomaž Curk 4, Jernej
iclip Predicts the Dual Splicing Effects of TIA-RNA Interactions Zhen Wang 1., Melis Kayikci 1., Michael Briese 1, Kathi Zarnack 2, Nicholas M. Luscombe 2,3, Gregor Rot 4, Blaž Zupan 4, Tomaž Curk 4, Jernej
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
MCB Chapter 11. Topic E. Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes. Reading :
 MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
MCB Chapter 11 Topic E Splicing mechanism Nuclear Transport Alternative control modes Reading : 419-449 Topic E Michal Linial 14 Jan 2004 1 Self-splicing group I introns were the first examples of catalytic
Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus:
 RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
RNA Processing Eukaryotic mrna is covalently processed in three ways prior to export from the nucleus: Transcripts are capped at their 5 end with a methylated guanosine nucleotide. Introns are removed
Alternative splicing. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6
 Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons
 Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons T.A. Thanaraj 1 and S. Stamm 2 The completion of large genomic sequencing projects revealed that metazoan organisms abundantly use alternative
Prediction and Statistical Analysis of Alternatively Spliced Exons T.A. Thanaraj 1 and S. Stamm 2 The completion of large genomic sequencing projects revealed that metazoan organisms abundantly use alternative
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 18, 2004 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation Discovered by P. Sharp and R. Roberts in late 1970s
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Splicing
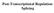 Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Splicing Pre-RNA terminal modifications Splicing Editing chemical modifications cutting capping polya base change X X pre-rrna 45S (poli) intron removal new chemical groups
Post-Transcriptional Regulation: Splicing Pre-RNA terminal modifications Splicing Editing chemical modifications cutting capping polya base change X X pre-rrna 45S (poli) intron removal new chemical groups
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
Figure mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic).
 Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
Splicing Figure 14.3 mouse globin mrna PRECURSOR RNA hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mouse globin MATURE mrna hybridized to cloned gene (genomic). mrna Splicing rrna and trna are also sometimes spliced;
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Minor point: In Table S1 there seems to be a typo - multiplicity of the data for the Sm3+ structure 134.8?
 PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Finogenova and colleagues investigated aspects of the structural organization of the Nuclear Exosome Targeting (NEXT) complex,
PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Finogenova and colleagues investigated aspects of the structural organization of the Nuclear Exosome Targeting (NEXT) complex,
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
 Acknowlegements I would like to thank Nick Luscombe and Kathi Zarnack to have accepted me for this internship after only two phone calls. It is really a pleasure to work with you! Thanks to Jernej Ule,
Acknowlegements I would like to thank Nick Luscombe and Kathi Zarnack to have accepted me for this internship after only two phone calls. It is really a pleasure to work with you! Thanks to Jernej Ule,
Eukaryotic transcription (III)
 Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
V24 Regular vs. alternative splicing
 Regular splicing V24 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
Regular splicing V24 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control
 Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
TRANSCRIPTION. DNA à mrna
 TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
MECHANISMS OF ALTERNATIVE PRE-MESSENGER RNA SPLICING
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003. 72:291 336 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720 Copyright 2003 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on February 27, 2003
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 13, 2006
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 13, 2006 Precursor mrna: introns and exons Intron: Transcribed RNA sequence removed from precursor RNA during the process of maturation (for class II genes:
V23 Regular vs. alternative splicing
 Regular splicing V23 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
Regular splicing V23 Regular vs. alternative splicing mechanistic steps recognition of splice sites Alternative splicing different mechanisms how frequent is alternative splicing? Effect of alternative
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302. February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm
 Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
Processing of RNA II Biochemistry 302 February 14, 2005 Bob Kelm What s an intron? Transcribed sequence removed during the process of mrna maturation (non proteincoding sequence) Discovered by P. Sharp
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences
 Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2. November 13, 2006
 Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
SR Proteins. The SR Protein Family. Advanced article. Brenton R Graveley, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Connecticut, USA
 s s Brenton R Graveley, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Connecticut, USA Klemens J Hertel, University of California Irvine, Irvine, California, USA Members of the serine/arginine-rich
s s Brenton R Graveley, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Connecticut, USA Klemens J Hertel, University of California Irvine, Irvine, California, USA Members of the serine/arginine-rich
Alternative splicing: a pivotal step between eukaryotic transcription and translation
 Alternative splicing: a pivotal step between eukaryotic transcription and translation Alberto R. Kornblihtt, Ignacio E. Schor, Mariano Alló, Gwendal Dujardin, Ezequiel Petrillo and Manuel J. Muñoz Abstract
Alternative splicing: a pivotal step between eukaryotic transcription and translation Alberto R. Kornblihtt, Ignacio E. Schor, Mariano Alló, Gwendal Dujardin, Ezequiel Petrillo and Manuel J. Muñoz Abstract
Determinants of Plant U12-Dependent Intron Splicing Efficiency
 This article is published in The Plant Cell Online, The Plant Cell Preview Section, which publishes manuscripts accepted for publication after they have been edited and the authors have corrected proofs,
This article is published in The Plant Cell Online, The Plant Cell Preview Section, which publishes manuscripts accepted for publication after they have been edited and the authors have corrected proofs,
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 April 22, 2002 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
RNA-seq Introduction
 RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
Studying Alternative Splicing
 Studying Alternative Splicing Meelis Kull PhD student in the University of Tartu supervisor: Jaak Vilo CS Theory Days Rõuge 27 Overview Alternative splicing Its biological function Studying splicing Technology
Studying Alternative Splicing Meelis Kull PhD student in the University of Tartu supervisor: Jaak Vilo CS Theory Days Rõuge 27 Overview Alternative splicing Its biological function Studying splicing Technology
Chapter II. Functional selection of intronic splicing elements provides insight into their regulatory mechanism
 23 Chapter II. Functional selection of intronic splicing elements provides insight into their regulatory mechanism Abstract Despite the critical role of alternative splicing in generating proteomic diversity
23 Chapter II. Functional selection of intronic splicing elements provides insight into their regulatory mechanism Abstract Despite the critical role of alternative splicing in generating proteomic diversity
Translation. Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation of eukaryotic translation involves many initiation factors
 Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Histones modifications and variants
 Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Protein Synthesis
 Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Alternative pre-mrna splicing is a fundamental mechanism for
 Caspase-2 pre-mrna alternative splicing: Identification of an intronic element containing a decoy 3 acceptor site Jocelyn Côté*, Sophie Dupuis*, Zhi-Hong Jiang, and Jane Y. Wu Department of Pediatrics
Caspase-2 pre-mrna alternative splicing: Identification of an intronic element containing a decoy 3 acceptor site Jocelyn Côté*, Sophie Dupuis*, Zhi-Hong Jiang, and Jane Y. Wu Department of Pediatrics
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression. (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs)
 Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Pyrimidine Tracts between the 5 Splice Site and Branch Point Facilitate Splicing and Recognition of a Small Drosophila Intron
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 1997, p. 2774 2780 Vol. 17, No. 5 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Pyrimidine Tracts between the 5 Splice Site and Branch Point
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 1997, p. 2774 2780 Vol. 17, No. 5 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Pyrimidine Tracts between the 5 Splice Site and Branch Point
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit
 Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Control of Pre-mRNA Splicing by the General Splicing Factors PUF60 and U2AF 65
 Control of Pre-mRNA Splicing by the General Splicing Factors PUF60 and U2AF 65 Michelle L. Hastings, Eric Allemand, Dominik M. Duelli, Michael P. Myers, Adrian R. Krainer* Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory,
Control of Pre-mRNA Splicing by the General Splicing Factors PUF60 and U2AF 65 Michelle L. Hastings, Eric Allemand, Dominik M. Duelli, Michael P. Myers, Adrian R. Krainer* Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory,
Frank Rigo and Harold G. Martinson*
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Jan. 2008, p. 849 862 Vol. 28, No. 2 0270-7306/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mcb.01410-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Functional Coupling
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Jan. 2008, p. 849 862 Vol. 28, No. 2 0270-7306/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mcb.01410-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Functional Coupling
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
The CUGBP2 Splicing Factor Regulates an Ensemble of Branchpoints from Perimeter Binding Sites with Implications for Autoregulation
 The CUGBP2 Splicing Factor Regulates an Ensemble of Branchpoints from Perimeter Binding Sites with Implications for Autoregulation Jill A. Dembowski, Paula J. Grabowski* Department of Biological Sciences,
The CUGBP2 Splicing Factor Regulates an Ensemble of Branchpoints from Perimeter Binding Sites with Implications for Autoregulation Jill A. Dembowski, Paula J. Grabowski* Department of Biological Sciences,
DEGRADE, MOVE, REGROUP: signaling control of splicing proteins
 Review DEGRADE, MOVE, REGROUP: signaling control of splicing proteins Florian Heyd and Kristen W. Lynch Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia,
Review DEGRADE, MOVE, REGROUP: signaling control of splicing proteins Florian Heyd and Kristen W. Lynch Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia,
TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING
 Messenger RNA Eucaryotic gene expression transcription START site exons upstream elements promoter elements TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING introns gene m 7 G pre-mrna m 7 G SPLICING POLYADENYLATION AAAAAAAAAn
Messenger RNA Eucaryotic gene expression transcription START site exons upstream elements promoter elements TRANSCRIPTION CAPPING introns gene m 7 G pre-mrna m 7 G SPLICING POLYADENYLATION AAAAAAAAAn
Evidence that U5 snrnp recognizes the 3 splice site for catalytic step II in mammals
 The EMBO Journal Vol.16 No.15 pp.4746 4759, 1997 Evidence that U5 snrnp recognizes the 3 splice site for catalytic step II in mammals Maria Dolores Chiara 1, Leon Palandjian, sites in pre-mrna very near
The EMBO Journal Vol.16 No.15 pp.4746 4759, 1997 Evidence that U5 snrnp recognizes the 3 splice site for catalytic step II in mammals Maria Dolores Chiara 1, Leon Palandjian, sites in pre-mrna very near
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4)
 Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) regulating alternative splicing in developmental or differentiation contexts RBP Context where RBP regulates alternative splicing Binding motif from CLIP-sequencing
Supplementary Table 1. RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) regulating alternative splicing in developmental or differentiation contexts RBP Context where RBP regulates alternative splicing Binding motif from CLIP-sequencing
particles at the 3' splice site
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 1725-1729, March 1992 Biochemistry The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between Ul and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 1725-1729, March 1992 Biochemistry The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between Ul and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles
Regulation of Alternative Splicing: More than Just the ABCs *
 MINIREVIEW This paper is available online at www.jbc.org THE JOURNA OF BIOOGICA CHEMISTRY VO. 283, NO. 3, pp. 1217 1221, January 18, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
MINIREVIEW This paper is available online at www.jbc.org THE JOURNA OF BIOOGICA CHEMISTRY VO. 283, NO. 3, pp. 1217 1221, January 18, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
The Multifunctional Nature of the Adenovirus L4-22K Protein
 Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1185 The Multifunctional Nature of the Adenovirus L4-22K Protein SUSAN LAN ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2016
Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 1185 The Multifunctional Nature of the Adenovirus L4-22K Protein SUSAN LAN ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA 2016
Received 26 January 1996/Returned for modification 28 February 1996/Accepted 15 March 1996
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1996, p. 3012 3022 Vol. 16, No. 6 0270-7306/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Base Pairing at the 5 Splice Site with U1 Small Nuclear RNA
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1996, p. 3012 3022 Vol. 16, No. 6 0270-7306/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Base Pairing at the 5 Splice Site with U1 Small Nuclear RNA
Functional insights from genetic channelopathies Stephanie Schorge
 Functional Insights From Genetic Channelopathies Dr. 1 Royal Society University Research Fellow Department of Clinical and Experimental Epilepsy Aims of channelopathies lecture Describe channelopathies
Functional Insights From Genetic Channelopathies Dr. 1 Royal Society University Research Fellow Department of Clinical and Experimental Epilepsy Aims of channelopathies lecture Describe channelopathies
Dynamic Integration of Splicing within Gene Regulatory Pathways
 Leading Edge Review Dynamic Integration of Splicing within Gene Regulatory Pathways Ulrich Braunschweig, 1,4 Serge Gueroussov, 1,2,4 Alex M. Plocik, 3,4 Brenton R. Graveley, 3, * and Benjamin J. Blencowe
Leading Edge Review Dynamic Integration of Splicing within Gene Regulatory Pathways Ulrich Braunschweig, 1,4 Serge Gueroussov, 1,2,4 Alex M. Plocik, 3,4 Brenton R. Graveley, 3, * and Benjamin J. Blencowe
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project
 Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project Introduction RNA splicing is a critical step in eukaryotic gene
Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project Introduction RNA splicing is a critical step in eukaryotic gene
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 10: Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression control in eukaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A)
Genome-wide Characterization of RNA Expression and Processing
 Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 939 Genome-wide Characterization of RNA Expression and Processing AMMAR ZAGHLOOL ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA
Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Medicine 939 Genome-wide Characterization of RNA Expression and Processing AMMAR ZAGHLOOL ACTA UNIVERSITATIS UPSALIENSIS UPPSALA
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Breast cancer. Risk factors you cannot change include: Treatment Plan Selection. Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data
 Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
The In Vivo Kinetics of RNA Polymerase II Elongation during Co-Transcriptional Splicing
 The In Vivo Kinetics of RNA Polymerase II Elongation during Co-Transcriptional Splicing Yehuda Brody 1, Noa Neufeld 1, Nicole Bieberstein 2, Sebastien Z. Causse 3, Eva-Maria Böhnlein 2, Karla M. Neugebauer
The In Vivo Kinetics of RNA Polymerase II Elongation during Co-Transcriptional Splicing Yehuda Brody 1, Noa Neufeld 1, Nicole Bieberstein 2, Sebastien Z. Causse 3, Eva-Maria Böhnlein 2, Karla M. Neugebauer
Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder Labs August 30, 2012
 Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
Page 32 AP Biology: 2013 Exam Review CONCEPT 6 REGULATION
 Page 32 AP Biology: 2013 Exam Review CONCEPT 6 REGULATION 1. Feedback a. Negative feedback mechanisms maintain dynamic homeostasis for a particular condition (variable) by regulating physiological processes,
Page 32 AP Biology: 2013 Exam Review CONCEPT 6 REGULATION 1. Feedback a. Negative feedback mechanisms maintain dynamic homeostasis for a particular condition (variable) by regulating physiological processes,
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
A. Personal Statement
 NAME: Ravinder Singh BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Provide the following information for the Senior/key personnel and other significant contributors. Follow this format for each person. DO NOT EXCEED FIVE PAGES.
NAME: Ravinder Singh BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Provide the following information for the Senior/key personnel and other significant contributors. Follow this format for each person. DO NOT EXCEED FIVE PAGES.
Alternative Splicing and Genomic Stability
 Alternative Splicing and Genomic Stability Kevin Cahill cahill@unm.edu http://dna.phys.unm.edu/ Abstract In a cell that uses alternative splicing, the total length of all the exons is far less than in
Alternative Splicing and Genomic Stability Kevin Cahill cahill@unm.edu http://dna.phys.unm.edu/ Abstract In a cell that uses alternative splicing, the total length of all the exons is far less than in
The Alternative Choice of Constitutive Exons throughout Evolution
 The Alternative Choice of Constitutive Exons throughout Evolution Galit Lev-Maor 1[, Amir Goren 1[, Noa Sela 1[, Eddo Kim 1, Hadas Keren 1, Adi Doron-Faigenboim 2, Shelly Leibman-Barak 3, Tal Pupko 2,
The Alternative Choice of Constitutive Exons throughout Evolution Galit Lev-Maor 1[, Amir Goren 1[, Noa Sela 1[, Eddo Kim 1, Hadas Keren 1, Adi Doron-Faigenboim 2, Shelly Leibman-Barak 3, Tal Pupko 2,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region
 Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Transcription and chromatin. General Transcription Factors + Promoter-specific factors + Co-activators
 Transcription and chromatin General Transcription Factors + Promoter-specific factors + Co-activators Cofactor or Coactivator 1. work with DNA specific transcription factors to make them more effective
Transcription and chromatin General Transcription Factors + Promoter-specific factors + Co-activators Cofactor or Coactivator 1. work with DNA specific transcription factors to make them more effective
The RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain promotes splicing activation through recruitment of a U2AF65 Prp19 complex
 The RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain promotes splicing activation through recruitment of a U2AF65 Prp19 complex Charles J. David, 1 Alex R. Boyne, Scott R. Millhouse, 2 and James L. Manley 3 Department
The RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain promotes splicing activation through recruitment of a U2AF65 Prp19 complex Charles J. David, 1 Alex R. Boyne, Scott R. Millhouse, 2 and James L. Manley 3 Department
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone
 Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
Messenger RNA (mrna) is never alone mrna is coated and compacted by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), forming large messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mrnps). RBPs assemble on nascent and mature mrnas.
For all of the following, you will have to use this website to determine the answers:
 For all of the following, you will have to use this website to determine the answers: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast.cgi We are going to be using the programs under this heading: Answer the following
For all of the following, you will have to use this website to determine the answers: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast.cgi We are going to be using the programs under this heading: Answer the following
ChIP-seq data analysis
 ChIP-seq data analysis Harri Lähdesmäki Department of Computer Science Aalto University November 24, 2017 Contents Background ChIP-seq protocol ChIP-seq data analysis Transcriptional regulation Transcriptional
ChIP-seq data analysis Harri Lähdesmäki Department of Computer Science Aalto University November 24, 2017 Contents Background ChIP-seq protocol ChIP-seq data analysis Transcriptional regulation Transcriptional
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers.
 Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design
 Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
Alan Weiner BIOCHEM 530 Friday, MEB 248 October 23, 2015 RNA structure, the ribosome, structure-based drug design Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes RNA makes protein Crick's "Central Dogma"? DNA makes
'''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
 '''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Anggraini'Barlian,' Iriawa-' Tjandra'Anggraeni' SITH4ITB' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
'''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Anggraini'Barlian,' Iriawa-' Tjandra'Anggraeni' SITH4ITB' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015
 MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Problem 8 Problem 9 Problem 10 (14 points) (9 points) (10 points) (9 points) (5 points) (6 points) (7
MCB 102 Third Exam Spring 2015 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Problem 8 Problem 9 Problem 10 (14 points) (9 points) (10 points) (9 points) (5 points) (6 points) (7
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
