Human Anatomy. Brain and Cranial Nerves
|
|
|
- Steven Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Anatomy Brain and Cranial Nerves 1
2 Brain and Cranial Nerves An adult brain weighs between 1.35 and 1.4 kilograms (kg) (around 3 pounds) and has a volume of about 1200 cubic centimeters (cc). Brain size is not directly correlated with intelligence It is not the physical size of the brain that determines intelligence it is the number of active synapses. 15-2
3 The Brain s 4 Major Regions Cerebrum, the diencephalon, the brainstem, and the cerebellum. The cerebrum is divided into two halves, called the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere is subdivided into five functional areas called lobes. Outer surface of an adult brain exhibits folds called gyri (gyrus) and shallow depressions between those folds called sulci (sulcus). The brain is associated with 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 15-3
4 4
5 5
6 6
7 The Brain s 4 Major Regions Prosencephalon (forebrain) Telencephalon: cerebrum Diencephalon: epithalamus, thalamus,hypothalamus Mesencephalon (midbrain) Mesencephalon: cerebral peduncles, colliculi Rhombencephalon (hindbrain) Metencephalon: pons, cerebellum Myelencephalon: medulla oblongata 15-7
8 8
9 9
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 Organization of Brain Tissue Gray matter: motor neuron and interneuron cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals unmyelinated axons. White matter: composed primarily of myelinated axons. During brain development, an outer, superficial region of gray matter forms from migrating peripheral neurons. External sheets of gray matter, called the cortex, cover the surface of most of the adult brain (the cerebrum and the cerebellum)
14 Organization of Brain Tissue White matter lies deep to the gray matter of the cortex. Within the masses of white matter: discrete innermost clusters of gray matter called cerebral nuclei (or basal nuclei). are oval, spherical, or sometimes irregularly shaped clusters of neuron cell bodies
15 15
16 16
17 Support and Protection of the Brain The brain is protected and isolated by multiple structures: bony cranium Meninges: Protective connective tissue membranes surround and partition portions of the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) acts as a cushioning fluid. Blood-brain barrier: prevents entry of harmful materials from the bloodstream
18 Cranial Meninges Three dense regular connective tissue layers: separate the soft tissue of the brain from the bones of the cranium. Enclose and protect blood vessels that supply the brain. Contain and circulate cerebrospinal fluid. Parts of the cranial meninges form some of the veins that drain blood from the brain. From superficial to deep, the cranial meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid, and the pia mater
19 19
20 Dura Mater Tough membrane composed of two fibrous layers. Strongest of the meninges. Dura mater is composed of two layers. periosteal layer, the more superficial layer, attaches to the periosteum of the cranial bones meningeal layer lies deep to the periosteal layer The meningeal layer is usually fused to the periosteal layer Exception: in specific areas where the two layers separate to form large, blood-filled spaces called dural venous sinuses
21 Arachnoid Also called the arachnoid mater or the arachnoid membrane. Lies immediately internal to the dura mater. Partially composed of a delicate web of collagen and elastic fibers, termed the arachnoid trabeculae. Between the arachnoid and the overlying dura mater is the subdural space. Immediately deep to the arachnoid is the subarachnoid space
22 Pia Mater The innermost of the cranial meninges. Thin layer of delicate connective tissue that tightly adheres to the brain and follows every contour of the brain surface
23 23
24 Cranial Dural Septa The meningeal layer of the dura mater extends as flat partitions (septa) deep into the cranial cavity; at four locations called cranial dural septa. Membranous partitions separate specific parts of the brain and provide additional stabilization and support to the entire brain. falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli falx cerebelli diaphragma sellae 15-24
25 25
26 26
27 Brain Ventricles Cavities or expansions within the brain that are derived from the lumen (opening) of the embryonic neural tube. Continuous with one another as well as with the central canal of the spinal cord. Four ventricles in the brain. two lateral ventricles are in the cerebrum, separated by a thin medial partition called the septum pellucidum within the diencephalon is a smaller ventricle called the third ventricle each lateral ventricle communicates with the third ventricle through an opening called the interventricular foramen The fourth ventricle is located within the pons and cerebellum
28 28
29 29
30 Cerebrospinal Fluid A clear, colorless liquid that circulates in the ventricles and subarachnoid space. Bathes the exposed surfaces of the central nervous system and completely surrounds it. Performs several important functions. buoyancy protection environmental stability Formed by the choroid plexus in each ventricle. Produced by secretion of a fluid from the ependymal cells that originate from the blood plasma. Is similar to blood plasma
31 31
32 32
33 Blood-Brain Barrier Nervous tissue is protected from the general circulation by the blood-brain barrier. Strictly regulates what substances can enter the interstitial fluid of the brain. Prevents exposure of neurons in the brain to drugs, waste products in the blood, and variations in levels of normal substances (ions, hormones) that could adversely affect brain function
34 Blood-Brain Barrier Tight junctions prevent materials from diffusing across the capillary wall. Astrocytes act as gatekeepers that permit materials to pass to the neurons after leaving the capillaries. Is markedly reduced or missing in three distinct locations in the CNS: the choroid plexus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland
35 35
36 Cerebrum Account for 83% of brain mass Fissures deep grooves separate major regions of the brain Transverse fissure separates cerebrum and cerebellum Longitudinal fissure separates cerebral hemispheres Sulci grooves on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres Gyri twisted ridges between sulci Prominent gyri and sulci are similar in all people 15-36
37 Cerebrum Deeper sulci divide cerebrum into lobes Lobes are named for the skull bones overlying them Central sulcus separates frontal and parietal lobes Bordered by two gyri Precentral gyrus Postcentral gyrus Parieto-occipital sulcus Separates the occipital from the parietal lobe Lateral sulcus Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes Insula deep within the lateral sulcus 15-37
38 38
39 39
40 40
41 Cerebrum: functional areas Home of our conscious mind Enables us to: Be aware of ourselves and our sensations Initiate and control voluntary movements Communicate, remember, and understand 15-41
42 Cerebral cortex Composed of gray matter Neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, and short axons Folds in cortex triples its size Approximately 40% of brain s mass Brodmann areas 52 structurally distinct areas 15-42
43 Cerebrum 15-43
44 Functional areas of the cortex Three kinds of functional areas Motor areas Sensory areas Association areas 15-44
45 Motor areas Controls motor functions Primary motor cortex (somatic motor area) Located in precentral gyrus (Brodmann area 4) Pyramidal cells large neurons of primary motor cortex 15-45
46 Motor areas Corticospinal tracts descend through brainstem and spinal cord Axons signal motor neurons to control skilled movements Contralateral pyramidal axons cross over to opposite side of the brain 15-46
47 Motor areas Specific pyramidal cells control specific areas of the body Face and hand muscles controlled by many pyramidal cells Motor homunculus body map of the motor cortex 15-47
48 48
49 Sensory cortex Cortical areas involved in conscious awareness of sensation Located in parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes Distinct area for each of the major senses 15-49
50 Primary Somatosensory Cortex Located along the postcentral gyrus Corresponds to Brodmann areas 1-3 Involved with conscious awareness of general somatic senses Spatial discrimination precisely locates a stimulus 15-50
51 Primary Somatosensory Cortex Projection is contralateral Cerebral hemispheres Receive sensory input from the opposite side of the body Sensory homunculus a body map of the sensory cortex 15-51
52 52
53 Somatosensory Association Area Lies posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex Corresponds to Brodmann areas 5 and 7 Integrates different sensory inputs Touch, pressure, and others Draws upon stored memories of past sensory experiences 15-53
54 Sensory Areas Visual Areas Primary visual cortex Corresponds to Brodmann area 17 Located deep within the calcarine sulcus On the posterior and medial part of the occipital lobe Receives visual information that originates on the retina First of a series of areas that interprets visual input 15-54
55 Sensory Areas Visual Areas Visual association area Surrounds the primary visual area Coincides with Brodmann areas 18 and 19 Continues the processing of visual information Complex visual processing extends into: Temporal and parietal lobes 15-55
56 Sensory Areas Auditory Areas Primary auditory cortex Function conscious awareness of sound Location superior edge of the temporal lobe Corresponds to Brodmann areas 41 and
57 Sensory Areas Auditory Areas Auditory association area Lies posterior to the primary auditory cortex Located within Brodmann area 22 Permits evaluation of different sounds Lies in the center of Wernicke s area Involved in recognizing and understanding speech 15-57
58 Sensory Areas Gustatory Cortex Involved in the conscious awareness of taste stimuli Corresponds to Brodmann area 43 Located on the roof of the lateral sulcus 15-58
59 Sensory Areas Vestibular Cortex Located in the posterior part of the insula Deep to the lateral sulcus 15-59
60 Sensory Areas Olfactory Cortex Lies on the medial aspect of the cerebrum Located in a region called the piriform lobe Olfactory nerves transmit impulses to the olfactory cortex Provides conscious awareness of smells 15-60
61 Sensory Areas Olfactory Cortex Part of the rhinencephalon nose brain Includes the piriform lobe, olfactory tract, and olfactory bulb Connects the brain to the limbic system Explains why smells trigger emotions Orbitofrontal cortex Involved with consciously identifying and recalling specific smells 15-61
62 Association areas Make associations between different types of sensory information Associate new sensory input with memories of past experiences New name for association areas higher order processing areas 15-62
63 Association Areas Prefrontal Cortex Large region of the frontal lobe anterior to motor areas Performs cognitive functions All aspects of thinking and perceiving Remembering and recalling information Also related to mood Has close links to the limbic part of the forebrain 15-63
64 Association Areas Prefrontal Cortex Functional neuroimaging techniques Reveal functions of specific parts of the prefrontal cortex Anterior pole of frontal cortex Active in solving the most complex problems The farther rostrally one goes in the CNS, the more complex the neural functions 15-64
65 Association Areas Prefrontal Cortex Functional areas located on the medial side of the frontal lobe Regions anterior to the corpus callosum Involved in complex personal and social interactions Regions superior to the corpus callosum Involved in mentalization 15-65
66 Association Areas General Interpretation Area Function is currently under investigation Located at the interface of: The visual, auditory, and somatosensory association areas Newer studies show most of this region is involved in the visual processing of spatial relationships 15-66
67 Association Areas Language Area Surrounds the lateral sulcus in the left cerebral hemisphere Five parts have been identified Broca s area speech production Wernicke s area speech comprehension Lateral prefrontal cortex conceptual analysis of spoken words 15-67
68 Association Areas Language Area Five parts have been identified (continued) Most of the lateral and inferior temporal lobe Coordination of auditory and visual aspects of language Parts of the insula Initiation of word articulation Recognition of rhymes and sound sequences 15-68
69 Association Areas Insula Functions of its cortex not well understood Some parts function in language and the sense of balance Other parts visceral function Conscious perception of: Upset stomach Full bladder Some aspects of the sense of smell 15-69
70 Lateralization of Cortical Functioning The two hemispheres control opposite sides of the body Hemispheres are specialized for different cognitive functions 15-70
71 Lateralization of Cortical Functioning Left cerebral hemisphere more control over: Language abilities, math, and logic Right cerebral hemisphere more involved with: Visual-spatial skills Reading facial expressions Intuition, emotion, artistic and musical skills 15-71
72 Cerebral White Matter Different areas of the cerebral cortex communicate: With each other With the brainstem and spinal cord Fibers are usually myelinated and bundled into tracts 15-72
73 Cerebral White Matter Types of tracts Commissures composed of commissural fibers Allows communication between cerebral hemispheres Corpus callosum the largest commissure Association fibers Connect different parts of the same hemisphere 15-73
74 74
75 75
76 Cerebral White Matter Types of tracts (continued) Projection fibers run vertically Descend from the cerebral cortex Ascend to the cortex from lower regions 15-76
77 77
78 Projection tracts Internal capsule projection fibers form a compact bundle Passes between the thalamus and basal nuclei Corona radiata superior to the internal capsule Fibers run to and from the cerebral cortex 15-78
79 Basal nuclei A group of nuclei deep within the cerebral white matter Caudate nucleus arches over the thalamus Lentiform nucleus lens shaped Amygdala sits on top of the caudate nucleus Functionally belongs with the limbic system 15-79
80 Basal nuclei Lentiform nucleus Divided into two parts Globus pallidus Putamen 15-80
81 81
82 82
83 Basal nuclei Cooperate with the cerebral cortex in controlling movements Receive input from many cortical areas Evidence shows that they: Start, stop, and regulate intensity of voluntary movements In some way estimate the passage of time 15-83
84 The Diencephalon Forms the center core of the forebrain Surrounded by the cerebral hemispheres Composed of three paired structures: Thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus Border the third ventricle Primarily composed of gray matter 15-84
85 The Thalamus Makes up 80% of the diencephalon Contains approximately a dozen major nuclei Send axons to regions of the cerebral cortex Nuclei act as relay stations for incoming sensory messages 15-85
86 86
87 87
88 The Thalamus Afferent impulses converge on the thalamus Synapse in at least one of its nuclei Is the gateway to the cerebral cortex Nuclei organize and amplify or tone down signals 15-88
89 The Diencephalon The Hypothalamus Lies between the optic chiasm and the mammillary bodies Pituitary gland projects inferiorly Contains approximately a dozen nuclei Main visceral control center of the body 15-89
90 The Hypothalamus Functions include the following: Control of the autonomic nervous system Control of emotional responses Regulation of body temperature Regulation of hunger and thirst sensations Control of behavior Regulation of sleep-wake cycles Control of the endocrine system Formation of memory 15-90
91 91
92 The Diencephalon The Epithalamus Forms part of the roof of the third ventricle Consists of a tiny group of nuclei Includes the pineal gland (pineal body) Secretes the hormone melatonin Under influence of the hypothalamus 15-92
93 93
94 The Brain Stem Includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata Several general functions Produces automatic behaviors necessary for survival Passageway for all fiber tracts running between the cerebrum and spinal cord Heavily involved with the innervation of the face and head 10 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves attach to it 15-94
95 The Brain Stem The Midbrain Lies between the diencephalon and the pons Central cavity the cerebral aqueduct Cerebral peduncles located on the ventral surface of the brain Contain pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts Superior cerebellar peduncles Connect midbrain to the cerebellum 15-95
96 96
97 The Brain Stem The Midbrain Periaqueductal gray matter surrounds the cerebral aqueduct Involved in two related functions Fright-and-flight reaction Mediates response to visceral pain 15-97
98 98
99 The Brain Stem The Midbrain Corpora quadrigemina the largest nuclei Divided into the superior and inferior colliculi Superior colliculi nuclei that act in visual reflexes Inferior colliculi nuclei that act in reflexive response to sound 15-99
100 100
101 The Brain Stem The Midbrain Imbedded in the white matter of the midbrain Two pigmented nuclei Substantia nigra neuronal cell bodies contain melanin Functionally linked to the basal nuclei Red nucleus lies deep to the substantia nigra Largest nucleus of the reticular formation
102 102
103 The Brain Stem The Pons Located between the midbrain and medulla oblongata Contains the nuclei of cranial nerves V, VI, and VII Two general groups of cranial nerve nuclei Motor nuclei Sensory nuclei
104 104
105 105
106 The Brain Stem The Medulla Oblongata Most caudal level of the brain stem Continuous with the spinal cord Choroid plexus lies in the roof of the fourth ventricle Pyramids of the medulla lie on its ventral surface Decussation of the pyramids crossing over of motor tracts Cranial nerves VIII XII attach to the medulla
107 The Brain Stem The Medulla Oblongata The core of the medulla contains: Much of the reticular formation Nuclei influence autonomic functions Visceral centers of the reticular formation include: Cardiac center Vasomotor center The medullary respiratory center Centers for hiccupping, sneezing, swallowing, and coughing
108 108
109 109
110 The Cerebellum Located dorsal to the pons and medulla Smoothes and coordinates body movements Helps maintain equilibrium
111 The Cerebellum Consists of two cerebellar hemispheres Surface folded into ridges called folia Separated by fissures Hemispheres each subdivided into: Anterior lobe Posterior lobe
112 112
113 The Cerebellum Composed of three regions Cortex gray matter Internal white matter Deep cerebellar nuclei deeply situated gray matter Cerebellum must receive information On equilibrium On current movements of limbs, neck, and trunk From the cerebral cortex
114 The Cerebellum Cerebellar Peduncles Fibers to and from the cerebellum are ipsilateral Run to and from the same side of the body Thick tracts connecting the cerebellum to the brain stem Superior cerebellar peduncles Middle cerebellar peduncles Inferior cerebellar peduncles
115 115
116 Functional Brain Systems Networks of neurons functioning together The limbic system spread widely in the forebrain The reticular formation spans the brain stem
117 Functional Brain Systems The Limbic System Location Medial aspect of cerebral hemispheres Also within the diencephalon Composed of: Septal nuclei, cingulate gyrus, and hippocampal formation Part of the amygdala The fornix and other tracts link the limbic system together
118 118
119 Functional Brain Systems The Limbic System The emotional brain Cingulate gyrus Allows us to shift between thoughts Interprets pain as unpleasant Hippocampal formation Hippocampus and the parahippocampal gyrus
120 Functional Brain Systems The Reticular Formation Runs through the central core of the medulla, pons, and midbrain Forms three columns Midline raphe nuclei Medial nuclear group Lateral nuclear group
121 Functional Brain Systems The Reticular Formation
122 Functional Brain Systems The Reticular Formation Widespread connections Ideal for arousal of the brain as a whole Reticular activating system (RAS) Maintains consciousness and alertness Functions in sleep and arousal from sleep
123 Functional Brain Systems The Reticular Formation
124 124
125 125
126 126
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Brain. Brain. Spinal Cord. Cauda Equina
 The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head
 CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head Highest level reached in human brain 1 Mostly to orient
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head Highest level reached in human brain 1 Mostly to orient
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 13
 I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System 1 The Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Components 2 Protection of the Brain The brain is protected from injury by The skull enough said! You already know this. What else
The Central Nervous System 1 The Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Components 2 Protection of the Brain The brain is protected from injury by The skull enough said! You already know this. What else
Embryonic Brain Development
 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain. MDL231 Principle of Anatomy
 Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory.
 Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
Anatomy of the Human Brain
 Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline *
 Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 12.1 Overview of the Central Nervous System (Figures 12.1, 12.2, 12.3) A. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the and, and is involved
Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 12.1 Overview of the Central Nervous System (Figures 12.1, 12.2, 12.3) A. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the and, and is involved
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal
 I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally
 KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg Three Main Regions of the Brain. Forebrain
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Divisions of the Nervous System
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Lecture 19 1 Divisions of the Nervous System You are here CNS PNS 3 Brain Embryology & Overview Table & Figure From:
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Lecture 19 1 Divisions of the Nervous System You are here CNS PNS 3 Brain Embryology & Overview Table & Figure From:
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Page. Ch 11 A CNS. This set. Major Landmarks: Brain size is proportional to body size only and can be divided into three major portions;
 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 11 A CNS This set Ch 11 B Notes: PNS Somatic ANS Ch 11 C ANS Dr. Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 11 A CNS This set Ch 11 B Notes: PNS Somatic ANS Ch 11 C ANS Dr. Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Gross Morphology of the Brain
 Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
8.3 The Central Nervous System. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
Protection of the Brain. Overview of the Brain. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober. Chapter 13. Lecture 20
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Note to Self. The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Organization of the Brain
 Note to Self Despite what you think you can get through this chapter in 1 class period, or one with only a few slides left over The Brain and Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Organization of the Brain The brain
Note to Self Despite what you think you can get through this chapter in 1 class period, or one with only a few slides left over The Brain and Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Organization of the Brain The brain
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
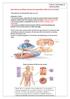 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Unit 3 : Nervous System
 Unit 3 : Nervous System Mind Map Structural Classification The nervous Tissue Disorders of The nervous system Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System The brain Spinal Cord Sensory
Unit 3 : Nervous System Mind Map Structural Classification The nervous Tissue Disorders of The nervous system Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System The brain Spinal Cord Sensory
PET Scans. External Appearance. The Brain: Anatomy & Functions. Cerebral Hemispheres
 PET Scans The Brain: Anatomy & Functions Click for PET Scan video Cerebral Hemispheres External Appearance a pattern of ridges and shallow grooves ridges - gyri (sing. gyrus) grooves - sulci (sing. sulcus)
PET Scans The Brain: Anatomy & Functions Click for PET Scan video Cerebral Hemispheres External Appearance a pattern of ridges and shallow grooves ridges - gyri (sing. gyrus) grooves - sulci (sing. sulcus)
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
The Nervous System. Lab Exercise 29. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Nervous System Objectives -You should be able to recognize a neuron and identify its components. - Be able to identify the principal components of the brain and be able to name at least
Lab Exercise The Nervous System Objectives -You should be able to recognize a neuron and identify its components. - Be able to identify the principal components of the brain and be able to name at least
Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain
 Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain An avg. human brain weighs 1.4 kg (3lbs.) and has a volume of 1200 cc brains average about 10% bigger than
Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain An avg. human brain weighs 1.4 kg (3lbs.) and has a volume of 1200 cc brains average about 10% bigger than
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
Stanley Pruisinger 1980's
 Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES NERVOUS SYSTEM TISSUES: HISTOLOGY SLIDES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
BIO 210 CHAPTER 13. The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2. PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM
 BIO 210 CHAPTER 13 The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2 PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM Second Largest Division of the Brain Lies Below the Posterior Portion of
BIO 210 CHAPTER 13 The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2 PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM Second Largest Division of the Brain Lies Below the Posterior Portion of
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
A recap of the Brain- Bio 230
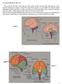 A recap of the Brain- Bio 230 This recap of the brain is to help you make sense of that 3 pound tofu blob that you carry around everyday. My hope is that if you get these basics, you can build and add
A recap of the Brain- Bio 230 This recap of the brain is to help you make sense of that 3 pound tofu blob that you carry around everyday. My hope is that if you get these basics, you can build and add
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 12.3 Using Figure 12.3, match the following: 1) Site of efferent soma. 2) Site of axons
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 12.3 Using Figure 12.3, match the following: 1) Site of efferent soma. 2) Site of axons
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU
 If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
