action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
|
|
|
- Emma Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses toward the central nervous system; initiates nerve impulses following receptor stimulation. arachnoid Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. astrocytes CNS cells responsible for physical support and maintaining blood brain barrier autonomic nervous system Efferent division of the peripheral nervous system that innervates cardiac and smooth muscles and glands; also called the involuntary or visceral motor system.
2 axon bipolar neurons blood brain barrier brain stem Neuron process that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body; efferent process; the conducting portion of a nerve cell. neuron with 2 processes extending for it's cell body-- one axon, one dendrite; common in sensory systems Mechanism that inhibits passage of materials from the blood into brain tissues; reflects relative impermeability of brain capillaries. The part of the brain composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata and connecting the spinal cord with the forebrain and cerebrum. cerebral spinal fluid a fluid produced by the choroid plexus within the ventricular system of the brain
3 depolarization Loss of a state of polarity; loss or reduction of negative membrane potential. diencephalon Composed of the epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus; begins where midbrain ends dura mater Outermost and toughest of the three membranes (meninges) covering the brain and spinal cord. efferent neurons neurons that conduct impulses away from the central nervous system. ependymal cells Line cavities of brain and spinal cord; secrete and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
4 gray matter Gray area of the central nervous system; contains cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers of neurons. hypothalamus a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion interneuron neuron neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and motor neuron; also called association neurons Meissner's corpuscle A sensory receptor located in the dermis of the skin, which is sensitive fine touch. microglia are phagocytes, destroys and breaks down damaged cells
5 myelin Fatty insulating sheath that surrounds all but the smallest nerve fibers. neuroglia Nonexcitable cells of neural tissue that support, protect, and insulate the neurons. neuron Cell of the nervous system specialized to generate and transmit nerve impulses. nuclei collections of nerve cell bodies inside the central nervous system oligodendrocytes a cell that holds nerve fibers together and produces the myelin sheath around axons in the central nervous system
6 Pacinian corpuscle a type of nerve ending located in the subcutaneous layer that is sensitive to pressure parasympathetic nervous system the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy; rest and digest response peripheral nervous system cranial and spinal nerves that extend beyond the CNS proprioceptors Receptor located in a joint, muscle, or tendon; concerned with locomotion, posture and muscle tone. reflex Automatic reaction to stimuli.
7 repolarization Movement of the membrane potential to the initial resting (polarized) state. saltatory conduction Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelinsheathed regions of membrane. Schwann cells somatic nervous system subarachnoid space Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin. Division of the peripheral nervous system that provides the motor innervation of skeletal muscles; also called the voluntary nervous system. a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
8 sympathetic nervous system A subdivision of the autonomic nervous system that activates nerves, glands and visceral muscles in times of stress or threat; fight or flight response synaptic cleft The gap between two communicating neurons thalamus the structure of the brain that relays messages from the sense organs to the cerebral cortex tract A collection of nerve fibers in the central nervous system having the same origin, termination, and function. white matter located in the CNS; myelinated axons in bundles (tracts) with few cell bodies
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Structural Organization of Nervous System
 Nervous System Structural Organization of Nervous System Myelinated Neuron Myelin White, fatty material which covers nerve fibers(axons) Protects and insulates fiber Increases the rate of transmission
Nervous System Structural Organization of Nervous System Myelinated Neuron Myelin White, fatty material which covers nerve fibers(axons) Protects and insulates fiber Increases the rate of transmission
sensory input receptors integration Human Anatomy motor output Ch. 7 effectors Structural classification
 Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
The Nervous System 7PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
Meyers' A&P February 15, Unit 7. The Nervous System. I. Functions of the Nervous System. Monitors body's internal and external enviornments
 Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
The Nervous System & Nervous tissue. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Nervous System & Nervous tissue Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of the Nervous System 1. Nervous system and endocrine system are the chief control centers in maintaining body homeostasis. 2. Nervous
The Nervous System & Nervous tissue Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of the Nervous System 1. Nervous system and endocrine system are the chief control centers in maintaining body homeostasis. 2. Nervous
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue. Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells. The Nervous System. The Nervous System 21/12/2010
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
Unit 3 : Nervous System
 Unit 3 : Nervous System Mind Map Structural Classification The nervous Tissue Disorders of The nervous system Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System The brain Spinal Cord Sensory
Unit 3 : Nervous System Mind Map Structural Classification The nervous Tissue Disorders of The nervous system Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System The brain Spinal Cord Sensory
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Nervous System. Basic Divisions of the Nervous System C H A P T E R 12.
 C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
The Nervous System. Chapter 7. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Elaine N. Marieb. Seventh Edition
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 7 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 7 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2
 NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Nervous System. Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson
 Nervous System Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 2 Types of cells in the nervous system: Neurons & Neuroglial cells Neuroglial (aka glial) cells perform functions that are vital to neurons by filling
Nervous System Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 2 Types of cells in the nervous system: Neurons & Neuroglial cells Neuroglial (aka glial) cells perform functions that are vital to neurons by filling
Bell Work. Materials Needed: writing utensil and A&P book. Quietly pick up a Lesson 6.5 worksheet from the back table and work on it independently.
 Bell Work Materials Needed: writing utensil and A&P book Quietly pick up a Lesson 6.5 worksheet from the back table and work on it independently. The Nervous System ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Overview Controls
Bell Work Materials Needed: writing utensil and A&P book Quietly pick up a Lesson 6.5 worksheet from the back table and work on it independently. The Nervous System ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Overview Controls
! BIOL 2401! Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY
 Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which part of a neuron receives an impulse
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which part of a neuron receives an impulse
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 7. The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. This figure depicts a typical neuron. What structures
BIO 115 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 4: The Nervous System & The Senses This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. This figure depicts a typical neuron. What structures
Nervous System. Lesson 11
 Nervous System Lesson 11 Reflex Arcs 1. Patellar reflex Causes leg to kick up 2. Achilles reflex Causes foot to jerk forward 3. Triceps reflex Causes arm to straighten 4. Babinski reflex 4. Pupil Dilation
Nervous System Lesson 11 Reflex Arcs 1. Patellar reflex Causes leg to kick up 2. Achilles reflex Causes foot to jerk forward 3. Triceps reflex Causes arm to straighten 4. Babinski reflex 4. Pupil Dilation
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Collin County Community College BIOL Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Chapter 7 The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System Fxns of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor Δs occurring inside and outside the body (Δs = stimuli) 2. Integration to process and interpret
Chapter 7 The Nervous System Fxns of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor Δs occurring inside and outside the body (Δs = stimuli) 2. Integration to process and interpret
Unit 2 Notes: Cells & Organization
 Unit 2 Notes: Cells & Organization (1) Neurons A neuron is a nerve cell. There are 2 types of neurons: Multipolar and Unipolar Every neuron has the same structural parts: Dendrites Receive incoming messages.
Unit 2 Notes: Cells & Organization (1) Neurons A neuron is a nerve cell. There are 2 types of neurons: Multipolar and Unipolar Every neuron has the same structural parts: Dendrites Receive incoming messages.
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System. Total 33 points
 Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS
 Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet
 The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s
 Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
II. Nervous System (NS) Organization: can be organized by location/ structure or by function A. Structural Organization 1. Central N.S.
 Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Nerve Cell Flashcards
 1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
The Nervous System An overview
 Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Dispose of debris Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Ependymal cells Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord Circulate cerebrospinal fluid Nervous
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory
48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells
 48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells 48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes
48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells 48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
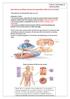 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1
 Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1 I. Unit 7: The Nervous System A. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input - gathering information a) To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body b) Changes
Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1 I. Unit 7: The Nervous System A. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input - gathering information a) To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body b) Changes
Nervous System CHAPTER 9. Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc.
 Nervous System CHAPTER 9 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. Neurons and Supporting Cells Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. 2 Communication and Control Systems nervous system endocrine system uses chemicals
Nervous System CHAPTER 9 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. Neurons and Supporting Cells Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. 2 Communication and Control Systems nervous system endocrine system uses chemicals
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system)
 Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology
 BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
Organiza?on of the nervous system. Organiza?on of the nervous system. BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 8 The Nervous System. I. CNS (Central Nervous System)
 BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 8 The Nervous System Organiza?on of the nervous system I. CNS (Central Nervous System) brain and spinal cord: central command center integrates and coordinates all voluntary and
BIOL 164 Human Biology Ch 8 The Nervous System Organiza?on of the nervous system I. CNS (Central Nervous System) brain and spinal cord: central command center integrates and coordinates all voluntary and
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1).
 1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
D) around, bypassing B) toward
 Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Functions of Nervous System Neuron Structure
 Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Somatic (SNS) - Fibers send impulses from CNS to control voluntary action of skeletal muscle. impulses from visceral organs to the CNS
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The master controlling and communicating system of the body --- cells communicate via electrical and chemical signals. Signals are rapid, specific and cause almost immediate responses. Functions
NERVOUS SYSTEM The master controlling and communicating system of the body --- cells communicate via electrical and chemical signals. Signals are rapid, specific and cause almost immediate responses. Functions
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION STRUCTURE AND DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major functions of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM a memory (the smell of a meal), or it could be discarded
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major functions of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM a memory (the smell of a meal), or it could be discarded
The Nervous System. Chapter 9
 The Nervous System Chapter 9 Objectives To identify the basic structure of a neuron. To explain the main components of the nervous system. To compare and contrast the central nervous system and the peripheral
The Nervous System Chapter 9 Objectives To identify the basic structure of a neuron. To explain the main components of the nervous system. To compare and contrast the central nervous system and the peripheral
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Man and his environment
 Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Efferent or Motor Division. Afferent or Sensory Division
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The master controlling and communicating system of the body --- cells communicate via electrical and chemical signals. Signals are rapid, specific and cause almost immediate responses. Functions
NERVOUS SYSTEM The master controlling and communicating system of the body --- cells communicate via electrical and chemical signals. Signals are rapid, specific and cause almost immediate responses. Functions
