Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor
|
|
|
- Clyde Wells
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu Ding 5 Abstract- Brain abscesses and brain tumors may have similar clinical presentations. For example, only 50% brain abscess patients have fever, which could be masked by corticosteroid therapy. Also, the differential diagnosis of brain abscesses versus cystic or necrotic tumors may be difficult based on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) imaging findings. However, the strategies of management for abscess and neoplasm are very different, and it is especially imperative to have a correct diagnosis before any surgical intervention of cystic brain lesions. The MR special techniques, e.g. diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and proton (1H) MR spectroscopy, are useful as additional diagnostic modalities for differentiating brain abscesses from cystic or necrotic brain tumors. DWI shows high signal intensity in most cases of pyogenic abscesses and low signal intensity in most cases of cystic or necrotic tumors. MR spectroscopy shows characteristic metabolites in pyogenic abscesses, distinct from those in cystic or necrotic tumors. Key Words: Brain abscess, Brain tumor, Diffusion MR imaging, MR spectroscopy Acta Neurol Taiwan 2004;13: INTRODUCTION Differentiation between brain abscesses and cystic or necrotic tumors with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) imaging may be difficult. Difficulties in the diagnosis of intracranial abscess are mainly due to the combination of nonspecific clinical findings and possible similarities in the radiological appearances of cystic gliomas, metastases, and brain abscesses (1). With conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), typical brain abscess has low signal intensity on T1-weighted images, high signal intensity on T2-weighted images, and ring enhancement after contrast medium administration. However, cystic or necrotic brain tumors may have very similar pictures, making the differential diagnosis difficult. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and proton (1H) MR spectroscopy (MRS) are results of recent progress in MR technique, and could serve as useful diagnostic modalities for between brain abscesses and cystic or necrotic brain tumors. We would divide the following discussion into three parts: (a) DWI of Pyogenic Brain From the Departments of 1 Radiology 2 Neurosurgery, and 3 Neurology, Veterans General Hospital-Kaohsiung, 4 National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan; 5 Department of Chemistry, National Sun Yat-Sen University, Taiwan. Received May 17, Revised and Accepted July 18, Reprint requests and correspondence to: Ping-Hong Lai, MD. Department of Radiology, Veterans General Hospital- Kaohsiung, No. 386, Ta-Chung 1st Road., Kaohsiung, Taiwan. phlai@isca.vghks.gov.tw
2 108 Abscesses and Necrotic Brain Tumors; (b) 1H MRS of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses and Necrotic Brain Tumors; and (c) DWI vs. 1H MRS of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses and Necrotic Brain Tumor. DWI of pyogenic brain abscesses and necrotic brain tumors DWI provides a unique way to evaluate the diffusion properties of water molecules in tissue (Brownian motion), and has been demonstrated to be useful in the diagnosis and treatment of ischemia, tumors, epilepsy and white matter disorders (2). Application of DWI in the differential diagnosis between brain abscess and cystic or necrotic brain tumors has been well documented in the literature (3-10). In 1996, Ebisu et al. (3) first reported a case of brain abscess with high signal intensity on DWI and a low ADC value. The pus itself (verified by aspiration) could account for the restricted diffusion and therefore high DWI signal intensity (Fig. 1). The other studies showed very similar or the same results (4-12). The low ADC values for pyogenic abscesses varied (5-10). The variation might be ascribable to differences in the concentration of inflammatory cells, the necrotic tissue debris and bacteria, and the viscosity of the abscess fluid. These differences may be in turn related to the age of the abscess, the causative organism, and the host s immune responses (5-10). The signal intensity of pyogenic brain abscess on DWI is not always high, and the ADC value could be higher than that of the normal brain parenchyma. Krabbe et al. (13) reported a cerebral abscess with a high ADC value, but did not mention the signal intensity on DWI. The explanation for this might be the partial volume effect proposed by Desprechins et al. (6). Guo et al. (14) reported two small cerebral abscesses (mean area of 90 mm 2 ) with high signal on DWI but ADC values similar to that of normal parenchyma (the ADC ratios were 1.01 and 1.03). This similarity was postulated to be due to a partial volume effect or to intrinsic differences in diffusion properties of the smaller abscesses. However, signal intensity on DWI was high and ADC value was low regardless of the lesion size, and these results were supposed to have improved in-plane resolution (8). All tumors showed low signal intensities on DWI in the cystic or necrotic area, and their cystic or necrotic areas had high ADC values [ (2-10,13,15) -Fig. 2]. However, contradictory DWI findings of cystic or necrotic tumors do exist in the literature (7,8,16). Park et al. reported two cases of cystic or necrotic brain metastasis with markedly high signal intensity on DWI, with surgical findings showing that the cyst had a thick and creamy necrotic content similar to pus (7). Chang et al. reported a ringenhanced fibrillary low-grade astrocytoma with high signal intensity on DWI and a low ADC value, mimicking that of abscesses, and viscous creamy fluid within the tumor was found at surgery (8). Holtas et al. reported a ring-enhanced brain metastatsis with hyperintensity on DWI and a low ADC value in the necrotic part of the tumor. The reason for restricted diffusion was possibly due to early necrosis with intracellular edema of the lesion (16). In summary, DWI may be a much more valuable diagnostic tool in the differential diagnosis between brain abscesses and cystic or necrotic brain tumors than conventional MRI. However, there are some conflicting DWI reports in the literature, and we still need to be cautious about making the diagnosis with DWI findings. 1H MRS of pyogenic brain abscess and necrotic brain tumors Findings from several studies have suggested that in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS), a non-invasive examination, might contribute to the establishment of the differential diagnosis between brain tumors and abscesses (17-29). The predominant resonance lines (N-acetyl-aspartate, choline, and creatine/phosphocreatine) that are usually observed in the parenchyma of the normal brain were hardly detectable in either tumor or abscess necrosis. The main characteristic features of pyogenic abscesses were the resonances of amino acids (valine, leucine, and isoleucine) (0.9 ppm), acetate (1.9 ppm), alanine (1.5 ppm), lactate (1.3 ppm), and succinate (2.4 ppm) (Fig. 1). In contrast, Spectra in patients with cystic or necrotic tumor showed only the peak attributed to lactate (1.3 ppm) (Fig. 2). Lipid ( ppm) may also be found in patients with a tumor. Lactate and lipids are nonspecific metabolites pro-
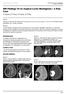
3 109 A B C D Ac Suc Lac AA Ala Chemical shift (ppm) Figure 1. A 58-year-old man with surgically proven pyogenic brain abscess in the right parietal lobe. (A) Axial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (500/30[TR/TE]) MR image shows a ring-shape cystic lesion and surrounding edema. The cm voxel (box) in the center of the lesion represents the 1H-MRS volume of interest. (B) Diffusion-weighted image (10,000/93; b = 1000 s/mm 2 ) shows markedly hyperintensity in the abscess cavity and isointensity surrounding the edema. (C) Apparent diffusion coefficient map reveals hypointensity in the abscess cavity, indicating restricted diffusion and hyperintense areas surrounding the edema. (D) In vivo 1H spectrum (2000/270) from the abscess cavity shows resonances representing succinate (Suc) at 2.4 ppm, acetate (Ac) at 1.9 ppm, alanine (Ala) at 1.5 ppm, lactate (Lac) at 1.3 ppm, and the other amino acids (AA) at 0.9 ppm. duced by anaerobic glycolysis and necrotic brain tissue in brain abscesses. Both lactate and lipids peaks can also be observed in necrotic tumors (19,20,22-25). Increases in acetate and succinate presumably originate from the enhanced glycolysis and fermentation by the infecting microorganisms (19-26). Amino acids such as valine and leucine are probably end products of proteolysis by enzymes released from neutrophils in pus (19-26). Discrimination between amino acids (i.e., valine, leucine, and isoleucine at 0.9 ppm) and lipid (at 0.8 to 1.2 ppm) is important. Lipid signals may exist in both brain tumors and abscesses, whereas amino acids are not seen in proton MR spectra of brain tumors in vivo and are only detectable in vitro (21). It is known that with an echo time of 135, phase inversion occurs as a result of J- coupling between lactate and amino acids, but not in lipid, a feature which may be helpful in differential diagnosis between brain abscess and tumor (19,22). The findings of lactate and lipid peaks after long term treatment with antibiotics may become nonspecific and thus can be easily missed in patients with cystic or necrotic tumors (25,27-29). Dev et al. demonstrated a decline of the acetate and pyruvate in 5 patients after 1 week of aspiration and medical treatment. The authors proposed that the disappearance of metabolites of bacterial origin might suggest a positive response to therapy (25).
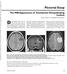
4 110 A B C D Lac Chemical shift (ppm) Figure 2. A 65-year-old man with a pathologically proven left frontoparietal lobe metastasis from primary lung adenocarcinoma. (A) Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (500/30) MR image shows a ring-enhanced lesion in left frontoparietal lobe. The cm voxel (box) in the center of the lesion represents the 1H-MRS volume of interest. (B) Diffusion-weighted image (10,000/93; b = 1000 s/mm 2 ) shows markedly low signal intensity in the necrotic part of the tumor. (C) Apparent diffusion coefficient map reveals high signal intensity in the necrotic part of the tumor that is similar to cerebrospinal fluid, indicatin marked diffusion. (D) In vivo 1H spectrum (2000/270) from the necrotic center of the tumor shows a lactate (Lac) peak at 1.3 ppm. Burtscher et al. also showed dramatic changes in the follow-up MR spectroscopy of abscesses 29 and 113 days after the beginning antibiotic treatment. All resonances (representing succinate, acetate, alanine, and amino acids) except that of lactate disappeared (27). The fact that these spectral changes disappear with effective antibiotic treatment, as shown in previous studies (25,27-29), underlines the need for 1) the neuroradiologist or spectroscopist interpreting the spectra to be aware of the case history and 2) the MR spectroscopic examinations to be performed as early as possible, preferably before the start of antibiotic therapy. Knowledge of the expected spectral changes after treatment also offers the possibility of evaluating the efficacy of nonsurgical treatment of brain abscesses. Further prospective studies with a large number of cases will be necessary for thorough evaluation of particular spectral peaks and time courses of the spectral changes with antibiotic treatment. In recent studies, it is possible to differentiate anaerobic from aerobic brain abscesses on the basis of metabolite patterns observed on in vivo 1H MRS (30,31). The spectral metabolite pattern of the lactate, amino acids, alanine, acetate, and succinate would suggest an obligate anaerobic or a mixture of obligate and facultative anaerobic abscess. On the other hand, the lack of acetate and succinate signal would suggest an obligate
5 111 aerobic or a facultative anaerobic abscess. This information may be useful for a timely and appropriate treatment of the abscesses. Compared with the in vivo spectra, a number of additional resonance peaks of lysine at 1.73 and 3.0 ppm, of glutamate/glutamine at ppm, of taurine at 3.24 and 3.42 ppm, of glycine at 3.55 ppm; and of the other amino acids at 3.75 ppm could be observed on the in vitro one-dimensional single-pulse or spin echo spectrum, and in the two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy 1H MR spectra (19,23,30,31). It is noteworthy that the in vitro measurements may offer complementary information that cannot be extracted from in vivo MRS spectra. DWI vs. 1H MRS of pyogenic brain abscess and necrotic brain tumor DWI is a more practical and accurate method compared with 1H MRS (28). There are several reasons for this conclusion. First, DWI scan time is very short (about 40 sec), whereas MR spectroscopy takes a much longer scan time. Single-voxel 1H MRS takes around several minutes and 2D chemical shift imaging takes about 10 minutes according to the repetition time, excitation number, etc. DWI thus is more practical in clinical use, especially in emergent conditions. Second, single-voxel 1H MRS is more limited in voxel size (roughly cm to cm) than DWI, and the smaller lesion in MRS will be more affected by the partial volume effect. This is true even in chemical shift imaging, although 2D chemical shift imaging may have a smaller voxel than the single-voxel technique in the case of small lesions. In any case it is likely that 2D chemical shift imaging would still be more time consuming. If the lesion is located peripherally, images of the lesion produced by either single-voxel MRS or 2D chemical shift imaging might be contaminated by the signals from the fat close-by. Third, the treated pyogenic abscess may have high signal on DWI, whereas MR spectroscopic examination shows only lactate/lipid peaks (no amino acid peak [end-products of bacterial breakdown]), a spectrum the same as what is found in necrotic tumor. Nevertheless, there are some advantages of 1H MRS. First, 1H MRS may provide valuable information on the changes of metabolites after nonsurgical treatment of brain abscesses, and may thus helpful for the evaluation of the efficacy of antimicrobial therapy (25,27-29). Second, 1H MRS may differentiate anaerobic from aerobic brain abscesses on the basis of metabolite patterns (30,31). This would be an important information for prompt and appropriate treatment of patients with brain abscesses. In summary, DWI and 1H MRS are useful tools for the differential diagnosis between brain abscesses and cystic or necrotic brain tumors. The combination of DWI and 1H MRS modalities may provide a more accurate diagnosis of brain abscesses and cystic or necrotic brain tumors than the use of only a single modality. CONCLUSION The MR special techniques, e.g. DWI and 1H MRS, are useful tools for the differential diagnosis between brain abscesses and cystic or necrotic brain tumors. Moreover, it is possible to differentiate anaerobic from aerobic brain abscesses based on the metabolite patterns on the in vivo 1H MRS. Further studies should evaluate the possibility of the detection of the overlapped metabolites that cannot be differentiated with one-dimensional localized spectroscopy. Probably one may be able to subcategorize these abscesses in the future with the application of two-dimensional or three-dimensional localized in vivo spectroscopy. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS National Science Council NSC B-075B- 003 (PHL) and NSC B-075B-010 [RG3](PHL) and NSC M (SD) and Ministry of Education A-92-N-FA (SD) provided financial support for this project. REFERENCES 1. Lau DW, Klein NC, Cunha BA. Brain abscess mimicking brain tumor. Heart Lung 1989;18: Rowley HA, Grant PE, Roberts TP. Diffusion MR imaging. Theory and applications. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 1999;
6 112 9: Ebisu T, Tanaka C, Umeda M, et al. Discrimination of brain abscess from necrotic or cystic tumors by diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 1996;14: Kim YJ, Chang KH, Song IC, et al. Brain abscess and necrotic or cystic brain tumor: discrimination with signal intensity on diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;171: Noguchi K, Watanabe N, Nagayoshi T, et al. Role of diffusion-weighted echo-planar MRI in distinguishing between brain abscess and tumour: a preliminary report. Neuroradiology 1999;41: Desprechins B, Stadnik T, Koerts G, et al. Use of diffusionweighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20: Park SH, Chang KH, Song IC, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in cystic or necrotic intracranial lesions. Neuroradiology 2000;42: Chang SC, Lai PH, Chen WL, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI features of brain abscess and cystic or necrotic brain tumors: comparison with conventional MR imaging. Clin Imaging 2002;26: Guzman R, Barth A, Lövblad K, et al. Use of diffusionweighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating purulent brain processes from cystic brain tumors. J Neurosurg 2002;97: Desbarats LN, Herlidou S, de Marco G, et al. Differential MRI diagnosis between brain abscess and necrotic or cystic brain tumors using the apparent diffusion coefficient and normalized diffusion-weighted images. Magn Reson Imaging 2003;21: Ikeda K, Kuwajima A, Tamura M, et al. Dynamic changes of MRI in brain abscesses. Neuroradiology 2002;44: Rana S, Albayram S, Lin DD, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient maps in a case of intracerebral abscess with ventricular extension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23: Krabbe K, Gideon P, Wagn P, et al. MR diffusion imaging of human intracranial tumours. Neuroradiology 1997;39: Guo AC, Provenzale JM, Cruz LC Jr, et al. Cerebral abscesses: investigation using apparent diffusion coefficient maps. Neuroradiology 2001;43: Tien RD, Felsberg GJ, Friedman H, et al. MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas: value of diffusion-weighted echoplanar pulse sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994; 162: Holtas S, Geijer B, Stromblad LG, et al. A ring-enhancing metastasis with central high signal on diffusion-weighted imaging and low apparent diffusion coefficients. Neuroradiology 2000;42: Demaerel P, Van Hecke P, Van Oostende S, et al. Bacterial metabolism shown by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet 1994;344: Harada M, Tanouchi M, Miyoshi H, et al. Brain abscess observed by localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging 1994;12: Remy C, Grand S, Lai ES, et al. 1H MRS of human brain abscesses in vivo and in vitro. Magn Reson Med 1995;34: Poptani H, Gupta RK, Jain VK, et al. Cystic intracranial mass lesions: possible role of in vivo MR spectroscopy in its differential diagnosis. Magn Reson Imaging 1995;13: Grand S, Lai ES, Esteve F, et al. In vivo 1H MRS of brain abscesses versus necrotic brain tumors. Neurology 1996;47: Kim SH, Chang KH, Song IC, et al. Brain abscess and brain tumor: discrimination with in vivo H-1 MR spectroscopy. Radiology 1997;204: Martinez-Perez I, Moreno A, Alonso J, et al. Diagnosis of brain abscess by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Neurosurg 1997;86: Chang KH, Song IC, Kim SH, et al. In vivo single voxel proton MR spectroscopy in intracranial cystic masses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1998;19: Dev R, Gupta RK, Poptani H, et al. Role of in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the diagnosis and management of brain abscesses. Neurosurgery 1998;42: Grand S, Passaro G, Ziegler A, et al. Necrotic tumor versus brain abscess: importance of amino acids detected at 1H MR spectroscopy - initial results. Radiology 1999;213: Burtscher IM, Holtas S. In vivo proton MR spectroscopy of untreated and treated brain abscesses. AJNR Am J
7 113 Neuroradiol 1999;20: Lai PH, Ho JT, Chen WL, et al. Brain abscess and necrotic brain tumor: discrimination with proton MR spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23: Akutsu H, Matsumura A, Isobe T, et al. Chronological change of brain abscess in 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuroradiology 2002;44: Garg M, Gupta RK, Husain N, et al. Brain abscesses: etiologic categorization with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2004;230: Lai PH, Li KT, Hsu SS, et al. Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of the Pyogenic Brain Abscess: In vivo 1.5 T and In vitro 11.7 T Findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol (in press)
In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1049 1053, June/July 1999 Case Report In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses Isabella M. Burtscher and Stig Holtås Summary: MR spectroscopy was
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1049 1053, June/July 1999 Case Report In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses Isabella M. Burtscher and Stig Holtås Summary: MR spectroscopy was
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
High-field MR imaging systems such as 3T strength aid in
 TECHNICAL NOTE H.-S. Liu H.-W. Chung C.-J. Juan S.-Y. Tsai C.-Y. Wang C.-C. Chan G.-S. Huang M.-C. Chou C.-S. Lee C.-W. Ko N.-Y. Cho C.-Y. Chen Anomalous J-Modulation Effects on Amino Acids in Clinical
TECHNICAL NOTE H.-S. Liu H.-W. Chung C.-J. Juan S.-Y. Tsai C.-Y. Wang C.-C. Chan G.-S. Huang M.-C. Chou C.-S. Lee C.-W. Ko N.-Y. Cho C.-Y. Chen Anomalous J-Modulation Effects on Amino Acids in Clinical
Discrimination of Brain Abscess and Cystic Tumor by In Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 41, 121 126, 2001 Discrimination of Brain Abscess and Cystic Tumor by In Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Osamu KADOTA, KanehisaKOHNO, Shiro OHUE, YoshiakiKUMON, Saburo
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 41, 121 126, 2001 Discrimination of Brain Abscess and Cystic Tumor by In Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Osamu KADOTA, KanehisaKOHNO, Shiro OHUE, YoshiakiKUMON, Saburo
Role of MR Spectroscopy and Diffusion Weighted Techniques in Discrimination between Capsular Stage Brain Abscesses, Necrotic and Cystic Brain Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 1, December: 699-710, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Role of MR Spectroscopy and Diffusion Weighted Techniques in Discrimination between Capsular Stage Brain
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 80, No. 1, December: 699-710, 2012 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Role of MR Spectroscopy and Diffusion Weighted Techniques in Discrimination between Capsular Stage Brain
Brain abscess is a focal intracerebral infection, which begins
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D. Pal A. Bhattacharyya M. Husain K.N. Prasad C.M. Pandey R.K. Gupta In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy Evaluation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses: A Report of 194 Cases BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D. Pal A. Bhattacharyya M. Husain K.N. Prasad C.M. Pandey R.K. Gupta In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy Evaluation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses: A Report of 194 Cases BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners
 Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners
 Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455 1460, June/July 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence Chiaki Asao, Yukunori Korogi, Mika Kitajima, Toshinori
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455 1460, June/July 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence Chiaki Asao, Yukunori Korogi, Mika Kitajima, Toshinori
Prospective evaluation of in vivo proton MR spectroscopy in differentiation of similar appearing intracranial cystic lesions
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 (2001) 103 110 Prospective evaluation of in vivo proton MR spectroscopy in differentiation of similar appearing intracranial cystic lesions A. Shukla-Dave a, R. K. Gupta a,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 (2001) 103 110 Prospective evaluation of in vivo proton MR spectroscopy in differentiation of similar appearing intracranial cystic lesions A. Shukla-Dave a, R. K. Gupta a,
Differentiation of Tuberculous from Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy and Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1503 1509, September 2001 Differentiation of Tuberculous from Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy and Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging Rakesh K. Gupta,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1503 1509, September 2001 Differentiation of Tuberculous from Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy and Magnetization Transfer MR Imaging Rakesh K. Gupta,
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:633 637, April 2003 Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Daniel L. A. Camacho, J. Keith Smith, and Mauricio Castillo
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:633 637, April 2003 Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Daniel L. A. Camacho, J. Keith Smith, and Mauricio Castillo
Proton MR Spectroscopy and Preoperative Diagnostic Accuracy: An Evaluation of Intracranial Mass Lesions Characterized by Stereotactic Biopsy Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:84 93, January 2 Proton MR Spectroscopy and Preoperative Diagnostic Accuracy: An Evaluation of Intracranial Mass Lesions Characterized by Stereotactic Biopsy Findings Isabella
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:84 93, January 2 Proton MR Spectroscopy and Preoperative Diagnostic Accuracy: An Evaluation of Intracranial Mass Lesions Characterized by Stereotactic Biopsy Findings Isabella
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Pyogenic abscesses of hematogenous origin are solitary in
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Luthra A. Parihar K. Nath S. Jaiswal K.N. Prasad N. Husain M. Husain S. Singh S. Behari R.K. Gupta Comparative Evaluation of Fungal, Tubercular, and Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with Conventional
ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Luthra A. Parihar K. Nath S. Jaiswal K.N. Prasad N. Husain M. Husain S. Singh S. Behari R.K. Gupta Comparative Evaluation of Fungal, Tubercular, and Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with Conventional
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries
 1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
General Identification. Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27
 General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
DWI that measures overall diffusivity in terms of directionally
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
MR spectroscopy in diagnosing intracranial lesions: comparison of diagnostic accuracy at different TE
 MR spectroscopy in diagnosing intracranial lesions: comparison of diagnostic accuracy at different TE Poster No.: C-1359 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. S. DUNGDUNG;
MR spectroscopy in diagnosing intracranial lesions: comparison of diagnostic accuracy at different TE Poster No.: C-1359 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. S. DUNGDUNG;
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Role of in Correlation with Mr Spectroscopy R. Archana 1, P. Sunil Kumar 2, Anurudh Kishore 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Post Graduate, Department of Radiodiagnosis:
Original Research Article Role of in Correlation with Mr Spectroscopy R. Archana 1, P. Sunil Kumar 2, Anurudh Kishore 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Post Graduate, Department of Radiodiagnosis:
Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/523 Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study Bulabai Karpagam 1, V Vadanika 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/523 Brain Space Occupying Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Prospective Study Bulabai Karpagam 1, V Vadanika 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
Diagnostic Value of Peritumoral Minimum Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for Differentiation of Glioblastoma Multiforme From Solitary Metastatic Lesions
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1645 1649, October 2000 Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and Lester Kwock BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: In a
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1645 1649, October 2000 Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and Lester Kwock BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: In a
DISTINCTION BETWEEN RECURRENT GLIOMA AND RADIATION INJURY USING MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY IN COMBINATION WITH DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1107 1114, May 2005 High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions Rakesh K. Gupta, Khader M. Hasan, Asht M. Mishra, Deepak Jha, Mazhar
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1107 1114, May 2005 High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions Rakesh K. Gupta, Khader M. Hasan, Asht M. Mishra, Deepak Jha, Mazhar
Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors.
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
Comparison of 1.5T and 3T 1 H MR Spectroscopy for Human Brain Tumors
 Comparison of 1.5T and 3T 1 H MR Spectroscopy for Human Brain Tumors Ji-hoon Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun Chang, MD 2-4 Dong Gyu Na, MD 2 In Chan Song, PhD 2,3 Seung Ja Kim, MD 2 Bae Ju Kwon, MD 2 Moon Hee Han,
Comparison of 1.5T and 3T 1 H MR Spectroscopy for Human Brain Tumors Ji-hoon Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun Chang, MD 2-4 Dong Gyu Na, MD 2 In Chan Song, PhD 2,3 Seung Ja Kim, MD 2 Bae Ju Kwon, MD 2 Moon Hee Han,
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) MR sequence showed an hyposignal of the lesion eliminating a cerebral pyogenic abscess which usually presents an
 Cerebral toxoplasmosis is one of the most common opportunistic neurological infections in AIDS patients, and is typically observed in the later stages of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. 1,2
Cerebral toxoplasmosis is one of the most common opportunistic neurological infections in AIDS patients, and is typically observed in the later stages of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. 1,2
MRS and Perfusion of Brain Tumors
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MRS and Perfusion of Brain Tumors John R. Hesselink, M.D. MRS & Perfusion of Brain Tumors Tumor histology Degree of malignancy Delineate tumor
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MRS and Perfusion of Brain Tumors John R. Hesselink, M.D. MRS & Perfusion of Brain Tumors Tumor histology Degree of malignancy Delineate tumor
Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging features of intracranial lesions
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF HEALTH RESEARCH IN MODERN INTEGRATED MEDICAL SCIENCES, ISSN 2394-8612 (P), ISSN 2394-8620 (O), Vol-2, Issue-4, Oct-Dec 2015 35 Original Article Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
Imaging is routinely used for the
 Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain Ajay Kumar Singh, MD; Ay-Ming Wang, MD; William Sanders, MD In vivo magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy is a noninvasive imaging modality useful for obtaining
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain Ajay Kumar Singh, MD; Ay-Ming Wang, MD; William Sanders, MD In vivo magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy is a noninvasive imaging modality useful for obtaining
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
The MRI Appearance of Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions
 ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to
 125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
SSRG International Journal of Medical Science (SSRG-IJMS) volume 2 Issue 2 Feb 2015
 Study of Brain Mass Lesions by MRI- On Special Sequences Ravi Ningappa 1, Bagath Singh K 2 1. Associate Professor, 2. Resident, Dept. of Radio diagnosis BMC&RI, Bangalore, India Author s address: Department
Study of Brain Mass Lesions by MRI- On Special Sequences Ravi Ningappa 1, Bagath Singh K 2 1. Associate Professor, 2. Resident, Dept. of Radio diagnosis BMC&RI, Bangalore, India Author s address: Department
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. No financial relationships to disclose. Education Goals and Objectives To describe the utility of diffusion-weighted
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. No financial relationships to disclose. Education Goals and Objectives To describe the utility of diffusion-weighted
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls.
 Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
Brain abscess is a focal suppurative process within the brain
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH V. Tomar A. Yadav R.K.S. Rathore S. Verma R. Awasthi V. Bharadwaj B.K. Ojha K.N. Prasad R.K. Gupta Apparent Diffusion Coefficient with Higher b-value Correlates Better with Viable Cell
ORIGINAL RESEARCH V. Tomar A. Yadav R.K.S. Rathore S. Verma R. Awasthi V. Bharadwaj B.K. Ojha K.N. Prasad R.K. Gupta Apparent Diffusion Coefficient with Higher b-value Correlates Better with Viable Cell
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Characterization of In-Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Patterns of Intracranial Space-Occupying Lesions: A 1-Year Observational Study Rajendra V. Mali 1, Aseem Katyal
Original Research Article Characterization of In-Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Patterns of Intracranial Space-Occupying Lesions: A 1-Year Observational Study Rajendra V. Mali 1, Aseem Katyal
Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction
 Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Altought liver (75%) and lung (15%) are the most commonly involved
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:168 174 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI of extrahepatic hydatid cysts Nagihan İnan, Nilay
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:168 174 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Conventional and diffusion-weighted MRI of extrahepatic hydatid cysts Nagihan İnan, Nilay
Role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in diagnosis of pilocytic astrocytoma in children
 Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2012) 48, 131 137 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2012) 48, 131 137 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Brain Pain Infections of the CNS
 FRIDAY, OCTOBER 28, 2016 Brain Pain Infections of the CNS Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC Assistant Professor of Radiology & Neurosurgery Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine
FRIDAY, OCTOBER 28, 2016 Brain Pain Infections of the CNS Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC Assistant Professor of Radiology & Neurosurgery Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine
Multivoxel MR Spectroscopic Imaging Distinguishing Intracranial Tumours from Non-neoplastic Disease
 Original Article 309 Multivoxel MR Spectroscopic Imaging Distinguishing Intracranial Tumours from Non-neoplastic Disease Veena Arpit Nagar, 1 MBBS, MD, Jieru Ye, 1 BSc, Maosheng Xu, 4 PhD, Wai-Hoe Ng,
Original Article 309 Multivoxel MR Spectroscopic Imaging Distinguishing Intracranial Tumours from Non-neoplastic Disease Veena Arpit Nagar, 1 MBBS, MD, Jieru Ye, 1 BSc, Maosheng Xu, 4 PhD, Wai-Hoe Ng,
Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Mediastinal and Pulmonary Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Brain tumors are very often associated with perilesional
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R. Ricci A. Bacci V. Tugnoli S. Battaglia M. Maffei R. Agati M. Leonardi Metabolic Findings on 3T 1 H-MR Spectroscopy in Peritumoral Brain Edema BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Little is known
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R. Ricci A. Bacci V. Tugnoli S. Battaglia M. Maffei R. Agati M. Leonardi Metabolic Findings on 3T 1 H-MR Spectroscopy in Peritumoral Brain Edema BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Little is known
Clinical application of 3.0 T proton MR spectroscopy in evaluation of pancreatic diseases
 Clinical application of 3.0 T proton MR spectroscopy in evaluation of pancreatic diseases Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1762 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Su, E. Jin; Beijing/CN
Clinical application of 3.0 T proton MR spectroscopy in evaluation of pancreatic diseases Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1762 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Su, E. Jin; Beijing/CN
Central nervous system (CNS) infections constitute a group
 REVIEW ARTICLE Imaging Aspects of Pyogenic Infections of the Central Nervous System Nelson Paes Diniz Fortes Ferreira, MD,* Gilberto Miyazaki Otta, MD,* Lázaro Luís Faria do Amaral, MD,* and Antônio José
REVIEW ARTICLE Imaging Aspects of Pyogenic Infections of the Central Nervous System Nelson Paes Diniz Fortes Ferreira, MD,* Gilberto Miyazaki Otta, MD,* Lázaro Luís Faria do Amaral, MD,* and Antônio José
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
 Iran J Radiol. 2015 July; 12(3): e15478. Published online 2015 July 22. MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.15478v2 Research Article Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted
Iran J Radiol. 2015 July; 12(3): e15478. Published online 2015 July 22. MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.15478v2 Research Article Characterization of Soft Tissue Tumors by Diffusion-Weighted
Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Deakin Research Online
 Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Silberstein, Morry, Lane, Dianne, Dodd, Seetal and Opeskin, Kenneth 2002, Identification of a by-product of nitric oxide synthase activity in human
Deakin Research Online This is the published version: Silberstein, Morry, Lane, Dianne, Dodd, Seetal and Opeskin, Kenneth 2002, Identification of a by-product of nitric oxide synthase activity in human
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Usefulness of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Diffusion- Weighted Imaging for Differential Diagnosis of Primary Solid and Cystic Renal Masses
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 209-215 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899984 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.06.08 Accepted: 2016.08.16 Published: 2017.04.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 209-215 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899984 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.06.08 Accepted: 2016.08.16 Published: 2017.04.13 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Proton MR spectroscopy of brain tumors: The cause of wrong diagnosis and grading
 Proton MR spectroscopy of brain tumors: The cause of wrong diagnosis and grading Poster No.: C-2644 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Neuro Authors: S. J. Lee, K. J. Ahn, S. L. Jung,
Proton MR spectroscopy of brain tumors: The cause of wrong diagnosis and grading Poster No.: C-2644 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Neuro Authors: S. J. Lee, K. J. Ahn, S. L. Jung,
Chordoid glioma: CT and MR features
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 225-229 225 Chordoid glioma: CT and MR features YI-CHIH HSU HUNG-WEN KAO CHUNG-PING LO CHUN-JUNG JUAN SHY-CHYI CHIN CHENG-YU CHEN Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 225-229 225 Chordoid glioma: CT and MR features YI-CHIH HSU HUNG-WEN KAO CHUNG-PING LO CHUN-JUNG JUAN SHY-CHYI CHIN CHENG-YU CHEN Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
Classification of Biopsy-Confirmed Brain Tumors Using Single-Voxel MR Spectroscopy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:117 123, January 1999 Classification of Biopsy-Confirmed Brain Tumors Using Single-Voxel MR Spectroscopy M. Elizabeth Meyerand, J. Marc Pipas, Alex Mamourian, Tor D. Tosteson,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:117 123, January 1999 Classification of Biopsy-Confirmed Brain Tumors Using Single-Voxel MR Spectroscopy M. Elizabeth Meyerand, J. Marc Pipas, Alex Mamourian, Tor D. Tosteson,
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
Role of Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Intracranial Tumors with Pathological Correlation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com with Pathological Correlation J. S. Aswini Jyothi, P. Sree Hari 2, V. Karuna 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Intracranial tumors can occur in all age groups and can be grossly
ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com with Pathological Correlation J. S. Aswini Jyothi, P. Sree Hari 2, V. Karuna 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Intracranial tumors can occur in all age groups and can be grossly
Refractive Index As Surrogate Biological Marker Of Tumefactive And Other Form Of Multiple Sclerosis And Its Superiority Over Other Methods
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 19 Number 1 Refractive Index As Surrogate Biological Marker Of Tumefactive And Other Form Of Multiple Sclerosis And Its Superiority Over Other Methods
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 19 Number 1 Refractive Index As Surrogate Biological Marker Of Tumefactive And Other Form Of Multiple Sclerosis And Its Superiority Over Other Methods
Role of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of intra and extra axial intracranial lesions
 International Surgery Journal Chakra VV et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3107-3112 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173897
International Surgery Journal Chakra VV et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):3107-3112 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173897
The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1570 1574, September 2003 The Natural History of Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau Disease Andrew Slater, Niall R. Moore, and Susan M. Huson BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas: Does Lower ADC Predict a Worse Prognosis Independent of Grade of Tumor?
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Thalamic Tuberculoma Mimicking a Malignant Brain Tumor
 122 CASE REPORT Thalamic Tuberculoma Mimicking a Malignant Brain Tumor Hung-Lin Lin, Jung-Tsung Chen, Yu-Fang Liu 1, Der-Yang Cho Department of Neurosurgery, 1 Department of Anesthesia, China Medical University
122 CASE REPORT Thalamic Tuberculoma Mimicking a Malignant Brain Tumor Hung-Lin Lin, Jung-Tsung Chen, Yu-Fang Liu 1, Der-Yang Cho Department of Neurosurgery, 1 Department of Anesthesia, China Medical University
Case Report Cystic Meningioma Simulating Arachnoid Cyst: Report of an Unusual Case
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 371969, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/371969 Case Report Cystic Meningioma Simulating Arachnoid Cyst: Report of an Unusual Case Docampo Jorge, 1 Gonzalez
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 371969, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/371969 Case Report Cystic Meningioma Simulating Arachnoid Cyst: Report of an Unusual Case Docampo Jorge, 1 Gonzalez
Diffusion Measurements in Intracranial Hematomas: Implications for MR Imaging of Acute Stroke
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1190 1194, August 2000 Diffusion Measurements in Intracranial Hematomas: Implications for MR Imaging of Acute Stroke Scott W. Atlas, Philip DuBois, Michael B. Singer, and Dongfeng
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1190 1194, August 2000 Diffusion Measurements in Intracranial Hematomas: Implications for MR Imaging of Acute Stroke Scott W. Atlas, Philip DuBois, Michael B. Singer, and Dongfeng
Proton MR Spectroscopy in Patients with Acute Temporal Lobe Seizures
 AJN Am J Neuroradiol 22:152 157, January 2001 Proton M Spectroscopy in Patients with Acute Temporal obe Seizures Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and ester Kwock BACKGOUND AND PUPOSE: Decreases in N-acetyl
AJN Am J Neuroradiol 22:152 157, January 2001 Proton M Spectroscopy in Patients with Acute Temporal obe Seizures Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and ester Kwock BACKGOUND AND PUPOSE: Decreases in N-acetyl
Correlation of quantitative proton MR spectroscopy with local histology from stereotactic brain biopsy to evaluate heterogeneity of brain tumors
 Correlation of quantitative proton MR spectroscopy with local histology from stereotactic brain biopsy to evaluate heterogeneity of brain tumors Steve H. Fung, MD 1, Edward F. Jackson, PhD 2, Samuel J.
Correlation of quantitative proton MR spectroscopy with local histology from stereotactic brain biopsy to evaluate heterogeneity of brain tumors Steve H. Fung, MD 1, Edward F. Jackson, PhD 2, Samuel J.
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
