Appendix I. A Summary of Common Pitfalls in Diagnostic Gynecologic and Obstetric Pathology
|
|
|
- Phebe Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix I. A Summary of Common Pitfalls in Diagnostic Gynecologic and Obstetric Pathology Section Chapter Mistaken for Comments Candidiasis A premalignant lesion (VIN) Chronically rubbed skin can produce a striking acanthosis. A yeast infection must always be kept in mind if there is minimal atypia or any epithelial neutrophils. Syphilis Inflammatory dermatosis This is still a rare disease in vulvar pathology. However, any dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, including those accompanied by acanthosis or which is arranged around vessels, should be investigated. Psoriasis VIN1 We have seen these occasionally misdiagnosed as VIN1. Chronic erosive herpes Sclerotic Hidradenoma Basal cell Pseudobowenoid papulosis VIN with superimposed lichen simplex chronicus Non- infectious inflammatory conditions Invasive adeno Adenoid basal HIVIL or Bowenoid Papulosis Differentiated VIN or lichen simplex chronicus Epithelial hyperplasia rather than erosion may be seen. The viral inclusions may not be obvious. The degree of sclerosis can be striking with epithelial entrapment. Adenocaricnoma can be excluded with a p63 stain, which will highlight the basal cells. These can be misclassified as adenoid cystic s. Basal- squamous lesions may be difficult to classify as well. The abundant pseudomitoses seen with apoptosis can be confusing. At the same time similar changes can be seen in high grade VIN so caution is needed in both directions. Presumably if a VIN is rubbed or scratched, a prominent superimposed lichen simplex chronicus can occur. This may either make the lesion less conspicuous or prompt a diagnosis of differentiated VIN. Classic VIN can be confirmed with a p16 immunostain. Pagetoid VIN Glandular or urothelial lesion A p16 stain may be helpful to support VIN; CK7/CK20/CDX2 can be used to investigate for spread from a GI or urothelial primary. VIN with columnar Paget Disease CK7 and GATA3 positivity is seen in
2 differentiation Paget disease cells (normal epithelium is CK 5/6 positive). EBV- like atypia Classic VIN or atypia NOS A history of immunosuppression may be helpful. Giant Condyloma (GC) Pseudoepithelioma tous hyperplasia (PEH) Keratoacanthoma Aggressive angiomyxoma Synovial sarcoma of Vulva Verrucous or papillary squamous Squamous cell Under or over- diagnosis of squamous Usually over- diagnosed Mullerian or vulvar adeno or carcinosarcoma GC can occur on the vulva, vagina and cervix. Care should be excercised in making the diagnosis of a "verrucous" in a young woman with an exophytic well differentiated squamous lesion in this region. The key is lack of atypia and the characteristic interlacing strands of epithelium. Also watch out for a Granular cell tumor, syphilis, etc., and be aware that some s can mimic PEH. Remains a controversial diagnosis. Look for the deep location and characteristic vascular pattern. Clinically it may be difficult to completely resect and it may be locally invasive. The epithelium, if prominent, is disarmingly benign appearing and the stroma may not be markedly atypical, mimicking endometrial stroma. Mullerian markers (PAX8) will be absent; the presence of TLE1 would support synovial sarcoma. Ill defined, asymmetric, prominent collagen deposition. Prepubertal Angiomyxoma fibroma Hymenal ring Condyloma A common pitfall. These are small filiform polyps without atypia. Melanoma Undifferentiated or sarcoma Vaginal melanoma may not have pigment and may not initially be clinically recognized. Always consider melanoma when confronted with apoorly differentiated spindle or epithelioid lesion in the vagina. Spindle cell epithelioma Sarcoma The epithelial component is often quite subtle but the spindle cells are bland appearing; well circumscribed. Cytokeratin stains will be focally positive. Pseudo crypt HSIL with crypt involvement Stromal reaction, loss of cell polarity
3 pattern of invasive squamous Lymphoepithelial like Superficial adeno in situ Extensive cervical adeno in situ (AIS) Signet ring cell of the cervix Adenoid basal Prostatic metaplasia Microglandular hyperplasia (MGH) of the endocervix Mesonephric Minimal deviation adeno Endocervicosis Lymphoma, undifferentiated Tubal metaplasia, non- specific changes Invasive adeno Metastatic breast or gastrointestinal Squamous cell Adenoid basal, squamous intraepithelial lesion Adeno Sarcoma, conventional adeno Endocervical hyperplasia Adeno, adenosarcoma and central necrosis typify pseudo- crypt involvement by. The squamous nests may be subtle but are strongly p63 positive. Mitoses and atypia may be inconspicuous or absent; look for discrete appearance, apoptosis, luminal eosinophilia. P16 stain very helpful. Controversial and cut- offs difficult to define; however, approach any extensive AIS with caution. This is a diagnosis of exclusion but look for evidence of a precursor (ACIS) lesion. Immunostains can be helpful. Look for the uniform nests, lack of desmoplasia and the tell- tale rim of basal- type cells around the squamous nests. Look for the signature finding of small acini suspended in the squamo- transitional nests This can occur with solid growth, lacking signficant acinar architecture. P16 will be patchy in MGH versus diffuse in The spindled variety tends to be remarkably uniform; glandular elements can resemble endometrial or sex cord differentiation and are typically closer to the surface, with the typical mesonephric histology at the periphery. The presence of GATA3 is supportive of mesonephric origin. Can be mistaken for each other. Irregular glands and intraglandular papillae with mitoses and atypia are key for MDA or its precursor. Remember both MDA and SCTATs are associated with Peutz Jeghers syndrome. More typically the problem is not whether the lesion is malignant but why it is in the odd location. Best
4 explanation is misplaced endocervix from a prior C- section Adenosarcoma of the cervix, atypical polyp, adenomyoma All three can be confused with each other Beware that all three of these entities can have overlapping morphologic features. Smooth muscle fascicles are seen in adenomyoma. Stromal breakdown Adeno and visa versa The key is separating congealed aggregates of stroma from clusters of tumor cells. Rimming of stromal aggregates by reactive epithelium can help identify breakdown. Yolk sac tumor of the vagina Mullerian Adeno A primitive appearing vaginal in a young woman raises this possibility Pyometra Malignant and visa versa May need to resample to confirm or exclude malignancy. Exfoliation artifact Adeno or EIN Note the adjacent stroma will usually demonstrate preservation artifacts and hemorrhage. Transition from normal to abnormal may be gradual and superficial. Atypical polypoid adenomyoma Myoinvasive and visa versa A compact investing smooth muscle component typifies APA. Squamous cell of endometrium Microacinar endometrioid Involvement of adenomyosis by adeno Benign squamous epithelium or metaplasia Microglandular changes in the cervix Myoinvasive adeno The neoplastic squamous epithelium may be papillary and can be remarkably bland appearing in endometrial primaries Collagen stroma separates acini more typical in benign MGH; slightly more amphophilic glands and a soft appearance to the glands in. This cuts both ways. Extensive "vertical" growth or myxoid stromal reaction may indicate myoinvasion. Most important if present deeper than 50 of the myometrial thickness. Glandular epithelium absent Intraperitoneal Metastatic keratin granulomas Histiocytes Neoplastic cells Histiocytes can form sheets with mitotic activity; lack of cell polarity, nuclear folds/grooves, and indistinct edges Ischemic atypia Clear cell or serous Seen most commonly in necrotic polyps; typically there is stromal hyaline change in a zonal
5 configuration reflecting partial ischemic degenerative changes. Adeno with spindle features Carcinosarcoma Juxtaposed well differentiated adeno and plump spindled cells (keratin positive). PECOMA Epithelioid smooth muscle tumor Inherent overlap between the two tumor types. Prominent capillary vascular network and clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm in PECOMA, including ESS- like invasion. HMB- 45 stain helpful but will not always discriminate he two. Myxoid low grade endometrial stromal sarcoma Adenomyosis or adenomyomatosis, leiomyoma Exceedingly bland with numerous normal appearing vessels but the growth pattern is distinctly ESS- like. Leiomyoma in Reed s syndrome STUMP, leiomyosarcoma The key is a diffuse mild hypercellularity and nuclear atypia with prominent nucleoli. If suspected stain for FH. Pregnancy and inflammatory related tubal atypia Tubal intraepithelial or invasive Look for cilia, normal/wild- type p53 expression pattern, low N/C ratio in Arias- Stella like atypias. Secretory cell outgrowths (benign epithelial hyperplasia) Endometrioid/tubal neoplasia These foci closely resemble endometrioid epithelium and have an increased proliferative index but are self limited with normal p53 expression. Tangentially sectioned follicle Stromal tumor Typically small and concentric with indistinct interface with the ovarian stroma; mitoses common. Clear cell and yolk sac s Either and occasionally both in one tumor Classic Schiller- Duval bodies and SALL4 favor YST; HNF1b present in CC s. Spindled Granulosa cell tumor Fibro- thecoma and rarely a smooth muscle tumor Carefully evaluate highly cellular "thecomas", particularly with foci of nested epithelioid areas, high mitotic index. Pericellular reticulin preservation is common in fibo- thecomas. Follicle Cyst Cystic granulosa cell tumor Look for monotonous growth pattern of granulosa cells, call- exner bodies, nuclear grooves in the cystic GCT. Juvenile granulosa cell tumor Retiform Sertoli Leydig cell tumor Small cell, hypercalcemic type Borderline serous tumor Granulosa cell tumors can exhibit considerable nuclear atypia. WT1 positive in small cell. Young patients, retiform pattern in a portion of the lesion, heterologous
6 (RSLCT) Heterologous elements in sex cord tumors Benign germinal matrix in teratomas Extravillous trophoblast Degenerating decidual cells Focal mature villi or an old implantation site in first trimester curetting Localized endometrial proliferation of pregnancy Early complete mole Intraplacental chorio Placental site trophoblastic tumor Epithelioid leiomyoma Mesenchymal dysplasia Histiocytic intervillositis Metastatic, sex cord differentiation, sarcomas Immature teratoma Chorio Can mimic mature extravillous trophoblast and visa versa Intrauterine pregnancy EIN or adeno Hydropic abortus Infarct Exaggerated implantation site Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor in a small sample Partial Mole Unremarkable abortus elements, strong inhibin staining typify RSLCT Hepatic differentiation can mimic breast, the latter is positive for GATA3. Be aware of normal cerebellar differentiation. Immature neuroepithelium typically contains abundant mitoses and apoptosis. No necrosis or marked trophoblastic atypia. Be familiar with pre- villous trophoblast. Cytokeratin stains Mature villi, old implantation site and even recent implantation site (via contamination) can mimic a current intrauterine pregnancy. Found typically in a 'products of conception' specimen. Watch out for stromal basophilia and karyorrhexis, mild concentric thickening of the trophoblastic rim. Sample all infarcts for histologic exam! Mel- Cam/MIB1 staining should highlight over 15% of cells in PSTT. Look for sheets of tumor cells between smooth muscle fascicles. Desmin positive. Cytokeratins may stain both tumors. Abnormally large stem villi. Lack of cistern formation in mesenchymal dysplasia. The histiocytes can be present but unappreciated in early second trimester pregnancy. This can recur and be associated with repeated pregnancy loss. Listeria Conventional intervillositis Acute intervillositis; order appropriate stains for microorganisms Fetal vascular thrombosis (FTV) Chronic villitis, fetal death Chronic villitis can be inconspicuous in villitis mediated villous sclerosis;
7 Maternal- fetal hemorrhage Candida Chorioamnionitis No abnormality Conventional chorioamnionitis remote fetal death will cause widespread villous changes mimicking FTV. Look for pale placenta, bloodless villi, normoblastemia Order a Kleihauer- Betke test Can be lethal if undetected Search for neutrophils on the surface of the cord.
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
6/5/2010. Outline of Talk. Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Metaplastic / reactive changes. Problems in Biopsies/Curettages
 Outline of Talk Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Problems in Biopsies/Curettages Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia
Outline of Talk Endometrial Alterations That Mimic Cancer & Vice Versa: Problems in Biopsies/Curettages Metaplastic / reactive changes Mucinous change Microglandular hyperplasia-like change Squamous metaplasia
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory.
 Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions
 Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Disclosure. Case. Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix. I have nothing to disclose
 Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
Endometrial pathology. Dr Tom Dodd and Dr Georgina England
 Endometrial pathology Dr Tom Dodd and Dr Georgina England Case 1 Female age 35 Case 1 Proliferative endometrium Case 2 Female age 38 Case 2 Secretory endometrium Dating endometrium Assessed on the
Endometrial pathology Dr Tom Dodd and Dr Georgina England Case 1 Female age 35 Case 1 Proliferative endometrium Case 2 Female age 38 Case 2 Secretory endometrium Dating endometrium Assessed on the
Pathology of the female genital tract
 Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
Pathology of the female genital tract Common illnesses of the female genital tract Before menarche Developmental anomalies Tumors (ovarial teratoma) Amenorrhea Fertile years PCOS, ovarian cysts Endometriosis
64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus
 Case 6 64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus Numerous irregular, large glands with leaf-like pattern Large glands with broad-based papillary infolding into the
Case 6 64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus Numerous irregular, large glands with leaf-like pattern Large glands with broad-based papillary infolding into the
Case year female. Routine Pap smear
 Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Vulva Inflammatory Disorders Lichen Planus Fixed Drug Eruption Erythema Multiforme Plasmacytosis Mucosae (Zoon) Lichen Sclerosus Allergic Contact
 Vulva Inflammatory Disorders Lichen Planus Fixed Drug Eruption Erythema Multiforme Plasmacytosis Mucosae (Zoon) Lichen Sclerosus Allergic Contact Dermatitis Psoriasis Lichen Simplex Chronicus Foreign Body
Vulva Inflammatory Disorders Lichen Planus Fixed Drug Eruption Erythema Multiforme Plasmacytosis Mucosae (Zoon) Lichen Sclerosus Allergic Contact Dermatitis Psoriasis Lichen Simplex Chronicus Foreign Body
05/07/2018. Types of challenges. Challenging cases in uterine pathology. Case 1 ` 65 year old female Post menopausal bleeding Uterine Polyp
 Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN
 EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box?
 When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
Tinh hoàn
 Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
VULVAR CARCINOMA. Page 1 of 5
 VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience
 Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Endometrial Stromal Tumors
 Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Gynaecological Malignancies
 Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia
 Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination. Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner
 Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner General Remarks The part II practical examination involved 15 cases which were presented with sufficient clinical data to
Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner General Remarks The part II practical examination involved 15 cases which were presented with sufficient clinical data to
Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens
 How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix
 The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
2/9/2015. Bartholin Cyst. Vulva: Squamous epithelium skin. Vagina: Squamous epithelium mucosa. Cervix: Ectocervix: squamous Endocervix: glandular
 Vulva: Squamous epithelium skin Bartholin Cyst Vagina: Squamous epithelium mucosa Cervix: Ectocervix: squamous Endocervix: glandular Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal
Vulva: Squamous epithelium skin Bartholin Cyst Vagina: Squamous epithelium mucosa Cervix: Ectocervix: squamous Endocervix: glandular Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal Slide courtesy of Dr. Lodge Rigal
Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms
 Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms Current Clinical Pathology ANTONIO GIORDANO, MD, PHD SERIES EDITOR For further titles published in this series, go to http://www.springer.com/springer/series/7632
Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms Current Clinical Pathology ANTONIO GIORDANO, MD, PHD SERIES EDITOR For further titles published in this series, go to http://www.springer.com/springer/series/7632
Case 3 - GYN. History: 66 year old, routine Pap test. Dr. Stelow
 Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours. Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh
 Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo. Case Discussions. 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC
 BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate
 Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].
![of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2]. of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].](/thumbs/80/81450506.jpg) - - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
- - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma
 Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Page # 1. Endometrium. Cellular Components. Anatomical Regions. Management of SIL Thomas C. Wright, Jr. Most common diseases:
 Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
Endometrium Pathology of the Endometrium Thomas C. Wright Columbia University, New York, NY Most common diseases: Abnormal uterine bleeding Inflammatory conditions Benign neoplasms Endometrial cancer Anatomical
ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS
 ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University, Stanford,
ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University, Stanford,
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology
 New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
Index. Cytoplasm, nonepithelial malignant tumor features 70
 Accurette device 23 Adenosarcoma, differential diagnosis 80, 81 Arias-Stella reaction 65 Atypical endocervical cells 8 Atypical endometrial cells 8 Atypical glandular cells (AGC) 8, 9 Atypical glandular
Accurette device 23 Adenosarcoma, differential diagnosis 80, 81 Arias-Stella reaction 65 Atypical endocervical cells 8 Atypical endometrial cells 8 Atypical glandular cells (AGC) 8, 9 Atypical glandular
Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland.
 UTERINE ADENOSARCOMA W Glenn McCluggage Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland. Definition of Adenosarcoma: A mixed tumor composed of benign neoplastic glandular
UTERINE ADENOSARCOMA W Glenn McCluggage Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland. Definition of Adenosarcoma: A mixed tumor composed of benign neoplastic glandular
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis
 Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Effusion Cytology: Diagnostic Challenges
 Effusion Cytology: Diagnostic Challenges Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director, Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Outside Consult Case 45 year old woman, presented with nausea, dyspnea,
Effusion Cytology: Diagnostic Challenges Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director, Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Outside Consult Case 45 year old woman, presented with nausea, dyspnea,
May 2017 TSL workshops. EQA 012 Final analysis with Diagnoses
 May 2017 TSL workshops EQA 012 Final analysis with Diagnoses CASE 1 28 yr old female with menorrhagia. Well diff endometrioid adenocarcinoma (back ground complex hyperplasia) 4 Non-atypical endometrial
May 2017 TSL workshops EQA 012 Final analysis with Diagnoses CASE 1 28 yr old female with menorrhagia. Well diff endometrioid adenocarcinoma (back ground complex hyperplasia) 4 Non-atypical endometrial
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Trophoblastic tumors
 Trophoblastic tumors Uterus tumor course Oslo, 21-22/1/16 Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway Cases 45 38 39 4 Case 45
Trophoblastic tumors Uterus tumor course Oslo, 21-22/1/16 Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway Cases 45 38 39 4 Case 45
In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis
 In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis Rouba Ali-Fehmi,MD The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Global incidence of cervical
In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis Rouba Ali-Fehmi,MD The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Global incidence of cervical
PSA. HMCK, p63, Racemase. HMCK, p63, Racemase
 Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA
 Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA Jack Yang, MD Department of Pathology, Medical University of South Carolina Objectives Understand the indication of EUS
Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA Jack Yang, MD Department of Pathology, Medical University of South Carolina Objectives Understand the indication of EUS
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Outline 11/2/2017. Pancreatic EUS-FNA general aspects. Cytomorphologic features of solid neoplasms/lesions of the pancreas
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND GUIDED-FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY OF PANCREAS Khalid Amin M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Minnesota Outline Pancreatic
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND GUIDED-FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY OF PANCREAS Khalid Amin M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Minnesota Outline Pancreatic
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors
 An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000
 Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid.
 Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
PATHOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL TRACT
 MBBS 2 nd Yr. Lecture Dr. Annie Cheung September 30, 2002 9:30 am LT2,G/F, Academic and Administration Block Faculty of Medicine Building UROGENITAL SYSTEM PATHOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL TRACT Learning
MBBS 2 nd Yr. Lecture Dr. Annie Cheung September 30, 2002 9:30 am LT2,G/F, Academic and Administration Block Faculty of Medicine Building UROGENITAL SYSTEM PATHOLOGY OF THE FEMALE GENITAL TRACT Learning
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
 SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Salivary Gland Cytology
 Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
Fig. 1 (above). Endometrial hyperplasia, simple. Hyperplastic glands of unequal size, some of which are cystically dilated Fig. 2 (below).
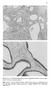 81 Fig. 1 (above). Endometrial hyperplasia, simple. Hyperplastic glands of unequal size, some of which are cystically dilated Fig. 2 (below). Endometrial hyperplasia, simple. Proliferative type epithelium
81 Fig. 1 (above). Endometrial hyperplasia, simple. Hyperplastic glands of unequal size, some of which are cystically dilated Fig. 2 (below). Endometrial hyperplasia, simple. Proliferative type epithelium
MULLERIAN PAPILLOMA ENTITY RECOGNITION FAILURE 04/04/2016 OUT OF SIGHT, OUT OF MIND: LESSER KNOWN LESIONS OF THE VULVOVAGINAL TRACT
 OUT OF SIGHT, OUT OF MIND: LESSER KNOWN LESIONS OF THE VULVOVAGINAL TRACT 23 rd ANNUAL SEMINAR IN PATHOLOGY 30 APRIL 2016 W. Dwayne Lawrence MD MSc (Path.) Chief of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Women
OUT OF SIGHT, OUT OF MIND: LESSER KNOWN LESIONS OF THE VULVOVAGINAL TRACT 23 rd ANNUAL SEMINAR IN PATHOLOGY 30 APRIL 2016 W. Dwayne Lawrence MD MSc (Path.) Chief of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Women
Male Genital Cancers in the US in Frequency of Types
 Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY. Jonathan I. Epstein.
 1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses
 Chapter 2 Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses Introduction Included in this chapter are nasal cavities, frontal sinus, ethmoid complex, sphenoid sinus, and maxillary sinuses. These cavities and sinuses
Chapter 2 Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses Introduction Included in this chapter are nasal cavities, frontal sinus, ethmoid complex, sphenoid sinus, and maxillary sinuses. These cavities and sinuses
FINALIZED SEER SINQ QUESTIONS
 0076 Source 1: WHO Class CNS Tumors pgs: 33 MP/H Rules/Histology--Brain and CNS: What is the histology code for a tumor originating in the cerebellum and extending into the fourth ventricle described as
0076 Source 1: WHO Class CNS Tumors pgs: 33 MP/H Rules/Histology--Brain and CNS: What is the histology code for a tumor originating in the cerebellum and extending into the fourth ventricle described as
Workshop for O& G trainees and paramedics 17 Dec 2011 Cytological Interpretation
 Workshop for O& G trainees and paramedics 17 Dec 2011 Cytological Interpretation May Yu Director of Cytology Laboratory Service Department of Anatomical & Cellular Pathology Prince of Wales Hospital Cervical
Workshop for O& G trainees and paramedics 17 Dec 2011 Cytological Interpretation May Yu Director of Cytology Laboratory Service Department of Anatomical & Cellular Pathology Prince of Wales Hospital Cervical
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER. Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D.
 NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
Problems in the Differential Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia and Carcinoma
 THE 1999 LONG COURSE ON PATHOLOGY OF THE UTERINE CORPUS AND CERVIX Problems in the Differential Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia and Carcinoma Steven G. Silverberg, M.D. Department of Pathology, University
THE 1999 LONG COURSE ON PATHOLOGY OF THE UTERINE CORPUS AND CERVIX Problems in the Differential Diagnosis of Endometrial Hyperplasia and Carcinoma Steven G. Silverberg, M.D. Department of Pathology, University
Testicular Tumors: What s New, True, Important Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD
 Testicular Tumors: What s New, True, Important Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD Director, Genitourinary Pathology R.J. Tomsich Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Professor of Pathology, Lerner College
Testicular Tumors: What s New, True, Important Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD Director, Genitourinary Pathology R.J. Tomsich Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Professor of Pathology, Lerner College
Pancreas. Atrophy, acinar cell. Pathogenesis: Diagnostic key features:
 Pancreas Atrophy, acinar cell Pathogenesis: Decrease in number and/or size of acinar cells may be due to spontaneous or experimentally induced degenerative changes, apoptosis, or a sequel of chronic inflammation.
Pancreas Atrophy, acinar cell Pathogenesis: Decrease in number and/or size of acinar cells may be due to spontaneous or experimentally induced degenerative changes, apoptosis, or a sequel of chronic inflammation.
Index 179. Genital tract contaminants, 17, 20, 22, 150 papilloma virus-infected cells, 47 squamous cells, sources of, 7
 Index Accuracy of urinary cytology, 166 Acute inflammatory cells, 38 catheter sample, 39 herpes simplex infections, 44 carcinomas, 104, 105 non-viral inclusions, 52, 53 voided urine, 17 Adenocarcinoma
Index Accuracy of urinary cytology, 166 Acute inflammatory cells, 38 catheter sample, 39 herpes simplex infections, 44 carcinomas, 104, 105 non-viral inclusions, 52, 53 voided urine, 17 Adenocarcinoma
Colposcopy. Attila L Major, MD, PhD
 Colposcopy Attila L Major, MD, PhD Histology Colposcopy Cytology It has been estimated that annual Pap smear testing reduces a woman s chance of dying of cervical cancer from 4 in 1000 to about 5 in 10,000
Colposcopy Attila L Major, MD, PhD Histology Colposcopy Cytology It has been estimated that annual Pap smear testing reduces a woman s chance of dying of cervical cancer from 4 in 1000 to about 5 in 10,000
Interesting Cases in Gynecologic Pathology. Michael Ward, MD Surgical Pathology Fellow University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, UT
 Interesting Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Michael Ward, MD Surgical Pathology Fellow University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, UT Case 1 History: 50 year old woman with a uterine mass
Interesting Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Michael Ward, MD Surgical Pathology Fellow University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, UT Case 1 History: 50 year old woman with a uterine mass
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Case 1. Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno
 Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
They Do Look Alike : Mimics of Prostate Cancer in Biopsy Samples
 They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
What is New in the 2015 WHO Lung Cancer Classification? Zhaolin Xu, MD, FRCPC, FCAP
 What is New in the 2015 WHO Lung Cancer Classification? Zhaolin Xu, MD, FRCPC, FCAP Professor, Dept of Pathology, Dalhousie University, Canada Pulmonary Pathologist and Cytopathologist, QEII HSC Senior
What is New in the 2015 WHO Lung Cancer Classification? Zhaolin Xu, MD, FRCPC, FCAP Professor, Dept of Pathology, Dalhousie University, Canada Pulmonary Pathologist and Cytopathologist, QEII HSC Senior
Histologic diagnosis of gestational trophoblastic diseases (GTD)
 1 Histologic diagnosis of gestational trophoblastic diseases (GTD) Masaharu Fukunaga, M.D. Department of Pathology, the Jikei University Daisan Hospital, Tokyo, Japan Hydatidiform moles With the increased
1 Histologic diagnosis of gestational trophoblastic diseases (GTD) Masaharu Fukunaga, M.D. Department of Pathology, the Jikei University Daisan Hospital, Tokyo, Japan Hydatidiform moles With the increased
7 Mousa. Obada Zalat. Mohammad Badi
 7 Mousa Obada Zalat Mohammad Badi Tumors of the ovaries Last lecture we talked about surface epithelial tumors of the ovaries (the most common type). But there are many other types of tumors of germ cell
7 Mousa Obada Zalat Mohammad Badi Tumors of the ovaries Last lecture we talked about surface epithelial tumors of the ovaries (the most common type). But there are many other types of tumors of germ cell
Intravascular Endometrium Mimicking Vascular Invasion
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
3/24/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Mixed Epithelial Endometrial Carcinoma. ISGyP Endometrial Cancer Project
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship
