PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
|
|
|
- Cameron McGee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version
2 Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns and Directional Statistics AARON S. FIELD, a,b YU-CHIEN WU, c AND ANDREW L. ALEXANDER c,d Departments of a Radiology, b Biomedical Engineering, c Medical Physics, and d Psychiatry, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, Wisconsin, USA ABSTRACT: The ability of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to probe the ultrastructural properties of biological tissues presents new possibilities for DTIbased tissue characterization, with the potential for greater pathologic specificity than conventional imaging methods. This is urgently needed in the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral neoplasms, where clinical decisions depend on the ability to discriminate tumor-involved from uninvolved tissue, a major shortcoming of conventional imaging. Several investigators have attempted to make this determination on the basis of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) or the fractional anisotropy (FA), with mixed results. The directionally encoded color map, with hues reflecting tensor orientation and intensity weighted by FA, provides an aesthetic and informative summary of DTI features throughout the brain in an easily interpreted format. The use of these maps is becoming increasingly common in both basic and clinical research, as well as in purely clinical settings. These examples serve to demonstrate our approach to the quantitation of regional diffusion tensor distributions using directional statistical methods. KEYWORDS: diffusion tensor imaging (DTI); apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC); fractional anisotropy (FA); color map; direction; edema; glioma INTRODUCTION The ability of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to probe the ultrastructural properties of biological tissues presents new possibilities for DTI-based tissue characterization, with the potential for greater pathologic specificity than conventional imaging methods. This is urgently needed in the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral neoplasms, where clinical decisions depend on the ability to discriminate tumor-involved from uninvolved tissue, a major shortcoming of conventional imaging. For example, it is frequently impossible to determine whether T2 prolongation in the white matter (WM) surrounding a glioma represents tumor infiltration or bland (tumor-free) edema. Several investigators have attempted to make this determination on the basis of the Address for correspondence: Aaron S. Field, M.D., Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology, University of Wisconsin, 600 Highland Avenue, CSC E3/311, Madison, WI Voice: ; fax: as.field@hosp.wisc.edu Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1064: (2005) New York Academy of Sciences. doi: /annals
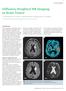
3 194 ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) 1 12 and/or the fractional anisotropy (FA), 5,9 11 with mixed results. The most recent studies employing the most sophisticated DTI methodology have revealed a tendency for tumor infiltration to cause greater FA reductions than edema. 5,10,11 However, these differences have been small and they may prove less significant to decision-making in individual patients than to statistical comparisons of sizable groups. We have observed substantial overlap of FA distributions between infiltrating gliomas and bland edema. 13 The ADC and FA constitute just a fraction of the information available from the diffusion tensor. The examination of individual eigenvalues, as well as measures of FIGURE 1. T2-weighted (T2W), ADC, FA, and FA-weighted, directionally encoded DTI color maps (FA ε 1 ) in a patient with a region of bland (tumor-free) vasogenic edema involving the left corona radiata and superior longitudinal fasciculus. 16 This region shows reduced FA, but normal color hues (arrow).
4 FIELD et al.: PRINCIPAL DIFFUSION DIRECTION 195 tensor shape and orientation, opens many new possibilities for tissue characterization. For example, the major eigenvalue of the diffusion tensor has been found to be significantly lower in the WM surrounding high-grade gliomas than in the WM surrounding metastases, even when the anisotropy has shown no difference. 14 Tensor shape metrics have revealed a relative shift from linear diffusion (prolate tensors) to planar diffusion (oblate tensors) in peritumoral fiber tracts, relative to contralateral tracts. 15 Such examples in which the diffusion tensor is exploited beyond the ADC and FA for purposes of tumoral or peritumoral tissue characterization are only just beginning to be explored. The directionally encoded color map, with hues reflecting tensor orientation and intensity weighted by FA, provides an aesthetic and informative summary of DTI features throughout the brain in an easily interpreted format. The use of these maps is becoming increasingly common in both basic and clinical research, as well as in purely clinical settings. Our group has described four distinct patterns of tumorrelated pathology in WM tracts on FA-weighted, directionally encoded color maps, categorized on the basis of tensor anisotropy and orientation. 16 Unfortunately, these FIGURE 2. T2-weighted (T2W), ADC, FA, and FA-weighted, directionally encoded DTI color maps (FA ε 1 ) in a patient with an infiltrating glioma involving the left corona radiata and subcortical U-fibers. 16 This region shows both reduced FA and abnormal color hues (arrow), which are not explained by any apparent tract deviation.
5 196 ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES patterns rely on subjective assessments of color hue and intensity; although such assessments can be clinically relevant, a more objective, quantitative approach is needed for purposes of further research. Specifically, a formal methodology for analyzing regional distributions of tensor orientations, including measures of regional directional tendency and dispersion, intervoxel coherence, and interhemispheric symmetry, is needed in order to exploit DTI more reliably in the setting of cerebral neoplasm. We are developing various metrics to meet this need, 17 employing the theory and methods of directional statistics. For example, we have observed several WM tracts infiltrated by bland edema where anisotropy is reduced with no appreciable change in hue on directionally encoded color maps, while several tracts infiltrated by gliomas have had anisotropy reductions accompanied by altered hues that were unexplained by visible tract deviations (FIGS. 1 and 2). Subjective impressions such as these must be validated quantitatively, motivating our development of directional statistical approaches. REGIONAL METRICS FOR TENSOR ORIENTATION AND SYMMETRY Directional Histograms ( Rose Diagrams) The distribution of major eigenvectors in a region of interest (ROI) can be described in terms of their polar and azimuthal angles (θ and φ, respectively) in 3D space. 17 FIGURE 3. The distribution of major eigenvectors in a region of interest can be described in terms of their polar and azimuthal angles (θ and φ, respectively) in 3D space. 17 Specifically, the polar angle (θ) denotes the angle between the eigenvector and the x-y plane, and the azimuthal angle (φ) denotes the angle between the eigenvector s projection in the x-y plane and the x-axis.
6 FIELD et al.: PRINCIPAL DIFFUSION DIRECTION 197 Specifically, the polar angle (θ) denotes the angle between the eigenvector and the x-y ( axial ) plane, and the azimuthal angle (φ) denotes the angle between the eigenvector s projection in the x-y plane and the x-axis (right-left direction) (FIG. 3). Since the WM tract orientations will be mirrored across the cerebral hemispheres, the rotation conventions of φ are reversed for regions in the left and the right hemispheres to facilitate symmetry comparisons. The distribution of major eigenvector directions can be calculated for any ROI and subjected to further analysis or displayed as a pair of spherical-coordinate histograms (polar and azimuthal), or rose diagrams. In a rose diagram, the arc subtended by each sector bin represents a range of angles, and the length of each bin reflects the frequency of occurrence for that range (FIG. 4). Note that this approach is not rotationally invariant unless θ and φ are referenced to anatomically standardized planes. For example, the y-z ( sagittal ) FIGURE 4. Directional histograms (rose diagrams) for posterior limb of internal capsule (PLIC), superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF), and genu of the corpus callosum (CC) in a normal subject. Note the unique distributions characterizing each of these major tracts. These distributions can be subjected to statistical analysis seeking changes related to pathology.
7 198 ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES plane could be defined along the interhemispheric fissure, and the x-y plane along the intercommissural line and perpendicular to the y-z plane. Scatter Matrix The preferred orientation and dispersion of major eigenvectors (analogous to mean and variance, respectively, of eigenvector orientation) in an ROI can also be summarized in terms of the scatter matrix. 17 If ε 1i is the major eigenvector of the diffusion tensor for the i-th voxel within an ROI containing n voxels, then the scatter matrix for the ROI is defined as T = n ( 1 n) t ε 1i ε 1i i = 1 where t denotes the vector transpose. Like the diffusion tensors themselves, T is a 3 3 diagonally symmetric matrix with its own eigenvectors, t 1, t 2, and t 3, which describe the orientation of the tensor distribution within the ROI. Symmetry Index A measure of interhemispheric symmetry for homologous ROIs in the brain may be defined as the dot product of the scatter matrix major eigenvectors for left and right ROIs: 17 S = t1l t1r. A value of S approaching unity indicates a high degree of interhemispheric symmetry, while S near zero indicates that the left and right tensor distributions are nearly orthogonal. Note that accurate S measurements require the y-z plane to be parallel to the interhemispheric fissure. CASE EXAMPLES: VASOGENIC EDEMA AND INFILTRATING GLIOMA Case 1: Vasogenic Edema A patient with a small ( 1 cm) brain metastasis surrounded by a much larger region of vasogenic edema (presumed tumor-free) involving the corona radiata (CR) underwent DTI at 1.5 T using a quadrature head coil and a single-shot, diffusionweighted spin-echo EPI sequence with diffusion encoding in 23 directions (b = 0 and 912 s/mm 2, slice thickness = 3 mm, TR/TE = 4000/72 ms, FOV = 24 cm, matrix = interpolated to , NEX = 4). The diffusion tensor at each voxel was estimated and diagonalized, and maps of FA were generated, using published methods. 18,19 A 3D ROI was manually traced within the edematous CR on FA maps and a homologous ROI was traced in the contralateral CR. Directional histograms for these ROIs (FIG. 5) revealed only nominal changes in tensor distributions, and the symmetry index, calculated as described above, was S = 0.99, indicating a high degree of interhemispheric symmetry.
8 FIELD et al.: PRINCIPAL DIFFUSION DIRECTION 199 FIGURE 5. ROI rose diagrams of the corona radiata (CR) in case 1, a patient with bland vasogenic edema. 17 (Left) Edema ROI. (Right) Homologous ROI in normal contralateral CR. Only nominal changes in tensor distributions are evident. Symmetry index S = Case 2: Infiltrating Glioma A patient with an oligodendroglioma (WHO grade II) infiltrating the superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) underwent DTI with postprocessing as described for case 1. Directional histograms for homologous SLF ROIs (FIG. 6) revealed more substantial changes in tensor distributions than those seen in the edema case, and the symmetry index was S = 0.74, indicating a lesser degree of interhemispheric symmetry. CONCLUSIONS These examples serve to demonstrate our approach to the quantitation of regional diffusion tensor distributions using directional statistical methods. Other approaches are certainly possible (e.g., ref. 20). Quantitation along these lines is urgently needed in order to validate the subjective impressions derived from the popular directionally encoded color maps and to enable statistical data analysis whenever relevant changes in fiber tract orientations are postulated or (subjectively) observed. The rose diagrams enable histogram-based analyses of major eigenvector distributions within ROIs;
9 200 ANNALS NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES FIGURE 6. ROI rose diagrams of the superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) in case 2, a patient with an infiltrating oligodendroglioma. 17 (Left) Tumor ROI. (Right) Homologous ROI in normal contralateral CR. Changes in tensor distributions are more significant than for bland edema in case 1. Symmetry index S = major CNS fiber tracts are expected to have characteristic profiles on these histograms (e.g., FIG. 4), which may be tested for changes resulting from pathology. The symmetry index, derived from the scatter matrix, enables a patient whose disease is limited to one hemisphere to serve as his/her own control. The lesser degree of interhemispheric symmetry that our approach revealed in an infiltrating glioma, as compared to vasogenic edema, suggests that regional analysis of tensor orientation may have an important role to play in this and other problems of tissue characterization. Further study is needed to determine the sensitivity and specificity of our approach in the face of variations in tumor type, grade, location, prior treatment, etc. REFERENCES 1. BRUNBERG, J.A., T.L. CHENEVERT, P.E. MCKEEVER et al In vivo MR determination of water diffusion coefficients and diffusion anisotropy: correlation with structural alteration in gliomas of the cerebral hemispheres. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 16: STADNIK, T.W., C. CHASKIS, A. MICHOTTE et al Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of intracerebral masses: comparison with conventional MR imaging and histologic findings. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 22:
10 FIELD et al.: PRINCIPAL DIFFUSION DIRECTION KONO, K., Y. INOUE, K. NAKAYAMA et al The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 22: SINHA, S., M.E. BASTIN, I.R. WHITTLE & J.M. WARDLAW Diffusion tensor MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 23: BASTIN, M.E., S. SINHA, I.R. WHITTLE & J.M. WARDLAW Measurements of water diffusion and T1 values in peritumoral oedematous brain. Neuroreport 13: TIEN, R.D., G.J. FELSBERG, H. FRIEDMAN et al MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas: value of diffusion-weighted echo planar pulse sequences. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 162: KRABBE, K., P. GIDEON, P. WAGN et al MR diffusion imaging of human intracranial tumours. Neuroradiology 39: CASTILLO, M., J.K. SMITH, L. KWOCK & K. WILBER Apparent diffusion coefficients in the evaluation of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 22: LU, S., D. AHN, G. JOHNSON & S. CHA Peritumoral diffusion tensor imaging of highgrade gliomas and metastatic brain tumors. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 24: LU, S., D. AHN, G. JOHNSON et al Diffusion-tensor MR imaging of intracranial neoplasia and associated peritumoral edema: introduction of the tumor infiltration index. Radiology 232: PROVENZALE, J.M., P. MCGRAW, P. MHATRE et al Peritumoral brain regions in gliomas and meningiomas: investigation with isotropic diffusion-weighted MR imaging and diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 232: MAIER, S.E., P. BOGNER, G. BAJZIK et al Normal brain and brain tumor: multicomponent apparent diffusion coefficient line scan imaging. Radiology 219: FIELD, A.S., A.L. ALEXANDER, V.M. HAUGHTON et al Effect of vasogenic edema on sensitivity of white matter tractography with diffusion tensor imaging. In ASNR 2002 Proceedings, American Society of Neuroradiology 40th Annual Meeting, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, May 11 17, 2002; O-269, p WIEGELL, M.R., J.W. HENSON, D.S. TUCH & A.G. SORENSEN Diffusion tensor imaging shows potential to differentiate infiltrating from non-infiltrating tumors. In Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) 11th Scientific Meeting, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, July 10 16, 2003, p ZHANG, S., M.E. BASTIN, D.H. LAIDLAW et al Visualization and analysis of white matter structural asymmetry in diffusion tensor MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 51: FIELD, A.S., A.L. ALEXANDER, Y-C. WU et al Diffusion tensor eigenvector directional color imaging patterns in the evaluation of cerebral white matter tracts altered by tumor. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 20: WU, Y-C., A.S. FIELD, M. CHUNG et al Quantitative analysis of diffusion tensor orientation: theoretical framework. Magn. Reson. Med. 52: HASAN, K.M., D.L. PARKER & A.L. ALEXANDER Comparison of gradient encoding schemes for diffusion-tensor MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 13: HASAN, K.M., P.J. BASSER, D.L. PARKER & A.L. ALEXANDER Analytical computation of the eigenvalues and eigenvectors in DT-MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 152: SCHWARTZMAN, A., R.F. DOUGHERTY & J.E. TAYLOR Comparison of principal diffusion directions using directional statistics. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, Budapest, Hungary, June 13 17, 2004; WE-300.
Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography
 Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Diagnostic Value of Peritumoral Minimum Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for Differentiation of Glioblastoma Multiforme From Solitary Metastatic Lesions
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a sensitive technique
 Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Diffusion MRI explores new indications
 DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS
 Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
DWI is a powerful technique that measures the microscopic
 Published November 8, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3327 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Improved Conspicuity and Delineation of High-Grade Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumors Using Restriction Spectrum Imaging : Quantitative
Published November 8, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3327 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Improved Conspicuity and Delineation of High-Grade Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumors Using Restriction Spectrum Imaging : Quantitative
Meningiomas account for between 16% and 20% of primary
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.-H. Toh M. Castillo A.M.-C. Wong K.-C. Wei H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng Y.-L. Wan Differentiation Between and s with Use of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The differentiation
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results.
 Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results. Sarah M. E. Gierhan 1,2, Peter Rhone 3,4, Alfred Anwander 1, Isabel Jost 3, Clara Frydrychowicz 3, Karl-Titus Hoffmann 4, Jürgen Meixensberger
Tracking the language pathways in edema patients: Preliminary results. Sarah M. E. Gierhan 1,2, Peter Rhone 3,4, Alfred Anwander 1, Isabel Jost 3, Clara Frydrychowicz 3, Karl-Titus Hoffmann 4, Jürgen Meixensberger
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Assessment of Brain White Matter Maturation During the First Postnatal Year
 DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity
 Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity ISMRM 2017: http://submissions.mirasmart.com/ismrm2017/viewsubmissionpublic.aspx?sei=8t1bikppq Jeroen
Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity ISMRM 2017: http://submissions.mirasmart.com/ismrm2017/viewsubmissionpublic.aspx?sei=8t1bikppq Jeroen
Diffusion Anisotropy of the Internal Capsule and the Corona Radiata in Association with Stroke and Tumors as Measured by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :56 6, March 1 Diffusion Anisotropy of the Internal Capsule and the Corona Radiata in Association with Stroke and Tumors as Measured by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Shuichi Higano,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :56 6, March 1 Diffusion Anisotropy of the Internal Capsule and the Corona Radiata in Association with Stroke and Tumors as Measured by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Shuichi Higano,
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy
 DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors.
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology
 Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic?
 Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
The role of diffusion and perfusion weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of cerebral tumors: a review and future perspectives
 Svolos et al. Cancer Imaging 2014, 14:20 REVIEW Open Access The role of diffusion and perfusion weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of cerebral tumors: a review and future perspectives Patricia
Svolos et al. Cancer Imaging 2014, 14:20 REVIEW Open Access The role of diffusion and perfusion weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of cerebral tumors: a review and future perspectives Patricia
Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain
 Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain Andrew L. Alexander,* Jee Eun Lee,* Mariana Lazar, and Aaron S. Field *Departments
Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Brain Andrew L. Alexander,* Jee Eun Lee,* Mariana Lazar, and Aaron S. Field *Departments
Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $
 Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $ Savannah C. Partridge, a Pratik Mukherjee, a Roland G. Henry, a Steven P. Miller, b,c Jeffrey I. Berman,
Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns $ Savannah C. Partridge, a Pratik Mukherjee, a Roland G. Henry, a Steven P. Miller, b,c Jeffrey I. Berman,
During human aging, the brain exhibits both macro- and
 Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
ajnr am j. neuroradiol apr; 28(4):
 ajnr am j. neuroradiol. 2007 apr; 28(4): 724-30 7 Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic
ajnr am j. neuroradiol. 2007 apr; 28(4): 724-30 7 Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Brain Tumor
 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Brain Tumor L. Celso Hygino da Cruz Jr.; Emerson L. Gasparetto; Roberto C. Domingues; Romeu C. Domingues CDPI e Multi-Imagem Ressonância Magnética, Rio de Janeiro RJ, Brazil
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Brain Tumor L. Celso Hygino da Cruz Jr.; Emerson L. Gasparetto; Roberto C. Domingues; Romeu C. Domingues CDPI e Multi-Imagem Ressonância Magnética, Rio de Janeiro RJ, Brazil
Overview. Fundamentals of functional MRI. Task related versus resting state functional imaging for sensorimotor mapping
 Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans
 Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Axial Diffusivity of the Corona Radiata Correlated With Ventricular Size in Adult Hydrocephalus
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Cauley and Cataltepe Imaging Adult Hydrocephalus Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Keith A Cauley Oguz Cataltepe 2 Cauley KA,
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Cauley and Cataltepe Imaging Adult Hydrocephalus Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Keith A Cauley Oguz Cataltepe 2 Cauley KA,
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients. SDM (39) 221 Left superior longitudinal
 Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Supplemental Data Table S1 Summary of findings from the previous meta-analyses of DTI studies in MDD patients Study Analysis Method Included studies, n MDD (medicated) HC Results (MDDHC)
Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
Traumatic axonal injury is a frequent cause of impaired clinical
 Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
Published July 10, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1213 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.R. Rutgers P. Fillard G. Paradot M. Tadié P. Lasjaunias D. Ducreux Diffusion Tensor Imaging Characteristics of the Corpus Callosum in Mild,
Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension pathogenesis?: Diffusion weighted MR imaging study
 Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Available online at www.medicinescience.org ORIGINAL RESEARCH Medicine Science International Medical Journal Medicine Science 2019; ( ): Is cerebral edema effective in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Published July 31, 2014 as /ajnr.A4050
 Published July 31, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4050 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuromyelitis Optica: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study T.M. Doring, F.C.R. Lopes, T.T.A. Kubo, G. Tukamoto, M.C. Kimura, R.M. Strecker,
Published July 31, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4050 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuromyelitis Optica: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study T.M. Doring, F.C.R. Lopes, T.T.A. Kubo, G. Tukamoto, M.C. Kimura, R.M. Strecker,
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:633 637, April 2003 Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Daniel L. A. Camacho, J. Keith Smith, and Mauricio Castillo
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:633 637, April 2003 Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Daniel L. A. Camacho, J. Keith Smith, and Mauricio Castillo
Diffusion Anisotropy in the Corpus Callosum
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:803 808, May 2002 Diffusion Anisotropy in the Corpus Callosum Neeraj B. Chepuri, Yi-Fen Yen, Jonathan H. Burdette, Hong Li, Dixon M. Moody, and Joseph A. Maldjian BACKGROUND AND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:803 808, May 2002 Diffusion Anisotropy in the Corpus Callosum Neeraj B. Chepuri, Yi-Fen Yen, Jonathan H. Burdette, Hong Li, Dixon M. Moody, and Joseph A. Maldjian BACKGROUND AND
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Diffusion-tensor imaging in brain tumors
 REVIEW Diffusion-tensor imaging in brain tumors Diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) is the only novel imaging technique that is able to demonstrate white matter tracts and their structural changes related to
REVIEW Diffusion-tensor imaging in brain tumors Diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) is the only novel imaging technique that is able to demonstrate white matter tracts and their structural changes related to
The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:115 119 (2001) Original Research Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner Yoshiaki Mamata, MD, PhD, Hatsuho Mamata, MD, Arya Nabavi,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 13:115 119 (2001) Original Research Intraoperative Diffusion Imaging on a 0.5 Tesla Interventional Scanner Yoshiaki Mamata, MD, PhD, Hatsuho Mamata, MD, Arya Nabavi,
Magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is
 Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Sulci density map to aid in use of apparent diffusion coefficient for therapy evaluation
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Magnetic Resonance Imaging 26 (2008) 20 25 Sulci density map to aid in use of apparent diffusion coefficient for therapy evaluation Lars A. Ewell4, Christopher
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Magnetic Resonance Imaging 26 (2008) 20 25 Sulci density map to aid in use of apparent diffusion coefficient for therapy evaluation Lars A. Ewell4, Christopher
Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality
 The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis. Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
The Effect of Local Fiber Model On Population Studies
 The Effect of Local Fiber Model On Population Studies James G. Malcolm Marek Kubicki Martha E. Shenton Yogesh Rathi Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA VA Boston Healthcare
The Effect of Local Fiber Model On Population Studies James G. Malcolm Marek Kubicki Martha E. Shenton Yogesh Rathi Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA VA Boston Healthcare
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging 12/06/2013
 12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491 1499, September 1999 Investigation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Diffusion Tensor Anisotropy in Acute and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Andrew L. Tievsky, Thomas
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
/13/$ IEEE
 Multivariate Discriminant Analysis of Multiparametric Brain MRI to Differentiate High Grade and Low Grade Gliomas - A Computer- Aided Diagnosis Development Study *, Zeynep Firat, Ilhami Kovanlikaya, Ugur
Multivariate Discriminant Analysis of Multiparametric Brain MRI to Differentiate High Grade and Low Grade Gliomas - A Computer- Aided Diagnosis Development Study *, Zeynep Firat, Ilhami Kovanlikaya, Ugur
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging
 Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
Diffusional Anisotropy of the Human Brain Assessed with Diffusion Weighted MR: Relation with Normal Brain Development and Aging Yoshiyuki Nomura, Hajime Sakuma, Kan Takeda, Tomoyasu Tagami, Yasuyuki Okuda,
MR Diffusion Tensor Imaging, Fiber Tracking, and Single-Voxel Spectroscopy Findings in an Unusual MELAS Case
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1840 1844, August 2005 Case Report MR Diffusion Tensor Imaging, Fiber Tracking, and Single-Voxel Spectroscopy Findings in an Unusual MELAS Case Denis Ducreux, Ghaidaa Nasser, Catherine
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1840 1844, August 2005 Case Report MR Diffusion Tensor Imaging, Fiber Tracking, and Single-Voxel Spectroscopy Findings in an Unusual MELAS Case Denis Ducreux, Ghaidaa Nasser, Catherine
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Original Article Artigo Original
 Original Article Artigo Original Itagiba VGA et al. Use of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of patterns of white matter involvement in patients with brain tumors: is it useful
Original Article Artigo Original Itagiba VGA et al. Use of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of patterns of white matter involvement in patients with brain tumors: is it useful
3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions
 110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry
 2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries
 1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!!
 Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Water Diffusion Changes in Wallerian Degeneration and Their Dependence on White Matter Architecture
 NeuroImage 13, 1174 1185 (2001) doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0765, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Water Diffusion Changes in Wallerian Degeneration and Their Dependence on White Matter Architecture
NeuroImage 13, 1174 1185 (2001) doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0765, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Water Diffusion Changes in Wallerian Degeneration and Their Dependence on White Matter Architecture
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Stereotactic Diffusion Tensor Tractography For Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Supratentorial brain tumors in the first year of life are challenging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Diffusion Imaging for Tumor Grading of Supratentorial Brain Tumors in the First Year of Life S.F. Kralik, A. Taha, A.P. Kamer, J.S. Cardinal, T.A. Seltman, and C.Y. Ho ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Diffusion Imaging for Tumor Grading of Supratentorial Brain Tumors in the First Year of Life S.F. Kralik, A. Taha, A.P. Kamer, J.S. Cardinal, T.A. Seltman, and C.Y. Ho ABSTRACT
Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor
 107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine are potentially catastrophic.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
Use of Diffusion Tensor Images in Glioma Growth Modeling for Radiotherapy Target Delineation
 Use of Diffusion Tensor Images in Glioma Growth Modeling for Radiotherapy Target Delineation Florian Dittmann, Bjoern Menze, Ender Konukoglu, Jan Unkelbach To cite this version: Florian Dittmann, Bjoern
Use of Diffusion Tensor Images in Glioma Growth Modeling for Radiotherapy Target Delineation Florian Dittmann, Bjoern Menze, Ender Konukoglu, Jan Unkelbach To cite this version: Florian Dittmann, Bjoern
Journal of Ningxia Medical University. Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI b 500 s / mm s / mm 2
 786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
786 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 34 8 2012 8 1674-6309 2012 08-0786 - 04 MRI 1 2 2 2 2 1 1. 750002 2. 750004 MR Diffusion Weighted Imaging DWI 27 38 DWI2 b 500 s / mm 2 1000 s / mm 2 Apparent
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Characterization of central nervous system structures by magnetic resonance diffusion anisotropy
 Neurochemistry International 45 (2004) 553 560 Characterization of central nervous system structures by magnetic resonance diffusion anisotropy Hatsuho Mamata, Ferenc A Jolesz, Stephan E Maier Department
Neurochemistry International 45 (2004) 553 560 Characterization of central nervous system structures by magnetic resonance diffusion anisotropy Hatsuho Mamata, Ferenc A Jolesz, Stephan E Maier Department
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT FOR DEGREE OF DM (NEUROIMAGING AND INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY) ( ) OF THE
 COMPARISON OF DIFFUSION TENSOR IMAGING, SUSCEPTIBILITY-WEIGHTED IMAGING AND DYNAMIC SUSCEPTIBILITY CONTRAST-ENHANCED MRI IN DIFFERENTIATING HIGH-GRADE INTRA-AXIAL CEREBRAL TUMORS THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL
COMPARISON OF DIFFUSION TENSOR IMAGING, SUSCEPTIBILITY-WEIGHTED IMAGING AND DYNAMIC SUSCEPTIBILITY CONTRAST-ENHANCED MRI IN DIFFERENTIATING HIGH-GRADE INTRA-AXIAL CEREBRAL TUMORS THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL
CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]
![CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE] CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]](/thumbs/86/94270487.jpg) ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
Gliomas are the most common primary brain tumors.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S.J. Price R. Jena N.G. Burnet P.J. Hutchinson A.F. Dean A. Peña J.D. Pickard T.A. Carpenter J.H. Gillard Improved Delineation of Glioma Margins and Regions of Infiltration with the Use
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S.J. Price R. Jena N.G. Burnet P.J. Hutchinson A.F. Dean A. Peña J.D. Pickard T.A. Carpenter J.H. Gillard Improved Delineation of Glioma Margins and Regions of Infiltration with the Use
High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1107 1114, May 2005 High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions Rakesh K. Gupta, Khader M. Hasan, Asht M. Mishra, Deepak Jha, Mazhar
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1107 1114, May 2005 High Fractional Anisotropy in Brain Abscesses versus Other Cystic Intracranial Lesions Rakesh K. Gupta, Khader M. Hasan, Asht M. Mishra, Deepak Jha, Mazhar
DISTINCTION BETWEEN RECURRENT GLIOMA AND RADIATION INJURY USING MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY IN COMBINATION WITH DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
C ognitive and vocational sequelae are common complications
 850 PAPER Evidence for white matter disruption in traumatic brain injury without macroscopic lesions N Nakayama, A Okumura, J Shinoda, Y-T Yasokawa, K Miwa, S-I Yoshimura, T Iwama... J Neurol Neurosurg
850 PAPER Evidence for white matter disruption in traumatic brain injury without macroscopic lesions N Nakayama, A Okumura, J Shinoda, Y-T Yasokawa, K Miwa, S-I Yoshimura, T Iwama... J Neurol Neurosurg
High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
