Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients
|
|
|
- Bertina Todd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , April 2003 Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Daniel L. A. Camacho, J. Keith Smith, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Distinguishing between toxoplasmosis and lymphoma brain lesions in AIDS patients is difficult but clinically relevant. This study was performed to test the hypothesis that diffusion-weighted (DW) imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps can be used to distinguish these two lesions. METHODS: The ADC values were calculated in regions of interest placed in 13 brain toxoplasmosis lesions and eight brain lymphoma lesions in patients with AIDS. These values were compared with those of normal white matter. ADC ratios in lymphoma lesions then were compared with those in toxoplasmosis lesions by using a two-sample two-tailed t test. RESULTS: Toxoplasmosis lesions demonstrated significantly greater diffusion than that of lymphoma lesions (P.004). ADC ratios were (mean standard deviation) in the 13 toxoplasmosis lesions and in the eight lymphoma lesions. While considerable overlap was present for ADC ratios between 1.0 and 1.6, ADC ratios greater than 1.6 were associated solely with toxoplasmosis, accounting for seven of 13 toxoplasmosis lesions. CONCLUSION: ADC values are helpful in differentiating toxoplasmosis from lymphoma in patients with AIDS. Accurate radiographic differentiation of focal brain masses in patients with AIDS is critical to the timely initiation of appropriate therapy. The two most common etiologies in this population, toxoplasmosis and lymphoma, frequently have similar characteristics on both CT and conventional contrast-enhanced MR images (1, 2). Some of these patients are presumptively treated for toxoplasmosis, and they may proceed to surgical biopsy if their subsequent clinical and radiologic response is unfavorable. By delaying therapy for lymphoma lesions and by exposing the patient to the potential toxicities of anti-toxoplasma medications, the patient s neurologic status may deteriorate (3, 4). Furthermore, the concomitant use of steroids during this therapy trial may falsely suggest that a central nervous system lymphoma has responded to Toxoplasma therapy (5). Recently, diffusion-weighted (DW) MR imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient maps (ADC) has been used as a tool for characterizing infectious and neoplastic brain lesions. Restricted water diffusion Received September 23, 2002; accepted after revision November 12. From the Department of Radiology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Address reprint requests to Daniel L. A. Camacho, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Radiology, University of North Carolina, CB 7510, Chapel Hill, NC American Society of Neuroradiology has been demonstrated within the cores of brain abscesses (6 14). Numerous investigators have explored the diffusion properties of brain tumors, describing increased water diffusibility within necrotic tumor centers and correlating increased tumor cellularity with restricted diffusion (6, 8, 11 13, 15 21). To our knowledge, no groups have reported the MR diffusion properties of infectious abscesses or neoplastic tumors in the AIDS population, whose impaired cellular immune response may confer unique diffusion properties to these lesions. The purpose of this study is to test the hypothesis that toxoplasmosis lesions and lymphoma lesions in AIDS patients can be differentiated by using DW imaging with ADC maps. Methods Through a computerized search of electronic medical records at our institution, we identified AIDS patients with proved or presumed (based on response to treatment) brain toxoplasmosis and patients with proved brain lymphoma who were evaluated with MR imaging during Within this group of patients, initial MR imaging studies that demonstrated rim-enhancing brain lesions larger than 1 cm were included in the institutional review board approved study. Three investigators (D.L.A.C., J.K.S., M.C.) retrospectively analyzed the conventional contrast-enhanced brain MR images and echo-planar DW images with ADC maps, and differences in opinion were solved by consensus. A diagnosis was established by means of biopsy in all patients with lymphomas and in two patients with toxoplasmosis. Positive serum antibody re- 633
2 634 CAMACHO AJNR: 24, April 2003 Findings in seven patients with toxoplasmosis (13 lesions) and four with lymphoma (eight lesions) Patient Age, y/sex, Diagnosis and Location Size, cm Rim Characteristics* Lesion Shape Lesion ADC, 10 3 mm 2 /s ADC Ratio 26/F, toxoplasmosis R parietal 1.8 Thin, uniform Round /M, toxoplasmosis L basal ganglia 3.3 Thick, nodular Irregular /M, toxoplasmosis R basal ganglia 3.2 Thick, nodular Round /M, toxoplasmosis L thalamus 1.3 Thin, uniform Round /M, toxoplasmosis R occipital 1.4 Thin, nodular Irregular R frontal 1.6 Thin, nodular Round L frontal 1.1 Thin, nodular Round /M, toxoplasmosis R frontal 2.0 Thick, nodular Irregular Cerebellar vermis 2.1 Thin, irregular Irregular /F, toxoplasmosis L frontal 1.4 Thin, nodular Round L frontal 3.0 Thin, irregular Irregular R basal ganglia 2.2 Thin, irregular Irregular R frontal 1.3 Thin, irregular Irregular /M, lymphoma L frontoparietal 5.8 Thick, nodular Irregular /M, lymphoma R temporal 1.6 Thin, nodular Round L occipital 1.7 Thin, uniform Round L occipital 2.6 Thick, nodular Irregular L frontal 1.8 Thin, uniform Irregular /F, lymphoma R parietal 2.1 Thin, uniform Irregular L parietal 1.8 Thin, uniform Round /M, lymphoma L frontal 3.8 Thin, uniform Round * On T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced MR images. sults and a favorable treatment response at 3 and 6 weeks were used to establish the diagnosis in five patients with toxoplasmosis. Conventional MR imaging was performed on a 1.5-T system (Vision or Sonata; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) by using precontrast T1- (TR/TE, /12; matrix, ; field of view, mm) and T2-weighted (TR/TE, ; matrix, ; field of view, mm) sequences in multiple planes, and postcontrast (Omniscan; Nycomed, Oslo, Norway) T1-weighted images were acquired in sagittal, axial, and coronal projections by using the same parameters as those of precontrast T1-weighted sequences. ADC maps were acquired by using echo planar diffusion-weighted sequences (TR/TE, 5100/137; matrix, ; field of view, mm) at b values of 50, 500, and 1000 s/mm 2 in all patients. Diffusion gradients were applied in the z, y, and x directions. Postprocessing of the ADC maps was performed offline on an independent computer workstation. For purposes of analysis, we chose only those lesions measuring more than 1 cm in diameter. For each lesion, regions of interest (ROIs) were manually selected in the nonenhancing central core of the lesion and in contralateral, normal-appearing white matter. ROI diameters were approximately one-half the diameter of the portion of the lesion within the enhancing rim. An ADC ratio was computed as the ratio of the mean ADC within the lesion to the mean ADC in normal white matter. Lymphoma ADC ratios were compared with toxoplasmosis ADC ratios by using a two-sample two-tailed t test, with an assumption of unequal variances. A significant difference was accepted if the P value was less than.05. Results We identified seven patients with toxoplasmosis (13 lesions) and four with lymphoma (eight lesions) (Table 1). The ages of the patients with toxoplasmosis (five men and two women) ranged from 26 to 46 years (mean, 35.7 years), and the ages of the lymphoma patients (three men and one woman) ranged from 36 to 51 years (mean, 40.8 years). In both the lymphoma group and the toxoplasmosis group, T2-weighted images demonstrated edema around all lesions, and gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted images showed rim enhancement with a dark central core. Toxoplasmosis lesions demonstrated diffusion significantly greater than that of lymphoma lesions (P.004) (Figs 1 3). ADC ratios were (mean SD) (range, ) in the 13 toxoplasmosis lesions and (range, ) in the eight lymphoma lesions. While considerable overlap was present for the ADC ratios between 1.0 and 1.6, ADC ratios greater than 1.6 were associated solely with
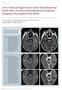
3 AJNR: 24, April 2003 BRAIN LESIONS IN AIDS 635 FIG 1. ADC ratios in toxoplasmosis and lymphoma lesions. Column heights and error bars represent the mean and SD, respectively. ADC ratios in the toxoplasmosis lesions are significantly greater than those in the lymphoma lesions. toxoplasmosis, accounting for seven of 13 toxoplasmosis lesions. No toxoplasmosis lesion had an ADC less than that of uninvolved white matter. Discussion Given the difficulty in differentiating infectious lesions from malignant brain masses in AIDS patients by using conventional CT and MR imaging and given the potential morbidity associated with delayed diagnosis and surgical biopsy, additional noninvasive tools are needed to direct appropriate therapy. Numerous investigators have advocated the use of thallium-201 single photon emission CT as a means to distinguish lymphoma from nonmalignant brain lesions in AIDS patients, demonstrating sensitivities of as high as 100% (22 25). Recent studies, however, yielded less promising results, with sensitivities of 60% and 71%, respectively (26, 27). Positron emission tomography (PET) has been shown to be useful in the accurate differentiation of hypometabolic toxoplasmosis lesions (28, 29), with a reported sensitivity and specificity of more than 90% (28). In one series (27), the sensitivity of PET was lower (50% 66%), but the authors acknowledged that their small sample sizes could have influenced their results. The limited availability of PET scanners and the substantial cost of the study may preclude its widespread use in this clinical setting. Proton MR spectroscopy has also been used to study brain lymphoma and toxoplasmosis. Chang and Ernst (30) and Chang et al (31) found unique metabolite profiles in toxoplasmosis and lymphoma lesions by using MR spectroscopy. In contrast, two other studies (27, 32) demonstrated an overlap in the metabolite profiles of these lesions, and the investigators suggested that other imaging modalities may be more reliable in this setting. Ernst et al (3) used perfusion MR imaging and reported a significantly increased relative cerebral blood volume in lymphoma lesions. They recommended further studies with larger sample sizes to confirm their findings. Contrary to many of the previously mentioned methods that require special acquisition and postprocessing, DW imaging is readily available and rapidly performed, and the images are easily postprocessed. Because of these reasons, we sought to determine if DW imaging could be used to differentiate toxoplasmosis from lymphoma in patients with AIDS. In our study, the ADC values in toxoplasmosis lesions were significantly greater than those in lymphoma lesions. This finding suggests that this method might provide valuable additional information in differentiating toxoplasmosis from lymphoma in AIDS patients. FIG 2. Axial images in an AIDS patient with toxoplasmosis. A, Axial T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced MR image. The lesion in the right basal ganglia has an irregular, enhancing rim. B, DW image (b 1000 s/mm 2 ). The core of the lesion demonstrates unrestricted diffusion. C, ADC map of a toxoplasmosis lesion in the right basal ganglia. The outline indicates the ROI within the lesion used for ADC computation. The core of the lesion has a mean ADC that is increased relative to that in normal white matter (ADC ratio, 2.23).
4 636 CAMACHO AJNR: 24, April 2003 FIG 3. Axial images in an AIDS patient with lymphoma. A, Axial T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced MR image. A lesion with an enhancing rim is present in the left frontal lobe. B, DW image (b 1000 s/mm 2 ). The signal intensity of the core of the lesion is similar to that of uninvolved white matter. C, ADC map of a lymphoma lesion in the left frontal lobe. The outline indicates the ROI within the lesion used for ADC computation. The core of the lesion has a mean ADC that is similar to that of normal white matter (ADC ratio, 1.25). All toxoplasmosis lesions in our patients revealed increased diffusion relative to that in white matter, in contradistinction to the restricted diffusion within brain abscesses described in numerous earlier investigations (6 14). Toxoplasmosis ADC ratios in our study were , with no ADC ratio less than 1.0, whereas mean ADC ratios within brain abscesses in other studies ranged from 0.36 to 0.83 (7, 8). Chang and Ernst (30) reported an ADC ratio of 1.05 in a single toxoplasmosis lesion. Whether the ROI used for ADC computation in that last study included the contrast-enhancing rim is unclear. The restricted diffusion within a brain abscess is thought to be due to a restriction of microscopic movement of water molecules within a complex matrix of proteins, inflammatory cells, cellular debris, and bacteria in high-viscosity pus. Water molecules in abscesses are bound to carboxyl, hydroxyl, and amino groups on the surfaces of macromolecules, which further restrict their translational motion. Like other abscesses, the abscesses of toxoplasmosis consist of an outer astroglial reaction that surrounds a proliferating zone of capillaries and fibroblasts, which in turn surround a central region of dead and dying brain infiltrated by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and histiocytes (2). Increased diffusion within toxoplasmosis lesions may reflect relatively decreased viscosity within their central cores; this is perhaps due to an impaired cellular immune response in these immunocompromised patients. Further pathologic studies to quantify the viscosity and cellularity, both in toxoplasmosis abscesses and in other brain abscesses, may provide further insight into these radiologic findings. In our patients, diffusion within lymphoma lesions was more restricted than in toxoplasmosis lesions, and this difference likely reflected the highly cellular, aggressive nature of lymphoma lesions, even within their nonenhancing central cores. Lymphoma ADC ratios in this study ( ) were similar to those reported by Guo et al ( ) (33). Several studies have demonstrated that diffusion within lymphoma lesions is typically less than that in most other brain malignancies (13, 18, 20, 35). Guo et al (33) also compared the cellularity in high-grade astrocytomas and lymphomas by histologically quantifying the nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio (N/C). They found that mean N/C was 1.45 in lymphomas and 0.24 in highgrade astrocytomas, while the mean ADC ratio was 1.15 in lymphomas and 1.68 in high-grade astrocytomas. They concluded that the higher cellularity of lymphoma lesions contributes to their more restricted diffusion. The results of our study suggest that ADC values can play a role in the therapeutic algorithm for neurologically impaired AIDS patients whose brain lesions show a nonspecific appearance. If a focal brain mass is identified on initial brain MR images and if the ADC ratio in that lesion is greater than 1.6, the patient may be able to safely tolerate a trial of antitoxoplasma therapy. However, if the ADC ratio is less than 1.6, and particularly if it is less than 1.0, a lower clinical threshold should be used for advancing to other imaging modalities or early surgical biopsy. This information should be readily available in most patients, as DW imaging with ADC mapping are currently included in most routine brain MR imaging protocols. Our study has some limitations. One is that the ADC maps were computed by using three b values (50, 500, and 1000 s/mm 2 ). However, Burdette et al (34) reported a mean percentage difference of 0.84% between ADCs calculated by using a six-point technique (b 1, 100, 200, 500, 800, and 1000 s/mm 2 ) and ADCs calculated by using a two-point technique (b 1 and 1000 s/mm 2 ). Their results suggested that potential errors introduced by using only a three-point technique should be negligible. The method used for drawing ROIs and computing ADC ratios were stan-
5 AJNR: 24, April 2003 BRAIN LESIONS IN AIDS 637 dardized across all lesions and performed by a single observer. We were not, however, blinded to the diagnosis of each lesion at the time of ADC computation. Further, although the difference in mean ADC ratios in the two groups was statistically significant, the relatively small sample sizes currently preclude the prescription of a threshold ADC ratio for use in the clinical setting, especially given the substantial overlap between the groups involving ADC ratios of Blinded, prospective studies with larger sample sizes are needed to firmly establish the sensitivity and specificity of this tool in differentiating toxoplasmosis from lymphoma in patients with AIDS. Conclusion Our results demonstrate that ADC values are helpful in distinguishing toxoplasmosis from lymphoma brain lesions in patients with AIDS. We found that lesion white matter ADC ratios greater than 1.6 were seen only in toxoplasmosis. Because DW images and ADC maps are easily obtained, postprocessed, and interpreted, this technique may play an important role in the early diagnosis of these lesions, and the results may influence the care of AIDS patients for whom brain images show lesions with nonspecific appearances. References 1. Dina TS. Primary central nervous system lymphoma versus toxoplasmosis in AIDS. Radiology 1991;179: Smirniotopoulos JG, Koeller KK, Nelson AM, Murphy FM. Neuroimaging-autopsy correlations in AIDS. Neuroimaging Clinics N Am 1997;7: Ernst TM, Chang L, Witt MD, et al. Cerebral toxoplasmosis and lymphoma in AIDS: perfusion MR imaging experience in 13 patients. Radiology 1998;208: Mamidi A, DeSimone JA, Pomerantz RJ. Central nervous system infections individuals with HIV-1 infection. J Neurovirol 2002;8: Ramsey RG, Gean AD. Central nervous system toxoplasmosis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 1997;7: Desprechins B, Stadnik T, Koerts G, Shabana W, Breucq C, Osteaux M. Use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20: Ebisu T, Tanaka C, Umeda M, et al. Discrimination of brain abscess from necrotic or cystic tumors by diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging. Magn Res Imaging 1996;14: Guo AC, Provenzale JM, Cruz LCH, Patrella JR. Cerebral abscesses: investigation using apparent diffusion coefficient maps. Neuroradiology 2001;43: Hollinger P, Zurcher R, Schroth G, Mattle HP. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging findings in cerebritis and brain abscesses in a patient with septic encephalopathy. J Neurol 2000;247: Ketelslegers E, Duprez T, Ghariani S, Thauvoy C, Cosnard G. Time-dependence of serial diffusion-weighted imaging features is a case of pyogenic brain abscess. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2000;24: Kim YJ, Chang KH, Song IC, et al. Brain abscess and necrotic or cystic brain tumor: discrimination with signal intensity on diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171: Noguchi K, Watanabe N, Nagayoshi T, et al. Role of diffusionweighted echo-planar MRI in distinguishing between brain abscess and tumour: a preliminary report. Neuroradiology 1999;41: Okamoto K, Ito J, Ishikawa K, Sakai K, Tokiguchi S. Diffusionweighted echo-planar MR imaging in differential diagnosis of brain tumors and tumor like conditions. Eur Radiol 2000;10: Tung GA, Evalgelista P, Rogg JM, Duncan JA. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of rim-enhancing brain masses: Is markedly decreased water diffusion specific for brain abscess? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001;177: Hartmann M, Jansen O, Heiland S, Sommer C, Munkel K, Sartor K. Restricted diffusion within ring enhancement is not pathognomonic for brain abscess. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22: Krabbe K, Gideon P, Wagn P, Hansen U, Thomsen C, Madsen F. MR diffusion imaging of intracranial tumors. Neuroradiology 1997; 39: Sinha S, Bastin ME, Whittle IR, Wardlaw JM. Diffusion tensor MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23: Stadnik TW, Chaskis C, Michotte A, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of intracerebral masses: comparison with conventional MR imaging and histologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001; 22: Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, et al. Usefulness of diffusionweighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 1999;9: Teich DL, Bradley WG, Mandelker EM, et al. Some tumors are bright on diffusion imaging. Radiology 1998;209(P): Tien RD, Felsberg GJ, Friedman H, Brown M, MacFall J. MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1993;162: Loberboym M, Wallach F, Estok L, et al. Thallium-201 retention in focal intracranial lesions for differential diagnosis of primary lymphoma and nonmalignant lesions in AIDS patients. J Nucl Med 1998;39: Skiest DJ, Erdman W, Chang WE, Oz OK, Ware A, Fleckenstein J. SPECT thallium-201 combined with toxoplasma serology for the presumptive diagnosis of focal central nervous system mass lesions in patients with AIDS. J Infect 2000;40: De La Pena RC, Ketonen L, Villanueva-Meyer J. Imaging of brain tumors in AIDS patients by means of dual-isotope thallium-201 and technetium-99m sestamibi single photon emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 1998;25: Ruiz A, Ganz WI, Post MJ, et al. Use of thallium-201 brain SPECT to differentiate cerebral lymphoma from toxoplasmosis in AIDS patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1994;15: Licho R, Litofsky NS, Senitko M, George M. Inaccuracy of T1 201 Brain SPECT in Distinguishing Cerebral Infections from Lymphoma in Patients with AIDS. Clin Nucl Med 2002;27(2): Pomper MG, Constantinides CD, Barker PB, et al. Quantitative MR spectroscopic imaging of brain lesions in patients with AIDS. Acad Radiol 2002;9: Heald AE, Hoffman JM, Bartlett JA, Waskin HE. Differentiation of central nervous system lesions in AIDS patients using positron emission tomography (PET). Intl J STD AIDS 1996;7: Pierce MA, Johnson MD, Maciunas RJ, et al. Evaluating contrastenhancing brain lesions in patients with AIDS using positron emission tomography. Ann Intern Med 1995;123: Chang L, Ernst T. MR spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted MR imaging in focal brain lesions in AIDS. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 1997;3: Chang L, Miller BL, McBride D, et al. Brain lesions in patients with AIDS: H-1 MR spectroscopy. Radiology 1995;197: Chinn RJS, Wilkinson ID, Hall-Craggs MA, et al. Toxoplasmosis and primary central nervous system lymphoma in HIV infection: diagnosis with MR spectroscopy. Radiology 1995;197: Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM. Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology 2002;224: Burdette JH, Elster AD, Ricci PE, et al. Calculation of apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) in brain using two-point and sixpoint methods. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22:
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor
 107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455 1460, June/July 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence Chiaki Asao, Yukunori Korogi, Mika Kitajima, Toshinori
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455 1460, June/July 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence Chiaki Asao, Yukunori Korogi, Mika Kitajima, Toshinori
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Case Report. Case Report
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:274 278, February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted,
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
Robert J. Young, Munir V. Ghesani, Nolan J. Kagetsu, and Andrew J. DeRogatis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1973 1979, September 2005 Lesion Size Determines Accuracy of Thallium- 201 Brain Single-Photon Emission Tomography in Differentiating between Intracranial Malignancy and Infection
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1973 1979, September 2005 Lesion Size Determines Accuracy of Thallium- 201 Brain Single-Photon Emission Tomography in Differentiating between Intracranial Malignancy and Infection
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Diagnostic Value of Peritumoral Minimum Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for Differentiation of Glioblastoma Multiforme From Solitary Metastatic Lesions
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
DWI that measures overall diffusivity in terms of directionally
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C.H. Toh K.-C. Wei C.-N. Chang P.-W. Hsu H.-F. Wong S.-H. Ng M. Castillo C.-P. Lin Differentiation of Pyogenic Brain Abscesses from Necrotic Glioblastomas with Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Perfusion MR Imaging in Gliomas: Comparison with Histologic Tumor Grade
 Perfusion MR Imaging in Gliomas: Comparison with Histologic Tumor Grade Sun Joo Lee, MD 1 Jae Hyoung Kim, MD 1,4 Young Mee Kim, MD 1 Gyung Kyu Lee, MD 1 Eun Ja Lee, MD 1 In Sung Park, MD 2,4 Jin-Myung
Perfusion MR Imaging in Gliomas: Comparison with Histologic Tumor Grade Sun Joo Lee, MD 1 Jae Hyoung Kim, MD 1,4 Young Mee Kim, MD 1 Gyung Kyu Lee, MD 1 Eun Ja Lee, MD 1 In Sung Park, MD 2,4 Jin-Myung
Unusual Presentation of Central Nervous System Cryptococcal Infection in an Immunocompetent Patient
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2522 2526, November/December 2005 Case Report Unusual Presentation of Central Nervous System Cryptococcal Infection in an Immunocompetent Patient Gaurav Saigal, M. Judith Donovan
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2522 2526, November/December 2005 Case Report Unusual Presentation of Central Nervous System Cryptococcal Infection in an Immunocompetent Patient Gaurav Saigal, M. Judith Donovan
SSRG International Journal of Medical Science (SSRG-IJMS) volume 2 Issue 2 Feb 2015
 Study of Brain Mass Lesions by MRI- On Special Sequences Ravi Ningappa 1, Bagath Singh K 2 1. Associate Professor, 2. Resident, Dept. of Radio diagnosis BMC&RI, Bangalore, India Author s address: Department
Study of Brain Mass Lesions by MRI- On Special Sequences Ravi Ningappa 1, Bagath Singh K 2 1. Associate Professor, 2. Resident, Dept. of Radio diagnosis BMC&RI, Bangalore, India Author s address: Department
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a sensitive technique
 Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Brain toxoplasmosis: typical and atypical imaging features.
 Brain toxoplasmosis: typical and atypical imaging features. Poster No.: C-1661 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. G. Macías, A. D. Sotomayor, J. berenguer, M. T. PUJOL 1 2 3 4 1 1
Brain toxoplasmosis: typical and atypical imaging features. Poster No.: C-1661 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. G. Macías, A. D. Sotomayor, J. berenguer, M. T. PUJOL 1 2 3 4 1 1
Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors.
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1049 1053, June/July 1999 Case Report In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses Isabella M. Burtscher and Stig Holtås Summary: MR spectroscopy was
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1049 1053, June/July 1999 Case Report In Vivo Proton MR Spectroscopy of Untreated and Treated Brain Abscesses Isabella M. Burtscher and Stig Holtås Summary: MR spectroscopy was
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 20:555 562 (2004) Original Research Diffusion Tensor Eigenvector Directional Color Imaging Patterns in the Evaluation of Cerebral White Matter Tracts Altered by Tumor
Supratentorial brain tumors in the first year of life are challenging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Diffusion Imaging for Tumor Grading of Supratentorial Brain Tumors in the First Year of Life S.F. Kralik, A. Taha, A.P. Kamer, J.S. Cardinal, T.A. Seltman, and C.Y. Ho ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Diffusion Imaging for Tumor Grading of Supratentorial Brain Tumors in the First Year of Life S.F. Kralik, A. Taha, A.P. Kamer, J.S. Cardinal, T.A. Seltman, and C.Y. Ho ABSTRACT
DISTINCTION BETWEEN RECURRENT GLIOMA AND RADIATION INJURY USING MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY IN COMBINATION WITH DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
General Identification. Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27
 General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1645 1649, October 2000 Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and Lester Kwock BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: In a
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1645 1649, October 2000 Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and Lester Kwock BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: In a
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Case Report Hemorrhage in the Wall of Pyogenic Brain Abscess on Susceptibility Weighted MR Sequence: A Report of 3 Cases
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 907584, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/907584 Case Report Hemorrhage in the Wall of Pyogenic Brain Abscess on Susceptibility Weighted MR Sequence: A Report
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 907584, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/907584 Case Report Hemorrhage in the Wall of Pyogenic Brain Abscess on Susceptibility Weighted MR Sequence: A Report
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Table 9: Vascularity and Hemorrhage
 Table 9: Vascularity and Hemorrhage Di Ieva (2007) 120 Fractal dimension as a quantitator the microvasculat ure normal and adenomatous tissue. Clinical experience characterizing vascular surface fractal
Table 9: Vascularity and Hemorrhage Di Ieva (2007) 120 Fractal dimension as a quantitator the microvasculat ure normal and adenomatous tissue. Clinical experience characterizing vascular surface fractal
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]
![CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE] CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]](/thumbs/86/94270487.jpg) ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Correspondence should be addressed to Doniel Drazin;
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 650939, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/650939 Clinical Study Differentiation of Benign Angiomatous and Microcystic Meningiomas with Extensive Peritumoral
BioMed Research International, Article ID 650939, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/650939 Clinical Study Differentiation of Benign Angiomatous and Microcystic Meningiomas with Extensive Peritumoral
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Magn Reson Imaging. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 June 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 June ; 31(6): 1469 1472. doi:10.1002/jmri.22192. Eccentric Target Sign in Cerebral Toxoplasmosis neuropathological
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 June ; 31(6): 1469 1472. doi:10.1002/jmri.22192. Eccentric Target Sign in Cerebral Toxoplasmosis neuropathological
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is a rare inflammatory
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.L. White W.L. Hadley Y. Zhang M.A. Dogar Analysis of Central Nervous System Vasculitis with Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of the Normal-Appearing
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.L. White W.L. Hadley Y. Zhang M.A. Dogar Analysis of Central Nervous System Vasculitis with Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of the Normal-Appearing
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Stereotactic Brain Biopsies in AIDS Patients - Early Local Experience
 Singapore Med J 2000 Vol 41(4) : 161-166 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Stereotactic Brain Biopsies in AIDS Patients - Early Local Experience K K Yeo, T T Yeo, C Y Chan, Y Y Sitoh, J Teo, S Y Wong ABSTRACT
Singapore Med J 2000 Vol 41(4) : 161-166 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Stereotactic Brain Biopsies in AIDS Patients - Early Local Experience K K Yeo, T T Yeo, C Y Chan, Y Y Sitoh, J Teo, S Y Wong ABSTRACT
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Pyogenic abscesses of hematogenous origin are solitary in
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Luthra A. Parihar K. Nath S. Jaiswal K.N. Prasad N. Husain M. Husain S. Singh S. Behari R.K. Gupta Comparative Evaluation of Fungal, Tubercular, and Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with Conventional
ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Luthra A. Parihar K. Nath S. Jaiswal K.N. Prasad N. Husain M. Husain S. Singh S. Behari R.K. Gupta Comparative Evaluation of Fungal, Tubercular, and Pyogenic Brain Abscesses with Conventional
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to
 125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, since both J. L. Kline, R. B. Noto, and M. Glantz
 Single-Photon Emission CT in the Evaluation of Recurrent Brain Tumor in Patients Treated with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery or Conventional Radiation Therapy J. L. Kline, R. B. Noto, and M. Glantz PURPOSE:
Single-Photon Emission CT in the Evaluation of Recurrent Brain Tumor in Patients Treated with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery or Conventional Radiation Therapy J. L. Kline, R. B. Noto, and M. Glantz PURPOSE:
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors
 Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
The diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) MR sequence showed an hyposignal of the lesion eliminating a cerebral pyogenic abscess which usually presents an
 Cerebral toxoplasmosis is one of the most common opportunistic neurological infections in AIDS patients, and is typically observed in the later stages of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. 1,2
Cerebral toxoplasmosis is one of the most common opportunistic neurological infections in AIDS patients, and is typically observed in the later stages of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. 1,2
ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas: Does Lower ADC Predict a Worse Prognosis Independent of Grade of Tumor?
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma on Diffusion-weighted Images: Influence of T2- shine-through and T2-blackout Effects
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:236 241, February 2005 Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma on Diffusion-weighted Images: Influence of T2- shine-through and T2-blackout Effects Stéphane Silvera, Catherine Oppenheim,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:236 241, February 2005 Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma on Diffusion-weighted Images: Influence of T2- shine-through and T2-blackout Effects Stéphane Silvera, Catherine Oppenheim,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH. with AIDS develop PML during the course of their disease, 1 and PML is the cause of death in 0.7% of them. 2
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C. Buckle M. Castillo Use of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging to Evaluate the Initial Response of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy to Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy: Early Experience
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C. Buckle M. Castillo Use of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging to Evaluate the Initial Response of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy to Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy: Early Experience
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
KEY WORDS gamma knife surgery metastatic brain tumor radiation injury tumor recurrence thallium-201 single-photon emission computerized tomography
 J Neurosurg (Suppl) 102:266 271, 2005 Diagnostic value of thallium-201 chloride single-photon emission computerized tomography in differentiating tumor recurrence from radiation injury after gamma knife
J Neurosurg (Suppl) 102:266 271, 2005 Diagnostic value of thallium-201 chloride single-photon emission computerized tomography in differentiating tumor recurrence from radiation injury after gamma knife
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detects Local Recurrence After Radical Prostatectomy: Initial Experience
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 61 (2012) 616 620 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detects Local Recurrence
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 61 (2012) 616 620 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Detects Local Recurrence
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rhombencephalitis due to Listeria
 cta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rhombencephalitis due to Listeria monocytogenes
cta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rhombencephalitis due to Listeria monocytogenes
Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience
 African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Mediastinal and Pulmonary Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
Diffusion Measurements in Intracranial Hematomas: Implications for MR Imaging of Acute Stroke
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1190 1194, August 2000 Diffusion Measurements in Intracranial Hematomas: Implications for MR Imaging of Acute Stroke Scott W. Atlas, Philip DuBois, Michael B. Singer, and Dongfeng
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1190 1194, August 2000 Diffusion Measurements in Intracranial Hematomas: Implications for MR Imaging of Acute Stroke Scott W. Atlas, Philip DuBois, Michael B. Singer, and Dongfeng
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners
 Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners
 Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Brain abscesses: magnetic resonance imaging findings, diffusion weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy at 1,5 T and 3T MR imaging scanners Poster No.: C-0711 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) comprise
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
The MRI Appearance of Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions
 ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist
 Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist Poster No.: C-0679 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gargallo Vaamonde, M. Iridoy Zulet, I. Rubio
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesions: Diagnostic challenge for the radiologist Poster No.: C-0679 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gargallo Vaamonde, M. Iridoy Zulet, I. Rubio
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175)
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences
 Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Experimental Assessment of Infarct Lesion Growth in Mice using Time-Resolved T2* MR Image Sequences Nils Daniel Forkert 1, Dennis Säring 1, Andrea Eisenbeis 2, Frank Leypoldt 3, Jens Fiehler 2, Heinz Handels
Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with Brain MR Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 925-931, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Diffusion in Assessment of Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; MARIAN FAYEK,
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms
 New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction
 Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Original Article ISSN (o):2321 7251 Diffusion Weighted Imaging - Application In Cerebral Tumors / Infection / Infarction Kalidindi Ravi Kumar Varma 1, Chaparla Lakshmana Rao 2 1 - Associate Professor,Maharajah
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features
 Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
