MRI imaging in meningeal diseases
|
|
|
- Poppy Jackson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article MRI imaging in meningeal diseases 1Dr. Narendrakumar M Shah, 2 Dr Vaishali D M 1Associate professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, SDM Medical college, Dharwad 2Consultant radiologist, NMR imaging centre, Hubli Name of the Institute/college: SDM medical college Corresponding author : Dr. Vaishali D. M. Abstract: Meninges are the outer coverings of the neuraxis. A variety of diseases can affect the meninges. Contrast enhaced MR imaging is the non invasive investigation of choice in the evaluation of these diseases. We conducted a retrospective study of meningeal diseases detected on MR images, We hereby describe the MR imaging findings in meningeal disease. Introduction: 6 patients had infectious/inflammatory diseases, 4 Meninges are the membranous coverings of brain patients had abnormal meningeal enhancement and spinal cord. Mutlitude of diseases can affect related to other causes like subacute cerebral the meninges, different diseases may affect infarcts and previous surgery.all the patients with different parts of the meninges. The pattern of meningeal carcinomatosis had known primary contrast enhancement on MR images also differs in tumors breast carcinoma (n= 4), adenocarcinoma various diseases. In this article, we discuss the MR colon (n= 2), nasopharyngeal carcinoma (n= appearance and enhancement pattern of various 1).Dural enhancement was seen in 12 patients, out meningeal diseases. of which 8 patients had primary meningeal tumors, Methodology : two post operative patients and two patients had Gadolinium enhanced MR images of head were dural metastasis (primary breast carcinoma). reviewed and the scans of 25 patients in whom Leptomeningeal enhancement was seen in 13 abnormal enhancement of the meninges was seen patients, out of which 5 patients had were studied retrospectively. We studied the leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, 6 patients had amount and pattern of meningeal enhancement in infectious/inflammatory diseases and 2 patients had various disease processes. Axial short TR and long subacute cerebral infarcts. TR sequences were acquired prior to the Discussion: administration of contrast material. Gadolinium The cranial meninges comprise the dura mater, the DTPA was given intravenously in a concentration arachnoid and the pia mater. The dura mater has of 0.1mmol/kg and short TR sequences acquired in two layers. The outer layer composed of fibroblasts all three planes. is closely applied to inner table of skull and Results: corresponds to periosteum. The inner layer Out of the 25 patients with meningeal composed of epithelial cells is closely applied to abnormalities, 7 patients had meningeal carcinomatosis, arachnoid. Within the arachnoid is the CSF. The 8 patients had primary meningeal tumors, pia mater is the innermost layer which is closely 569
2 applied to the brain surface and invests itself into the sulci. The piamater and the arachnoid together are referred to as leptomeninges. [1] MR imaging is more sensitive than CT in the evaluation of meningeal disease processes. A typical protocol consists of unenhanced short TR and long TR axial sequences followed by contrast enhanced short TR sequence. Various pathological conditions can affect the meninges and produce abnormal meningeal enhancement. Two types of meningeal enhancement have been noted. Pachymeningeal enhancement ( or dura arachnoid enhancement) appears as smooth, linear enhancement adjacent to the ineer table of skull or may involve dural reflections of falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, falx cerebelli, and cavernous sinus. Leptomeningeal enhancement, also described as gyriform or serpentine appearance, follows along the pial surface of brain and fills the subarachnoid spaces of sulci and cistern. [2] Meninges can be involved in various disease processes such as infectious/ inflammatory conditions, primary and secondary tumors, cerebral infarction and iatrogenic conditions. The imaging findings in these conditions are discussed in the subsequent paragraphs. Primary tumors: The most common primary dural neoplasm is meningioma. It is a slow growing, WHO grade I tumor arising from meningothelial cells. Meningiomas typically appear as extraxial masses with a broad dural base, that are homogenous, well circumscribed, T1 isointense, T2 hyperintense and show intense homogenous contrast enhancement (figure. 1). The dural tail is a curvilinear region of dural enhancement seen adjacent to a meningioma, which may be secondary to infiltration by the tumor or may be caused by a reactive process. [3, 4] Certain meningioma subtypes are associated with more aggressive clinical behaviour and less favourable outcomes. Atypical meningioma is a WHO grade II tumor with indistinct tumor margins and inhomogenous contrast enhacement. Malignant meningiomas typically invade brain and may exhibit a mushrooming configuration. Other less common primary tumors of the meninges include sarcomas (of many histologic types), hemangiopericytomas, solitary fibrous tumors, primary melanocytoma. Hemangiopericytoma is a primary malignant mesenchymal nonmenigothelial neoplasm thought to arise from the blood vessel pericytes. On MR imaging, they appear as dural based masses that are isointense on T1, of variable intensity on T2 with prominent flow voids and show avid, heterogenous contrast enhancement. Melanocytomas are low grade tumors. The paramagnetic properties of melanin cause T1 shortening, so hyperintensity on T1 and hypointensity on T2 is characteristic. [5]. Meningeal carcinomatosis: Meningeal carcinomatosis is an important diagnosis to make. Untreated meningeal carcinomatosis decreases the survival time and hence specific therapy for leptomeningeal disease must be initiated to slow down progression of disease. Imaging plays a key role in the diagnosis and management of leptomeningeal metastases. Primary CNS tumors that commonly metastasise to the meninges include medulloblastomas, ependymomas in children and glioblastoma multiforme in adults. Non CNS malignancies that spread to meninges include breast, lung, melanoma, gastrointestinal, genitourinary and haematological malignancies. [6] Contrast enhanced T1 weighted MR imaging has been the technique of choice for assessing leptomeningeal disease with a reported sensitivity as high as 71%. [7] Meningeal carcinomatosis may 570
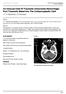
3 involve the dura mater, the leptomeninges or both (figures 2,3). Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis appears as thin lines of contrast enhancement following the convolutions of gyri or as small nodular deposits on the surface of brain. [8] Infectious and inflammatory diseases: Meningitis may be caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, and granulomatous agents. Bacterial and viral menigitis is usually associated with leptomeningeal enhancement that is thin and linear (figure 4). [2]Fungal meningitis may produce thicker, nodular enhancement of the meninges. However nodular enhancement is more specific for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. [9][10] In granulomatous infections, intracranial contrast enhancement is often confined to the basal cistern and may be associated with other findings such as hydrocephalus, ischemia/ifarct, subdural fluid collection or brain parenchymal lesions (figure 5).[11] Sarcoidosis may involve the meninges. Usually the leptomeninges are involved, and contrast enhancement usually follows the contour of the brain, extending into sulci. Other findings include periventricular mutliofocal white matter lesions, enhancing granulomas and enhancing cranial nerve lesions. [1] Iatrogenic conditions and others: Post operative meningeal enhancement can be dural or leptomeningeal. In some cases this decreases while in others it may persist for a long duration. It can be either due to meningeal meningeal irritation caused by blood in the subarachnoid space as a result of the craniotomy. Longer-term localized enhancement at the operative site may result from fibrotic meningeal changes. [1][6] Meningeal contrast enhancement may be seen in subarachnoid hemorrhage, vasculitis, Sturge Weber syndrome, idiopathic pachymeningitis, idiopathic intracranial hypotension and various other conditions. [6] Conclusion: A variety of diseases can affect the meninges. Contrast enhanced MR imaging with its superior spatial resolution is an excellent non invasive technique for the diagnosis of these conditions. Knowledge of the normal MR anatomy of the meninges and patterns of meningeal enhancement in various diseases improves image assessment and differential diagnosis. Figure 1: Coronal and sagittal contrast enhanced T1 weighted MR images showing a suprasellar meningioma with associated dural enhancement along the floor of anterior cranial fossa. 571
4 Figure 2: Axial contrast enhanced MR images of brain showing abnormal dural enhancement in the left frontal region. Figure 3 (a,b): Axial contrast enhanced T1 weighted MR images in two patients of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis with positive CSF cytology and known primaries. Figure a showing abnormal thick and irregular meningeal enhancement in the posterior fossa in a patient with left breast carcinoma. Figure b showing diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement and enhancement of ventricular margins in a case of right frontoparietal astrocytoma
5 Figure 4: Axial contrast enhanced T1 weighted MR in a patient with meningitis showing thin linear diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement. Figure 5: Axial contrast enhanced T1 weighted MR images in a patient with Tuberculosis showing multiple enhancing granulomas in cerebral parenchyma with abnormal dural enhancement in the left parietal region. References 1. Sze G. Disease of intracranial meninges:mr imaging features. AJR 1993;160: Smirniotopoulos GJ, Murphy MF.Patterns of Contrast Enhancement in the Brain and Meninges. RadioGraphics 2007; 27: Nakau H, Miyazawa T, Tamai S, et al. Pathologic significance of meningeal enhancement ( flare sign ) of meningiomas on MRI. Surg Neurol 1997;48:
6 4. Nagele T, Petersen D, Klose U, Grodd W, Opitz H, Voigt K. The dural tail adjacent to meningiomas studied by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: a comparison with histopathology. Neuroradiology 1994;36: Tumors of the meninges. In: Osborne AG. Osborn s brain: Imaging, pathology and anatomy, 1 st edition. Amirsys Publishing, Inc, 2013: Grossman SA, Krabak MJ. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer treatment reviews : Sze G, Soletsky S, Bronen R, Krol G. MR imaging of the cranial meninges with emphasis on contrast enhancement and meningeal carcinomatosis AJNR 1989;10: Pakko E, Patronas NJ, Schellinger D. Meningeal Gd-DTPA enhancement in patients with malignancies. J ComputAssist Tomogr 1990;14: Phillips ME, Ryals RJ, Kambhu SA, Yuh WT. Neoplastic vs. inflammatory meningeal enhancement with Gd-DTPA. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1990; 14: Sage MR, Wilson AJ, Scroop R. Contrast media and the brain: the basis of CT and MR imaging enhancement. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 1998;8: ]. 11. Chang KH, Han MH, Roh JK, Kim 10, Han MC, Kim CW. Gd-DTPA enhanced MR imaging of the brain in patients with meningitis: comparison with CT. AJR 1989;154:
Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies
 Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hssine, N. Mallat, M. Limeme, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, H. Amara, D. Bakir,
Meningeal thickening in MRI: from signs to etiologies Poster No.: C-1979 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hssine, N. Mallat, M. Limeme, H. Zaghouani, S. Majdoub, H. Amara, D. Bakir,
MR Imaging of the Cranial Meninges with Emphasis on Contrast Enhancement and Meningeal Carcinomatosis
 965 MR Imaging of the Cranial Meninges with Emphasis on Contrast Enhancement and Meningeal Carcinomatosis Gordon Sze 1 2 Susan Soletsky 1 Richard Bronen 2 George Krol 1 MR imaging was used to investigate
965 MR Imaging of the Cranial Meninges with Emphasis on Contrast Enhancement and Meningeal Carcinomatosis Gordon Sze 1 2 Susan Soletsky 1 Richard Bronen 2 George Krol 1 MR imaging was used to investigate
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features
 Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:817 821, May 2002 MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences Sanjay K. Singh, Norman E. Leeds, and Lawrence E. Ginsberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Case Report Multiple Dural Tuberculomas Presenting as Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 581230, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/581230 Case Report Multiple Dural Tuberculomas Presenting as Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Hasan Kocaeli,
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 581230, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/581230 Case Report Multiple Dural Tuberculomas Presenting as Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Hasan Kocaeli,
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis
 Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
Patterns of contrast enhancement in the brain and meninges. A Pictorial Review.
 Patterns of contrast enhancement in the brain and meninges. A Pictorial Review. Poster No.: C-0716 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, S. Medrano, D. Garcia, M. Cuadrado,
Patterns of contrast enhancement in the brain and meninges. A Pictorial Review. Poster No.: C-0716 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, S. Medrano, D. Garcia, M. Cuadrado,
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
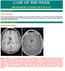 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE 26 years old male patient presented clinically with a grand male fit, confusion, fever, headache, and nausea. Examination showed bilateral papilledema and left sided extensor
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE 26 years old male patient presented clinically with a grand male fit, confusion, fever, headache, and nausea. Examination showed bilateral papilledema and left sided extensor
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
Menigitidis. Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
Menigitidis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Review Normal Microanatomy Image Ref: www.histology-world.com
Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Leptomeningeal metastasis: management and guidelines. Emilie Le Rhun Lille, FR Zurich, CH
 Leptomeningeal metastasis: management and guidelines Emilie Le Rhun Lille, FR Zurich, CH Definition of LM LM is defined as the spread of tumor cells within the leptomeninges and the subarachnoid space
Leptomeningeal metastasis: management and guidelines Emilie Le Rhun Lille, FR Zurich, CH Definition of LM LM is defined as the spread of tumor cells within the leptomeninges and the subarachnoid space
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Malignant melanoma and the central nervous system A guide for classification based on the clinical findings
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 526-530 Malignant melanoma and the central nervous system A guide for classification based on the clinical findings R. D. HAYWARD From the Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 526-530 Malignant melanoma and the central nervous system A guide for classification based on the clinical findings R. D. HAYWARD From the Department
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis
 Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis Schwannomas (also called neurinomas or neurilemmomas) constitute the most common primary cranial nerve tumors. They are benign slow-growing
Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis Schwannomas (also called neurinomas or neurilemmomas) constitute the most common primary cranial nerve tumors. They are benign slow-growing
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS. Kim Learned, MD
 PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales
 28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation
 American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms
 Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT
 IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
IMAGING OF A CASE OF SPINAL MENINGIOMA- A CASE REPORT Ramneet Wadi 1, Anil Kumar Shukla 2, Seetha Pramila V. V 3, Sabyasachi Basu 4, Sonam Sanjay 5 1Postgraduate Student, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
MR imaging spectrum in intracranial meningiomas-a retrospective study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.7 March. (2018), PP 47-64 www.iosrjournals.org MR imaging spectrum in intracranial meningiomas-a
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.7 March. (2018), PP 47-64 www.iosrjournals.org MR imaging spectrum in intracranial meningiomas-a
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas: is differential diagnosis possible?
 Neuroradiology (1997) 39: 633 638 Springer-Verlag 1997 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY I. Ikushima Y. Korogi J. Kuratsu T. Hirai S. Hamatake M. Takahashi Y. Ushio Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas:
Neuroradiology (1997) 39: 633 638 Springer-Verlag 1997 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY I. Ikushima Y. Korogi J. Kuratsu T. Hirai S. Hamatake M. Takahashi Y. Ushio Dynamic MRI of meningiomas and schwannomas:
Imaging of Normal Leptomeningeal Melanin
 Imaging of Normal Leptomeningeal Melanin Stephen S. Gebarski and Mila A. Blaivas PURPOSE: To find the CT and MR characteristics of normal leptomeningeal melanin, which can be macroscopically visible at
Imaging of Normal Leptomeningeal Melanin Stephen S. Gebarski and Mila A. Blaivas PURPOSE: To find the CT and MR characteristics of normal leptomeningeal melanin, which can be macroscopically visible at
Intracranial Hemangiopericytomas: MR and CT Features
 Intracranial Hemangiopericytomas: MR and CT Features Maria V. Chiechi, James G. Smirniotopoulos, and Hernando Mena PURPOSE: To describe the MR and CT imaging features of hemangiopericytoma and to identify
Intracranial Hemangiopericytomas: MR and CT Features Maria V. Chiechi, James G. Smirniotopoulos, and Hernando Mena PURPOSE: To describe the MR and CT imaging features of hemangiopericytoma and to identify
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Gd-DTPA-Enhanced MR Imaging of the Brain in Patients with Meningitis: Comparison with CT
 69 Gd-DTPA-Enhanced MR Imaging of the Brain in Patients with Meningitis: Comparison with CT Kee Hyun Chang 1 Moon Hee Han 1 Jae Kyu Roh 2 In One Kim 1 Man Chung Han 1 Chu-Wan Kim 1 Plain and Gd-DTPA-enhanced
69 Gd-DTPA-Enhanced MR Imaging of the Brain in Patients with Meningitis: Comparison with CT Kee Hyun Chang 1 Moon Hee Han 1 Jae Kyu Roh 2 In One Kim 1 Man Chung Han 1 Chu-Wan Kim 1 Plain and Gd-DTPA-enhanced
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
Waneerat Galassi, Warinthorn Phuttharak, John R. Hesselink, John F. Healy, Rosalind B. Dietrich, and Steven G. Imbesi
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:553 559, March 2005 Intracranial Meningeal Disease: Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging with Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery and Fat-Suppressed T1-Weighted Sequences
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:553 559, March 2005 Intracranial Meningeal Disease: Comparison of Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging with Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery and Fat-Suppressed T1-Weighted Sequences
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses)
 Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Case Studies in the Skull Base
 Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MENINGIOMA CNS Site Group Meningioma Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MENINGIOMA CNS Site Group Meningioma Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves. Chapter 14 Part A
 Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
681 Value of Subtraction Images in the Detection of Hemorrhagic Brain Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Soheil L. Hanna 1 James W. Langston Suzanne A. Gronemeyer Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR images
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Peter Canoll MD. PhD.
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization
 Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
A Journey Down The Canal
 A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases
 Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
Supratentorial Gangliocytoma Mimicking Extra-axial Tumor: A Report of Two Cases Ho Sung Kim, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Ae Kyung Jeong, MD 1 Ji Hoon Shin, MD 1 Choong Gon Choi, MD 1 Shin Kwang Khang, MD 2 We
Chapter 14. The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
 Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Cranial Postoperative Site: MR Imaging Appearance
 27 Cranial Postoperative Site: MR Imaging Appearance Charles F. Lanzieri1 Mark Larkins2 Andrew Mancall 1 Ronald Lorig 1 Paul M. Duchesneau 1 Scott A. Rosenbloom 1 Meredith A. Weinstein 1 The ability to
27 Cranial Postoperative Site: MR Imaging Appearance Charles F. Lanzieri1 Mark Larkins2 Andrew Mancall 1 Ronald Lorig 1 Paul M. Duchesneau 1 Scott A. Rosenbloom 1 Meredith A. Weinstein 1 The ability to
Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma
 July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Neuroimaging Core Curriculum
 Neuroimaging Core Curriculum Program Content The purpose of the training program is to prepare the physician for the independent practice of neuroimaging. Neuroimaging is the subspecialty of Neurology
Neuroimaging Core Curriculum Program Content The purpose of the training program is to prepare the physician for the independent practice of neuroimaging. Neuroimaging is the subspecialty of Neurology
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment
 Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
Tumors of the Central Nervous System
 Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
Tumors of the Central Nervous System 1 Financial Disclosures I have NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Introduction General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect
MRI findings in childhood neurohypophyseal germinomas
 MRI findings in childhood neurohypophyseal germinomas Poster No.: C-1587 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Laganâ, S. I. Sirvent, M. A. Lopez-Pino, G. Albi, I. Solis Muniz, E. García
MRI findings in childhood neurohypophyseal germinomas Poster No.: C-1587 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Laganâ, S. I. Sirvent, M. A. Lopez-Pino, G. Albi, I. Solis Muniz, E. García
An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic Cleft
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Meningioma tumor. Meningiomas are named according to their location (Fig. 1) and cause various symptoms: > 1
 Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Cranial Pachymeningeal Involvement in POEMS Syndrome: Evaluation by Pre- and Post-contrast FLAIR and T 1. -weighted Imaging MAJOR PAPER.
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; 231 237 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2015-0014 Published Online: December 22, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Cranial Pachymeningeal Involvement in POEMS Syndrome: Evaluation by Pre- and Post-contrast
Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; 231 237 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2015-0014 Published Online: December 22, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Cranial Pachymeningeal Involvement in POEMS Syndrome: Evaluation by Pre- and Post-contrast
Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma at the Falx Cerebri
 Chin J Radiol 2004; 29: 337-341 337 Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma at the Falx Cerebri YI-LUAN HUANG 1,3 PING-HONG LAI 1,3 SHONG-LING LIN 2,3 MEI-KANG YUAN 1,3 HUAY-BEN PAN 1,3 Department of Radiology 1, Department
Chin J Radiol 2004; 29: 337-341 337 Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma at the Falx Cerebri YI-LUAN HUANG 1,3 PING-HONG LAI 1,3 SHONG-LING LIN 2,3 MEI-KANG YUAN 1,3 HUAY-BEN PAN 1,3 Department of Radiology 1, Department
Spinal Meningeal Melanocytoma with Benign Histology Showing Leptomeningeal Spread: Case Report
 Case Report Musculoskeletal Imaging A 37-year-old previously healthy man presented with a 2 months history of increasing posterior neck pain and radiating pain to the right upper extremity. Neurological
Case Report Musculoskeletal Imaging A 37-year-old previously healthy man presented with a 2 months history of increasing posterior neck pain and radiating pain to the right upper extremity. Neurological
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
