Cancer Cell Self Sufficiency in Growth Signals
|
|
|
- Jonas Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Date Cancer Cell Self Sufficiency in Growth Signals Part 1: Introduction Read the introduction. Draw a flower in the box when finished with this step. RAS Diagram Use the space below the diagram to describe what s going on. Part 2: Learn Read How Cancer Cells Beat the System. Draw a bee in the box when finished. Write down 3 things you think everyone should remember about this hallmark Growth Factor Pathway Diagram Use the space below the diagram to describe the diagram. Mnemonic Device Come up with your own mnemonic device for Cancer Makes Growth Signals (ex Chopping Musty Garlic Stinks ) Part 3: Flashcards Go through the flashcard set. Draw a cell during telophase in the box when done. Part 4: Quiz Time! Take the 10 question quiz. Draw a smiley face in the box when you re done.
2 Part 5: Word Search! U S L P Q W A T U M O R S T U D W W T T J I X U F N S Y G P A R E A J B I C U U F E E D B A C K E B L V X C X G Y I J Z N H B S X M S L Z M R E L Z E R U S P R L M S E G H B B B U M Z F B N P X P P P U I E C Z V E A F Q N H I Q V Q T N E B W Y N I N V Y L G G B P H U F Y R O N D L Z H H N W D M G F F G Z M M V M O R U W D O C I D W O P G H P Q U D R I T F O H B Z R H B E Y V I A G R F H T H P S L L X M E H R I P B I D G P H C G E U F T I U Y Y T H G T E L O Q G U J P R T C D S V T O L F K L O N B K D V B N C V Y I U X T B M X M Z W R D S N O J G E S I V A E F P Z W C A N R N E U D V L P V M I A C Y X A N N T Z A W G N Y L P T R A S F D F T U R I U R O O B G C C R I W S I N Q F E C M U T A T I O N U E N N S U O L X V Q O P P L K N V K W Z X A V J E N F G M N K Y M A W W C Q R E M W N H B D WORD BANK DIVISION FEEDBACK HERCEPTIN INDEPENDENCE INHIBITOR MUTATION RAS RECEPTOR TUMORS TRANSDUCTION 2
3 Saul, Ivan, Giakhoue, Robert Insensitivity to Antigrowth Signals 1. Read the introduction. 2. Read Anti-growth Signals. 3. How do anti-growth signals normally work? 4. Which molecules inhibit what in normal cells? In cancerous cells? a. b. 5. Examine the diagram 6. Label this diagram: a b c d 7. Explain how the retinoblastoma can be inactivated. 8. Read Evidence. 9. Read Treatment.
4 10. Describe how chemotherapy and chemoprevention differ. 11. Go through slideshow 12. Go through the flashcard deck. Complete the crossword!!!!!! Across 3. RBp is short for Protein 6. The human produces a protein known as E7, which binds to and inactivates Retinoblastoma. 10. The presence of this blocks advancement of the cell cycle. 11. to Antigrowth Signals 14. Cancer cells have that change the way their proteins function. 15. When DNA is, normal cells do not divide. 16. Inhibition prevents cells from dividing when they get too crowded. 17. Tumor genes prevent cells from dividing when they have problems. Down 1. Some inhibitors are located in the matrix. 2. A primary function of Retinoblastoma is to bind to and inactivate E2F. 4. signals prevent healthy cells from dividing out of control. 5. How many stages does the cell cycle have? 7. What number hallmark of cancer is Insensitivity to Antigrowth Signals? 8. Cells that divide without stopping are considered to be 9. Regulatory protein that starts with a c 12. A mass of cells that has the potential to become cancerous. 13. Cyclin Dependent Kinases
5 Name: Period: Date: Module 1000: Evading Apoptosis :) Instructions: 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. You can t really log in so just do this paper. 3. Go to Ezra Torio s Webpage on qwizcards.berkeley.net Tutorial 2: Slideshow Watch the Evading Apoptosis Google slideshow Look at Two Main Pathways for Apoptosis. Which pathway do you think seems more likely to be evaded and why? Tutorial 1: Description of Apoptosis in Cancer Read: Description of Apoptosis in Cancer Summarize: What are the key differences between intrinsic and extrinsic pathways? Create a key to the diagram below What is the consequence of cancer cells evading apoptosis? Key Terms: Term Caspase Death Signal P53 BCL-2 BAX Cytochrome C Definition I II a b c d e f g h
6 i j k l m n Who first linked oncogenes to the evasion of apoptosis? Name two ways that cancer cells can evade apoptosis Tutorial 4: Quiz Use your knowledge gained from the description, slideshow, and flashcards to complete the quiz Name a catalyst that induces apoptosis Name an enzyme that performs cell death Compare E6 and BCL-2 Checking Understanding: Your highly intelligent talking monkey asks you about how apoptosis is related to cancer. In the space below, provide an explanation using the information gained from the webpage! What are some possible treatments that include apoptosis? Tutorial 3: Interactive Flashcards Use the flashcards until you feel comfortable answering each one According to the mice study, what is the effect of inactivating the p53 gene? What is the link between apoptosis and cancer treatments? Define the functions of the following: Sensors: Effectors:
7 Name: Date: Period: Hallmark of Cancer: Limitless Replicative Potential Work in pairs (share a computer). 1. Answer all questions for full credit. 2. Go to Noah Dilworth s AP Biology Limitless Replicative Potential Qwizcards page. 3. Do the best you can!! Introduction: Limitless Replicative Potential 1. Read the introduction, and fill in the blanks. a. Cancer cells can beyond the limits of a regular cell. This is why they are often referred to as, meaning they are not bound to the limit after a given number of divisions. This is what allows to increase in almost indefinitely. Part 1: Description of Limitless Replicative Potential 1. Read the description, and write a one paragraph summary. 2. Answer the questions about Limitless Replicative Potential. Paragraph: What is the role of telomeres in the chromosome? What is the Hayflick Limit? What is the end replication problem? What is the role of telomerase in cancer cells? What is some evidence to support this? Part 2: TEST YOUR MIGHT! 1. Review the slideshow presentation. 2. Quiz yourself with all 20 flashcards. 3. Give us your score as a comment Part 3: Final Summary 1. Did you actually read it? I hope so because now that you ve read all there is to know about Limitless Replicative Potentia l, you are going to right a 5 paragraph essay about what you have learned. Just kidding, but you will tell us three of your favorite facts from everything that you just learned
8 Name: Period: Date: Sustained Angiogenesis as a Hallmark of Cancer 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. So that you can get credit, turn in this paper! 3. Go to Colleen Burns AP Biology Sustained Angiogenesis Qwizcards page. 4. Start exploring the page! Why is sustained angiogenesis important to the development of cancer cells? How can angiogenesis be influenced to create an excessive number of blood cells? Introduction: Sustained Angiogenesis 1. Read the introduction, and fill in the blanks. a. Angiogenesis is the of blood vessels and capillaries to bring nutrients and oxygen to cells. Normally, angiogenesis occurs during. When tumors form, they develop the ability to angiogenic genes and initiate the growth of new and so that they can grow and expand. This process involves the of growth factors that stimulate cells to move towards tumors. The formation of vessels and capillaries provides tumors with and essential to growth and development. Part 1: Description of Angiogenesis 1. Read the description, and write a one paragraph summary of what you have read. 2. Answer the questions about angiogenesis. Summary Paragraph: What is the role of VEGF in angiogenesis? What kinds of studies have been conducted to learn more about sustained angiogenesis? Part 2: Interacting with Angiogenesis 1. Review the slideshow presentation. 2. Quiz yourself with 10 flashcards. 3. Test your knowledge with the interactive diagrams and multiple choice questions. 4. Leave us a comment at the bottom of the page! :) Part 3: Final Summary 1. Now that you have read all of the information about sustained angiogenesis, it s time to write a final piece about what you have learned. In bullet points, write out three interesting facts that you learned from the webpage.
9 Sustained Angiogenesis Crossword ACROSS 4) The process of developing or being developed 8) Physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels 10) Group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body 14) Development of organs within an animal 15) Interior lining of blood vessels DOWN 1) A tubular structure carrying blood through the tissues and organs 2) Deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues 3) A substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life 5) Chemical element with symbol O and atomic number 8 6) Outline the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels 7) Continuing for an extended period or without interruption 9) Any of the fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles and venules 12) Activated in a pericyte cell 13) Vascular endothelial growth factor
10 Name Date Period Tissue Invasion and Metastasis Work in pairs Getting to the website Go to Click on Aidan, Camila, Emily and then start by reading the introduction Introduction: An Into to Metastasis Read the introduction, check the box when completed. Answer the following questions: 1. What is Metastasis? 5. Explain the evidence that supports the theory that Metastasis did not occur randomly. 500 Word Summary 1. The formation of new tumors ultimately leads to what percent of cancer deaths? 2. Explain the difference between a benign and a malignant tumor? I II a b 3. Why is it important to distinguish between these two tumor types? c d e Review slideshow if needed Complete the flashcard Deck Complete the Multiple Choice Review 4. What is the EMT process? Why is it important? Reflection: What is the most important piece about metastasis? Why is it a hallmark of cancer?
11 Name: Period: Date: 1. Read the introduction 2. Read the description of the cancer hallmark 3. Why do cancer cells have an accelerated metabolism? 4. How many ATPs per glucose do cancer cells make? 5. Review the slide show 7. Finish the interactive quiz 8. What does the P53 gene do in normal cells? 9. What does the P53 gene do in cancerous cells? 10. How do chemotherapeutic drugs inhibit the energy pathways in cancerous cells? 6. Review all of the flashcards 11. Letter Molecule/Process A B C D E
12 Name: _ Date: Evading the Immune System 1. List the three immune hallmarks that cells develop as they form a tumor: A. B. C. 2. The Three E s: In, the immune system manages to destroy such cells before they can spread or cause significant harm. is when the immune system doesn t eliminate the tumor right away, but is able to contain it. To grow into a full-blown cancer, the cells will have the immune system s defenses. 3. Briefly summarize what immunosurveillance is. Explain the role of immunogenicity in it. 4. Immunosuppression works by the system. Tumors release factors and molecules to transform naive T-cells into. In a healthy environment cells help shut down activated T-cells at the end of an immune response. However, in a cancerous microenvironment, cells are used to autoimmune responses. 5. Choose two types of immunotherapy. Briefly describe each. A. : B. : 6. Write down one thing that surprised/interested you from the presentation and interactive webpage.
13 Name: Date: Faux Biology180: Genomic Instability Read Introduction Cancer develops through the multitude of that can occur from genome, a hallmark of. It is an increased risk of genome transformations during the cell cycle, which can negatively affect the body. Overtime, with age, as people s cells divide more, their susceptibility to mutations. How can mutations be prevented? Complete the diagram below Read What is Genome Instability? What are harmful mutations? How are cancer cells different than non-cancer cells? What are some selective advantages cancer cells have? What is the chance of a single nucleotide mutation occurring? Why are cancer mutations more likely than we think? What genes are known to lead to breast cancer?
14 Why is it important to get tested for cancer often? Has the death rate of cancer in the U.S. gone down in recent years? Look through the slideshow Do the Genome Instability Flashcards Take the multiple choice/interactive quiz!
15 Name: Period: Date: Inflammation as a Hallmark of Cancer 1. Work in pairs (share a computer). 2. So that you can get credit, turn in this paper! 3. Go to Kenneth Sieu s AP Biology Inflammation Qwizcards page. 4. Start exploring the page! Introduction Read the introduction and fill in the blanks below. Inflammation is natural process within the body to kill and promote. However, inflammation can inadvertently cause more damage to the body by aiding the growth and spread of cancer. It is one of the Hallmarks of cancer and is intertwined with, evading the, and. Inflammation, although a helpful process from the immune system, can assist in the growth, replication, and creation of. 2. Read Inflammation and DNA damage. Answer the questions below. How does inflammation lead to genomic instability? 3. Read What Happens Next? and Tumor Growth and Inflammation. Answer the questions below. What role does inflammation play in the promotion of angiogenesis? Inflammation and Cancer: Overview 1. Read What is Inflammation? Answer the questions below. What are the 2 types of inflammation and how are they different? How do cancer cells use cells from the immune response for their own purposes during inflammation? How is chronic inflammation related to cancer? (general)
16 Name: Period: Date: Inflammation as a Hallmark of Cancer 6. Now practice what you ve learned with the flashcard deck. See if you can get all 10 right before moving on! Write down three things you learned from the flashcard review. Label the diagram above. 1. a b 2. c d e 3. f g 4. Read How was the link between cancer and inflammation discovered? Summarize the study in two sentences. Finally, do the quiz. Now that you ve learned about how inflammation can cause cancer, write down a four sentence summary of this hallmark. 5. Read Treatments Write down one question you have about possible cancer treatments related to inflammation.
17 Name: Period: Date: Inflammation as a Hallmark of Cancer
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CANCER.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture:
 Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Module 7: Cell Structure and Function
 Name: Period: Date: Module : Cell Structure and Function. Work in pairs (share a computer).. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit.. Go to http://www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
Name: Period: Date: Module : Cell Structure and Function. Work in pairs (share a computer).. Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit.. Go to http://www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
Module 27: Immune System, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Module 27: Immune System, Student Learning Guide Instructions: Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
Name: Period: Date: Module 27: Immune System, Student Learning Guide Instructions: Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of November
 Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Name: Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Quiz 1 Cell Communication, Cancer and The Cell Cycle Week of 16-20 November Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
Basic tumor nomenclature
 Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM VOCABULARY blood vessel - arteries veins capillaries blood plasma white blood cells red blood cells platelets WHAT IS CIRCULATION? What messenger makes trillions
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM VOCABULARY blood vessel - arteries veins capillaries blood plasma white blood cells red blood cells platelets WHAT IS CIRCULATION? What messenger makes trillions
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA
 PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November
 Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Cell Cycle - Introduction
 Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Functional Limitations
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Your World: Fighting Cancer with Biotechnology
 Cancer Education Project Your World: Fighting Cancer with Biotechnology Overview: This series of 6 activities is designed to accompany Your World: Fighting Cancer with Biotechnology magazine available
Cancer Education Project Your World: Fighting Cancer with Biotechnology Overview: This series of 6 activities is designed to accompany Your World: Fighting Cancer with Biotechnology magazine available
Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off
 Lesson Overview 10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off When cells are grown in the laboratory, most cells will divide until they come into contact
Lesson Overview 10.3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Question #1 Controls on cell growth and division turned on and off When cells are grown in the laboratory, most cells will divide until they come into contact
Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage
 1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
Evolution Webquest. This website is a treasure trove of information about evolution. I encourage you to explore this website on your own time.
 Name: Date: Per: Evolution Webquest In this webquest you will be exploring evolution and the mechanisms that drive evolution. You will use three websites to answer the following questions and complete
Name: Date: Per: Evolution Webquest In this webquest you will be exploring evolution and the mechanisms that drive evolution. You will use three websites to answer the following questions and complete
Cellular Reproduction Section 9.1 Cellular Growth
 Cellular Reproduction Section 9.1 Cellular Growth Scan the titles, boldfaced words, pictures, figures, and captions in Section 1. Write three facts you discovered about cellular growth as you scanned the
Cellular Reproduction Section 9.1 Cellular Growth Scan the titles, boldfaced words, pictures, figures, and captions in Section 1. Write three facts you discovered about cellular growth as you scanned the
Lecture 1: Course Introduction and Cancer ʻby the Numbersʼ. biochemistry 4450a
 Lecture 1: Course Introduction and Cancer ʻby the Numbersʼ biochemistry 4450a Introduction Rationale for this course Course ʻPhilosophyʼ Course Outline Evaluation Themes Critical Thinking Cancer ʻby the
Lecture 1: Course Introduction and Cancer ʻby the Numbersʼ biochemistry 4450a Introduction Rationale for this course Course ʻPhilosophyʼ Course Outline Evaluation Themes Critical Thinking Cancer ʻby the
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy. Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI
 A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
SNC2D BIOLOGY 3/24/2013. TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Cancer Cell Division Gone Wrong (P.32-34) Cancer Cell Division Gone Wrong
 SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Cancer Cell Division Gone Wrong (P.32-34) Cancer Cell Division Gone Wrong A cell s DNA controls everything that happens in that cell, including cell division.
SNC2D BIOLOGY TISSUES, ORGANS & SYSTEMS OF L Cancer Cell Division Gone Wrong (P.32-34) Cancer Cell Division Gone Wrong A cell s DNA controls everything that happens in that cell, including cell division.
Cancer arises from the mutation of a normal gene. A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen.
 Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
UNIT 4: DNA, Chromosomes, and Cell Division DAYSHEET 46: Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 UNIT 4: DNA, Chromosomes, and Cell Division DAYSHEET 46: Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Name Biology I Date: Catalyst/Bellringer: Use your reading strategies as you read the article below about cancer.
UNIT 4: DNA, Chromosomes, and Cell Division DAYSHEET 46: Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Name Biology I Date: Catalyst/Bellringer: Use your reading strategies as you read the article below about cancer.
General Pathology VPM 152. Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
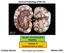 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle
 Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5-6 DNA Replication Notes 7-8 DNA replication
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5-6 DNA Replication Notes 7-8 DNA replication
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
Chapter 10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle Vocabulary: Cyclin Cancer Key Concepts: How is the cell cycle regulated? How are cancer cells different from other cells? I. Introduction A. An Interesting Fact About
C) The graph should look exactly like the graph on the left (Mut1 cells + Mating Pheromone for 3 hours at 25 degrees). The cells arrest in G1.
 706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS
 TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS AZIZA SHAD, MD AMEY DISTINGUISHED PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY, BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION LOMBARDI CANCER CENTER GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS AZIZA SHAD, MD AMEY DISTINGUISHED PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY, BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION LOMBARDI CANCER CENTER GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Chapter 8 Guiding Questions
 Chapter 8 Guiding Questions If there is something that you don t know how to answer, please seek help so you understand and master each concept! 1. What does the cell cycle include? 2. What are the phases
Chapter 8 Guiding Questions If there is something that you don t know how to answer, please seek help so you understand and master each concept! 1. What does the cell cycle include? 2. What are the phases
- is a common disease - 1 person in 3 can expect to contract cancer at some stage in their life -1 person in 5 can expect to die from it
 MBB157 Dr D Mangnall The Molecular Basis of Disease CANCER Lecture 1 One of the simpler (and better) definitions of cancer comes from the American Cancer Society, who define cancer as; 'Cancer is a group
MBB157 Dr D Mangnall The Molecular Basis of Disease CANCER Lecture 1 One of the simpler (and better) definitions of cancer comes from the American Cancer Society, who define cancer as; 'Cancer is a group
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen. Any agent that causes cancer is called a carcinogen and is described as carcinogenic.
 Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
Cancer Cancer is one of the most common diseases in the developed world: 1 in 4 deaths are due to cancer 1 in 17 deaths are due to lung cancer Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men Breast cancer
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION
 CELL GROWTH & DIVISION A- ANA- AUTO CARCIN- CHEMO- CHROMA- CYTO- DI- FERTIL- HAPLO- IMPORTANT WORD ROOTS Homo- like not, without Inter- between of each, re Karyo- nucleus self Kinet- move ulcer Meta- A
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION A- ANA- AUTO CARCIN- CHEMO- CHROMA- CYTO- DI- FERTIL- HAPLO- IMPORTANT WORD ROOTS Homo- like not, without Inter- between of each, re Karyo- nucleus self Kinet- move ulcer Meta- A
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie L. Bay, Jo K. Perry and Peter E. Lobie
 LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie L. Bay, Jo K. Perry and Peter E. Lobie Breast Cancer Each year in New Zealand, approximately 2,400 women and 20 men are
LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie L. Bay, Jo K. Perry and Peter E. Lobie Breast Cancer Each year in New Zealand, approximately 2,400 women and 20 men are
Regulation of Cell Division
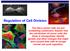 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials. What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think.
 Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Lesson 1 Instructional Materials What do you OBSERVE about this image? State what you SEE, not what you think. Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials Lesson 1 Instructional Materials
Living Environment / Diffusion Lab Report Analysis Questions
 Living Environment / Diffusion Lab Report Analysis Questions Name: Family: Date: January 5 th, 2015 Base your answers to questions 1-3 on the diagram of a compound light microscope below and on your knowledge
Living Environment / Diffusion Lab Report Analysis Questions Name: Family: Date: January 5 th, 2015 Base your answers to questions 1-3 on the diagram of a compound light microscope below and on your knowledge
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
BIG FIVE: Review your notes about the Big Five theory and your self-rating before beginning.
 Name: Date: Hour: 1 Personality Tests Please follow the directions to complete both major types of personality tests. You must take at least 4 personality tests to complete this assignment. Please go to
Name: Date: Hour: 1 Personality Tests Please follow the directions to complete both major types of personality tests. You must take at least 4 personality tests to complete this assignment. Please go to
Regulating the Cell Cycle. Lesson Overview THINK ABOUT IT. How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide?
 THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
THINK ABOUT IT How do cells know when to divide? Review: Why do cells divide? Controls on Cell Division How is the cell cycle regulated? The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins both inside
Period: Date: Module 28: Nervous System, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: Module 28: Nervous System, Student Learning Guide Instructions: Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
Name: Period: Date: Module 28: Nervous System, Student Learning Guide Instructions: Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get credit. Go to www.sciencemusicvideos.com.
Biology Diagrams. Biology Review
 Biology Diagrams Biology Review Matching A) Light source B) Respiratory System C) Mitochondria D) Nucleus E) Vacuole F) Cytokinesis G) Daughter cells H) Interphase I) Telophase J) Ocular lens K) Fine
Biology Diagrams Biology Review Matching A) Light source B) Respiratory System C) Mitochondria D) Nucleus E) Vacuole F) Cytokinesis G) Daughter cells H) Interphase I) Telophase J) Ocular lens K) Fine
sciencemusicvideos AP Bio Module 10: Cellular Respiration
 Name: Period: Date: sciencemusicvideos P io Module 0: Cellular Respiration. Work in pairs (share a computer).. If your instructor is tracking your performance on qwizcards.com, make sure that you log in
Name: Period: Date: sciencemusicvideos P io Module 0: Cellular Respiration. Work in pairs (share a computer).. If your instructor is tracking your performance on qwizcards.com, make sure that you log in
CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY. Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University
 CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University Padang 18 Mei 2013 INTRODUCTION Tumor: cells that continue to replicate, fail to differentiate into specialized cells, and become
CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University Padang 18 Mei 2013 INTRODUCTION Tumor: cells that continue to replicate, fail to differentiate into specialized cells, and become
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle
 Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
Unit 9: The Cell Cycle Name: Period: Test Date: 1 Table of Contents Title of Page Page Number Teacher Stamp Unit 9 Warm-Ups 3-4 Cell Cycle/Interphase Notes 5 DNA Replication Video 6 Cancer Notes 15-16
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION
 AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION CELL CYCLE 2 crucial factors for normal growth: Timing and rate of cell division Cell division frequency depends on cell type: skin cells: frequently Liver cells: can divide when
AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION CELL CYCLE 2 crucial factors for normal growth: Timing and rate of cell division Cell division frequency depends on cell type: skin cells: frequently Liver cells: can divide when
Camel Milk and Cancer: A Possible Cure?
 Camel Milk and Cancer: A Possible Cure? You may have heard that camel milk has many amazing therapeutic benefits, but did you know that it also has anti-cancer properties? In 2016 it was estimated that
Camel Milk and Cancer: A Possible Cure? You may have heard that camel milk has many amazing therapeutic benefits, but did you know that it also has anti-cancer properties? In 2016 it was estimated that
Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie Bay, Jo Perry, Michal Denny and Peter Lobie
 LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie Bay, Jo Perry, Michal Denny and Peter Lobie Breast Cancer Each year in New Zealand, approximately 2,400 women and 20 men
LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Breast Cancer and Biotechnology Jacquie Bay, Jo Perry, Michal Denny and Peter Lobie Breast Cancer Each year in New Zealand, approximately 2,400 women and 20 men
Mitosis Exploration Pd. Objective: Describe the purpose and process of cellular reproduction. 1. What is a cell?
 Mitosis Exploration Name Pd Objective: Describe the purpose and process of cellular reproduction. Review: 1. What is a cell? 2. Describe the main differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
Mitosis Exploration Name Pd Objective: Describe the purpose and process of cellular reproduction. Review: 1. What is a cell? 2. Describe the main differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
Name: Cell division and cancer review
 Name: Cell division and cancer review 1. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gamete cells or Somatic cells 2. Define homologous chromosomes. 2 chromosomes with similar structure 3. For each of the following
Name: Cell division and cancer review 1. What type of cell undergoes meiosis? Gamete cells or Somatic cells 2. Define homologous chromosomes. 2 chromosomes with similar structure 3. For each of the following
The Body s Transport System (pp )
 The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
Chapter 13 Summary Experiments and Observational Studies
 Chapter 13 Summary Experiments and Observational Studies What have we learned? We can recognize sample surveys, observational studies, and randomized comparative experiments. o These methods collect data
Chapter 13 Summary Experiments and Observational Studies What have we learned? We can recognize sample surveys, observational studies, and randomized comparative experiments. o These methods collect data
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
2. Was there a scientific way to predict the outcome of a cross between two parents?
 Name Date Period Heredity WebQuest DNA from the Beginning Mendelian Genetics Go to http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Children resemble their parents Read the text and answer the following
Name Date Period Heredity WebQuest DNA from the Beginning Mendelian Genetics Go to http://www.dnaftb.org/dnaftb/1/concept/index.html Children resemble their parents Read the text and answer the following
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Chapter 13. Experiments and Observational Studies. Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Experiments and Observational Studies Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Observational Studies In an observational study, researchers don t assign choices; they simply observe
Chapter 13 Experiments and Observational Studies Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Observational Studies In an observational study, researchers don t assign choices; they simply observe
Cytology and Histology Practice Test
 Cytology and Histology Practice Test 1. Which of the following manufactures proteins: A. lysosomes B. chromosomes C. ribosomes D. golgi apparatus 2. Which of the following contain digestive enzymes: A.
Cytology and Histology Practice Test 1. Which of the following manufactures proteins: A. lysosomes B. chromosomes C. ribosomes D. golgi apparatus 2. Which of the following contain digestive enzymes: A.
Pink Is Not Enough Breast Cancer Awareness Month National Breast Cancer Coalition Advocate Toolkit
 Pink Is Not Enough National Breast Cancer Coalition Advocate Toolkit 2 INTRODUCTION Awareness of breast cancer is at an all-time high. Yet breast cancer still kills almost as many Americans each year as
Pink Is Not Enough National Breast Cancer Coalition Advocate Toolkit 2 INTRODUCTION Awareness of breast cancer is at an all-time high. Yet breast cancer still kills almost as many Americans each year as
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Thanks. Connect. You Might Also Like. Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback.
 Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
Biology Day 9. Planner: Ch. 1 Vocab WS ToC due! See Ms. Fleming for stamps. Table of Contents #1 24. Do-Now 9/8 25.Chapter 1 Vocab Review WS
 Biology Day 9 Monday, September 8 Tuesday, September 9, 2014 Title your paper: Do-Now 9/8 Then, underneath, answer the following: 1. Write down today s FLT. 2. Write down two things you have learned about
Biology Day 9 Monday, September 8 Tuesday, September 9, 2014 Title your paper: Do-Now 9/8 Then, underneath, answer the following: 1. Write down today s FLT. 2. Write down two things you have learned about
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction
 Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 MITOSIS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1
2. What is the difference between a compound eye and your eye?
 INTRODUCTION: If numbers alone are used as a measure of success, the jointedlegged animals are the most successful animals. Their body segmentation suggests that they evolved from segmented worms. The
INTRODUCTION: If numbers alone are used as a measure of success, the jointedlegged animals are the most successful animals. Their body segmentation suggests that they evolved from segmented worms. The
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Let s quickly return to that siliconbased life form, since
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Let s quickly return to that siliconbased life form, since
CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES. THE HEART Student Pages. Designers Brianne Miller, Molly Bugaile
 CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES THE HEART Student Pages Designers Brianne Miller, Molly Bugaile The heart is the most important muscle in the body! Heart Activity I Just beat it! The heart is the most important muscle
CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES THE HEART Student Pages Designers Brianne Miller, Molly Bugaile The heart is the most important muscle in the body! Heart Activity I Just beat it! The heart is the most important muscle
Cancer Cells. It would take another 20 years and a revolution in the techniques of biological research to answer these questions.
 Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Cancer Cells Cancer, then, is a disease in which a single normal body cell undergoes a genetic transformation into a cancer cell. This cell and its descendants, proliferating across many years, produce
Cancer. October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
Lesson Title: Viruses vs. Cells Standards to be Addressed: Acquisition
 Readiness Standards: 4.C: compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza
Readiness Standards: 4.C: compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza
Write It! Station Directions
 Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
You might be interested in reading an excerpt from Dimensions
 Take notes (minimum 1 page) on the following reading. Then review using the animation (link at bottom) and answer the quiz questions at the bottom of the webpage. To get credit for this assignment you
Take notes (minimum 1 page) on the following reading. Then review using the animation (link at bottom) and answer the quiz questions at the bottom of the webpage. To get credit for this assignment you
Biologics Effects of Targeted Therapeutics
 Report on the isbtc Mini-symposium on Biologics Effects of Targeted Therapeutics Michael B. Atkins, MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Louis Weiner, M.D. Fox Chase Cancer Center Report on the isbtc
Report on the isbtc Mini-symposium on Biologics Effects of Targeted Therapeutics Michael B. Atkins, MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Louis Weiner, M.D. Fox Chase Cancer Center Report on the isbtc
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
The Cell Cycle 1 What controls the life and development of a cell?
 The Cell Cycle 1 What controls the life and development of a cell? Why? An old piece of poetry says to everything there is a season... a time to be born, a time to die. For cells, the line might say a
The Cell Cycle 1 What controls the life and development of a cell? Why? An old piece of poetry says to everything there is a season... a time to be born, a time to die. For cells, the line might say a
2013 Holiday Lectures on Science Medicine in the Genomic Era
 INTRODUCTION You may have read articles that talk about cancer genes. But what exactly are cancer genes and what do they do? Cancer consists of a group of diseases caused by mutations in the DNA of cells.
INTRODUCTION You may have read articles that talk about cancer genes. But what exactly are cancer genes and what do they do? Cancer consists of a group of diseases caused by mutations in the DNA of cells.
Cancer and the Cell Cycle was developed by OpenStax College, licensed by Rice University, and available on the Connexions website, is available under
 Cancer and the Cell Cycle was developed by OpenStax College, licensed by Rice University, and available on the Connexions website, is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- ShareAlike
Cancer and the Cell Cycle was developed by OpenStax College, licensed by Rice University, and available on the Connexions website, is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- ShareAlike
Overcoming the Seven Hallmarks
 Overcoming the Seven Hallmarks A Guide for Christians with Cancer By Richard W. Moulton, M.S., M.Div., D.Min The first in a series of articles on overcoming the Hallmarks of Cancer The seven hallmarks
Overcoming the Seven Hallmarks A Guide for Christians with Cancer By Richard W. Moulton, M.S., M.Div., D.Min The first in a series of articles on overcoming the Hallmarks of Cancer The seven hallmarks
SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections & Steve Thompson:
 SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections 20585 & 20586 Steve Thompson: steven.thompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 We ll start with the exam review. A few people did well,
SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections 20585 & 20586 Steve Thompson: steven.thompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 We ll start with the exam review. A few people did well,
Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
c) Macrophages and B cells present antigens to helper T_-cells. (Fill in blanks.) 2 points
 Question 1 You are an immunologist who wants to make the big bucks. You decide to leave the world of science and get a job as a script-consultant on a new medical drama (ER-like) show. You test the writers
Question 1 You are an immunologist who wants to make the big bucks. You decide to leave the world of science and get a job as a script-consultant on a new medical drama (ER-like) show. You test the writers
