MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer. Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee
|
|
|
- Bruno Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee
2 Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary
3 What is MicroRNA?
4 What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) - They are short non-coding RNAs of nucleotide not translated into proteins. - They have emerged as key regulators of cancer-related pathways. Proliferation Cell cycle control Apoptosis Differentiation Migration
5 What is MicroRNA? Three types of Pre-miRNA (Primary-miRNA) - Intronic mirnas are processed from a protein-coding transcript by Microprocessor. - Precursor mirtrons are produced by the spliceosome. Rainer, J., et al. "Glucocorticoid-regulated micrornas and mirtrons in acute lymphoblastic leukemia." Leukemia 23.4 (2009):
6 What is MicroRNA? Pathway of mirna biogenesis and processing Lin, Shuibin, and Richard I. Gregory. "MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer." Nature Reviews Cancer 15.6 (2015):
7 mirna dysregulation in cancer
8 mirna dysregulation in cancer 1. Pri-miRNA transcription 2. Defective Microprocessor 3. Pre-miRNA export 4. Pre-miRNA processing 5. Other mirna regulators
9 mirna dysregulation in cancer 1. Pri-miRNA transcription - The locus of mirna on chromosome is frequently deleted in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL), which target BCL-2 mrna ecoding anti-apoptotic protein. - The CpG islands at the gene promoters of mirnas are frequently hypermethylated in cancer, leading to silencing of these mirnas. - Proto-oncoprotein MYC can contribute to the widespread repression of tumour suppressive mirnas in B cell lymphoma. Jansson, Martin D., and Anders H. Lund. "MicroRNA and cancer." Molecular oncology 6.6 (2012):
10 mirna dysregulation in cancer 2. Defective Microprocessor - In cervical squamous cell carcinomas, DROSHA expression levels are upregulated. - In lung adenocarcinoma cells, downregulation of DROSHA acting as a tumour suppressor increases proliferation and tumour growth. - Particulary, DROSHA and DGCR8 are frequently mutated in Wilms tumour samples. Jansson, Martin D., and Anders H. Lund. "MicroRNA and cancer." Molecular oncology 6.6 (2012):
11 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3. Pre-miRNA export - Pre-miRNAs are exported into the cytoplasm to be processed into mature mirnas. - The export of pre-mirnas is mediated by XPO5 and its cofactor, RanGTP41. - XPO5 mutations impair pre-mirna export and result in an accumulation of pre-mirnas in the nucleus, leading to defects in mirna biogenesis.
12 mirna dysregulation in cancer 4. Pre-miRNA processing - The mutation hot spots occur in the metal-binding residues which do not change DICER1 protein expression but instead cause defects in the function. - DICER1 RNase IIIb mutations reduce the expression of the members of the let-7 tumour-suppressive mirna family.
13 mirna dysregulation in cancer 5. Other mirna regulators Hippo?
14 Introduction Hippo signaling pathway in cancer - It controls organ size in animals through the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. - The pathway takes its name from one of its key signaling components-the protein kinase Hippo (Hpo). - Mutations in this gene lead to tissue overgrowth, or a hippopotamus -like phenotype. Fruitfly Mouse liver Johnson, Randy, and Georg Halder. "The two faces of Hippo: targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment." Nature reviews Drug discovery 13.1 (2014):
15 Introduction Mode of action of Hippo signaling pathway Johnson, Randy, and Georg Halder. "The two faces of Hippo: targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment." Nature reviews Drug discovery 13.1 (2014):
16 Introduction Regulation of Microprocessor by Hippo pathway - At low cell density, Hippo pathway is inactive, and nuclear YAP1 binds to and sequesters DDX17(p72) to suppress pri-mirna processing. - At high cell densities, Hippo pathway is active, which leads to YAP1 phosphorylation and its retention in the cytoplasm. DDX17 is able to bind to pri-mirna, resulting in enhanced mirna biogenesis. Mori, Masaki, et al. "Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent mirna biogenesis to cancer." Cell (2014):
17 Introduction Cell-density-dependent mirna biogenesis Mori, Masaki, et al. "Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent mirna biogenesis to cancer." Cell (2014):
18 Introduction Cell-density-dependent mirna biogenesis - qrt-pcr analysis of mirna expression in HaCaT cells. - Elevated mirna expression at high cell density was observed. Mori, Masaki, et al. "Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent mirna biogenesis to cancer." Cell (2014):
19 Introduction Localization of YAP and p72 - Immunocytochemistry analysis of YAP localization - Immunocytochemistry of YAP and p72 in HaCaT cells at high density. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Mori, Masaki, et al. "Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent mirna biogenesis to cancer." Cell (2014):
20 Summary
21 Summary - MicroRNAs have emerged as key regulators of cancer-related pathways. - In cancer, dysregulation of the mirna biogenesis pathway is occurred, resulted from primirna transcription, defective microprocessor, pre-mirna export, pre-mirna processing, - And also, there are various cancer-related pathways involved in the regulation of mirna biogenesis such as hippo signaling pathway.
22 THANK YOU
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
reported to underlie diverse aspects of biology, including developmental timing, differentiation, proliferation, cell death, and metabolism.
 1100 MicroRNA in Cancer: The Involvement of Aberrant MicroRNA Biogenesis Regulatory Pathways Genes & Cancer 1(11) 1100 1114 The Author(s) 2011 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
1100 MicroRNA in Cancer: The Involvement of Aberrant MicroRNA Biogenesis Regulatory Pathways Genes & Cancer 1(11) 1100 1114 The Author(s) 2011 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNAs and Cancer
 MicroRNAs and Cancer MicroRNAs are an abundant class of small (20-25 nucleotides) non-protein coding RNAs that function as negative gene regulators. The human genome contains up to 1000 micrornas which
MicroRNAs and Cancer MicroRNAs are an abundant class of small (20-25 nucleotides) non-protein coding RNAs that function as negative gene regulators. The human genome contains up to 1000 micrornas which
Dottorato di Ricerca in Genetica e Biologia Cellulare. MUTANT P53 INHIBITS microrna BIOGENESIS BY INTERFERING WITH THE MICROPROCESSOR COMPLEX
 Dipartimento di Ecologia e Biologia Dottorato di Ricerca in Genetica e Biologia Cellulare Ciclo XXVII Settore scientifico-disciplinare BIO/11 MUTANT P53 INHIBITS microrna BIOGENESIS BY INTERFERING WITH
Dipartimento di Ecologia e Biologia Dottorato di Ricerca in Genetica e Biologia Cellulare Ciclo XXVII Settore scientifico-disciplinare BIO/11 MUTANT P53 INHIBITS microrna BIOGENESIS BY INTERFERING WITH
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna
 Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna Carl Novina Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Qiagen Webinar 05-17-11 Outline 1. The biology
Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna Carl Novina Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Qiagen Webinar 05-17-11 Outline 1. The biology
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer
 The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
10/31/2017. micrornas and cancer. From the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis to. microrna DNA RNA. Transcription factors.
 micrornas and cancer Cellular and Molecular Biology of Cancer (PATH G4500-001) November 1 st, 2017 -Katia Basso- Columbia University Katia Basso, PhD Office: ICRC RM506 E-mail: kb451@cumc.columbia.edu
micrornas and cancer Cellular and Molecular Biology of Cancer (PATH G4500-001) November 1 st, 2017 -Katia Basso- Columbia University Katia Basso, PhD Office: ICRC RM506 E-mail: kb451@cumc.columbia.edu
THE EFFECT OF HSA-MIR-105 ON PROSTATE CANCER GROWTH
 THE EFFECT OF HSA-MIR-105 ON PROSTATE CANCER GROWTH by David Rice Honeywell Bachelor of Science, Queen s University, 2010 THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
THE EFFECT OF HSA-MIR-105 ON PROSTATE CANCER GROWTH by David Rice Honeywell Bachelor of Science, Queen s University, 2010 THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research
 MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy
 Lidia Park Genomics and Medicine November 23, 2008 MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy When Victor Ambros, Rosalind Lee, and Rhonda Feinbaum published the first finding of a microrna,
Lidia Park Genomics and Medicine November 23, 2008 MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy When Victor Ambros, Rosalind Lee, and Rhonda Feinbaum published the first finding of a microrna,
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
The Role of micrornas in Pain. Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan
 The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
General Biology 1004 Chapter 11 Lecture Handout, Summer 2005 Dr. Frisby
 Slide 1 CHAPTER 11 Gene Regulation PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Slide 1 CHAPTER 11 Gene Regulation PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control
 Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Objectives. Morphology and IHC. Flow and Cyto FISH. Testing for Heme Malignancies 3/20/2013
 Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
micrornas: the future for cancer therapy?
 micrornas: the future for cancer therapy? Improving cervical cancer treatment Tim Huitema - 02-07-2010 Medical Oncology and Gynaecological Oncology, UMC Groningen Supervisor: Dr. Bea Wisman Abstract Cervical
micrornas: the future for cancer therapy? Improving cervical cancer treatment Tim Huitema - 02-07-2010 Medical Oncology and Gynaecological Oncology, UMC Groningen Supervisor: Dr. Bea Wisman Abstract Cervical
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression. (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs)
 Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Novel RNAs along the Pathway of Gene Expression (or, The Expanding Universe of Small RNAs) Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein replication transcription translation Central Dogma DNA RNA Spliced RNA Protein
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: molecular features and role in cancer.
 MicroRNAs: molecular features and role in cancer. Elodie Lages, Hélène Ipas, Audrey Guttin, Houssam Nesr, François Berger, Jean-Paul Issartel To cite this version: Elodie Lages, Hélène Ipas, Audrey Guttin,
MicroRNAs: molecular features and role in cancer. Elodie Lages, Hélène Ipas, Audrey Guttin, Houssam Nesr, François Berger, Jean-Paul Issartel To cite this version: Elodie Lages, Hélène Ipas, Audrey Guttin,
Mechanism of splicing
 Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Outline of Splicing Mechanism of splicing Em visualization of precursor-spliced mrna in an R loop Kinetics of in vitro splicing Analysis of the splice lariat Lariat Branch Site Splice site sequence requirements
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0249 TITLE: Detection of genes modifying sensitivity to proteasome inhibitors using a shrna Library in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Gregory J. Hannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0249 TITLE: Detection of genes modifying sensitivity to proteasome inhibitors using a shrna Library in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Gregory J. Hannon, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Translational Application of microrna Profiling to Detect Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Jennifer Gyoba
 Translational Application of microrna Profiling to Detect Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers by Jennifer Gyoba A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Translational Application of microrna Profiling to Detect Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers by Jennifer Gyoba A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Multistep Model of Cervical Cancer: Participation of mirnas and Coding Genes
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15700-15733; doi:10.3390/ijms150915700 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Multistep Model of Cervical Cancer:
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15700-15733; doi:10.3390/ijms150915700 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Multistep Model of Cervical Cancer:
MicroRNA expression patterns and signalling pathways in the development and progression of childhood solid tumours
 Leichter et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:15 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0584-0 REVIEW MicroRNA expression patterns and signalling pathways in the development and progression of childhood solid tumours Anna
Leichter et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:15 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0584-0 REVIEW MicroRNA expression patterns and signalling pathways in the development and progression of childhood solid tumours Anna
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Suresh Alahari Editor. MicroRNA in Cancer
 MicroRNA in Cancer Suresh Alahari Editor MicroRNA in Cancer 1 3 Editor Suresh Alahari Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center LSU Health Science center New Orleans,
MicroRNA in Cancer Suresh Alahari Editor MicroRNA in Cancer 1 3 Editor Suresh Alahari Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center LSU Health Science center New Orleans,
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing. Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM
 MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
Evidence for dietary regulation of microrna expression in cancer cells
 Emerging Science Evidence for dietary regulation of microrna expression in cancer cells Cindy D Davis and Sharon A Ross MicroRNAs (mirnas) are an abundant class of short noncoding RNAs that are widely
Emerging Science Evidence for dietary regulation of microrna expression in cancer cells Cindy D Davis and Sharon A Ross MicroRNAs (mirnas) are an abundant class of short noncoding RNAs that are widely
Alternative regulation of MYC in lung cancer
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations 3-2016 Alternative regulation of MYC in lung cancer Patrick N. Backman Purdue University Follow this and additional works at:
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations 3-2016 Alternative regulation of MYC in lung cancer Patrick N. Backman Purdue University Follow this and additional works at:
Non-coding RNAs in lung cancer
 2014, Vol.1, No.11 Non-coding RNAs in lung cancer Biagio Ricciuti 1, Carmen Mecca 2, Lucio Crinò 1, Sara Baglivo 1, Matteo Cenci 1 and Giulio Metro 1 1 Medical Oncology, Santa Maria della Misericordia
2014, Vol.1, No.11 Non-coding RNAs in lung cancer Biagio Ricciuti 1, Carmen Mecca 2, Lucio Crinò 1, Sara Baglivo 1, Matteo Cenci 1 and Giulio Metro 1 1 Medical Oncology, Santa Maria della Misericordia
Reprogramming through micrornas Stefanie Dimmeler
 Klinikum der Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main Reprogramming through micrornas Stefanie Dimmeler Conflict of interest: T2cure GmbH, Miragen Non-coding DNA & RNA and micrornas Human Genome
Klinikum der Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main Reprogramming through micrornas Stefanie Dimmeler Conflict of interest: T2cure GmbH, Miragen Non-coding DNA & RNA and micrornas Human Genome
Activation of cellular proto-oncogenes to oncogenes. How was active Ras identified?
 Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions. 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19
 Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19 1 MicroRNA biogenesis 1. Pri mirna: primary mirna 2. Drosha: RNaseIII 3. DCR 1: Dicer 1 RNaseIII
Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19 1 MicroRNA biogenesis 1. Pri mirna: primary mirna 2. Drosha: RNaseIII 3. DCR 1: Dicer 1 RNaseIII
Molecular Markers. Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC
 Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
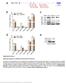 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
SUMO1 modification of KHSRP regulates tumorigenesis by preventing the TL-G-Rich mirna biogenesis
 Yuan et al. Molecular Cancer (217) 16:157 DOI 1.1186/s12943-17-724-6 RESEARCH Open Access SUMO1 modification of KHSRP regulates tumorigenesis by preventing the TL-G-Rich mirna biogenesis Haihua Yuan 1,2,
Yuan et al. Molecular Cancer (217) 16:157 DOI 1.1186/s12943-17-724-6 RESEARCH Open Access SUMO1 modification of KHSRP regulates tumorigenesis by preventing the TL-G-Rich mirna biogenesis Haihua Yuan 1,2,
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Nuclear micrornas and their unconventional role in regulating non-coding RNAs
 Protein Cell 2013, 4(5): 325 330 DOI 10.1007/s13238-013-3001-5 MINI-REVIEW Nuclear micrornas and their unconventional role in regulating non-coding RNAs Hongwei Liang, Junfeng Zhang, Ke Zen, Chen-Yu Zhang,
Protein Cell 2013, 4(5): 325 330 DOI 10.1007/s13238-013-3001-5 MINI-REVIEW Nuclear micrornas and their unconventional role in regulating non-coding RNAs Hongwei Liang, Junfeng Zhang, Ke Zen, Chen-Yu Zhang,
MicroRNAs in Normal and Malignant Lymphocytes
 MicroRNAs in Normal and Malignant Lymphocytes The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link
MicroRNAs in Normal and Malignant Lymphocytes The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
MicroRNAs in Human Diseases: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Disease
 DOI 10.4110/in.2011.11.3.135 pissn 1598-2629 eissn 2092-6685 REVIEW ARTICLE MicroRNAs in Human Diseases: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Disease * Department of Immunology, Chonbuk National University Medical
DOI 10.4110/in.2011.11.3.135 pissn 1598-2629 eissn 2092-6685 REVIEW ARTICLE MicroRNAs in Human Diseases: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Disease * Department of Immunology, Chonbuk National University Medical
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Molecular Mechanism of MicroRNA-203 Mediated Epidermal Stem Cell Differentiation
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2011 Molecular Mechanism of MicroRNA-203 Mediated Epidermal Stem Cell Differentiation Sarah Jackson University
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2011 Molecular Mechanism of MicroRNA-203 Mediated Epidermal Stem Cell Differentiation Sarah Jackson University
(,, ) microrna(mirna) 19~25 nt RNA, RNA mirna mirna,, ;, mirna mirna. : microrna (mirna); ; ; ; : R321.1 : A : X(2015)
 35 1 Vol.35 No.1 2015 1 Jan. 2015 Reproduction & Contraception doi: 10.7669/j.issn.0253-357X.2015.01.0037 E-mail: randc_journal@163.com microrna ( 450052) microrna() 19~25 nt RNA RNA ; : microrna (); ;
35 1 Vol.35 No.1 2015 1 Jan. 2015 Reproduction & Contraception doi: 10.7669/j.issn.0253-357X.2015.01.0037 E-mail: randc_journal@163.com microrna ( 450052) microrna() 19~25 nt RNA RNA ; : microrna (); ;
mir-17 in imatinib resistance and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
 JBUON 2013; 18(2): 437-441 ISSN: 1107-0625 www.jbuon.com E-mail: info@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE mir-17 in imatinib resistance and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
JBUON 2013; 18(2): 437-441 ISSN: 1107-0625 www.jbuon.com E-mail: info@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE mir-17 in imatinib resistance and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure
 Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure Frederick E. Domann, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology The University of Iowa Iowa City,
Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure Frederick E. Domann, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology The University of Iowa Iowa City,
CRS4 Seminar series. Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4. Biomedicine. Bioinformatics. Paolo Uva July 11, 2012
 CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
Cancer and Gene Regulation
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44548 1 Cancer and Gene Regulation OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44548 1 Cancer and Gene Regulation OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Chapter 11. How Genes Are Controlled. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and
MicroRNA-mediated loss of ADAR1 in metastatic melanoma promotes tumor growth
 Research article MicroRNA-mediated loss of ADAR1 in metastatic melanoma promotes tumor growth Yael Nemlich, 1,2 Eyal Greenberg, 1,3 Rona Ortenberg, 1,3 Michal J. Besser, 1,3 Iris Barshack, 4 Jasmine Jacob-Hirsch,
Research article MicroRNA-mediated loss of ADAR1 in metastatic melanoma promotes tumor growth Yael Nemlich, 1,2 Eyal Greenberg, 1,3 Rona Ortenberg, 1,3 Michal J. Besser, 1,3 Iris Barshack, 4 Jasmine Jacob-Hirsch,
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Regulation of Cardiac Cell Fate by micrornas: Implications for Heart Regeneration
 Cells 2014, 3, 996-1026; doi:10.3390/cells3040996 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Regulation of Cardiac Cell Fate by micrornas: Implications for Heart Regeneration Margarida
Cells 2014, 3, 996-1026; doi:10.3390/cells3040996 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Regulation of Cardiac Cell Fate by micrornas: Implications for Heart Regeneration Margarida
Molecular Diagnosis. Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology
 Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Objectives Describe uses of NAT in Oncology Diagnosis, Prediction, monitoring. Genetics Screening, presymptomatic testing, diagnostic testing,
Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Objectives Describe uses of NAT in Oncology Diagnosis, Prediction, monitoring. Genetics Screening, presymptomatic testing, diagnostic testing,
Expression of p53, p21 /waf l, bcl-2, bax, Rb and Ki67 proteins in Hodgkin's lymphomas
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 445-453 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Expression of p53, p21 /waf l, bcl-2, bax, Rb and Ki67 proteins in
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 445-453 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Expression of p53, p21 /waf l, bcl-2, bax, Rb and Ki67 proteins in
Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology. Molecular Diagnosis. Gain/Loss of Nucleic Acid. Objectives. MYCN and Neuroblastoma. Molecular Diagnosis
 Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Gross alterations in DNA content of tumors (ploidy) Gain/Loss of nucleic acids Markers of Clonality Oncogene/Tumor
Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Gross alterations in DNA content of tumors (ploidy) Gain/Loss of nucleic acids Markers of Clonality Oncogene/Tumor
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression
 omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Cancer Problems in Indonesia
 mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS
 GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS Dra. Margarita Sánchez-Beato Lymphoma Group Molecular Pathology Programme CNIO Agilent Microarray and Sequencing Roadshow,
GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS Dra. Margarita Sánchez-Beato Lymphoma Group Molecular Pathology Programme CNIO Agilent Microarray and Sequencing Roadshow,
mirnas as Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Assessment of Prognosis of Coronary Artery Disease
 Open Journal of Internal Medicine, 2018, 8, 54-63 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojim ISSN Online: 2162-5980 ISSN Print: 2162-5972 mirnas as Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Assessment of Prognosis of Coronary
Open Journal of Internal Medicine, 2018, 8, 54-63 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojim ISSN Online: 2162-5980 ISSN Print: 2162-5972 mirnas as Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Assessment of Prognosis of Coronary
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: progress in validating and targeting micrornas for cancer therapy
 EPIGENETICS AND GENETICS MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: progress in validating and targeting micrornas for cancer therapy Andrea L. Kasinski and Frank J. Slack Abstract In normal cells multiple micrornas
EPIGENETICS AND GENETICS MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: progress in validating and targeting micrornas for cancer therapy Andrea L. Kasinski and Frank J. Slack Abstract In normal cells multiple micrornas
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer
 BIOINFORMATICS Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer M. BRYAN WARF, 1 W. EVAN JOHNSON, 2 and BRENDA L. BASS 1
BIOINFORMATICS Improved annotation of C. elegans micrornas by deep sequencing reveals structures associated with processing by Drosha and Dicer M. BRYAN WARF, 1 W. EVAN JOHNSON, 2 and BRENDA L. BASS 1
Inside the Pediatric Cancer Genetics Clinic
 Inside the Pediatric Cancer Genetics Clinic August 23, 2014 Joyce Turner, MS, CGC Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC Pediatric Cancer Genetic Syndromes Aims over next 20-30 minutes: 1) Case
Inside the Pediatric Cancer Genetics Clinic August 23, 2014 Joyce Turner, MS, CGC Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC Pediatric Cancer Genetic Syndromes Aims over next 20-30 minutes: 1) Case
REGULATION OF MDM2 MEDIATED NFκB2 PATHWAY IN HUMAN LUNG CANCER
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2008 REGULATION OF MDM2 MEDIATED NFκB2 PATHWAY IN HUMAN LUNG CANCER Lathika Mohanraj Virginia Commonwealth
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2008 REGULATION OF MDM2 MEDIATED NFκB2 PATHWAY IN HUMAN LUNG CANCER Lathika Mohanraj Virginia Commonwealth
3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS
 3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS 3.1 Histopathology 3.1.1 Normal Squamous Epithelium The squamous epithelium that covers the ectocervix of the uterus is composed of different layers starting at the basement membrane
3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS 3.1 Histopathology 3.1.1 Normal Squamous Epithelium The squamous epithelium that covers the ectocervix of the uterus is composed of different layers starting at the basement membrane
The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors
 Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Review. Ageing 2: Cancer! Review: Mutations. Mutations 2/14/11. The Raw Material for Evolution. The Double Edged Sword
 Ageing 2: Cancer! Review: The force of natural selection declines with ageing due to increase in extrinsic mortality (= weakening of natural selection) and reduction in reproduction with age (selection
Ageing 2: Cancer! Review: The force of natural selection declines with ageing due to increase in extrinsic mortality (= weakening of natural selection) and reduction in reproduction with age (selection
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
