Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
|
|
|
- Eugene Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting protei. (c) Proportion of total read counts sequenced per pool. cntl, pool. (d) Scatterplot depicting the concordance of shrna abundance (log 2 normalized read counts) between each one of the replicates and its respective group (median log 2 normalized read counts). (e) Diagrams showing the number of hairpi represented with a minimum arbitrary threshold (normalized counts >100). (f) Waterfall plot depicting normalized depletion levels for all shrnas in the spleen (SP). Control shrnas and hairpi targeting selected candidate genes are highlighted. (g) Table showing seven candidate genes. (h) Validation of efficient knockdown of target genes in mouse MLL-AF9 leukemia cells. Cells were selected under puromycin treatment for 48 h before qrt PCR. Actb serves as a housekeeping gene. All data represent the mea + s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments. P < 5, P < 1, P < 01, two-tailed t test.
2 Supplementary Figure 2 SYNCRIP is required for survival of leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. (a) Efficient knockdown of SYNCRIP in mouse MLL-AF9 leukemia cells. MLL-AF9 cells were traduced with lentiviruses expressing shrna (directed agait luciferase) or shrnas directed agait Syncrip (shrna 1 and shrna 2). Cells were selected under puromycin for 24 h before immunoblotting. Cells were collected and assayed 3 d after viral traduction. Actin serves as a loading. (b) shrna depletion of SYNCRIP promoted myeloid differentiation of leukemia cells. Myeloid differentiation status was assayed by FACS analysis of F-480 and CD115 expression. A representative FACS plot is shown of and SYNCRIP-KD leukemia cells. (c) Quantitative summary of FACS analysis of F-480 and CD115 expression in and SYNCRIP-KD leukemia cells 3 and 4 d after traduction. (d) Quantitative summary of FACS analysis of the percentage of c-kit high cells in and SYNCRIP-KD leukemia cells 4 d after traduction. (e) Increased apoptosis was not observed in SYNCRIP-KD leukemia cells at 3 and 4 d after traduction. Quantitative summary of Annexin-V assessed by flow cytometry. (f) Annexin-V assessed by flow cytometry 5 d after traduction of and SYNCRIP-KD leukemia cells. Representative of FACS analysis in Figure 2e. (g) qpcr showing efficient knockdown of Syncrip in mouse AML1-ETO9a-driven leukemia cells. Cells were selected under puromycin for 48 h before qrt PCR. Actb serves as a housekeeping gene. (h) Cells from g were plated into methylcellulose and scored for the number of colonies (average of three independent experiments). (i) Assessment of disease burden, including spleen weight and liver weight, for the recipient mice in Figure 2f. (j) Immunoblots showing SYNCRIP expression in the bone marrow of mice that succumbed to disease in i and Figure 2f. (Mice injected with Syncrip-KD1 with reduced disease burden (group 1) maintained a better Syncrip knockdown level than mice that manifested similar disease to the group (group 2).) (k) qpcr showing efficient knockdown of Syncrip assayed by primers designed for specific grna targeting regio (grna-specific primers) in RN2 cells traduced with CRISPR Cas9-containing Tetinducible grnas specific for Syncrip (grna1 grna3) in comparison to, Cas9-EV. (l) Quantitative summary of FACS analysis of
3 the percentage of Gr-1 + and Mac-1 + cells in the Cas9-EV- and Syncrip-gRNA-traduced leukemia cells in Figure 2i. (m) Quantitative summary of FACS analysis of the percentage of c-kit high cells in the Cas9-EV- and Syncrip-gRNA-traduced leukemia cells Figure 2i. (n) Immunoblot analysis of RN2 cells overexpressing different isoforms of SYNCRIP corresponding to protei of 527, 562 and 623 aa. The SYNCRIP 562-aa isoform was the predominantly expressed isoform in leukemia cells. Actin serves as a loading. (o) SYNCRIP overexpression in RN2 cells promotes colony formation (average of three independent experiments). (p) qpcr showing mouse Syncrip expression as assayed by grna-specific primers and human SYNCRIP expression for Figure 2k. (q) Immunoblot analysis of the RN2 cells overexpressing SYNCRIP or carrying the (empty vector) traduced with CRISPR Cas9-containing Tet-inducible grna1 and grna3 cotructs or Cas9-EV in Figure 2j. All data represent the mea + s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments. P < 5, P < 1, P < 01, two-tailed t test.
4 Supplementary Figure 3 Syncrip-deleted hematopoietic cells retain colony-forming and in vivo engraftment capacity. (a) Representative PCR analysis for genotyping of Syncrip deletion in fetal liver cells. (b) Quantitative summary of FACS analysis of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the WT and Syncrip-CR-KO fetal livers in Figure 3c (WT n = 7, CR-KO n = 7). (c) Quantitative summary of the number of all colony types formed by WT and Syncrip-CR-KO fetal liver cells (average of six biological samples). BFU-E, burst-forming unit erythroid; M, macrophage; G, granulocyte; GM, granulocyte, macrophage; GEMM, granulocyte, erythroid, macrophage, megakaryocyte. (d) Assessment of disease burden, including spleen weight and liver weight, for the recipient mice in Figure 3j. P < 5, two-tailed t test.
5 Supplementary Figure 4 SYNCRIP is expressed in human AML, and SYNCRIP depletion results in apoptosis and increased myeloid differentiation in AML cell lines. (a) The graph shows the log 2 expression of SYNCRIP from tracript profiling of bone marrow cells from healthy donors and patients with various types of hematological malignancies, including ALLs, B-ALLs, CLL, MDS, CML and subtypes of AML. Hypodiploid B-ALL, n = 40; ALL with t(1;19), n = 36; ALL with t(12;21), n = 58; B-ALL with t(8;14), n = 13; c-/pre-b-all without t(9;22), n = 237; c-/pre-b-all with t(9;22), n = 122; pro-b-all with t(11q23)/mll, n = 70; CLL, n = 448; T-ALL, n = 174; MDS, n = 206; CML, n = 76; complex AML, n = 48; AML with inv(16), n = 28; AML MLL, n = 38; AML with a normal karyotype, n = 351; AML with t(15;17), n = 37; AML with t(8;21), n = 40; healthy donors, n = 73. P < 1, P < 01, P < 001, Student s t test. (Hemaexplorer data for SYNCRIP probe _s_at from the U133 and U133 Plus 2.0 arrays.) (b) qpcr showing SYNCRIP mrna levels in multiple human AML cell lines and normal cord blood derived CD34 + (CB-CD34 + ) cells. ACTB served as a housekeeping gene. Relative mrna level was normalized to the SYNCRIP mrna level in CB-CD34 + cells. (c f) Immunoblots showing efficient SYNCRIP knockdown in the indicated human AML cell lines. (g) Quantitative summary of CD14 high and CD13 high cells and CD14 and CD13 MFI in MOLM13, NB4 and NOMO- 1 cells traduced with shrna or shrnas agait SYNCRIP (shrna 1 and shrna 2) 4 d after traduction. (h) Representative FACS plots of the cells in Figure 4h. All data represent the mea + s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments. P < 5, P < 1, P < 01, two-tailed t test.
6 Supplementary Figure 5 Elevated expression of SYNCRIP correlates with expression profiles of the HOXA9 and MEIS1 target genes IKZF2 and MYC in patients with AML. (a) Plots showing the distribution of mean normalized counts of KD1 correlating with normalized mean counts of KD2 from the RNA sequencing data in Figure 5a. (b) Normalized read counts of Syncrip, Hoxa9, Myc, Ikzf2 and Meis1 from the RNA sequencing data in Figure 5a. (c f) log 2 mrna levels of the indicated genes in patients with high versus low SYNCRIP mrna expression in the data sets for patients with AML reported in Figure 4a (high SYNCRIP was defined as individuals with a value greater than the average + 1 s.d. while low SYNCRIP was defined as individuals with a value greater than the average 1 s.d.). (c) MSI2 mrna. (d) Target genes upregulated by HOXA9 MEIS1. (e) Target genes downregulated by HOXA9 MEIS1. (f) IZKF2 mrna. (g) MYC mrna. P < 5, P < 1, P < 01, two-tailed t test.
7 NOMARLIZED TOTAL RNA a b c MOLM13 cells - puromycin 4 days post traduciton d dsred cells - 3 days post traduction KD-1 KD-2 e dsred cells - 4 days post traduction KD-1 KD-2 f dsred cells - 4 days post traduction co ntro l KD -1 MSI2 KD -2 MSI2 Syncrip Hoxa9 c-myc Ikzf2 Syncrip Hoxa9 c-myc Ikzf2 SYNCRIP HOXA9 c-myc ACTIN g dsred cells - 4 days post traduction MSI2-KD1 MSI2-KD2 h RN2 cells - 24h after induction Cas9-EV grna1 grna2 i 2.0 MOLM13 cells- 3 days post traduction shrna#1 shrna#2 j MOLM13 cells- 4 days post traduction 3 2 shrna#1 shrna#2 1 Msi2 Syncrip Hoxa9 c-myc Ikzf2 Hoxa9 c-myc Ikzf2 SYNCRIP HOXA9 c-myc IKZF2 0 SYNCRIP c-myc HOXA9 IKZF2 k KD-1 KD-2 Cas9 TOTAL RNA grna-1 grna-2 shrna#1 shrna#2 dsred cells RN2 cells MOLM13 cells l m KD-2 KD-1 Syncrip Syn3 Syn1 Cas9 Syncrip Hoxa Hoxa c-myc c-myc Ikzf Ikzf Supplementary Figure 6 SYNCRIP post-tracriptionally s HOXA9 expression. (a) MOLM13 human myeloid leukemia cells carrying the MLL-AF9 tralocation overexpressing MSI2 were immunoprecipitated for endogenous MSI2 and SYNCRIP. (b) Immunoblots showing protein expression of HOXA9, MYC and IKZF2 upon SYNCRIP knockdown in dsred MLL-AF9 cells 3 and 4 d after traduction. Actin serves as a loading. (c) Immunoblots showing protein expression of HOXA9 and MYC upon SYNCRIP knockdown in MOLM13 cells after 2 d of puromycin selection (4 d after traduction). (d,e) qpcr measuring the mrna expression of Syncrip, Hoxa9, Myc and Ikzf2 in dsred tertiary MLL-AF9 leukemia cells 3 and 4 d after traduction. (f) Immunoblots showing protein expression of HOXA9, MYC and SYNCRIP upon MSI2 knockdown in dsred MLL-AF9 cells at 4 d after traduction. (g) qpcr measuring mrna expression of Syncrip, Hoxa9, Myc and Ikzf2 upon MSI2 knockdown in dsred MLL-AF9 cells at 4 d after traduction. (h) qpcr measuring mrna expression of Syncrip, Hoxa9, Myc and Ikzf2 in RN2 cells 24 h after induction. (i) qpcr measuring mrna expression of SYNCRIP, HOXA9, MYC and IKZF2 in human MOLM13 leukemia cells 3 d after traduction. (j) qpcr measuring mrna expression of SYNCRIP, HOXA9, MYC and IKZF2 in human MOLM13 leukemia cells 4 d after traduction. (k) Normalized total RNA levels in dsred MLL-AF9, RN2 and MOLM13 cells upon SYNCRIP depletion. (l) mrna stability of Syncrip, Hoxa9, Myc and Ikzf2 in dsred cells traduced with and SYNCRIP shrnas 4 d after traduction. (m) mrna stability of Syncrip, Hoxa9, Myc and Ikzf2 in RN2 cells expressing Cas9-EV or grna1 and grna3 targeting Syncrip after 24 h of Dox induction. Actin served as a loading. Actb served as a housekeeping gene. All data represent the mea + s.e.m. of at least three independent experiments. P < 5, P < 1, P < 01, two-tailed t test.
8 Supplementary Figure 7 HOXA9 but not MYC overexpression partially rescues the colony-forming ability of SYNCRIP-depleted cells. (a) qpcr measuring mrna expression showing that MSI2 overexpression increased the mrna levels of Hoxa9, Myc and Ikzf2. (b) Immunoblots showing efficient depletion of SYNCRIP and protein expression of HOXA9 for the cells in a. (c) Colony formation was rescued in dsred SYNCRIP-KD leukemia cells overexpressing full-length HOXA9. (d) Immunoblots showing efficient depletion of SYNCRIP and protein expression of HOXA9 for the cells in c. (e) Colony formation was not rescued in dsred SYNCRIP-KD leukemia cells overexpressing MYC. (f) Immunoblots showing efficient depletion of SYNCRIP and protein expression of MYC for the cells in e. (g) Cell growth was not rescued in MOLM13 SYNCRIP-KD cells overexpressing MYC. (h) Immunoblots showing efficient depletion of SYNCRIP and protein expression of MYC for the cells in g. Actin served as a loading. Actb served as a housekeeping gene. All data represent the mea + s.e.m. of at least three independent replicates. P < 5, P < 1, P < 01, P < 001, two-tailed t test.
Control shrna#9 shrna#12. shrna#12 CD14-PE CD14-PE
 a Control shrna#9 shrna#12 c Control shrna#9 shrna#12 e Control shrna#9 shrna#12 h 14 12 CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM b Colony number 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 6 pm A pa pc CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM pu pgm A p pg B d f CD11b-APC
a Control shrna#9 shrna#12 c Control shrna#9 shrna#12 e Control shrna#9 shrna#12 h 14 12 CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM b Colony number 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 6 pm A pa pc CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM pu pgm A p pg B d f CD11b-APC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion. (A-B) WT and HT mice infused with saline or glucose had overlapping achieved blood glucose and insulin levels, necessitating
Supplementary Figure 1. Blood glucose and insulin levels in mice during 4-day infusion. (A-B) WT and HT mice infused with saline or glucose had overlapping achieved blood glucose and insulin levels, necessitating
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
Supplement Material. Spleen weight (mg) LN cells (X106) Acat1-/- Acat1-/- Mouse weight (g)
 Supplement Material A Spleen weight (mg) C Mouse weight (g) 1 5 1 2 9 6 3 2 5 2 1 5 Male LN cells (X16) 4 ** ** Female B 3 2 1 Supplemental Figure I. Spleen weight (A), Inguinal lymph node (LN) cell number
Supplement Material A Spleen weight (mg) C Mouse weight (g) 1 5 1 2 9 6 3 2 5 2 1 5 Male LN cells (X16) 4 ** ** Female B 3 2 1 Supplemental Figure I. Spleen weight (A), Inguinal lymph node (LN) cell number
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
Supplemental Information. Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and. Monocyte-Dendritic Cell Progenitors Independently
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and
 Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and survival of mice with different genotypes. (a) The proper excision of Pten, p110α, p110α and p110δ was
Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and survival of mice with different genotypes. (a) The proper excision of Pten, p110α, p110α and p110δ was
The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice
 Supplementary information The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice Kanako Tatsumi 1, 2, Harumi Yamamoto-Mukai 2, Ritsuko Shimizu 3, Satoshi Waguri 4, Yu-Shin
Supplementary information The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice Kanako Tatsumi 1, 2, Harumi Yamamoto-Mukai 2, Ritsuko Shimizu 3, Satoshi Waguri 4, Yu-Shin
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/339/339ra69/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The caspase-8 inhibitor emricasan combines with the SMAC mimetic birinapant to induce necroptosis and
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/339/339ra69/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The caspase-8 inhibitor emricasan combines with the SMAC mimetic birinapant to induce necroptosis and
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Sirt1 Hmg20b Gm (0.17) 24 (17.3) 877 (857)
 3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
Functional screen of MSI2 interactors identifies an essential role for SYNCRIP in myeloid leukemia stem cells
 Functional screen of MSI2 interactors identifies an essential role for SYNCRIP in myeloid leukemia stem cells The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Functional screen of MSI2 interactors identifies an essential role for SYNCRIP in myeloid leukemia stem cells The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
X P. Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Nilotinib LSK LT-HSC. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus
 a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
Hosoya et al. TRIM28 is essential for erythroblast differentiation in the mouse (supplemental information)
 TaqMan assay Gene TRIM28 GATA-1 Applied Biosystems TaqMan assay Mm00495594_m1 Mm01352636_m1 SYBR Green assay Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Reference adult α-globin CCCGGTGCCTTGTCTGCT GTGAAATCGGCAGGGTGG
TaqMan assay Gene TRIM28 GATA-1 Applied Biosystems TaqMan assay Mm00495594_m1 Mm01352636_m1 SYBR Green assay Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Reference adult α-globin CCCGGTGCCTTGTCTGCT GTGAAATCGGCAGGGTGG
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3412
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous
 Cancer Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate Bin Zhang,
Cancer Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate Bin Zhang,
Musashi2 sustains the mixed-lineage leukemia driven stem cell regulatory program
 Musashi2 sustains the mixed-lineage leukemia driven stem cell regulatory program Sun-Mi Park, 1 Mithat Gönen, 2 Ly Vu, 1 Gerard Minuesa, 1 Patrick Tivnan, 1 Trevor S. Barlowe, 1 James Taggart, 1 Yuheng
Musashi2 sustains the mixed-lineage leukemia driven stem cell regulatory program Sun-Mi Park, 1 Mithat Gönen, 2 Ly Vu, 1 Gerard Minuesa, 1 Patrick Tivnan, 1 Trevor S. Barlowe, 1 James Taggart, 1 Yuheng
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Supplemental Information. Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection. Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15
 Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Details of sequencing analysis.
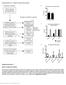 Supplementary Figure 1 Details of sequencing analysis. (a) Flow chart showing which patients fall into each category and were used for analysis. (b) Graph showing the average and median coverage for all
Supplementary Figure 1 Details of sequencing analysis. (a) Flow chart showing which patients fall into each category and were used for analysis. (b) Graph showing the average and median coverage for all
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL 33136, USA, 3 State Key Laboratory
 Supplementary File ASXL1 plays an important role in erythropoiesis Hui Shi 1,2,3, Shohei Yamamoto 1,2,4, Mengyao Sheng 3, Jie Bai 3, Peng Zhang 1,2, Runze Chen 1,2, Shi Chen 1,2, Lihong Shi 3, Omar Abdel-Wahab
Supplementary File ASXL1 plays an important role in erythropoiesis Hui Shi 1,2,3, Shohei Yamamoto 1,2,4, Mengyao Sheng 3, Jie Bai 3, Peng Zhang 1,2, Runze Chen 1,2, Shi Chen 1,2, Lihong Shi 3, Omar Abdel-Wahab
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
AHI-1 interacts with BCR-ABL and modulates BCR-ABL transforming activity and imatinib response of CML stem/progenitor cells
 AHI-1 interacts with BCR-ABL and modulates BCR-ABL transforming activity and imatinib response of CML stem/progenitor cells Liang L. Zhou, 1 Yun Zhao, 1 Ashley Ringrose, 1 Donna DeGeer, 1 Erin Kennah,
AHI-1 interacts with BCR-ABL and modulates BCR-ABL transforming activity and imatinib response of CML stem/progenitor cells Liang L. Zhou, 1 Yun Zhao, 1 Ashley Ringrose, 1 Donna DeGeer, 1 Erin Kennah,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
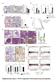 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT) and NQO1-null (NQO1-/-) mice.
 competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
Fasting selectively blocks development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia via leptin-receptor upregulation
 a r t i c l e s Fasting selectively blocks development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia via leptin-receptor upregulation 7 Nature America, Inc., part of Springer Nature. All rights reserved. Zhigang Lu,,
a r t i c l e s Fasting selectively blocks development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia via leptin-receptor upregulation 7 Nature America, Inc., part of Springer Nature. All rights reserved. Zhigang Lu,,
Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma.
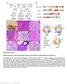 Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Highly Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Long-Term Engraftment of Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
 Highly Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Long-Term Engraftment of Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells J. M. Heath, A. Chalishazar, C.S. Lee, W. Selleck, C. Cotta-Ramusino, D. Bumcrot, J.L.
Highly Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing and Long-Term Engraftment of Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells J. M. Heath, A. Chalishazar, C.S. Lee, W. Selleck, C. Cotta-Ramusino, D. Bumcrot, J.L.
Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 *** Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Pten pc-/- ;Zbtb7a pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Pml pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Trp53 pc-/-
 Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
The U2AF1 S34F mutation induces lineage-specific splicing alterations in myelodysplastic syndromes
 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Journal of Clinical Investigation The U2AF1 S34F mutation induces lineage-specific splicing alterations in myelodysplastic syndromes Bon Ham Yip, 1 Violetta Steeples, 1 Emmanouela
RESEARCH ARTICLE The Journal of Clinical Investigation The U2AF1 S34F mutation induces lineage-specific splicing alterations in myelodysplastic syndromes Bon Ham Yip, 1 Violetta Steeples, 1 Emmanouela
Activation of a PML/TP53 axis underlies acute promyelocytic. leukemia cure
 Activation of a PML/TP53 ais underlies acute promyelocytic leukemia cure Julien Ablain, Kim Rice, Hassane Soilihi, Aurélien de Reynies, Saverio Minucci & Hugues de Thé a PLZF-RARA vs PLZF-RARA pathway
Activation of a PML/TP53 ais underlies acute promyelocytic leukemia cure Julien Ablain, Kim Rice, Hassane Soilihi, Aurélien de Reynies, Saverio Minucci & Hugues de Thé a PLZF-RARA vs PLZF-RARA pathway
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplemental Fig. 1. Relative mrna Expression. Relative mrna Expression WT KO WT KO RT 4 0 C
 Supplemental Fig. 1 A 1.5 1..5 Hdac11 (ibat) n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 WT KO WT KO WT KO WT KO RT 4 C RT 4 C Supplemental Figure 1. Hdac11 mrna is undetectable in KO adipose tissue. Quantitative
Supplemental Fig. 1 A 1.5 1..5 Hdac11 (ibat) n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 n=4 WT KO WT KO WT KO WT KO RT 4 C RT 4 C Supplemental Figure 1. Hdac11 mrna is undetectable in KO adipose tissue. Quantitative
Supplementary Figure 1
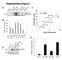 A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
 SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Crystal violet assay Cells were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured in media supplemented with % FBS for 7 days. Media were then removed, plates were briefly washed
SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Crystal violet assay Cells were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured in media supplemented with % FBS for 7 days. Media were then removed, plates were briefly washed
Supplemental Figure 1. Activated splenocytes upregulate Serpina3g and Serpina3f expression.
 Relative Serpin expression 25 2 15 1 5 Serpina3f 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 6 4 2 Serpina3g 1 2 3 4 5 6 C57BL/6 DBA/2 Supplemental Figure 1. Activated splenocytes upregulate Serpina3g and Serpina3f expression. Splenocytes
Relative Serpin expression 25 2 15 1 5 Serpina3f 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 6 4 2 Serpina3g 1 2 3 4 5 6 C57BL/6 DBA/2 Supplemental Figure 1. Activated splenocytes upregulate Serpina3g and Serpina3f expression. Splenocytes
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity
 Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity Mikyoung Chang 1,*, Wei Jin 1,5,*, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Yi-chuan Xiao 1, George Brittain 1, Jiayi Yu 1, Xiaofei Zhou 1, Yi-Hong Wang
Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity Mikyoung Chang 1,*, Wei Jin 1,5,*, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Yi-chuan Xiao 1, George Brittain 1, Jiayi Yu 1, Xiaofei Zhou 1, Yi-Hong Wang
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
The role of DNMT3A and HOXA9 hypomethylation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
 Campbell Drohan BIOL 463 December 2016 The role of DNMT3A and HOXA9 hypomethylation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Introduction Epigenetic modifications of DNA and histones are key to gene regulation
Campbell Drohan BIOL 463 December 2016 The role of DNMT3A and HOXA9 hypomethylation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Introduction Epigenetic modifications of DNA and histones are key to gene regulation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
BCR-ABL - LSK BCR-ABL + LKS - (%)
 Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Molecular Characterization of Leukemia Stem Cell Development. Scott A. Armstrong MD, Ph.D.
 Molecular Characterization of Leukemia Stem Cell Development Scott A. Armstrong MD, Ph.D. Normal and Leukemic Hierarchies NORMAL HSC (SRC) Myeloid progenitor LTC-IC CFU AML LSC (SL-IC) Leukemic LTC-IC
Molecular Characterization of Leukemia Stem Cell Development Scott A. Armstrong MD, Ph.D. Normal and Leukemic Hierarchies NORMAL HSC (SRC) Myeloid progenitor LTC-IC CFU AML LSC (SL-IC) Leukemic LTC-IC
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Downregulation of the c-myc target gene, peroxiredoxin III, contributes to Arsenic Trioxide-induced apoptosis in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL)
 Downregulation of the c-myc target gene, peroxiredoxin III, contributes to Arsenic Trioxide-induced apoptosis in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) Pablo E. Vivas-Mejía, Ph.D. Research Scientist, University
Downregulation of the c-myc target gene, peroxiredoxin III, contributes to Arsenic Trioxide-induced apoptosis in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) Pablo E. Vivas-Mejía, Ph.D. Research Scientist, University
c-myb binds MLL through menin in human leukemia cells and is an important driver of MLL-associated leukemogenesis
 Research article c-myb binds MLL through menin in human leukemia cells and is an important driver of MLL-associated leukemogenesis Shenghao Jin, Huiwu Zhao, Yan Yi, Yuji Nakata, Anna Kalota, and Alan M.
Research article c-myb binds MLL through menin in human leukemia cells and is an important driver of MLL-associated leukemogenesis Shenghao Jin, Huiwu Zhao, Yan Yi, Yuji Nakata, Anna Kalota, and Alan M.
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with
 Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death
 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a.
 pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a. Quantification by RT-qPCR of YFV-17D and YFV-17D pol- (+) RNA in the supernatant of cultured Huh7.5 cells following viral RNA electroporation of respective
pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a. Quantification by RT-qPCR of YFV-17D and YFV-17D pol- (+) RNA in the supernatant of cultured Huh7.5 cells following viral RNA electroporation of respective
Tumor stage : I II III IV. well differentiated. moderately differentiated. adenocarcinoma. normal colon (adjacent to cancer) Log (T/H) SLAP mrna level
 moderately differentiated well differentiated Log (T/H) mrna level a Tumor stage : I II III IV.4.4.8 1.2 1.6 2. 2.4 2.8 3.2 N 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 # patient b normal colon (adjacent
moderately differentiated well differentiated Log (T/H) mrna level a Tumor stage : I II III IV.4.4.8 1.2 1.6 2. 2.4 2.8 3.2 N 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 # patient b normal colon (adjacent
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
