NON- HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
|
|
|
- Louise O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NON- HODGKIN LYMPHOMA non - Hodgkin lymphoma This medical guide is designed for educational purposes to help patients understand. Please consult your doctor on specific questions and details about your symptoms.
2 02 03 NON- HODGKIN LYMPHOMA How does the lymphatic system work? The lymphatic system is part of the immune system. It includes the lymph nodes and related organs that are part of s immune and blood-forming systems, such as the spleen and bone marrow. There are about 600 lymph nodes throughout. 1,2 Lymph nodes: Contents How does the lymphatic system work? What is (NHL)? What causes NHL? What are the symptoms of NHL? How is NHL diagnosed? How is NHL treated? Living with NHL Frequently asked questions Lymph nodes are located throughout Lymph nodes are located throughout Thymus Spleen Bone marrow small, bean-shaped glands throughout carrying fluid (lymph fluid), nutrients, and waste material between tissues and the bloodstream Thymus: an organ that produces a specific type of white blood cells Spleen: an organ found in the upper left part of the abdomen that filters the blood and helps the immune system fight infection Bone marrow: a spongy tissue comprising the center of large bones that contains stem cells that produce blood cells
3 04 05 What is? What causes NHL? Within the lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow are white blood cells called lymphocytes. The exact cause of NHL is unknown. However, NHL is associated with some risk factors including: 1,4 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)* is a type of cancer that occurs when these lymphocytes start growing in an uncontrolled manner to form tumours. 1,2 There are at least 61 different types of NHL, depending on the type of lymphocyte involved, where the tumour is, whether the tumour is fast-growing or slow-growing, and how the tumour affects. 3 1 Age Getting older is a strong risk factor for lymphoma overall, with most cases occurring in people in their 60s or older. Lymphocytes in the lymph node 2 Gender Overall, the risk of NHL is higher in men than in women. Normal cells Cells with damaged DNA 3 Weakened or abnormal immune system If you have a weakened immune system for certain reasons (organ transplants, HIV, genetic syndromes, or immune disorders), your risk of NHL may increase. 4 Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation Exposure to radiation and some chemicals such as weed-and insect-killing substances may be linked with an increased risk of NHL. In normal cells, cell division eventually stops * Also known as non-hodgkin s lymphoma, NHL, or sometimes just lymphoma Cancer cell division 5 Viral or bacterial infections Exposure to certain viruses and bacteria, including the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human herpes virus 8 (HHV-8), may increase the risk of NHL. HIV, Human Immunodeficiency Virus
4 06 07 What are the symptoms of NHL? How is NHL diagnosed? NHL can cause many different signs and symptoms, depending on where it is in. In some cases, it might not cause any symptoms until it grows quite large. 1,2 Confirming the diagnosis may require a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, imaging tests (CT, MRI, and PET scans) and biopsies. 5 Common signs and symptoms include: 1,2 Diagnosis of NHL 5 Swollen lymph nodes Night sweats Shortness of breath Physical exam To check for symptoms and signs of NHL Blood test To check general health and white and red blood cell levels Biopsy: the removal of a small amount of tissue from to examine under a microscope CT (computerized tomography) scan: a type of scan that uses a series of X-rays to build up a 3D picture of inside MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan: a type of scan that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of inside Unexplained weight loss Chest pain or pressure Fever Imaging tests To check the spread of cancer through detailed images of with CT, MRI, or PET scans Biopsy To examine parts of affected lymph nodes or bone marrow samples for cancerous cells PET (positron emission tomography) scan: a type of scan that uses a radioactive drug (tracer) to produce detailed 3D images of
5 08 09 How is NHL treated? The main goal of treatment is to improve your quality of life by helping you become cancer-free. 3 Once you develop symptoms that are severe enough for treatment, your options may include: 7 The form of treatment chosen depends on the type and stage of lymphoma, as well as other factors including your age, prior therapies received, and overall health. 3 Staging of NHL Diaphragm level Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a drug treatment, given orally or by injection, that kills cancer cells. Radiation therapy During radiation therapy, you are positioned on a table and a large machine directs radiation at precise points on your body to kill cancerous cells and shrink tumours. STAGE I STAGE II STAGE III STAGE IV The cancer is found only in a single lymph node or in one organ. The cancer is found in two or more lymph node regions on one side of the diaphragm. The cancer involves lymph nodes both above and below the diaphragm. The cancer is found in several parts of one or more organs or tissues. Biological therapy Stem cell transplant WAIT If your symptoms are mild and thought to be low-grade, starting immediate treatment may not be necessary. In this case, your doctors may decide to wait and see until you develop troublesome symptoms. 6 Biological drugs help your body s immune system fight cancer. For example, a biological drug called rituximab attacks the cancerous cells in so that s immune system can destroy them. After cancer cells are killed with high dose chemotherapy, healthy stem cells (your own or from a donor) are injected into your body, where they can form new healthy blood cells.
6 Living with NHL Frequently Asked Questions A diagnosis of cancer can be overwhelming. At first, you are likely to feel very upset, frightened and confused. 8 When you are having treatment, or when you are recovering, you might not be able to do all the things you used to. But as you begin to feel better it might be helpful to stay positive and active by: 9 planning a healthy, well balanced diet learning relaxation techniques exercising regularly People who are well informed about their illness and treatment are more able to cope with what happens. So, it is very important to get the right information about your type of NHL by frequently communicating with your doctor Can I get another type of cancer after having NHL? 10 Unfortunately, being treated for cancer does not mean you cannot get another cancer. Survivors of NHL have a 15% increased chance of getting new cancers compared to the general population. The risk of getting a second cancer is higher in those who were diagnosed and treated at younger ages (20 years old and younger). 2. Can I lower my risk of NHL progressing or coming back? 11 Currently, there is little evidence to support that specific lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of NHL progressing or coming back. Adopting healthy behaviors such as not smoking, eating well, and staying at a healthy weight may help, but more studies are required in this area. However, we do know that these types of changes can have positive effects on your health that can extend beyond your risk of NHL or other cancers. 3. Will treatment affect my appearance and physical image? 12 Treatments including chemotherapy and radiotherapy can change the way your body looks, works or feels. The effects may vary depending on the treatment, but it is common for patients to experience hair loss, dry skin, rashes, brittle nails during treatment. However, most symptoms will disappear once treatment is completed. Questions
7 NON- HODGKIN LYMPHOMA REFERENCES 1. Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Available at: default/files/file_assets/nhl.pdf 2. American Cancer Society. What is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma? Available at: cancer/non-hodgkin-lymphoma/about/what-is-non-hodgkin-lymphoma.html 3. Lymphoma Research Foundation. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL). Available at: org/site/pp.asp?c=bkltkaoqlmk8e&b= &gclid=cj0keqjwhpngbrdkpy-my9rdutabeiqa- WNcslEXEF2BsyiHBn5qC5FRMo-h6OklA9TRi-4xYgT9OL7saAoee8P8HAQ# 4. American Cancer Society. What Are the Risk Factors for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma? Available at: Accessed March NHS Choices. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Diagnosis. Available at: non-hodgkins-lymphoma/pages/diagnosis.aspx 6. NHS Choices. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment. Available at: non-hodgkins-lymphoma/pages/treatment.aspx 7. Mayo Clinic. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Treatment and drugs. Available at: diseases-conditions/non-hodgkins-lymphoma/basics/treatment/con Cancer Research UK. Coping with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Available at: org/about-cancer/type/non-hodgkins-lymphoma/living/coping-with-non-hodgkins-lymphoma 9. Cancer Research UK. Coping with Cancer- What you can do. Available at: org/about-cancer/coping/practically/what-you-can-do 10. American Cancer Society. Can I Get Another Cancer After Having Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma? Available at: American Cancer Society. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Available at: Macmillan cancer support. What might happen. Available at: Celltrion Healthcare Co., Ltd HCTRU-00 PB-0317/01
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA This medical guide is designed for educational purposes to help patients understand. Please consult your doctor on specific questions and details about your symptoms. 02 03
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA This medical guide is designed for educational purposes to help patients understand. Please consult your doctor on specific questions and details about your symptoms. 02 03
Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Symptoms. Types
 Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells (lymphocytes) of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center
 LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
7.342 Chronic infection and inflammation: What are the consequences on your health? Instructors Eva Frickel and Sara Gredmark
 7.342 Chronic infection and inflammation: What are the consequences on your health? Instructors Eva Frickel and Sara Gredmark How to read a scientific paper Organization of a paper - Title - Authors and
7.342 Chronic infection and inflammation: What are the consequences on your health? Instructors Eva Frickel and Sara Gredmark How to read a scientific paper Organization of a paper - Title - Authors and
What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
 Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Indolent Lymphomas. Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital
 Indolent Lymphomas Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital What does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with
Indolent Lymphomas Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital What does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
GAZYVA: for follicular lymphoma that has not responded to or has returned after treatment
 GAZYVA: for follicular lymphoma that has not responded to or has returned after treatment GAZYVA is a prescription medicine used with the chemotherapy drug, bendamustine, followed by GAZYVA alone for follicular
GAZYVA: for follicular lymphoma that has not responded to or has returned after treatment GAZYVA is a prescription medicine used with the chemotherapy drug, bendamustine, followed by GAZYVA alone for follicular
GPA & MPA GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS &MICROSCOPIC POLYANGIITIS. What you need to know about GPA & MPA
 GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS &MICROSCOPIC POLYANGIITIS GPA & MPA This medical guide is designed for educational purposes to help patients understand GPA & MPA. Please consult your doctor on specific
GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS &MICROSCOPIC POLYANGIITIS GPA & MPA This medical guide is designed for educational purposes to help patients understand GPA & MPA. Please consult your doctor on specific
Tongue cancer. Patient information
 What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This process ensures each part of
What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly way. This process ensures each part of
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect
 Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Lymphatic system component
 Introduction Lymphatic system component Statistics Overview Lymphoma Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Non- Hodgkin's is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. It is estimated to be the sixth most
Introduction Lymphatic system component Statistics Overview Lymphoma Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Non- Hodgkin's is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. It is estimated to be the sixth most
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Esophageal cancer. What is esophageal cancer? Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Cancer of the oropharynx
 Cancer of the oropharynx Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly
Cancer of the oropharynx Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly
Understanding your diagnosis. Dr Graham Collins Consultant Haemtologist Oxford University Hospitals
 Understanding your diagnosis Dr Graham Collins Consultant Haemtologist Oxford University Hospitals Common questions I get asked What is lymphoma? What subtype do I have and what does that mean? What are
Understanding your diagnosis Dr Graham Collins Consultant Haemtologist Oxford University Hospitals Common questions I get asked What is lymphoma? What subtype do I have and what does that mean? What are
guide to living with cancer Brought to you by Alliance Health.
 guide to living with cancer Brought to you by Alliance Health. The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice
guide to living with cancer Brought to you by Alliance Health. The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice
Blood Cancer: Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia
 Published on: 30 May 2017 Blood Cancer: Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells that grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep dividing and growing without
Published on: 30 May 2017 Blood Cancer: Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells that grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep dividing and growing without
GAZYVA for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
 GAZYVA for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) GAZYVA is a prescription medicine used with the chemotherapy drug, chlorambucil, to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in adults who have not had previous
GAZYVA for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) GAZYVA is a prescription medicine used with the chemotherapy drug, chlorambucil, to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in adults who have not had previous
Indolent Lymphomas: Current. Dr. Laurie Sehn
 Indolent Lymphomas: Current Dr. Laurie Sehn Why does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with current standard
Indolent Lymphomas: Current Dr. Laurie Sehn Why does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with current standard
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know www.lymphoma.org.au Lymphoma What You Need to Know Whilst Lymphoma Australia (LA) has made every effort to confirm the accuracy of the information contained herein, it makes
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know www.lymphoma.org.au Lymphoma What You Need to Know Whilst Lymphoma Australia (LA) has made every effort to confirm the accuracy of the information contained herein, it makes
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program. Patient information for. Last revised: November
 Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
Cancer. University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing
 Cancer University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants will be better able to: 1. Develop a basic understanding of cancer 2. Describe
Cancer University of Illinois at Chicago College of Nursing 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants will be better able to: 1. Develop a basic understanding of cancer 2. Describe
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect
 Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Leukemia. There are different types of leukemia and several treatment options for each type.
 Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Breast Cancer. Common kinds of breast cancer are
 Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Gangrene. Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply.
 Gangrene Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply. Gangrene can happen on the surface of the body, such as on the skin. It
Gangrene Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply. Gangrene can happen on the surface of the body, such as on the skin. It
General Information Key Points
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy
 What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer
 Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
Lymphoma FACTSHEET. Summary. About the lymphatic system. Who is at risk for lymphoma? What is lymphoma?
 FACTSHEET Lymphoma Summary Lymphoma is a cancer that affects a part of the immune system called the lymphatic system. Like any cancer, the earlier lymphoma is diagnosed, the easier it is to treat. In general,
FACTSHEET Lymphoma Summary Lymphoma is a cancer that affects a part of the immune system called the lymphatic system. Like any cancer, the earlier lymphoma is diagnosed, the easier it is to treat. In general,
Bone Marrow Transplantation
 Bone Marrow Transplantation Introduction Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside all of your bones, including your hip and thigh bones. The bone marrow is like a factory that makes different types of blood
Bone Marrow Transplantation Introduction Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside all of your bones, including your hip and thigh bones. The bone marrow is like a factory that makes different types of blood
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points The survival rate for many types of cancer has improved in recent years; however, cancer is still the second leading cause of death in the United States (see paragraph
Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points The survival rate for many types of cancer has improved in recent years; however, cancer is still the second leading cause of death in the United States (see paragraph
Hodgkin Disease Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Hodgkin Disease Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Hodgkin Disease Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Care at National Jewish Health. Causes
 Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a chronic disease that can affect any organ in the body, but most commonly affects the lungs. Very small (microscopic) clusters of inflammation or white cells, called granulomas,
Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a chronic disease that can affect any organ in the body, but most commonly affects the lungs. Very small (microscopic) clusters of inflammation or white cells, called granulomas,
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Carries essential nutrients to the cells Collects cellular waste Plays an important role in the immune system of the body Lymph A fluid that
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Carries essential nutrients to the cells Collects cellular waste Plays an important role in the immune system of the body Lymph A fluid that
Safety Systems. The Immune System. The Lymphatic System. lymphocyte fighting bacteria
 Safety Systems There are many things that cause disease. One cause is infection. Microbes are very small living things. Viruses and bacteria are microbes. Some kinds of fungi are microbes, too. Microbes
Safety Systems There are many things that cause disease. One cause is infection. Microbes are very small living things. Viruses and bacteria are microbes. Some kinds of fungi are microbes, too. Microbes
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER
 The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
CAT 13. Coping with cancer. The charity dedicated to helping sick, injured and homeless pets since 1897.
 CAT 13 Coping with cancer The charity dedicated to helping sick, injured and homeless pets since 1897. Coping with cancer As with people, cats commonly get cancer, especially as they get older although
CAT 13 Coping with cancer The charity dedicated to helping sick, injured and homeless pets since 1897. Coping with cancer As with people, cats commonly get cancer, especially as they get older although
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
National Cancer Institute
 National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Hodgkin Lymphoma U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health How Can We Help? You may want information about cancer
National Cancer Institute What You Need To Know About Hodgkin Lymphoma U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health How Can We Help? You may want information about cancer
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
CLL: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA
 CLL: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA MYELOMA Introduction In the U.S. In 2006, about 91,000 people were living with CLL In 2007, more than 15,000 people
CLL: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA MYELOMA Introduction In the U.S. In 2006, about 91,000 people were living with CLL In 2007, more than 15,000 people
EVALUATION. When is a Heart Transplanted?
 EVALUATION When is a Heart Transplanted? The heart is a pump. Its only job is to move blood into the lungs and throughout the body. This movement of blood is essential to supply the body tissue with nutrients
EVALUATION When is a Heart Transplanted? The heart is a pump. Its only job is to move blood into the lungs and throughout the body. This movement of blood is essential to supply the body tissue with nutrients
The exact cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. However, gender, race, and genetics can increase the risk of developing the condition:
 What is sarcoidosis? Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease in which granulomas, or clumps of inflammatory cells, form in various organs. This causes organ inflammation. Sarcoidosis may be triggered by
What is sarcoidosis? Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease in which granulomas, or clumps of inflammatory cells, form in various organs. This causes organ inflammation. Sarcoidosis may be triggered by
Diagnosed with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer?
 ESSENTIALS Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Diagnosed with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer? It can be frightening to learn you or a loved one has been diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer. It is important
ESSENTIALS Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Diagnosed with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer? It can be frightening to learn you or a loved one has been diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer. It is important
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
 Page 1 of 10 PATIENT EDUCATION Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Introduction Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer of the lymphocytes (a kind of white blood cell). It is also referred
Page 1 of 10 PATIENT EDUCATION Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Introduction Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer of the lymphocytes (a kind of white blood cell). It is also referred
What is Thyroid Cancer?
 Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
HODGKIN DISEASE. What is cancer?
 HODGKIN DISEASE What is cancer? Cancer develops when cells in a part of the body begin to grow out of control. Although there are many kinds of cancer, they all start because of out-of-control growth of
HODGKIN DISEASE What is cancer? Cancer develops when cells in a part of the body begin to grow out of control. Although there are many kinds of cancer, they all start because of out-of-control growth of
Wilms' tumor most often occurs in just one kidney, though it can sometimes be found in both kidneys at the same time.
 Wilms' Tumor Wilms' tumor is a rare kidney cancer that primarily affects children. Also known as nephroblastoma, Wilms' tumor is the most common cancer of the kidneys in children. Wilms' tumor most often
Wilms' Tumor Wilms' tumor is a rare kidney cancer that primarily affects children. Also known as nephroblastoma, Wilms' tumor is the most common cancer of the kidneys in children. Wilms' tumor most often
Lymphoma. What is cancer? What are signs that my cat has lymphoma. How is Lymphoma diagnosed?
 What is cancer? Lymphoma Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of a small population of abnormal cells. These abnormal cells form by a mutation during the normal division cycle and are able to escape detection
What is cancer? Lymphoma Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of a small population of abnormal cells. These abnormal cells form by a mutation during the normal division cycle and are able to escape detection
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Types
 Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Types Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Types Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1
 GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1 S16-1661-01A Pre-release Article for Examination in May 2016 1661 01A001 CJ*(S16-1661-01A) 2 Information for Teachers The pre-release article is intended
GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1 S16-1661-01A Pre-release Article for Examination in May 2016 1661 01A001 CJ*(S16-1661-01A) 2 Information for Teachers The pre-release article is intended
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Cancer 101 Spring Family Cancer Retreat 4/18/15. Amish Shah, M.D. New Mexico Cancer Center
 Cancer 101 Spring Family Cancer Retreat 4/18/15 Amish Shah, M.D. New Mexico Cancer Center Topics to cover What is Cancer? Screening Diagnosis/Staging Treatment Basics Clinical Trials Surveillance What
Cancer 101 Spring Family Cancer Retreat 4/18/15 Amish Shah, M.D. New Mexico Cancer Center Topics to cover What is Cancer? Screening Diagnosis/Staging Treatment Basics Clinical Trials Surveillance What
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated.
 How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
Anemia: A condition in which the number of red blood cells is below normal.
 Veterinary Teaching Hospital Oncology Service Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine 245 Duck Pond Drive Blacksburg, VA 24061 Phone: 540-231-4621 Definitions This fact sheet is based
Veterinary Teaching Hospital Oncology Service Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine 245 Duck Pond Drive Blacksburg, VA 24061 Phone: 540-231-4621 Definitions This fact sheet is based
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
CELL AGING. Process of getting older. Losing hair, wrinkled skin Fingernails- the new cells push out the old cells
 CELL AGING & CANCER CELL AGING What is aging? Process of getting older. Losing hair, wrinkled skin Fingernails- the new cells push out the old cells As a person ages, mitosis slows down CELL AGING COMPARISON
CELL AGING & CANCER CELL AGING What is aging? Process of getting older. Losing hair, wrinkled skin Fingernails- the new cells push out the old cells As a person ages, mitosis slows down CELL AGING COMPARISON
Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) with Drug-Eluting Beads
 Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) with Drug-Eluting Beads A minimally invasive treatment for liver cancer Provided as an educational service by Biocompatibles UK Ltd, a BTG International group company
Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) with Drug-Eluting Beads A minimally invasive treatment for liver cancer Provided as an educational service by Biocompatibles UK Ltd, a BTG International group company
DOG 13. Coping with cancer. The charity dedicated to helping sick, injured and homeless pets since 1897.
 DOG 13 Coping with cancer The charity dedicated to helping sick, injured and homeless pets since 1897. Coping with cancer As with people, dogs often get cancer, especially as they get older. By far the
DOG 13 Coping with cancer The charity dedicated to helping sick, injured and homeless pets since 1897. Coping with cancer As with people, dogs often get cancer, especially as they get older. By far the
 Page 1 of 9 Title Authored By Course No Contact Hours 2 ABCs of Lymphoma Anita Rothera RNC, BS, CDE LYM020108 Purpose The goal of this course is to help health care professionals learn about the different
Page 1 of 9 Title Authored By Course No Contact Hours 2 ABCs of Lymphoma Anita Rothera RNC, BS, CDE LYM020108 Purpose The goal of this course is to help health care professionals learn about the different
Scrub In. Lymphocytes are a type of what?
 Scrub In Lymphocytes are a type of what? a. WBC s b. RBC s c. Thrombocytes d. Plasma The nurse received an injection for immediate immunity following exposure to a patient with an infectious disease. What
Scrub In Lymphocytes are a type of what? a. WBC s b. RBC s c. Thrombocytes d. Plasma The nurse received an injection for immediate immunity following exposure to a patient with an infectious disease. What
The Lymphatic System
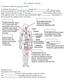 The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three main functions: It maintains the balance of between the and, known as fluid homeostasis. It forms part of the body's system and helps defend against
The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three main functions: It maintains the balance of between the and, known as fluid homeostasis. It forms part of the body's system and helps defend against
DEFINITION. Breast cancer is cancer that forms in the. more common in women.
 BREAST CANCER DEFINITION Breast cancer is cancer that forms in the cells of the breasts. Breast cancer can occur in both men and women, but it's far more common in women. Normal Breast Tissue DEFINITION
BREAST CANCER DEFINITION Breast cancer is cancer that forms in the cells of the breasts. Breast cancer can occur in both men and women, but it's far more common in women. Normal Breast Tissue DEFINITION
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
Lymph Node Enlargement in Dogs & Cats A Swelling Not to Be Ignored!
 Lymph Node Enlargement in Dogs & Cats A Swelling Not to Be Ignored! A common clinical scenario I encounter is a pet referred to me for evaluation of enlarged lymph nodes. Parents may incidentally discover
Lymph Node Enlargement in Dogs & Cats A Swelling Not to Be Ignored! A common clinical scenario I encounter is a pet referred to me for evaluation of enlarged lymph nodes. Parents may incidentally discover
Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma
 Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Follicular lymphoma Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Small lymphocytic lymphoma Mantle cell lymphoma Marginal zone lymphomas Cutaneous (skin)
Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Follicular lymphoma Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Small lymphocytic lymphoma Mantle cell lymphoma Marginal zone lymphomas Cutaneous (skin)
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
Cancer. Chapter 31 Lesson 2
 Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
COMENIUS-Project: SM&CLIL Radiation & Medicine
 Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma
 Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma small lymphocytic lymphoma nodal marginal zone CLL Waldenström s macroglobulinaemia marginal zone gastric MALT chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma Low-grade non-hodgkin lymphoma small lymphocytic lymphoma nodal marginal zone CLL Waldenström s macroglobulinaemia marginal zone gastric MALT chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Blood and the Lymphatic System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Blood and the Lymphatic System
 Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
Aggressive Lymphomas - Current. Dr Kevin Imrie Physician-in-Chief, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre
 Aggressive Lymphomas - Current Dr Kevin Imrie Physician-in-Chief, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Conflicts of interest I have no conflicts of interest to declare Outline What does aggressive lymphoma
Aggressive Lymphomas - Current Dr Kevin Imrie Physician-in-Chief, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Conflicts of interest I have no conflicts of interest to declare Outline What does aggressive lymphoma
Information. about cancer
 1 Information about cancer This chapter may help you answer simple questions about what cancer is and how it is treated. There are more than 200 different types of cancer and a range of treatments. Being
1 Information about cancer This chapter may help you answer simple questions about what cancer is and how it is treated. There are more than 200 different types of cancer and a range of treatments. Being
EVALUATION & LISTING. Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation. What is the Liver?
 EVALUATION & LISTING Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation The University of Michigan is a national leader in liver transplantation, as well as the surgical and medical management of patients with liver
EVALUATION & LISTING Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation The University of Michigan is a national leader in liver transplantation, as well as the surgical and medical management of patients with liver
All about Leukaemia. An Easy Read Document
 All about Leukaemia An Easy Read Document What is in this booklet About this booklet and leukaemia Page 4 How are blood cells made Page 5 Different types of leukaemia Page 9 Things that might mean you
All about Leukaemia An Easy Read Document What is in this booklet About this booklet and leukaemia Page 4 How are blood cells made Page 5 Different types of leukaemia Page 9 Things that might mean you
How is primary breast cancer treated?
 How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
Non- Hodgkin Handbook
 Non- Hodgkin Handbook Everything you need to know to create a more confident cancer journey. Brought to you by PearlPoint Cancer Support Download at MyPearlPoint.org 2014 PearlPoint Cancer Support. All
Non- Hodgkin Handbook Everything you need to know to create a more confident cancer journey. Brought to you by PearlPoint Cancer Support Download at MyPearlPoint.org 2014 PearlPoint Cancer Support. All
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung.
 Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
Different Types of Cancer
 Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
What Does HIV Do to You?
 What Does HIV Do to You? HIV and the immune system Your immune system is supposed to protect you from viruses and other infections. Why, then, doesn t it protect you from HIV? The answer is complicated,
What Does HIV Do to You? HIV and the immune system Your immune system is supposed to protect you from viruses and other infections. Why, then, doesn t it protect you from HIV? The answer is complicated,
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer
 Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY. Learn more at
 PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Ask your doctor about screening and treatment options. WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? 4 WATCHFUL
PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Ask your doctor about screening and treatment options. WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? 4 WATCHFUL
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 LECTURE #4 1 LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 2 CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY T-lymphocytes (activated in the thymus) identify aggressors and try to destroy them through the production of lymphokines (synthesized proteins) Killer
LECTURE #4 1 LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 2 CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY T-lymphocytes (activated in the thymus) identify aggressors and try to destroy them through the production of lymphokines (synthesized proteins) Killer
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer
 Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream (fluid balance) Immunity. Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
 Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
