Definition gastritis
|
|
|
- Louisa Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gastritis
2 Definition The term gastritis is used to denote inflammation associated with mucosal injury Gastritis is mostly a histological term that needs biopsy to be confirmed Gastritis is usually due to infectious agents (such as Helicobacter pylori) and autoimmune and hypersensitivity reactions.
3 Definition Epithelial cell damage and regeneration without associated inflammation is properly referred to as "gastropathy. Gastropathy may be referred without histological evidence and just according to gross appearance in endoscopy or radiology Gastropathy is usually caused by irritants such as drugs (eg, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents and alcohol), bile reflux, hypovolemia, and chronic congestion.
4 Gross histologic correlation?
5 Research evidence Among 98 patients with endoscopic mucosal changes attributed to gastritis, 27 percent had a normal endoscopic biopsy specimen; i.e. PPV of 73 percent or at least 1 in four false positive diagnosis
6 Research evidence among 69 patients with a normal endoscopic appearance, 63 percent had histological evidence of gastritis. NPV equals to 27 percent
7 Classification Acute vs. chronic Acute refers to short term inflammation Acute refering to neurophilic infiltrate Chronic referring to long standing forms Chronic referring to mononuclear cell infiltrate especially lymphocyte and maccrophages
8 Anatomical site CARDIA MUCOUS SECRETING ENDOCRINE BODY ANTRUM SPECIALISED SECRETORY PARIETAL - ACID CHIEF - PEPSINOGEN ENDOCRINE HIST, SOMASTATIN MUCOUS SECRETING ENDOCRINE GASTRIN, 5HT
9
10 Non HP gastritis (ICD10) 1. Chemical gastritis (acute chronic) Alcoholic gastritis Drug induced gastritis (e.g., NSAID) Reflux ( due to duodenal juice or bile) gastritis Other chemical gastritis 2. Radiation gastritis 3. Allergic gastritis 4. Autoimmune gastritis 5. Special forms of gastritis 6. Gastritis NOS 7. Duodenitis
11 CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS ACUTE COMMON CHRONIC STRESS BILE HP EMAG NSAID AMAG
12 CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS ACUTE COMMON CHRONIC STRESS BILE HP EMAG NSAID AMAG
13 Acute hemorrhagic erosive hemorrhagic and erosive lesions shortly after exposure of the gastric mucosa to various injurious substances or a substantial reduction in mucosal blood flow
14 ACUTE GASTRITIS - MORPHOLOGY Mucosal congestion, oedema, inflammation & ulceration
15 Acute hemorrhagic erosive nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAIDs], alcohol, or bile acids) or to mucosal hypoxia (such as in trauma, burns [Curling's ulcers] or sepsis) or to a combination of factors such as with antineoplastic chemotherapy Gastric and duodenal ulceroinflammatory ulcers occurring during severe damage to the central nervous system (Cushing's ulcers) are often considered in this group
16 Acute hemorrhagic erosive Gastric and duodenal ulceroinflammatory ulcers occurring during severe damage to the central nervous system (Cushing's ulcers) are often considered in this group
17 Acute hemorrhagic erosive specific pathogenetic factor in NSAID-induced acute hemorrhagic and erosive gastropathy is the inhibition of prostaglandin production. Prostaglandins, especially those of the E class, protect against acute mucosal injury due to NSAIDs and other injurious substances by several mechanisms, including the stimulation of mucus and bicarbonate secretion, and maintenance of mucosal blood flow
18 NSAID GI toxicity risk factor Prior history of an adverse GI event (ulcer, hemorrhage) increases risk four to fivefold Age >60 increases risk five to sixfold High (more than twice normal) dosage of a NSAID increases risk 10-fold Concurrent use of glucocorticoids increases risk four to fivefold Concurrent use of anticoagulants increases risk 10- to 15-fold
19 HP and NSAID Patients with a history of uncomplicated or complicated peptic ulcers (gastric, duodenal) should be tested for H. pylori prior to beginning a NSAID or low dose aspirin. If present, H. pylori should be treated with appropriate therapy, even if it is believed that the prior ulcer was due to NSAIDs
20 Acute hemorrhagic erosive Hemorrhagic or erosive gastropathy may be associated with the development of gastric or duodenal ulcers. Acute ulceration is most likely to occur in relation to shock-induced hemodynamic instability (ie, the stress ulcer syndrome).
21 NSAID prophylaxis For patients who are at high risk for NSAID-related gastroduodenal toxicity, primary therapy with a COX-2 selective inhibitor such as rofecoxib is a reasonable option.
22 NSAID prophylaxis For high-risk patients taking nonselective NSAIDs, misoprostol (at a dose of 200 µg four times daily) and lansoprazole (15 or 30 mg daily) have received FDA approval for prophylaxis against NSAID-induced ulcer disease and its complications.
23 Stress ulcer pathophysiology Hypersecretion of acid head trauma. Defects in gastric glycoprotein mucus In critically ill patients, increased concentrations of refluxed bile salts or the presence of uremic toxins can denude the glycoprotein mucous barrier Ischemia Shock, sepsis, and trauma can lead to impaired perfusion of the gut.
24 Stress ulcer risk factors Risk factors two major risk factors for clinically significant bleeding due to stress ulcers are: mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours (odds ratio 15.6); and coagulopathy (odds ratio 4.3). The risk of clinically important bleeding in patients without either of these risk factors was only 0.1 percent.
25 Stress ulcer risk factors Shock Sepsis Hepatic failure Renal failure Multiple trauma Burns over 35 percent of total body surface area Organ transplant recipients Head or spinal trauma Prior history of peptic ulcer disease or upper GI bleeding
26 Common type of gastritides
27 CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS ACUTE COMMON CHRONIC STRESS BILE HP EMAG NSAID AMAG
28 Helicobacter pylori is a spiral shaped, microaerophilic, gram negative bacterium measuring approximately 3.5 microns in length and 0.5 microns in width
29 urease forms ammonia and bicarbonate that neutralize gastric acid and form a protective cloud around the organism
30 Urease appears to be vital for its survival and colonization; it is produced in abundance, making up more than 5 percent of the organism's total protein weight.
31 spiral shape, flagella facilitate its passage through the mucus layer
32 H. pylori then attaches to gastric epithelial cells by means of specific receptor-mediate d adhesion
33 Helicobacter pylori is the most common chronic bacterial infection in humans ;50 percent of the world's population is affected.
34 Therefore, the frequency of H. pylori infection for any age group in any locality reflects that particular cohort's rate of bacterial acquisition during childhood years
35 Factors such as density of housing, overcrowding, number of siblings, sharing a bed, and lack of running water have all been linked to a higher acquisition of H. pylori infection
36 The route by which infection occurs remains unknown Person-to-person transmission of H. pylori through either fecal/oral or oral/oral exposure seems most likely
37 Humans appear to be the major reservoir of infection; however, bacteria have been isolated from primates in and from domestic cats and in milk and gastric tissue of sheep
38 Non GI associated disorders Coronary heart disease Rosacea Iron deficiency Anorexia in aging
39 Platelet aggregation mediated by an H. pylori interaction with von Willebrand factor is speculated to contribute to infection related ulcer disease but also possibly non-gi manifestations of infection such as cardiovascular disease and idiopathic thrombocytopenia
40 A B cell response to H. pylori (with production of IgG and IgA antibodies) occurs locally in the gastroduodenal mucosa and systemically. The role of local antibodies in producing tissue injury or modulating inflammation in H. pylori infection remains controversial.prolonged stimulation of gastric B cells by activated T cells can lead to MALT lymphoma in rare cases
41 Vac A & Cag A vacuolating cytotoxin (VacA) which causes cell injury in vitro and gastric tissue damage in vivo. All H. pylori contain the gene coding for VacA; however, only those strains with the cytotoxin-associated gene A (caga) Strains producing VacA and CagA cause more intense tissue inflammation and induce cytokine production
42 Approximately 85 to 100 percent of patients with duodenal ulcers have CagA+ strains, compared to 30 to 60 percent of infected patients who do not develop ulcers CagA strains may be associated with a higher frequency of precancerous lesions.
43 Host polymorphism of IL-1 beta (and possibly IL-10) appears to determine the degree of inflammatory response to infection, resulting alteration in acid secretion (hyper or hypo secretion), and risk for subsequent gastric cancer
44 IgA antibodies may modulate mucosal injury by inhibiting antigen uptake, disrupting bacterial adherence and motility, and neutralizing various toxins. IgG presumably augments inflammatory injury by activating complement and facilitating neutrophil activation.
45 Bile reflux gastropathy Bile reflux gastropathy typically results from the regurgitation of bile into the stomach because of an operative stoma, an incompetent pyloric sphincter, or abnormal duodenal motility
46 Bile reflux gastropathy The effect of bile salts on gastric mucosa is comparable to that seen after chronic NSAID use
47 Chronic metaplastic gastritides
48 CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS ACUTE COMMON CHRONIC STRESS BILE HP EMAG NSAID AMAG
49 metaplastic atrophic gastritis Metaplasia, especially of the intestinal type, is virtually a universal feature of atrophic gastritis and is often the most dependable defining morphologic feature. Metaplasia is highly relevant to the pathogenesis of atrophic gastritis and to its complications (eg, pernicious anemia, gastric ulcer, and gastric cancer).
50 metaplastic atrophic gastritis The term metaplastic atrophic gastritis makes a sharp distinction between metaplastic and nonmetaplastic forms of gastric atrophy, especially the atrophic change (gastrinopenic type) often noted in the oxyntic mucosa (ie, mucosa of the body and fundus), which remains in place after antrectomy for peptic ulcer.
51 metaplastic atrophic gastritis Endoscopic surveillance in patients from developed countries who do not have dysplasia is probably unnecessary
52 metaplastic atrophic gastritis AUTOIMMUNE METAPLASTIC ATROPHIC GASTRITIS (AMAG) is an inherited form that is associated with an immune response in the oxyntic mucosa directed against parietal cells and intrinsic factor. AMAG is inherited as an autosomal dominant disorder
53 SYNONYMS OF AMAG TYPE A GASTRITIS AUTOIMMUNE GASTRITIS DIFFUSE CORPORAL GASTRITIS
54 metaplastic atrophic gastritis The chronic inflammation, gland atrophy, and epithelial metaplasia of AMAG are closely paralleled by elevated serum antibodies to parietal cells and to intrinsic factor, reflecting its autoimmune origin.
55
56 metaplastic atrophic gastritis The loss of parietal cell mass leads to profound hypochlorhydria, while the inadequate production of intrinsic factor leads to vitamin B12 malabsorption and pernicious anemia.
57 metaplastic atrophic gastritis Patients with AMAG are at increased risk for the development of gastric carcinoid tumors and adenocarcinoma. CANCE R
58 metaplastic atrophic gastritis surveillance strategy for patients diagnosed with pernicious anemia Upper endoscopy soon after diagnosis Removal of gastric polyps if possible; most of these polyps will be benign Frequent reinvestigation in patients whose polyps are not removed or who have severe mucosal dysplasia; in the remaining patients follow-up endoscopies should be performed at approximately five-year intervals.
59 metaplastic atrophic gastritis Patients with AMAG are less likely to be infected by H. pylori than aged-matched controls. Two possible explanations are that the metaplastic epithelium is unsuitable for H. pylori colonization, and that the associated hypochlorhydria encourages overgrowth by other bacterial species
60 metaplastic atrophic gastritis Environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritis (EMAG) is due to environmental factors, such as diet and H. pylori infection, on the gastric mucosa.
61 metaplastic atrophic gastritis Unlike AMAG, mucosal changes in patients with EMAG affect both the corpus and antrum in a multifocal distribution, but with heaviest involvement of the antrum.
62 metaplastic atrophic gastritis EMAG vs AMAG Gastric acid production does not disappear entirely Serum gastrin is not elevated Parietal cell and intrinsic factor autoantibodies and pernicious anemia are absent
63 metaplastic atrophic gastritis There is an increased risk for gastric ulcer compared to AMAG, presumably due to the accompanying hypochlorhydria the latter disorder CANCE R
64 metaplastic atrophic gastritis diagnosis of EMAG should not be made from biopsy specimens unless at least 20 percent of the available antral or transitional mucosa is replaced by metaplastic glands, or there is unequivocal atrophy.
65 metaplastic atrophic gastritis Possible exceptions are nitroso compounds, which may be important in EMAG and in the development of gastric cancer. Nitroso compounds, which are known carcinogens, are generated in the gastric lumen by bacterial metabolism of nitrates.
66 metaplastic atrophic gastritis chronic infection cell injury/ inflammation susceptibility to mutagenic factors.
67 Hyperplastic gastropathies proliferative, inflammatory, and infiltrative conditions are associated with large folds due to excessive number of mucosal epithelial cells
68 Ménétrier's disease Epithelial hyperplasia involving the surface and foveolar mucous cells (ie, foveolar hyperplasia); the oxyntic glands can be normal or atrophic.
69 Zollinger-Ellison syndrome Increased numbers of parietal cells with no change in surface and foveolar mucous cells.
70 Hyperplastic gastropathies mixed-type in which both mucous and oxyntic glandular cells show hyperplasia, may be seen in as lymphocytic and H. pylori gastritis.
71 Large gastric folds > 1.0 cm Chronic gastritis/lymphoid hyperplasia 40 Benign tumors 16 Gastric malignancy 12 Zollinger-Ellison syndrome 10 Menetrier's disease 8
72 Ménétrier's Epigastric pain 65 percent Asthenia 60 percent Anorexia 45 percent Weight loss 45 percent Edema 38 percent Vomiting 38 percent 80 percent of patients had hypoalbuminemia
73 Ménétrier's Surgery has been advocated for patients with intractable pain, hypoalbuminemia with edema, hemorrhage, pyloric obstruction, and for those in whom a malignancy cannot be excluded
74 Ménétrier's Gastric atrophy?> Gastric cancer?>
75 Zollinger-Ellison syndrome 0.1 to 1 percent of patients with peptic ulcer disease. Underestimation! symptoms similar to typical peptic ulcer. symptoms may be controlled by standard doses of an antisecretory drug patients may not be tested for hypergastrinemia
76 ZES Most patients are diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50. The male to female ratio ranges between to 2:1.
77 ZES Gastrinomas can be either sporadic (80 percent) or associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
78 Diarrhea in ZES The high rate of acid volume load that cannot be absorbed by the intestine The excess acid exceeds the neutralizing capacity of pancreatic bicarbonate. The exceptionally low ph of the intestinal contents inactivates pancreatic digestive enzymes, interferes with the emulsification of fat by bile acids, and damages intestinal epithelial cells and villi. The extremely high serum gastrin concentrations may inhibit absorption of sodium and water by the small intestine,
79 Signs of ZES Multiple ulcers diarrhea ulcer in atypical site resistant ulcer enlarged folds severe esophagirtis FH of MEN1
80 Exclude hpoacidity! ZES diagnosis Check gastrin, if >1000=ZES. <1000 but abnormal secretin test to be performed,+200 pg/ml is ZES
81 Localization of gastrinoma SPECT imaging with pentetreotide should be the first test because of its high sensitivity for both primary tumors and hepatic metastases If no tumor or metastases are found but clinical suspicion remains high, endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) or dual phase helical CT scan should be performed.
82 ZES treatment Omeprazole effectively controlled acid output in all patients. No patients experienced tachyphylaxis, and no hematologic, metabolic, or gastric toxicity was noted.
83 ZES treatment any patient with a sporadic gastrinoma and without evidence of metastatic spread of disease should be offered exploratory laparotomy with curative intent
84 ZES treatment laparotomy is not routinely recommended for patients with ZES as part of MEN 1 since the multifocal nature of the tumors in this disorder almost uniformly precludes cure of gastrin hypersecretion
85 Portal hypertensive gastropathy Portal hypertensive gastropathy characteristically appears as a fine white reticular pattern separating areas of pinkish mucosa on endoscopy, giving the gastric mucosa a "snakeskin" appearance
86 Portal hypertensive gastropathy
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
The surface mucous cells and the cardiac and pyloric glands secrete mucus which protects the stomach from self-digestion.
 PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
PATHOLOGY OF THE STOMACH Stomach mucosa Gastric mucosa is covered by a layer of mucus. The mucosal glands comprise the cardiac glands, the fundic glands in the fundus and body of the stomach, and the pyloric
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Disease of the Stomach
 Disease of the Stomach Jack Bragg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I. Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Missouri School of Medicine Columbia, Missouri I have no disclosures
Disease of the Stomach Jack Bragg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I. Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Missouri School of Medicine Columbia, Missouri I have no disclosures
Peptic ulcer disease. Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531
 Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Pathogenesis Most individuals with the infection also have the associated gastritis but are asymptomatic
 STOMACH Chronic Gastritis The presence of chronic inflammatory changes in the mucosa leading eventually to mucosal atrophy and epithelial metaplasia. In the Western world the prevalence of chronic gastritis
STOMACH Chronic Gastritis The presence of chronic inflammatory changes in the mucosa leading eventually to mucosal atrophy and epithelial metaplasia. In the Western world the prevalence of chronic gastritis
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen
 Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
 PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs Prof. Sheila Crowe
 Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------
 A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------ The pain can be relieved by food or antiacids------ He denies taking aspirin or NSAID------ Lab
A 35 yr old man presents with a month history of burning epigastric pain that occurs between meals------ The pain can be relieved by food or antiacids------ He denies taking aspirin or NSAID------ Lab
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic Ulcer Disease & Gastritis Michel-Jose Charles, MD
 Peptic Ulcer Disease & Gastritis Michel-Jose Charles, MD Internal Medicine Gastroenterology Board Certified Assistant Professor 2016 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Gastritis Michel-Jose Charles, MD Gastroenterology
Peptic Ulcer Disease & Gastritis Michel-Jose Charles, MD Internal Medicine Gastroenterology Board Certified Assistant Professor 2016 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Gastritis Michel-Jose Charles, MD Gastroenterology
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
Stomach. R.B. Kolachalam, MD
 Stomach R.B. Kolachalam, MD Relevent Anatomy 1.four regions: Cardia, Fundus, Body, and the Pylorus 2. fixed in two locations- at the GEJ and the duodenum Gastric Anatomy body of the stomach: site of mechanical
Stomach R.B. Kolachalam, MD Relevent Anatomy 1.four regions: Cardia, Fundus, Body, and the Pylorus 2. fixed in two locations- at the GEJ and the duodenum Gastric Anatomy body of the stomach: site of mechanical
Disorders of the Stomach
 CHAPTER 29 Disorders of Gastrointestinal Function 705 protrusion of the stomach above the diaphragm, and the paraesophageal hernia, in which a portion of the stomach enters the thorax through a widened
CHAPTER 29 Disorders of Gastrointestinal Function 705 protrusion of the stomach above the diaphragm, and the paraesophageal hernia, in which a portion of the stomach enters the thorax through a widened
2nd week. preexam. GIT system. Atyaf group. Qs team
 2nd week preexam GIT system Qs team 2nd week 2009 Atyaf group بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم 1) a patient with autoimmune gastritis. He is not likely to develop: A. H.pylori colonization. B. pernicious anemia.
2nd week preexam GIT system Qs team 2nd week 2009 Atyaf group بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم 1) a patient with autoimmune gastritis. He is not likely to develop: A. H.pylori colonization. B. pernicious anemia.
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Helicobacter Pylori Testing HELICOBACTER PYLORI TESTING HS-131. Policy Number: HS-131. Original Effective Date: 9/17/2009
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Gastritis General standpoints
 Gastritis General standpoints Histologically documented inflammation ~60% in mucosal biopsy specimens. Heterogeneous etiology. More than 100 classification system. Classified based on time course (acute
Gastritis General standpoints Histologically documented inflammation ~60% in mucosal biopsy specimens. Heterogeneous etiology. More than 100 classification system. Classified based on time course (acute
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
HELICOBACTER PYLORI UPDATE
 HELICOBACTER PYLORI UPDATE PROF. TAWHEED MOWAFY DEAN OF AZAL FACULTY OF MEDICINE INTRODUCTION (H. pylori) is recognised as the most common chronic human bacterial infection,1 affecting up to 50% of the
HELICOBACTER PYLORI UPDATE PROF. TAWHEED MOWAFY DEAN OF AZAL FACULTY OF MEDICINE INTRODUCTION (H. pylori) is recognised as the most common chronic human bacterial infection,1 affecting up to 50% of the
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005
 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
AN ARGUMENT FOR SURGERY FOR GASTRINOMA. Lauren Wilson R1 General Surgery
 AN ARGUMENT FOR SURGERY FOR GASTRINOMA Lauren Wilson R1 General Surgery WHAT IS A GASTRINOMA? Gastrin secreting cells derived from multipotential stem cells of endodermal origin or enteroendocrine cells
AN ARGUMENT FOR SURGERY FOR GASTRINOMA Lauren Wilson R1 General Surgery WHAT IS A GASTRINOMA? Gastrin secreting cells derived from multipotential stem cells of endodermal origin or enteroendocrine cells
GI Pharmacology. Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018
 GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications
 594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
594 Lewin, Weinstein, and Riddell s Gastrointestinal Pathology and Its Clinical Implications Figure 13-20. Stages in the natural history of H. pylori. Biopsies from the antrum are on the left and the oxyntic
Gastrointestinal pathology 1. Upper GI tract
 Gastrointestinal pathology 1. Upper GI tract Tumors of The Salivary Glands Benign Malignant Pleomorphic adenoma (50%) Mucoepidermoid cc (15%) Warthin tumor (5%) Adenocarcinoma NOS (6%) Oncocytoma (2%)
Gastrointestinal pathology 1. Upper GI tract Tumors of The Salivary Glands Benign Malignant Pleomorphic adenoma (50%) Mucoepidermoid cc (15%) Warthin tumor (5%) Adenocarcinoma NOS (6%) Oncocytoma (2%)
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus. Barbora Konečná
 Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
The usual dose is 40 mg daily with amoxycillin 1.5 g (750 mg b.d.) for 2 weeks. Up to 2 g/day of amoxycillin has been used in clinical trials.
 Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Unexpected Findings at Endoscopy
 The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
Gastritis from NSAIDS to Helicobacter pylori
 Abdominal Imaging ª Springer Science+Business Media, Inc. 2004 Published online: 30 December 2004 Abdom Imaging (2005) 30:142 159 DOI: 10.1007/s00261-004-0210-7 Gastritis from NSAIDS to Helicobacter pylori
Abdominal Imaging ª Springer Science+Business Media, Inc. 2004 Published online: 30 December 2004 Abdom Imaging (2005) 30:142 159 DOI: 10.1007/s00261-004-0210-7 Gastritis from NSAIDS to Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter 2008;13:1-6. Am J Gastroent 2007;102: Am J of Med 2004;117:31-35.
 An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
Review article: potential gastrointestinal effects of long-term acid suppression with proton pump inhibitors
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: 651±668. Review article: potential gastrointestinal effects of long-term acid suppression with proton pump inhibitors L. LAINE*, D. AHNEN, C.MCCLAINà, E.SOLCIA &J.H.WALSH±
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: 651±668. Review article: potential gastrointestinal effects of long-term acid suppression with proton pump inhibitors L. LAINE*, D. AHNEN, C.MCCLAINà, E.SOLCIA &J.H.WALSH±
GI update. Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about
 GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
Understandings, Applications & Skills
 D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
D.2 Digestion Understandings, Applications & Skills Statement D.2.U1 Nervous and hormonal mechanisms control the secretion of digestive juices. D.2.U2 Exocrine glands secrete to the surface of the body
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
Gastric Polyps. Bible class
 Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
 Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES)? ZES
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES)? ZES
Safety Of. long-term PPI. Layli Eslami, MD Tehran, 1393
 Safety Of long-term PPI Layli Eslami, MD Tehran, 1393 n The introduction of PPIs in the late 1980s optimized the medical treatment of acidrelated disorders n In some cases such as GERD patients given the
Safety Of long-term PPI Layli Eslami, MD Tehran, 1393 n The introduction of PPIs in the late 1980s optimized the medical treatment of acidrelated disorders n In some cases such as GERD patients given the
Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy
 Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE JOHN R SALTZMAN, MD. Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School
 PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE JOHN R SALTZMAN, MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School No disclosures Disclosures Overview Causes of peptic ulcer disease
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE JOHN R SALTZMAN, MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School No disclosures Disclosures Overview Causes of peptic ulcer disease
CHAPTER 18. PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE, SELF-ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS. 1. Which of the following is not a common cause of peptic ulcer disease (PUD)?
 CHAPTER 18. PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE, SELF-ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following is not a common cause of peptic ulcer disease (PUD)? A. Chronic alcohol ingestion B. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
CHAPTER 18. PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE, SELF-ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following is not a common cause of peptic ulcer disease (PUD)? A. Chronic alcohol ingestion B. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Presented by Dr. 張瀚文
 Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
Clinical Management of Obscure- Overt Gastrointestinal Bleeding Presented by Dr. 張瀚文 Definition Obscure: : hard to understand; not clear. Overt: : public; not secret. Occult: : hidden from the knowledge
Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師
 Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師 Hp : Helicobacter pylori Part 1. Pathophysiology and immune response Pathogenesis of Hp infection Part 2. Clinical manifestation Part 3. Dx tests for
Helicobacter pylori 幽門螺旋桿菌 馬偕紀念醫院新竹分院一般內科, 肝膽腸胃科陳重助醫師 Hp : Helicobacter pylori Part 1. Pathophysiology and immune response Pathogenesis of Hp infection Part 2. Clinical manifestation Part 3. Dx tests for
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions
 2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
Original Report. Carcinoid Tumors of the Stomach: A Clinical and Radiographic Study
 Aaron J. Binstock 1 C. Daniel Johnson 1 David H. Stephens 1 Ricardo V. Lloyd 2 Joel G. Fletcher 1 Received July 25, 2000; accepted after revision September 29, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
Aaron J. Binstock 1 C. Daniel Johnson 1 David H. Stephens 1 Ricardo V. Lloyd 2 Joel G. Fletcher 1 Received July 25, 2000; accepted after revision September 29, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk groups? Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk groups? Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk
Hompes Method. Practitioner Training Level II. Lesson Seven Part A DRG Pathogen Plus Interpretation
 Hompes Method Practitioner Training Level II Lesson Seven Part A DRG Pathogen Plus Interpretation Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Hompes Method is a trading name of
Hompes Method Practitioner Training Level II Lesson Seven Part A DRG Pathogen Plus Interpretation Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Hompes Method is a trading name of
1. Esophageal diverticulum located above the upper esophageal sphincter is called
 Test Bank for Robbins Basic Pathology 9th Edition by Kumar Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-basic-pathology-9thedition-by-kumar/ Chapter 14: Oral Cavity and Gastrointestinal
Test Bank for Robbins Basic Pathology 9th Edition by Kumar Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-basic-pathology-9thedition-by-kumar/ Chapter 14: Oral Cavity and Gastrointestinal
Gastroduodenal Stress Ulceration. Bryan Woolridge POS Rounds 29 October 2003
 Gastroduodenal Stress Ulceration Bryan Woolridge POS Rounds 29 October 2003 Objectives Define entity Etiology Differentiation of UGI ulcers Pathophysiology Identify population at risk/risk factors Clinical
Gastroduodenal Stress Ulceration Bryan Woolridge POS Rounds 29 October 2003 Objectives Define entity Etiology Differentiation of UGI ulcers Pathophysiology Identify population at risk/risk factors Clinical
ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID
 ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID Manoop S. Bhutani, MD, FASGE, FACG, FACP, AGAF, Doctor Honoris Causa Professor of Medicine Eminent Scientist of the Year 2008, World
ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID Manoop S. Bhutani, MD, FASGE, FACG, FACP, AGAF, Doctor Honoris Causa Professor of Medicine Eminent Scientist of the Year 2008, World
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
UPPER GI DISEASES 11/15/2014. Lesson Objectives. GI Tract Review. NUTR 2050 Nutrition for Nursing Professionals. Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD
 UPPER GI DISEASES NUTR 2050 Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Describe causes and contributing
UPPER GI DISEASES NUTR 2050 Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Describe causes and contributing
Pathology of the oesophagus and the stomach. Neil A Shepherd Gloucester, UK. Bristol Pathology 1 st Year Training School, The layers of the GI tract
 Pathology of the oesophagus and the stomach Neil A Shepherd Gloucester, UK Bristol Pathology 1 st Year Training School, The layers of the GI tract 1 Some facts about Histopathology and the upper GI tract
Pathology of the oesophagus and the stomach Neil A Shepherd Gloucester, UK Bristol Pathology 1 st Year Training School, The layers of the GI tract 1 Some facts about Histopathology and the upper GI tract
Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case
 Case Report Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case Yuanliang Li, Xin Su, Huangying Tan Department of Integrative Oncology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Correspondence
Case Report Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case Yuanliang Li, Xin Su, Huangying Tan Department of Integrative Oncology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Correspondence
Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 133-138 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Histopathological Characteristics of Atrophic Gastritis in Adult Population Marija Milićević,
Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY 235 Case 41 Peptic Ulcer Disease: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Abe Rosenfeld, who is 47 years old, owns a house painting business with his brothers. The brothers pride themselves
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R
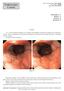 Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
GI Pharmacology. Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018
 GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Mar;21 Suppl:111-6. [Effect of antacids on intestinal motility]. [Article in German] Wienbeck M, Erckenbrecht J, Strohmeyer G. Abstract
GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Mar;21 Suppl:111-6. [Effect of antacids on intestinal motility]. [Article in German] Wienbeck M, Erckenbrecht J, Strohmeyer G. Abstract
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile Dr. Gabriella Kékesi The mechanism and regulation of gastric juice secretion (Lo.) 64. Secretory cells in stomach Composition and role
Case Presentations: Gastric Polyps and The Company They Keep. Elizabeth Montgomery, MD Department of Pathology Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD
 Case Presentations: Gastric Polyps and The Company They Keep Elizabeth Montgomery, MD Department of Pathology Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD Case 1 A 68 year old woman with dyspepsia underwent upper
Case Presentations: Gastric Polyps and The Company They Keep Elizabeth Montgomery, MD Department of Pathology Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD Case 1 A 68 year old woman with dyspepsia underwent upper
Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection
 Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection Klaus Mönkemüller Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology und Infectius Diseases Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg bb
Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection Klaus Mönkemüller Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology und Infectius Diseases Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg bb
Disorders of the Stomach. 3- Pancreatic and gastric heteretopia.
 GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT Lec 5-6 TUCOM-DEP. OF PATHOLOGY CONGENITAL ANOMALIES: 1- Diaphragmatic Hernia. 2- pyloric stenosis. Disorders of the Stomach 3- Pancreatic and gastric heteretopia. Diaphragmatic
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT Lec 5-6 TUCOM-DEP. OF PATHOLOGY CONGENITAL ANOMALIES: 1- Diaphragmatic Hernia. 2- pyloric stenosis. Disorders of the Stomach 3- Pancreatic and gastric heteretopia. Diaphragmatic
EMILOK Global. (omeprazole) Composition: Each capsule contains 20 mg omeprazole as enteric-coated
 EMILOK Global (omeprazole) Composition: Each capsule contains 20 mg omeprazole as enteric-coated granules. Properties: Emilok (omeprazole) belongs to the group of proton pump inhibitors, inhibits both
EMILOK Global (omeprazole) Composition: Each capsule contains 20 mg omeprazole as enteric-coated granules. Properties: Emilok (omeprazole) belongs to the group of proton pump inhibitors, inhibits both
Stomach and duodenum Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS
 Stomach and duodenum Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS asymmetrical, pearshaped,most proximal abdominal organ of the digestive tract. Cardia connected to esophagus. Fundus bounded superiorly by diaphragm and laterally
Stomach and duodenum Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS asymmetrical, pearshaped,most proximal abdominal organ of the digestive tract. Cardia connected to esophagus. Fundus bounded superiorly by diaphragm and laterally
-Mohammad Ashraf. -Anas Raed. -Alia Shatnawi. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
-1 -Mohammad Ashraf -Anas Raed -Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e Dr. Alia started the lecture by talking about subjects we are going to cover through this course; you can refer to the record if you are interested.
From The Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
 From The Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Etiological aspects of gastroesophageal cancers - An epidemiological approach Shahram Bahmanyar Stockholm
From The Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Etiological aspects of gastroesophageal cancers - An epidemiological approach Shahram Bahmanyar Stockholm
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) PATHOLOGY LAB #1. January 06, 2012
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) PATHOLOGY LAB #1 GOAL: January 06, 2012 Faculty Copy 1. Describe the basis morphologic and pathophysiologic changes which occur in
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) PATHOLOGY LAB #1 GOAL: January 06, 2012 Faculty Copy 1. Describe the basis morphologic and pathophysiologic changes which occur in
Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Gastric Antral Mucosa Before and After Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 94, No. 5, 1999 1999 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(99)00126-4 Cyclooxygenase-2
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 94, No. 5, 1999 1999 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(99)00126-4 Cyclooxygenase-2
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY. Robin Warren
 - Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
- Helicobacter - THE EASE AND DIFFICULTY OF A NEW DISCOVERY Robin Warren EARLY DAYS First reports 100 years ago considered spirochaetes 1940 Freedburg saw curved organisms in the stomach 1954 Palmer: Freedburg
Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Neuroendocrine Tumors
 Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Stomach! First, a few pitfalls. Case Presentations: Gastric Polyps and The Company They Keep - Gastritis
 Case Presentations: Gastric Polyps and The Company They Keep - Gastritis Elizabeth Montgomery, MD Department of Pathology Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD Stomach! We will begin with a whirwind tour
Case Presentations: Gastric Polyps and The Company They Keep - Gastritis Elizabeth Montgomery, MD Department of Pathology Johns Hopkins Hospital Baltimore MD Stomach! We will begin with a whirwind tour
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Accepted Manuscript. Classical features of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, in images. Ali Alshati, MD, Toufic Kachaamy, MD
 Accepted Manuscript Classical features of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, in images Ali Alshati, MD, Toufic Kachaamy, MD PII: S0016-5107(19)30069-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2019.01.026 Reference:
Accepted Manuscript Classical features of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, in images Ali Alshati, MD, Toufic Kachaamy, MD PII: S0016-5107(19)30069-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2019.01.026 Reference:
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS
 SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
SARCINA VENTICULARI IS A POSSIBLE CAUSATIVE MICROORGANISM OTHER THAN H.PYLORI IN GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION PATHOGENESIS 55 years old male, Farm worker, married, from Ibb Heavy Smoker, Khat chewer non-alcohol
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
S. Sandberg-Lewis, ND, DHANP
 Functional Gastroenterology Webinar One 6-28-13 S. Sandberg-Lewis, ND, DHANP Proton pump inhibitors- Effects on: secretion gastric mucosa food allergy bile reflux Barrett metaplasia and dysplasia esophageal
Functional Gastroenterology Webinar One 6-28-13 S. Sandberg-Lewis, ND, DHANP Proton pump inhibitors- Effects on: secretion gastric mucosa food allergy bile reflux Barrett metaplasia and dysplasia esophageal
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3.
 The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile LO.: 64,65,66 Prof. Gyula Sáry While studying functions of the gastrointestinal system, Pavlov described the conditional response, a
The physiology of gastrointestinal system 3. Stomach, pancreas, bile LO.: 64,65,66 Prof. Gyula Sáry While studying functions of the gastrointestinal system, Pavlov described the conditional response, a
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer
 Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer MANFRED STOLTE, ALEXANDER MEINING Department of Pathology, Klinikum Bayreuth, Bayreuth, Germany Key Words. Cancer Gastritis Helicobacter pylori Prevention ABSTRACT
Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer MANFRED STOLTE, ALEXANDER MEINING Department of Pathology, Klinikum Bayreuth, Bayreuth, Germany Key Words. Cancer Gastritis Helicobacter pylori Prevention ABSTRACT
Gastrointestinal Markers
 Gastrointestinal Markers Session 2 Gastrointestinal System Reference Ranges Optimal Range Ttl Total Protein ti 69 6.9 74 7.4 Globulin 2.4 2.8 BUN 10 16 Creatinine 0.8 1.1 Phosphorous 3.0 4.0 Eosinophils
Gastrointestinal Markers Session 2 Gastrointestinal System Reference Ranges Optimal Range Ttl Total Protein ti 69 6.9 74 7.4 Globulin 2.4 2.8 BUN 10 16 Creatinine 0.8 1.1 Phosphorous 3.0 4.0 Eosinophils
Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
