Development of Natural Killer Cells from Lymphohematopoietic Progenitors of Murine Fetal Liver
|
|
|
- Gladys Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Development of Natural Killer Cells from Lymphohematopoietic Progenitors of Murine Fetal Liver YUKHI AIBA, MAKIO OGAWA Ralph H. Johnson Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina, USA Key Words. Natural killer cells Lymphohematopoietic cells lnterleukins Growth factors ABSTRACT We established a clonal culture system which supports the growth of murine immature natural killer (NK) cells. When we plated day 14 fetal thymocytes in methylcellulose media containing interleukin 2 (IL-2), IL-7 and steel factor (SF), we observed diffuse colonies which could not be classified into known colony types. Cells in the colonies were blast-like and expressed Thy-1 and CD25 but not lineage-specific markers. Cells in the colonies developed into NK1.l' cells in fetal thymus organ culture indicating that the colonies consist of immature NK cells. We then examined the colony-forming ability of fetal liver cells. The combination of IL-2, IL- 7 and SF with or without IL-11 supported formation of few immature NK cell colonies from purified progenitors. Interestingly, addition of IL-11 to the culture stimulated formation of mixed colonies consisting of immature NK cells, B cells, macrophages and/or mast cells. The clonal origin of the mixed NK cell colonies was confirmed by micromanipulation of the colony-forming cells. This culture assay should facilitate the analysis of the pathway and cytokine regulation of NK cell development. Stem Cells 1998;16(suppl I): INTRODUCTION Natural killer (NK) cells comprise a small subset of lymphocytes and are thought to play important roles in various immune responses [I, 21. Although the functions of NK cells are being extensively studied, their ontogeny and regulation of development are largely unknown. It was reported that NK cells are closely related to T lymphocytes in their developmental pathways [3]. Sunchez et al. [4] have shown that NWT common progenitors are present in human fetal thymus. However. it still remains to be clarified how NK or NWT common progenitors develop from multipotential hematopoietic progenitors, and how and when NWT common progenitors diverge to form separate NK and T cell lineages. The lineage relationship of NK cells with B and myeloid cells should also be clarified. To investigate the pathway of NK cell development, it is necessary to establish a clonal culture system which supports the development of NK cells from multipotential hematopoietic progenitors. Here, we report that murine fetal thymocytes and liver cells plated in methylcellulose culture form immature NK cell colonies. We also found that mixed colonies consisting of NK, B and myeloid cells Characteristics and Potentials of Blood Stem Cells STEM CELLS 1998;16(suppl 1): OAlphaMed Press. All rights reserved
2 I94 Hematopoietic Origin of Natural Killer Cells can develop from purified hematopoietic progenitors of fetal liver cells in the presence of interleukin 2 (IL-2), IL-7, steel factor (SF) and IL-11. We believe that this quantitative clonal culture is useful for analyzing the developmental pathway and cytokine regulation of NK cell progenitors. MATERIALS AND METHODS Mice and Cell Preparation Female C57BL16-Ly5.2 and male DBA/2 mice were purchased from Charles River (Raleigh, NC). Male C57BL16-Ly5.1 mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME). Mice were allowed to mate for 18 h. The day of vaginal plugging was designated as day 0 of gestation. On day 14 of gestation, the mice were sacrificed and cell suspensions of fetal thymus and liver were prepared by gently pressing these organs between two slide glasses and by repeated pipetting. Purification of fetal liver progenitors had been described previously [5]. Cytokines Purified murine recombinant IL-2 was purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). Recombinant human IL-7 was provided by Sanofi Winthrop, Inc. (Malvern, PA). Recombinant murine SF was a gift from Immunex (Seattle, WA). Recombinant human IL-11 was provided by Genetics Institute (Cambridge, MA). Concentrations of cytokines used were as follows: IL-2, 20 ng/ml; IL-7, SF, 100 nglml; 200 U/ml(20ng/ml); IL-11, 100 ng/ml. Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting The following monoclonal antibodies were used for flow cytometric analysis and cell sorting: biotin-conjugated-anti-cd3 (clone;145-2cll) (Pharmingen; San Diego, CA); fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) conjugated-anti-cd4 (YTS 191.1) (Caltag Laboratories; South San Francisco, CA); phycoerythrin (PE) conjugated-anti-cd8 (YTS 169.4) (Caltag); PE-conjugated-anti-CD25 (PC61 S.3) (Caltag); FITC-conjugated-anti-Thy1.2 (30-H12) (Pharmingen); biotin-conjugated-anti-nkl.1 (PK 136) (Pharmingen); PE-conjugated-anti-B220 (RA3-6B2) (Pharmingen); biotin-conjugated-anti-ckit (ACK4), biotin-conjugated-anti-mac-1 (M1/70), biotin-conjugated-anti-gr-1 (RB6-8C5) (Pharmingen); biotin-conjugated-anti-ter (TER119) (Pharmingen); FITC-conjugated-anti-Ly5.1 (A20-1.7, kindly provided by Dr. H. Fleming of Emory University, Atlanta, GA), and FITC-conjugated-anti-Ly5 (30F11.1). Basic techniques of cell staining had been described previously [6]. In all experiments, cells stained with appropriate isotype-matched control immunoglobulins were prepared as negative controls. After staining, cells were analyzed and/or sorted by using FACS Vantage (Becton Dickinson; Mountain View, CA). Clonal Culture for Immature NK Cell Colonies Methylcellulose culture was carried out by using 35mm Falcon suspension culture dishes (Becton Dickinson Labware; Lincoln Park, NJ). Fetal thymocytes or purified progenitor cells of fetal liver were cultured in the medium consisting of a-medium (Flow Laboratories; Rockville, MD), 1.2% 1,500-centipoise methylcellulose (Shinetsu Chemical; Tokyo, Japan), 5% fetal bovine serum, 1 % deionized fraction-v bovine serum albium and 0.lmM 2-mercaptoethanol and cytokines. Dishes were incubated at 37 C in a humidified atmosphere flushed with 5% C02 for 14 or 18 days. Single-cell manipulation of colony-forming cells was carried out as described previously [7]. Fetal Thymus Organ Culture Fetal thymus organ culture was performed as described previously [8]. Briefly, fetal thymi were first incubated with 4 X 10' test cells in a hanging drop culture for 20 h. Samples were then
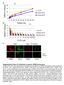
3 Aiba, Ogawa 195 transferred onto filter membranes (Costar; Cambridge, MA; pore size, 8mm) and cultured for 11 days. Cells were recovered from the thymic lobes, stained with antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. RE s u L T s Immature NK Cell Colony Formation from Fetal Thymocytes We chose day 14 murine fetal thymocytes as the material for growing candidate NK cell colonies because relatively high percentages of the cells had been shown to have the potential of developing into NK cells [9]. After testing several cytokine combinations, we found that fetal thymocytes cultured in the methylcellulose media containing IL-2, IL-7 and SF form diffuse colonies which cannot be classified into known colony types (Fig. 1). May-Griinwald Giemsa staining of the colonies revealed that the cells in the colonies are blast-like, showing no signs of cytoplasmic differentiation. Colony-forming frequency of the fetal thymocytes was about 1%. We then examined expression of surface molecules of the cells in the colonies by flow cytometry. As shown in Figure 2, the cells expressed Thy-1 and CD25 but not Mac-1, Gr-1, TER, CD3 or B220. Because the cells in the colonies expressed Thy- 1 and CD25, it was likely that these cells are immature NK or T cells. Therefore, we next examined the NK and T cell potentials by culturing these cells in fetal thymus organ culture. Fetal thymocytes of CS7BL/6-Ly5.1/Ly5.2 Fl mice were cultured in the methylcellulose media in the presence of IL-2, IL-7 and SF. After incubation for 14 days, candidate NK cell colonies were individually picked, pooled and plated in culture with fetal thymic lobes of CS7BL/6-Ly5.2 mice. Ten days later cells recovered from the thymic lobes were analyzed for the expression of Ly5.1, CD3, NK1.l and B220. As shown in Figure 3, most of test LyS. I' cells expressed NK1.l but neither CD3 nor B220. This result indicated that the diffuse colonies derived from the fetal thymocytes are immature NK cell colonies. Mixed NK Cell Colony Formation from Fetal Liver Progenitors We next examined the colonyforming ability of purified hematopoietic progenitors of fetal Figure I. A photomicrograph of an immature NK cell colony. One quarter of a representative immature NK cell colony seen on an inverted microscope. -Mac- 1, Gr- 1, TER - CD25- Figure 2. Surface phenotypes of the cells in the immature NK cell colonies. Fetal thymocytes were cultured in methylcellulose media with IL-2, IL-7 and SF. After 14 days of culture, immature NK cell colonies were individually picked, pooled and stained with monoclonal antibodies specific for molecules indicated in each FACS profile.
4 ~ -~ 196 Hematopoietic Origin of Natural Killer Cells -Ly-5. t- Figure 3. Surface phenotypes of the cells developing in fetal thymus organ culture. Fetal thymocytes from C57BW6-Ly5. I/C57BW- 6-Ly5.2 Fl mice (LyS.l/Ly5.2) were plated in rlzethylcellulose culture with IL-2, 1L-7 and SF. After 14 days of culture, immature NK cell colonies were individually picked, pooled and incubated in a hanging drop culture for 20 h with fetal thymus lobes from BDFl (Ly5.2) mice. The lobes were then cultured on filter membranes for I0 days. Cells harvested from the lobes were stained with monoclonal antibodies specific for molecules indicated in each FACS profile. liver cells. Low density (<1.0770), lineage marker-negative, c-kit'sca- 1' cells were prepared from day 14 murine fetal liver. We have previously shown that colony-forming cells can be enriched by this method [5]. The cells were plated in methylcellulose media with 1L-2. IL-7 and SF. As shown in Table 1, immature NK cell colonies developed although their frequencies were low. In an effort to increase the frequency of the colonies, we found that addition of IL-11 to the culture increases the frequency of colony-forming cells (Table 1). More interestingly, mixed colonies consisting of diffuse round cells characteristic of immature NK cells and other types of cells were also detected (Fig. 4). Table 1 shows the results of a representative study. In the same table, colony-forming ability of the fetal thymocytes is also shown. To confirm the clonality of the mixed colonies, we next plated the c-kit'sca-1' cells individually by micromanipulation into methylcellulose media containing IL-2, IL-7, IL-11 and SF. From 100 individually plated cells, 12 mixed NK cell colonies developed after 18 days of culture. This study established the clonal origin of the mixed NK cell colonies. To characterize the cells in the mixed colonies in more detail, each colony was lifted individually from the culture and divided into two aliquots. Cells in one aliquot were examined for the expression of B220 and Thy-1 by flow cytometry. All colonies contained Thy-1' B220- cells. Eleven out of the 12 colonies contained B220' cells, suggesting that most of the colonies have B lineage cells. Representative fluorescence-activated cell sort profiles were shown in Figure 5. Cells in the other aliquot of the colonies were subjected to May-Grunwald Giemsa staining for examination of myeloid lineage cells. All mixed colonies contained macrophages; two out of the 12 contained mast cells. These results indicated that most of the mixed Table 1. Colun! tornidtion from feial Incr and li'tdl th!mus cells Cells plated # of Colonies Type #/Dish Cytokines Mixed NK PureNK Pre-B M Mast M-mast Sca-l'c-kit'FL 50 IL-2, IL-7, SF 0 1t t1 2t1 IL-2, IL-7, L ll, SF t1 2t1 FT 1,000 IL-2, IL-7, SF t1 0 IL-2, IL-7, IL-I 1, SF 0 13t t2 0 Sca- I'c-kit' FL cells were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were cultured for 18 days in methylcellulose media in the presence of designated cytokines. Data represent mean + SD of quadruplicate cultures. Abbreviations: Mixed NK: mixed NK colonies; Pure NK: NK cell colonies; Pre-B: Pre-B cell colonies; M: macrophage colony; mast: mast cell colony; M- mast: macrophage-mast cell mixed colony; FL: fetal liver; FT: fetal thymus.
5 Aiba, Ogawa 197 NK cell colonies contain immature K, B and myeloid cells and suggested that the colonies are derived from lymphohematopoietic progenitors. DISCUSSION Although much effort has been made to clarify the pathway and regulation of NK cell development, there are still questions to be resolved in NK cell ontogeny. This is mainly because of the lack of a clonal culture system which supports the growth and development of NK cells from uncommitted progenitors. Here, we report the establishment of a clonal culture which supports the growth of immature NK cells, B cells, macrophages and/or mast cells from single hematopoietic progenitors of murine fetal liver. Recently, several reports suggested that NK, T and B cells arise from common lymphoid progenitors [lo-141. However, because of the lack of a clonal culture which supports the growth of multiple lymphoid lineage cells simultaneously, the concept of common lymphoid progenitors was not established unequivocally. The culture system reported here will greatly facilitate identification of the common lymphoid progenitors. Our study revealed that fetal thy- Figure 4. A photomicropraph of a mixed NK cell colony. One quarter of a representative mixed NK cell colony seen on an inverted microscope is shown. Thy- 1 Figure 5. Representative FACS profiles of colonies derived from single cells. Sca-l'c-kit' cells were prepared from fetal liver and were plated individually by micromanipulation into methylcellulose media containing IL-2, 1L-7, IL-I1 and SF. After 18 days of culture, colonies were identified in situ and picked individually. Cells from each colony were stained with PE-anti-B220 and FITC-anti-Thy-I and analyzed by FACS Vantage. Left: a mixed NK colony with B lineage cells. Right: a mixed NK colony without B lineage cells. mocytes cannot form mixed colonies containing NK and B lineage cells. This appears to indicate that fetal thymi contain committed NK and B cell progenitors but not common NK/B progenitors. Alternatively, very few thymocytes have the potential to develop to both NK and B cells and our culture is not sensitive enough to detect the few common progenitors. Regardless, our culture system will now allow direct study of the mechanisms regulating commitment of multipotent progenitors to NK cell lineage. ACKNOWLEDGMENT We thank Dr. Haiqun Zeng for assistance in cell sorting and Dr. Pamela N. Pharr and Mrs. Anne G. Leary in preparation of this manuscript.
6 198 Hematopoietic Origin of Natural Killer Cells REFERENCES Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol 1989;47: Herberman RB, Reynolds CW, Ortaldo JR. Mechanism of cytotoxicity by natural killer (NK) cells. Annu Rev Immunol 1986;4: Lanier LL, Spits H, Phillips JH. The developmental relationship between NK cells and T cells. Immunol Today 1992; 13: Sinchez MJ, Muench MO, Roncarolo MG et al. Identification of a common Thatural killer cell progenitor in human fetal thymus. J Exp Med 1994; 180: Fujimoto K, Lyman SD, Hirayama F et al. Isolation and characterization of primitive hematopoietic progenitors of murine fetal liver. Exp Hematol 1996;24: Hirayama, F, Shih J-P, Awgulewitsch A et al. Clonal proliferation of murine lymphohemopoietic progenitors in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89: Suda T, Suda J, Ogawa M. Single-cell origin of mouse hemopoietic colonies expressing multiple lineages in variable COmbindtiOnS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1983;80: Aiba Y, Hirayama F, Ogawa M. Clonal proliferation and cytokine requirement of murine progenitors for natural killer cells. Blood 1997;89: Rodewald H-R, Moingeon P, Lucich JL et al. A population of early fetal thymocytes expressing FcgRIIhII contains precursors of T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Cell 1992;69: Galy A, Travis M, Cen D et al. Human T, B, natural killer, and dendritic cells arise from a common bone marrow progenitor cell subset. Immunity 1995;3: Georgopoulos K, Bigby M, Wang J-H et al. The ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell 1994;79: Matsuzaki Y, Gyotoku J-I, Ogawa M et al. Characterization of c-kit positive intrathymic stem cells that are restricted to lymphoid differentiation. J Exp Med 1993;178: Wu L, Antica M, Johnson GR et al. Developmental potential of the earliest precursor cells from the adult mouse thymus. J Exp Med l991;174: Zufiiga-Pflucker JC, Jiang D, Lenardo MJ. Requirement for TNF-(w and IL- 1 a in fetal thymocyte commitment and differentiation. Science 1995;268:1906-I 909.
In Vitro Differentiation of Murine Sca-1 + Lin Cells into Myeloid, B Cell and T Cell Lineages
 In Vitro Differentiation of Murine Sca-1 + Lin Cells into Myeloid, B Cell and T Cell Lineages Maki Ito, Kazuaki Anan, Mahito Misawa, Shunrou Kai, Hiroshi Hara Department of Transfusion Medicine, Hyogo
In Vitro Differentiation of Murine Sca-1 + Lin Cells into Myeloid, B Cell and T Cell Lineages Maki Ito, Kazuaki Anan, Mahito Misawa, Shunrou Kai, Hiroshi Hara Department of Transfusion Medicine, Hyogo
Cytokine Regulation of Early Lymphohematopoietic Development
 Concise Review Cytokine Regulation of Early Lymphohematopoietic Development Fumiya Hirayama, Makio Ogawa The Department of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina and the Ralph H. Johnson Department
Concise Review Cytokine Regulation of Early Lymphohematopoietic Development Fumiya Hirayama, Makio Ogawa The Department of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina and the Ralph H. Johnson Department
By James R. Carlyle,* Alison M. Michie,* Caren Furlonger, Toru Nakano, Michael J. Lenardo, Christopher J. Paige,* and Juan Carlos Zúñiga-Pflücker*
 Published Online: 21 July, 1997 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.186.2.173 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 2, 2018 Identification of a Novel Developmental Stage Marking Lineage Commitment
Published Online: 21 July, 1997 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.186.2.173 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on September 2, 2018 Identification of a Novel Developmental Stage Marking Lineage Commitment
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and
 Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
EML Erythroid and Neutrophil Differentiation Protocols Cristina Pina 1*, Cristina Fugazza 2 and Tariq Enver 3
 EML Erythroid and Neutrophil Differentiation Protocols Cristina Pina 1*, Cristina Fugazza 2 and Tariq Enver 3 1 Department of Haematology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK; 2 Dipartimento de Biotecnologie
EML Erythroid and Neutrophil Differentiation Protocols Cristina Pina 1*, Cristina Fugazza 2 and Tariq Enver 3 1 Department of Haematology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK; 2 Dipartimento de Biotecnologie
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplemental Information. Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and. Monocyte-Dendritic Cell Progenitors Independently
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a. Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease
 Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, and Applications to Human Disease Dr. Michael A. Caligiuri
 Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Although the thymus is the predominant source of T cells in
 Identification of an early T cell progenitor for a pathway of T cell maturation in the bone marrow Sussan Dejbakhsh-Jones and Samuel Strober* Division of Immunology and Rheumatology, Department of Medicine,
Identification of an early T cell progenitor for a pathway of T cell maturation in the bone marrow Sussan Dejbakhsh-Jones and Samuel Strober* Division of Immunology and Rheumatology, Department of Medicine,
NK cells express two families of receptors, which in the
 Brief Definitive Report Generation of Lytic Natural Killer 1.1, Ly-49 Cells from Multipotential Murine Bone Marrow Progenitors in a Stroma-free Culture: Definition of Cytokine Requirements and Developmental
Brief Definitive Report Generation of Lytic Natural Killer 1.1, Ly-49 Cells from Multipotential Murine Bone Marrow Progenitors in a Stroma-free Culture: Definition of Cytokine Requirements and Developmental
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia
 Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
Sipper BK Experimental Animal Co. (Shanghai, China) and bred in a specific. pathogen-free environment. The animal study protocol was approved by the
 Supplementary information, Data S1 Materials and Methods Mice, Ad vectors and reagents Female C57BL/6 mice, 8-10 weeks of age, were purchased from Joint Ventures Sipper BK Experimental Animal Co. (Shanghai,
Supplementary information, Data S1 Materials and Methods Mice, Ad vectors and reagents Female C57BL/6 mice, 8-10 weeks of age, were purchased from Joint Ventures Sipper BK Experimental Animal Co. (Shanghai,
Thymic dendritic cells (DCs) reside in the medulla and at the
 Developmental dissociation of thymic dendritic cell and thymocyte lineages revealed in growth factor receptor mutant mice Hans-Reimer Rodewald*, Thomas Brocker, and Corinne Haller Basel Institute for Immunology,
Developmental dissociation of thymic dendritic cell and thymocyte lineages revealed in growth factor receptor mutant mice Hans-Reimer Rodewald*, Thomas Brocker, and Corinne Haller Basel Institute for Immunology,
0.0 All T-lymph B-lymph Sarcomas Carcinomas Germ cell. Tumor type
 Fig S1 A B Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 All T-lymph B-lymph Sarcomas Carcinomas Germ cell Tumor type -/- (n = 46) Q/- (n = 76) Q/Q (n = 31) Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0
Fig S1 A B Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 All T-lymph B-lymph Sarcomas Carcinomas Germ cell Tumor type -/- (n = 46) Q/- (n = 76) Q/Q (n = 31) Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0
Scientific report: Delineating cellular stages and regulation of human NK cell development to improve NK cell-based therapy for cancer (Dnr )
 Scientific report: Delineating cellular stages and regulation of human NK cell development to improve NK cell-based therapy for cancer (Dnr 130259) The main goal of this project focuses on establishing
Scientific report: Delineating cellular stages and regulation of human NK cell development to improve NK cell-based therapy for cancer (Dnr 130259) The main goal of this project focuses on establishing
Defensive mechanisms include :
 Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
units with extensive capability to self-renew and generate
 Proc. NatL Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 79, pp. 3843-3847, June 98 Medical Sciences Identification in culture of a class of hemopoietic colony-forming units with extensive capability to self-renew and generate
Proc. NatL Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 79, pp. 3843-3847, June 98 Medical Sciences Identification in culture of a class of hemopoietic colony-forming units with extensive capability to self-renew and generate
ulation of NK cells that retain the capability of expressing the HNK-1 differentiation antigen. Children with the Chediak-Higashi (CH)' syndrome,
 RAPID PUBLICATIONS Natural Killer (HNK-1l) Cells in Chediak-Higashi Patients Are Present in Numbers but Are Abnormal in Function and Morphology TORu ABO, JOHN C. RODER, WATARU ABO, MAX D. COOPER, and CHARLES
RAPID PUBLICATIONS Natural Killer (HNK-1l) Cells in Chediak-Higashi Patients Are Present in Numbers but Are Abnormal in Function and Morphology TORu ABO, JOHN C. RODER, WATARU ABO, MAX D. COOPER, and CHARLES
Rapid Decline of Clonogenic Hemopoietic Progenitors in Semisolid Cultures of Bone Marrow Samples Derived from Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Original Manuscript International Journal of Cell Cloning 7314-321 (1989) Rapid Decline of Clonogenic Hemopoietic Progenitors in Semisolid Cultures of Bone Marrow Samples Derived from Patients with Chronic
Original Manuscript International Journal of Cell Cloning 7314-321 (1989) Rapid Decline of Clonogenic Hemopoietic Progenitors in Semisolid Cultures of Bone Marrow Samples Derived from Patients with Chronic
pro-b large pre-b small pre-b CCCP (µm) Rag1 -/- ;33.C9HCki
 a TMRM FI (Median) b TMRM FI (Median) c 20 15 10 5 0 8 6 4 2 0 pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 TMRM (nm) pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 CCCP (mm)
a TMRM FI (Median) b TMRM FI (Median) c 20 15 10 5 0 8 6 4 2 0 pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 TMRM (nm) pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 CCCP (mm)
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
BCR-ABL - LSK BCR-ABL + LKS - (%)
 Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis EasySep Mouse Monocyte Isolation Kit Catalog #19861 For processing 1 x 10^9 cells Description Isolate untouched and highly purified monocytes from mouse
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis EasySep Mouse Monocyte Isolation Kit Catalog #19861 For processing 1 x 10^9 cells Description Isolate untouched and highly purified monocytes from mouse
Supplemental Information. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls. Monocyte Differentiation. into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells
 Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Essential Requirement for c-kit and Common Chain in Thymocyte Development Cannot be Overruled by Enforced Expression of Bcl-2
 Published Online: 18 June, 2001 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.193.12.1431 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 9, 2018 Brief Definitive Report Essential Requirement for c-kit and Common Chain
Published Online: 18 June, 2001 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.193.12.1431 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 9, 2018 Brief Definitive Report Essential Requirement for c-kit and Common Chain
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Meeting Report. From December 8 to 11, 2012 at Atlanta, GA, U.S.A
 Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration. Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research.
 Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Factors Which Predispose to the Onset of Autoimmune Disease. A Senior Honors Thesis
 Factors Which Predispose to the Onset of Autoimmune Disease A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for graduation with distinction in Biology in the College of Biological
Factors Which Predispose to the Onset of Autoimmune Disease A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for graduation with distinction in Biology in the College of Biological
Comprehensive evaluation of human immune system reconstitution in NSG. and NSG -SGM3 mouse models toward the development of a novel ONCO-HU
 Comprehensive evaluation of human immune system reconstitution in NSG and NSG -SGM3 mouse models toward the development of a novel ONCO-HU xenograft model Aaron Middlebrook, 1 Eileen Snowden, 2 Warren
Comprehensive evaluation of human immune system reconstitution in NSG and NSG -SGM3 mouse models toward the development of a novel ONCO-HU xenograft model Aaron Middlebrook, 1 Eileen Snowden, 2 Warren
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3412
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia"
 Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia" Hoelzer, D.,l, Harriss, E. B.l, Kurrle, E.l, Schmücker, H.l, Hellriegel,
Differentiation Ability of Peripheral Blood Cells from Patients with Acute Leukemia or Blast Crisis in Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia" Hoelzer, D.,l, Harriss, E. B.l, Kurrle, E.l, Schmücker, H.l, Hellriegel,
THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON THE CLONOGENECITY OF HUMAN HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS: PRELIMINARY REPORT
 168 Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 4 168-173 2 Research Report THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON THE CLONOGENECITY OF HUMAN HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS: PRELIMINARY REPORT Boguslaw Machaliński, a Maria Zejmo,
168 Fluoride Vol. 33 No. 4 168-173 2 Research Report THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON THE CLONOGENECITY OF HUMAN HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS: PRELIMINARY REPORT Boguslaw Machaliński, a Maria Zejmo,
Development of B and T lymphocytes
 Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
Diluent B (a phagocytic cell-labeling solution, Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) anti-maci antibody (1:100 dilution, BMA Biomedical, Switzerland)
 Sawada et al. 1 Isolation of two distinct subpopulations of microglia Reagents PKH26 (Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) Diluent B (a phagocytic cell-labeling solution, Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) FITC-labeled IgG (Cappel,
Sawada et al. 1 Isolation of two distinct subpopulations of microglia Reagents PKH26 (Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) Diluent B (a phagocytic cell-labeling solution, Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) FITC-labeled IgG (Cappel,
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Effects of Mast Cell Growth Factor on Ara-C Mediated Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Killing
 Effects of Mast Cell Growth Factor on Ara-C Mediated Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Killing A. Tafuri, L. De Felice, M. G. Mascolo, T. Valentini, M. T. Petrucci, M. C. Petti University La Sapienza of Rome,
Effects of Mast Cell Growth Factor on Ara-C Mediated Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Killing A. Tafuri, L. De Felice, M. G. Mascolo, T. Valentini, M. T. Petrucci, M. C. Petti University La Sapienza of Rome,
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
TITLE: Effects of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Age on CML Disease Progression
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0795 TITLE: Effects of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Age on CML Disease Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kenneth Dorshkind, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0795 TITLE: Effects of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Age on CML Disease Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kenneth Dorshkind, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California,
Hematopoiesis. BHS Liège 27/1/2012. Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne
 Hematopoiesis BHS Liège 27/1/2012 Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne Hematopoiesis: definition = all the phenomenons to produce blood cells Leukocytes = White Blood Cells Polynuclear = Granulocytes Platelet
Hematopoiesis BHS Liège 27/1/2012 Dr Sonet Anne UCL Mont-Godinne Hematopoiesis: definition = all the phenomenons to produce blood cells Leukocytes = White Blood Cells Polynuclear = Granulocytes Platelet
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Figures
 Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Pleiotrophin Regulates the Expansion and Regeneration of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Heather A Himburg 1, Garrett G Muramoto 1 *, Pamela Daher 1*, Sarah K Meadows 1, J. Lauren Russell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Pleiotrophin Regulates the Expansion and Regeneration of Hematopoietic Stem Cells Heather A Himburg 1, Garrett G Muramoto 1 *, Pamela Daher 1*, Sarah K Meadows 1, J. Lauren Russell
MYRIAM CAPONE*, RICHARD D. HOCKETT, JR., AND ALBERT ZLOTNIK* MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 12522 12527, October 1998 Immunology Kinetics of T cell receptor,, and rearrangements during adult thymic development: T cell receptor rearrangements are present
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 12522 12527, October 1998 Immunology Kinetics of T cell receptor,, and rearrangements during adult thymic development: T cell receptor rearrangements are present
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas
 University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
 Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
T H 1, T H 2 and T H 17 polarization of naïve CD4 + mouse T cells
 A complete workflow for cell preparation, isolation, polarization and analysis T H 1, T H 2 and T H 17 polarization of naïve CD4 + mouse T cells Introduction Workflow CD4 + T helper (T H) cells play a
A complete workflow for cell preparation, isolation, polarization and analysis T H 1, T H 2 and T H 17 polarization of naïve CD4 + mouse T cells Introduction Workflow CD4 + T helper (T H) cells play a
T cell development October 28, Dan Stetson
 T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
The Adaptive Immune Response. T-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Accelerated Cell-Cycling of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells by Growth Factors
 Accelerated Cell-Cycling of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells by Growth Factors By Ryuhei Tanaka, Naoyuki Katayama, Kohshi Ohishi, Nadim Mahmud, Ryugo Itoh, Yuka Tanaka, Yoshihiro Komada, Nobuyuki Minami,
Accelerated Cell-Cycling of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells by Growth Factors By Ryuhei Tanaka, Naoyuki Katayama, Kohshi Ohishi, Nadim Mahmud, Ryugo Itoh, Yuka Tanaka, Yoshihiro Komada, Nobuyuki Minami,
IL-3. Alternative names. Structure. Discovery. Main activities and pathophysiological roles. John W. Schrader * SUMMARY BACKGROUND
 IL-3 John W. Schrader * The Biomedical Research Centre, University of British Columbia, 2222 Health Sciences Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada V6T 1Z3 * corresponding author tel: 604-822-7810,
IL-3 John W. Schrader * The Biomedical Research Centre, University of British Columbia, 2222 Health Sciences Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada V6T 1Z3 * corresponding author tel: 604-822-7810,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production activates T- and natural killer cells
 Eur Respir J 22; 2: 686 69 DOI:.1183/931936.2.222 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 22 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production
Eur Respir J 22; 2: 686 69 DOI:.1183/931936.2.222 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 22 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Organic dust-induced interleukin-12 production
BD IMag Cell Separation System
 BD IMag Cell Separation System Table of Contents Magnetic Cell Separation with BD IMag Particles.............................................................. 3 BD IMag Enrichment Protocol Flow Chart......................................................................
BD IMag Cell Separation System Table of Contents Magnetic Cell Separation with BD IMag Particles.............................................................. 3 BD IMag Enrichment Protocol Flow Chart......................................................................
MagniSort Mouse CD4 Naive T cell Enrichment Kit Catalog Number: RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
 Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse CD4 Naive T cell Enrichment Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse splenocytes were unsorted (left) or sorted with the MagniSort Mouse CD4
Page 1 of 2 MagniSort Mouse CD4 Naive T cell Enrichment Kit RUO: For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Mouse splenocytes were unsorted (left) or sorted with the MagniSort Mouse CD4
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Immune Reconstitution Following Hematopoietic Cell Transplant
 Immune Reconstitution Following Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Patrick J. Kiel, PharmD, BCPS, BCOP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Indiana University Simon Cancer Center Conflicts of Interest Speaker Bureau
Immune Reconstitution Following Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Patrick J. Kiel, PharmD, BCPS, BCOP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Indiana University Simon Cancer Center Conflicts of Interest Speaker Bureau
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS
 DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
An intrinsic thyrotropin-mediated pathway of TNF- production by bone marrow cells
 HEMATOPOIESIS An intrinsic thyrotropin-mediated pathway of TNF- production by bone marrow cells Heuy-Ching Wang, Jolene Dragoo, Qin Zhou, and John R. Klein Recent studies have identified a role for thyroid-stimulating
HEMATOPOIESIS An intrinsic thyrotropin-mediated pathway of TNF- production by bone marrow cells Heuy-Ching Wang, Jolene Dragoo, Qin Zhou, and John R. Klein Recent studies have identified a role for thyroid-stimulating
Interleukin-l Production in Patients with Nonlymphocytic Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes
 Interleukin-l Production in Patients with Nonlymphocytic Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes N. J. Simbirtseva 1 A common feature of all cases of myeloid leukemia is a block in normal maturation of
Interleukin-l Production in Patients with Nonlymphocytic Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes N. J. Simbirtseva 1 A common feature of all cases of myeloid leukemia is a block in normal maturation of
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Examples of staining for each antibody used for the mass cytometry analysis.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Examples of staining for each antibody used for the mass cytometry analysis. To illustrate the functionality of each antibody probe, representative plots illustrating the expected
Supplementary Figure 1 Examples of staining for each antibody used for the mass cytometry analysis. To illustrate the functionality of each antibody probe, representative plots illustrating the expected
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19814 Figure 3e - - - Beads: Hep SA Sup Hep SA Sup Hep - SA - Sup 150 102 76 102 76 Blot: NP-1 Blot: MECA-32 Blot: VEGF Figure 3f Rbt IgG ctrl IP VEGF IP Extended
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19814 Figure 3e - - - Beads: Hep SA Sup Hep SA Sup Hep - SA - Sup 150 102 76 102 76 Blot: NP-1 Blot: MECA-32 Blot: VEGF Figure 3f Rbt IgG ctrl IP VEGF IP Extended
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Generation of monocytederived Dendritic Cells (modcs)
 monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
Generation of ST2-GFP reporter mice and characterization of ILC1 cells following infection
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of ST2-GFP reporter mice and characterization of ILC1 cells following infection with influenza virus. (a) ST2-GFP reporter mice were generated as described in Methods.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of ST2-GFP reporter mice and characterization of ILC1 cells following infection with influenza virus. (a) ST2-GFP reporter mice were generated as described in Methods.
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
In Vitro Growth of Erythropoietic Progenitor Cells in Long-%rm Remission of Acute Leukemia
 International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 186-191 (1986) In Vitro Growth of Erythropoietic Progenitor Cells in Long-%rm Remission of Acute Leukemia C. Peschel, G. Konwalinka, D. Geissler, H. Bmunsteiner
International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 186-191 (1986) In Vitro Growth of Erythropoietic Progenitor Cells in Long-%rm Remission of Acute Leukemia C. Peschel, G. Konwalinka, D. Geissler, H. Bmunsteiner
CD44
 MR1-5-OP-RU CD24 CD24 CD44 MAIT cells 2.78 11.2 WT RORγt- GFP reporter 1 5 1 4 1 3 2.28 1 5 1 4 1 3 4.8 1.6 8.1 1 5 1 4 1 3 1 5 1 4 1 3 3.7 3.21 8.5 61.7 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 TCRβ 2 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 CD44 1 2 GFP
MR1-5-OP-RU CD24 CD24 CD44 MAIT cells 2.78 11.2 WT RORγt- GFP reporter 1 5 1 4 1 3 2.28 1 5 1 4 1 3 4.8 1.6 8.1 1 5 1 4 1 3 1 5 1 4 1 3 3.7 3.21 8.5 61.7 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 TCRβ 2 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 CD44 1 2 GFP
Recommended reading: Abbas et al. 5th edition, chapters 7 and 10; Janeway and Travers, 5th edition, chapter 7.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
BMP4/Smad5 dependent stress erythropoiesis is required for the expansion of erythroid progenitors during fetal development
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Developmental Biology 317 (2008) 24 35 www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology BMP4/Smad5 dependent stress erythropoiesis is required for the expansion of erythroid
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Developmental Biology 317 (2008) 24 35 www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology BMP4/Smad5 dependent stress erythropoiesis is required for the expansion of erythroid
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
NK cell lytic activity is often inhibited by MHC class I
 Acquisition of Ly49 Receptor Expression by Developing Natural Killer Cells By Jeffrey R. Dorfman and David H. Raulet From the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology and the Cancer Research Laboratory,
Acquisition of Ly49 Receptor Expression by Developing Natural Killer Cells By Jeffrey R. Dorfman and David H. Raulet From the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology and the Cancer Research Laboratory,
Efficient Isolation of Mouse Liver NKT Cells by Perfusion
 Efficient Isolation of Mouse Liver NKT Cells by Perfusion Xianfeng Fang 1,2, Peishuang Du 1, Yang Liu 3 *, Jie Tang 1 * 1 Center for Infection and Immunity, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of
Efficient Isolation of Mouse Liver NKT Cells by Perfusion Xianfeng Fang 1,2, Peishuang Du 1, Yang Liu 3 *, Jie Tang 1 * 1 Center for Infection and Immunity, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Leptin is a small 16-KDa protein produced primarily by
 A role for leptin in sustaining lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis Kate Claycombe*, Louis E. King, and Pamela J. Fraker* Departments of *Food Science and Human Nutrition and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
A role for leptin in sustaining lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis Kate Claycombe*, Louis E. King, and Pamela J. Fraker* Departments of *Food Science and Human Nutrition and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1175194/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Vital Role for Interleukin-21 in the Control of a Chronic Viral Infection John S. Yi, Ming Du, Allan J. Zajac* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1175194/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Vital Role for Interleukin-21 in the Control of a Chronic Viral Infection John S. Yi, Ming Du, Allan J. Zajac* *To whom
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Idoyaga et al. 10.1073/pnas.0812247106 SSC a) Single cell suspension 99 Aqua b) Live cells 96 -W c) Singlets 92 -A CD19+ER119 d) CD19 ER119 cells 97 CD3 e) CD3 cells 27 f) DX5 cells
Supporting Information Idoyaga et al. 10.1073/pnas.0812247106 SSC a) Single cell suspension 99 Aqua b) Live cells 96 -W c) Singlets 92 -A CD19+ER119 d) CD19 ER119 cells 97 CD3 e) CD3 cells 27 f) DX5 cells
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet
 Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
123 J. Exp. Med. 9 The Rockefeller University Press /94/07/0123/10 $2.00 Volume 180 July
 Lymphoid and Myeloid Differentiation of Fetal Liver CD34+Lineage - Cells in Human Thymic Organ Culture By Alicia B~ircena, Anne H. M. Galy, Juha Punnonen, Marcus O. Muench, Dominique Schols, Maria Grazia
Lymphoid and Myeloid Differentiation of Fetal Liver CD34+Lineage - Cells in Human Thymic Organ Culture By Alicia B~ircena, Anne H. M. Galy, Juha Punnonen, Marcus O. Muench, Dominique Schols, Maria Grazia
FLOW CYTOMETRY PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE. Toby Eyre Consultant Haematologist Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust June 2018
 FLOW CYTOMETRY PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE Toby Eyre Consultant Haematologist Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust June 2018 Aims and Objectives Principles of flow cytometry Preparation Steps involved
FLOW CYTOMETRY PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE Toby Eyre Consultant Haematologist Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust June 2018 Aims and Objectives Principles of flow cytometry Preparation Steps involved
Key Words. AC133 antigen CD34 antigen Cord blood Peripheral blood 2003;21:
 Stem Cells Original Article Differences Between Peripheral Blood and Cord Blood in the Kinetics of Lineage-Restricted Hematopoietic Cells: Implications for Delayed Platelet Recovery Following Cord Blood
Stem Cells Original Article Differences Between Peripheral Blood and Cord Blood in the Kinetics of Lineage-Restricted Hematopoietic Cells: Implications for Delayed Platelet Recovery Following Cord Blood
Fig. S1 A. week 4 week 6
 Fig. S1 Trabecular Number Trabecular Thickness number/mm 3.5 3. 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 mm.45.4.35.3.25.2.15.1.5 SKG-c SKG-A mm 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4.2 Trabecular Spacing D. week 4 week 6 Figure S1. MicroCT analysis
Fig. S1 Trabecular Number Trabecular Thickness number/mm 3.5 3. 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 mm.45.4.35.3.25.2.15.1.5 SKG-c SKG-A mm 1.4 1.2 1..8.6.4.2 Trabecular Spacing D. week 4 week 6 Figure S1. MicroCT analysis
Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas
 University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen Feasibility of hyperthermia as a purging modality in autologous bone marrow transplantation Wierenga, Pieter Klaas IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
