Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
|
|
|
- Egbert Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1 (SSTR1), meiotic recombination protein 8 (REC8), and interleukin 15 receptor, alpha (IL15RA) were identified as novel Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) driven promoter hypermethylated genes in EBV-positive AGS- EBV, compared with EBV-negative AGS. 2. Transcriptional silence of SSTR1 and REC8 in EBV-associated gastric cancers is mediated by promoter methylation. This association was not observed for IL15RA. 3. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments revealed that SSTR1 and REC8 acted as tumour suppressors through modulating cell proliferation, cell cycling, apoptosis, and migration. Hong Kong Med J 2017;23(Suppl 5):S17-22 RFCID project number: J Yu, KF To, QY Liang Institute of Digestive Disease, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong * Principal applicant and corresponding author: junyu@cuhk.edu.hk Introduction Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) associated gastric cancer accounts for 8% to 10% of all gastric cancers. Its clinicopathological features are distinct from EBVnegative gastric cancer. 1 EBV-associated gastric cancer has been reported to involve promoter hypermethylation of tumour suppressors. 2,3 We identified Somatostatin receptor 1 (SSTR1), meiotic recombination protein 8 (REC8), and interleukin 15 receptor, alpha (IL15RA) to be novel EBV-driven promoter hypermethylated genes in EBV-positive AGS-EBV, compared with EBV-negative AGS. 4 SSTR proteins belong to the G protein-coupled receptor family and are crucial in regulating the growth inhibitory effect of somatostatin and reducing tumour cell growth. The meiotic cohesin REC8 belongs to the cohesin protein complex, which is essential for correct chromosome disjunction and homologous recombination during mitosis and meiosis. Whether these hypermethylated genes are associated with EBV-associated gastric cancer remains elusive. In this study, we examined the epigenetic regulation, clinical significance, biological function, and molecular mechanism of these genes in gastric cancer. Methods Gastric cancer tissue samples were collected at the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou from 1999 to 2006 and Prince of Wales Hospital, The Chinese University of Hong Kong from 2005 to The presence of EBV was determined by detection of EBV-encoded RNA (EBER). This study was approved by the ethics committees of both The Chinese University of Hong Kong and the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen University. Informed consent was obtained from each subject. The methylation status was evaluated using bisulfite genomic sequencing, combined bisulfite restriction analysis, and pyrosequencing. Loss- and gain-of-function experiments on SSTR1 and REC8 were performed after knock-down by shrna transfection and overexpression by vector transfection in gastric cancer cell lines. Cell growth was evaluated by cell viability and colony formation assay. The cell cycle distribution and apoptosis were determined by flow cytometry. Migration ability and invasiveness were assessed by wound healing and Matrigel invasion assays. Molecular mechanisms were elucidated by Human Cancer Pathway Array. Results SSTR1 mrna expression was reduced or silenced in 63.4% (7/11) of gastric cancer cell lines, but readily expressed in normal gastric tissues. Promoter hypermethylation of SSTR1 was detected in cells with SSTR1 down-regulation (Fig 1). The promoter methylation level of SSTR1 was higher in EBV-positive than EBV-negative gastric cancers (15.04±8.69% vs 6.93±3.01%, P=0.004). Using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, a cut-off value of 9.675% in SSTR1 promoter methylation could discriminate EBV-positive from EBV-negative gastric cancers, with 75% sensitivity and 85.7% specificity (area under the ROC curve [AUC]=0.777, 95% confidence interval [CI]= ). SSTR1 promoter methylation was associated with male gender (P=0.024) and EBER positive staining (P<0.005). Hong Kong Med J Volume 23 Number 4 (Supplement 5) August
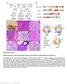
2 # Yu et al # (a) (b) (c) P=0.004 (d) (e) (f) (g) Sensitivity (%) 100% - Specificity (%) Years FIG 1. Promoter methylation of SSTR1 and REC8 in gastric cancer: (a) SSTR1 mrna expression was down-regulated in AGS Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and other gastric cancer cells but expressed at a high level in normal stomach mucosa. (b) SSTR1 methylation level was higher in EBV-positive than EBVnegative gastric cancer. (c) SSTR1 methylation correlated with EBV infection in gastric cancers. (d) Transcriptional silencing of REC8 in gastric cancer was associated with DNA methylation. REC8 expression was silenced in 9 of 13 tested gastric cancer cell lines and correlated with promoter methylation. (e) REC8 methylation level was higher in EBV-positive and EBV-negative gastric cancers than normal stomach. (f) REC8 methylation level could discriminate gastric cancer from normal mucosa, as well as EBV-positive from EBV-negative gastric cancer. (g) High methylation level of REC8 (>55%) correlated with shortened survival in gastric cancer patients. 18 Hong Kong Med J Volume 23 Number 4 (Supplement 5) August
3 # Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer # REC8 mrna expression was silenced in 9 of 13 tested gastric cancer cell lines, and this was correlated with promoter methylation (Fig 1). Promoter methylation level of REC8 was higher in EBV-positive than EBV-negative gastric cancers (74.8±3.9% vs 48.9±4.3%, P=0.0005), and in both gastric cancers than normal stomach mucosa (14.4±2.0%, both P<0.0001). REC8 promoter methylation was associated with EBER positive staining (r=23.73, 95% CI= , P=0.001) but not with other clinicopathological features. Using ROC curve analysis, a cut-off value of 33.4% in REC8 promoter methylation could discriminate gastric cancer from normal mucosa, with 93.3% sensitivity and 100% specificity (AUC=0.96, 95% CI= ). A cut-off value of 68.1% could discriminate EBVpositive from EBV-negative gastric cancer, with 84.6% sensitivity and 94.1% specificity (AUC=0.91, 95% CI= ). REC8 was down-regulated by promoter methylation in gastric cancer, especially in the EBV-positive subtype. In patients with EBV-negative gastric cancer, a high level of REC8 promoter methylation (>55%) predicted shortened survival (P=0.025). IL15RA was down-regulated via promoter methylation specifically in AGS-EBV but this was not a common phenomenon in gastric cancer (data not shown). To investigate the function of SSTR1 in gastric cancer, SSTR1 expression was knocked down by shrna transfection in BGC823 cells as evidenced by western blot (Fig 2). SSTR1 knock-down increased cell viability as indicated by MTS assay (P<0.05) and clonogenicity of BGC823 as indicated by colony assay (P<0.05). Cell cycle progression was promoted, with decreased cells in G1 phase (P<0.01) and increased cells in S phase (P<0.001). SSTR1 knockdown also increased migration ability (P<0.01) and invasiveness (P<0.01) of BGC823 cells. Similar effects were also observed in AGS cells (data not shown). In gain-of-function experiments, ectopic expression of SSTR1 in MGC803 cells was evidenced by western blot. SSTR1 inhibited clonogenicity of MGC803 cells (P<0.01) and growth of xenograft tumours derived from MGC803 in vivo (n=9/group). The molecular basis of SSTR1 was revealed by pathway cdna array and western blot. SSTR1 functioned as a tumour suppressor through regulating cell cycle progression, inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and suppressing migration/invasion. We overexpressed REC8 in AGS-EBV cells for gain-of-function experiments. Ectopic expression of REC8 was evidenced by western blot (Fig 3). Cell viability was decreased as indicated by MTS assay (P<0.05). REC8 also inhibited clonogenicity of AGS-EBV cells (P<0.01) and cell cycle progression, with increased cells in G1 phase (P<0.05) and decreased cells in S phase (P<0.001). REC8 also induced apoptosis and suppressed the migration ability of AGS-EBV cells. Similar effects were also observed in BGC823 cells (data not shown). When REC8 expression was knocked down in GES-1 cells, cell growth was promoted as evidenced by increased cell viability and clonogenicity. REC8 knock-down also increased cell migration ability. REC8 also functioned as a tumour suppressor through regulating cell cycle progression, inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and suppressing migration/invasion. Discussion SSTR1 promoter methylation was associated with EBV infection and may play a role in the development of EBV-associated gastric cancer. EBV infection was the only factor associated with a high REC8 promoter methylation level. Higher REC8 promoter methylation correlated with shortened survival in gastric cancer patients. Promoter methylationmediated silencing of REC8 may play a role in gastric carcinogenesis. SSTR1 might exert its tumour suppressive function through proliferation and apoptosis regulators, inducing MDM2, AKT, PI3KR1, BCL-XL, and MET. The increased G1/S phase transition by SSTR1 knock-down might be associated with downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p15, p16, p21, and p27 and upregulation of MYC and CDC25A. The suppressive effect of SSTR1 on migration and invasion ability might be due to the down-regulation of integrin family members (ITGA1, ITGA2, ITGA3, and ITGB5 subunits), and other important migration/invasion-related genes MMP1, PLAUR, and IL8. The anti-growth effect of REC8 might be mediated by inhibiting the cell proliferation regulators (G6PD and SLC2A1) and apoptosis inhibitor (NOL3), while inducing expression of the apoptosis regulator (GADD45G) and tumour suppressors (PinX1, IGFBP3, and ETS2). REC8 caused cell-cycle arrest at G1/S transition through inhibiting MCM2 and increasing PinX1. The anti-migration function of REC8 may be mediated through inhibiting EMT promoters SNAI1 and SNAI2 (that are involved in generating de-differentiated cells) and inducing the migration inhibitor LDHA. Whether these cancerassociated genes modulated by altered expression of SSTR1 or REC8 are direct downstream targets requires further investigation. Conclusion Both SSTR1 and REC8 are novel EBV-associated promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer. They play a role in suppressing gastric cancer through modulating the expression of important effectors involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, Hong Kong Med J Volume 23 Number 4 (Supplement 5) August
4 # Yu et al # (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) FIG 2. SSTR1 as a tumour suppressor in gastric cancer: (a) SSTR1 expression was knocked down by shrna transfection. (b) SSTR1 knock-down increased cell viability. (c) SSTR1 knock-down increased clonogenicity in BGC823 (52.6±9.1% increase, P<0.05). (d) SSTR1 knock-down promoted cell cycle progression (G1 phase, P<0.01; S phase, P<0.001). (e) SSTR1 knock-down increased the migration ability (1.2±0.0 fold, P<0.01) and invasiveness (1.9±0.4 fold, P<0.01) of BGC823. (f) Ectopic expression of SSTR1 in MGC803 cells. (g) SSTR1 inhibited tumour cell clonogenicity of MGC803 (68.8±10.9% decrease, P<0.01). (h) SSTR1 inhibited growth of xenograft tumours derived from MGC803 in vivo (n=9/group). (i) Schematic diagram of the molecular events for SSTR1 function as a tumour suppressor through regulating cell cycle progression, inhibiting proliferation, inducing apoptosis and suppressing migration/invasion. 20 Hong Kong Med J Volume 23 Number 4 (Supplement 5) August
5 # Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer # (a) (b) (c) P<0.001 (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) Gene expression Down-regulated Up-regulated Cellular activity Inhibited Promoted FIG 3. REC8 as a tumour suppressor in gastric cancer: (a) ectopic expression of REC8 in AGS Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cells. (b) REC8 suppressed cell viability in both AGS-EBV cells. (c) REC8 reduced clonogenicity in both AGS-EBV cells (66.7±6.0%, P<0.05). (d) REC8 inhibited cell cycle progression by increasing cells in G1 phase (P<0.05) and reducing cells in S phase (P<0.001). (e) REC8 induced cell apoptosis in AGS-EBV cells. (f) REC8 inhibited the migration ability of AGS-EBV (60.9±6.2%, P<0.01). (g) REC8 was knocked down in GES-1. (h) REC8 knock-down increased cell viability in GES-1 cells. (i) REC8 knock-down increased clonogenicity in GES-1 cells. (j) REC8 knock-down increased the migration ability of GES-1 cells (P<0.01). (k) Schematic diagram of the molecular events for REC8 function as a tumour suppressor through inhibiting proliferation, regulating cell cycle progression, inducing apoptosis, and suppressing cell migration. Hong Kong Med J Volume 23 Number 4 (Supplement 5) August
6 # Yu et al # cell cycle, apoptosis, and cell migration/invasion. Epigenetic silencing of REC8 or SSTR1 by EBV infection may contribute to the pathogenesis of EBV-associated gastric cancer. Acknowledgement This study was supported by the Research Fund for the Control of Infectious Diseases, Food and Health Bureau, Hong Kong SAR Government (# ). Results of this study have been published in: (1) Yu J, Liang Q, Wang J, et al. REC8 functions as a tumor suppressor and is epigenetically downregulated in gastric cancer, especially in EBV-positive subtype. Oncogene 2017;36: (2) Zhao J1, Liang Q, Cheung KF, et al. Somatostatin receptor 1, a novel EBV-associated CpG hypermethylated gene, contributes to the pathogenesis of EBV-associated gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 2013;108: References 1. Uozaki H, Fukayama M. Epstein-Barr virus and gastric carcinoma--viral carcinogenesis through epigenetic mechanisms. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2008;1: Sudo M, Chong JM, Sakuma K, et al. Promoter hypermethylation of E-cadherin and its abnormal expression in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2004;109: Kaneda A, Matsusaka K, Aburatani H, Fukayama M. Epstein-Barr virus infection as an epigenetic driver of tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2012;72: Zhao J, Liang Q, Cheung KF, et al. Genome-wide identification of Epstein-Barr virus-driven promoter methylation profiles of human genes in gastric cancer cells. Cancer 2013;119: Hong Kong Med J Volume 23 Number 4 (Supplement 5) August
Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p.
 Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
CH Cho *, J Yu, WKK Wu 1,2
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Identification of pathogenic micrornas in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer using a combined approach of animal study and clinical sample
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Identification of pathogenic micrornas in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer using a combined approach of animal study and clinical sample
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes ~ 4.6 -
 Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD
 RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus entry
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed.
 Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
Dynamic cohesin-mediated chromatin architecture controls epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in cancer
 Article Dynamic cohesin-mediated chromatin architecture controls epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in cancer Jiyeon Yun,, Sang-Hyun Song, Hwang-Phill Kim, Sae-Won Han,, Eugene C Yi & Tae-You Kim,,, Abstract
Article Dynamic cohesin-mediated chromatin architecture controls epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in cancer Jiyeon Yun,, Sang-Hyun Song, Hwang-Phill Kim, Sae-Won Han,, Eugene C Yi & Tae-You Kim,,, Abstract
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer. Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee
 MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
Title: LATS2 is De-methylated and Overexpressed in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Predicts Poor Prognosis of the Patients
 Author's response to reviews Title: LATS2 is De-methylated and Overexpressed in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Predicts Poor Prognosis of the Patients Authors: Yan Zhang (zhangy2@sysucc.org.cn) Chun-Fang
Author's response to reviews Title: LATS2 is De-methylated and Overexpressed in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Predicts Poor Prognosis of the Patients Authors: Yan Zhang (zhangy2@sysucc.org.cn) Chun-Fang
Paul Murray University of Birmingham
 Paul Murray University of Birmingham College of Medical and Dental Sciences The people of the Midlands have every reason to be supremely proud of this great centre of healing, of teaching and of research.
Paul Murray University of Birmingham College of Medical and Dental Sciences The people of the Midlands have every reason to be supremely proud of this great centre of healing, of teaching and of research.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical Informatics (CoSBBI) Outline. Molecular Biology of Cancer AND. Goals/Expectations. David Boone 7/1/2015
 Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 mutation as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study PKS Chan *, JSY Chor, AC Vlantis, TL
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and p53 as risk factors in oropharyngeal cancer: a case-control study PKS Chan *, JSY Chor, AC Vlantis, TL
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition
 Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Clinical and experimental role of ring finger protein 180 on lymph node metastasis and survival in gastric cancer
 Original article Clinical and experimental role of ring finger protein 180 on lymph node metastasis and survival in gastric cancer J. Deng 1,H.Liang 1, R. Zhang 1,Y.Hou 1,Y.Liu 1, G. Ying 2,Y.Pan 3 and
Original article Clinical and experimental role of ring finger protein 180 on lymph node metastasis and survival in gastric cancer J. Deng 1,H.Liang 1, R. Zhang 1,Y.Hou 1,Y.Liu 1, G. Ying 2,Y.Pan 3 and
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
ROLE OF TGF-BETA SIGNALING IN PIK3CA-
 ROLE OF TGF-BETA SIGNALING IN - DRIVEN HEAD AND NECK CANCER INVASION AND METASTASIS 1,2 Sophia Bornstein, 3 Jingping Shen, 3 Jacob Minor, 3 Frank Hall, 3 Fang Zhang, 4 Sherif Said, 4 Xiao-Jing Wang, 1
ROLE OF TGF-BETA SIGNALING IN - DRIVEN HEAD AND NECK CANCER INVASION AND METASTASIS 1,2 Sophia Bornstein, 3 Jingping Shen, 3 Jacob Minor, 3 Frank Hall, 3 Fang Zhang, 4 Sherif Said, 4 Xiao-Jing Wang, 1
Down-regulated expression of OPCML predicts an unfavorable prognosis and promotes disease progression in human gastric cancer
 Xing et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:268 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3203-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Down-regulated expression of OPCML predicts an unfavorable prognosis and promotes disease progression in
Xing et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:268 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3203-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Down-regulated expression of OPCML predicts an unfavorable prognosis and promotes disease progression in
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
BIO360 Quiz #1. September 14, Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points)
 Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS
 R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS EPIGENETICS THE STUDY OF CHANGES IN GENE EXPRESSION THAT ARE POTENTIALLY HERITABLE AND THAT DO NOT ENTAIL A
R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS EPIGENETICS THE STUDY OF CHANGES IN GENE EXPRESSION THAT ARE POTENTIALLY HERITABLE AND THAT DO NOT ENTAIL A
Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis
 Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs
 p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Review Article Effect of mir-200b on metastasis of gastric cancer
 Am J Digest Dis 2017;4(1):1-5 www.ajdd.us /ISSN:2329-6992/AJDD0040112 Review Article Effect of mir-200b on metastasis of gastric cancer Leyu Chiu 1, Brock Humphries 2,3 1 College of Human Medicine, 2 Department
Am J Digest Dis 2017;4(1):1-5 www.ajdd.us /ISSN:2329-6992/AJDD0040112 Review Article Effect of mir-200b on metastasis of gastric cancer Leyu Chiu 1, Brock Humphries 2,3 1 College of Human Medicine, 2 Department
http / /cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology A431 . Western aza-dC FUT4-siRNA
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
mir-26a inhibits invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal cancer by targeting EZH2
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS mir-26a inhibits invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal cancer by targeting EZH2 LI YU 1, JUAN LU 1, BAO ZHANG 2, XIONG LIU 1, LU WANG 1, SI-YANG LI 1, XIAO-HONG PENG 1, XIA XU 1, WEN-DONG
ONCOLOGY LETTERS mir-26a inhibits invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal cancer by targeting EZH2 LI YU 1, JUAN LU 1, BAO ZHANG 2, XIONG LIU 1, LU WANG 1, SI-YANG LI 1, XIAO-HONG PENG 1, XIA XU 1, WEN-DONG
Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing SOX4
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK
 TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
Expression of p53, p21 /waf l, bcl-2, bax, Rb and Ki67 proteins in Hodgkin's lymphomas
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 445-453 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Expression of p53, p21 /waf l, bcl-2, bax, Rb and Ki67 proteins in
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 445-453 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Expression of p53, p21 /waf l, bcl-2, bax, Rb and Ki67 proteins in
EBV infection B cells and lymphomagenesis. Sridhar Chaganti
 EBV infection B cells and lymphomagenesis Sridhar Chaganti How EBV infects B-cells How viral genes influence the infected B cell Differences and similarities between in vitro and in vivo infection How
EBV infection B cells and lymphomagenesis Sridhar Chaganti How EBV infects B-cells How viral genes influence the infected B cell Differences and similarities between in vitro and in vivo infection How
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association with Pathological Features
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
MiRNA-516b inhibits ameloblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating MYCBP/c-myc/RECK/MMP pathway
 Original Article MiRNA-516b inhibits ameloblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating MYCBP/c-myc/RECK/MMP pathway Liming Duan 1, You Wu 1, Yancan Liang 1, Di Wan 2, Daming Zhang 1, Bin Zhang
Original Article MiRNA-516b inhibits ameloblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating MYCBP/c-myc/RECK/MMP pathway Liming Duan 1, You Wu 1, Yancan Liang 1, Di Wan 2, Daming Zhang 1, Bin Zhang
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development
 Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development Sen-Yung Hsieh, MD, PhD Liver Research Unit Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Taoyuan, Taiwan Aims To identify genes controlling tumor
Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development Sen-Yung Hsieh, MD, PhD Liver Research Unit Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Taoyuan, Taiwan Aims To identify genes controlling tumor
Course Title Form Hours subject
 Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
Oncolytic virus strategy
 Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
Molecular Probes Introducing 14 new probes
 Molecular Probes Introducing 14 new probes Gene and Chromosome Probes Dual Colour ISH INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail Assay Product Part Number INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail 800-4422
Molecular Probes Introducing 14 new probes Gene and Chromosome Probes Dual Colour ISH INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail Assay Product Part Number INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail 800-4422
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
 Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets PUMA to promote host cell survival
 An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
Introduction. Methods RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Human epigenetic alterations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection: a novel platform to eavesdrop interactions between M tuberculosis and host immunity
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Human epigenetic alterations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection: a novel platform to eavesdrop interactions between M tuberculosis and host immunity
Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery & VP Integrated Health Services University of Saskatchewan & Saskatoon Health Region
 Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
TITLE: TREATMENT OF ENDOCRINE-RESISTANT BREAST CANCER WITH A SMALL MOLECULE C-MYC INHIBITOR
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-13-1-0159 TITLE: TREATMENT OF ENDOCRINE-RESISTANT BREAST CANCER WITH A SMALL MOLECULE C-MYC INHIBITOR PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Qin Feng CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College of
AD Award Number: W81XWH-13-1-0159 TITLE: TREATMENT OF ENDOCRINE-RESISTANT BREAST CANCER WITH A SMALL MOLECULE C-MYC INHIBITOR PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Qin Feng CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College of
Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 131-136, 2014 Prognostic significance of nemo like kinase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SIZE CHEN 1,2*, ZHIJIAN MA 3*, XUEMEI CHEN 4 and JIREN ZHANG 1 1 Department of Oncology,
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Introduction. Methods RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES. TCW Poon *, HLY Chan, HWC Leung, A Lo, RHY Lau, AY Hui, JJY Sung
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Liver specific glycoforms of serum proteins in chronic hepatitis B infection: identification by lectin affinity chromatography and quantitative proteomic
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Liver specific glycoforms of serum proteins in chronic hepatitis B infection: identification by lectin affinity chromatography and quantitative proteomic
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Hsin-Pai Li ( 黎欣白 ) School: University of Southern California/ USA (Department of Microbiology)
 Title: Assistant Professor Highest Degree: Ph.D. Ext: #3593 Location: Rm 0757 MS students (at present): 2 Undergraduate students (at present): 2 Hsin-Pai Li ( 黎欣白 ) Lab: Tumor Virus and Cancer Research
Title: Assistant Professor Highest Degree: Ph.D. Ext: #3593 Location: Rm 0757 MS students (at present): 2 Undergraduate students (at present): 2 Hsin-Pai Li ( 黎欣白 ) Lab: Tumor Virus and Cancer Research
Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer
 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer Robert A. Weinberg 1 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer 2 Review (V1) - Number of somatic mutations in human cancers Top: children vs. adults Numbers in parentheses
Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer Robert A. Weinberg 1 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer 2 Review (V1) - Number of somatic mutations in human cancers Top: children vs. adults Numbers in parentheses
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Gene therapy: State of the art. Ramon Gomis MD, PhD, MAE. Hospital Clínic. IDIBAPS. University of Barcelona.
 Gene therapy: State of the art Ramon Gomis MD, PhD, MAE. Hospital Clínic. IDIBAPS. University of Barcelona. Gene Therapy: First Steps Type 1 diabetes: An islet disease Alpha cell Beta cell Pancreatic
Gene therapy: State of the art Ramon Gomis MD, PhD, MAE. Hospital Clínic. IDIBAPS. University of Barcelona. Gene Therapy: First Steps Type 1 diabetes: An islet disease Alpha cell Beta cell Pancreatic
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
Targeting Kinases Critical for TMPRSS2-ERG Function in Prostate Cancer
 Targeting Kinases Critical for TMPRSS2-ERG Function in Prostate Cancer Kyle Nakatsuka David Takeda, MD, PhD Lab of William Hahn, M.D., Ph.D. Broad Institute Summer Research Program in Genomics TMPRSS2-ERG
Targeting Kinases Critical for TMPRSS2-ERG Function in Prostate Cancer Kyle Nakatsuka David Takeda, MD, PhD Lab of William Hahn, M.D., Ph.D. Broad Institute Summer Research Program in Genomics TMPRSS2-ERG
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics. DNA methylation in prostate cancer
 Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Case Study - Informatics
 bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
