mirna-378 reverses chemoresistance to cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting secreted clusterin
|
|
|
- Ashley Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Rhode Island Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences Faculty Publications Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2016 mirna-378 reverses chemoresistance to cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting secreted clusterin Xuesong Chen Ying Jiang See next page for additional authors Creative Commons License This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. Follow this and additional works at: Citation/Publisher Attribution Chen, X. et al. mirna-378 reverses chemoresistance to cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting secreted clusterin. Sci. Rep. 6, 19455; doi: /srep19455 (2016). Available at: This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences at DigitalCommons@URI. It has been accepted for inclusion in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences Faculty Publications by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@URI. For more information, please contact digitalcommons@etal.uri.edu.
2 Authors Xuesong Chen, Ying Jiang, Zheping Huang, Dandan Li, Xiaodi Chen, Mengru Cao, Qingwei Meng, Hui Pang, Lichun Sun, Yanbin Zhao, and Li Cai This article is available at
3 OPEN received: 21 November 2014 accepted: 14 December 2015 Published: 19 January 2016 mirna-378 reverses chemoresistance to cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting secreted clusterin Xuesong Chen 1,*, Ying Jiang 1,*, Zheping Huang 2,*, Dandan Li 1, Xiaodi Chen 3, Mengru Cao 1, Qingwei Meng 1, Hui Pang 1, Lichun Sun 1, Yanbin Zhao 1 & Li Cai 1 Cisplatin resistance is a major obstacle in the treatment of NSCLC, and its mechanism has not been fully elucidated. The objectives of the study were to determine the role of mir-378 in the sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin (cddp) and its working mechanism. With TargetScan and luciferase assay, mir-378 was found to directly target sclu. mir-378 and sclu were regulated in A549/cDDP and Anip973/cDDP cells to investigate the effect of mir-378 on the sensitivity and apoptotic effects of cddp. The effect of mir-378 upregulation on tumor growth was analyzed in a nude mouse xenograft model. The correlation between mir-378 and chemoresistance was tested in patient samples. We found that upregulation of mir-378 in A549/cDDP and Anip973/cDDP cells significantly down-regulated sclu expression, and sensitized these cells to cddp. mir-378 overexpression inhibited tumor growth and sclu expression in a xenograft animal model. Analysis of human lung adenocarcinoma tissues revealed that the cddp sensitive group expressed higher levels of mir-378 and lower levels of sclu. mir-378 and sclu were negatively correlated. To conclude, we identified sclu as a novel mir-378 target, and we showed that targeting sclu via mir-378 may help disable the chemoresistance against cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in both males and females worldwide 1. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for 80 85% of all lung cancer cases 2. Cisplatin, a DNA-damaging cytotoxic agent, is the first-line therapy in NSCLC treatment, but its efficacy is often impaired by the development of drug resistance 3. Although lots of studies have been done on the resistance to cisplatin 3,4, the mechanisms involved are not fully understood, so further study is needed. Clusterin (CLU) is a secreted glycoprotein which is involved in many physiological processes, such as apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, and DNA repair 5 7. It has two main isoforms: secreted form (sclu) and nuclear form (nclu). A previous study in our lab showed that sclu is associated with resistance to cddp in NSCLC 8. Other reports have also demonstrated that sclu is a key contributor to chemoresistance to anticancer agents 6. sclu is expressed in aggressive late stage tumors. Its expression can lead to the development of broad-based resistance to different chemotherapeutic agents. Inhibition of sclu could improve the effect of chemotherapy on human tumor cells 9. MicroRNAs are a class of short, non-coding RNA molecules involved in numerous biological processes, such as cell self-renewal and cancer development 10. By binding with the 3 untranslated region (UTR) of target mrnas, mirna works as a guide molecule in post-transcriptional gene silencing, leading to degradation of target mrna, or repression of translation 11. A growing body of evidence suggests that mirnas may be involved in the development of chemoresistance, and may also play a role in the modulation of drug resistance-related pathways in cancer cells Department of Internal Medical Oncology, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin, Heilongjiang Province, China. 2 Department of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI, USA. 3 Department of Pediatrics, The Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island, Providence, RI, * These authors contributed equally to this work. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to L.C. ( caiwenxin76@163.com) or Y.Z. ( zhaoyanbin1978@sina.com) 1
4 Figure 1. mir-378 directly Targets sclu. (A) The upper panel is the predicted mir-378 binding site with CLU3 UTR. The lower panel is the mir-378 sequence containing the putative sclu binding site and its mutant sequence. (B) Dual luciferase assay was performed with co-transfection of mir-378 mimics and the reporter containing sclu 3 -UTR wild-type versus mutant. (C) RT-PCR results showed that A549 cells had higher expression of mir-378 compared with A549/cDDP cells. The lower panel is the representative picture of DNA electrophoresis after PCR. (D) The Western blot analysis showed the protein level of sclu in A549 cells and A549/cDDP cells. The lower panel showed the representative blots. All results are from three separate experiments. (*P < 0.05, ***P < Full-length blots are presented in Supplement.). In this report, we demonstrated that mir-378 targets sclu, and explored its possible roles in chemoresistance to cddp in lung adenocarcinoma cells. With TargetScan software, we found a group of mirnas (including mir- 378) that target CLU. Meanwhile, we found two sets of observations that helped us to focus our research on mir Using the microrna microarray to examine tumor microrna expression patterns, Eitan et al. found that seven micrornas had significantly different expressions in tumors from platinum-sensitive vs. platinum-resistant patients 15. In another article, Lu discovered that 34 mirnas were differentially expressed between the A549 and A549/cDDP cell line 16. Both reports demonstrated that mir-378 might be important in the chemoresistance to platinum, but the mechanisms for the effect remain poorly understood. Therefore, we selected mir-378 as the target of our research. Here we demonstrate that mirna-378 regulates sclu-mediated chemosensitivity to cddp in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Results mir-378 directly targets sclu. As our previous research showed that sclu is related to the development of chemoresistance to cddp, We used the bioinformatics tool (TargetScan, to search the mirnas that may target sclu, which revealed many candidates (including mir-378). As two sets of observations showed that mir-378 is important in chemoresistance to cddp 15,16, and as we found that mir-378 was identified as one of the mirna that target sclu, we focused our research on mir-378. As shown in Fig. 1A, the sequence of mir-378 was partially complementary to the 3 untranslated region (UTR) of the sclu mrnas (7 nucleotides completely match). To verify that mir-378 targets sclu, we cloned a fragment of CLU 3 UTR containing the putative mir-378 binding site, or its mutated one, into a luciferase reporter vector, and performed dual luciferase assays in 293T cells. The results showed that up-regulation of mir-378 significantly decreased the relative luciferase activity of wild type but had no effect on the mutant 3 UTR of sclu (Fig. 1B). Next, we compared the expression of mir-378 and sclu in the cisplatin-resistant A549 cell line (A549/cDDP) with its parental A549 cell line. The A549/cDDP cell line had a lower level of mir-378 and a higher level of sclu compared with the A549 cell line (Fig. 1C,D). In addition, our previous research showed that Anip973/cDDP had a higher level of sclu 8, 2
5 Figure 2. mir-378 and sclu affects A549/cDDP cell s sensitivity to cddp and apoptosis in cells. (A) MTT assay results showed that both mir-378 overexpression or sclu knockdown in A549/cDDP significantly decreased the IC 50 ; after sclu knockdown, mir-378 overexpression had no effect. (B,C) Hoechst staining assay showed that the apoptosis rate significantly increased in mir-378 overexpression cells compared with vector controls; after sclu knockdown, mir-378 overexpression had no effect on apoptosis. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, # P > 0.05). and here we showed that Anip973/cDDP had a lower level of mir-378 compared with the Anip973 (supplementary Figure 1A).Taken together, these results suggest that mir-378 suppresses sclu gene expression through the 3 -UTR binding and silencing of sclu mrna. The A549/cDDP and Anip973/cDDP cell lines were used in later experiments due to its higher expression of sclu. mir-378 increases sensitivity of A549/cDDP to cddp and apoptosis through sclu. To test mir- 378 s effect on A549/cDDP s sensitivity to cddp, MTT assay was performed. The results showed that overexpression of mir-378, or knockdown of sclu, both sensitized the cells to cddp (Fig. 2A). Similar results also could be seen in Anip973/cDDP, another cell line with high CLU expression 8. After sclu knockdown, mir-378 transfection had no effect on the sensitivity of the cells (Supplementary Figure 1B). In addition, overexpression of mir- 378 in A549 cells or Anip973 (both with low CLU expression 8 ) also had no effect on the sensitivity of the cells. mir-378 transfection sensitized these cells to cddp only after sclu overexpression (supplementary Figure 2). We went further to test mir-378 s effect on apoptosis. Hoechst staining assay showed that either downregulation of sclu or overexpression of mir-378 increased cell apoptosis in A549/cDDP cells and Anip973/cDDP. On the contrary, after sclu knockdown, transfection of mir-378 did not change the apoptotic rate (Fig. 2B,C, and supplementary Figure 3). These results showed that mir-378 s effect on the sensitivity of the cells to cddp or apoptosis depended on the presence of higher levels of sclu, so it strongly indicated that mir-378 affected sensitivity of the cell and apoptosis through sclu. sclu is involved in mir-378-induced cisplatin resistance in vitro. To test whether sclu is a target of mir-378, Western blot was used to check the effect of mir-378 transfection on sclu in the A549/cDDP cell line. The result showed that upregulation of mir-378 led to a significant decrease of sclu protein in A549/cDDP cells (Fig. 3A). The Western blot results also demonstrated that downregulation of sclu led to a significant decrease of perk1/2, pakt, Bcl-2, and pcaspase-3 signal in A549/cDDP cells (Fig. 3B). To further examine whether sclu is involved in mir-378 induced chemoresistance, we performed gain-of-function and loss-of-function analysis. We transfected A549/cDDP cells with the mir-378 mimics(mir-378), and performed MTT assay. The results showed that upregulation of mir-378 led to a significantly increased sensitivity to cddp in A549/cDDP cells (Fig. 3B).To test whether the above-observed phenotype was indeed due to the suppression of sclu, a rescue experiment was performed. We transfected A549/cDDP cell with an expression construct that encoded sclu coding sequence but lacked the 3 UTR. Forced expression of sclu eliminated most of the gains in the sensitivity to cddp in mir-378-overexpressing cells (Fig. 4A), and reversed the decrease of Bcl-2, pcas-3, perk1/2 and pakt (Fig. 4B). Collectively, these data strongly suggest that mir-378 regulate chemo-resistance to cddp by targeting sclu. mir-378 inhibited tumor growth and sclu expression in a nude mouse tumor xenograft model. To investigate how mir-378 overexpression affected sclu expression and tumor growth, agomir-378 3
6 Figure 3. mir-378 targets sclu and regulated its cell signal. (A) Western blot showed upregulation of mir-378 led to a significant decrease of sclu protein in A549/cDDP cells. Results are from three separate experiments. **P < (B) Western blot showed that down-regulation of sclu led to a significant decrease of perk1/2, pakt, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 in A549/cDDP cells. Full-length blots are presented in Supplement. Figure 4. sclu is involved in mir-378-induced cisplatin resistance. (A) A549/DDP cells were transfected with Mock, mir-378 mimics or sclu plasmid lacking 3 UTR along with mir-378, MTT assays were used to measure cisplatin sensitivity (*P < 0.05 **P < 0.01). (B) sclu, perk1/2, pakt, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 protein levels were detected by Western blot analysis. cells and cells with agomir-nc(mock) were injected into the flank of nude mice. The tumor growth curve analysis showed that mir-378 significantly inhibited the tumor growth in 18 days after the injection of cells (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5A). Western blot demonstrated that sclu was significantly down-regulated in the A549/cDDP-miR-378 cells (P < 0.05) (Fig. 5B). mir-378 and sclu correlated with sensitivity to cddp in lung adenocarcinoma tissues. To investigate the association between mir-378 and sclu expression, 33 tumor tissue samples were obtained from patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma. The characteristics of the patients were detailed in table 1 (see supplement). Based on the patients response to chemotherapy, they were divided into sensitive and insensitive groups, and the mir-378 levels and sclu expression levels of each sample were analyzed. We found that mir-378 expression level was significantly lower in the insensitive group tissues (0.40 ± 0.02) compared to the sensitive group (0.51 ± 0.03) ( P < 0.05) (Fig. 6A). On the contrary, sclu levels were significantly higher in the insensitive group tissues (0.51 ± 0.03vs 0.42 ± 0.02) (P < 0.05) (Fig. 6B). Correlation analysis showed that mir-378 was negatively correlated with sclu expression level (r = 0.538). (Fig. 6C) Discussion Resistance to cisplatin-based chemotherapy is one of the major obstacles in the treatment of NSCLC 17. Evidence demonstrates that dysregulation of specific mirnas causes the development of chemoresistance in different cancers 18,19. In this study, we identified sclu as a novel target of mir-378; we demonstrated that mir-378 overexpression could decrease sclu, enhance cell apoptosis, and sensitize lung adenocarcinoma to cddp both in vitro and in vivo. To our knowledge, our study is the first to demonstrate the association of mir-378 with the development of cddp chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma. 4
7 Figure 5. mir-378 inhibited tumor growth and sclu expression in Nude mouse tumor xenograft model. (A) Analysis of the tumor growth curves showed mir-378 significantly inhibited tumor growth 18 days after cell injection (P < 0.05). The upper panel showed the growth curves, and the lower panel showed the representative picture of tumors with mir-378 overexpression (right) and Mock (left); (B) Western blot showed mir-378 inhibited sclu expression. The upper panel showed the results of three separate experiments, and the lower panel showed the representative blot. (*P < Full-length blots are presented in Supplement). Figure 6. mir-378 and sclu are correlated with sensitivity to cddp in lung adenocarcinoma tissues. (A) RT-PCR results showed that mir-378 expression levels were significantly lower in the insensitive group than in the sensitive group, *P < 0.05; (B) The Western blot analysis showed that sclu levels were significantly higher in the insensitive group compared with the sensitive group (*P < 0.05). C. Correlation analysis shows that mir-378 negatively correlates with the sclu mrna expression level, r = (*P < 0.05). Drug resistance can develop at many levels, including increase of drug efflux, alterations in drug target, cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, and evasion of apoptosis. It has been shown previously that selective regulation of microrna activity can improve responsiveness to chemotherapy 20. mir-378 expression is found in a number of cancer cell lines 21,22, and is related to the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor 23,24. Also, mir-378 is shown to be important in chemoresistance to cddp, but no detailed mechanism is reported 15,16. We found that mir-378 is partially complementary to the 3 untranslated region (UTR) of the CLU mrnas using Bioinformatics (TargetScan) (Fig. 1A), and mir-378 can affect the luciferase activity due to canonical binding to sclu 3 -UTR (Fig. 1B). This data is corroborated by the expression of mir-378 and sclu in A549 vs A549/ cddp (Fig. 1C,D) and Anip973 vs Anip973/cDDP 8 (supplementary Figure 1A). Thus, we clearly established an inverse relationship between mir-378 and sclu. Furthermore, overexpression of mir-378 can reduce the sclu level (Fig. 3A), sensitize A549/cDDP and Anip973/cDDP cells to cddp (Fig. 2A, supplement Figures 1B and 4A), and inhibit the tumor growth in nude mice model (Fig. 5A). Moreover, our data are also corroborated by the observations in human tumor tissues obtained from patients who showed sensitivity or insensitivity to cddp, and we found an inverse correlation between mir-378 and sclu expression levels in tumor tissues samples. Interestingly, previous studies have indicated that mir-378 transfection enhanced cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis in NSCLC cells, but target genes were not identified 23,24. Also, there are some inconsistent results. Wang et al. found that mir-378 inhibited cell growth and enhanced L-OHP-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer by targeting CDC Fei et al. reported that mir-378 suppress HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth by directly targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor 26. A single mirna has the 5
8 Figure 7. A mechanistic model of regulation of lung adenocarcinoma s sensitivity to cddp via mir-378 and sclu. Upregulation of mir-378 in A549/cDDP cells significantly down-regulates sclu expression, and enhances the sensitivity of A549/cDDP cells to cddp. potential to disrupt multiple pathways involved in regulating cancer cell survival or drug response. With this in mind, the effect of mir-378 was determined by the function of target genes in the current study. Clusterin (CLU), in its cytoplasmic secretory form (sclu), has been demonstrated to mediate chemoresistance to numerous unrelated anticancer agents, and its presence has been observed in a variety of solid tumors and lymphomas 27,28. sclu can also mediate the development of resistance to targeted death-inducing molecules, tumor necrosis factor, Fas, TRAIL, or histone deacetylase inhibitors 4 6. sclu is expressed in around 40% of human NSCLC 7,29, and down-regulation of sclu by sequence-specific antisense oligonucleotides or sirna can enhance paclitaxel chemosensitivity in human lung cancer cells 6. nclu is generally associated with cell death 30 33, but it does not exist in non-small cell lung cancer 7. Downregulation of sclu sensitized the DDP-based chemotherapy in human osteosarcoma cell and in human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts in immunodeficient mice by inactivating downstream cell signal pakt and perk1/2 34,35. In contrast, overexpression of sclu in MCF-7/sClu cells promoted TNF-alpha-mediated NF-kappaB activity and Bcl-2 overexpression 36. Here our research further confirms that sclu plays an important role on sensitivity to cddp in human lung adenocarcinoma cells by downregulating Bcl-2, pcas-3, perk1/2 and pakt. In conclusion, we report altered expression of mir-378 in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines with varying sensitivities to cddp, and have shown that mir-378 can restore cddp chemosensitivity in the human lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting sclu and downregulating Bcl-2, pcas-3, perk1/2 and pakt (Fig. 7). Therefore, targeting this mir-378-sclu interaction may be a potential strategy for reversing cddp chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma. Methods Cell culture. All human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines (A549, Anip973, A549/cDDP, Anip973/cDDP) were purchased from the Cancer Research Institute of Heilongjiang Province [Harbin, China, (STR profiling)] and passaged in our laboratory for fewer than six months after resuscitation. The cells were grown in RPMI-1640 medium with 10% fetal calf serum under atmospheric conditions of 5% CO2 with humidity at 37 C. MTT assay. MTT assay was performed as described previously 37. Briefly, the stably transfected cells were seeded into 96-well plates and incubated overnight. Freshly prepared cddp was added. After 48 h, MTT solution (5 mg/ml) was added (20 μ l/well), and cells were incubated for 4 more hours. The culture supernatant was removed and DMSO was added (100 μ l/well). Cells were incubated in a shaker at 37 C for 10 min until the crystals were completely dissolved. A microplate reader was used to measure the absorbance at 490 nm. The concentration at which the drug produced 50% inhibition of growth (IC50) was estimated by the relative survival curve. mirna and transfection. mir-378 mimics, sclu sirna, sclu(plasmid) or their controls were purchased from Sigma. Transfection was performed with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Mountain View, CA, USA) following the manufacturer s protocol. 48 h after transfection, cells were collected for RNA isolation or Western blot. Hoechst staining assay. Cells were cultured on six-well plates and treated with cddp for 12 h. Then, Hoechst (Sigma, USA) was added to the medium. The changes in nuclear morphology were analyzed with fluorescence microscopy. The percentages of Hoechst-positive nuclei per optical field were counted. RNA extraction and RT-PCR assay. Total RNA was isolated with TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Gaithersburg, MD). RT-PCR was performed using TaKaRa one-step RNA PCR kit (TaKaRa Bio Inc, Japan). The expression level of mir-378 was detected with gene-specific primers as described 38. U6 was validated as an internal control by comparing its expression levels in each of the specimens. 6
9 Western blot. The proteins from cell lysates were separated on 12% SDS polyacrylamide gels and blotted onto PVDF membranes. All gels have been run under the same experimental conditions. Membranes were then probed with an antibody. Antibodies against sclu, pcaspase-3, Caspase and Bcl-2 were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Antibodies against perk1/2, ERK1/2, pakt, AKT were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA). We used BCIP/NBT color development system to detect the bands. Images were photographed using the Bio-Rad gel imaging system (Bio-Rad, CA). Dual Luciferase Activity Assay. To generate luciferase report constructs, the 3 UTR of sclu was amplified by PCR and cloned downstream of the luciferase-coding sequence in the psicheck-2 vector between Xho I and Not I restriction site. Mutations were introduced into the mirna-binding sites by using the QuickChange Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene). HEK293T cells were seeded in a 24-well plate and transfected with 20 μ M of either mir-378 mimics or mir-nc vectors, and 50 ng of psicheck-2 vectors. Cells were harvested for luciferase activity assays 48 hours after transfection. A luciferase assay kit (dual-luciferase assay kit, E2920, Promega) was used according to the manufacturer s protocol. Animal experiment. A549/cDDP cells ( in 0.2 ml of HBSS) were suspended in serum-free RPMI/ Matrigel mixture and were injected into the flanks of BALB/c nude mice under isoflurane inhalation (Nu/Nu, female, 4 6 weeks old, n = 5/group), which were maintained under pathogen-free conditions. One day after tumor cell implantation, mice were treated with cddp (3.0 mg/kg body weight; i.p., thrice per week), and health of mice was checked every day. After 8 days, Agomir-miR-378 or agomir-nc (RiboBio Co., Ltd, Guangzhou, China) was directly injected into the implanted tumor at the dose of 1 nmol per mouse every 4 days for seven times. Tumor volume was monitored for 4 weeks and measured once weekly. The tumor volume formed was calculated by the following formula: Volume = (Length width 2 ) 0.5. Mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation. Tumors were harvested; half of each tumor was frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at 80 C; the other half was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and stored in 70% ethanol. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University, and carried out in accordance with approved guidelines. Patients and tissue samples. 33 cases of tissue samples were obtained from patients who were diagnosed with advanced lung adenocarcinoma and had received chemotherapy in the Third Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Heilongjiang Province (China). Patients met all of the 4 following requirements: 1) histological diagnosed with primary lung adenocarcinoma, 2) had at least one measurable lesion, 3) clinically classified as stage IIIB-IV, 4) being treated with cisplatin. Samples were divided into sensitive (complete response or partial response) and insensitive (stable disease or progressive disease) groups after 2 cycles of cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University, and written informed consents were obtained from the participants. The study was carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines. Statistical Analysis Each experiment was repeated at least 3 times. Numerical data were presented as mean ± SD. The difference between means was analyzed with Student s t-test. The correlation was assessed by the Pearson coefficient. All statistical analyzes were performed using SPSS11.0 software. Differences were considered significant when P < References 1. Jemal, A. et al. Cancer statistics, CA Cancer J Clin. 59, (2009). 2. Reck, M., Heigener, D. F., Mok, T., Soria, J. C. & Rabe, K. F. Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: recent developments. Lancet. 382, (2013). 3. Davidoff, A. J., Tang, M., Seal, B. & Edelman, M. J. Chemotherapy and survival benefit in elderly patients with advanced non-smallcell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28, (2010). 4. Lee, C. H. et al. Suppression of clusterin expression enhanced cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity on renal cell carcinoma cells. Urology. 60, (2002). 5. Hoeller, C. et al. Clusterin regulates drug-resistance in melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 124, (2005). 6. Djeu, J. Y. & Wei, S. Clusterin and chemoresistance. Adv Cancer Res. 105, (2009). 7. Albert, J. M. et al. Cytoplasmic clusterin expression is associated with longer survival in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16, (2007). 8. Chen, X. et al. Expression and Significance of Clusterin in Anip973/CDDP Cell Lines. Chin J lung cancer. 12, (2009). 9. Djeu, J. Y. & Wei, S. Clusterin and chemoresistance. Adv Cancer Res. 105, (2009). 10. Di Leva, G., Garofalo, M. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Ann Rev Pathol. 9, (2014). 11. Lujambio, A. & Lowe, S. W. The microcosmos of cancer. Nature. 482, (2012). 12. Du, L. et al. mir-337-3p and its targets STAT3 and RAP1A modulate taxane sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS One. 7, e39167 (2012). 13. Feng, B., Wang, R., Song, H. Z. & Chen, L. B. MicroRNA-200b reverses chemoresistance of docetaxel-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting E2F3. Cancer. 118, (2012). 14. Tan, S., Wu, Y., Zhang, C. Y. & Li, J. Potential MicroRNA Targets for Cancer Chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem.20, (2013). 15. Eitan, R. et al. Tumor microrna expression patterns associated with resistance to platinum based chemotherapy and survival in ovarian cancer patients. Gynecol Oncol. 114, (2009). 16. Lu, X., Sun, J., Gao, W., Xu, X. T. & Shu, Y. Q. Analysis of micrornas in drug-resistant NSCLC cell line A549/DDP. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat. 179, (2010). 17. Kim, E. S. et al. Tissue platinum concentration and tumor response in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 30, (2012). 18. Bian, H. B., Pan, X., Yang, J. S., Wang, Z. X. & De, W. Upregulation of microrna-451 increases cisplatin sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cell line (A549). J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30, 20 (2011). 19. Du, L. & Pertsemlidis, A. microrna regulation of cell viability and drug sensitivity in lung cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 12, (2012). 20. Garofalo, M. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in chemoresistance. Drug Resist Update. 16, (2013). 7
10 21. Deng, Z. et al. The intermediate filament vimentin mediates microrna mir-378 function in cellular self-renewal by regulating the expression of the Sox2 transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 288, (2013). 22. Deng, H. et al. MicroRNA-195 and microrna-378 mediate tumor growth suppression by epigenetic regulation in gastric cancer. Gene. 518, (2013). 23. Chen, L. T. et al. MicroRNA-378 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis by promoting cell migration, invasion and tumor angiogenesis. Med Oncol. 29, (2012). 24. Skrzypek, K. et al. Interplay Between Heme Oxygenase-1 and mir-378 Affects Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Growth, Vascularization, and Metastasis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19, (2013). 25. Wang, K. Y. et al. MicroRNA-378 inhibits cell growth and enhances L-OHP-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer. IUBMB Life. 66, (2014). 26. Li, L.H., Gao, Q., Wang, X.Y. & Guo, Z.J. mir-378 suppresses HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth by directly targeting the insulin-like growth factor1receptor. ZhonghuaGanZangBingZaZhi. 21, (2013). 27. Kapoor, S. Clusterin inhibition to enhance tumor chemosensitivity in systemic tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.71, 1101 (2013). 28. Muramaki, M. et al. Chemosensitization of gemcitabine-resistant human bladder cancer cell line both in vitro and in vivo using antisense oligonucleotide targeting the anti-apoptotic gene, clusterin. BJU Int. 103, (2009). 29. Cheng, C. Y. et al. Regulation of chemosensitivity and migration by clusterin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69, (2012). 30. Caccamo, A. E., Desenzani, S., Belloni, L., Borghetti, A. F. & Bettuzzi, S. Nuclear clusterin accumulation during heat shock response: implications for cell survival and thermo-tolerance induction in immortalized and prostate cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 207, (2006). 31. Leskov, K. S., Klokov, D. Y., Li, J., Kinsella, T. J. & Boothman, D. A. Synthesis and functional analyzes of nuclear clusterin, a cell death protein. J Biol Chem. 278, (2003). 32. Moretti, R. M. et al. Molecular mechanisms of the antimetastatic activity of nuclear clusterin in prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 39, (2011). 33. Kim, N. et al. Human nuclear clusterin mediates apoptosis by interacting with Bcl-XL through C-terminal coiled-coil domain. J Cell Physiol. 227, (2012). 34. Huang, H., Wang, L., Li, M., Wang, X. & Zhang, L. Secreted clusterin (sclu) regulates cell proliferation and chemosensitivity to cisplatin by modulating ERK1/2 signals in human osteosarcoma cells. World J Surg Oncol. 12, 255 (2014). 35. Zhang, B., Liu, Z. M., Hao, F. G. & Wang, M. sirna-directed clusterin silencing promotes cisplatin antitumor activity in human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts in immunodeficient mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18, (2014). 36. Wang, Y., Wang, X., Zhao, H., Liang, B. & Du, Q. Clusterin confers resistance to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells through NF-kappaB activation and Bcl-2 overexpression. J Chemother. 24, (2012). 37. Chen, X. et al. Tea polyphenols induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells by suppressing the expression of Survivin. Sci Rep. 4, 4416 (2014). 38. Lee, D. Y., Deng, Z., Wang, C. H. & Yang, B. B. MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFuand Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104, (2007). Acknowledgements This research is supported by the following funding: Funding from National Natural Science Foundation Grant of China (No ) to YZ, National Natural Science Foundation Grant of China (No ) to LC, National Natural Science Foundation Grant of China (No ), Heilongjiang Provincial Department of Education Project (No ) and Heilongjiang Province Foundation for returnees (No. LC201438) to XC. Author Contributions X.C., Y.Z. and L.C. were responsible for the experimental design. X.C., Y.J., D.L., Z.H., X.C., M.C. and Q.M. carried out the experiments. X.C., H.P. and L.S. performed data analysis and prepared the figures and tables. X.C., Y.J., Z.H., Y.Z. and L.C. wrote, reviewed, and revised the manuscript. L.C. and Z.H. provided administrative, technical, or material support. L.C., Y.Z. and X.C. supervised the study. Additional Information Supplementary information accompanies this paper at Competing financial interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests. How to cite this article: Chen, X. et al. mirna-378 reverses chemoresistance to cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting secreted clusterin. Sci. Rep. 6, 19455; doi: /srep19455 (2016). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit 8
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
http / /cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology A431 . Western aza-dC FUT4-siRNA
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
Bhatnagar et al, 2010 Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS T
 Bhatnagar et al, Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS--98-T Supplemental Materials. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure (A) WPE-NA and WPE-NB6 cells were treated with 4 nm of Docetaxel
Bhatnagar et al, Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS--98-T Supplemental Materials. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure (A) WPE-NA and WPE-NB6 cells were treated with 4 nm of Docetaxel
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: , 2019
 326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Original Article mir-181 regulation of BAX controls cisplatin sensitivity of prostate cancer cells
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):10127-10133 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0057301 Original Article mir-181 regulation of BAX controls cisplatin sensitivity of prostate cancer cells Zhi-Ping Cai,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):10127-10133 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0057301 Original Article mir-181 regulation of BAX controls cisplatin sensitivity of prostate cancer cells Zhi-Ping Cai,
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 1977-1984, 2017 mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9 Hua Liang, Ruoyu Luo, Xiaoqi Chen, Yuzi Zhao and Aili Tan Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 1977-1984, 2017 mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9 Hua Liang, Ruoyu Luo, Xiaoqi Chen, Yuzi Zhao and Aili Tan Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
http / / cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology COX-2 NTera-2 NTera-2 RT-PCR FasL caspase-8 caspase-3 PARP.
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues. suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by
 Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7
 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Original Article Overexpression of mir-96 promotes cell proliferation by targeting FOXF2 in prostate cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(7):7596-7602 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0053748 Original Article Overexpression of mir-96 promotes cell proliferation by targeting FOXF2 in prostate cancer Wu-Ran
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(7):7596-7602 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0053748 Original Article Overexpression of mir-96 promotes cell proliferation by targeting FOXF2 in prostate cancer Wu-Ran
Long non-coding RNA Loc is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
MicroRNA-590-5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating GAB1
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5954-5963 MicroRNA-590-5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating GAB1 B.-B. XU 1, Z.-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5954-5963 MicroRNA-590-5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating GAB1 B.-B. XU 1, Z.-F.
Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant molecular mechanism.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
The effect of elemene reversing the multidurg resistance of A549/DDP lung cancer cells
 213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing SOX4
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Down regulation of mir 210 3p encourages chemotherapy resistance of renal cell carcinoma via modulating ABCC1
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-018-0209-3 Cell & Bioscience RESEARCH Open Access Down regulation of mir 210 3p encourages chemotherapy resistance of renal cell carcinoma via modulating ABCC1 Songchao Li
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-018-0209-3 Cell & Bioscience RESEARCH Open Access Down regulation of mir 210 3p encourages chemotherapy resistance of renal cell carcinoma via modulating ABCC1 Songchao Li
LncRNA NKILA suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and migration by inactivating PI3K/Akt pathway
 Original Article LncRNA NKILA suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and migration by inactivating PIK/Akt pathway Jian Huang #, Lingfeng Zhao #, Wei Chen #, Jian Duan 4, Dibesh Shrestha, Ruize Zhou,
Original Article LncRNA NKILA suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and migration by inactivating PIK/Akt pathway Jian Huang #, Lingfeng Zhao #, Wei Chen #, Jian Duan 4, Dibesh Shrestha, Ruize Zhou,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
mir-132 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4
 Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of
 Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10413-10418 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058793 Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma Chao-Bing
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10413-10418 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058793 Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma Chao-Bing
microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression
 1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Original Article MiR195 downregulating Siah-1S level to inhibit cell growth and promote cell apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells SW620
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):5937-5943 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0023331 Original Article MiR195 downregulating Siah-1S level to inhibit cell growth and promote cell apoptosis in colorectal
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):5937-5943 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0023331 Original Article MiR195 downregulating Siah-1S level to inhibit cell growth and promote cell apoptosis in colorectal
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 35: 1757-1763, 2016 MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy Ruida Xu, Shuzhong Liu, Haihong Chen
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 35: 1757-1763, 2016 MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy Ruida Xu, Shuzhong Liu, Haihong Chen
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 15: , 2018
 10098 MicroRNA 154 functions as a tumor suppressor in non small cell lung cancer through directly targeting B cell specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1 SIDA LIU 1, YANG YANG 2, LU CHEN
10098 MicroRNA 154 functions as a tumor suppressor in non small cell lung cancer through directly targeting B cell specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1 SIDA LIU 1, YANG YANG 2, LU CHEN
MicroRNA-377 suppresses initiation and progression of esophageal cancer by inhibiting CD133 and VEGF
 Oncogene (7) 6, 986 www.nature.com/onc OPEN ORIGINAL ARTICLE MicroRNA-77 suppresses initiation and progression of esophageal cancer by inhibiting CD and VEGF BLi,,,,,WWXu,,,,LHan,,KTChan,SWTsao,, NPY Lee,,SLaw,,LYXu
Oncogene (7) 6, 986 www.nature.com/onc OPEN ORIGINAL ARTICLE MicroRNA-77 suppresses initiation and progression of esophageal cancer by inhibiting CD and VEGF BLi,,,,,WWXu,,,,LHan,,KTChan,SWTsao,, NPY Lee,,SLaw,,LYXu
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table File Name: Peer Review File Description: Supplementary Table 1 Primers and taqman probes used were the following:
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table File Name: Peer Review File Description: Supplementary Table 1 Primers and taqman probes used were the following:
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
microrna 200a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FOXA1 in glioma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE microrna 200a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FOXA1 in glioma XIAOFENG CHEN 1, KUN LIU 1, PING YANG 2, WEIPING KUANG 1, HONGXING HUANG 1, EWEN TU 3, BO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE microrna 200a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FOXA1 in glioma XIAOFENG CHEN 1, KUN LIU 1, PING YANG 2, WEIPING KUANG 1, HONGXING HUANG 1, EWEN TU 3, BO
Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel
 KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
Yuriko Saiki, 1 Takenori Ogawa, 1, 2 Kiyoto Shiga, 2 Makoto Sunamura, 1, 3 Toshimitsu Kobayashi, 2 and Akira Horii 1. 1.
 International Otolaryngology Volume 211, Article ID 521852, 4 pages doi:1.1155/211/521852 Research Article A Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line with Acquired cis-diamminedichloroplatinum-resistance
International Otolaryngology Volume 211, Article ID 521852, 4 pages doi:1.1155/211/521852 Research Article A Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line with Acquired cis-diamminedichloroplatinum-resistance
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
microrna-342-3p targets FOXQ1 to suppress the aggressive phenotype of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
 Cui and Zhao BMC Cancer (2019) 19:104 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5225-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access microrna-342-3p targets FOXQ1 to suppress the aggressive phenotype of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Cui and Zhao BMC Cancer (2019) 19:104 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5225-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access microrna-342-3p targets FOXQ1 to suppress the aggressive phenotype of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1
 Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis
 Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
Effects of AFP gene silencing on Survivin mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells
 mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
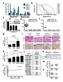 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test
 FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors
 Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
