Cost-effectiveness analysis of anastrozole as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer in postmenopausal women
|
|
|
- Lambert Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Cost-effectiveness analysis of anastrozole as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer in postmenopausal women Andre Deeke Sasse 1*, Emma Chen Sasse 2 Study conducted at CEVON - Centro de Evidências em Oncologia Departamento de Clínica Médica, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas UNICAMP, Campinas, SP, Brazil *Correspondence Departamento de Clínica Médica, Centro de Evidências em Oncologia CEVON, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas - UNICAMP CEP Campinas - SP ABSTRACT Objectives. To carry out an economic analysis of the possibility of adoption of anastrozole in Brazil as adjuvant hormone therapy for postmenopausal women with breast cancer. Methods. The estimate of the cost-effectiveness of anastrozole in comparison to tamoxifen for postmenopausal women was calculated from three different perspectives: private patients, health insurance plans, and the government (in the form of the Brazilian National Health Service - SUS). A Markov model was designed for a hypothetical cohort of 1000 postmenopausal women in Brazil, based on data from the ATAC trial after 100 months follow-up, using outcome projections for a 25-year period. Resource utilization and the costs associated with it were obtained from preselected sources and specialist opinion. Treatment costs varied according to the perspective used. The incremental benefit was also included in the model in order to obtain the cost of each quality-adjusted life-year gained (QALY). Results. Extrapolation of observed benefits over a 25-year period arrived at an estimate of 0.29 QALY gained if anastrozole is used instead of tamoxifen. The cost-effectiveness ratio per QALY gained depended on which perspective was used. There was an increment of R$32,403.00/QALY from the government/sus perspective, R$32,230.00/QALY for health insurance plans, and R$55,270.00/ QALY for private patients. Conclusion. The benefit of using adjuvant anastrozole with postmenopausal patients with post-surgery breast cancer is linked to major differences in the cost-effectiveness ratio and varies depending on perspective. According to current WHO parameters, the increment is considered acceptable from the perspective of the public healthcare system and the health insurance companies, but not from that of private patients. Keywords: Tamoxifen. Aromatase inhibitors. Adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast cancer. Neoplasms. Costeffectiveness analysis. Markov chains. Introduction Currently, breast cancer affects more women worldwide than any other neoplasm and it is the principal cause of death among them. Estimates published by the Instituto Nacional do Câncer (INCA) indicate that approximately 50,000 new cases of breast cancer were expected to be detected during 2008 in Brazil. 1 However, little is known about the characteristics of Brazilian patients with breast cancer. The Hospital Cancer Register for the Fundação Oncocentro do Estado de São Paulo (FOSP) shows that more than 80% of the 7,000 cases of breast cancer diagnosed in the State during 2006 and 2007 were detected when the disease was in stage I, II or III. 2 these cases are considered potentially curable using surgery plus supplementary treatments, known as adjuvant therapies, which may be any of, or a combination of, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and/or hormone therapy. One important characteristic of breast cancer which is used to guide the choice of treatment is tumoral expression of hormone receptors (estrogen or progesterone). Approximately 75% to 80% of patients with neoplasms in the breast have tumors that are positive for hormone receptors. 3 Published data demonstrate that women with potentially curable cases of the disease and whose tumors do express hormone receptors benefit from the use of adjuvant hormone therapy. 4 Tamoxifen is an anti-estrogen agent which binds to the estrogen receptors that are found in a proportion of breast cancers. This interaction results in a blockade of processes that are fundamental to cell transcription and of transduction signaling pathways that are necessary to cell growth and proliferation. 5 It was developed in the nineteen seventies and is a well-established option for adjuvant hormone therapy. Among women whose disease is detected at an early 1. Médico Assistente da Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas UNICAMP, Campinas, SP 2. Pesquisadora de avaliação de tecnologias em saúde da Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas UNICAMP, Campinas, SP Rev Assoc Med Bras 2009; 55(5):
2 Sasse AD et al stage and who are positive for hormone receptors, a compilation of extant studies shows that treatment with tamoxifen for 5 years is associated with an annual reduction in breast cancer mortality of 31% when compared with no treatment. 4 anastrozole is an aromatase inhibitor that has been developed more recently and whose mechanism of action is by blocking the conversion of adrenal androgens into estrogens. The efficacy and safety of anastrozole, as compared with tamoxifen as initial adjuvant treatment for postmenopausal women, were evaluated in a large scale randomized multicenter study entitled Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in a Combination (the ATAC study). 6,7 The results after a median follow-up of 100 months demonstrated that patients given anastrozole enjoyed a longer disease-free period (Hazard Ratio: 0.85; p=0.003) and suffered a lower incidence of certain adverse events during treatment. 6,8 Many different authors have recommended using anastrozole rather than tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for breast cancer in postmenopausal women. 9 Notwithstanding these benefits, initial use of aromatase inhibitors involves new concerns because of its toxicity profile. 10 The ATAC long-term safety analysis demonstrated that patients taking anastrozole had an increased incidence of bone mass loss, arthralgia and fractures. 7,11 Furthermore, anastrozole use is also associated with a three-times greater risk of hypercholesterolemia. 11 In addition to the concerns over these new side effects, the costs involved in introducing anastrozole into daily clinical practice is also a cause of controversy worldwide. Breast cancer is a neoplasm with high incidence rates and, as a result, the costs associated with its treatment have a major impact on healthcare system budgets, whether they be public or private systems. Currently, systemic treatments, whether chemotherapy or hormone therapy, are responsible for a large proportion of the costs incurred treating patients with breast cancer. Since the increase in healthcare costs is a worldwide phenomenon, in many developed countries economic assessments have become the rule before approval will be granted by regulatory bodies. In developing countries, such as Brazil, where the financial resources available for healthcare are even more limited, it is imperative that the costs involved with the potentially greater efficacy and effectiveness of a new antineoplastic drug are assessed. 12 Nevertheless, cost-effectiveness analyses are still not the rule within Brazilian healthcare systems. Brazil has its own peculiarities and the private and public healthcare systems are highly interconnected. Medical care costs have traditionally been divided between the government, health insurance plans and individual patients. Very few patients are able to pay for all of their medical costs and the majority use the public and private healthcare systems in conjunction. 13 Technological innovations have also had an impact on all levels. As the costs of new technologies are incorporated into health insurance plans, fewer people have the financial capacity to pay for these plans and more people become dependent on the government to provide access to healthcare. When costs are assumed by the government, fixed budgets lead to restricted access to high cost technologies and, sometimes, even to social and preventative programs. This cycle increases even further the need for formal cost-effectiveness analyses to be undertaken before new technologies are adopted in our country. Such assessments should theoretically evaluate a perspectives that could possibly influence acceptance of the costs of adopting a new drug. Cost-effectiveness analyses of the use of anastrozole as an adjuvant treatment for breast cancer have been published from the perspective of the societies in other countries, such as Great Britain, 14 Belgium, 15 the United States 16 and Canada. 17 These studies have concluded that, from the perspective of their respective countries, anastrozole is a cost-effective treatment that is comparable with other antineoplastic treatments that are accepted in general routine oncology No studies have been published in Brazil on the subject. The lack of conclusive data and the nonexistence of studies comparing the perspectives of the government, the health insurance companies and the individual patients, demand that a cost-effectiveness analysis be undertaken reflecting the situation in Brazil, which can then be used to answer important questions. Methods The ATAC study 7 recruited postmenopausal women with early-stage invasive neoplasms of the breast who had completed primary treatment (surgery ± radiotherapy ± chemotherapy) and who were eligible for adjuvant hormone treatment and randomized them to receive anastrozole or tamoxifen or both every day for 5 years. Since an early assessment showed that the branch of the study using both drugs did not exhibit benefits over tamoxifen in terms of efficacy and safety that branch was discontinued and so the analysis presented here is based only on the two single treatment groups (tamoxifen or anastrozole). Model TreeAge Pro Suite 2008 (TreeAge Software Inc., Williamstown, MA, USA) was used to develop a probabilistic Markov model, 18 projecting outcomes for a hypothetical cohort of 1000 postmenopausal women, aged 64, with neoplasms of the breast positive for hormone receptors and treated in Brazil. The Markov model assumes that a patient is always in one of a finite number of predefined health states, and that all possible events are represented as transitions from one state to another. The model constructed for this study projected events up to a 25-year horizon. At a given point in time, the women in this model are allocated to one of six health states: 1) on adjuvant hormone treatment (in this case, anastrozole or tamoxifen); 2) off treatment, in remission; 3) locoregional relapse; 4) distant metastasis; 5) death caused by breast cancer or 6) death from other causes (Figure 1). All of the women enter the model in the in treatment state and move between health states in 6-month cycles. Probabilities and costs Rates of events for relapse and death from breast cancer were derived from the ATAC study and extrapolated for 25 years. The probabilities of other variables, such as adverse events and dropouts were taken from the ATAC results published after 100 months follow-up 6,7,11 and can be found in Table 1. The probability 536 Rev Assoc Med Bras 2009; 55(5):
3 Cost-effectiveness analysis of anastrozole as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer in postmenopausal women Figure1. Markov model for health states Table 2. Costs used in cost-effectiveness analysis for the three different perspectives: government, health insurance companies and private patients Costs Government Health insurance plans Private patients Medications All Some All Supplementary tests All All None Adverse effects All All None Relapse All All Some Table 3. Estimated costs per cycle (6 months) used in the model, including costs related to essential tests and to adverse events. (Sources: APAC, ABCFARMA magazine, 20 CBHPM 21 ) Table 1. Coefficients for the probability of transition (per cycle) extracted from the results published by the ATAC 6,7,11 study and employed in the Markov model Outcome Locoregional relapse Tamoxifen anastrozole Distant metastasis Tamoxifen anastrozole Metastasis after locoregional relapse 1-5 years > 5 years of death from causes other than breast cancer was calculated from WHO data on the life expectancy of the female population within different age groups (from 2006). Coefficients for the probability of distant metastasis occurring after locoregional relapse were obtained from a study published by Kamby and Sengelov. 19 Consumption of resources such as follow-up tests and specific treatments for each health state and adverse event was estimated for each of the groups analyzed on the basis of specialist opinion. Rev Assoc Med Bras 2009; 55(5): Coefficient of probability Death after metastasis Death from other causes years years years years years years years 100 years Cost of Tamoxifen (including the drug itself, tests and adverse events) Cost of anastrozole (including the drug itself, tests and adverse events) SUS Health insurance plans Private patients R$ R$ R$ R$ 1, R$ 2, R$ 2, Cost of follow-up R$ R$ Cost of locoregional relapse Cost of distant metastasis R$ 2, R$ 9, R$ 4, R$ 22, Cost of death R$ R$ 2, R$ 2, The costs accruing from use of these resources were assessed from three different perspectives from the point of view of the government, (in the form of the Brazilian National Health Service - SUS), health insurance and private patients. For the SUS perspective, the costs of medications and tests were taken from the official table for authorization of high-cost and complex procedures (APAC) and from the SIA/SUS table of procedures, April 2005 edition. The health insurance perspective was assessed by taking the costs of medications as the highest price offered to the public in issue 198, from February of 2008, of the periodical ABCFARMA 20 and taking the medical fees and supplementary tests from the fifth edition of the Hierarchical Classification of Medical Procedures (CBHPM, Classificação Hierarquizada de Procedimentos Médicos) 21. For the private patients perspective, the costs of medications were taken as the lowest price quoted by the medication distribution market in the city of São Paulo in March of The types of costs included in each perspective are described in Table 2 and the prices are given in Table
4 Sasse AD et al Because of the peculiarities of Brazilian healthcare, the costs used for calculations vary depending on the perspective used. In the analysis from the perspective of the SUS, all of the costs analyzed were taken from the APAC price table (in the case of anastrozole, the price paid for the aromatase inhibitor for treatment of metastatic disease was used). In the analysis from the perspective of their health insurance companies, all of the costs involved were included with the exception of the provision of tamoxifen, since currently Brazilian legislation allows home-use medication to be excluded contractually. The cost of supplying anastrozole was included in order to assess the economic viability of changing the policy on contractual coverage specifically for this case. Only direct medication costs were included in the analysis from the point of view of private patients, on the assumption that they would have follow-up tests and treatment for relapses covered either by the SUS or by health insurance. When relevant to one of the three points of view analyzed in this study, the probabilities and costs of adverse events (hysterectomy, endometrial neoplasm, cerebral vascular accident, deep venous thrombosis and skeletal events) were included in drug costs. International tables that had been published previously were used to adjust for quality of life the number of years gained through treatment. The mean patient-rated utility scores used in the Markov model were obtained from work published by Sorensen et al. (Table 4). 22 The scores derived from the model were then used to estimate the number of years of life gained adjusted by the quality of that life (QALY). The objective of this analysis was to evaluate the economic consequences of substituting tamoxifen by anastrozole, in terms of the number of QALY gained and the increase in costs per QALY gained. The increase in costs was calculated by taking the difference between the total costs associated with using anastrozole and total costs associated with using tamoxifen and dividing it by the number of QALY gained by using anastrozole, for each of the three different perspectives. 23 An annual reduction of 3% was applied to future costs and benefits. Results On the basis of the results of the ATAC study, extrapolated to a 25-year follow-up horizon for subsets of a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients on tamoxifen or anastrozole, the analysis returned a mean QALY of and per Utility Table 4. Mean patient-rated utilities used in the model 22 Value Remission of disease, without treatment Distant metastasis, palliative treatment Locoregional relapse On treatment with tamoxifen On treatment with anastrozole patient, respectively, giving an estimated gain of QALY per patient when using anastrozole. Incremental cost-effectiveness from the perspective of the SUS Neither strategy is dominant over the other. The costs associated with treatment using anastrozole, with treating its adverse events and with later treatments during relapses were estimated at a little over R$26 thousand, whereas the costs incurred by the tamoxifen group were approximately R$17 thousand, leaving a cost increment of R$9 thousand. The incremental cost-effectiveness analysis arrived at a cost of R$32, per QALY gained. Incremental cost-effectiveness from the perspective of health insurance plans In common with the analysis from the perspective of the government, neither strategy proved dominant over the other. The costs associated with treatment using anastrozole, with treating its adverse events and with later treatments during relapses were estimated at over R$65 thousand, whereas the costs incurred by the tamoxifen group were R$56 thousand. The incremental cost-effectiveness analysis arrived at a cost of R$32, per QALY gained. Incremental cost-effectiveness from the perspective of private patients Once more, neither strategy proved dominant over the other. The costs associated with treatment with anastrozole were estimated at R$20 thousand per patient, whereas the costs associated with using tamoxifen were around R$4 thousand per patient, leaving a cost increment of around R$16 thousand. The incremental cost-effectiveness analysis arrived at a cost of R$55, per QALY gained. Discussion Our analysis shows that the benefits accruing from using anastrozole rather than tamoxifen for adjuvant hormone therapy for women with early-stage breast cancer positive for hormone receptors would translate, over a 25-year period, to a lower number of deaths and improved quality of life. These benefits would represent an approximate incremental cost of R$32 thousand per QALY gained from the perspective of the SUS and from the perspective of their health insurance companies and of R$55 thousand per QALY gained seen from the perspective of private patients. Cost-effectiveness analyses carried out with cost parameters and, most importantly, from the perspective of the economic situations of other countries have concluded that anastrozole is highly cost-effective as an adjuvant treatment for patients with breast cancer. In the United States, the cost increment calculated was US$ 20, (approximately R$38,467.40) per QALY gained. 16 In Great Britain, the increment calculated was 17, (or approximately R$67,092.80) per QALY gained. 14 Within the context of these two countries, these increments are acceptable and comparable with other antineoplastic treatments that have already been approved and incorporated into clinical practice. 538 Rev Assoc Med Bras 2009; 55(5):
5 Cost-effectiveness analysis of anastrozole as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer in postmenopausal women In Brazil, however, there is not yet any regulation, recommendation or standard defining what incremental cost would be acceptable for adopting a new healthcare technology. Employing the WHO concept, which is that a value of between one and three times the gross domestic product (GDP) per capita is acceptable, the incremental value to be used in Brazil would be a maximum of R$ 40, per QALY gained. If we accept this figure as the cutoff for cost-effectiveness, our study demonstrates that adopting anastrozole would be considered cost-effective from the perspective of the SUS and of health insurance plans, but not from the perspective of private patients. However, if we put the WHO recommendation into perspective and compare this limit of three times the GDP per capita with figures acceptable in more developed countries, it will be observed that this figure of R$40, per QALY gained may be an overestimation. The current limit for incremental cost-effectiveness accepted in Great Britain is no more than 20 thousand to 30 thousand, which is slightly greater than one times the country s GDP per capita. While the United States does not formally use a limit for adoption of technology, they do have a reference figure of US$ 50, per QALY gained, which is also equivalent to a little more than one times the GDP per capita. We can trace a parallel with that situation. If we consider one times the GDP per capita as a cutoff for cost-effectiveness in Brazil (R$14,000.00), then using the aromatase inhibitor as adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with breast cancer would no longer be cost-effective from any of the perspectives analyzed. In common with many cost-effectiveness analyses, there are limitations to this study that should be taken into consideration. Our Markov model was constructed based on a randomized international study and includes a certain number of assumptions and estimates. The 25-year time period was chosen because, according to specialist opinion, it represents a period that is acceptable from a clinical point of view, for postmenopausal women with breast cancer. Nevertheless, the incremental cost-effectiveness values would vary substantially if the horizon was shorter or longer, since the costs are generally incurred in the early stages while benefits very often can only be measured later on. Furthermore, we based our assumptions of treatment effect on the relapse curves that continue to diverge after 100 months follow-up on the ATAC study. 6 It was therefore assumed that anastrozole would offer incremental benefits during the period analyzed in our study. The model may need to be updated if results are published after longer follow-up periods. Including data on clinical course and costs among Brazilian patients originating from a retrospective database or from a prospective study within the adjuvant hormone treatment scenario in Brazil would undoubtedly increase the model s power. In general, there are still barriers to carrying out cost-effectiveness analyses in Brazil that are integrated with healthcare policies. National data are lacking, whether related to the effects of the interventions investigated or to the quality of life of patients treated in the public and private health systems. There are also no trustworthy records relating to diagnoses and no adequate Rev Assoc Med Bras 2009; 55(5): record of mortality or information on costs met by patients that could be the responsibility of the SUS or of the private healthcare system. As a result, we often have to rely on the experience and opinions of specialists and on the results of studies undertaken with populations are different to ours, in order to be able to estimate benefits and costs. Although our study found that the incremental cost-effectiveness was acceptable according to WHO standards, there are no cost-effectiveness data from Brazil for other antineoplastic treatments that have been approved here. It would be interesting to compare the use of anastrozole as adjuvant therapy with other oncological treatments that have already been adopted as routine by health insurance plans or the SUS. It is possible that we would observe that the majority of antineoplastic treatments that are available today would not be considered cost-effective according to very restrictive criteria. In many different countries health-related expenditure has increased drastically. In the majority of cases this has been in association with the adoption of new technologies and treatments. Even in developed countries which have more resources available to spend on the population s health, the cost of treating cancer patients has a major impact on society, on the government and on health insurance plans. 24 However, patients who have been diagnosed with cancer need information and access to the new technologies that do exist, but are not provided with assistance to cover the costs associated with treatment, whether directly (drug costs) or indirectly (transport, lost working days and others). 25 In Brazil, the decision on who is responsible for paying for the treatment of a cancer patient involves factors that are interrelated in a complex manner. In general, health insurance plans do not cover oral medications, because they are for home-use. However, if the risk of relapse is greater there may be a need for palliative chemotherapy later on and over the long-term. This, in general, is covered by health insurance, in accordance with legislation. Costeffectiveness analyses such as the one we present here could lead to significant changes in treatment coverage policies within private practice if it were to be demonstrated that oral treatments reduced total costs. In practice, in order to add a new oral drug to clinical routine, currently either the patient takes on the cost burden themselves or seeks support from governmental organizations. The results of this study are highly relevant to healthcare managers, both in the public and private spheres, and could contribute to the development of a process for the adoption of new healthcare technologies, as is the case of aromatase inhibitors. It is of concern that there is still no routine process in Brazil for analyzing the costeffectiveness of healthcare technologies, and that there are no regulations for making formal recommendations. It is of fundamental importance to initiate a movement to stimulate critical thinking and publicize strategies for rationalizing expenditure, without prejudice to patients. The final result would be the creation of improved health services for the Brazilian population. 539
6 Sasse AD et al No conflicts of interest declared concerning the publication of this article. References 1. Instituto Nacional do Câncer - INCA. Estimativa 2008: incidência de câncer no Brasil [citado 01 set 2008]. Disponível em: estimativa Fundação Oncocentro do Estado de São Paulo FOSP. Banco de dados do Registro Hospitalar de Câncer [citado 15 ago 2008]. Disponível em: 3. Kapoor A, Vogel VG. Prognostic factors for breast cancer and their use in the clinical setting. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2005;5(2): Hochster HS. Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin vs infusional 5-fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Con: Pumpin FU (or, avoiding that oral fixation). Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2005;3(5): Rochefort H, Borgna JL. Differences between oestrogen receptor activation by oestrogen and antioestrogen. Nature. 1981;292(5820): Forbes JF, Cuzick J, Buzdar A, Howell A, Tobias JS, Baum M. Effect of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: 100-month analysis of the ATAC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(1): Howell A, Cuzick J, Baum M, Buzdar A, Dowsett M, Forbes JF, et al. Results of the ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination) trial after completion of 5 years adjuvant treatment for breast cancer. Lancet. 2005;365(9453): Duffy SR, Distler W, Howell A, Cuzick J, Baum M. A lower incidence of gynecologic adverse events and interventions with anastrozole than with tamoxifen in the ATAC trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;200(1):80 e Colozza M, Califano R, Minenza E, Dinh P, Azambuja E. Aromatase inhibitors: a new reality for the adjuvant endocrine treatment of early-stage breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008;8(6): Balducci L. Treating elderly patients with hormone sensitive breast cancer: what do the data show? Cancer Treat Rev. 2009;35(1): Buzdar A, Howell A, Cuzick J, Wale C, Distler W, Hoctin-Boes G, et al. Comprehensive side-effect profile of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: long-term safety analysis of the ATAC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(8): Mano M. The burden of scientific progress: growing inequalities in the delivery of cancer care. Acta Oncol. 2006;45(1): Barros AJ, Bertoldi AD. Out-of-pocket health expenditure in a population covered by the Family Health Program in Brazil. Int J Epidemiol. 2008;37(4): Mansel R, Locker G, Fallowfield L, Benedict A, Jones D. Cost-effectiveness analysis of anastrozole vs tamoxifen in adjuvant therapy for early stage breast cancer in the United Kingdom: the 5-year completed treatment analysis of the ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen alone or in combination) trial. Br J Cancer. 2007;97(2): Moeremans K, Annemans L. Cost-effectiveness of anastrozole compared to tamoxifen in hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer. Analysis based on the ATAC trial. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006;16(Suppl 2): Locker GY, Mansel R, Cella D, Dobrez D, Sorensen S, Gandhi SK. Costeffectiveness analysis of anastrozole versus tamoxifen as primary adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with early breast cancer: a US healthcare system perspective. The 5-year completed treatment analysis of the ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen Alone or in Combination) trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106(2): Rocchi A, Verma S. Anastrozole is cost-effective vs tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy in early breast cancer: Canadian perspectives on the ATAC completedtreatment analysis. Support Care Cancer. 2006;14(9): Sonnenberg FA, Beck JR. Markov models in medical decision making: a practical guide. Med Decis Making. 1993;13(4): Kamby C, Sengelov L. Pattern of dissemination and survival following isolated locoregional recurrence of breast cancer. A prospective study with more than 10 years of follow up. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1997;45(2): Anexo da Revista ABCFARMA Lista de Preços.Fevereiro 2008.Ano 16, Edição Associação Médica Brasileira. Classificação Brasileira Hierarquizada de Procedimentos Médicos.Setembro 2008, 5º edição. ISBN Sorensen SV, Benedict A, Flood D, Revicki D, Brown R. Patient-rated utilities in postmenopausal early breast cancer (EBC): a cross-country comparison. Value Health. 2004;7(6): Muennig P. Designing and conducting cost-effectiveness analyses in medicine and health care Meropol NJ, Schulman KA. Cost of cancer care: issues and implications. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(2): Rawlins M. Paying for modern cancer care--a global perspective. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(9): Artigo recebido: 31/10/08 Aceito para publicação: 3/6/ Rev Assoc Med Bras 2009; 55(5):
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium anastrozole 1mg tablets (Arimidex ) No. (198/05) AstraZeneca UK Ltd New indication: for adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptorpositive early invasive
Scottish Medicines Consortium anastrozole 1mg tablets (Arimidex ) No. (198/05) AstraZeneca UK Ltd New indication: for adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptorpositive early invasive
Setting The setting was secondary care. The economic study was carried out in Canada.
 Anastrozole is cost-effective vs tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy in early breast cancer: Canadian perspectives on the ATAC completed-treatment analysis Rocchi A, Verma S Record Status This is a critical
Anastrozole is cost-effective vs tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy in early breast cancer: Canadian perspectives on the ATAC completed-treatment analysis Rocchi A, Verma S Record Status This is a critical
ATAC Trial. 10 year median follow-up data. Approval Code: AZT-ARIM-10005
 ATAC Trial 10 year median follow-up data Approval Code: AZT-ARIM-10005 Background FDA post-approval commitment analysis to update DFS, TTR, OS and Safety Prof. Jack Cuzick on behalf of ATAC/LATTE Trialists
ATAC Trial 10 year median follow-up data Approval Code: AZT-ARIM-10005 Background FDA post-approval commitment analysis to update DFS, TTR, OS and Safety Prof. Jack Cuzick on behalf of ATAC/LATTE Trialists
Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer
 Society for Endocrinology comments on the assessment report for the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Appraisal of Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer
Society for Endocrinology comments on the assessment report for the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Appraisal of Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer
Cost-Effectiveness of Switching to Exemestane after 2 to 3 Years of Therapy with Tamoxifen in Postmenopausal Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer
 Volume 10 Number 5 2007 VALUE IN HEALTH Cost-Effectiveness of Switching to Exemestane after 2 to 3 Years of Therapy with Tamoxifen in Postmenopausal Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer David Thompson,
Volume 10 Number 5 2007 VALUE IN HEALTH Cost-Effectiveness of Switching to Exemestane after 2 to 3 Years of Therapy with Tamoxifen in Postmenopausal Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer David Thompson,
Genomic Health, Inc. Oncotype DX Colon Cancer Assay Clinical Compendium March 30, 2012
 Economic Validity Eligibility and Addressability for Use of the Assay An important distinction should be made between the total population of patients eligible for the Oncotype DX Colon Cancer assay, and
Economic Validity Eligibility and Addressability for Use of the Assay An important distinction should be made between the total population of patients eligible for the Oncotype DX Colon Cancer assay, and
Setting The study setting was secondary care. The economic study was carried out in Norway.
 Comparing cost/utility of giving an aromatase inhibitor as monotherapy for 5 years versus sequential administration following 2-3 or 5 years of tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for postmenopausal breast
Comparing cost/utility of giving an aromatase inhibitor as monotherapy for 5 years versus sequential administration following 2-3 or 5 years of tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for postmenopausal breast
Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early oestrogenreceptor-positive
 Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early oestrogenreceptor-positive breast cancer Issued: November 2006 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta112 NICE 2006 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 Clinical need and practice...
Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early oestrogenreceptor-positive breast cancer Issued: November 2006 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta112 NICE 2006 Contents 1 Guidance... 3 2 Clinical need and practice...
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta496
 Ribociclib with an aromatase inhibitor for previously untreated, hormone receptor- positive, HER2-negative, e, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 20 December
Ribociclib with an aromatase inhibitor for previously untreated, hormone receptor- positive, HER2-negative, e, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 20 December
Generalised cost-effectiveness analysis for breast cancer prevention and care in Hong Kong Chinese. Wong, IOL; Tsang, JWH; Cowling, BJ; Leung, GM
 Title Generalised cost-effectiveness analysis for breast cancer prevention and care in Hong Kong Chinese Author(s) Wong, IOL; Tsang, JWH; Cowling, BJ; Leung, GM Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2015,
Title Generalised cost-effectiveness analysis for breast cancer prevention and care in Hong Kong Chinese Author(s) Wong, IOL; Tsang, JWH; Cowling, BJ; Leung, GM Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2015,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Overview
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Overview Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early oestrogen-receptor positive breast cancer The overview is written by members of the
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Overview Hormonal therapies for the adjuvant treatment of early oestrogen-receptor positive breast cancer The overview is written by members of the
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 14 December 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta239
 Fulvestrant for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 14 December 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta239 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject
Fulvestrant for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 14 December 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta239 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject
Cost-effectiveness of androgen suppression therapies in advanced prostate cancer Bayoumi A M, Brown A D, Garber A M
 Cost-effectiveness of androgen suppression therapies in advanced prostate cancer Bayoumi A M, Brown A D, Garber A M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria
Cost-effectiveness of androgen suppression therapies in advanced prostate cancer Bayoumi A M, Brown A D, Garber A M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
William J. Gradishar MD
 Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy For Postmenopausal Women SOBO 2013 William J. Gradishar MD Betsy Bramsen Professor of Breast Oncology Director, Maggie Daley
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy For Postmenopausal Women SOBO 2013 William J. Gradishar MD Betsy Bramsen Professor of Breast Oncology Director, Maggie Daley
Extended Hormonal Therapy
 Extended Hormonal Therapy Dr. Caroline Lohrisch, Medical Oncologist, BC Cancer Agency Vancouver Centre November 1, 2014 www.fpon.ca Optimal Endocrine Therapy for Women with Hormone Receptor Positive Early
Extended Hormonal Therapy Dr. Caroline Lohrisch, Medical Oncologist, BC Cancer Agency Vancouver Centre November 1, 2014 www.fpon.ca Optimal Endocrine Therapy for Women with Hormone Receptor Positive Early
Evaluation of breast cancer risk assessment techniques: a cost-effectiveness analysis Ozanne E M, Esserman L J
 Evaluation of breast cancer risk assessment techniques: a cost-effectiveness analysis Ozanne E M, Esserman L J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria
Evaluation of breast cancer risk assessment techniques: a cost-effectiveness analysis Ozanne E M, Esserman L J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
R. A. Nout Æ W. E. Fiets Æ H. Struikmans Æ F. R. Rosendaal Æ H. Putter Æ J. W. R. Nortier
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2008) 109:567 572 DOI 10.1007/s10549-007-9681-x EPIDEMIOLOGY The in- or exclusion of non-breast cancer related death and contralateral breast cancer significantly affects estimated
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2008) 109:567 572 DOI 10.1007/s10549-007-9681-x EPIDEMIOLOGY The in- or exclusion of non-breast cancer related death and contralateral breast cancer significantly affects estimated
Pamidronate in prevention of bone complications in metastatic breast cancer: a costeffectiveness
 Pamidronate in prevention of bone complications in metastatic breast cancer: a costeffectiveness analysis Hillner B E, Weeks J C, Desch C E, Smith T J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
Pamidronate in prevention of bone complications in metastatic breast cancer: a costeffectiveness analysis Hillner B E, Weeks J C, Desch C E, Smith T J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
HORMONAL THERAPY IN ADJUVANT CARE
 ADVANCES IN ENDOCRINE THERAPY FOR BREAST CANCER* Matthew J. Ellis, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Endocrine therapy is used frequently in breast cancer management, particularly in the setting of adjuvant care, but outstanding
ADVANCES IN ENDOCRINE THERAPY FOR BREAST CANCER* Matthew J. Ellis, MD, PhD ABSTRACT Endocrine therapy is used frequently in breast cancer management, particularly in the setting of adjuvant care, but outstanding
Study population The study population comprised patients with completely resected Stage III colon cancer.
 Cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine in the adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer Eggington S, Tappenden P, Pandor A, Paisley S, Saunders M, Seymour M, Sutcliffe P, Chilcott J Record
Cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin and capecitabine in the adjuvant treatment of stage III colon cancer Eggington S, Tappenden P, Pandor A, Paisley S, Saunders M, Seymour M, Sutcliffe P, Chilcott J Record
EVIDENCE IN BRIEF OVERALL CLINICAL BENEFIT
 large impact on cost-effectiveness. perc discussed that one of the main factors affecting the costeffectiveness estimates was the survival estimates used in the economic model. In reviewing the clinical
large impact on cost-effectiveness. perc discussed that one of the main factors affecting the costeffectiveness estimates was the survival estimates used in the economic model. In reviewing the clinical
EVIDENCE IN BRIEF OVERALL CLINICAL BENEFIT
 perc deliberated upon the cost-effectiveness of lapatinib plus letrozole and discussed the challenges of using letrozole alone as a comparator and/or using trastuzumab plus anastrozole as a comparator.
perc deliberated upon the cost-effectiveness of lapatinib plus letrozole and discussed the challenges of using letrozole alone as a comparator and/or using trastuzumab plus anastrozole as a comparator.
Setting The setting was primary care. The economic study was carried out in Brazil, France, Germany and Italy.
 The cost-effectiveness of influenza vaccination for people aged 50 to 64 years: an international model Aballea S, Chancellor J, Martin M, Wutzler P, Carrat F, Gasparini R, Toniolo-Neto J, Drummond M, Weinstein
The cost-effectiveness of influenza vaccination for people aged 50 to 64 years: an international model Aballea S, Chancellor J, Martin M, Wutzler P, Carrat F, Gasparini R, Toniolo-Neto J, Drummond M, Weinstein
Radiotherapy is a cost-effective palliative treatment for patients with bone metastasis from prostate cancer Konski A
 Radiotherapy is a cost-effective palliative treatment for patients with bone metastasis from prostate cancer Konski A Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the
Radiotherapy is a cost-effective palliative treatment for patients with bone metastasis from prostate cancer Konski A Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Everolimus in combination with exemestane for the treatment of advanced or metastatic HER2 negative, oestrogen
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Everolimus in combination with exemestane for the treatment of advanced or metastatic HER2 negative, oestrogen
An Overview of Health Economics Data and Expertise in Cancer
 An Overview of Health Economics Data and Expertise in Cancer Peter Smith, (Professor of Health Policy, Imperial College London) Mauro Laudicella (Research Fellow, Imperial College London) Source: A. Maynard
An Overview of Health Economics Data and Expertise in Cancer Peter Smith, (Professor of Health Policy, Imperial College London) Mauro Laudicella (Research Fellow, Imperial College London) Source: A. Maynard
BREAST CANCER AND BONE HEALTH
 BREAST CANCER AND BONE HEALTH Rowena Ridout, MD, FRCPC Toronto Western Hospital Osteoporosis Program University Health Network / Mount Sinai Hospital rowena.ridout@uhn.ca None to declare Conflicts of Interest
BREAST CANCER AND BONE HEALTH Rowena Ridout, MD, FRCPC Toronto Western Hospital Osteoporosis Program University Health Network / Mount Sinai Hospital rowena.ridout@uhn.ca None to declare Conflicts of Interest
Chapter 5: Epidemiology of MBC Challenges with Population-Based Statistics
 Chapter 5: Epidemiology of MBC Challenges with Population-Based Statistics Musa Mayer 1 1 AdvancedBC.org, Abstract To advocate most effectively for a population of patients, they must be accurately described
Chapter 5: Epidemiology of MBC Challenges with Population-Based Statistics Musa Mayer 1 1 AdvancedBC.org, Abstract To advocate most effectively for a population of patients, they must be accurately described
Hormone therapy in Breast Cancer patients with comorbidities
 Hormone therapy in Breast Cancer patients with comorbidities Diana Crivellari Centro di Riferimento Oncologico Aviano- ITALY Madrid November 9th, 2007 Main issues Comorbidities in elderly women Hormonal
Hormone therapy in Breast Cancer patients with comorbidities Diana Crivellari Centro di Riferimento Oncologico Aviano- ITALY Madrid November 9th, 2007 Main issues Comorbidities in elderly women Hormonal
Effect of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: 10-year analysis of the ATAC trial
 Effect of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: 1-year analysis of the ATAC trial Jack Cuzick, Ivana Sestak, Michael Baum, Aman Buzdar, Anthony Howell, Mitch Dowsett,
Effect of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer: 1-year analysis of the ATAC trial Jack Cuzick, Ivana Sestak, Michael Baum, Aman Buzdar, Anthony Howell, Mitch Dowsett,
Study population The study population comprised a hypothetical cohort of patients with Stage D2 prostate cancer.
 Is combined androgen blockade with bicalutamide cost-effective compared with combined androgen blockade with flutamide Ramsey S, Veenstra D, Clarke L, Gandhi S, Hirsch M, Penson D Record Status This is
Is combined androgen blockade with bicalutamide cost-effective compared with combined androgen blockade with flutamide Ramsey S, Veenstra D, Clarke L, Gandhi S, Hirsch M, Penson D Record Status This is
Emerging Approaches for (Neo)Adjuvant Therapy for ER+ Breast Cancer
 Emerging Approaches for (Neo)Adjuvant Therapy for E+ Breast Cancer Cynthia X. Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Outline Current status of adjuvant endocrine
Emerging Approaches for (Neo)Adjuvant Therapy for E+ Breast Cancer Cynthia X. Ma, M.D., Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Outline Current status of adjuvant endocrine
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Pertuzumab (Perjeta) Neoadjuvant Breast Cancer July 16, 2015
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Pertuzumab (Perjeta) Neoadjuvant Breast Cancer July 16, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report is primarily
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Pertuzumab (Perjeta) Neoadjuvant Breast Cancer July 16, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report is primarily
Is proton beam therapy cost effective in the treatment of adenocarcinoma of the prostate? Konski A, Speier W, Hanlon A, Beck J R, Pollack A
 Is proton beam therapy cost effective in the treatment of adenocarcinoma of the prostate? Konski A, Speier W, Hanlon A, Beck J R, Pollack A Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Is proton beam therapy cost effective in the treatment of adenocarcinoma of the prostate? Konski A, Speier W, Hanlon A, Beck J R, Pollack A Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Breast Cancer? Breast cancer is the most common. What s New in. Janet s Case
 Focus on CME at The University of Calgary What s New in Breast Cancer? Theresa Trotter, MD, FRCPC Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women in Canada, accounting for almost a third of
Focus on CME at The University of Calgary What s New in Breast Cancer? Theresa Trotter, MD, FRCPC Breast cancer is the most common malignancy affecting women in Canada, accounting for almost a third of
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta183
 Topotecan for the treatment of recurrent and stage IVB cervical cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta183 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice
Topotecan for the treatment of recurrent and stage IVB cervical cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 28 October 2009 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta183 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice
Setting The setting was secondary care. The economic study was conducted in the USA.
 HER-2 testing and trastuzumab therapy for metastatic breast cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis Elkin E B, Weinstein K C, Winer E P, Kuntz K M, Schnitt S J, Weeks J C Record Status This is a critical
HER-2 testing and trastuzumab therapy for metastatic breast cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis Elkin E B, Weinstein K C, Winer E P, Kuntz K M, Schnitt S J, Weeks J C Record Status This is a critical
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Palbociclib (Ibrance) for Advanced Breast Cancer Resubmission November 21, 2016
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Palbociclib (Ibrance) for Advanced Breast Cancer Resubmission November 21, 2016 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Palbociclib (Ibrance) for Advanced Breast Cancer Resubmission November 21, 2016 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This
Have you been newly diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer? Have you discussed whether chemotherapy will be part of your treatment plan?
 Have you been newly diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer? Have you discussed whether chemotherapy will be part of your treatment plan? This guide is designed to educate newly diagnosed women with early-stage
Have you been newly diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer? Have you discussed whether chemotherapy will be part of your treatment plan? This guide is designed to educate newly diagnosed women with early-stage
Start strong or switch? Adjuvant endocrine strategies for postmenopausal women with hormone-sensitive breast cancer
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 63 (2009) 1e10 Short review Start strong or switch? Adjuvant endocrine strategies for postmenopausal women with hormone-sensitive
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 63 (2009) 1e10 Short review Start strong or switch? Adjuvant endocrine strategies for postmenopausal women with hormone-sensitive
Watchful Waiting: Well Behaved Breast Cancers Non-Surgical Management of Breast Cancer
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10002 Watchful Waiting: Well Behaved Breast Cancers Non-Surgical Management of Breast Cancer Received:
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10002 Watchful Waiting: Well Behaved Breast Cancers Non-Surgical Management of Breast Cancer Received:
J Clin Oncol 23: by American Society of Clinical Oncology INTRODUCTION
 VOLUME 23 NUMBER 30 OCTOBER 20 2005 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Retrospective Analysis of Time to Recurrence in the ATAC Trial According to Hormone Receptor Status: An Hypothesis-Generating
VOLUME 23 NUMBER 30 OCTOBER 20 2005 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R T Retrospective Analysis of Time to Recurrence in the ATAC Trial According to Hormone Receptor Status: An Hypothesis-Generating
Pharmacoeconomics of Trastuzumab (Herceptin )
 Pharmacoeconomics of Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) Breast Cancer Press Seminar (2008.3.3) Department of Health Economics and Epidemiology Research Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo Takashi
Pharmacoeconomics of Trastuzumab (Herceptin ) Breast Cancer Press Seminar (2008.3.3) Department of Health Economics and Epidemiology Research Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo Takashi
ORMONOTERAPIA ADIUVANTE: QUALE LA DURATA OTTIMALE? MARIANTONIETTA COLOZZA
 ORMONOTERAPIA ADIUVANTE: QUALE LA DURATA OTTIMALE? MARIANTONIETTA COLOZZA THE NATURAL HISTORY OF HORMONE RECEPTOR- POSITIVE BREAST CANCER IS VERY LONG Recurrence hazard rate 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 ER+ (n=2,257)
ORMONOTERAPIA ADIUVANTE: QUALE LA DURATA OTTIMALE? MARIANTONIETTA COLOZZA THE NATURAL HISTORY OF HORMONE RECEPTOR- POSITIVE BREAST CANCER IS VERY LONG Recurrence hazard rate 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 ER+ (n=2,257)
Breast Cancer & Personalized Medicine
 Principles of Drug Development and Discovery Breast Cancer & Personalized Medicine Grace Leung, Efrat Shalom-Berensohn, Felipe Castro, Kate Burke-Wallace and Shiv Gaglani Breast Cancer... 2 nd most common
Principles of Drug Development and Discovery Breast Cancer & Personalized Medicine Grace Leung, Efrat Shalom-Berensohn, Felipe Castro, Kate Burke-Wallace and Shiv Gaglani Breast Cancer... 2 nd most common
Real-world observational data in costeffectiveness analyses: Herceptin as a case study
 Real-world observational data in costeffectiveness analyses: Herceptin as a case study DR BONNY PARKINSON, PROFESSOR ROSALIE VINEY, ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR STEPHEN GOODALL AND PROFESSOR MARION HAAS ISPOR AUSTRALIA
Real-world observational data in costeffectiveness analyses: Herceptin as a case study DR BONNY PARKINSON, PROFESSOR ROSALIE VINEY, ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR STEPHEN GOODALL AND PROFESSOR MARION HAAS ISPOR AUSTRALIA
5 AstraZeneca, Parklands, Macclesfield, SK10 4TF, UK
 British Journal of Cancer (2007) 97, 152 161 All rights reserved 0007 0920/07 $30.00 www.bjcancer.com Cost-effectiveness analysis of anastrozole vs tamoxifen in adjuvant therapy for early stage breast
British Journal of Cancer (2007) 97, 152 161 All rights reserved 0007 0920/07 $30.00 www.bjcancer.com Cost-effectiveness analysis of anastrozole vs tamoxifen in adjuvant therapy for early stage breast
Cost effectiveness of
 Cost effectiveness of brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris ) for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory CD30 positive Hodgkin Lymphoma who have failed at least one autologous stem cell transplant.
Cost effectiveness of brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris ) for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory CD30 positive Hodgkin Lymphoma who have failed at least one autologous stem cell transplant.
Adjuvant Systemic Therapy in Early Stage Breast Cancer
 Adjuvant Systemic Therapy in Early Stage Breast Cancer Julie R. Gralow, M.D. Director, Breast Medical Oncology Jill Bennett Endowed Professor of Breast Cancer Professor, Global Health University of Washington
Adjuvant Systemic Therapy in Early Stage Breast Cancer Julie R. Gralow, M.D. Director, Breast Medical Oncology Jill Bennett Endowed Professor of Breast Cancer Professor, Global Health University of Washington
Intervention(s) Results primary outcome Results secondary and other outcomes
 Uitgangsvraag 4: evidence tables Welke nieuwe vormen van risicoprofilering zijn - in tegenstelling tot de traditionele prognostische factoren als tumorgrootte, lymfklierstatus en tumorgradering - van invloed
Uitgangsvraag 4: evidence tables Welke nieuwe vormen van risicoprofilering zijn - in tegenstelling tot de traditionele prognostische factoren als tumorgrootte, lymfklierstatus en tumorgradering - van invloed
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Initial Economic Guidance Report Fulvestrant (Faslodex) for Metastatic Breast Cancer November 30, 2017
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Initial Economic Guidance Report Fulvestrant (Faslodex) for Metastatic Breast Cancer November 30, 2017 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Initial Economic Guidance Report Fulvestrant (Faslodex) for Metastatic Breast Cancer November 30, 2017 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report
Update from the 25th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 11 14, 2002
 Update from the 25th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 11 14, 2002 Nearly 5,000 physicians, oncologists, radiologists, epidemiologists, basic scientists, and breast cancer advocates from
Update from the 25th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 11 14, 2002 Nearly 5,000 physicians, oncologists, radiologists, epidemiologists, basic scientists, and breast cancer advocates from
4. Aflibercept showed significant improvement in overall survival (OS), the primary
 Cost effectiveness of aflibercept (Zaltrap ) in combination with FOLFIRI in the treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mcrc) that is resistant to or has progressed after an oxaliplatin
Cost effectiveness of aflibercept (Zaltrap ) in combination with FOLFIRI in the treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mcrc) that is resistant to or has progressed after an oxaliplatin
Adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, fluorouracil (CMF) in breast cancer: is it costeffective
 Adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, fluorouracil (CMF) in breast cancer: is it costeffective Norum J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for
Adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, fluorouracil (CMF) in breast cancer: is it costeffective Norum J Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for
Oncotype DX tools User Guide
 Oncotype DX tools User Guide This guide provides an overview of the data and quick access to the Oncotype DX tools Oncotype DX tools offers two quantitative calculator tools that may be used together with
Oncotype DX tools User Guide This guide provides an overview of the data and quick access to the Oncotype DX tools Oncotype DX tools offers two quantitative calculator tools that may be used together with
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 June 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta257
 Lapatinib or trastuzumab in combination with an aromatase inhibitor for the firstline treatment of metastatic hormone- receptor-positive e breast cancer that overexpresses HER2 Technology appraisal guidance
Lapatinib or trastuzumab in combination with an aromatase inhibitor for the firstline treatment of metastatic hormone- receptor-positive e breast cancer that overexpresses HER2 Technology appraisal guidance
SYSTEMIC THERAPY OPTIONS FOR BREAST CANCER IN 2014
 SYSTEMIC THERAPY OPTIONS FOR BREAST Oncology Day 2014 CANCER IN 2014 Dr. Katherine Enright, M.D., M.P.H., F.R.C.P.(C) Katherine.enright@Trilliumhealthpartners.ca OBJECTIVES 1. Outline an approach to the
SYSTEMIC THERAPY OPTIONS FOR BREAST Oncology Day 2014 CANCER IN 2014 Dr. Katherine Enright, M.D., M.P.H., F.R.C.P.(C) Katherine.enright@Trilliumhealthpartners.ca OBJECTIVES 1. Outline an approach to the
Treatment Options for Breast Cancer in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Adjuvant and Metastatic Systemic Therapy
 Women s Empowerment Cancer Advocacy Network (WE CAN) Conference Bucharest, Romania October 2015 Treatment Options for Breast Cancer in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Adjuvant and Metastatic Systemic
Women s Empowerment Cancer Advocacy Network (WE CAN) Conference Bucharest, Romania October 2015 Treatment Options for Breast Cancer in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Adjuvant and Metastatic Systemic
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 April 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta440
 Pegylated liposomal irinotecan for treating pancreatic cancer after gemcitabine Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 April 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta440 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject
Pegylated liposomal irinotecan for treating pancreatic cancer after gemcitabine Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 April 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta440 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject
Source of effectiveness data The effectiveness data were derived from a review of completed studies and authors' assumptions.
 Cost-effectiveness of hepatitis A-B vaccine versus hepatitis B vaccine for healthcare and public safety workers in the western United States Jacobs R J, Gibson G A, Meyerhoff A S Record Status This is
Cost-effectiveness of hepatitis A-B vaccine versus hepatitis B vaccine for healthcare and public safety workers in the western United States Jacobs R J, Gibson G A, Meyerhoff A S Record Status This is
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 18 April 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta518
 Tocilizumab for treating giant cell arteritis Technology appraisal guidance Published: 18 April 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta518 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Tocilizumab for treating giant cell arteritis Technology appraisal guidance Published: 18 April 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta518 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Clinical Oncology - Science in focus - Editorial. Understanding oestrogen receptor function in breast cancer, and its interaction with the
 Clinical Oncology - Science in focus - Editorial TITLE: Understanding oestrogen receptor function in breast cancer, and its interaction with the progesterone receptor. New preclinical findings and their
Clinical Oncology - Science in focus - Editorial TITLE: Understanding oestrogen receptor function in breast cancer, and its interaction with the progesterone receptor. New preclinical findings and their
The Study of Tamoxifen and Raloxifene (STAR): Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s The Study of Tamoxifen
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s The Study of Tamoxifen
Faecal DNA testing compared with conventional colorectal cancer screening methods: a decision analysis Song K, Fendrick A M, Ladabaum U
 Faecal DNA testing compared with conventional colorectal cancer screening methods: a decision analysis Song K, Fendrick A M, Ladabaum U Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Faecal DNA testing compared with conventional colorectal cancer screening methods: a decision analysis Song K, Fendrick A M, Ladabaum U Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Health technology Prophylactic mastectomy and oophorectomy in BRCA1-positive or BRCA2-positive patients.
 Decision analysis of prophylactic mastectomy and oophorectomy in BRCA1-positive or BRCA2-positive patients Grann V R, Panageas K S, Whang W, Antman K H, Neugut A I Record Status This is a critical abstract
Decision analysis of prophylactic mastectomy and oophorectomy in BRCA1-positive or BRCA2-positive patients Grann V R, Panageas K S, Whang W, Antman K H, Neugut A I Record Status This is a critical abstract
information was available on the following: pre-specification of the analysis a priori, sample size calculation and power estimation, stratification t
 information was available on the following: pre-specification of the analysis a priori, sample size calculation and power estimation, stratification to ensure balance across treatment groups, and formal
information was available on the following: pre-specification of the analysis a priori, sample size calculation and power estimation, stratification to ensure balance across treatment groups, and formal
4.3 Input parameters Patient
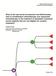 Table of Content 1 Introduction -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 Summary -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table of Content 1 Introduction -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7 Summary -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Background 1. Comparative effectiveness of nintedanib
 NCPE report on the cost effectiveness of nintedanib (Vargatef ) in combination with docetaxel for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced, metastatic or locally recurrent non-small cell lung
NCPE report on the cost effectiveness of nintedanib (Vargatef ) in combination with docetaxel for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced, metastatic or locally recurrent non-small cell lung
Nothing to disclose. Disclosures
 Low Dose-Rate Brachytherapy vs. Standard External Beam Radiotherapy vs. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Low Risk Prostate Cancer: A Cost-Utility Analysis Joelle Helou, Sofia Torres, Hima Bindu Musunuru,
Low Dose-Rate Brachytherapy vs. Standard External Beam Radiotherapy vs. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Low Risk Prostate Cancer: A Cost-Utility Analysis Joelle Helou, Sofia Torres, Hima Bindu Musunuru,
Outcomes assessed in the review The outcomes assessed in the review and used as model inputs were the incident rates of:
 The cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion compared with multiple daily injections for the management of diabetes Scuffham P, Carr L Record Status This is a critical abstract of
The cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion compared with multiple daily injections for the management of diabetes Scuffham P, Carr L Record Status This is a critical abstract of
Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease
 Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Combined chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Patients with Breast Cancer and Extensive Nodal Involvement.
 Combined chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Patients with Breast Cancer and Extensive Nodal Involvement. Ung O, Langlands A, Barraclough B, Boyages J. J Clin Oncology 13(2) : 435-443, Feb 1995 STUDY DESIGN
Combined chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Patients with Breast Cancer and Extensive Nodal Involvement. Ung O, Langlands A, Barraclough B, Boyages J. J Clin Oncology 13(2) : 435-443, Feb 1995 STUDY DESIGN
The efficacy of second-line hormone therapy for recurrence during adjuvant hormone therapy for breast cancer
 517734TAM6210.1177/1758834013517734Therapeutic Advances in Medical OncologyR Mori and Y Nagao research-article2013 Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology Original Research The efficacy of second-line
517734TAM6210.1177/1758834013517734Therapeutic Advances in Medical OncologyR Mori and Y Nagao research-article2013 Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology Original Research The efficacy of second-line
Clinical Policy Title: Breast cancer index genetic testing
 Clinical Policy Title: Breast cancer index genetic testing Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.22 Effective Date: January 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: October 19, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: October 19, 2016
Clinical Policy Title: Breast cancer index genetic testing Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.22 Effective Date: January 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: October 19, 2016 Most Recent Review Date: October 19, 2016
Type of intervention Screening and treatment. Economic study type Cost-utility analysis.
 Cost-effectiveness of testing for hypercoagulability and effects on treatment strategies in patients with deep vein thrombosis Auerbach A D, Sanders G D, Hambleton J Record Status This is a critical abstract
Cost-effectiveness of testing for hypercoagulability and effects on treatment strategies in patients with deep vein thrombosis Auerbach A D, Sanders G D, Hambleton J Record Status This is a critical abstract
Cost-effectiveness of evolocumab (Repatha ) for hypercholesterolemia
 Cost-effectiveness of evolocumab (Repatha ) for hypercholesterolemia The NCPE has issued a recommendation regarding the cost-effectiveness of evolocumab (Repatha ). Following NCPE assessment of the applicant
Cost-effectiveness of evolocumab (Repatha ) for hypercholesterolemia The NCPE has issued a recommendation regarding the cost-effectiveness of evolocumab (Repatha ). Following NCPE assessment of the applicant
CADTH CANADIAN DRUG EXPERT COMMITTEE FINAL RECOMMENDATION
 CADTH CANADIAN DRUG EXPERT COMMITTEE FINAL RECOMMENDATION Edoxaban (Lixiana SERVIER Canada Inc.) Indication: Prevention of Stroke and Systemic Embolic Events in Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
CADTH CANADIAN DRUG EXPERT COMMITTEE FINAL RECOMMENDATION Edoxaban (Lixiana SERVIER Canada Inc.) Indication: Prevention of Stroke and Systemic Embolic Events in Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 6 September 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta476
 Paclitaxel as albumin-bound nanoparticles with gemcitabine for untreated metastatic pancreatic cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 6 September 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta476 NICE 2018. All
Paclitaxel as albumin-bound nanoparticles with gemcitabine for untreated metastatic pancreatic cancer Technology appraisal guidance Published: 6 September 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta476 NICE 2018. All
Contributions from the systematic review of economic evaluations: the case of childhood hepatitis A vaccination in Brazil
 REVISÃO REVIEW 211 Contributions from the systematic review of economic evaluations: the case of childhood hepatitis A vaccination in Brazil Contribuições da revisão sistemática de avaliações econômicas:
REVISÃO REVIEW 211 Contributions from the systematic review of economic evaluations: the case of childhood hepatitis A vaccination in Brazil Contribuições da revisão sistemática de avaliações econômicas:
Cost-effectiveness of uterine artery embolization and hysterectomy for uterine fibroids Beinfeld M T, Bosch J L, Isaacson K B, Gazelle G S
 Cost-effectiveness of uterine artery embolization and hysterectomy for uterine fibroids Beinfeld M T, Bosch J L, Isaacson K B, Gazelle G S Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Cost-effectiveness of uterine artery embolization and hysterectomy for uterine fibroids Beinfeld M T, Bosch J L, Isaacson K B, Gazelle G S Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Does fasting during Ramadan trigger non-adherence to oral hormonal therapy in breast cancer patients?
 Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2012) 24, 133 137 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Original article Does fasting
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2012) 24, 133 137 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Original article Does fasting
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Technology Appraisals. Patient Access Scheme Submission Template
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals Patient Access Scheme Submission Template Bevacizumab in combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for the first-line
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Technology Appraisals Patient Access Scheme Submission Template Bevacizumab in combination with fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for the first-line
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 30 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta472
 Obinutuzumab with bendamustine for treating follicular lymphoma refractory to rituximab Technology appraisal guidance Published: 30 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta472 NICE 2018. All rights reserved.
Obinutuzumab with bendamustine for treating follicular lymphoma refractory to rituximab Technology appraisal guidance Published: 30 August 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta472 NICE 2018. All rights reserved.
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 February 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta306
 Pixantrone monotherapy for treating multiply relapsed or refractory aggressive e non-hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 February 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta306 NICE
Pixantrone monotherapy for treating multiply relapsed or refractory aggressive e non-hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma Technology appraisal guidance Published: 26 February 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta306 NICE
Delayed adjuvant tamoxifen: Ten-year results of a collaborative randomized controlled trial in early breast cancer (TAM-02 trial)
 Annals of Oncology 11: 515-519, 2000. 2000 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Original article Delayed adjuvant tamoxifen: Ten-year results of a collaborative randomized controlled
Annals of Oncology 11: 515-519, 2000. 2000 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. Original article Delayed adjuvant tamoxifen: Ten-year results of a collaborative randomized controlled
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 15 February 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 15 February 2006 Taxotere 20 mg, concentrate and solvent for solution for infusion B/1 vial of Taxotere and 1 vial
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 15 February 2006 Taxotere 20 mg, concentrate and solvent for solution for infusion B/1 vial of Taxotere and 1 vial
J 13 (10) : , 1995 STUDY DESIGN AND CONDUCT
 High-Dose Chemotherapy With Hematopoietic Rescue as Primary Treatment for Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Randomized Trial. Bezwoda WR, Seymour L and Dansey RD. J Clin Oncology, 13 (10) : 2483-2489, Oct 1995
High-Dose Chemotherapy With Hematopoietic Rescue as Primary Treatment for Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Randomized Trial. Bezwoda WR, Seymour L and Dansey RD. J Clin Oncology, 13 (10) : 2483-2489, Oct 1995
Precise Disease Classification Optimizes Bundled Payments. Session #99, March 7, 2018 Stuart Goldberg MD and Andrew Pecora MD
 Precise Disease Classification Optimizes Bundled Payments Session #99, March 7, 2018 Stuart Goldberg MD and Andrew Pecora MD 1 Conflict of Interest Stuart L Goldberg MD Salary: Cota Inc. Ownership Interests:
Precise Disease Classification Optimizes Bundled Payments Session #99, March 7, 2018 Stuart Goldberg MD and Andrew Pecora MD 1 Conflict of Interest Stuart L Goldberg MD Salary: Cota Inc. Ownership Interests:
trabectedin, 0.25 and 1mg powder for concentrate for solution for infusion (Yondelis ) SMC No. (452/08) Pharma Mar S.A. Sociedad Unipersonal
 trabectedin, 0.25 and 1mg powder for concentrate for solution for infusion (Yondelis ) SMC No. (452/08) Pharma Mar S.A. Sociedad Unipersonal 08 October 2010 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
trabectedin, 0.25 and 1mg powder for concentrate for solution for infusion (Yondelis ) SMC No. (452/08) Pharma Mar S.A. Sociedad Unipersonal 08 October 2010 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
Source of effectiveness data The effectiveness evidence was derived from a single study that was identified from a review of the literature.
 Costs and consequences of using pamidronate compared with zoledronic acid in the management of breast cancer patients in the UK Guest J F, Clegg J P, Davie A M, McCloskey E Record Status This is a critical
Costs and consequences of using pamidronate compared with zoledronic acid in the management of breast cancer patients in the UK Guest J F, Clegg J P, Davie A M, McCloskey E Record Status This is a critical
CONCLUSIONS (Random Thoughts and Take Home Questions) gianluigi casadei
 CONCLUSIONS (Random Thoughts and Take Home Questions) gianluigi casadei IL SOLE 24 ORE (September 4, 2012) Sustainability of health spending is a known issue for a long time The current crisis has dramatized
CONCLUSIONS (Random Thoughts and Take Home Questions) gianluigi casadei IL SOLE 24 ORE (September 4, 2012) Sustainability of health spending is a known issue for a long time The current crisis has dramatized
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Crizotinib (Xalkori) Resubmission for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Crizotinib (Xalkori) Resubmission for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer May 2, 2013 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Economic Guidance Report Crizotinib (Xalkori) Resubmission for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer May 2, 2013 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice
Priority setting at a national level NICE - England. Gillian Leng Deputy Chief Executive, NICE September 2016
 Priority setting at a national level NICE - England Gillian Leng Deputy Chief Executive, NICE September 2016 Areas to cover The role of NICE in the UK health system General approach to appraising new drugs
Priority setting at a national level NICE - England Gillian Leng Deputy Chief Executive, NICE September 2016 Areas to cover The role of NICE in the UK health system General approach to appraising new drugs
Setting The setting was a hospital. The economic study was conducted in the USA.
 Incremental cost-effectiveness of laser therapy for visual loss secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion Brown G C, Brown M M, Sharma S, Busbee B, Brown H Record Status This is a critical abstract of
Incremental cost-effectiveness of laser therapy for visual loss secondary to branch retinal vein occlusion Brown G C, Brown M M, Sharma S, Busbee B, Brown H Record Status This is a critical abstract of
As a country in economic transition, China faces fundamental barriers to
 Challenges of Health Economics and Observational Research in China Graeme Jacombs, MA, MSc (with Marco DiBonaventura, PhD) China Healthcare Reform As a country in economic transition, China faces fundamental
Challenges of Health Economics and Observational Research in China Graeme Jacombs, MA, MSc (with Marco DiBonaventura, PhD) China Healthcare Reform As a country in economic transition, China faces fundamental
Cost-effectiveness of Ivacaftor (Kalydeco ) for the treatment of cystic fibrosis in patients age 6 years and older who have the G551D mutation
 Cost-effectiveness of Ivacaftor (Kalydeco ) for the treatment of cystic fibrosis in patients age 6 years and older who have the G551D mutation January 2013 1. A rapid review submission on the drug ivacaftor
Cost-effectiveness of Ivacaftor (Kalydeco ) for the treatment of cystic fibrosis in patients age 6 years and older who have the G551D mutation January 2013 1. A rapid review submission on the drug ivacaftor
Monitoring Metastatic Breast Cancer with Serum HER-2/neu: Individual Patient Profiles
 Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, a global leader in clinical diagnostics, provides healthcare professionals in hospital, reference, and physician office laboratories and point-of-care settings with the
Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, a global leader in clinical diagnostics, provides healthcare professionals in hospital, reference, and physician office laboratories and point-of-care settings with the
