Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP)
|
|
|
- Erin Wilson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Information for patients
2 This information is for people with cancer of unknown primary (CUP) and covers symptoms, investigations/tests and treatment options. If there is anything you do not understand, please ask your doctor or nurse specialist. Cancer of unknown primary is a term that covers many different types of cancers. It affects around 3-5% of people with cancer. People who have a cancer of unknown primary often have more than one area of cancer. CUP is more common in people aged 60 and over, but it can also affect people younger than this. When a new tumour is found it is not always obvious what type of cancer it is. There will need to be tests and investigations to find out whether what has been found is a primary cancer or a secondary cancer. Sometimes doctors find where the cancer has spread but cannot find where in the body the cancer first began to grow. This type of cancer is called a cancer of unknown primary (CUP) or occult primary tumour. If the doctors are not sure where the primary cancer is they may be able to suggest a part of the body where the cancer may have started. This information will be based on where the secondary cancers are found, the symptoms which you are experiencing or from test results. The test results can also tell how the cancer will behave. This will then help a specialist doctor to organise your treatment plan. What are primary and secondary cancers? The place where a cancer starts growing in the body is known as the primary site. Cells from the primary site can break away and spread to the other parts of the body through the blood or lymphatic system. These form other cancers known as secondary cancers or metastases. The lymphatic system is part of the immune system which is the body s natural defence against infection and disease. Lymph nodes (glands) are part of this system. They exist throughout the body and are linked by a network of tiny tubes called ducts that carry fluid known as lymph.
3 The secondary cancer is named according to the primary site. For example, a cancer that starts in the lung is known as a lung cancer but if it spreads to the liver it is still known as lung cancer. The secondary cancer in the liver would be made up of the lung cancer cells and not liver cancer cells. Secondary cancers of metastases are usually treated according to the primary cancer. Knowing where the cancer starts helps doctors to know which treatment is needed. Why can t my primary cancer be found? There are several different reasons why a primary cancer cannot always be found. It may be that the primary cancer is too small to be seen on a scan or it may be hidden behind a larger secondary cancer. It also may have disappeared even though it has now spread to other parts of the body. This can sometimes happen if the body s immune system has successfully disposed of it. If your primary cancer is found then you will be passed on to the relevant team for treatment and be directed to the correct specialist nurse team. Symptoms of cancer of uknown primary (CUP) Symptoms of cancer of unknown primary will differ depending on where the secondary cancer is found. General symptoms include: Unexplained weight loss. Reduced appetite. Feeling very tired all the time Feeling breathless or looking pale - usually due to lack of red blood cells in the blood, known as anaemia. Secondary cancer can also cause different symptoms to different parts of the body depending where the cancer is. 2
4 Secondary cancer to the liver If the secondary cancer is in the liver you may find that you get: Swelling in your tummy (abdomen). Feel sick of have a lack of appetite. Yellowing of the skin or eye known as jaundice Have a collection of fluid in the abdomen known as ascites. Secondary cancer in the bone This may cause a dull pain in the bones, more commonly as night. If bones are weakened by cancer they can break more easily. Types of cancers of unknown primary (CUP) The doctor may request a sample of the tissue from the secondary cancer site; this is known as a biopsy. Looking at the appearance of the biopsy under a microscope and doing other tests of the tissue, it makes it easier to determine the type of cancer which has been found. This will assist the doctors to give them more information about the likely behaviour of the cancer and how to treat it. The pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells and to find out the type of cancer, such as: Adenocarcinoma Most cancers of unknown primary are known as adenocarcinomas (a type of carcinoma) which make up between 60-90% of cancers. Adenocarcinomas develop from the gland cells that cover certain parts of the body. The most common parts of the body for them to be are: the lungs, pancreas, bowel, kidneys, liver and stomach. In women they can also be seen in the ovaries, womb and breasts. Poorly differentiated carcinomas Poorly differentiated means that the cells look very different from normal cells so it is difficult to distinguish what type of cancer the primary is. Squamous cell cancers These develop from flat cells usually found on the surface of the skin or 3
5 in the lining of internal surfaces of your body. Only 1 in 20 people with CUP have this cancer. These can be found in the lung, skin, head, neck, oesophagus and cervix. Tests and diagnosis As previously mentioned tests may need to be performed to determine a diagnosis. X-rays and CT scans X-rays and CT scans use a low level of radiation to take pictures of the inside of your body. This test is useful for doctors to see the whole of the body to look for the primary cancer or further secondary cancers. Ultrasound An ultrasound scan will use sound waves. This test is painless and has no side effects. It is useful in finding abnormalities in the tummy (abdomen). Having a biopsy If an area of abnormality is found then you may be asked to have a biopsy. This means taking a sample of tissue from the site either with help of an ultrasound or an endoscopy. This is the most important test when finding an unknown primary cancer. Endoscopy An endoscopy is a camera test that looks inside your body. It is performed using an endoscope which is a long flexible tube with a tiny camera and light on the end. There are different types of endoscopes depending on which area of the body the doctor is looking at. When inside the body it can also be used to take biopsies if needed. Once a scan and a biopsy have been taken, the results will then be discussed at a multi-disciplinary team (MDT) Meeting. Treatment options There are different types of treatment for patients with carcinoma of unknown primary (CUP). For most patients with CUP, current 4
6 treatments unfortunately do not cure the cancer. Four types of standard treatment are used: Surgery (only in selected patients). Radiation therapy: a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. Chemotherapy: a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, by killing the cells. Hormone therapy: a cancer treatment that removes hormones or blocks their action and stops cancer cells from growing. New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials (if available). The Multi-Disciplinary Team It is the policy of the MDT that all patients (irrespective of age and stage of disease) with a new diagnosis of cancer of unknown primary (CUP) will be discussed at the multi-disciplinary team (MDT) meeting. At this meeting the team will discuss each patient s scans or biopsies and organise treatment plans and follow-up arrangements to ensure that every patient with cancer receives multi-disciplinary management. These meetings will also be an opportunity to discuss difficult cases later in the patient pathway, if necessary. In rare cases, urgent treatment may be needed to be carried out without an MDT decision. In these situations, efforts will be made by the relevant specialist team to discuss your treatment with other members of the MDT. Who are the CUP MDT? Designated lead clinician (chair) who will take overall responsibility for the service. Designated surgeon(s). Gastroenterologist(s). Oncologist(s). Oncology expert in radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Radiologist. 5
7 Histopathologist. Clinical Nurse Specialists. Information and support for patients. Dietitian. Provides specialist dietary advice. MDT Co-ordinator. User s issues and Patient Information Lead. Research Nurse. Provides information to the team on any trials. A Key Worker is appointed from the MDT members for each individual patient. The name of your current key worker will be recorded in your case notes. The Key Worker for CUP patients will be the Upper GI Clinical Nurse Specialists. Any changes to this will be made after discussion with the patient or if the primary cancer is found. Useful numbers Dr E Pintus (Oncologist) CUP Lead Secretary Tel: Dr J Gildersleve (Oncologist) Secretary Tel: Dr E Hill (Oncologist) Secretary Tel: Mr M Booth (Surgeon) Secretary Tel: Miss M Sampson (Surgeon) Secretary Tel: Dr N Chandra (Gastroenterologist) Secretary Tel: Dr J Booth (Gastroenterologist) Secretary Tel: Adelaide Ward Tel: Sidmouth Ward Tel: Berkshire Cancer Centre (9am-5pm) Tel: King Edward Ward (8:30am-5pm) Tel: Radiotherapy Clinic (9am-5pm) Tel: Bracknell Healthspace Tel: Your Key Worker/Clinical Nurse Specialist is: Ruth Moxon, Emma Hogbin and Hilary Fagan They can be contacted on: Tel: or Pager:
8 Support groups Macmillan Cancer Support, Freephone Provides information, emotional support and practical advice by telephone or letter. Also provides information in other languages British Association for Counselling BACP House, 15 St John s Business Park, Lutterworth, Leicestershire, LE17 4HB Tel: Can provide a list of local counsellors for cancer patients and their families. Cancer Research UK Cancer Research UK Angel Building, 407 St John Street, London, EC1V 4AD Tel: Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust London Road Reading RG1 5AN Telephone This document can be made available in other languages and formats upon request. Berkshire Cancer Centre, November 2018 Review due: November
Treatment for cancer of the gall bladder
 Treatment for cancer of the gall bladder Hepatobiliary Services Information for Patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction The aim of this booklet is to help you understand more about
Treatment for cancer of the gall bladder Hepatobiliary Services Information for Patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction The aim of this booklet is to help you understand more about
Uterine sarcoma. Information for patients Gynaecology
 Uterine sarcoma Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 12 This leaflet is intended to offer you support and information at a very difficult and stressful time in your life. To be told that you
Uterine sarcoma Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 12 This leaflet is intended to offer you support and information at a very difficult and stressful time in your life. To be told that you
Colorectal multidisciplinary team. Information for patients
 Colorectal multidisciplinary team Information for patients About this booklet Following your diagnosis of bowel (colorectal) cancer, you will be cared for by a team of medical experts and health professionals
Colorectal multidisciplinary team Information for patients About this booklet Following your diagnosis of bowel (colorectal) cancer, you will be cared for by a team of medical experts and health professionals
Pancreatic Cancer (1 of 5)
 i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated.
 How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
Gynae Cancer Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information
 Gynae Cancer Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information Introduction This booklet is for people who have been diagnosed with gynaecological cancers which include cancer of the cervix, ovary, vulva, vagina
Gynae Cancer Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information Introduction This booklet is for people who have been diagnosed with gynaecological cancers which include cancer of the cervix, ovary, vulva, vagina
Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Explained
 The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre Pan Glasgow Urology / Oncology Patient Information Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Explained The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre 1053 Great Western Road, Glasgow
The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre Pan Glasgow Urology / Oncology Patient Information Testicular Germ Cell Cancer Explained The Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre 1053 Great Western Road, Glasgow
Gastric (stomach) cancer
 Gastric (stomach) cancer Information for patients This booklet is for patients who have been diagnosed with gastric (stomach) cancer and will explain your treatment options. For anyone, receiving news
Gastric (stomach) cancer Information for patients This booklet is for patients who have been diagnosed with gastric (stomach) cancer and will explain your treatment options. For anyone, receiving news
Hepatobiliary investigations
 Hepatobiliary investigations Hepatobiliary Services Information for patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction You have been referred to the Hepatobiliary Unit. We specialise in procedures
Hepatobiliary investigations Hepatobiliary Services Information for patients Liver i Stomach Pancreas Gall bladder Introduction You have been referred to the Hepatobiliary Unit. We specialise in procedures
Surgery. In this fact sheet. Surgery: English
 Surgery: English Surgery This information is about surgery (having an operation). Any words that are underlined are explained in the glossary at the end. Many people with cancer will have surgery as part
Surgery: English Surgery This information is about surgery (having an operation). Any words that are underlined are explained in the glossary at the end. Many people with cancer will have surgery as part
This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated.
 A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer
 Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Investigating your suspected cancer. Having a malignancy of unknown origin (MUO)
 Investigating your suspected cancer Having a malignancy of unknown origin (MUO) Contents 3 What is MUO? 4 What tests might you need? 6 Getting your results 6 Who can you talk to? 7 Contact details 2 What
Investigating your suspected cancer Having a malignancy of unknown origin (MUO) Contents 3 What is MUO? 4 What tests might you need? 6 Getting your results 6 Who can you talk to? 7 Contact details 2 What
Post-operative Internal High Dose Rate (HDR) brachytherapy for gynaecological cancers
 Post-operative Internal High Dose Rate (HDR) brachytherapy for gynaecological cancers In the clinic today, you and your doctor have agreed that you are going to have radiotherapy treatment for your cancer.
Post-operative Internal High Dose Rate (HDR) brachytherapy for gynaecological cancers In the clinic today, you and your doctor have agreed that you are going to have radiotherapy treatment for your cancer.
What is Cancer? Treatment. What is a MDT meeting?
 i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
Urology Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information
 Urology Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information Introduction This booklet is for people who have been diagnosed with urological cancers which include prostate, bladder, kidney, testicular and penile
Urology Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information Introduction This booklet is for people who have been diagnosed with urological cancers which include prostate, bladder, kidney, testicular and penile
Breast Cancer. Common kinds of breast cancer are
 Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer
 Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Breast Cancer Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information
 Breast Cancer Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information Introduction This booklet is for people who have been diagnosed with breast cancer. It tells you about the breast multidisciplinary team and other
Breast Cancer Multi Disciplinary Team Patient Information Introduction This booklet is for people who have been diagnosed with breast cancer. It tells you about the breast multidisciplinary team and other
Information for patients
 Information for patients Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT) with Yttrium-90 Micro-spheres Leading Interventional Oncology Network Contents Introduction 3 What to tell the doctor 3 What is Selective
Information for patients Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT) with Yttrium-90 Micro-spheres Leading Interventional Oncology Network Contents Introduction 3 What to tell the doctor 3 What is Selective
Gall bladder cancer. Information for patients Hepatobiliary
 Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
Gall bladder cancer Information for patients Hepatobiliary page 2 of 12 Who will provide my care? You will be cared for by a number of professionals who work together. These professionals will be specialist
How is primary breast cancer treated?
 How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
Esophageal cancer. What is esophageal cancer? Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Retroperineal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND)
 Acute Services Division Information for patients about Retroperineal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Introduction This booklet gives you information about surgery to remove the residual lymph nodes at the
Acute Services Division Information for patients about Retroperineal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Introduction This booklet gives you information about surgery to remove the residual lymph nodes at the
The organs and tissues of the body are made up of tiny building blocks called cells. Cancer is a disease of these cells.
 Surgery: English Surgery This fact sheet is about surgery for cancer. This is when someone has an operation to remove part of the body where the cancer is growing. It is also used to help diagnose cancer.
Surgery: English Surgery This fact sheet is about surgery for cancer. This is when someone has an operation to remove part of the body where the cancer is growing. It is also used to help diagnose cancer.
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Understanding desmoid-type fibromatosis
 Understanding desmoid-type fibromatosis Sarcoma UK Support Line 0808 801 0401 supportline@ The bone & soft tissue cancer charity About this booklet This booklet is for anyone who has been diagnosed with
Understanding desmoid-type fibromatosis Sarcoma UK Support Line 0808 801 0401 supportline@ The bone & soft tissue cancer charity About this booklet This booklet is for anyone who has been diagnosed with
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
Understanding GIST: Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours
 Understanding GIST: Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours Sarcoma UK Support Line 0808 801 0401 supportline@ The bone & soft tissue cancer charity About this booklet This booklet is for anyone who has been
Understanding GIST: Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours Sarcoma UK Support Line 0808 801 0401 supportline@ The bone & soft tissue cancer charity About this booklet This booklet is for anyone who has been
Bowel Cancer Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
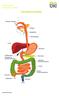 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
Radiotherapy to the oesophagus
 Radiotherapy to the oesophagus Information for patients The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about radiotherapy to the oesophagus, including the reasons for giving radiotherapy, details
Radiotherapy to the oesophagus Information for patients The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about radiotherapy to the oesophagus, including the reasons for giving radiotherapy, details
Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile)
 Patient information - Radiology Unit Tel 0118 322 7991 Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile) Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedures known as
Patient information - Radiology Unit Tel 0118 322 7991 Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile) Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedures known as
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect
 Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
Northern Ireland breast screening. Helping you decide
 Northern Ireland breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer? 4 What is breast screening? 5 Breast screening results 8 Making a choice the possible benefits 11 and risks of breast screening
Northern Ireland breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer? 4 What is breast screening? 5 Breast screening results 8 Making a choice the possible benefits 11 and risks of breast screening
Information for Breast Patients having a Sentinel Node Biopsy
 Information for Breast Patients having a Sentinel Node Biopsy Information for patients Excellent Care with Compassion What is sentinel node? The sentinel node (gland) is the first lymph node or nodes in
Information for Breast Patients having a Sentinel Node Biopsy Information for patients Excellent Care with Compassion What is sentinel node? The sentinel node (gland) is the first lymph node or nodes in
Northern Ireland breast screening. Helping you decide
 Northern Ireland breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 4 What is breast screening? 5 Breast screening results 9 Making a choice the possible benefits and risks of breast screening
Northern Ireland breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 4 What is breast screening? 5 Breast screening results 9 Making a choice the possible benefits and risks of breast screening
Radiotherapy to the abdomen
 Radiotherapy to the abdomen Information for patients The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about radiotherapy to the abdomen, including the side effects that you may experience. Although
Radiotherapy to the abdomen Information for patients The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about radiotherapy to the abdomen, including the side effects that you may experience. Although
Breast cancer. In this fact sheet: Breast cancer: English
 Breast cancer: English Breast cancer This information is about breast cancer and treatments for breast cancer. Any words that are underlined are explained in the word list at the end. If you have any questions,
Breast cancer: English Breast cancer This information is about breast cancer and treatments for breast cancer. Any words that are underlined are explained in the word list at the end. If you have any questions,
What is an ultrasound scan?
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphoma-action.org.uk www.lymphoma-action.org.uk Ultrasound scan An ultrasound scan uses sound waves to make pictures of the inside of your body. It can help
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphoma-action.org.uk www.lymphoma-action.org.uk Ultrasound scan An ultrasound scan uses sound waves to make pictures of the inside of your body. It can help
Aviva Group Protection Our guide to cancer
 ww For employers use only. Aviva Group Protection Our guide to cancer 1 2 In 2013, 131 million working days were lost due to sickness absence in the UK, at an average of 4.4 working days per employee 1.
ww For employers use only. Aviva Group Protection Our guide to cancer 1 2 In 2013, 131 million working days were lost due to sickness absence in the UK, at an average of 4.4 working days per employee 1.
Skull Base Tumour Service. The Multi-Disciplinary Team (MDT) Explained. Jan 2018 v1
 Skull Base Tumour Service The Multi-Disciplinary Team (MDT) Explained Jan 2018 v1 Skull base tumours grow in the bones of the skull that form the bottom of the head and the body ridge between the nose
Skull Base Tumour Service The Multi-Disciplinary Team (MDT) Explained Jan 2018 v1 Skull base tumours grow in the bones of the skull that form the bottom of the head and the body ridge between the nose
Wilms Tumour A brief note for the parents
 Wilms Tumour A brief note for the parents By Dr. Abid Qazi!1 PARENT S GUIDE FACTSHEET Cancer is not an incurable disease any more in many circumstances. The key for cure is early diagnosis. However, it
Wilms Tumour A brief note for the parents By Dr. Abid Qazi!1 PARENT S GUIDE FACTSHEET Cancer is not an incurable disease any more in many circumstances. The key for cure is early diagnosis. However, it
Head and Neck Cancer
 Head and Neck Cancer What Happens Next? Information for patients and carers Introduction You will be looked after by a multidisciplinary team (MDT). This is a group of health professionals with specialist
Head and Neck Cancer What Happens Next? Information for patients and carers Introduction You will be looked after by a multidisciplinary team (MDT). This is a group of health professionals with specialist
Investigations for Pancreatic, Biliary Tract and Duodenal Cancers
 Investigations for Pancreatic, Biliary Tract and Duodenal Cancers Information for Patients Excellent Care with Compassion 2 The following investigations will help your Cancer Specialist Team decide on
Investigations for Pancreatic, Biliary Tract and Duodenal Cancers Information for Patients Excellent Care with Compassion 2 The following investigations will help your Cancer Specialist Team decide on
Skin cancer nurse specialist and multi-disciplinary team
 University Teaching Trust Skin cancer nurse specialist and multi-disciplinary team This leaflet contains details of information resources which you may find useful (see last page) Dermatology Irving Building
University Teaching Trust Skin cancer nurse specialist and multi-disciplinary team This leaflet contains details of information resources which you may find useful (see last page) Dermatology Irving Building
Quick Facts about Ampullary Cancer
 Quick Facts about Ampullary Cancer What is the Ampulla of Vater? Princess Margaret The liver, gallbladder and pancreas produce important fluids to help you digest food. These fluids are carried through
Quick Facts about Ampullary Cancer What is the Ampulla of Vater? Princess Margaret The liver, gallbladder and pancreas produce important fluids to help you digest food. These fluids are carried through
What is Testicular cancer?
 Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Unknown Primary Service for patients at Chesterfield Royal Hospital
 Unknown Primary Service for patients at Chesterfield Royal Hospital David Brooks Macmillan Consultant in Palliative Medicine Louise Merriman GP Cancer Lead With thanks to Macmillan Cancer Support, who
Unknown Primary Service for patients at Chesterfield Royal Hospital David Brooks Macmillan Consultant in Palliative Medicine Louise Merriman GP Cancer Lead With thanks to Macmillan Cancer Support, who
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Spinal cord compression: what it means and how it can be treated
 Spinal cord compression: what it means and how it can be treated Patient Information Oncology Department Author ID: Acute Oncology Nurse Specialist Leaflet Number: CC 036 Version: 2.1 Name of Leaflet:
Spinal cord compression: what it means and how it can be treated Patient Information Oncology Department Author ID: Acute Oncology Nurse Specialist Leaflet Number: CC 036 Version: 2.1 Name of Leaflet:
Sentinel Node Biopsy in the Treatment of Oral Cancer. Patient Information Leaflet
 Sentinel Node Biopsy in the Treatment of Oral Cancer Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Please read carefully through this information sheet, which describes a new procedure we are providing at this
Sentinel Node Biopsy in the Treatment of Oral Cancer Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Please read carefully through this information sheet, which describes a new procedure we are providing at this
Haematuria Clinic. Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST
 Haematuria Clinic Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST The Haematuria Clinic You have been referred to the Haematuria Clinic as
Haematuria Clinic Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST The Haematuria Clinic You have been referred to the Haematuria Clinic as
General Information Key Points
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect
 Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) with Drug-Eluting Beads
 Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) with Drug-Eluting Beads A minimally invasive treatment for liver cancer Provided as an educational service by Biocompatibles UK Ltd, a BTG International group company
Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) with Drug-Eluting Beads A minimally invasive treatment for liver cancer Provided as an educational service by Biocompatibles UK Ltd, a BTG International group company
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for Brain Metastases. Information for patients
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for Brain Metastases Information for patients Northern Centre for Cancer Care Freeman Hospital Introduction This leaflet has been written to give you general information
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for Brain Metastases Information for patients Northern Centre for Cancer Care Freeman Hospital Introduction This leaflet has been written to give you general information
National Breast Cancer Audit next steps. Martin Lee
 National Breast Cancer Audit next steps Martin Lee National Cancer Audits Current Bowel Cancer Head & Neck Cancer Lung cancer Oesophagogastric cancer New Prostate Cancer - undergoing procurement Breast
National Breast Cancer Audit next steps Martin Lee National Cancer Audits Current Bowel Cancer Head & Neck Cancer Lung cancer Oesophagogastric cancer New Prostate Cancer - undergoing procurement Breast
Ovarian Cancer. What you should know. making cancer less frightening by enlightening
 Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
SURVEY ON THE EXPERIENCE AND NEEDS OF PATIENTS
 SURVEY ON THE EXPERIENCE AND NEEDS OF PATIENTS LIVING WITH OESOPHAGEAL OR GASTRIC CANCER I am writing to you on behalf of EuropaColon, a not-for-profit organization established in 00, dedicated to saving
SURVEY ON THE EXPERIENCE AND NEEDS OF PATIENTS LIVING WITH OESOPHAGEAL OR GASTRIC CANCER I am writing to you on behalf of EuropaColon, a not-for-profit organization established in 00, dedicated to saving
Bowel cancer screening the facts. Bowel cancer screening: the facts
 Bowel cancer screening the facts Bowel cancer screening: the facts What is this leaflet about? This leaflet is about the benefits and risks of the Northern Ireland bowel cancer screening programme and
Bowel cancer screening the facts Bowel cancer screening: the facts What is this leaflet about? This leaflet is about the benefits and risks of the Northern Ireland bowel cancer screening programme and
Groin lymph node dissection surgery for penile cancer
 Urology department Groin lymph node dissection surgery for penile cancer Introduction This information is for patients who need surgery to remove the lymph nodes in one or both groins. The operation is
Urology department Groin lymph node dissection surgery for penile cancer Introduction This information is for patients who need surgery to remove the lymph nodes in one or both groins. The operation is
(Whole Central Nervous System)
 The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the Brain and Spinal Cord (Whole Central Nervous System) Information for adult patients You have been given this leaflet as your doctor has recommended that
The Radiotherapy Department Radiotherapy to the Brain and Spinal Cord (Whole Central Nervous System) Information for adult patients You have been given this leaflet as your doctor has recommended that
Your urgent assessment in head and neck
 Your urgent assessment in head and neck This leaflet will answer some of your questions about why you have been sent to us for an urgent assessment, and what the tests might involve. If you have more questions,
Your urgent assessment in head and neck This leaflet will answer some of your questions about why you have been sent to us for an urgent assessment, and what the tests might involve. If you have more questions,
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer?... 3 What is breast screening?... 4 Breast screening results... 7 Making a choice the possible benefits and risks of breast screening... 11
NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer?... 3 What is breast screening?... 4 Breast screening results... 7 Making a choice the possible benefits and risks of breast screening... 11
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer?... 3 What is breast screening?... 3 Breast screening results... 5 Making a choice the possible benefits and risks of breast screening... 8
NHS breast screening Helping you decide What is breast cancer?... 3 What is breast screening?... 3 Breast screening results... 5 Making a choice the possible benefits and risks of breast screening... 8
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy. Issued by the Breast Team
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Issued by the Breast Team Why do my Lymph Nodes require investigation? The lymphatic system is a pathway of lymph vessels and
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Breast Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Issued by the Breast Team Why do my Lymph Nodes require investigation? The lymphatic system is a pathway of lymph vessels and
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Inflammatory breast cancer. This booklet describes what inflammatory breast cancer is, the symptoms, how it is diagnosed and how it may be treated.
 Inflammatory breast cancer This booklet describes what inflammatory breast cancer is, the symptoms, how it is diagnosed and how it may be treated. 2 Call our Helpline on 0808 800 6000 Introduction We hope
Inflammatory breast cancer This booklet describes what inflammatory breast cancer is, the symptoms, how it is diagnosed and how it may be treated. 2 Call our Helpline on 0808 800 6000 Introduction We hope
SELF ASSESSMENT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM)
 SELF ASSESSMENT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM) Network Trust MDT MDT Lead Clinician ASWCN TAUNTON AND SOMERSET Taunton Lung MDT (11-2C-1) - 2011/12 Dr Sarah Foster Compliance Self Assessment LUNG MDT
SELF ASSESSMENT REPORT (MULTI-DISCIPLINARY TEAM) Network Trust MDT MDT Lead Clinician ASWCN TAUNTON AND SOMERSET Taunton Lung MDT (11-2C-1) - 2011/12 Dr Sarah Foster Compliance Self Assessment LUNG MDT
Delivering 62 Day GP Cancer Waits in a Complex Landscape. Hannah Marder Cancer Manager University Hospitals Bristol
 Delivering 62 Day GP Cancer Waits in a Complex Landscape Hannah Marder Cancer Manager University Hospitals Bristol Overview The 62 day GP target Cancer pathways What causes breaches? Good practice and
Delivering 62 Day GP Cancer Waits in a Complex Landscape Hannah Marder Cancer Manager University Hospitals Bristol Overview The 62 day GP target Cancer pathways What causes breaches? Good practice and
Primary Liver Cancer or Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 Primary Liver Cancer or Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Patient Information Booklet UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Primary Liver Cancer or Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Patient Information Booklet UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Vascular malformations and their management
 Information for patients Vascular malformations and their management Introduction This leaflet tells you about the condition known as vascular malformation, including venous malformation, arteriovenous
Information for patients Vascular malformations and their management Introduction This leaflet tells you about the condition known as vascular malformation, including venous malformation, arteriovenous
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet. Under review
 Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Transrectal Ultrasound (Trus) Guided Prostate Biopsies Urology Patient Information Leaflet What is the purpose of my appointment? Your doctor has informed us that you have an elevated Prostate Specific
Health Bites Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer. Normal breast
 Health Bites Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Normal breast The normal breast tissue varies in size and shape. The breasts rest in front of the rib cage. The breasts are made up of fatty tissue, milk ducts
Health Bites Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Normal breast The normal breast tissue varies in size and shape. The breasts rest in front of the rib cage. The breasts are made up of fatty tissue, milk ducts
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Protocol
 1 Department of Oncology. Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Protocol Version: Document type: Document sponsor Designation Document author [ s] Designation[s] Approving committee / Group Ratified by: Date
1 Department of Oncology. Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Protocol Version: Document type: Document sponsor Designation Document author [ s] Designation[s] Approving committee / Group Ratified by: Date
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Merkel Cell Carcinoma UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Merkel Cell Carcinoma UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm What is this booklet about? This booklet
Merkel Cell Carcinoma UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm What is this booklet about? This booklet
Radiotherapy to one side of the mouth and neck
 Clinical Oncology Radiotherapy to one side of the mouth and neck Consent information for patients Radiotherapy may be given on its own or with chemotherapy (separate information will be given about chemotherapy).
Clinical Oncology Radiotherapy to one side of the mouth and neck Consent information for patients Radiotherapy may be given on its own or with chemotherapy (separate information will be given about chemotherapy).
The incidence of pancreatic cancer is rising in India and is higher in the urban male population in the western and northern parts of India.
 Published on: 9 Jun 2015 Pancreatic Cancer What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells, which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control, causing an abnormal growth
Published on: 9 Jun 2015 Pancreatic Cancer What Is Cancer? The body is made up of cells, which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control, causing an abnormal growth
Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Department of Urology Information for patients
 Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Department of Urology Information for patients i What is a retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND)? You have probably already undergone surgery and treatment
Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) Department of Urology Information for patients i What is a retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND)? You have probably already undergone surgery and treatment
University College Hospital. Neck dissection. Cancer Services Head and Neck Centre
 Alternatively: Telephone: 0808 800 1234 09:00 to 20:00 Monday to Friday. Cancer information nurse specialists can answer questions about cancer types, treatment and what to expect following a diagnosis.
Alternatively: Telephone: 0808 800 1234 09:00 to 20:00 Monday to Friday. Cancer information nurse specialists can answer questions about cancer types, treatment and what to expect following a diagnosis.
Bowel cancer. In this fact sheet: Page 1 of 13 Macmillan fact sheet 2017: Bowel cancer. Bowel Cancer: English
 Bowel Cancer: English Bowel cancer This information is about bowel cancer and treatments for bowel cancer. Any words that are underlined are explained in the word list at the end. If you have any questions,
Bowel Cancer: English Bowel cancer This information is about bowel cancer and treatments for bowel cancer. Any words that are underlined are explained in the word list at the end. If you have any questions,
BOWEL CANCER. Cancer information.
 BOWEL CANCER Cancer information www.cancervic.org.au What is bowel cancer? Bowel cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women in Australia1 and is more common in people over the age of
BOWEL CANCER Cancer information www.cancervic.org.au What is bowel cancer? Bowel cancer is the second most common cancer in both men and women in Australia1 and is more common in people over the age of
Jaundice , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. syf80102 Last reviewed: 05/05/2017 1
 Jaundice Introduction Jaundice causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow. Too much bilirubin causes jaundice. Bilirubin is a yellow chemical in hemoglobin, the substance that carries
Jaundice Introduction Jaundice causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow. Too much bilirubin causes jaundice. Bilirubin is a yellow chemical in hemoglobin, the substance that carries
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Dr Candice Silverman MBBS (HONS) FRACS General & Laparoscopic Surgeon
 Dr Candice Silverman MBBS (HONS) FRACS General & Laparoscopic Surgeon Core Specialist Group Suite 5G, John Flynn Medical Centre 42 Inland Drive TUGUN QLD 4224 Tel: 07 5598 0955 Write questions or notes
Dr Candice Silverman MBBS (HONS) FRACS General & Laparoscopic Surgeon Core Specialist Group Suite 5G, John Flynn Medical Centre 42 Inland Drive TUGUN QLD 4224 Tel: 07 5598 0955 Write questions or notes
The Urology One-Stop Clinic
 The Urology One-Stop Clinic Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered The aim of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about the Urology One-Stop Clinic. What is the Urology One-Stop
The Urology One-Stop Clinic Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered The aim of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about the Urology One-Stop Clinic. What is the Urology One-Stop
A trial looking at selumetinib for thyroid cancer that has stopped taking up radioactive iodine (SEL-I-METRY)
 Page 1 of 6 A trial looking at selumetinib for thyroid cancer that has stopped taking up radioactive iodine (SEL-I-METRY) Cancer type: Thyroid cancer Status: Open Phase: Phase 2 This trial is for people
Page 1 of 6 A trial looking at selumetinib for thyroid cancer that has stopped taking up radioactive iodine (SEL-I-METRY) Cancer type: Thyroid cancer Status: Open Phase: Phase 2 This trial is for people
Having CT Enterography Information for Patients
 Having CT Enterography Information for Patients In this leaflet: Introduction 2 What is CT Enterography?.....2 How does it work?. 2 Are there any risks?.3 Are there any alternatives to CT Enterography?..3
Having CT Enterography Information for Patients In this leaflet: Introduction 2 What is CT Enterography?.....2 How does it work?. 2 Are there any risks?.3 Are there any alternatives to CT Enterography?..3
Locally advanced prostate cancer
 Diagnosis Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose locally advanced prostate
Diagnosis Helpline 0800 074 8383 prostatecanceruk.org 1 Locally advanced prostate cancer In this fact sheet: What is locally advanced prostate cancer? What tests are used to diagnose locally advanced prostate
Sentinel lymph node biopsy for early oral cancer
 Sentinel lymph node biopsy for early oral cancer Information for patients from the Oral and Maxillofacial Department When cancer cells start to spread from the main cancer this represents an important
Sentinel lymph node biopsy for early oral cancer Information for patients from the Oral and Maxillofacial Department When cancer cells start to spread from the main cancer this represents an important
COSD & Source of Referral
 COSD & Source of Referral A Brief guide October 2014 Michael Sharpe Data Improvement Manager National Cancer Registration Service What is COSD? Cancer and Outcomes Services Dataset Clinical dataset for
COSD & Source of Referral A Brief guide October 2014 Michael Sharpe Data Improvement Manager National Cancer Registration Service What is COSD? Cancer and Outcomes Services Dataset Clinical dataset for
Treating cancer of the endometrium. Information for patients Gynaecology
 Treating cancer of the endometrium Information for patients Gynaecology We have written this leaflet to provide you with information following your diagnosis of cancer of the endometrium. We understand
Treating cancer of the endometrium Information for patients Gynaecology We have written this leaflet to provide you with information following your diagnosis of cancer of the endometrium. We understand
