In vitro and Intracellular Activities of Peptide Deformylase. Inhibitor GSK against Legionella pneumophila Isolates
|
|
|
- Clara Short
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 October 2014 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi: /aac Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 In vitro and Intracellular Activities of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitor GSK against Legionella pneumophila Isolates Jacques Dubois 1, Maïtée Dubois 1, Jean-François Martel 1, Kelly Aubart 2 and Deborah Butler 2# 1 M360, Sherbrooke, Québec, Canada; 2 Antibacterial Discovery Performance Unit, Infectious Disease Therapeutic Area, GlaxoSmithKline, Collegeville, PA, USA 8 9 Running Title: GSK activity against L. pneumophila # corresponding author, address, Deborah.L.Butler@gsk.com
2 ABSTRACT GSK , a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor currently in development as an oral and intravenous agent for the treatment of hospitalized community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, showed poor in vitro activity against a panel of 50 L. pneumophila strains, with MICs ranging from 1 to 16 μg/ml, and an MIC 90 of 16 μg/ml, but very potent intracellular activity, with MIECs ranging from 0.12 to 2 μg/ml, and 98% of the strains being inhibited by concentrations 1 μg/ml
3 TEXT The opportunistic Gram-negative bacterium Legionella pneumophila, which can grow free-living or as a facultative intracellular organism in amoebae or human alveolar macrophages, is the major causative agent of Legionnaire s disease, a severe form of pneumonia (1). Although there are at least 15 serogroups identified, L. pneumophila serogroup 1 accounts for over 80% of the cases worldwide (2). Except in the event of a Legionnaire s disease outbreak, L. pneumophila is treated empirically as part of the therapy used for hospitalized pneumonia and, given the severity of the disease, it is important to ensure that the antibacterial agent to be utilized shows good activity against this pathogen. GSK is a novel peptide deformylase (PDF) inhibitor with good safety and pharmacokinetic properties (3-5) currently in Phase II development as an oral and intravenous agent for the treatment of hospitalized community-acquired bacterial pneumonia and acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections. GSK has demonstrated good antibacterial activity against other bacterial pneumonia causative agents, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus and Haemophilus influenzae (6) and it was, therefore, important to investigate its potency against this atypical pathogen. In order to assess the in vitro activity of GSK , susceptibility studies were performed against 50 L. pneumophila strains: 25 from serogroup 1, and 5 each from serogroups 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. L. pneumophila isolates were collected from 1992 to present, mostly from human respiratory tract, and grown on buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar to produce pure cultures. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) endpoints were determined by broth microdilution according to Clinical and Laboratory 3
4 Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines (7). MIC plates, containing approximately 5x10 5 colony forming units (CFU)/mL in BYE broth (with Legionella BCYE Growth supplement), were incubated at 35 o C in aerobic conditions for 48 h. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of antimicrobial agent that completely inhibited visible growth after the appropriate incubation time. GSK showed variable activity against this panel of 50 L. pneumophila strains, with MICs ranging from 1 to 16 μg/ml, and MIC 50 and MIC 90 values of 8 and 16 μg/ml respectively (Table 1). No significant differences could be observed in the activity of GSK against strains from different serogroups, with 8 μg/ml being the most frequent MIC in all sets (Table 1). Both, azithromycin and levofloxacin showed more potent extracellular activity with MIC 50 /MIC 90 values of 0.06/0.5 μg/ml, and 0.008/0.016 μg/ml, respectively (Table 1). The results of this study indicate that GSK is substantially less active in vitro against L. pneumophila serogroups 1 to 6 than azithromycin or levofloxacin, the drugs normally used for the treatment of Legionellosis. The GSK MIC for S. aureus ATCC29213 tested in Mueller- Hinton broth was identical or within a 2-fold dilution of the MIC obtained using BYE, indicating that there is not drug inactivation by the test medium. As L. pneumophila is a facultative intracellular bacterium that multiplies within phagocytic cells, the ability of GSK to effectively inhibit growth of L. pneumophila in human monocytes was investigated. In these studies, human mononuclear cells (U-937) (8) cultured at a final concentration of approximately 10 4 cell/well in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) containing 10% heatinactivated fetal bovine serum, were infected as a suspension with of each of the 4
5 L. pneumophila strains grown to logarithmic phase, by incubating together for 1 h in a shaking incubator. Infected cultures were transferred to flat-bottomed wells and maintained without shaking thereafter at 37 o C in 5% CO 2 and 95% air for 7 days. After 24 h, infected cultures were washed three times with drug-free broth to remove extracellular bacteria, and GSK (1 to 16 μg/ml), azithromycin (0.03 to 0.05 μg/ml), or erythromycin (0.06 to 1 μg/ml), were added to the wells at a concentration equal to the corresponding MIC/strain combination. At Day 3, cultures were washed, split into two groups, and incubated for an additional 4 days with or without antibiotic. CFUs were determined in duplicate using BCYE agar at time 0, and then every 24 h until Day 7. The results demonstrated that MIC concentrations of GSK not only prevented growth of L. pneumophila inside macrophages but also reduced intracellular bacterial counts by an average of 1.21og 10 with respect to the original inocula (Figure 1A). Although some growth could be observed after Day 5, bacterial counts never reached those present in the culture prior to the addition of the antibiotic. Azithromycin also reduced bacterial counts by an average of 1.5log 10 by Day 3, but a significantly less reduction of growth was observed with erythromycin (Figure 1A). Neither of the macrolides could prevent bacterial growth during the last 4 days of exposure, perhaps due to metabolism or changes in uptake, by either the bacterium or the monocytes. None of the three drugs demonstrated a strong post-antibiotic effect, and re-growth could be observed in all cases after the removal of the antibiotic at Day 3 (Figure 1B) although exposure to GSK seemed to delay re-growth slightly more. Given the clear intracellular activity demonstrated by GSK , the minimum extracellular concentration capable of inhibiting intracellular proliferation (MIEC) of 5
6 these 50 L. pneumophila strains was determined in human mononuclear cells (U-937) (8, 9) using the conditions described above except that, in this case, the infected cultures were maintained without shaking for 5 days. After 24 h, extracellular bacteria were removed, and GSK , azithromycin, or levofloxacin, were added at fractions of their MIC to determine the precise MIEC. The MIEC was defined as the lowest extracellular concentration of compound capable of preventing L. pneumophila intracellular proliferation and was calculated at Day 3 and at Day 5 of antibiotic exposure. Against the 50 strains of L. pneumophila with extracellular MICs ranging from 1 to 16 μg/ml, the GSK MIEC at Day 3 ranged from 0.12 to 2 μg/ml, with 98% of the strains being inhibited by concentrations 1 μg/ml (Table 2). MIECs of 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25 and 0.12 μg/ml, with a mean reduction of 73% in bacterial counts, were demonstrated against 1/50 (2%), 29/50 (58%), 9/50 (18%), 10/50 (20%) and 1/50 (2%) of the strains respectively (Table 2). In all cases the compound was at least 4-fold more potent intracellularly than extracellularly. Most of the strains showed GSK MIECs 8-fold (35/50; 70%) or 16-fold (11/50; 22%) below their extracellular MIC, with the remaining 3/50 and 1/50 strains demonstrating a 4-fold and a 32-fold difference between both values, respectively (Table 2). No significant differences were observed between the serogroups tested and in all cases MIECs were maintained at Day 5 of exposure. GSK was clearly much more effective at inhibiting proliferation of L. pneumophila within macrophages than in extracellular conditions. The azithromycin MIEC at Day 3 exposure was identical to its extracellular MIC in 94% of the strains (47/50) and it was 2-fold lower in the other 3 strains (Table 2). The levofloxacin MIEC 6
7 was 2-fold below its extracellular MIC in most of the strains (41/50; 82%), with 1/50 strains showing a MIEC 4-fold lower than the MIC and the other 7/50 (14%) demonstrating identical MIEC and MIC values (Table 2). It is not the first time that the extracellular activity of an antimicrobial agent against L. pneumophila does not correlate with its intracellular potency. β-lactams, for example, are highly active in vitro but do not penetrate the intracellular compartment and are therefore inactive in vivo. On the other hand, tetracyclines have poor in vitro activity against L. pneumophila, as they are inactivated by iron in the BYEα growth media, but are active in animal models of Legionnaires s disease and have been proven an effective treatment in humans (10). However, in the case of PDF inhibitors, the difference in extracellular and intracellular activities could be due to a change in the primary target of the antibacterial agent when the bacterium growths inside macrophages. L. pneumophila has three functional PDF enzymes that show different substrate specificities and catalytic efficiencies (11). Recently, it has been shown that PdfA plays an essential role in the extracellular growth of L. pneumophila and that activity against this enzyme is the main determinant of the compound s in vitro antibacterial activity. On the other hand, PdfC seems to play a critical role in L. pneumophila replication within macrophages and is indispensable for the bacterium to cause a productive infection in a guinea pig model of Legionellosis (Huang et al., submitted for publication). Therefore, the antibacterial activity shown by GSK against intracellular L. pneumophila could be due, at least in part, to its potent inhibition of PdfC (Glen Van Aller, unpublished results), although its accumulation inside macrophages may also contribute to it (12). 7
8 In conclusion, GSK demonstrates good intracellular activity against 50 L. pneumophila strains from serogroups 1 to 6, with an MIEC 90 of 1 μg/ml. In fact, its intracellular activity is similar to that demonstrated against other typical pneumonia causative agents which have GSK MIC 90 s of 2 μg/ml (S. pneumoniae) or 4 μg/ml (S. aureus and H. influenzae) (6). Moreover, plasma and intrapulmonary pharmacokinetic studies with GSK dosed intravenously twice daily for 4 days shows that its time course in epithelial lining fluid (ELF) and alveolar macrophages (AM) mirrors the plasma concentration-time profile. In fact, the AUC0-τ ratios of ELF and AM to total plasma were 1.2 and 2.5, respectively (12). Therefore, GSK should be active against intracellular L. pneumophila at the concentrations necessary to achieve efficacy versus the other bacterial respiratory tract pathogens and could be an effective treatment for lower respiratory tract infections caused by this atypical pathogen
9 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Editorial support in the form of development of manuscript first draft, collating author comments, assembling tables and preparing final version for publication was provided by Dr. Magdalena Zalacain at Zala Drug Discovery Consulting and was funded by GSK
10 REFERENCES 1. Edelstein PH, Meyer RD Legionnaires' disease. A review. Chest 85: Yu VL, Plouffe JF, Pastoris MC, Stout JE, Schousboe M, Widmer A, Summersgill J, File T, Heath CM, Paterson DL, Chereshsky A Distribution of Legionella species and serogroups isolated by culture in patients with sporadic community-acquired legionellosis: an international collaborative survey. J Infect Dis 186: Naderer OJ, Dumont E, Zhu J, Kurtinecz M, Jones LS Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of repeat dosing of the antibiotic GSK , a peptide deformylase inhibitor: a randomized placebocontrolled study. J Antimicrob Chemother 68: Naderer OJ, Dumont E, Zhu J, Kurtinecz M, Jones LS Effect of H2 blockade and food on single-dose pharmacokinetics of GSK , a peptide deformylase inhibitor antibacterial. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57: Naderer OJ, Dumont E, Zhu J, Kurtinecz M, Jones LS Single-dose safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of the antibiotic GSK , a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57: O'Dwyer K, Hackel M, Hightower S, Hoban D, Bouchillon S, Qin D, Aubart K, Zalacain M, Butler D Comparative analysis of the antibacterial 10
11 activity of a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor, GSK Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 8th ed. Approved standard M07-A8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, Pa, USA. 8. Horwitz MA Legionella, vol. Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium of the American Society for Microbiology. ASM Press, Washington DC. 9. Higa F, Kusano N, Tateyama M, Shinzato T, Arakaki N, Kawakami K, Saito A Simplified quantitative assay system for measuring activities of drugs against intracellular Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol 36: Edelstein PH Antimicrobial chemotherapy for legionnaires' disease: a review. Clin Infect Dis 21 Suppl 3:S Huang J, Van Aller GS, Taylor AN, Kerrigan JJ, Liu WS, Trulli JM, Lai Z, Holmes D, Aubart KM, Brown JR, Zalacain M Phylogenomic and biochemical characterization of three Legionella pneumophila polypeptide deformylases. J Bacteriol 188: Naderer OJ, Rodvold KA, Jones LS, Zhu JZ, Bowen CL, Chen L, Dumont E Penetration of GSK into epithelial lining fluid and alveolar macrophages as determined by bronchoalveolar lavage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:
12 FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. 1. Intracellular activity of GSK , azithromycin and erythromycin against L. pneumophila strains. At Day 1, drug was added to the infected cultures, at the appropriate concentration for each MIC/strain combination (GSK at 1 to 16 μg/ml; azithromycin at 0.03 to 0.05 μg/ml, and erythromycin at 0.06 to 1 μg/ml). At Day 3, cultures were washed, split into two groups and incubated until Day 7 with antibiotic (A) or without antibiotic (B). Each point represents the mean of the results obtained from duplicate or triplicate experiments (and duplicate quantitative plating) with each of the 50 L. pneumophila strains. Black arrows indicate the point at which the drugs were added
13 Table 1. Summary of the extracellular activity of GSK , azithromycin and levofloxacin against 50 L. pneumophila strains from serogroups 1 to 6 Antibiotic L. pneumophila (n) Number of strains inhibited by antibiotic at MIC* (μg/ml) All (50) Serogroup 1 (25) Serogroup 2 (5) 3 2 GSK Serogroup 3 (5) 4 1 Serogroup 4 (5) Serogroup 5 (5) Serogroup 6 (5) All (50) Serogroup 1 (25) Serogroup 2 (5) Azithromycin Serogroup 3 (5) Serogroup 4 (5) Serogroup 5 (5) 4 1 Serogroup 6 (5) 4 1 All (50) Serogroup 1 (25) Serogroup 2 (5) 5 Levofloxacin Serogroup 3 (5) 1 4 Serogroup 4 (5) 4 1 Serogroup 5 (5) 3 2 Serogroup 6 (5) 5 *All experiments were performed in duplicate or triplicate MIC 50s are in italics; MIC 90s are in bold 13
14 Table 2. Summary of the intracellular activity of GSK , azithromycin, and levofloxacin at Day 3 of exposure against 50 L. pneumophila strains with different MICs Antibiotic GSK Azithromycin L. pneumophila (# strains) MIC (μg/ml) Number of strains inhibited by antibiotic at MIEC* (μg/ml) Levofloxacin *All experiments were performed in duplicate or triplicate MIC 50s are in italics; MIC 90s are in bold 14
15
Comparison of Omadacycline and Tigecycline Pharmacodynamics in the Plasma, Epithelial Lining Fluid, and Alveolar Macrophages in Healthy Subjects
 Comparison of Omadacycline and Tigecycline Pharmacodynamics in the Plasma, Epithelial Lining Fluid, and Alveolar Macrophages in Healthy Subjects Karolyn S. Horn, Mark H. Gotfried, Judith N. Steenbergen,
Comparison of Omadacycline and Tigecycline Pharmacodynamics in the Plasma, Epithelial Lining Fluid, and Alveolar Macrophages in Healthy Subjects Karolyn S. Horn, Mark H. Gotfried, Judith N. Steenbergen,
Affinity of Doripenem and Comparators to Penicillin-Binding Proteins in Escherichia coli and ACCEPTED
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Determination of MIC & MBC
 1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds
 Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
Comparative Analysis of the Antibacterial Activity of a Novel Peptide
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 March 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.02566-12 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Comparative
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 March 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.02566-12 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Comparative
The spread of multidrug resistance among major causative
 Comparative Analysis of the Antibacterial Activity of a Novel Peptide Deformylase Inhibitor, GSK1322322 Karen O Dwyer, a Meredith Hackel, b Sarah Hightower, a Daryl Hoban, b Samuel Bouchillon, b Donghui
Comparative Analysis of the Antibacterial Activity of a Novel Peptide Deformylase Inhibitor, GSK1322322 Karen O Dwyer, a Meredith Hackel, b Sarah Hightower, a Daryl Hoban, b Samuel Bouchillon, b Donghui
Received 21 December 2012; returned 4 January 2013; revised 19 February 2013; accepted 23 February 2013
 J Antimicrob Chemother 013; 68: 1901 1909 doi:10.1093/jac/dkt097 Advance Access publication 3 April 013 Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of repeat dosing of the antibiotic GSK133, a peptide deformylase
J Antimicrob Chemother 013; 68: 1901 1909 doi:10.1093/jac/dkt097 Advance Access publication 3 April 013 Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of repeat dosing of the antibiotic GSK133, a peptide deformylase
Received 30 March 2005; returned 16 June 2005; revised 8 September 2005; accepted 12 September 2005
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
ACCEPTED. Comparison of disk diffusion and agar dilution methods for erythromycin and
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on January 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.000-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on January 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.000-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Multi-clonal origin of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates. determined by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
In vitro assessment of dual drug combinations to inhibit growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 26 January 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.04127-14 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 In vitro assessment
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 26 January 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.04127-14 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 In vitro assessment
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia. Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali
 Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Steven D. Brown* and Maria M. Traczewski. The Clinical Microbiology Institute, 9725 SW Commerce Circle, Wilsonville, Oregon 97070
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, May 2010, p. 2063 2069 Vol. 54, No. 5 0066-4804/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.01569-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Comparative
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, May 2010, p. 2063 2069 Vol. 54, No. 5 0066-4804/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.01569-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Comparative
Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital
 101 Research article Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital Abstract BN Dissanayake 1,, DE Jayawardena 2, CG Senevirathna 1, TM Gamage 1 Sri Lankan Journal
101 Research article Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital Abstract BN Dissanayake 1,, DE Jayawardena 2, CG Senevirathna 1, TM Gamage 1 Sri Lankan Journal
Biological Consulting Services
 Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
Basic Concepts of PK/PD -pharmacodynamic indices- Johan W. Mouton MD PhD FIDSA Professor pharmacokinetics and pharmacodymamics
 Basic Concepts of PK/PD -pharmacodynamic indices- Johan W. Mouton MD PhD FIDSA Professor pharmacokinetics and pharmacodymamics This patient needs antibiotics. But which ones? Intensive care patient Ceftazidime,
Basic Concepts of PK/PD -pharmacodynamic indices- Johan W. Mouton MD PhD FIDSA Professor pharmacokinetics and pharmacodymamics This patient needs antibiotics. But which ones? Intensive care patient Ceftazidime,
Retapamulin Inhibition of Translation and ACCEPTED. 50S Ribosomal Subunit Formation in. Staphylococcus aureus Cells
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 June 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00475-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 June 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00475-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITIES OF SELECTED MEDICINAL PLANTS AGAINST MRSA STRAINS ISOLATED FROM SURGICAL WOUND INFECTIONS
 ICAMS 2014 5 th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITIES OF SELECTED MEDICINAL PLANTS AGAINST MRSA STRAINS ISOLATED FROM SURGICAL WOUND INFECTIONS NİZAMİ DURAN
ICAMS 2014 5 th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITIES OF SELECTED MEDICINAL PLANTS AGAINST MRSA STRAINS ISOLATED FROM SURGICAL WOUND INFECTIONS NİZAMİ DURAN
Effect of efflux pump inhibitors on antimicrobial resistance and in vivo colonization of Campylobacter jejuni
 Effect of efflux pump inhibitors on antimicrobial resistance and in vivo colonization of Campylobacter jejuni J. Lin & M. Ensminger Department of Animal Science, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville,
Effect of efflux pump inhibitors on antimicrobial resistance and in vivo colonization of Campylobacter jejuni J. Lin & M. Ensminger Department of Animal Science, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville,
Comparison of Omadacycline and Tigecycline Pharmacokinetics in the. Plasma, Epithelial Lining Fluid, and Alveolar Cells in Healthy Adult Subjects
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 10 July 2017 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01135-17 Copyright 2017 Gotfried et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 10 July 2017 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01135-17 Copyright 2017 Gotfried et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the
NEW ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS IN 2003 : SPECTRUM AND INDICATIONS. 20th Symposium (spring 2003) Thursday May 22nd 2003
 NEW ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS IN 2003 : SPECTRUM AND INDICATIONS 20th Symposium (spring 2003) Thursday May 22nd 2003 The slides presented at this meeting are available on this site as "Web slide shows" and
NEW ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS IN 2003 : SPECTRUM AND INDICATIONS 20th Symposium (spring 2003) Thursday May 22nd 2003 The slides presented at this meeting are available on this site as "Web slide shows" and
Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR (1167)
 From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
Efficacy of Ceftaroline Fosamil against Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains in a rabbit meningitis model.
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 September 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00285-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Efficacy
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 September 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00285-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Efficacy
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
Department of Pharmacy Services, Hartford Hospital, 80 Seymour Street, Hartford, CT 06102, USA; 2
 Pathogens 2015, 4, 599-605; doi:10.3390/pathogens4030599 Article OPEN ACCESS pathogens ISSN 2076-0817 www.mdpi.com/journal/pathogens Assessing the Surrogate Susceptibility of Oxacillin and Cefoxitin for
Pathogens 2015, 4, 599-605; doi:10.3390/pathogens4030599 Article OPEN ACCESS pathogens ISSN 2076-0817 www.mdpi.com/journal/pathogens Assessing the Surrogate Susceptibility of Oxacillin and Cefoxitin for
Spectrum of vancomycin and susceptibility testing
 Spectrum of vancomycin and susceptibility testing Olivier Denis Service de Microbiologie Laboratoire de bactériologie Service de Microbiologie Hôpital Erasme Glycopeptides Vancomycin 1958 < Amycolatopsis
Spectrum of vancomycin and susceptibility testing Olivier Denis Service de Microbiologie Laboratoire de bactériologie Service de Microbiologie Hôpital Erasme Glycopeptides Vancomycin 1958 < Amycolatopsis
Adenium Biotech. Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes
 Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Legionnaire s Disease: Overview and Treatment
 Legionnaire s Disease: Overview and Treatment Sarah Newman, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Nicklaus Children s Hospital Disclosures Authors of this presentation have the following to disclose concerning
Legionnaire s Disease: Overview and Treatment Sarah Newman, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Nicklaus Children s Hospital Disclosures Authors of this presentation have the following to disclose concerning
NOSOCOMIAL LEGIONELLA SEPTICEMIA IN PATIENT WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW
 NOSOCOMIAL LEGIONELLA SEPTICEMIA IN PATIENT WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Theerawat Naksanguan and Pakpoom Phoompoung Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical
NOSOCOMIAL LEGIONELLA SEPTICEMIA IN PATIENT WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Theerawat Naksanguan and Pakpoom Phoompoung Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical
Activity of antibiotics against intracellular S. aureus
 Activity of antibiotics against intracellular S. aureus F. Van Bambeke Unité de Pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire Université catholique de Louvain Brussels, Belgium Disclosures Grants-in-aid from
Activity of antibiotics against intracellular S. aureus F. Van Bambeke Unité de Pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire Université catholique de Louvain Brussels, Belgium Disclosures Grants-in-aid from
Ueli von Ah, Dieter Wirz, and A. U. Daniels*
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2008, p. 2083 2087 Vol. 46, No. 6 0095-1137/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.00611-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Rapid Differentiation
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2008, p. 2083 2087 Vol. 46, No. 6 0095-1137/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.00611-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Rapid Differentiation
PHARMACOKINETIC & PHARMACODYNAMIC OF ANTIBIOTICS
 PHARMACOKINETIC & PHARMACODYNAMIC OF ANTIBIOTICS SITI HIR HURAIZAH MD TAHIR Bpharm (UKM), MSc (Clinical Microbiology) (UoN) CLINICAL PHARMACIST HOSPITAL MELAKA WHY STUDY PHARMACOKINETICS (PK) AND PHARMACODYNAMICS
PHARMACOKINETIC & PHARMACODYNAMIC OF ANTIBIOTICS SITI HIR HURAIZAH MD TAHIR Bpharm (UKM), MSc (Clinical Microbiology) (UoN) CLINICAL PHARMACIST HOSPITAL MELAKA WHY STUDY PHARMACOKINETICS (PK) AND PHARMACODYNAMICS
Activity of Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Against a Broad Spectrum of Recent Clinical Anaerobic Isolates
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 25 November 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.02253-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activity
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 25 November 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.02253-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activity
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Clin Microbiol Infect 2002; 8:
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE In vitro activity of levofloxacin against contemporary clinical isolates of Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae from North America and Europe I. A. Critchley
ORIGINAL ARTICLE In vitro activity of levofloxacin against contemporary clinical isolates of Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae from North America and Europe I. A. Critchley
Report on susceptibility of Salmonella serotypes in Belgium Vicky Jasson
 CODA-CERVA Report on susceptibility of Salmonella serotypes in Belgium 2014. Vicky Jasson Veterinary and Agrochemical Research Centre 1 Introduction Salmonella is one of the most important bacterial zoonotic
CODA-CERVA Report on susceptibility of Salmonella serotypes in Belgium 2014. Vicky Jasson Veterinary and Agrochemical Research Centre 1 Introduction Salmonella is one of the most important bacterial zoonotic
ANTIBACTERIAL TOOTHPASTE: DO NOT SWALLOW
 ANTIBACTERIAL TOOTHPASTE: DO NOT SWALLOW Sarah McCuaig BACKGROUND, PURPOSE, HYPOTHESES Market statistics indicate a significant increase in the use of antibacterial products in North American households.
ANTIBACTERIAL TOOTHPASTE: DO NOT SWALLOW Sarah McCuaig BACKGROUND, PURPOSE, HYPOTHESES Market statistics indicate a significant increase in the use of antibacterial products in North American households.
Action of Antifungal Imidazoles on Staphylococcus aureus
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 1982, p. 47 474 66-484/82/947-4$2./ Copyright 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 22, No. 3 Action of Antifungal Imidazoles on Staphylococcus aureus
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 1982, p. 47 474 66-484/82/947-4$2./ Copyright 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 22, No. 3 Action of Antifungal Imidazoles on Staphylococcus aureus
Setting The setting was secondary care. The economic study was carried out in the USA.
 Cost-effectiveness of IV-to-oral switch therapy: azithromycin vs cefuroxime with or without erythromycin for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia Paladino J A, Gudgel L D, Forrest A, Niederman
Cost-effectiveness of IV-to-oral switch therapy: azithromycin vs cefuroxime with or without erythromycin for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia Paladino J A, Gudgel L D, Forrest A, Niederman
SCMID Online Lecture Library. by author. Optimizing antimicrobial therapy in the elderly. Dose Finding - The Past
 Optimizing antimicrobial therapy in the elderly Johan W. Mouton MD PhD FIDSA Professor pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics Dosing should be such that the level of antmicrobial activity is associated
Optimizing antimicrobial therapy in the elderly Johan W. Mouton MD PhD FIDSA Professor pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics Dosing should be such that the level of antmicrobial activity is associated
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS
 CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
Synergism of Fosfomycin-Ampicillin and Fosfomycin-
 ANTIMICROBiAL AGENTS AND CHEMoTHERAPY, May 1978, p. 75-79 66-484/78/13-75$2./ Copyright 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Synergism of Fosfomycin-Ampicillin and Fosfomycin-
ANTIMICROBiAL AGENTS AND CHEMoTHERAPY, May 1978, p. 75-79 66-484/78/13-75$2./ Copyright 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Synergism of Fosfomycin-Ampicillin and Fosfomycin-
From the Laboratory of Cellular Physiology and Immunology, The Rockefeller University, New York 10021
 Published Online: 1 February, 1981 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.153.2.398 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on April 7, 2018 INTERACTION OF THE LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE BACTERIUM (LEGIONELLA PNEUMOPHILA)
Published Online: 1 February, 1981 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.153.2.398 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on April 7, 2018 INTERACTION OF THE LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE BACTERIUM (LEGIONELLA PNEUMOPHILA)
Differential impact of macrolide compounds in the selection of macrolide nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae
 Differential impact of macrolide compounds in the selection of macrolide nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae EDITORIAL JM Blondeau Department of Clinical Microbiology, Royal University Hospital and
Differential impact of macrolide compounds in the selection of macrolide nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae EDITORIAL JM Blondeau Department of Clinical Microbiology, Royal University Hospital and
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT.
 International Journal of Advanced Research and Review www.ijarr.in ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT. Dr.Mayuri Thanwar 1, Dr.Dhananjay Dwivedi 2 1. Scientific Officer,
International Journal of Advanced Research and Review www.ijarr.in ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF GYMNEMA SYLVESTRE HYDROALCOHOLIC LEAF EXTRACT. Dr.Mayuri Thanwar 1, Dr.Dhananjay Dwivedi 2 1. Scientific Officer,
Babak Valizadeh, DCLS
 Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Respiratory Tract Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1391. 02. 05 2012. 04. 25 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Biological Safety Cabinet Process specimens in biological
Synergists from Portulaca oleracea with macrolides against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and related mechanism
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Synergists from Portulaca oleracea with macrolides against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and related mechanism KP Fung *, QB Han, M Ip,
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Synergists from Portulaca oleracea with macrolides against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and related mechanism KP Fung *, QB Han, M Ip,
Discrepancies in the recovery of bacteria from multiple sinuses in acute and chronic sinusitis
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 879 885 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45655-0 Short Communication Correspondence Itzhak Brook ib6@georgetown.edu Received 1 March 2004 Accepted 18 May 2004 Discrepancies
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 879 885 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45655-0 Short Communication Correspondence Itzhak Brook ib6@georgetown.edu Received 1 March 2004 Accepted 18 May 2004 Discrepancies
JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, Suppl. B, 69 73 JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections G. Tatsis*, G.
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, Suppl. B, 69 73 JAC Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin versus clarithromycin in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections G. Tatsis*, G.
PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether each of the following statements are true or false.
 MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
PD Targets for Various Infection Types: Stasis vs. 1-Log Kill vs. 2 Log Kill
 PD Targets for Various Infection Types: Stasis vs. 1-Log Kill vs. 2 Log Kill G.L. Drusano, M.D. Professor and Director Institute for Therapeutic Innovation University of Florida To have insight into appropriate
PD Targets for Various Infection Types: Stasis vs. 1-Log Kill vs. 2 Log Kill G.L. Drusano, M.D. Professor and Director Institute for Therapeutic Innovation University of Florida To have insight into appropriate
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
Cefuroxime iv Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Azithromycin vs Cefuroxime Plus Erythromycin for Empirical Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Hospitalized Patients
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Azithromycin vs Cefuroxime Plus Erythromycin for Empirical Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Hospitalized Patients A Prospective, Randomized, Multicenter Trial Emanuel
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Azithromycin vs Cefuroxime Plus Erythromycin for Empirical Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Hospitalized Patients A Prospective, Randomized, Multicenter Trial Emanuel
Supplementary Figures
 Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
High-Dose Levofloxacin for the Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia
 High-Dose Levofloxacin for the Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Review Andrew F. Shorr, MD, MPH, FCCP Department of Medicine Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Washington Hospital Center, Washington,
High-Dose Levofloxacin for the Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Review Andrew F. Shorr, MD, MPH, FCCP Department of Medicine Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Washington Hospital Center, Washington,
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 March 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi: /aac
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 March 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01000-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 March 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01000-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Antimicrobial Chemotherapy for Legionnaires Disease: Levofloxacin versus Macrolides
 MAJOR ARTICLE Antimicrobial Chemotherapy for Legionnaires Disease: Levofloxacin versus Macrolides Rosa Mª Blázquez Garrido, 1 Francisco Javier Espinosa Parra, 1 Loreto Alemany Francés, 2 Rosa Mª Ramos
MAJOR ARTICLE Antimicrobial Chemotherapy for Legionnaires Disease: Levofloxacin versus Macrolides Rosa Mª Blázquez Garrido, 1 Francisco Javier Espinosa Parra, 1 Loreto Alemany Francés, 2 Rosa Mª Ramos
A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
Importance of Atypical Pathogens of Community-Acquired Pneumonia
 S35 Importance of Atypical Pathogens of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Joseph F. Plouffe Departments of Internal Medicine and Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Ohio State University College of Medicine,
S35 Importance of Atypical Pathogens of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Joseph F. Plouffe Departments of Internal Medicine and Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Ohio State University College of Medicine,
Cefepime versus Ceftriaxone for Empiric Treatment of Hospitalized Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1998, p. 729 733 Vol. 42, No. 4 0066-4804/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Cefepime versus Ceftriaxone for Empiric Treatment of
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1998, p. 729 733 Vol. 42, No. 4 0066-4804/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Cefepime versus Ceftriaxone for Empiric Treatment of
NTM Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium intracellulare Complex
 2006 67 NTM Mycobacterium aviummycobacterium intracellulare Complex 1) 1) 1) 1) 2) 1) 2) 17 8 29 18 2 9 Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium intracellulare 6 MIC NTM MIC 1 3 NTM 5 MIC MIC M. avium 1 M. intracellulare
2006 67 NTM Mycobacterium aviummycobacterium intracellulare Complex 1) 1) 1) 1) 2) 1) 2) 17 8 29 18 2 9 Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium intracellulare 6 MIC NTM MIC 1 3 NTM 5 MIC MIC M. avium 1 M. intracellulare
Analysis of Rifampin Disk Diffusion and Stability in 7H10 Agar
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 1975, p. 187-193 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 8, No. 2 Printed in U.SA. Analysis of Rifampin Disk Diffusion and Stability in 7H1 Agar
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Aug. 1975, p. 187-193 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 8, No. 2 Printed in U.SA. Analysis of Rifampin Disk Diffusion and Stability in 7H1 Agar
(multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; MDRP)
 220 2009 (multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; MDRP) 21 4 1 21 10 4 amikacin (AMK), imipenem/cilastatin (IPM), ciprofloxacin (CPFX) multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP) CHROMagar TM
220 2009 (multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; MDRP) 21 4 1 21 10 4 amikacin (AMK), imipenem/cilastatin (IPM), ciprofloxacin (CPFX) multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP) CHROMagar TM
Respiratory Infections
 Respiratory Infections NISHANT PRASAD, MD THE DR. JAMES J. RAHAL, JR. DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN QUEENS Disclosures Stockholder: Contrafect Corp., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co Research
Respiratory Infections NISHANT PRASAD, MD THE DR. JAMES J. RAHAL, JR. DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN QUEENS Disclosures Stockholder: Contrafect Corp., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co Research
Abstract. Introduction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY The occurrence of Legionella species other than Legionella pneumophila in clinical and environmental samples in Denmark identified by mip gene sequencing and matrix-assisted laser
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY The occurrence of Legionella species other than Legionella pneumophila in clinical and environmental samples in Denmark identified by mip gene sequencing and matrix-assisted laser
COAGULATION OF HUMAN PLASMA BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS'
 COAGULATION OF HUMAN PLASMA BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS' DANIEL M. EISLER Naval Biological Laboratory, School of Public Health, University of California, Berkeley, California Received for publication June 27,
COAGULATION OF HUMAN PLASMA BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS' DANIEL M. EISLER Naval Biological Laboratory, School of Public Health, University of California, Berkeley, California Received for publication June 27,
Norovirus Report. Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report
 Norovirus Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Introduction Norovirus is the leading cause of non-bacterial
Norovirus Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Introduction Norovirus is the leading cause of non-bacterial
Antibacterial Effect of Pulsatilla chinensis towards Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella dysenteriae, and Salmonella typhi
 292 AMJ June 2016 Antibacterial Effect of Pulsatilla chinensis towards Sim Chee Fong, 1 Yanti Mulyana, 2 Dolvy Girawan 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, 2 Department of Microbiology Faculty
292 AMJ June 2016 Antibacterial Effect of Pulsatilla chinensis towards Sim Chee Fong, 1 Yanti Mulyana, 2 Dolvy Girawan 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, 2 Department of Microbiology Faculty
Rifampin Resistance. Charlottesville, Virginia i0w organisms in Trypticase soy broth (BBL Microbiology
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1980, p. 658-662 0066-4804/80/04-0658/05$02.00/0 Vol. 17, No. 14 Treatment of Experimental Staphylococcal Infections: Effect of Rifampin Alone and in Combination
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1980, p. 658-662 0066-4804/80/04-0658/05$02.00/0 Vol. 17, No. 14 Treatment of Experimental Staphylococcal Infections: Effect of Rifampin Alone and in Combination
Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation
 Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation Ellen Laine, JD, MPH Emerging Infections Unit Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention and Control Division History of Legionnaires Disease
Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation Ellen Laine, JD, MPH Emerging Infections Unit Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention and Control Division History of Legionnaires Disease
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MORAXELLA CATARRHALIS INFECTIONS AMONG THAI PATIENTS TREATED AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, THAILAND DURING
 EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MORAXELLA CATARRHALIS INFECTIONS AMONG THAI PATIENTS TREATED AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, THAILAND DURING 2012-2015 Chanwit Tribuddharat and Somporn Srifuengfung Department of Microbiology, Faculty
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MORAXELLA CATARRHALIS INFECTIONS AMONG THAI PATIENTS TREATED AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, THAILAND DURING 2012-2015 Chanwit Tribuddharat and Somporn Srifuengfung Department of Microbiology, Faculty
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Increasing Genetic Relatedness of Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolated in Canada from 1997 to 2005
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Mar. 2008, p. 1190 1194 Vol. 52, No. 3 0066-4804/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.01260-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Increasing
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Mar. 2008, p. 1190 1194 Vol. 52, No. 3 0066-4804/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.01260-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Increasing
Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 1979, p. 6-6 0066-0/79/1-06/05$0.00/0 Vol., No. 6 In Vitro Activity of LY17935, a New 1-Oxa Cephalosporin, Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli DENNIS G. DELGADO,
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 1979, p. 6-6 0066-0/79/1-06/05$0.00/0 Vol., No. 6 In Vitro Activity of LY17935, a New 1-Oxa Cephalosporin, Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli DENNIS G. DELGADO,
Evaluation of the Oxoid Xpect Legionella test kit for Detection of Legionella
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Long Half-life Drugs in Infectious Diseases: Implications and Complications
 Long Half-life Drugs in Infectious Diseases: Implications and Complications In Session: Drugs That Just Won t Leave: From Stars of the Party to Unwelcome Guests Annual Meeting of the AAPS, San Diego, California
Long Half-life Drugs in Infectious Diseases: Implications and Complications In Session: Drugs That Just Won t Leave: From Stars of the Party to Unwelcome Guests Annual Meeting of the AAPS, San Diego, California
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
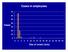 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Ceftazidime-Avibactam and Aztreonam an interesting strategy to Overcome β- Lactam Resistance Conferred by Metallo-β-Lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 19 June 2017 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01008-17 Copyright 2017 American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Ceftazidime-Avibactam
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 19 June 2017 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01008-17 Copyright 2017 American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Ceftazidime-Avibactam
Laboratory CLSI M100-S18 update. Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator
 Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
Nebraska Public Health Laboratory 2008 CLSI M100-S18 update Paul D. Fey, Ph.D. Associate Professor/Associate Director Josh Rowland, M.T. (ASCP) State Training Coordinator Agenda Discuss 2008 M100- S18
INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia
 Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was grown in a casein-based semisynthetic medium (C+Y) supplemented with yeast extract (1 mg/ml of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was grown in a casein-based semisynthetic medium (C+Y) supplemented with yeast extract (1 mg/ml of
Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin
 2009 21 1) 1, 2) 1, 2) 1) 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 20 2 29 21 1 14 Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin (STFX), DX619 S. pneumoniae S. pneumoniae 60
2009 21 1) 1, 2) 1, 2) 1) 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 20 2 29 21 1 14 Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin (STFX), DX619 S. pneumoniae S. pneumoniae 60
Below is an overview of the oral and poster presentations featuring cefiderocol and S at IDWeek 2017:
 SHIONOGI TO HIGHLIGHT RESEARCH ON CEFIDEROCOL (S-649266), A SIDEROPHORE CEPHALOSPORIN, AND S-033188, A CAP-DEPENDENT ENDONUCLEASE INHIBITOR FOR TREATMENT OF INFLUENZA, AT IDWEEK 2017 OSAKA, Japan and FLORHAM
SHIONOGI TO HIGHLIGHT RESEARCH ON CEFIDEROCOL (S-649266), A SIDEROPHORE CEPHALOSPORIN, AND S-033188, A CAP-DEPENDENT ENDONUCLEASE INHIBITOR FOR TREATMENT OF INFLUENZA, AT IDWEEK 2017 OSAKA, Japan and FLORHAM
CHAPTER 6 EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR ANTI-ACNE ACTIVITY
 CHAPTER 6 EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR School of Science, SVKM s NMIMS University Page 119 6. EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR 6.1 MATERIALS AND METHODS 6.1.1 Antimicrobial assays
CHAPTER 6 EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR School of Science, SVKM s NMIMS University Page 119 6. EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR 6.1 MATERIALS AND METHODS 6.1.1 Antimicrobial assays
The activity of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime against Bacteroides species compared to 7-methoxy cephems and other anti-anaerobe drugs
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (984) 4, Suppl. B, 39-43 The activity of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime against Bacteroides species compared to 7-methoxy cephems and other anti-anaerobe drugs
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (984) 4, Suppl. B, 39-43 The activity of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime against Bacteroides species compared to 7-methoxy cephems and other anti-anaerobe drugs
Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy
 MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy Analía Mykietiuk, 1 Jordi Carratalà, 1 Núria Fernández-Sabé,
MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy Analía Mykietiuk, 1 Jordi Carratalà, 1 Núria Fernández-Sabé,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2010) ewsletter Singh and Kochbar. Optimizing Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamics Principles & Role of
 Optimizing Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamics Principles & Role of Cefoperazone Sulbactam Singh M*, Kochhar P* Medical & Research Division, Pfizer India. Summary Antimicrobial resistance is associated with
Optimizing Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamics Principles & Role of Cefoperazone Sulbactam Singh M*, Kochhar P* Medical & Research Division, Pfizer India. Summary Antimicrobial resistance is associated with
Total Legionella Control TLC The Industry Standard
 Total Legionella Control TLC The Industry Standard Special Pathogens Laboratory provides a cohesive strategy to detect, control, and remediate Legionella and waterborne pathogens. Founded by Drs. Janet
Total Legionella Control TLC The Industry Standard Special Pathogens Laboratory provides a cohesive strategy to detect, control, and remediate Legionella and waterborne pathogens. Founded by Drs. Janet
Resistance among Streptococcus pneumoniae Clinical Isolates by Use of the E Test
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1994, p. 159-163 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 1 Detection of Penicillin and Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1994, p. 159-163 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 1 Detection of Penicillin and Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) S urveillance Report 2008 Background Methods
 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2008 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Department of Human Services
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Surveillance Report 2008 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Department of Human Services
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples
 Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
The Bacteriology of Bronchiectasis in Australian Indigenous children
 The Bacteriology of Bronchiectasis in Australian Indigenous children Kim Hare, Amanda Leach, Peter Morris, Heidi Smith-Vaughan, Anne Chang Presentation outline What is bronchiectasis? Our research at Menzies
The Bacteriology of Bronchiectasis in Australian Indigenous children Kim Hare, Amanda Leach, Peter Morris, Heidi Smith-Vaughan, Anne Chang Presentation outline What is bronchiectasis? Our research at Menzies
International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences. Available online at
 DOI:10.21276/ijprhs.2017.01.15 Pradeep et al CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original
DOI:10.21276/ijprhs.2017.01.15 Pradeep et al CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original
SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO. Iyyanuchamy, S.K and A. Periyanayagasamy*
 Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
Chapter 4. Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata. 4.1 Introduction
 Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata C o n t e n t s 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Materials and Methods 4.2.1 Extract Preparation and Determination of PUFA
Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata C o n t e n t s 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Materials and Methods 4.2.1 Extract Preparation and Determination of PUFA
