Breast MRI, digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis: Comparison of three methods for early detection of breast cancer
|
|
|
- Hortense Norton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BOSNIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES RESEARCH ARTICLE Breast MRI, digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis: Comparison of three methods for early detection of breast cancer Dragana Roganovic 1 *, Dragana Djilas 2, Sasa Vujnovic 3, Dag Pavic 4, Dragan Stojanov 5 1 Department of Radiology, Dom zdravlja, Banjaluka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2 Diagnostic Imaging Center, Oncology Institute of Vojvodina, Novi Sad, Serbia, 3 Institute of Clinical Radiology, University Hospital Clinical Center Banjaluka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 4 Department of Radiology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA, 5 Faculty of Medicine University of Nis, Department of Radiology, Nis, Serbia ABSTRACT Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women and early detection is important for its successful treatment. The aim of this study was to investigate the sensitivity and specificity of three methods for early detection of breast cancer: breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), digital mammography, and breast tomosynthesis in comparison to histopathology, as well as to investigate the intraindividual variability between these modalities. We included 57 breast lesions, each detected by three diagnostic modalities: digital mammography, breast MRI, and breast tomosynthesis, and subsequently confirmed by histopathology. Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) was used for characterizing the lesions. One experienced radiologist interpreted all three diagnostic modalities. Twenty-nine of the breast lesions were malignant while 28 were benign. The sensitivity for digital mammography, breast MRI, and breast tomosynthesis, was 72.4%, 93.1%, and 100%, respectively; while the specificity was 46.4%, 60.7%, and 75%, respectively. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis showed an overall diagnostic advantage of breast tomosynthesis over both breast MRI and digital mammography. with significant difference between breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography (p<0.001), while the difference between breast tomosynthesis and breast MRI was not significant (p = 0.20). KEY WORDS: Breast cancer; breast MRI; breast tomosynthesis; digital mammography DOI: Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2015;15(4): ABMSFBIH INTRODUCTION The only imaging modality that has been proven to significantly reduce breast cancer mortality in age-appropriate asymptomatic women is annual screening mammography. A screening mammogram is an x-ray examination of the breast of an asymptomatic woman, while a diagnostic mammogram is done in a patient with signs or symptoms of breast disease: a possible abnormality detected on screening mammography or other imaging, or prior mammography findings requiring imaging follow-up [1]. However, the sensitivity of mammography can be limited in dense breast tissue, due to the presence of overlapping fibroglandular tissue which reduces conspicuity of abnormalities [2]. Another factor influencing cancer visibility is the tumor growth pattern. Tumors which do not produce a mass are often difficult to detect on mammography *Corresponding author: Dragana Roganovic, Dom zdravlja Banjaluka, Jovana Ducica bb, Banjaluka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, dragana.roganovic@gmail.com Submitted: 08 July 2015 / Accepted 24 August 2015 [3]. Depending on these two factors, breast density and tumor growth pattern, the false-negative rate of mammography ranges from 8% to 66% in symptomatic women [4]. Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is a new and emerging x-ray imaging modality. Tomographic images from DBT are reconstructed in 3D from multiple low-dose 2D x-ray source projection images, acquired by varying the angle of the x-ray tube. By combining information from different projections, DBT clearly differentiates the adjacent anatomical structures, alleviating the superimposition effect [5]. The projection data sets are not what are usually interpreted by the radiologists, but rather the interpretation is based only on the reconstructed tomosynthesis images. Typically, the projection data sets are reconstructed into very thin (e.g. 1 mm) slices for radiologist review [6]. Breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a useful tool for detection and characterization of breast disease, assessment of the local extent of the disease, evaluation of treatment response, and guidance for biopsy and localization [7]. Reported sensitivity of this modality in detection of invasive 64
2 breast cancer has approached 100% in several series and that is one of the reasons why breast MRI is important in preoperative staging [8]. The limitation of breast MRI is low-to-moderate specificity ranging from 37% to 97% [9]. Low specificity could be a possible cause of overtreatment [10]. The aim of this study was to investigate the sensitivity and specificity of three methods for early detection of breast cancer: digital mammography (DM), breast MRI, and DBT in comparison to histopathology, as well as to investigate the intraindividual variability between these modalities. MATERIALS AND METHODS The study was prospective and approved by the Ethical Committee of the Oncology Institute of Vojvodina. Informed consent was obtained from all participating women. Patients The study population included symptomatic as well as asymptomatic women examined at the Imaging Center of the Oncology Institute of Vojvodina from April 2010 to February Most of these women were referred from other hospitals for a second opinion after suspicious findings on ultrasound examination or screening mammography. Image acquisition Breast MRI was performed on 3.0 T MR imaging system (Trio 3.0T; Siemens Medical Systems, Erlangen, Germany), with the patient in a prone position, using a dedicated breast surface coil (8-channel coil, Siemens, Erlangen, GE). Dynamic protocol was performed after the standard bilateral T2W axial and T2W fat saturated sagital sequences with T1W (3D) gradient-echo VIEWS sequences (flip angle of 10 ), with a total of seven dynamic acquisitions, one before and six immediately after an intravenous bolus injection of gadolinium-dimeglumine (Magnevist; Schering, Berlin, Germany) equal to 0.1 mmol per kg body weight, followed by 20 ml saline flush, with a slice thickness of 2 mm and an acquisition matrix of 512x512. With this parameter setting we obtained a voxel size of 0.6x0.6x1.7 mm and a temporal resolution of 72 sec per dynamic acquisition. Postprocessing included subtraction and MIP. All lesions were evaluated for their morphologic and kinetic characteristics in a pre- and postcontrast series. DM was performed using a dedicated digital mammography unit, Selenia DIMENSIONS (Hologic, Bedford, MA), in two standard projections (MLO and CC), kvp, max. 200 ma, amorphous selenium (Se) detector 24x29 cm, pixel size 70 μm, Rh and Ag filters, tungsten x-ray tube. DBT images were acquired on the same dedicated digital mammography unit with x-ray tube rotation through the angular range of 15 (-7.5 to +7.5 ) with the breast in standard compression, in both MLO and CC projections, kvp, max. 200 ma, selenium (Se) detector 24x29 cm, pixel size 140 μm, aluminium (Al) filter. Image acquisition was performed with a continuous exposure method (pulsed, short exposures during continuous motion of the x-ray tube), with an acquisition time of 5 seconds or less for one breast. Image reconstruction was performed immediately after image acquisition: slice thickness 1 mm, time of reconstruction 2-5 seconds, and a reconstructed pixel size of about 100 μm. Hospital Integrated Computer Aided Information System (BIRPIS) was used for data access and Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) was used for access to images from all three modalities. Image and tissue analysis Digital mammography, breast MRI, and DBT were performed in the Imaging Center of the Oncology Institute of Vojvodina. Histopathological analysis were done at the Department of Pathology, Oncology Institute of Vojvodina. One experienced radiologist (DD), with 10 years of experience in breast imaging, interpreted all the diagnostic modalities. The radiologist was provided with patients previous mammographic and ultrasound examinations, in order to ensure a proper clinical setting. Morphologic characteristics of all detected lesions were analyzed in all three diagnostic modalities, and their kinetic characteristics (enhancement curves and peak enhancement) were analyzed using breast MRI. All detected lesions were classified according to the American College of Radiology (ACR) BI-RADS lexicon criteria. The BI-RADS category of each lesion, of each diagnostic method, was compared with the histopathology report. BI-RADS categories 1, 2 and 3 were considered benign, while categories 4 and 5 were considered malignant. The final diagnosis was established by histopathological analysis of core biopsy, vacuum-assisted stereotaxic biopsy or surgical excision specimen. Statistical analysis We used SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 19.0 for statistical data analysis (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). We compared the results of all three modalities with the histopathology report. All three diagnostic methods were tested by Cochran s Q test, and afterwards they were all comparatively analyzed by McNemar s test. A receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve was generated for each diagnostic method. We used options in the SPSS package for the calculation and presentation of the ROC curve in accordance with BI-RADS classification. Cohen s Cappa test was used for the evaluation of agreement between 65
3 each diagnostic method and the histopathology report. The ROC curve interpretation was done as described in Park et al. [11]. Cohen s Cappa coefficient was interpreted based on guidelines from Altman (1991) [12]. Specificity, sensitivity and predictive values were processed in SPSS or MS Excel package (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). RESULTS All patients were female. The average age of patients was years (ranging from years). We evaluated imaging features of 60 breast lesions, depicted using three diagnostic modalities: breast MRI, DM and DBT. Three lesions were excluded from the study due to inconsistent findings, therefore we compared the results of imaging findings in 57 breast lesions with the histopathology report. The dataset consisted of 29 malignancies and 28 benign lesions, as follows: 22 invasive carcinomas (2 lobular, 20 invasive ductal carcinoma), 7 invasive + ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), 9 fibroadenomas, 6 fibrocystic changes, 4 sclerosing adenosis, 2 lymph nodes, 2 proliferative dysplasia, 1 fat necrosis, 1 columnar cell hyperplasia without atypia, 1 epithelial hyperplasia, 1 post-surgical scar, 1 radial scar (a border-line lesion which was excised after initial diagnosis at core biopsy, with the same result, and therefore it was considered benign in this study). There was a significant difference in performance between the three analyzed diagnostic methods (p = 0.001, Cochran s test). Also, there was a significant difference in performance between mammography and DBT (p = 0.001), a significant difference between mammography and breast MRI (p = 0.02), while there was no statistically significant difference between breast MRI and DBT (p = 0.07). McNemar s test. Based on the information obtained (Table 1) we analyzed sensitivity, specificity, predictive values and ROC curves, for all three diagnostic methods. The sensitivity of DM was 72.4% and its specificity was 46.4%, sensitivity of DBT was 100%, and specificity 75%, while the sensitivity and specificity of breast MRI were 93.1% and 60.7%, respectively. The positive predictive value was for tomosynthesis, while breast MRI and DM had lower positive predictive values (0.711 and 0.583, respectively). The negative predictive value was also higher in tomosynthesis (1.000) than in breast MRI (0.895) and DM (0.619). We compared area-under-the-curve for all three analyzed diagnostic methods in Figure 1. The greatest area-under-thecurve was under the DBT curve (0.925), next was the area under the breast MRI curve (0.884), and the lowest area was under the mammography curve (0.640). By comparing the ROC curves we showed that there was a statistically high significant difference between the diagnostic TABLE 1. Comparison of breast MRI, DM and DBT results with histopathology Type of lesion accuracy of DBT and DM (p < 0.001), as well as between breast MRI and DM (p = 0.002), while there was no statistically significant difference between DBT and breast MRI (p = 0.20). Most of the malignant lesions had irregular or spiculated margins with all three analyzed diagnostic methods (86% in breast MRI, 62% in DM, 90% in DBT) and a lobulated or irregular shape (65% in breast MRI, 59% in DM, 83% in DBT). With breast MRI, 86% of all malignant lesions had a wash-out postcontrast enhancement kinetic curve and 14% of lesions had a plateau curve. None of the malignant lesions had a persistent kinetic curve of postcontrast enhancement. Most of the malignant lesions had peak enhancement between 2 and 2.5 minutes (59% of lesions) or between 1 and 1.9 minutes (21% of lesions); in 10% of the lesions peak enhancement was between 2.6 and 3 minutes, while 10% of the lesions had peak enhancement after more than 3 minutes. DISCUSSION Histopathology Malignant Benign Total Breast MRI Malignant Benign DM Malignant Benign DBT Malignant Benign Total FIGURE 1. ROC curves for breast MRI, digital mammography (DM) and breast tomosynthesis (DBT). In this study, ROC curve analysis shows an overall diagnostic advantage of DBT over breast MRI and DM, clearly seen when we compare ROC curves for all three analyzed diagnostic methods (Figure 1). DM has significantly lower sensitivity and specificity than DBT and breast MRI in diagnosing malignant breast lesions. 66
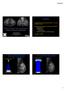
4 The sensitivity of DBT was 100% in this study, meaning that DBT detected all of the malignant tumors. This factor alone is a significant indication of the superiority of digital DBT over the other two diagnostic methods, especially over the DM. One of the factors that contribute to false-negative mammography reports, especially in mammographic detection of mass lesions, is breast density. Small, indistinct masses can be easily obscured by dense breast tissue [13]. Normal breast tissue elements that lie outside the plane of the lesion can obscure it, leading to false-negative results and decreasing sensitivity (Figure 2). Conversely, superimposed tissue elements may give the appearance of an abnormality and lead to false-positive results, diminishing the positive predictive value and specificity of the examination [14]. Possible causes of false-positive and false-negative results also include poor positioning or technique, perception error, incorrect interpretation of a suspect finding, subtle features of malignancy, and slow growth of a lesion [15]. Thus, in symptomatic patients with negative mammography additional diagnostic work-up using another breast imaging modality is obligatory. Distribution and density of fibroglandular breast tissue does not decrease sensitivity of DBT because the overlapping tissue effect is reduced by tomographic technique. Due to the basic principle of DBT which is reducing the anatomical noise, the sensitivity and specificity were increased, thus the lesions were better visualized and more accurately categorized according to the ACR BI-RADS lexicon criteria. Lesions were easier to distinguish on DBT, and the analysis of margins was also more precise. In several cases superimposed breast tissue caused false positive findings on mammography, later reported as normal breast parenchyma on DBT. Intramammary lymph nodes were best visualized and characterized on DBT, thanks to their typical reniform (kidney bean) shape, fatty hilum and well-defined margins. Intramammary lymph nodes could be mistaken for malignant foci on breast MRI because of the wash-out kinetic curve of postcontrast enhancement. In classifying breast lesions, the assessment of their margins and the qualitative enhancement intensity (at two minutes or less after contrast administration) are considered the most important features for breast mass characterization on breast MRI. The next most important feature is the qualitative assessment of the enhancement kinetics curve [16]. Specificity of breast MRI imaging is improved when both morphologic and kinetic features are considered in the interpretation. Therefore, the breast MRI imaging technique should be optimized to achieve high spatial and temporal resolution [16]. However, just as mammographic breast density influences mammographic sensitivity, the degree of background enhancement in breast MRI may influence the sensitivity of breast MRI [13]. Therefore, if strong background enhancement is present, it will be crucial to put it in a report so that referring physicians understand that the high sensitivity that they may expect from a breast MRI study may not be available in this particular case [17]. Breast MRI findings may be complex due to physiologic or postoperative changes, meaning that areas of normal breast parenchyma in premenopausal women may appear focally enhanced, a feature that may lead to a false-positive finding and a decrease of breast MRI specificity. Transiently enhancing foci have been observed in the breasts of many healthy women, especially during the second half of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, to minimize false-positive results, breast imaging should be performed during the first half of the menstrual cycle (days 3-14) [16,18]. According to the literature, generally, a persistent curve is suggestive of benign changes, a wash-out curve is suggestive of malignancy, and a plateau curve might be seen in both benign change and malignancy [19]. The results of our study are in accordance with this information, i.e. 86% of malignant lesions had a wash-out curve, while 14% had a plateau curve and none of the malignant lesions had a persistent curve. A limitation of this study was its small sample size and the fact that it involved a non-blinded review. For a more accurate a b c FIGURE 2. A 54-year-old patient who was referred to our institution for an additional diagnostic procedure because of the mass in the left breast seen with ultrasound (no image available). Digital mammography MLO projection right breast (a), left breast (b) classified as BI-RADS 1. Breast MRI, MIP (c) two lesions in the right breast with slow initial enhancement and a wash-out curve, classified as BI-RADS 5. Breast tomosynthesis right breast MLO projection (d) two spiculated masses classified as BI-RADS 5. Histopathology: Ductal invasive carcinoma, both lesions.. 67 d
5 evaluation of sensitivity and specificity of all three diagnostic modalities, a larger series of cases should be included with independent reading of images from all three modalities. Further research is needed and the results should be confirmed in large population-based studies. CONCLUSION Our study shows that DBT performs better in detection and characterization of breast lesions compared to DM and breast MRI. DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES 1. American College of Radiology. ACR practice parameter for the performance of screening and diagnostic mammography. Amended Resources Accessed December 9, Chan HP, Wei J, Sahiner B, Rafferty EA, Wu T, Roubidoux M, et al. Computer-aided detection system for breast masses on digital tomosynthesis mammograms: preliminary experience. Radiology 2005;237(3): Andersson I, Ikeda D, Zackrisson S, et al. Breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography: a comparison of breast cancer visibility and BIRADS classification in a population of cancer with subtle mammographic findings. Eur Radiol 2008;18: Teertstra H, Loo C, van den Bosch M, et al. Breast tomosynthesis in clinical practice: initial results. Eur Radiol 2010;20(1): Kontos D, Bakic PR, Carton AK, Troxel AB, Conant EF, Maidment A. Parenchymal texture analysis in digital breast tomosynthesis for breast cancer risk estimation: a preliminary study. Acad Radiol 2009;16(3): Helvie MA. Digital Mammography Imaging: Breast Tomosynthesis and Advanced Applications. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010;48(5): American College of Radiology. ACR practice parameter for the performance of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast. American College of Radiology; Orel SG, Schnall MD. MR Imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology 2001;220(1): Esserman L, Wolverton D, Hylton N. Magnetic resonance imaging for primary breast cancer management: current role and new applications. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2002;9: Van Goethem M, Schelfout K, Dijckmans L, et al. MR mammography in the pre-operative staging of breast cancer in patients with dense breast tissue: comparison with mammography and ultrasound. Eur Radiol 2004;14: Park SH, Goo JM, Jo CH. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve: Practical Review for Radiologists. Korean J Radiol 2004;5(1): Altman DG. Practical statistics for medical research. London: Chapman and Hall; Uematsu T, Kasami M, Watanabe J. Does the degree of background enhancement in breast MRI affect the detection and staging of breast cancer. Eur Radiol 2011;21: Poplack S, Tosteson T, Kogel C, Nagy H. Digital breast tomosynthesis: Initial experience in 98 women with abnormal digital screening mammography. AJR 2007;189: Majid AS, de Paredes ES, Doherty RD, Sharma N, Salvador X. Missed breast carcinoma: pitfalls and pearls. Radiographics 2003;23: Macura KJ, Ouwerkerk R, Jacobs MA, Bluemke DA. Patterns of enhancement on breast MR images: interpretation and imaging pitfalls. Radiographics 2006;26: Djilas-Ivanovic D, Schultze-Haack H, Pavic D, Semelka RC: Breast. In: Semelka RC (ed.). Abdominal-Pelvic MRI, 3rd edn. New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010, pp Mann RM, Kuhl CK, Kinkel K, Boetes C. Breast MRI: guidelines from the European Society of breast imaging. Eur Radiol 2008: Cheng L, Li X. Breast magnetic resonance imaging: kinetic curve assessment. Gland Surg 2013;2(1):
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors
 Eur Radiol (2011) 21:2475 2483 DOI 10.1007/s00330-011-2210-7 BREAST Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors Christian Sohns & Martin Scherrer
Eur Radiol (2011) 21:2475 2483 DOI 10.1007/s00330-011-2210-7 BREAST Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors Christian Sohns & Martin Scherrer
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis
 Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Contrast-Enhanced Breast Tomosynthesis: Combining the Best of Both Worlds for Better Breast-Cancer Diagnosis
 Contrast-Enhanced Breast Tomosynthesis: Combining the Best of Both Worlds for Better Breast-Cancer Diagnosis T Wu (twu2@partners.org), E Rafferty, R Moore, D Kopans, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston,
Contrast-Enhanced Breast Tomosynthesis: Combining the Best of Both Worlds for Better Breast-Cancer Diagnosis T Wu (twu2@partners.org), E Rafferty, R Moore, D Kopans, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston,
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine
 International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Patient Outcomes in Canceled MRI-Guided Breast Biopsies
 Women s Imaging Original Research Outcomes After Canceled MRI-Guided Breast Biopsies Women s Imaging Original Research Bethany L. Niell 1 Janie M. Lee 1, 2 Christopher Johansen 3 Elkan F. Halpern 4 Elizabeth
Women s Imaging Original Research Outcomes After Canceled MRI-Guided Breast Biopsies Women s Imaging Original Research Bethany L. Niell 1 Janie M. Lee 1, 2 Christopher Johansen 3 Elkan F. Halpern 4 Elizabeth
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS
 Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS Poster No.: C-0412 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Breast H. G. Toonen, R. Mann, H. Huisman, J. Veltman, C. Boetes; Nijmegen/NL
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS Poster No.: C-0412 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Breast H. G. Toonen, R. Mann, H. Huisman, J. Veltman, C. Boetes; Nijmegen/NL
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI
 Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
ORIGINAL PAPER. Background parenchymal enhancement in preoperative breast MRI
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 373 ~ 382, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER Background parenchymal enhancement in preoperative breast MRI Satoko Kohara 1, Satoko Ishigaki 1, Hiroko Satake 1, Akiko Kawamura 1, Hisashi Kawai
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 373 ~ 382, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER Background parenchymal enhancement in preoperative breast MRI Satoko Kohara 1, Satoko Ishigaki 1, Hiroko Satake 1, Akiko Kawamura 1, Hisashi Kawai
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Susan Orel Roth, MD
 Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Mammography limitations. Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study
 Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses
 The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Updates in Mammography. Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre
 Updates in Mammography Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre Updates in Mammography Breast Imaging Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical
Updates in Mammography Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre Updates in Mammography Breast Imaging Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical
Feasibility of MRI-guided large-core-needle biopsy of suspiscious breast lesions at 3T
 Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 1639 1644 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1310-0 BREAST Nicky H. G. M. Peters Carla Meeuwis Chris J. G. Bakker Willem P. Th. M. Mali Arancha M. Fernandez-Gallardo Richard van Hillegersberg
Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 1639 1644 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1310-0 BREAST Nicky H. G. M. Peters Carla Meeuwis Chris J. G. Bakker Willem P. Th. M. Mali Arancha M. Fernandez-Gallardo Richard van Hillegersberg
Detection and Classification of Calcifications on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and 2D Digital Mammography: A Comparison
 Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning. Dr. med. M. Golatta
 The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
Computer-aided detection (CAD) for breast MRI: evaluation of efficacy at 3.0 T
 Eur Radiol (2010) 20: 522 528 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1573-5 BREAST Carla Meeuwis Stephanie M. van de Ven Gerard Stapper Arancha M. Fernandez Gallardo Maurice A. A. J. van den Bosch Willem P. Th. M. Mali
Eur Radiol (2010) 20: 522 528 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1573-5 BREAST Carla Meeuwis Stephanie M. van de Ven Gerard Stapper Arancha M. Fernandez Gallardo Maurice A. A. J. van den Bosch Willem P. Th. M. Mali
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography, full-field digital mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis
 Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications?
 Original Article Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications? Shinya Yamamoto, Takashi Chishima Department of Breast Surgery, Yokohama Rosai Hospital, Yokohama 222-0036,
Original Article Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications? Shinya Yamamoto, Takashi Chishima Department of Breast Surgery, Yokohama Rosai Hospital, Yokohama 222-0036,
8/31/2016 HIDING IN PLAIN SITE, ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS AND BREAST ASYMMETRIES ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS
 HIDING IN PLAIN SITE, ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS AND BREAST ASYMMETRIES DEBORAH THAMES R.T. (R)(M)(QM) ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS Definition is disruption of the natural flow of breast pattern towards the
HIDING IN PLAIN SITE, ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS AND BREAST ASYMMETRIES DEBORAH THAMES R.T. (R)(M)(QM) ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS Definition is disruption of the natural flow of breast pattern towards the
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
 Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography
 BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
BI-RADS and Breast MRI. Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018
 BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update. Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view
 BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view DR CHANTEL THORNTON SPECIALIST BREAST CANCER SURGEON BMSc (hons) MBBS (hons) FRACS Epworth Hospital, Richmond- Agora Centre for Women s Health
BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view DR CHANTEL THORNTON SPECIALIST BREAST CANCER SURGEON BMSc (hons) MBBS (hons) FRACS Epworth Hospital, Richmond- Agora Centre for Women s Health
Rate of Malignancy in MRI-Detected Probably Benign (BI-RADS 3) Lesions
 Women s Imaging Original Research Spick et al. Malignancy in MRI BI-RADS 3 Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research Claudio Spick 1,2 Dieter H. M. Szolar 1 Pascal A. Baltzer 2 Manfred Tillich 1 Pia Reittner
Women s Imaging Original Research Spick et al. Malignancy in MRI BI-RADS 3 Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research Claudio Spick 1,2 Dieter H. M. Szolar 1 Pascal A. Baltzer 2 Manfred Tillich 1 Pia Reittner
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening?
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
RSNA, /radiol Appendix E1. Methods
 RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE?
 X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
MRI BI-RADS: How to make it out?
 MRI BI-RADS: How to make it out? Poster No.: C-1850 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Ben Ammar, A. Ben Miled, O. Ghdes, S. Harguem, A. Gaja, N. Mnif; Tunis/TN Keywords: Breast,
MRI BI-RADS: How to make it out? Poster No.: C-1850 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Ben Ammar, A. Ben Miled, O. Ghdes, S. Harguem, A. Gaja, N. Mnif; Tunis/TN Keywords: Breast,
Spiculated breast masses on MRI: Which category should we choose, 4 or 5?
 Spiculated breast masses on MRI: Which category should we choose, 4 or 5? Poster No.: C-1394 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Onishi, S. Kanao, M. Kataoka, M. Kawai, M. Iima, A.
Spiculated breast masses on MRI: Which category should we choose, 4 or 5? Poster No.: C-1394 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Onishi, S. Kanao, M. Kataoka, M. Kawai, M. Iima, A.
Research Article The Adjunctive Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
 BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 597253, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/597253 Research Article The Adjunctive Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Tsung-Lung
BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 597253, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/597253 Research Article The Adjunctive Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Tsung-Lung
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography
 2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients
 Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
8/3/2016. DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis. Tomosynthesis Pedigree
 DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
Successful Breast MRI Program : The ingredients
 Successful Breast MRI Program : The ingredients Dr. Smriti Hari Associate Professor Deptt. Of Radiology All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi How to perform Breast MRI Breast MRI descriptors
Successful Breast MRI Program : The ingredients Dr. Smriti Hari Associate Professor Deptt. Of Radiology All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi How to perform Breast MRI Breast MRI descriptors
BREAST MRI. VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece
 BREAST MRI VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece Breast ΜR Imaging (MRM) Breast MR imaging is an extremely powerful diagnostic tool, that when used in
BREAST MRI VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece Breast ΜR Imaging (MRM) Breast MR imaging is an extremely powerful diagnostic tool, that when used in
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Waldherr et al. One-View Breast Tomosynthesis Versus Two-View Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Christian Waldherr 1 Peter Cerny 1 Hans J. Altermatt 2 Gilles
Women s Imaging Original Research Waldherr et al. One-View Breast Tomosynthesis Versus Two-View Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Christian Waldherr 1 Peter Cerny 1 Hans J. Altermatt 2 Gilles
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
IBCM 2, April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
 Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in the Diagnostic Environment: A Subjective Side-by-Side Review
 Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Breast MR biopsy. I Thomassin-Naggara, A.Jalaguier-Coudray, J Chopier
 Breast MR biopsy I Thomassin-Naggara, A.Jalaguier-Coudray, J Chopier Background EUSOBI When a radiologist perform a MR breast imaging he has to be able to realize or to be apart of a network who is able
Breast MR biopsy I Thomassin-Naggara, A.Jalaguier-Coudray, J Chopier Background EUSOBI When a radiologist perform a MR breast imaging he has to be able to realize or to be apart of a network who is able
The Radiology Aspects
 REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
New Imaging Modalities for better Screening and Diagnosis
 New Imaging Modalities for better Screening and Diagnosis Miri Sklair-Levy, MD Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Department of Diagnostic
New Imaging Modalities for better Screening and Diagnosis Miri Sklair-Levy, MD Department of Diagnostic Imaging Sheba Medical Center, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Department of Diagnostic
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium. Sat Nov 12 th 2016
 Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
AB MR Interpretation Overview
 AB MR Interpretation Overview Goal of AB MR interpretation is to maintain high sensitivity and specificity In order to minimize false positives and short term follow ups, it is fundamental to focus only
AB MR Interpretation Overview Goal of AB MR interpretation is to maintain high sensitivity and specificity In order to minimize false positives and short term follow ups, it is fundamental to focus only
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
MRI in breast cancer: diagnosis and intervention. Dr Sue Barter Addenbrookes Hospital, Cambridge UK
 MRI in breast cancer: diagnosis and intervention Dr Sue Barter Addenbrookes Hospital, Cambridge UK Intervention will be discussed in High Risk Screening! Indications UK and Europe: Breast MRI is well established
MRI in breast cancer: diagnosis and intervention Dr Sue Barter Addenbrookes Hospital, Cambridge UK Intervention will be discussed in High Risk Screening! Indications UK and Europe: Breast MRI is well established
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Breast asymmetries in mammography: Management
 Breast asymmetries in mammography: Management Poster No.: C-1026 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan 1, F. J. Hidalgo Ramos 2, J. L. Ortega Garcia 3, Keywords: DOI:
Breast asymmetries in mammography: Management Poster No.: C-1026 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan 1, F. J. Hidalgo Ramos 2, J. L. Ortega Garcia 3, Keywords: DOI:
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 SAM - Breast MRI 1
 National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
BIRADS 3 and 4 lesions viewed by ultrasound and not seen in digital mammograms and tomosynthesis.
 Original article Anales de Radiología México 2016 Jul;15(3):205-213. BIRADS 3 and 4 lesions viewed by ultrasound and not seen in digital mammograms and tomosynthesis. García-Quintanilla JF 1, González-Coronado
Original article Anales de Radiología México 2016 Jul;15(3):205-213. BIRADS 3 and 4 lesions viewed by ultrasound and not seen in digital mammograms and tomosynthesis. García-Quintanilla JF 1, González-Coronado
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks
 Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS
 ABBY DUROJAYE,M.D CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS BOTH HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO BE EFFECTIVE TOOLS EARLY DETECTION OF BREAST
ABBY DUROJAYE,M.D CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS BOTH HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO BE EFFECTIVE TOOLS EARLY DETECTION OF BREAST
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI BREAST CANCER. The incidence of getting breast cancer is 1:19 in Malaysia
 Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
Breast Tomosynthesis. What is breast tomosynthesis?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS. Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015 No financial disclosures National Cancer Institute National Cancer Institute Increased Cancer Risk... DENSITY
MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015 No financial disclosures National Cancer Institute National Cancer Institute Increased Cancer Risk... DENSITY
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts. Reagan Leverett, MD, MS
 Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
Fundamentals of Breast Tomosynthesis
 Fundamentals of Breast Tomosynthesis Improving the Performance of Mammography Andrew Smith, Ph.D. This white paper is one in a series of research overviws on advanced technologies in women s healthcare.
Fundamentals of Breast Tomosynthesis Improving the Performance of Mammography Andrew Smith, Ph.D. This white paper is one in a series of research overviws on advanced technologies in women s healthcare.
Breast MRI Update. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography
 Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography Andrew Smith 1, Elizabeth Rafferty 2, Loren Niklason 1 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford MA, USA 2 Massachusetts
Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography Andrew Smith 1, Elizabeth Rafferty 2, Loren Niklason 1 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford MA, USA 2 Massachusetts
arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018 arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018](/thumbs/87/97094636.jpg) Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network Timothy de Moor a, Alejandro Rodriguez-Ruiz a, Albert Gubern Mérida a, Ritse Mann a, and
Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network Timothy de Moor a, Alejandro Rodriguez-Ruiz a, Albert Gubern Mérida a, Ritse Mann a, and
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions. Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea
 Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer
 What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
FDA Executive Summary
 Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
Pitfalls of Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MR Mammography (DCE-MRM) in Evaluation of Post-Biopsy Suspicious Breast Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 86, No. 3, June: 1513-1522, 2018 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Pitfalls of Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MR Mammography (DCE-MRM) in Evaluation of Post-Biopsy Suspicious
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 86, No. 3, June: 1513-1522, 2018 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Pitfalls of Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MR Mammography (DCE-MRM) in Evaluation of Post-Biopsy Suspicious
WHAT TO EXPECT. Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC. The Women's Health Company
 WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
The role of MRI in assessment of asymmetrical breast densities
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2010) 41, 501 508 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2010) 41, 501 508 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
