RADIOACTIVITY & RADIATION CHARACTERISTICS
|
|
|
- Shauna Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CEMP TRAINING SESSION JULY 2013 RADIOACTIVITY & RADIATION CHARACTERISTICS Instructor: Gary M. Sandquist, PhD, CHP 2013 Training Session Slide 1
2 Occupational Dose Equivalent Limits General Public 100 mrem/yr Any Occupational Worker (unmonitored) 100 mrem/yr Radiation Worker (monitored) 5,000 mrem/yr = 5 rem/yr Slide 2
3 Man-Made Sources Medical radiation ~ 48% Nuclear weapon tests < 0.1% Consumer products ~ 2% All energy production & research < 0.1% or < 0.5 mrem Industrial uses < 0.1% Fukushima: Dose ~ 1 ft elevation Slide 3
4 Medical Radiation X-rays - medical (CT s, etc.) & dental Radioactive material for diagnosis 131 I, 99 Tc, 32 P, 3 H, 14 C Radioactive material for therapy 60 Co, 137 Cs, 226 Ra, neutrons Annual dose ~298 mrem ~48% total Slide 4
5 EPA annual US (LNT) risk from cancer 1.16 E-3 cancer-inductions/person-rem 5.8 E-4 cancer-deaths/person-rem US population 330 million in 2006 and medical = 0.3 rem = 115,000 induced cancers from medical = 57,000 cancer deaths from medical Medical radiation increased since 2006 so cancer risks greater Industrial nuclear < 0.1% total 620 mrem radiation exposure Industrial radiation including all nuclear related activities = 230 induced cancers = 120 cancer deaths Slide 5
6 ALARA As Low As Reasonably Achievable (called ALARA by regulators) Radiation protection program manage exposures (individual & collective to workforce & public) as low as social, technical, economic, practical, public policy permit ALARA not dose limit but a process maintain dose levels As Low As Reasonably Achievable Slide 6
7 1925 Radium Effects Confirmed Suspicions develop around watch dial painters jaw lesions Dentists diagnose lesions as jaw necrosis due to radium deposits in jaw bone Doctor notes bone changes and anemia in dial painters Slide 7
8 Slide 8 What is Radiation? Radiation: energy in motion Radioactivity: spontaneous emission of radiation from nucleus of an unstable atom Isotope: atoms with same number of protons, but different number of neutrons Radioisotope: unstable isotope of an element that decays or disintegrates spontaneously, emitting radiation. About 5,000 natural and artificial radioisotopes identified
9 Types of Radiation Non-Ionizing Radiation: Radiation that does not have sufficient energy to dislodge orbital electrons. Examples of non-ionizing radiation: microwaves, ultraviolet light, lasers, radio waves, infrared light, and radar. Ionizing Radiation: Radiation that has sufficient energy to dislodge orbital electrons. Examples of ionizing radiation: alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons, gamma rays, and x-rays. Slide 9
10 Terrestrial Radiation Terrestrial radiation emitted from Primordial radio nuclides Radio nuclides left over when earth was created. Common radionuclides deposited during formation of earth: Radioactive Potassium (K-40) found in bananas, in human body, plant fertilizer and where potassium exists. Radioactive Rubidium (Rb-87) is found in brazil nuts among other things. Radioactive Carbon (C-14) produced in upper atmosphere from cosmic radiation Slide 10
11 Terrestrial Radiation 4 2 α ++ Greatest contributor is 226 Ra (Radium) with significant levels also from 238 U, 232 Th, and 40 K. - Igneous rock contains highest concentration followed by sedimentary, sandstone and limestone. - Fly ash from coal burning plants contains more radiation than that of nuclear or oil-fired plants. Slide 11
12 Compare Backgrounds Sea level - 30 mrem/year from cosmic radiation 10,000 ft. altitude mrem/year from cosmic radiation 30,000 ft. altitude - 10 mrem/hr Aircraft flight from cosmic radiation Slide 12
13 Consumer Products and Radioactive Material Slide 13 Many sources of radiation in consumer products Smoke detectors agricultural products - fertilizer long lasting light bulbs building materials (sheet rock) static eliminators in manufacturing luminous dials of watches clocks and compasses etc.
14 Radiation Postings Slide 14 n Radiation labeled on door, work area & storage area n Research laboratories work with radioactive materials n Contamination warning for work in lab with radioactive materials n Wear gloves, safety glasses, protective clothing, not eating or smoking
15 Radioactivity Units Rate of Disentegration or Decay Strength Curie (Ci) about 1 gram of radium 3.7 X disintegrations/sec Becquerel (Bq) = 1 (dps) 1 mci = 37 MBq Slide 15
16 Dose Equivalent Scale for equating relative hazards of various types of ionization in terms of equivalent risk Damage in tissue measured in rem - (Roentgen Equivalent Man) Q:risk of biological injury rem = Q * rad Sievert (Sv) 1 Sv = 100 rem Slide 16
17 What do we really need to know? 1 R 1 rad = 1 rem For gammas & betas 1 rad 1 rem For alphas, neutrons & protons 1 rem = 1 rad * Q Slide 17
18 Annual Radiation Exposure Limits Occupationally Exposed Worker: rem mrem Whole body Eye 15 15,000 Shallow 50 50,000 Minor Pregnant Worker 0.5* 500* *9 months_ General Public: 100 mrem/year or 2mrem/hour Slide 18
19 Ensuring Compliance to Radiation Exposure Limits Use established activity limit for each isotope Compare with similar situations Estimate with meter Calculate - Time, Distance, Shielding, Type, Energy, Geometry Measure - TLD Chip, Luxel - Bioassay Slide 19
20 Who should wear radiation dosimeters or badges? Those likely to exceed 10% of their annual limit are required Those who would like a badge Minors & Declared Pregnant Workers* Slide 20
21 Slide 21 Industrial use of nuclear materials < 0.1% radiation exposure to public and workers. Environmental Protection Agency asserts annual US radiation risk from cancer o 1.16 E-3 cancer-inductions/person-rem o 5.8 E-4 cancer-deaths/person-rem US population is 330 million so for 2006 o Annual cancer induction from medical = 115,000 induced cancers = 57,000 cancer deaths from medical o All industrial radiation including all nuclear related activities = 230 induced cancers = 120 cancer deaths
22 Perspective of Risk Estimated Loss of Life Expectancy during lifetime Health Risks 20 cigarettes/day 6 years 15% overweight 2 years Consuming alcohol 1 year All Accidents 1 year Motor vehicle 207 days Home accident 74 days Drowning 24 days Natural hazards 7 days Medical radiation 15 days 620 mrem/y for 47 y 31 days (US Background dose) 1 rem/y for 47 y 50 days Industrial Accidents All industries 60 days Agriculture 320 days Construction 227 days Mining 167 days Transportation 160 days Government 60 days Manufacturing 40 days Trade 27 days Services 27 days Nuclear Plant 27 days Slide 22
23 Declared Pregnant Worker (Embryo / Fetus) Policy: Female radiation worker encouraged to voluntarily notify supervisor (written) if pregnant Employer must provide agreeable work with limited (~no rad) exposure & no loss of pay or promotional opportunity Further occupational rad exposure unlikely during pregnancy Slide 23
24 External & Internal Radiation Dose Reduction Use shielding if possible Minimize time in radiation field Maximize distance to rad source Dose ~ Source x time / (distance) 2 Slide 24
25 Radiological Control Responsibilities Provide technical & programmatic control over radiation & radioactive materials Provide Health Physics (HP) personnel & monitoring equipment Issue Radiation Work Permits (RWPs) Maintain dosimetry program Maintain training program Slide 25
26 Radiological Control Responsibilities Provide technical & programmatic control over radiation & radioactive materials Provide Health Physics (HP) personnel & monitoring equipment Issue Radiation Work Permits (RWPs) Maintain dosimetry program Maintain training program Slide 26
27 Radiological Areas Radiological Buffer Area Radiation Area High Radiation Area Very High Radiation Area Contamination Area High Contamination Area Fixed Contamination Area Soil Contamination Area Airborne Radioactivity Area Slide 27
28 Contamination Area Area where surface has removable contamination > given limits Entry Requirements: Radiological Training II Worker signs RWP Requirements for work in area: Personnel dosimeter if necessary Minimize dust generation Respiratory protection if necessary Slide 28
29 Soil Contamination Area Area where surface soil contaminated above limits Entry Requirements: Radiological Training II Worker signs RWP Requirements for work in area: Personnel dosimeter if necessary Minimize dust generation Minimize earth disturbance Respiratory protection if necessary Slide 29
30 Radioactive Material Area Entry requirements into Rad Materials Area if whole body dose rate > 5 mrem/hour or contamination > specified limits Same for entry into Radiation Area or Contamination Area Depends on radiological hazard present Slide 30
31 Control of Radioactive Spills Stop or secure spill source Warn others in area Isolate spill if possible Minimize exposure & contamination Secure unfiltered ventilation Requirements for exiting - Site specific monitoring - Monitor per posted instructions before entry to clean area Notify Rad Control personnel Changing rad conditions. Actions don t create rad problems for others. Be alert for activities that change rad conditions Slide 31
32 Personnel Protective Clothing Protective Clothing used to enter areas with rad levels above specified limits to prevent skin contamination Clothing depends on work area, rad conditions, job, etc. Full protective clothing includes coveralls cotton glove liners & gloves hood shoe covers & rubber overshoes Slide 32
33 Radiation Damage Direct Effects: - Ionization can break chemical bonds Indirect Effects: - Ionized water results in radicals H + or HO - or H 2 O 2 - These radicals cause chemical damage Location of damage important: Cell Nucleus or Cytoplasm Slide 33
34 Possible Effects on Cells No damage evident Damage repaired & cell normal Damage not repaired & cell functions abnormally Cell dies Slide 34
35 Cell Sensitivity Cells have different rad sensitivity Most sensitive: Cells actively dividing (e.g., stem & blood cells) Moderate sensitive: Less specialized cells Least sensitive: Specialized cells or less actively dividing (nerve, brain, bone, muscle cells, skin ) Slide 35
36 Factors for Biological Damage Total dose (how much) Dose rate (how fast) Type of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma, neutron) Area exposed (total body, internal, hands, etc.) Cell sensitivity Individual person sensitivity Slide 36
37 Risk From Exposure No observed increase of risk at occupational exposures Risk factor: 4 x 10-4 latent health effects per rem (LNT model) Cancer formation latency time > 10 yr More solid tumor formation old age Slide 37
38 US radiation setting bodies constrained No deliberate exposure to radiation justified unless some benefit All radiation exposure must be kept As Low As Reasonably Achievable ALARA Radiation doses to individuals should not exceed mass maximum permissible doses - MPD's. Slide 38
39 No evidence for harm at low levels of radiation But following assumptions made linear non threshold dose relationship LNT applies for any radiation exposure (>0) no threshold for radiation doses below which no health effects occur No biological recovery from radiation effects at any dose level Slide 39
40 Risk of worker death from radiation only from CANCER No observable workers injuries for exposures at regulatory levels Regulatory dose limits far below threshold for observable stochastic effects Slide 40
Accelerator Laboratory GENERAL EMPLOYEE RADIATION TRAINING
 f Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory GENERAL EMPLOYEE RADIATION TRAINING Operated by Universities Research Association, Inc. under contract with the United States Department of Energy October, 1999
f Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory GENERAL EMPLOYEE RADIATION TRAINING Operated by Universities Research Association, Inc. under contract with the United States Department of Energy October, 1999
Understanding Radiation and Its Effects
 Understanding Radiation and Its Effects Prepared by Brooke Buddemeier, CHP University of California Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Presented by Jeff Tappen Desert Research Institute 1 Radiation
Understanding Radiation and Its Effects Prepared by Brooke Buddemeier, CHP University of California Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Presented by Jeff Tappen Desert Research Institute 1 Radiation
Radiation Safety Bone Densitometer
 Radiation Safety Bone Densitometer Outline I. State Regulations II. Fundamentals of Radiation Safety III. IV. i. Characteristics of x-ray radiation ii. Units of radiation dose iii. Biological effects iv.
Radiation Safety Bone Densitometer Outline I. State Regulations II. Fundamentals of Radiation Safety III. IV. i. Characteristics of x-ray radiation ii. Units of radiation dose iii. Biological effects iv.
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
Laboratory Safety 197/405. Types of Radiation 198/405
 Laboratory Safety 197/405 Types of Radiation 198/405 Particle Radiation Alpha He nucleus (heavy particle) +2 charge Internal hazard only Beta Electron -1 charge Internal and external hazard Neutron 199/405
Laboratory Safety 197/405 Types of Radiation 198/405 Particle Radiation Alpha He nucleus (heavy particle) +2 charge Internal hazard only Beta Electron -1 charge Internal and external hazard Neutron 199/405
Radiation Safety for Safety Wardens
 Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety for Safety Wardens - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications
Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety for Safety Wardens - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications
Radiation Safety Guide. Analytical X-Ray Equipment
 Radiation Safety Guide Analytical X-Ray Equipment Table of Content Page 1. Radiation 2 A. Radiation Quantities 2 B. Background Radiation 2 C. Biological Effect of Radiation 3 D. Radiation Injury To The
Radiation Safety Guide Analytical X-Ray Equipment Table of Content Page 1. Radiation 2 A. Radiation Quantities 2 B. Background Radiation 2 C. Biological Effect of Radiation 3 D. Radiation Injury To The
IONIZING RADIATION, HEALTH EFFECTS AND PROTECTIVE MEASURES
 May 2011 IONIZING RADIATION, HEALTH EFFECTS AND PROTECTIVE MEASURES KEY FACTS Ionizing radiation is a type of energy released by atoms in the form of electromagnetic waves or particles. People are exposed
May 2011 IONIZING RADIATION, HEALTH EFFECTS AND PROTECTIVE MEASURES KEY FACTS Ionizing radiation is a type of energy released by atoms in the form of electromagnetic waves or particles. People are exposed
Ionizing Radiation. Michael J. Vala, CHP. Bristol-Myers Squibb
 Ionizing Radiation Michael J. Vala, CHP Bristol-Myers Squibb michael.vala@bms.com 732-227-5096 2013 American Industrial Hygiene Association, New Jersey Section, Inc. Course Objectives At the end of this
Ionizing Radiation Michael J. Vala, CHP Bristol-Myers Squibb michael.vala@bms.com 732-227-5096 2013 American Industrial Hygiene Association, New Jersey Section, Inc. Course Objectives At the end of this
Radiation Safety. - Orientation Session - Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit
 Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications and Electronics
Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications and Electronics
Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/11/09
 Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/11/09 Health Physics NRC Dose Limits The NRC has established the following annual dose limits. Organ NRC Limit (mrem/year) Comments Whole Body 5000 (50 msv/yr) Lens of the Eye
Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/11/09 Health Physics NRC Dose Limits The NRC has established the following annual dose limits. Organ NRC Limit (mrem/year) Comments Whole Body 5000 (50 msv/yr) Lens of the Eye
RELIANT HOLDINGS LTD AND ITS AFFILIATES Safety Management System. Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: CEO Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 5
 Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: CEO Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 5 Purpose The purpose of this program is to protect employees who may encounter ionizing radiation and its hazards while performing
Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: CEO Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 5 Purpose The purpose of this program is to protect employees who may encounter ionizing radiation and its hazards while performing
PAGE 1 OF 5 HEALTH, SAFETY & ENVIROMENTAL MANUAL PROCEDURE: S560 Radiation Safety REV /14/2012
 PAGE 1 OF 5 RADIATION SAFETY PURPOSE: A wide usage of x-ray machines and isotopes for examination of steel plate fabricated and erected structures require a knowledge of the radiation hazard and the precautionary
PAGE 1 OF 5 RADIATION SAFETY PURPOSE: A wide usage of x-ray machines and isotopes for examination of steel plate fabricated and erected structures require a knowledge of the radiation hazard and the precautionary
Adult: > 18 Years ALARA: As low as reasonably achievable ALI:
 Health Physics Adult: > 18 Years ALARA: As low as reasonably achievable ALI: Annual Limit on Intake. The amount of an isotope that if taken into the body over the course of a year would result in in a
Health Physics Adult: > 18 Years ALARA: As low as reasonably achievable ALI: Annual Limit on Intake. The amount of an isotope that if taken into the body over the course of a year would result in in a
RADIATION SAFETY REFRESHER TRAINING FOR AUGUSTA UNIVERSITY USERS OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
 RADIATION SAFETY REFRESHER TRAINING FOR AUGUSTA UNIVERSITY USERS OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Environmental Health and Safety Division Course Content Radiation Safety Radiation Dose Limits and Dosimetry Postings
RADIATION SAFETY REFRESHER TRAINING FOR AUGUSTA UNIVERSITY USERS OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Environmental Health and Safety Division Course Content Radiation Safety Radiation Dose Limits and Dosimetry Postings
Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students
 Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students John Vetter, PhD Medical Physics Department UW School of Medicine & Public Health Background and Purpose of This Training This is intended as
Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students John Vetter, PhD Medical Physics Department UW School of Medicine & Public Health Background and Purpose of This Training This is intended as
Radiation physics and radiation protection. University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
Everyday Radiation. David D. Dixon HDT Rally Hutchinson, KS October 15, 2014
 Everyday Radiation David D. Dixon HDT Rally Hutchinson, KS October 15, 2014 Overview Types of radiation and radiation damage Sources of radiation Naturally Occurring Medical Energy Industry Other Man-Made
Everyday Radiation David D. Dixon HDT Rally Hutchinson, KS October 15, 2014 Overview Types of radiation and radiation damage Sources of radiation Naturally Occurring Medical Energy Industry Other Man-Made
Introduction To Nuclear Power Module 3: Understanding Radiation and Its Effects
 Introduction To Nuclear Power Module 3: Understanding Radiation and Its Effects Course # 9CCKN1002 Nathan Hoffman, PhD Greg Johnson, PhD, PE Phil Rutherford R.Z. Litwin (Editor) 1 Introduction To Nuclear
Introduction To Nuclear Power Module 3: Understanding Radiation and Its Effects Course # 9CCKN1002 Nathan Hoffman, PhD Greg Johnson, PhD, PE Phil Rutherford R.Z. Litwin (Editor) 1 Introduction To Nuclear
Radiation in Everyday Life
 Image not found Rincón http://www.rinconeducativo.org/sites/default/files/logo.jpg Educativo Published on Rincón Educativo (http://www.rinconeducativo.org) Inicio > Radiation in Everyday Life Recursos
Image not found Rincón http://www.rinconeducativo.org/sites/default/files/logo.jpg Educativo Published on Rincón Educativo (http://www.rinconeducativo.org) Inicio > Radiation in Everyday Life Recursos
GERT TRAINING STUDY GUIDE. Jefferson Lab Radiation Control Department (2010)
 GERT TRAINING STUDY GUIDE Jefferson Lab Radiation Control Department (2010) 1 Introduction General Employee Radiological Safety Training (GERT) is provided to inform the employee of basic radiation protection
GERT TRAINING STUDY GUIDE Jefferson Lab Radiation Control Department (2010) 1 Introduction General Employee Radiological Safety Training (GERT) is provided to inform the employee of basic radiation protection
Radiologic Units: What You Need to Know
 Radiologic Units: What You Need to Know TODD VAN AUKEN M.ED. RT (R)(MR) Agenda Greys, Sieverts, Coulombs per kg, & Becquerel's Conventional Units Other Concepts (LET, Q-Factor, Effective Dose, NCRP Report
Radiologic Units: What You Need to Know TODD VAN AUKEN M.ED. RT (R)(MR) Agenda Greys, Sieverts, Coulombs per kg, & Becquerel's Conventional Units Other Concepts (LET, Q-Factor, Effective Dose, NCRP Report
Section 7 ALARA Program
 Page 7-1 Section 7 ALARA Program Contents A. ALARA Principle... 7-2 1. Biological Basis... 7-2 2. Applied Practices... 7-3 3. Operational Dose Limits... 7-3 4. Collective Dose... 7-3 B. Radiation Safety
Page 7-1 Section 7 ALARA Program Contents A. ALARA Principle... 7-2 1. Biological Basis... 7-2 2. Applied Practices... 7-3 3. Operational Dose Limits... 7-3 4. Collective Dose... 7-3 B. Radiation Safety
Everyday Radiation. David D. Dixon HDT Rally Hutchinson, KS October 13, 2015
 Everyday Radiation David D. Dixon HDT Rally Hutchinson, KS October 13, 2015 Overview Nuclear Energy Industry Outlook Types of radiation and radiation damage Sources of radiation Naturally Occurring Medical
Everyday Radiation David D. Dixon HDT Rally Hutchinson, KS October 13, 2015 Overview Nuclear Energy Industry Outlook Types of radiation and radiation damage Sources of radiation Naturally Occurring Medical
Introduction. Chapter 15 Radiation Protection. Advisory bodies. Regulatory bodies. Main Principles of Radiation Protection
 Introduction Chapter 15 Radiation Protection Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. F.M. Khan, The Physics of Radiation Therapy, 4th ed., Chapter
Introduction Chapter 15 Radiation Protection Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. F.M. Khan, The Physics of Radiation Therapy, 4th ed., Chapter
Sources of ionizing radiation Atomic structure and radioactivity Radiation interaction with matter Radiation units and dose Biological effects
 INTRODUCTION TO RADIATION PROTECTION Sources of ionizing radiation Atomic structure and radioactivity Radiation interaction with matter Radiation units and dose Biological effects 3/14/2018 1 Wilhelm C.
INTRODUCTION TO RADIATION PROTECTION Sources of ionizing radiation Atomic structure and radioactivity Radiation interaction with matter Radiation units and dose Biological effects 3/14/2018 1 Wilhelm C.
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT
 RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
General Employee Radiological Training. Student s Guide
 (Part 3 of 3) Coordinated and Conducted for the Office of Health, Safety and Security U.S. Department of Energy DOE-HDBK-2007 This page intentionally left blank. ii Table of Contents TERMINAL GOAL... 1
(Part 3 of 3) Coordinated and Conducted for the Office of Health, Safety and Security U.S. Department of Energy DOE-HDBK-2007 This page intentionally left blank. ii Table of Contents TERMINAL GOAL... 1
Ionizing Radiation. Alpha Particles CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Ionizing Radiation Ionizing radiation is radiation that has sufficient energy to remove electrons from atoms. In this document, it will be referred to simply as radiation. One source of radiation
CHAPTER 1 Ionizing Radiation Ionizing radiation is radiation that has sufficient energy to remove electrons from atoms. In this document, it will be referred to simply as radiation. One source of radiation
Radioactive Exposure. Abstract of Article:
 Radioactive Exposure Abstract of Article: All ionizing radiations, at sufficiently large exposures, can cause cancer. Many, in carefully controlled exposures, are also used for cancer therapy. Ionizing
Radioactive Exposure Abstract of Article: All ionizing radiations, at sufficiently large exposures, can cause cancer. Many, in carefully controlled exposures, are also used for cancer therapy. Ionizing
What We Know and What We Don t Know About Radiation Health Effects
 What We Know and What We Don t Know About Radiation Health Effects An Educational Briefing By The HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY Specialists In Radiation Safety March 28, 2001 Presentation Agenda Radiation Exposure
What We Know and What We Don t Know About Radiation Health Effects An Educational Briefing By The HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY Specialists In Radiation Safety March 28, 2001 Presentation Agenda Radiation Exposure
Radiation Health Effects
 Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment
 ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 3, 4 & 5 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 3, 4 & 5 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy
Radiation Safety Manual
 King Abdulaziz University Faculty of Dentistry Radiation Safety Manual FOR X-RAY EQUIPMENT OPERATORS October 2009 Radioactivity and Radiation All matter in our environment is made of atoms. Most atoms
King Abdulaziz University Faculty of Dentistry Radiation Safety Manual FOR X-RAY EQUIPMENT OPERATORS October 2009 Radioactivity and Radiation All matter in our environment is made of atoms. Most atoms
Radiation Safety in the Workplace. v1.0
 Radiation Safety in the Workplace v1.0 Outline What is radiation? Different types of radiation Activity and Half-life Units of radiation dose Health effects of exposure to radiation Dose limits Common
Radiation Safety in the Workplace v1.0 Outline What is radiation? Different types of radiation Activity and Half-life Units of radiation dose Health effects of exposure to radiation Dose limits Common
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden
 Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Nuclear Radiation Today
 CHAPTER 10 13 SECTION Nuclear Changes Nuclear Radiation Today KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Where are some common sources of radiation? What are some beneficial uses
CHAPTER 10 13 SECTION Nuclear Changes Nuclear Radiation Today KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Where are some common sources of radiation? What are some beneficial uses
Part 7: Regulatory Issues and Quality Control. Part 1: Current NRC Regulations Related to Radiation Safety
 Part 7: Regulatory Issues and Quality Control Part 1: Current NRC Regulations Related to Radiation Safety 1. Secretarial space, hallways, and certain other areas of a department must qualify as an UNRESTRICTED
Part 7: Regulatory Issues and Quality Control Part 1: Current NRC Regulations Related to Radiation Safety 1. Secretarial space, hallways, and certain other areas of a department must qualify as an UNRESTRICTED
Basic radiation protection & radiobiology
 Basic radiation protection & radiobiology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient care & management 202 Wednesday, October 13, 2010 Ionizing radiation. Discussion issues Protecting the patient. Protecting the radiographer.
Basic radiation protection & radiobiology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient care & management 202 Wednesday, October 13, 2010 Ionizing radiation. Discussion issues Protecting the patient. Protecting the radiographer.
Radiation Protection in Laboratory work. Mats Isaksson, prof. Department of radiation physics, GU
 Radiation Protection in Laboratory work Mats Isaksson, prof. Department of radiation physics, GU mats.isaksson@radfys.gu.se Fundamental principles (ICRP) Justification Optimisation Application of dose
Radiation Protection in Laboratory work Mats Isaksson, prof. Department of radiation physics, GU mats.isaksson@radfys.gu.se Fundamental principles (ICRP) Justification Optimisation Application of dose
Environmental Health Physics
 Environmental Health Physics Jeffrey J. Whicker Bill Eisele Mike McNaughton U N C L A S S I F I E D Environmental health physics combines with many other scientific fields to protect people and the environment
Environmental Health Physics Jeffrey J. Whicker Bill Eisele Mike McNaughton U N C L A S S I F I E D Environmental health physics combines with many other scientific fields to protect people and the environment
The activity. Suggested Answers
 Teacher notes Introduction This activity encourages students to consider the principles of radiation protection and how they might apply in the nuclear industry and in medicine. They discuss and answer
Teacher notes Introduction This activity encourages students to consider the principles of radiation protection and how they might apply in the nuclear industry and in medicine. They discuss and answer
Radiation Safety General Awareness and ALARA Training
 Radiation Safety General Awareness and ALARA Training Authorized User The following materials should be used to provide training to laboratory personnel that do not use radioactive material. Have each
Radiation Safety General Awareness and ALARA Training Authorized User The following materials should be used to provide training to laboratory personnel that do not use radioactive material. Have each
Radiopharmaceuticals. Radionuclides in NM. Radionuclides NUCLEAR MEDICINE. Modes of radioactive decays DIAGNOSTIC THERAPY CHEMICAL COMPOUND
 Univerzita Karlova v Praze - 1. Lékařská fakulta Radiation protection NUCLEAR MEDICINE Involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear medicine study
Univerzita Karlova v Praze - 1. Lékařská fakulta Radiation protection NUCLEAR MEDICINE Involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear medicine study
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 2 & 3 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy radiation
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 2 & 3 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy radiation
Chapter 8. Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation
 Chapter 8 Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation Learning Objectives By the end of the chapter the reader will be able to: Define the terms ionizing radiation and nonionizing radiation State the differences
Chapter 8 Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation Learning Objectives By the end of the chapter the reader will be able to: Define the terms ionizing radiation and nonionizing radiation State the differences
Radiation Safety. Page 1. Introduction. Radiation is ENERGY IN TRANSIT in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves.
 Radiation Safety Introduction Radiation is ENERGY IN TRANSIT in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves. NOTE: We encounter electromagnetic ti waves every day. They make up our visible
Radiation Safety Introduction Radiation is ENERGY IN TRANSIT in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves. NOTE: We encounter electromagnetic ti waves every day. They make up our visible
Radiation Protection Guidance For Hospital Staff
 Radiation Protection Guidance For Hospital Staff Prepared for Stanford Health Care, Stanford Children s Health And Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System June 2017 Last revision June 29, 2017 For
Radiation Protection Guidance For Hospital Staff Prepared for Stanford Health Care, Stanford Children s Health And Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System June 2017 Last revision June 29, 2017 For
Application of the Commission's Recommendations for the Protection of People in
 ICRP Publication 127 ICRP Publication 126 ICRP Publication 125 ICRP Publication 124 ICRP Publication 123 ICRP Publication 122 ICRP Publication 121 ICRP Publication 120 ICRP 2011 Proceedings Radiological
ICRP Publication 127 ICRP Publication 126 ICRP Publication 125 ICRP Publication 124 ICRP Publication 123 ICRP Publication 122 ICRP Publication 121 ICRP Publication 120 ICRP 2011 Proceedings Radiological
Quiz True/False: Large amounts of radiation to insects will cause them to mutate!
 RADS, REMS & ROENTGENS Jack L. Barr, M.S., R.T.R., F.A.S.R.T. Quiz True/False: Large amounts of radiation to insects will cause them to mutate! LARGE AMOUNTS OF RADIATION WILL CAUSE VEGETABLES TO BECOME
RADS, REMS & ROENTGENS Jack L. Barr, M.S., R.T.R., F.A.S.R.T. Quiz True/False: Large amounts of radiation to insects will cause them to mutate! LARGE AMOUNTS OF RADIATION WILL CAUSE VEGETABLES TO BECOME
ICRP 128 ICRP ICRP ICRP 1928
 ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 1928 ICRP ICRP ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 129 ICRP 128 Radiological Protection in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Radiation Dose to Patients from Radiopharmaceuticals: A Compendium of Current
ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 1928 ICRP ICRP ICRP 1928 129 ICRP 129 ICRP 128 Radiological Protection in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Radiation Dose to Patients from Radiopharmaceuticals: A Compendium of Current
a. If dosimeters should be issued; b. What type(s) will be used and; c. The frequency that dosimeters will be exchanged
 Monitoring Criteria for External Radiation RMSO Standard Operating Procedure Risk Management & Safety Main Office, Merica Hall Room 323 Phone: (307) 766-3277 Fax: (307)766-6116 Regulated Materials Management
Monitoring Criteria for External Radiation RMSO Standard Operating Procedure Risk Management & Safety Main Office, Merica Hall Room 323 Phone: (307) 766-3277 Fax: (307)766-6116 Regulated Materials Management
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350.
 Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Absorbed Dose: The mean energy per unit mass imparted to any matter by any type of ionizing radiation.
 GLOSSARY Absorbed Dose: The mean energy per unit mass imparted to any matter by any type of ionizing radiation. Committed Dose Equivalent (CDE): The dose equivalent to organs or a tissues of reference
GLOSSARY Absorbed Dose: The mean energy per unit mass imparted to any matter by any type of ionizing radiation. Committed Dose Equivalent (CDE): The dose equivalent to organs or a tissues of reference
Y Physics Radiation Measurements and Monitoring
 90 Y Physics Radiation Measurements and Monitoring Mack L. Richard, MS, CHP Indiana University Medical Center Phone: (317) 274-0330 Email: mrichar@iupui.edu What type of measurements are required? Dosage
90 Y Physics Radiation Measurements and Monitoring Mack L. Richard, MS, CHP Indiana University Medical Center Phone: (317) 274-0330 Email: mrichar@iupui.edu What type of measurements are required? Dosage
Radiation Safety - Things You Need to Know
 Radiation Safety - Things You Need to Know Michael Casey Ph.D. Phlebotomy Autumn Seminar 13 th October 2012 Radiation is a form of energy transport What is Radiation? It is caused by electrical disturbances
Radiation Safety - Things You Need to Know Michael Casey Ph.D. Phlebotomy Autumn Seminar 13 th October 2012 Radiation is a form of energy transport What is Radiation? It is caused by electrical disturbances
PERSONNEL MONITORING AND DOSIMETRY POLICIES
 PERSONNEL MONITORING AND DOSIMETRY POLICIES All individuals who are required to have their exposure to ionizing radiation monitored must be trained prior to using the source(s) of radiation. The radioactive
PERSONNEL MONITORING AND DOSIMETRY POLICIES All individuals who are required to have their exposure to ionizing radiation monitored must be trained prior to using the source(s) of radiation. The radioactive
PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF RADIATION PROTECTION
 PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF RADIATION PROTECTION Lesson Outcomes At the end of the lesson, student should be able to: Define what is radiation protection (RP) Describe basic principles of RP Explain methods
PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF RADIATION PROTECTION Lesson Outcomes At the end of the lesson, student should be able to: Define what is radiation protection (RP) Describe basic principles of RP Explain methods
Controlling Natural Occurring Radioactive Material (NORM) Exposure
 Controlling Natural Occurring Radioactive Material (NORM) Exposure Agenda What is NORM? What is Radiation? Radiation Types Health Effects NORM Oil & Gas Where is NORM Located? How Could I Be Exposed? NORM
Controlling Natural Occurring Radioactive Material (NORM) Exposure Agenda What is NORM? What is Radiation? Radiation Types Health Effects NORM Oil & Gas Where is NORM Located? How Could I Be Exposed? NORM
ARRT Specifications Radiation Exposure & Monitoring
 Radiation Protection Review 15% (30) 11% (22) Gina Tice, MSRS, RT(R) Gadsden State Community College ARRT Specifications Radiation Exposure & Monitoring Radiation Protection (45) Biological Aspects of
Radiation Protection Review 15% (30) 11% (22) Gina Tice, MSRS, RT(R) Gadsden State Community College ARRT Specifications Radiation Exposure & Monitoring Radiation Protection (45) Biological Aspects of
Topic 6 Benefits and drawbacks of using radioactive materials
 Topic 6 Benefits and drawbacks of using radioactive materials CHANGING IDEAS When radioactivity was first discovered in the late 1800s, scientists did not know it was dangerous: o Becquerel handled radioactive
Topic 6 Benefits and drawbacks of using radioactive materials CHANGING IDEAS When radioactivity was first discovered in the late 1800s, scientists did not know it was dangerous: o Becquerel handled radioactive
Risk and Risk Reduction. Environmental Health and Safety. Radiation Safety. Radiation is all around us
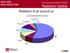 Risk and Risk Reduction Radiation is all around us Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Safety Risk and Risk Reduction Risk Webster s dictionary defines risk as the chance of injury, damage, or loss;
Risk and Risk Reduction Radiation is all around us Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Safety Risk and Risk Reduction Risk Webster s dictionary defines risk as the chance of injury, damage, or loss;
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation
 Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
Radiation Carcinogenesis
 Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
RADIATION HAZARDS. A dabbler s perspective. Jess H. Brewer
 RADIATION HAZARDS A dabbler s perspective by Jess H. Brewer Mortality Paraphrased from memory: Front page of special HEALTH edition of LA Free Press (around 1970): No matter how much money you have, how
RADIATION HAZARDS A dabbler s perspective by Jess H. Brewer Mortality Paraphrased from memory: Front page of special HEALTH edition of LA Free Press (around 1970): No matter how much money you have, how
Radiation Effects. Radiobiology Steve Curtis Desert Research Institute
 Radiation Effects Radiobiology Steve Curtis Desert Research Institute Background Radiation Cosmic Terrestrial In our Bodies Total Radiation About 300 mr per year Equals about 15 X-Rays Over half is from
Radiation Effects Radiobiology Steve Curtis Desert Research Institute Background Radiation Cosmic Terrestrial In our Bodies Total Radiation About 300 mr per year Equals about 15 X-Rays Over half is from
CRACKCast E146 Radiation Injuries
 CRACKCast E146 Radiation Injuries Key concepts: Patients contaminated with radiation pose very little risk to health care providers when appropriate precautions and decontamination procedures are employed.
CRACKCast E146 Radiation Injuries Key concepts: Patients contaminated with radiation pose very little risk to health care providers when appropriate precautions and decontamination procedures are employed.
RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N & B I O L O G Y - R H O D E S
 RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES 10-526- 1 9 7 R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N & B I O L O G Y - R H O D E S DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT OF IONIZING RADIATION Dosimeter Dose-measuring device Two classifications:
RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES 10-526- 1 9 7 R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N & B I O L O G Y - R H O D E S DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT OF IONIZING RADIATION Dosimeter Dose-measuring device Two classifications:
RADIATION SAFETY REVIEW UIHC Environmental Services
 RADIATION SAFETY REVIEW UIHC Environmental Services Original material/information by Laurie Taylor, HPO, May 1999 Revised format by Mary Thompson, UIHC EVS, April 2006 For example, the transfer of heat
RADIATION SAFETY REVIEW UIHC Environmental Services Original material/information by Laurie Taylor, HPO, May 1999 Revised format by Mary Thompson, UIHC EVS, April 2006 For example, the transfer of heat
Twelfth Annual Warren K. Sinclair Keynote Address
 THE INFLUENCE OF NCRP ON RADIATION PROTECTION IN THE U.S.: REGULATION AND GUIDANCE Twelfth Annual Warren K. Sinclair Keynote Address Kenneth R. Kase Annual Meeting of NCRP 16 March 2015 1 OUTLINE Introduction
THE INFLUENCE OF NCRP ON RADIATION PROTECTION IN THE U.S.: REGULATION AND GUIDANCE Twelfth Annual Warren K. Sinclair Keynote Address Kenneth R. Kase Annual Meeting of NCRP 16 March 2015 1 OUTLINE Introduction
RADIATION SAFETY GUIDE FOR ANALYTICAL X-RAY SYSTEM USERS
 DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY RADIATION PROTECTION DIVISION MAY 2001 FOR ANALYTICAL X-RAY SYSTEM USERS I INTRODUCTION The Minnesota Department of Health has established rules for the registration
DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY RADIATION PROTECTION DIVISION MAY 2001 FOR ANALYTICAL X-RAY SYSTEM USERS I INTRODUCTION The Minnesota Department of Health has established rules for the registration
What is the current risk of radiation-related health problems in Japan to those near the reactor at the time, and those in other parts of Japan?
 What is the current risk of radiation-related health problems in Japan to those near the reactor at the time, and those in other parts of Japan? The actions proposed by the Government of Japan are in line
What is the current risk of radiation-related health problems in Japan to those near the reactor at the time, and those in other parts of Japan? The actions proposed by the Government of Japan are in line
University of Maryland Baltimore. Radiation Safety Standard Operating Procedure
 University of Maryland Baltimore Radiation Safety Standard Operating Procedure Procedure Number: 3.1.1 Title: External Dosimetry Program Revision Number: 0 Technical Review and Approval: Radiation Safety
University of Maryland Baltimore Radiation Safety Standard Operating Procedure Procedure Number: 3.1.1 Title: External Dosimetry Program Revision Number: 0 Technical Review and Approval: Radiation Safety
RADIATION SAFETY. for Surgical & Invasive Procedures
 RADIATION SAFETY for Surgical & Invasive Procedures TABLE OF CONTENTS Purpose 3 Learning Objectives 3 Instructions 3 Introduction 4 Radioactivity and Radiation 5 Types of Radiation. 6 Primary... 6 Secondary..
RADIATION SAFETY for Surgical & Invasive Procedures TABLE OF CONTENTS Purpose 3 Learning Objectives 3 Instructions 3 Introduction 4 Radioactivity and Radiation 5 Types of Radiation. 6 Primary... 6 Secondary..
Absorbed Dose: The mean energy per unit mass imparted to any matter by any type of ionizing radiation.
 GLOSSARY Absorbed Dose: The mean energy per unit mass imparted to any matter by any type of ionizing radiation. Annual Limit on Intake (ALI): The quantity of a radionuclide which, if taken into the body,
GLOSSARY Absorbed Dose: The mean energy per unit mass imparted to any matter by any type of ionizing radiation. Annual Limit on Intake (ALI): The quantity of a radionuclide which, if taken into the body,
An update: Dealing with radiation as a hazard. WAJ Meintjes MBChB; DOM; FCPHM(SA) Occ Med; MMed (Occ Med)
 An update: Dealing with radiation as a hazard WAJ Meintjes MBChB; DOM; FCPHM(SA) Occ Med; MMed (Occ Med) Radiation The emission and propagation of energy in the form of rays Usually differentiate ionising
An update: Dealing with radiation as a hazard WAJ Meintjes MBChB; DOM; FCPHM(SA) Occ Med; MMed (Occ Med) Radiation The emission and propagation of energy in the form of rays Usually differentiate ionising
CHAPTER 28 RADIATION CONTROL
 CHAPTER 28 RADIATION CONTROL BOARD OF HEALTH ROLE AT A GLANCE Be aware of radioactive materials in the community and request technical assistance in response to incidents involving the possession, handling,
CHAPTER 28 RADIATION CONTROL BOARD OF HEALTH ROLE AT A GLANCE Be aware of radioactive materials in the community and request technical assistance in response to incidents involving the possession, handling,
The Basics of Radiation Safety
 Cardiac Imaging Symposium 2013 UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA HEART INSTITUTE The Basics of Radiation Safety Leah Shuparski-Miller Medical Health Physicist Radiation Safety & Emergency Preparedness Department The
Cardiac Imaging Symposium 2013 UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA HEART INSTITUTE The Basics of Radiation Safety Leah Shuparski-Miller Medical Health Physicist Radiation Safety & Emergency Preparedness Department The
Radiation Safety For Anesthesiologists. R2 Pinyada Pisutchareonpong R2 Nawaporn Sateantantikul Supervised by Aj Chaowanan Khamtuicrua
 Radiation Safety For Anesthesiologists R2 Pinyada Pisutchareonpong R2 Nawaporn Sateantantikul Supervised by Aj Chaowanan Khamtuicrua Modern World Non Ionizing VS Ionizing Non Ionizing Harmless Ex. visible
Radiation Safety For Anesthesiologists R2 Pinyada Pisutchareonpong R2 Nawaporn Sateantantikul Supervised by Aj Chaowanan Khamtuicrua Modern World Non Ionizing VS Ionizing Non Ionizing Harmless Ex. visible
Special Topic: Radiological Dispersal Device or Dirty Bomb EXPLOSION AND BLAST INJURIES
 Special Topic: Radiological Dispersal Device or Dirty Bomb EXPLOSION AND BLAST INJURIES Scenario Presentation Possible Scenarios Simple radiological device Improvised nuclear device (IND) Nuclear weapon
Special Topic: Radiological Dispersal Device or Dirty Bomb EXPLOSION AND BLAST INJURIES Scenario Presentation Possible Scenarios Simple radiological device Improvised nuclear device (IND) Nuclear weapon
Exposure to Background Radiation In Australia
 AU9816851 Exposure to Background Radiation In Australia S.B.SOLOMON, Australian Radiation Laboratory, Lower Plenty Road, Yallambie, Victoria, 3085 SUMMARY The average effective dose received by the Australian
AU9816851 Exposure to Background Radiation In Australia S.B.SOLOMON, Australian Radiation Laboratory, Lower Plenty Road, Yallambie, Victoria, 3085 SUMMARY The average effective dose received by the Australian
Pursuant to section 24 of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, this licence is issued to:
 I) LICENCE NUMBER: II) LICENSEE Pursuant to section 24 of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, this licence is issued to: Memorial University of Newfoundland 208 Elizabeth Avenue Department of Health and
I) LICENCE NUMBER: II) LICENSEE Pursuant to section 24 of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, this licence is issued to: Memorial University of Newfoundland 208 Elizabeth Avenue Department of Health and
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model
 Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Radiation. c) Terrestrial (solid materials) : like stones and soil, and based on that some places in the world has more radiation than others.
 Radiation **this sheet contains the two lectures by Dr madi together and doesn't follow the same order as in the records to simplify the info. ** check the tables as they contain important info the dr
Radiation **this sheet contains the two lectures by Dr madi together and doesn't follow the same order as in the records to simplify the info. ** check the tables as they contain important info the dr
Core Concepts in Radiation Exposure 4/10/2015. Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and. James Seward, MD MPP
 Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James P. Seward, MD MPP FACOEM Clinical Professor of Medicine, UCSF American Occupational Health Conf May 4, 2015 Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James
Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James P. Seward, MD MPP FACOEM Clinical Professor of Medicine, UCSF American Occupational Health Conf May 4, 2015 Ionizing Radiation, Cancer, and Causation James
Hand Dose in Nuclear Medicine Staff Members
 Hand Dose in Nuclear Medicine Staff Members T.M.Taha, Amany.Y.Shahein and R.Hassan* Radiation Protection Department, Nuclear Research Center, Atomic Energy Authority * National Cancer Institute, Cairo
Hand Dose in Nuclear Medicine Staff Members T.M.Taha, Amany.Y.Shahein and R.Hassan* Radiation Protection Department, Nuclear Research Center, Atomic Energy Authority * National Cancer Institute, Cairo
Refer to the N-GET Study Guide for answers to questions. 2. What is your role and responsibility as a worker in the Security program?
 UCLR - GRL MPLOY RG - Review Questions Page 121 Refer to the -G Study Guide for answers to questions. SCURY 1. What is the purpose of the Security program? 2. What is your role and responsibility as a
UCLR - GRL MPLOY RG - Review Questions Page 121 Refer to the -G Study Guide for answers to questions. SCURY 1. What is the purpose of the Security program? 2. What is your role and responsibility as a
Utilize radiation safety principles to reduce the amount of radiation used to achieve desired clinical result.
 Minimizing Dose Understand the importance and methods of pre-procedure patient assessment including a review of previous radiologic exams, disease processes and anatomical considerations that may increase
Minimizing Dose Understand the importance and methods of pre-procedure patient assessment including a review of previous radiologic exams, disease processes and anatomical considerations that may increase
Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter
 Ohio UNIVERSITY Fall 2018 Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter Alan Watts Radiation Safety Officer In This Issue: Instruction Concerning Risks From Occupational Radiation Exposure... pg.1-5 = Required = Optional
Ohio UNIVERSITY Fall 2018 Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter Alan Watts Radiation Safety Officer In This Issue: Instruction Concerning Risks From Occupational Radiation Exposure... pg.1-5 = Required = Optional
GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
 RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
in developing institutional policies, procedures, and /or protocols. The Canadian Society of
 1 TITLE: GUIDELINES FOR RADIATION SAFETY APPROVED; October 2015 REVISION DATE: February 2016 Disclaimer The Canadian Society of Gastroenterology Nurses and Associates present this guideline for use in
1 TITLE: GUIDELINES FOR RADIATION SAFETY APPROVED; October 2015 REVISION DATE: February 2016 Disclaimer The Canadian Society of Gastroenterology Nurses and Associates present this guideline for use in
UQ X-ray Safety Training Module
 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module 23 January 2018, v2 1 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module Course Overview: This training module has been developed for workers at the University of Queensland, and forms part
UQ X-ray Safety Training Module 23 January 2018, v2 1 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module Course Overview: This training module has been developed for workers at the University of Queensland, and forms part
The health risks of exposure to internal radiation. Korea National Assembly Seoul 22 nd August 2015
 The health risks of exposure to internal radiation Korea National Assembly Seoul 22 nd August 2015 Christopher Busby Green Audit UK/ Environmental Research SIA, Riga, Latvia Scientific Secretary: European
The health risks of exposure to internal radiation Korea National Assembly Seoul 22 nd August 2015 Christopher Busby Green Audit UK/ Environmental Research SIA, Riga, Latvia Scientific Secretary: European
Patient Management Image Selection Radiation Biology, Dosimetry & Protection
 Patient Management Image Selection Radiation Biology, Dosimetry & Protection Objectives: Following this course, the participants will have the information necessary to: 1. Identify the techniques used
Patient Management Image Selection Radiation Biology, Dosimetry & Protection Objectives: Following this course, the participants will have the information necessary to: 1. Identify the techniques used
Safety Training Topic ASBESTOS SAFETY
 Safety Training Topic Purpose of Meeting To remind workers that exposure to asbestos can result in serious injury. To educate workers about the risks, regulations and control measures related to working
Safety Training Topic Purpose of Meeting To remind workers that exposure to asbestos can result in serious injury. To educate workers about the risks, regulations and control measures related to working
Practice and Risk at Medical Facilities in Agency Operations
 Practice and Risk at Medical Facilities in Agency Operations Igor Gusev Radiation Protection Unit IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency Outline What is medical radiation exposure? Radiation sources and
Practice and Risk at Medical Facilities in Agency Operations Igor Gusev Radiation Protection Unit IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency Outline What is medical radiation exposure? Radiation sources and
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry
 Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
biological systems: alters electrolyte balance b. Solids trapped electrons and lattice defects modified conduction bands: impurities, Si bit upsets
 Lecture 21: Biological Effects of Radiation I. Radiation Chemistry Interaction of Radiation with Matter: Emphasis on effect of medium on incident radiation Biological Effects of Radiation: Emphasis on
Lecture 21: Biological Effects of Radiation I. Radiation Chemistry Interaction of Radiation with Matter: Emphasis on effect of medium on incident radiation Biological Effects of Radiation: Emphasis on
QUANTIFICATION OF THE RISK-REFLECTING STOCHASTIC AND DETERMINISTIC RADIATION EFFECTS
 RAD Conference Proceedings, vol. 2, pp. 104 108, 2017 www.rad-proceedings.org QUANTIFICATION OF THE RISK-REFLECTING STOCHASTIC AND DETERMINISTIC RADIATION EFFECTS Jozef Sabol *, Bedřich Šesták Crisis Department,
RAD Conference Proceedings, vol. 2, pp. 104 108, 2017 www.rad-proceedings.org QUANTIFICATION OF THE RISK-REFLECTING STOCHASTIC AND DETERMINISTIC RADIATION EFFECTS Jozef Sabol *, Bedřich Šesták Crisis Department,
