f(x) = x R² = RPKM (M8.MXB) f(x) = x E-014 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.
|
|
|
- Loraine Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 14 12 f(x) = x R² = RPKM (M8.MXA) RPKM (M8.MXB) f(x) = x E-14 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.XA) RPKM (M31.XB) Figure S1. Reproducibility between the biological replicates (MXA and MXB) for mixed cultures. Correlations for RPKM values were plotted once assigned to M8 (upper panel), with a R =.9956, or M31 (lower panel) with R =1.
2 Monitorización: Monitoring: ODDO 6 6,9.9 OD6,8.8,7.7,6.6,5.5,4.4 M8PureOD M31PureOD MXOD,3.3,2.2, Time (h) Monitorización: recuentos por DAPI y qpcr MM8 Pure (cells/ml) MM31 Pure (cells/ml) MMX (cells/ml) 9, ,5 8.5 MM8 Pure qpcr MM31Pure qpcr MM8X (qpcr) MM31X (qpcr) log cells/ml 7, , , , Time (h) Figure S2. Growth curves for pure cultures of M8 (blue) and M31 (red). In the upper figure lines represent OD reads for pure and mixed cultures, as indicated in the insert. The bottom figure show log cells/ml values for M8 and M31 cultures measured by quantitative PCR (black and red dots for mixed and triangles for pure cultures) and DAPI (continuous lines). Circled the point selected for sequencing.) and M31
3 Cumulative frequency curve. S. ruber M8, pure cultures Expression level (RPKM) Cumulative percentage (%) <2 RPKM 2-1 RPKM >1 RPKM (VHEG) Cumulative frequency curve. S. ruber M31, pure cultures Expression level (RPKM) Cumulative percentage (%) <2 RPKM 2-1 RPKM >1 RPKM (VHEG) Figure S3. RPKM transcription levels for M8 (upper panel) and M31 (lower panel) genes in pure cultures. Cumulative curves represents the percentage of genes with transcription levels between -2 RPKM (blue), 2-1 RPKM (orange) and above 1 RPKM (yellow).
4 S. ruber M31 replicons. Normalized expression frequency histogram Normalized frequency level S.ruber M31 replicons. Expression frequency histogram normalized Expression level RPKM (1bin=2 RPKM) S.ruber M31. plasmid psru S.ruber M31. plasmid psru S.ruber M31. Chromosome S. ruber M8 replicons. Normalized expression frequency histogram Normalized frequency level S.ruber M8 replicons. Expression frecuency histogram normalized S.ruber M8 plasmid psr11 S.ruber M8 plasmid psr11 psr56 plasmid psr56 S.ruber S.ruber M8 M8 plasmid plasmid psr61 psr61 psr84 S.ruber M8 plasmid psr84 S ruber M8 Chromosome S ruber M8 Chromosome Expression level RPKM (1bin=2 RPKM) Figure S4. Normalized gene distribution for M31 (upper figure) and M8 (bottom figure) based on their expression level (RPKM). All the replicons were represented in both cases.
5 M8 Pure culture. Relation between %GC and expression values A Expression level (RPKM) %GC Normalized frequency level %GC M31 Pure culture. Relation between %GC and expression values Expression level (RPKM) B %GC Normalized frequency level %GC Figure S5. Normalized gene distribution for M8 (A) and M31 (B) based on their % GC and RPKM expression levels. For each strain, genes with expression values below 3 RPKM are shown in bottom panels.
6 (<-.25) (-.25;-.5) (-.5;.5) (.5,.25) (>.25)5) Figure S6. M31 citrate cycle (TCA cycle) KEGG map (sru:2) showing the differential expression changes (log 2 fold change) of S.ruber M31 mean a percentage color gradient. The green boxes represent genes that increase their expression and the reds that decrease it. In red letters the genes that change its expression significantly (SRU_828 = ; (SRU_1969 = ). The circles show the increases (green) or decreases (red) of intermediate metabolites based on the genes expression levels that encode the enzymes that produce them.
7 Table S1. M8 (Gene ID SRM_) and M31 (Gene ID SRU_) genes with transcription below the detection threshold in pure culture. In blue, strain specific genes. In green, genes untranscribed both in M8 and M31.I: Island; CR: conserved region; HP: Hypothetical protein; CHP: Conserved hypothetical protein. GeneID Location Function GeneID Location Function SRM_4 HP SRM_87 I2 HP SRM_141 HP SRM_88 I2 HP SRM_142 CHP SRM_1218 HP SRM_143 HP SRM_145 HP SRM_152 HP SRM_1571 CHP SRM_22 HP SRM_1654 HP SRM_24 HP SRM_1683 HP SRM_239 I1 HP SRM_176 CHP SRM_318 I1 HP SRM_1835 HP SRM_328 I1 HP SRM_1949 HP SRM_332 I1 HP SRM_211 HP SRM_376 HP SRM_2231 HP SRM_41 HP SRM_232 CR HP SRM_479 HP SRM_2491 CR SRM_536 HP SRM_2677 CHP SRM_67 HP SRM_2688 HP SRM_686 I2 transposase SRM_2978 HP SRM_756 I2 HP PSR_5634 PSR56 HP SRM_765 I2 HP PSR_6115 PSR61 HP SRM_775 I2 HP PSR_6126 PSR61 HP SRM_784 I2 HP PSR_6131 PSR61 HP SRM_799 I2 transposase PSR_847 PSR84 HP SRM_875 HP PSR_8447 PSR84 HP SRM_116 HP PSR_8458 PSR84 HP SRM_147 CHP PSR_8461 PSR84 HP SRM_174 HP PSR_8463 PSR84 HP SRM_113 HP PSR_8467 PSR84 HP SRM_1182 HP SRU_13 HP SRU_863 I3 CHP SRU_125 CHP SRU_114 I3 HP SRU_181 I1 HP SRU_117 I3 HP SRU_186 I1 HP SRU_1376 CHP SRU_187 I1 Transcription regulator SRU_146 SRU_212 I1 CHP SRU_1562 CHP SRU_214 I1 CHP SRU_1834 HP SRU_215 I1 CHP SRU_221 CR HP SRU_217 I1 HP SRU_2339 HP SRU_25 I1 HP SRU_2394 HP sensor kinase protein rcsc
8 SRU_263 I1 HP SRU_2457 CHP SRU_284 HP SRU_2465 HP SRU_578 HP SRU_2634 HP SRU_593 I2 HP SRU_2862 SRU_625 I2 HP SRU_p8 tyrosine recombinase XerD
9 Table S2. Genes with expression above 1 RPKM (VHEG: Very highly expressed genes ). Pink: M8 VHEG. Blue: M31 VHEG. Gene ID RPKM Annotation Location a Ortholog. SRM_ hypothetical protein M8 specific SRM_ S ribosomal protein L13 SRU_38 SRM_ conserved hypothetical protein SRU_81 SRM_ hypothetical protein I1 M8 specific SRM_ hypothetical protein M8 specific SRM_ cytochrome c oxidase subunit II SRU_313 SRM_ hypothetical protein SRU_375 SRM_ AsnC family transcriptional regulator SRU_384 SRM_ glutamine synthetase SRU_385 SRM_ hypothetical protein SRU_435 SRM_ TonB protein SRU_51 SRM_ Chain length determinant protein SRU_594 SRM_ Phage integrase family protein I2 SRU_595 SRM_ UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase I2 M8 specific SRM_ hypothetical protein I2 M8 specific SRM_7 162 acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]--udp-n- I2 SRU_66 SRM_ succinyl-coa synthetase, alpha subunit SRU_67 SRM_ PKD repeat protein SRU_96 SRM_ ATP synthase subunit C SRU_912 SRM_ cold-shock DNA-binding protein SRU_966 SRM_ hypothetical protein M8 specific SRM_ S ribosomal protein S12 SRU_13 SRM_ S ribosomal protein S17 SRU_144 SRM_ S ribosomal protein L17 SRU_161 SRM_ hypothetical protein M8 specific SRM_ adenosylhomocysteinase SRU_1139 SRM_ S ribosomal protein L31 SRU_1162 SRM_ S ribosomal protein S21 M8 specific SRM_ ATP-dependent Clp protease, ATPase subunit SRU_1317 SRM_ iron-sulfur cluster assembly accessory protein SRU_1318 SRM_ S ribosomal protein L27 SRU_1419 SRM_ S ribosomal protein L21 SRU_142 SRM_ Aconitate hydratase SRU_1477 SRM_ Xanthorhodopsin SRU_15 SRM_ hypothetical protein SRU_1536 SRM_ Azurin SRU_159 SRM_ hypothetical protein M8 specific SRM_ MotA/TolQ/ExbB proton channel SRU_1681 SRM_ superoxide dismutase SRU_1724 SRM_ cold-shock protein SRU_1727 SRM_ hypothetical protein SRU_1731 SRM_ DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta' SRU_1757 SRM_ S ribosomal protein L7/L12 SRU_1759 SRM_ S ribosomal protein S15 SRU_1774 SRM_ conserved hypothetical protein SRU_1783 SRM_ S ribosomal protein S1 SRU_1787 SRM_ hypothetical protein SRU_1919 SRM_ kda chaperonin CR SRU_2121
10 SRM_ kda chaperonin CR SRU_2122 SRM_ TonB-dependent receptor CR SRU_2178 SRM_ hypothetical protein CR M8 specific SRM_ outer membrane protein CR SRU_2181 SRM_ TonB-dependent receptor CR SRU_2182 SRM_ peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase CR SRU_228 SRM_ conserved hypothetical protein SRU_2378 SRM_ ATP synthase beta chain SRU_2429 SRM_ ATP synthase subunit epsilon SRU_243 SRM_ cold-shock protein SRU_2449 SRM_ acyl carrier protein SRU_2754 SRM_ S ribosomal protein L35 SRU_284 SRM_ S ribosomal protein L2 SRU_285 SRM_ hypothetical protein M8 specific SRM_ conserved hypothetical protein SRU_287 PSR_ hypothetical protein containing Lambda repressor-like, DNA-binding domain PSR11 M8 specific M8ncRNA SAM (RF162)SAM riboswitch (S box leader) pb pb M31ncRNA1 M8ncRNA TmRNA (RF23) transfer-messenger RNA pb pb M31ncRNA2 M8ncRNA TPP (RF59) TPP riboswitch (THI element) pb pb M31ncRNA3 SRU_ ribosomal protein L28 SRM_22 SRU_ conserved hypothetical protein SRM_88 SRU_ chaperonin GroEL I1 SRM_297 SRU_ cytochrome c oxidase subunit II SRM_393 SRU_ hypothetical protein SRM_452 SRU_ putative AsnC-family transcriptional regulator SRM_46 SRU_ glutamine synthetase, type I SRM_461 SRU_ NADH-quinone oxidoreductase chain b SRM_47 SRU_ conserved hypothetical protein SRM_512 SRU_ TonB SRM_59 SRU_ Chain length determinant protein I2 SRM_689 SRU_ Phage integrase family protein I2 SRM_69 SRU_ UDP-glucose dehydrogenase I2 M31 specific SRU_ ABC transporter, multidrug efflux family I2 M31 specific SRU_ NDP-sugar dehydrogenase, putative I2 SRM_718 SRU_6 195 nucleoside-diphosphate-sugar epimerase I2 M31 specific SRU_ perosamine synthetase, putative I2 SRM_695 SRU_ succinyl-coa synthetase, alpha subunit SRM_846 SRU_ bioy family protein SRM_97 SRU_ hypothetical protein SRM_151 SRU_ conserved protein SRM_198 SRU_ ATP synthase F, C subunit SRM_115 SRU_ 'Cold-shock' DNA-binding domain, putative SRM_1159 SRU_ ribosomal protein L3 SRM_1236 SRU_ S ribosomal protein S17 SRM_1245 SRU_ ribosomal protein L24 SRM_1247 SRU_ ribosomal protein S13p/S18e SRM_1258 SRU_ ribosomal protein L17 SRM_1262 SRU_ adenosylhomocysteinase SRM_1319 SRU_ ribosomal protein L31 SRM_1343 SRU_ osmotically inducible protein C SRM_1497
11 SRU_ ATP-dependent Clp protease, ATPase subunit SRM_151 SRU_ iron-sulfur cluster assembly accessory protein, SRM_1511 SRU_ ribosomal protein L9 SRM_1562 SRU_ ribosomal protein L27 SRM_1611 SRU_ aconitate hydratase, putative SRM_167 SRU_ xanthorhodopsin SRM_1698 SRU_ putative cold shock-like protein cspg M31 specific SRU_ auracyanin A precursor SRM_1789 SRU_ MotA/TolQ/ExbB proton channel family protein SRM_1885 SRU_ Mn-superoxide dismutase SRM_1935 SRU_ conserved domain protein SRM_1939 SRU_ histone H1-like protein SRM_1942 SRU_ DNA-directed RNA polymerase, beta' subunit SRM_197 SRU_ ribosomal protein L7/L12 SRM_1972 SRU_ ribosomal protein S15 SRM_1986 SRU_ conserved hypothetical protein SRM_1995 SRU_ ribosomal protein S1, putative SRM_1999 SRU_ putative regulatory protein, FmdB family SRM_218 SRU_ conserved hypothetical protein SRM_213 SRU_ chaperonin, 1 kda CR SRM_2344 SRU_ chaperonin GroEL CR SRM_2345 SRU_ fasciclin domain protein CR SRM_2399 SRU_ putative outer membrane protein, probably CR SRM_241 SRU_ putative outer membrane protein probably CR SRM_245 SRU_ putative outer membrane protein probably CR SRM_246 SRU_ peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, FKBP-type CR SRM_2434 SRU_ tetratricopeptide repeat domain protein SRM_2581 SRU_ conserved hypothetical protein SRM_2598 SRU_ conserved domain protein SRM_2671 SRU_ acyl carrier protein SRM_2965 SRU_ oxidoreductase, putative SRM_2995 SRU_ hypothetical HIT-like protein slr1234 SRM_39 SRU_ ribosomal protein L2 SRM_321 SRU_ conserved hypothetical protein SRM_386 M31ncRNA SAM (RF162)SAM riboswitch (S box leader) pb pb M8ncRNA1 M31ncRNA TmRNA (RF23) transfer-messenger RNA pb pb M8ncRNA2 M31ncRNA3 595 TPP (RF59) TPP riboswitch (THI element) pb pb M8ncRNA3 a I: Island; CR: Conserved region
12 Table S3. Expression level differences between paralogous genes. 25 gene duplication events, 182 pre-m8/m31 divergence (1) and 23 post-m8/m31 divergence and detected in M8 strain (), and genes involved are shown in the table. An average of Log2 fold change value was obtained in order to estimate expression level differences, 1.31±1.26 and 2.5±2.13 for duplication events accounted after (; orange) and before (1; yellow) M8 and M31 strains divergence respectively. 1= Paralogs M8+M31 Gene ID Absolute value = Paralogs M8 Strain specific (log2foldchange) 1 SRM_ SRM_261; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_2262; SRM_ SRM_213; SRM_ SRM_27; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_221;SRM_ SRM_789; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_232; SRM_ SRM_1359; SRM_ SRM_231; SRM_ SRM_129; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_1838; SRM_ SRM_1954; SRM_ SRM_685; SRM_ SRM_49; SRM_ SRM_135; SRM_ SRM_468; SRM_ SRM_88; SRM_ SRM_627; SRM_ SRM_167; SRM_961; SRM_ SRM_31; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_322; SRM_1443; SRM_ SRM_73; SRM_173; SRM_ SRM_173; SRM_73; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_972; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_12; SRM_ SRM_546; SRM_ SRM_1932; SRM_ SRM_349; SRM_1219; SRM_
13 1 SRM_235; SRM_ SRM_8; SRM_113; SRM_ SRM_322; SRM_1284; SRM_ SRM_35; SRM_ SRM_1666; SRM_ SRM_1159; SRM_ SRM_221; SRM_1378; SRM_147; SRM_ SRM_221; SRM_686; SRM_1378; SRM_147; SRM_ SRM_118; SRM_ SRM_286; SRM_ SRM_145; SRM_ SRM_145; SRM_ SRM_136; SRM_ SRM_2; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_1585; SRM_ SRM_72; SRM_ SRM_197; SRM_ SRM_783; SRM_736; SRM_ SRM_23; SRM_243; SRM_ SRM_1276; SRM_ SRM_1276; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_383; SRM_ SRM_37; SRM_ SRM_181; SRM_ SRM_1264; SRM_ SRM_736; SRM_747; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_134; SRM_ SRM_1228; SRM_ SRM_891; SRM_ SRM_293; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_156; SRM_221; SRM_226; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_164; SRM_ SRM_224; SRM_2476; SRM_864; SRM_ SRM_432; SRM_ SRM_216; SRM_ SRM_751; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_128; SRM_ SRM_159; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_434; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_185; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_478; SRM_
14 1 SRM_885; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_296; SRM_627; SRM_832; SRM_ SRM_296; SRM_ SRM_216; SRM_685; SRM_1377; SRM_148; SRM_ SRM_222; SRM_ SRM_217; SRM_794; SRM_787; SRM_ SRM_229; SRM_ SRM_926; SRM_ SRM_291; SRM_ SRM_292; SRM_ SRM_2145; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_2; SRM_ SRM_1338; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_1667; SRM_ SRM_798; SRM_ SRM_435; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_351; SRM_ SRM_351; SRM_ SRM_792; SRM_937; SRM_2135; SRM_285; SRM_44; SRM_ SRM_793; SRM_ SRM_475; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_247; SRM_ SRM_31; SRM_929; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_94; SRM_15; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_75; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_2171; SRM_2555; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_251; SRM_ SRM_241; SRM_ SRM_745; SRM_ SRM_383; SRM_ SRM_819; SRM_ SRM_223; SRM_236; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_1464; SRM_ SRM_1464; SRM_ SRM_547; SRM_ SRM_356; SRM_
15 1 SRM_ SRM_435; SRM_ SRM_228; SRM_ SRM_93; SRM_157; SRM_2263; SRM_ SRM_549; SRM_115; SRM_ SRM_114; SRM_181; SRM_191; SRM_ SRM_691; SRM_ SRM_167; SRM_961; SRM_1947; SRM_853; SRM_98; SRM_157; SRM_158; SRM_1948; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_715; SRM_82; SRM_ SRM_561; SRM_ SRM_317; SRM_ SRM_316; SRM_129; SRM_2127; SRM_ SRM_34; SRM_ SRM_69; SRM_735; SRM_833; SRM_69; SRM_735; SRM_ SRM_186; SRM_ SRM_69; SRM_735; SRM_ SRM_11; SRM_412; SRM_433; SRM_549; SRM_115; SRM_117; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_338; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_161; SRM_ SRM_161; SRM_ SRM_315; SRM_ SRM_5; SRM_285; SRM_198; SRM_ SRM_88; SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_381 1 SRM_489 1 SRM_53; SRM_51; SRM_511 1 SRM_221; SRM_686; SRM_1378; SRM_147 1 SRM_765 1 SRM_78 1 SRM_781 1 SRM_86 1 SRM_89 1 SRM_115 1 SRM_ SRM_ SRM_156 1 SRM_ SRM_ SRM_ SRM_292 1 SRM_2141 1
16 1 1 SRM_ SRM_ SRM_271 1 SRM_2916 SRM_686; SRM_147 SRM_784; SRM_735
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Screening of strong constitutive promoters in the S. albus transcriptome via RNA-seq The total RNA of S. albus J1074 was isolated after 24 hrs and 72 hrs of cultivation at 30 C
Supplemental Information Screening of strong constitutive promoters in the S. albus transcriptome via RNA-seq The total RNA of S. albus J1074 was isolated after 24 hrs and 72 hrs of cultivation at 30 C
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function
 Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Supplemental Information:
 SupplementalInformation: Content: FigureS1.AccessibilityoftheL.interrogansproteomebyLC MSanalysis. FigureS2.Functionalannotationoftheidentifiedproteins. FigureS3.DistributionofMS1 featureintensities. FigureS4.ComparisonoftheDDA
SupplementalInformation: Content: FigureS1.AccessibilityoftheL.interrogansproteomebyLC MSanalysis. FigureS2.Functionalannotationoftheidentifiedproteins. FigureS3.DistributionofMS1 featureintensities. FigureS4.ComparisonoftheDDA
III. Metabolism The Citric Acid Cycle
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism The Citric Acid Cycle Slide 1 The Eight Steps of the Citric Acid Cycle Enzymes: 4 dehydrogenases (2 decarboxylation) 3
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism The Citric Acid Cycle Slide 1 The Eight Steps of the Citric Acid Cycle Enzymes: 4 dehydrogenases (2 decarboxylation) 3
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative phosphorylation
 Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative phosphorylation So far we have discussed the catabolism involving oxidation of 6 carbons of glucose to CO 2 via glycolysis and CAC without any oxygen molecule directly
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative phosphorylation So far we have discussed the catabolism involving oxidation of 6 carbons of glucose to CO 2 via glycolysis and CAC without any oxygen molecule directly
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH AEROBIC RESPIRATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF AEROBIC RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is a series of reactions involving electron transfers to breakdown molecules for (ATP) 1. Glycolytic pathway: Glycolysis
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF AEROBIC RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is a series of reactions involving electron transfers to breakdown molecules for (ATP) 1. Glycolytic pathway: Glycolysis
Biological processes. Mitochondrion Metabolic process Catalytic activity Oxidoreductase
 Full name Glyceraldehyde3 phosphate dehydrogenase Succinatesemialdehyde Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] 2',3'cyclicnucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase Dihydropyrimidinaserelated 2
Full name Glyceraldehyde3 phosphate dehydrogenase Succinatesemialdehyde Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] 2',3'cyclicnucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase Dihydropyrimidinaserelated 2
Figure S1: Abundance of Fe related proteins in oceanic Synechococcus sp. strain WH8102 in. Ferredoxin. Ferredoxin. Fe ABC transporter
 0.004 SW nm 0.04 0.03 nm nm 0.16 0.1 nm nm 0.40 0.3 nm nm 0.80 0.5 nm 1.6 1 nm 16 10 nm 160 100 nm 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm 0.80 nm 1.6 nm 16 nm 160 nm Spectral counts 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm
0.004 SW nm 0.04 0.03 nm nm 0.16 0.1 nm nm 0.40 0.3 nm nm 0.80 0.5 nm 1.6 1 nm 16 10 nm 160 100 nm 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm 0.80 nm 1.6 nm 16 nm 160 nm Spectral counts 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm
Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative
 1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
Chapter 16. The Citric Acid Cycle: CAC Kreb s Cycle Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: TCA
 Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle: CAC Kreb s Cycle Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: TCA The Citric Acid Cycle Key topics: To Know Also called Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA) or Krebs Cycle. Three names for the
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle: CAC Kreb s Cycle Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: TCA The Citric Acid Cycle Key topics: To Know Also called Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA) or Krebs Cycle. Three names for the
Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate. Chapter 16 Homework Assignment. Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
 Chapter 16 Homework Assignment The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 1, 3, 7, 10, 16, 19, 20 Additional Problem: Write out the eight reaction steps of the Citric Acid Cycle, using
Chapter 16 Homework Assignment The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 1, 3, 7, 10, 16, 19, 20 Additional Problem: Write out the eight reaction steps of the Citric Acid Cycle, using
MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW
 1 MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW A. MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW Mitochondrial Structure The arrangement of membranes: distinct inner and outer membranes, The location of ATPase, DNA and ribosomes The
1 MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW A. MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW Mitochondrial Structure The arrangement of membranes: distinct inner and outer membranes, The location of ATPase, DNA and ribosomes The
Characterization of the use of wastewater from hydrothermal liquefaction as a nitrogen source by the potential algal biofuel strain Picochlorum sp.
 Characterization of the use of wastewater from hydrothermal liquefaction as a nitrogen source by the potential algal biofuel strain Picochlorum sp. Shuyi Wang, Xinguo Shi, Fatima Foflonker, Debashish Bhattacharya,
Characterization of the use of wastewater from hydrothermal liquefaction as a nitrogen source by the potential algal biofuel strain Picochlorum sp. Shuyi Wang, Xinguo Shi, Fatima Foflonker, Debashish Bhattacharya,
Protein Name. IFLENVIR,DSVTYTEHAK,TV TALDVVYALK,KTVTALDVV YALK,TVTALDVVYALKR,IF LENVIRDSVTYTEHAK gi Histone H2B
 Table 1. A functional category list of proteins (Lentinula edodes) identified by 1-DGE and nesi-lc-ms/ms. The table lists indicated fraction numbers, matching peptides, scores, accession numbers, protein
Table 1. A functional category list of proteins (Lentinula edodes) identified by 1-DGE and nesi-lc-ms/ms. The table lists indicated fraction numbers, matching peptides, scores, accession numbers, protein
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit
 Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Chapter 10. 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation)
 Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Notes CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
Metabolism. Metabolic pathways. BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209. Petr Tůma Eva Samcová
 Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Citrate Cycle. Lecture 28. Key Concepts. The Citrate Cycle captures energy using redox reactions
 Citrate Cycle Lecture 28 Key Concepts The Citrate Cycle captures energy using redox reactions Eight reactions of the Citrate Cycle Key control points in the Citrate Cycle regulate metabolic flux What role
Citrate Cycle Lecture 28 Key Concepts The Citrate Cycle captures energy using redox reactions Eight reactions of the Citrate Cycle Key control points in the Citrate Cycle regulate metabolic flux What role
respiration mitochondria mitochondria metabolic pathways reproduction can fuse or split DRP1 interacts with ER tubules chapter DRP1 ER tubule
 mitochondria respiration chapter 3-4 shape highly variable can fuse or split structure outer membrane inner membrane cristae intermembrane space mitochondrial matrix free ribosomes respiratory enzymes
mitochondria respiration chapter 3-4 shape highly variable can fuse or split structure outer membrane inner membrane cristae intermembrane space mitochondrial matrix free ribosomes respiratory enzymes
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/2/e1602038/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Mitochondrial metabolic regulation by GRP78 Manoj Prasad, Kevin J. Pawlak, William E. Burak, Elizabeth E. Perry, Brendan
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/2/e1602038/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Mitochondrial metabolic regulation by GRP78 Manoj Prasad, Kevin J. Pawlak, William E. Burak, Elizabeth E. Perry, Brendan
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the
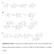 Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is converted into acetyl CoA.
 Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA is the fuel for the citric acid cycle, which processes the two carbon acetyl unit to two molecules
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA is the fuel for the citric acid cycle, which processes the two carbon acetyl unit to two molecules
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CITRIC ACID CYCLE (T.C.A) PRODUCTION OF ACETYL CoA REACTIONS OF THE CITIRC ACID CYCLE THE AMPHIBOLIC NATURE OF THE T.C.A CYCLE THE GLYOXYLATE CYCLE
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CITRIC ACID CYCLE (T.C.A) PRODUCTION OF ACETYL CoA REACTIONS OF THE CITIRC ACID CYCLE THE AMPHIBOLIC NATURE OF THE T.C.A CYCLE THE GLYOXYLATE CYCLE
Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Oxidative Phosphorylation Energy from Reduced Fuels Is Used to Synthesize ATP in Animals Carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids are the main reduced fuels for the cell. Electrons from reduced fuels are
Oxidative Phosphorylation Energy from Reduced Fuels Is Used to Synthesize ATP in Animals Carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids are the main reduced fuels for the cell. Electrons from reduced fuels are
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Photosynthesis: The light Reactions. Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU
 Photosynthesis: The light Reactions Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU When Molecules Absorb or Emit Light, They Change Their Electronic State lowest-energy, or ground state higher-energy, or excited, state extremely
Photosynthesis: The light Reactions Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU When Molecules Absorb or Emit Light, They Change Their Electronic State lowest-energy, or ground state higher-energy, or excited, state extremely
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6
 Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6 The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages
Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6 The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages
Ch 07. Microbial Metabolism
 Ch 07 Microbial Metabolism SLOs Differentiate between metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. Fully describe the structure and function of enzymes. Differentiate between constitutive and regulated enzymes.
Ch 07 Microbial Metabolism SLOs Differentiate between metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. Fully describe the structure and function of enzymes. Differentiate between constitutive and regulated enzymes.
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln
 The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 19 TCA Cycle
 Biochemical Engineering Prof. Dr. Rintu Banerjee Department of Agricultural and Food Engineering Asst. Prof. Dr. Saikat Chakraborty Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
Biochemical Engineering Prof. Dr. Rintu Banerjee Department of Agricultural and Food Engineering Asst. Prof. Dr. Saikat Chakraborty Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
Biochemistry 694:301. Please use BLOCK CAPITAL letters like this --- A, B, C, D, E. Not lowercase!
 Biochemistry 694:301 Third Test Dr. Deis Tue. Nov. 20, 2001 Name last 5 digits of I.D. Num Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions
Biochemistry 694:301 Third Test Dr. Deis Tue. Nov. 20, 2001 Name last 5 digits of I.D. Num Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions
Citrate Cycle Supplemental Reading
 Citrate Cycle Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - The Citrate Cycle captures energy using redox reactions - Eight enzymatic reactions of the Citrate Cycle - Key control points in the citrate cycle regulate
Citrate Cycle Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - The Citrate Cycle captures energy using redox reactions - Eight enzymatic reactions of the Citrate Cycle - Key control points in the citrate cycle regulate
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 20 The Electron-Transport Chain 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 20 Outline Oxidative phosphorylation captures the energy
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 20 The Electron-Transport Chain 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 20 Outline Oxidative phosphorylation captures the energy
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis
 Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM LAB SECTION
 BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS
 Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS Fatty acids obtained by hydrolysis of fats undergo different oxidative pathways designated as alpha ( ), beta ( ) and omega ( ) pathways. -oxidation -Oxidation of fatty
Lecture: 26 OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS Fatty acids obtained by hydrolysis of fats undergo different oxidative pathways designated as alpha ( ), beta ( ) and omega ( ) pathways. -oxidation -Oxidation of fatty
Cell Respiration Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date.
 Cell Respiration Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by alone or in a group, answer the following questions about Cell Respiration. This assignment is worth 30 points with the possible points for
Cell Respiration Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by alone or in a group, answer the following questions about Cell Respiration. This assignment is worth 30 points with the possible points for
Protein Homeostasis in Mitochondria: Chaperones and Proteases of the Mitochondrial Matrix Prof. Wolfgang Voos
 Protein Homeostasis in Mitochondria: Chaperones and Proteases of the Mitochondrial Matrix Institute for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IBMB) University of Bonn, Germany wolfgang.voos@uni-bonn.de 1
Protein Homeostasis in Mitochondria: Chaperones and Proteases of the Mitochondrial Matrix Institute for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IBMB) University of Bonn, Germany wolfgang.voos@uni-bonn.de 1
Yield of energy from glucose
 Paper : Module : 05 Yield of Energy from Glucose Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Prof. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dept. of Biosciences, Saurashtra University, Rajkot - 360005
Paper : Module : 05 Yield of Energy from Glucose Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Prof. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dept. of Biosciences, Saurashtra University, Rajkot - 360005
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.9 - RESPIRATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: REDOX REACTIONS Redox reaction a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: REDOX REACTIONS Redox reaction a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons
Triose-P isomerase Enolase
 Select the single best answer. 1 onsider the catabolism of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. In this metabolic direction, which of these enzymes catalyzes a reaction where the PRUTS have one more "high-energy"
Select the single best answer. 1 onsider the catabolism of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. In this metabolic direction, which of these enzymes catalyzes a reaction where the PRUTS have one more "high-energy"
Marah Bitar. Faisal Nimri ... Nafeth Abu Tarboosh
 8 Marah Bitar Faisal Nimri... Nafeth Abu Tarboosh Summary of the 8 steps of citric acid cycle Step 1. Acetyl CoA joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the CoA group and forming a six-carbon
8 Marah Bitar Faisal Nimri... Nafeth Abu Tarboosh Summary of the 8 steps of citric acid cycle Step 1. Acetyl CoA joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the CoA group and forming a six-carbon
NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry
 1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP SYNTHESIS (taken from Chapter 18 of Stryer)
 MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP SYNTHESIS (taken from Chapter 18 of Stryer) FREE ENERGY MOST USEFUL THERMODYNAMIC CONCEPT IN BIOCHEMISTRY Living things require an input of free energy for 3 major
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP SYNTHESIS (taken from Chapter 18 of Stryer) FREE ENERGY MOST USEFUL THERMODYNAMIC CONCEPT IN BIOCHEMISTRY Living things require an input of free energy for 3 major
Vocabulary. Chapter 19: The Citric Acid Cycle
 Vocabulary Amphibolic: able to be a part of both anabolism and catabolism Anaplerotic: referring to a reaction that ensures an adequate supply of an important metabolite Citrate Synthase: the enzyme that
Vocabulary Amphibolic: able to be a part of both anabolism and catabolism Anaplerotic: referring to a reaction that ensures an adequate supply of an important metabolite Citrate Synthase: the enzyme that
Pathway overview. Glucose + 2NAD + + 2ADP +2Pi 2NADH + 2pyruvate + 2ATP + 2H 2 O + 4H +
 Glycolysis Glycolysis The conversion of glucose to pyruvate to yield 2ATP molecules 10 enzymatic steps Chemical interconversion steps Mechanisms of enzyme conversion and intermediates Energetics of conversions
Glycolysis Glycolysis The conversion of glucose to pyruvate to yield 2ATP molecules 10 enzymatic steps Chemical interconversion steps Mechanisms of enzyme conversion and intermediates Energetics of conversions
Answer three from questions 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
 BCH 4053 May 1, 2003 FINAL EXAM NAME There are 9 pages and 9 questions on the exam. nly five are to be answered, each worth 20 points. Answer two from questions 1, 2, 3, and 4 Answer three from questions
BCH 4053 May 1, 2003 FINAL EXAM NAME There are 9 pages and 9 questions on the exam. nly five are to be answered, each worth 20 points. Answer two from questions 1, 2, 3, and 4 Answer three from questions
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2
 Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2 Biol 638, Exam-2 (Code-1) 1. Assume that 16 glucose molecules enter into a liver cell and are attached to a liner glycogen one by one. Later, this glycogen is broken-down
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2 Biol 638, Exam-2 (Code-1) 1. Assume that 16 glucose molecules enter into a liver cell and are attached to a liner glycogen one by one. Later, this glycogen is broken-down
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3: Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle
 Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3: Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle 2006-2007 Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip off (to
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3: Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle 2006-2007 Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip off (to
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush
 number 8 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Mamoon Mohamad Alqtamin Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 0 P a g e Oxidative phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation has 3 major aspects: 1. It involves flow of electrons
number 8 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Mamoon Mohamad Alqtamin Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 0 P a g e Oxidative phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation has 3 major aspects: 1. It involves flow of electrons
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name
 PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name Student ID # (U Number) A Before beginning this exam, please complete the following instructions: 1) Write your name and U number on the first page of this
PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name Student ID # (U Number) A Before beginning this exam, please complete the following instructions: 1) Write your name and U number on the first page of this
Chapter 14. Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior
 Chapter 14 Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior Why do you Eat and Breath? To generate ATP Foods, Oxygen, and Mitochodria Cells Obtain Energy by the Oxidation of Organic Molecules Food making ATP making
Chapter 14 Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior Why do you Eat and Breath? To generate ATP Foods, Oxygen, and Mitochodria Cells Obtain Energy by the Oxidation of Organic Molecules Food making ATP making
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION. C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
Supplementary Figures and Tables
 Supplementary Figures and Tables Supplementary Figure 1. Study design and sample collection. S.japonicum were harvested from C57 mice at 8 time points after infection. Total number of samples for RNA-Seq:
Supplementary Figures and Tables Supplementary Figure 1. Study design and sample collection. S.japonicum were harvested from C57 mice at 8 time points after infection. Total number of samples for RNA-Seq:
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
Department of Chemistry, Université de Montréal, C.P. 6128, Succursale centre-ville, Montréal, Québec, H3C 3J7, Canada.
 Phosphoproteome dynamics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under heat shock and cold stress Evgeny Kanshin 1,5, Peter Kubiniok 1,2,5, Yogitha Thattikota 1,3, Damien D Amours 1,3 and Pierre Thibault 1,2,4 * 1
Phosphoproteome dynamics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under heat shock and cold stress Evgeny Kanshin 1,5, Peter Kubiniok 1,2,5, Yogitha Thattikota 1,3, Damien D Amours 1,3 and Pierre Thibault 1,2,4 * 1
incorporation into fructose-6-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate (F6P/G6P); 2-
 Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
2. (12 pts) Given the following metabolic pathway (as it occurs in the cell):
 Answer Sheet 1 (Gold) 1. (1 pt) Write your exam ID (A) in the blank at the upper right of your answer sheet. 2. (12 pts) Given the following metabolic pathway (as it occurs in the cell): a. Would you expect
Answer Sheet 1 (Gold) 1. (1 pt) Write your exam ID (A) in the blank at the upper right of your answer sheet. 2. (12 pts) Given the following metabolic pathway (as it occurs in the cell): a. Would you expect
Chapter 8 Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration
 Chapter 8 Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water. The energy released is trapped in the form of
Chapter 8 Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water. The energy released is trapped in the form of
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at
 Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Notes CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
Protein Class/Name KEGG Pathways
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 4. Proteins Increased in Either Soil medium at 37 o C and 25 o C Table 4A. Proteins
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 4. Proteins Increased in Either Soil medium at 37 o C and 25 o C Table 4A. Proteins
Multiple choice: Circle the best answer on this exam. There are 12 multiple choice questions, each question is worth 3 points.
 CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
CHEM 4420 Exam 4 Spring 2015 Dr. Stone Page 1 of 6 Name Use complete sentences when requested. There are 120 possible points on this exam. Therefore there are 20 bonus points. Multiple choice: Circle the
Citric Acid Cycle: Central Role in Catabolism. Entry of Pyruvate into the TCA cycle
 Citric Acid Cycle: Central Role in Catabolism Stage II of catabolism involves the conversion of carbohydrates, fats and aminoacids into acetylcoa In aerobic organisms, citric acid cycle makes up the final
Citric Acid Cycle: Central Role in Catabolism Stage II of catabolism involves the conversion of carbohydrates, fats and aminoacids into acetylcoa In aerobic organisms, citric acid cycle makes up the final
TCA CYCLE (Citric Acid Cycle)
 TCA CYCLE (Citric Acid Cycle) TCA CYCLE The Citric Acid Cycle is also known as: Kreb s cycle Sir Hans Krebs Nobel prize, 1953 TCA (tricarboxylic acid) cycle The citric acid cycle requires aerobic conditions!!!!
TCA CYCLE (Citric Acid Cycle) TCA CYCLE The Citric Acid Cycle is also known as: Kreb s cycle Sir Hans Krebs Nobel prize, 1953 TCA (tricarboxylic acid) cycle The citric acid cycle requires aerobic conditions!!!!
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 What is the fate of Pyruvate? Stages of Cellular Respiration GLYCOLYSIS PYRUVATE OX. KREBS CYCLE ETC 2 The Krebs Cycle does your head suddenly hurt? 3 The Krebs Cycle An Overview
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 What is the fate of Pyruvate? Stages of Cellular Respiration GLYCOLYSIS PYRUVATE OX. KREBS CYCLE ETC 2 The Krebs Cycle does your head suddenly hurt? 3 The Krebs Cycle An Overview
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Assembly and Clustering of Natural Antibiotics Guides Target Identification Chad W. Johnston 1,2, Michael A. Skinnider 1,2, Chris A. Dejong 1,2, Philip N. Rees 1,2, Gregory M.
Supplementary Information Assembly and Clustering of Natural Antibiotics Guides Target Identification Chad W. Johnston 1,2, Michael A. Skinnider 1,2, Chris A. Dejong 1,2, Philip N. Rees 1,2, Gregory M.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
Chem 454, Spring Exam II F, Faraday's constant, = kcal/mol V
 Name Chem 454, Spring 2003 - Exam II F, Faraday's constant, = 23.06 kcal/mol V 1. Analysis of electron transport pathway in a pathogenic gram-negative bacterium reveals the presence of six electron transport
Name Chem 454, Spring 2003 - Exam II F, Faraday's constant, = 23.06 kcal/mol V 1. Analysis of electron transport pathway in a pathogenic gram-negative bacterium reveals the presence of six electron transport
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain. Pavla Balínová
 Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain Pavla Balínová Mitochondria Structure of mitochondria: Outer membrane Inner membrane (folded) Matrix space (mtdna, ribosomes, enzymes of CAC, β-oxidation of FA,
Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain Pavla Balínová Mitochondria Structure of mitochondria: Outer membrane Inner membrane (folded) Matrix space (mtdna, ribosomes, enzymes of CAC, β-oxidation of FA,
Protein Class/Name. Pathways. bat00250, bat00280, bat bat00640, bat00650 bat00270, bat00330, bat00410, bat00480 bat00270, bat00330,
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 2. Proteins Increased in Either Blood or Horizon media Table 2A. Proteins Increased
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 2. Proteins Increased in Either Blood or Horizon media Table 2A. Proteins Increased
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The conifer biomarkers dehydroabietic and abietic acids are widespread in Cyanobacteria Maria Sofia Costa, Adriana Rego, Vitor Ramos, Tiago Afonso, Sara Freitas, Marco Preto,
Supplementary Information The conifer biomarkers dehydroabietic and abietic acids are widespread in Cyanobacteria Maria Sofia Costa, Adriana Rego, Vitor Ramos, Tiago Afonso, Sara Freitas, Marco Preto,
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
True or False: 1. Reactions are called endergonic if they occur spontaneously and release free energy.
 True or False: 1. Reactions are called endergonic if they occur spontaneously and release free energy. 2. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy 3. Biochemical pathways are
True or False: 1. Reactions are called endergonic if they occur spontaneously and release free energy. 2. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy 3. Biochemical pathways are
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. A comparative study of outer membrane proteome between a paired colistinsusceptible
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A comparative study of outer membrane proteome between a paired colistinsusceptible and extremely colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains Raad Jasim, Mark A. Baker, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A comparative study of outer membrane proteome between a paired colistinsusceptible and extremely colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains Raad Jasim, Mark A. Baker, 2
Syllabus for BASIC METABOLIC PRINCIPLES
 Syllabus for BASIC METABOLIC PRINCIPLES The video lecture covers basic principles you will need to know for the lectures covering enzymes and metabolism in Principles of Metabolism and elsewhere in the
Syllabus for BASIC METABOLIC PRINCIPLES The video lecture covers basic principles you will need to know for the lectures covering enzymes and metabolism in Principles of Metabolism and elsewhere in the
Figure 1 Original Advantages of biological reactions being catalyzed by enzymes:
 Enzyme basic concepts, Enzyme Regulation I III Carmen Sato Bigbee, Ph.D. Objectives: 1) To understand the bases of enzyme catalysis and the mechanisms of enzyme regulation. 2) To understand the role of
Enzyme basic concepts, Enzyme Regulation I III Carmen Sato Bigbee, Ph.D. Objectives: 1) To understand the bases of enzyme catalysis and the mechanisms of enzyme regulation. 2) To understand the role of
Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3. Glycolysis is only the start. Cellular respiration. Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle.
 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3 Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle AP 2006-2007 Biology Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip
Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3 Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle AP 2006-2007 Biology Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip
FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS
 FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS Malonyl- CoA inhibits Carni1ne Palmitoyl Transferase I. Malonyl- CoA is a precursor for fa=y acid synthesis. Malonyl- CoA is produced from acetyl- CoA by the enzyme Acetyl- CoA Carboxylase.
FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS Malonyl- CoA inhibits Carni1ne Palmitoyl Transferase I. Malonyl- CoA is a precursor for fa=y acid synthesis. Malonyl- CoA is produced from acetyl- CoA by the enzyme Acetyl- CoA Carboxylase.
LUMC: LOPAC screen analysis
 LUMC: LOPAC screen analysis Preliminary results November 9, 2012 This document briefly presents the results from the LOPAC compounds screen performed at LUMC. It contains the following information: The
LUMC: LOPAC screen analysis Preliminary results November 9, 2012 This document briefly presents the results from the LOPAC compounds screen performed at LUMC. It contains the following information: The
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 -----> 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy (heat and ATP) 1. Energy Capacity to move or change matter Forms of energy are important to life include Chemical, radiant (heat
Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 -----> 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy (heat and ATP) 1. Energy Capacity to move or change matter Forms of energy are important to life include Chemical, radiant (heat
Supplemental Information. Host-Microbiota Interactions in the Pathogenesis. of Antibiotic-Associated Diseases
 Cell Reports, Volume Supplemental Information Host-Microbiota Interactions in the Pathogenesis of -Associated Diseases Joshua S. Lichtman, Jessica A. Ferreyra, Katharine M. Ng, Samuel A. Smits, Justin
Cell Reports, Volume Supplemental Information Host-Microbiota Interactions in the Pathogenesis of -Associated Diseases Joshua S. Lichtman, Jessica A. Ferreyra, Katharine M. Ng, Samuel A. Smits, Justin
PHM142 Energy Production + The Mitochondria
 PHM142 Energy Production + The Mitochondria 1 The Endosymbiont Theory of Mitochondiral Evolution 1970: Lynn Margulis Origin of Eukaryotic Cells Endosymbiant Theory: the mitochondria evolved from free-living
PHM142 Energy Production + The Mitochondria 1 The Endosymbiont Theory of Mitochondiral Evolution 1970: Lynn Margulis Origin of Eukaryotic Cells Endosymbiant Theory: the mitochondria evolved from free-living
These are example problems, which are similar to those you may see on the final exam.
 MCB102 / Metabolism Problem Set #3 Spring 2008 These are example problems, which are similar to those you may see on the final exam. QUESTION 1: /. Circle the correct answer, but if the answer is provide
MCB102 / Metabolism Problem Set #3 Spring 2008 These are example problems, which are similar to those you may see on the final exam. QUESTION 1: /. Circle the correct answer, but if the answer is provide
What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP
 2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There s got to be a better way!
2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There s got to be a better way!
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions
 CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB
 RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
Julia Vorholt Lecture 7:
 752-4001-00L Mikrobiologie Julia Vorholt Lecture 7: Chemoorganotrophy Nov 5, 2012 Brock Biology of Microorganisms, Twelfth Edition Madigan / Martinko / Dunlap / Clark Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Inc.,
752-4001-00L Mikrobiologie Julia Vorholt Lecture 7: Chemoorganotrophy Nov 5, 2012 Brock Biology of Microorganisms, Twelfth Edition Madigan / Martinko / Dunlap / Clark Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Inc.,
Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers.
 Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Why do we need it? Location & where is it in the picture? Electron (energy) carrying molecules Components Enzymes & cofactors
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Why do we need it? Location & where is it in the picture? Electron (energy) carrying molecules Components Enzymes & cofactors
Microbial Metabolism. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
Activity: Biologically Important Molecules
 Activity: Biologically Important Molecules AP Biology Introduction We have already seen in our study of biochemistry that the molecules that comprise living things are carbon-based, and that they are thought
Activity: Biologically Important Molecules AP Biology Introduction We have already seen in our study of biochemistry that the molecules that comprise living things are carbon-based, and that they are thought
