Non-targeted effects of ionising radiation
|
|
|
- Solomon Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Non-targeted effects of ionising radiation Sisko Salomaa STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Co-ordination Meeting on Low Dose Risk Research, Brussels, June /07/2007 NOTE,
2 General information Start date of the project: 1 September 2006 Duration: 48 months 19 partner organisations Coordinating organisation: STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Project coordinator: Prof. Sisko Salomaa EURATOM Specific Programme for Research and Training on Nuclear Energy, 6 th Framework Program Total eligible costs: M EC contribution: 6.33 M 06/07/2007 NOTE,
3 No List of NOTE partners Organisation name Acronym Country Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority STUK Finland University of Dundee UNDUN UK Leipzig University UL Germany MRC Radiation and Genome Stability Unit MRC UK Imperial College ICFM UK Gray Cancer Institute GCI UK Belgian Nuclear Research Centre SCK-CEN Belgium Dublin Institute of Technology RESC Ireland National Institute of Health ISS Italy University of Leicester ULEICS UK McMaster University MAC Canada Atomic Energy of Canada Limited AECL Canada National Research Institute for Radiobiology and Radiohygiene NRIRR Hungary National Research Centre for Environment and Health GSF Germany University of Pavia UNIPV Italy University of Erlangen-Nuremberg FAU Germany University of Duisburg-Essen UDE Germany Norwegian Radium Hospital NRH Norway University of Ottawa Heart Institute OHIR Canada Scientific contact person Prof. Sisko Salomaa Prof. Eric G. Wright Dr. Guido Hildebrandt Dr. Munira Kadhim Dr. Mark Little Dr. Kevin M. Prise Dr. Paul Jacquet Dr. Fiona Lyng Dr. Maria Antonella Tabocchini Prof. Yuri Dubrova Prof. Carmel Mothersill Dr. Ron Mitchel/Dr. Nick Priest Dr. Géza Sáfrány Dr. Werner Friedland Prof. Andrea Ottolenghi Dr. Franz Roedel Prof. George Iliakis Dr. Jostein Dahle Prof. Stewart Whitman 06/07/2007 NOTE,
4 System of radiation protection Knowledge of radiation risk is based on direct epidemiological evidence, as well as scientific study of radiation biology The system is designed to protect against both deterministic and stochastic effects A linear, non-threshold (LNT) dose-response relationship is used for all long-term health effects (e.g. cancer, genetic effects) A dose and dose-rate correction factor is used to relate the effects of acute exposures to chronic exposures (DDREF) Radiation dose is used as a surrogate for risk The effects produced by different types of radiation are qualitatively the same Doses can be summed to predict overall risk 06/07/2007 NOTE,
5 The classical paradigm in radiobiology - the basis of radiation-induced health effects DNA damage induced at the time of exposure mutation fixed in the first cell division clonal proliferation cancer hereditary effects HEALTH EFFECTS 06/07/2007 NOTE,
6 mutation and cell killing seen in cells that were not directly hit by radiation but were nearby Bystander effect These effects occur in cells that have never been irradiated. 06/07/2007 NOTE,
7 The progeny of irradiated cells show occurrence of aberrations or new mutations and/or new chromosomal other genomic damage lethal mutations (delayed cell death/apoptosis or reproductive cell death) Genomic instability These non-clonal effects occur in cells that have never been irradiated. 06/07/2007 NOTE,
8 Concept of dose as surrogate of risk LNT and radiation protection a linear dose response means that every increment of dose and the associated risk can be assessed separately, irrespective of prior or future doses, as long as doses are below deterministic effects a fixed dose increment is always associated with the same additional risk doses received by an individual at different time points canbesummedup(cumulativedose) (collective dose can be used to predict risk at the population level) 06/07/2007 NOTE,
9 Low-dose effects Effects targeted effects classical effects, dominant at high doses non-targeted effects bystander genomic instability Dose 06/07/2007 NOTE,
10 Non-targeted effects may be important modifiers of risk at the low dose region 06/07/2007 NOTE,
11 A new paradigm of Radiation Biology Targeted effects Classical paradigm of radiation biology DNA damage occurs during or very shortly after irradiation of the nuclei in targeted cells The potential for biological consequences can be expressed within one or two cell generations Non-targeted effects New evidence Bystander effect Genomic instability Adaptive response Clastogenic factors Delayed reproductive death Induction of genes by radiation Premature differentation Low dose hypersensitivity Abscopal (out-of-field) effects 06/07/2007 NOTE,
12 Paradigm shift Classical paradigm New evidence DNA-targeted cells considered as isolated units clonal effects linear / linear quadratic dose response classical radiation biology (effects on DNA) non-targeted cells are communicating tissue responses non-clonal effects plateau-like dose response (on/off) need for new methodological approaches 06/07/2007 NOTE,
13 Key questions from the radiation protection policy point of view For cancer risk: is there a deviation from LNT at low doses? Can ionising radiation cause non-cancer diseases or modify their risk at low / intermediate doses? Are there differences in the radiation sensitivity between individuals? 06/07/2007 NOTE,
14 General objectives of the NOTE IP To investigate the mechanisms of non-targeted effects, in particular, bystander effects, genomic instability and adaptive response To investigate if and how non-targeted effects modulate the cancer risk in the low dose region To investigate if ionising radiation can cause noncancer diseases or beneficial effects at low and intermediate doses To investigate individual susceptibility and other factors modifying non-targeted responses 06/07/2007 NOTE,
15 General objectives of the NOTE IP To contribute to the conceptualisation of a new paradigm in radiation biology that would cover both the classical direct (DNA-targeted) and non-targeted effects. To assess the relevance of non-targeted effects for radiation protection and to set the scientific basis for a modern, more realistic, radiation safety system 06/07/2007 NOTE,
16 WP1 WP6 WP7 Management activities Management board Administrative coordinator Sisko Salomaa WP leaders WP2 WP3 WP4 Infrastructures, training and mobility Kevin Prise Mechanisms of non-targeted effects Eric Wright Non-cancer diseases Guido Hildebrandt Factors modifying non-targeted responses Munira Kadhim Dissemination and exploitation activities Oleg Belyakov Task 1 Communication with public Riikka Laitinen-Sorvari Task 2 Relevance for radiation protection Sisko Salomaa Advisory committee WP5 Modelling of non-targeted effects Mark Little Task 3 Conceptualisation of new paradigm Oleg Belyakov 06/07/2007 NOTE,
17 WP2: Mechanisms of non-targeted effects Eric Wright What is the target for non-targeted effects? What cells produce signals? What is the trigger for the production of signals? What cells respond to signals? What intercellular processes are involved in responding to signals? What are the messengers of bystander responses? What are the mechanisms of non-targeted effects in tissues? What are the mechanisms of genomic instability perpetuation? What are the mechanisms of transgenerational instability? 06/07/2007 NOTE,
18 WP2 Examples of specific hypotheses to be tested Production of signals is cell-type and genotype-dependent and involves targets other than nuclear DNA; Responses to signals are cell-type and genotype-dependent mediated by the stress response pathways that have evolved to deal with cellular injury; Both damaging and protective responses may be elicited in a context-dependent manner; Involvement of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and cytokines are commonly involved; Perpetuation of genomic instability in both somatic and germ cells may be due to intrinsic epigenetic changes such as methylation; In vivo, an instability phenotype may not necessarily be a reflection of genomically unstable cells but responses to ongoing production of damaging signals; i.e. bystander-type processes; In vivo non-targeted effects may reflect inflammatory-type responses 06/07/2007 NOTE,
19 + WP2 Signals from irradiated cells Target cells Instability Adaptive response Bystander effects Clonogenic cell survival Cytogenetic aberrations Apoptosis / death Damage responses Signal transduction pathways Gene and protein expression 06/07/2007 NOTE,
20 WP2 Non-targeted mechanisms in vivo T 1 T 2 Instability Adaptive responses Bystander mechanisms Transgenerational effects Cytogenetic aberrations Apoptosis / death Mutation Gene and protein expression Damage responses Inter-cellular signalling Signal transduction pathways 06/07/2007 NOTE,
21 WP 3: Non-cancer diseases Guido Hildebrandt Main question: Can ionising radiation cause non-cancer diseases or beneficial effects at low and intermediate doses? 06/07/2007 NOTE,
22 WP 3: Non-cancer diseases Guido Hildebrandt Tasks: 3.1 Mechanisms of induction of cardiovascular diseases in vitro and in vivo 3.2 Inflammatory vs. anti-inflammatory effects 3.3 Role of non-targeted effects in developmental defects 06/07/2007 NOTE,
23 3.1. Mechanisms of cardiovascular diseases induction -in vitro GCI To determine the responses of endothelial cells and tissue-based models to targeted low dose exposure as a surrogate for determining the role of radiation damage to the vasculature in non-cancer diseases in vitro. 06/07/2007 NOTE,
24 3.2. Mechanisms of cardiovascular diseases induction in vivo AECL, OHIRC, ULMED, ICFM To investigate radiation dose response on atherosclerosis progression (aortic lesions) after exposure at early stage disease in knockouts (ApoE-/-) and in ApoE-/- TP 53+/- as compared to "normals" (ApoE+/+) in vivo. Since inflammatory and thrombotic changes in endothelial cells have an important impact on the development of atherosclerotic lesions we further want to study whether low dose radiation exposure at low dose rate or high dose rate induces vascular changes in the heart of ApoE-/- mice 06/07/2007 NOTE,
25 3.3. Inflammatory or anti-inflammatory responses? ULMED, NRIRR, FAU To investigate the effect of acute and chronic low dose IR on the maturation of dentritic cells (DC) generated from peripheral blood of healthy volunteers as compared to untreated DC, and to analyze treated DC with respect to their protective or augmenting capacities in immunological reactions major immune parameters (lymphocyte number, proliferation rate and cytokine secretion of lymphocytes after stimulation with non-specific mitogens, changes in the proportion of different lymphocyte subpopulations) the inflammatory properties of endothelial cells, subgroups of leukocytes isolated from peripheral blood and macrophages 06/07/2007 NOTE,
26 3.4. Role of non-targeted effects in developmental defects SCK-CEN To investigate transgenerational radiation effects at the level of developmental effects and genomic instability, after irradiation of 1-cell mouse embryos with low doses of X-rays. Reproductive effects, congenital anomalies, cytokine levels and chromosomal instability 06/07/2007 NOTE,
27 WP4: Factors modifying non-targeted responses Munira Kadhim influence of genetic factors on the in vivo production of non-targeted effects impact of genetic predisposition on non-targeted effects response in vitro molecular mechanisms determination that contribute to the distinct radiation responses at low dose radiations in mice with different radiosensitivity role of DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoint responses 06/07/2007 NOTE,
28 WP4 - Factors modifying non-targeted responses Genomic instability Bystander effects Transgenerational instability In vitro & in vivo Genetic Factors : -Inter-individual differences - cell lines differences Mechanistic Studies : -Involvement of repair, checkpoints and cell cycle control. -Role of epigenetic factors. Radiation dose and quality Link with WP2 - The influence of genetic factors on the in vivo production of bystander signals producing non-targeted effects and the genotypedependency of response mechanisms. 06/07/2007 NOTE,
29 WP4 Factors modifying non-targeted responses Summary of Deliverables 4.1 The genotype-dependence of signal production at different times after in vivo irradiation (UDUN) 4.2 Inter-individual differences in bystander response, and genomic comparison between primary and permanent cultures pre- and post-irradiation (NRIRR) 4.3 Role of particular proteins in the genetic differences observed in CBA and C57 in response to low dose low LET radiations (MRC) 4.4 Capacity of targeted and non-targeted bystander cells to repair DNA damage using NHEJ or HR (UDE) 06/07/2007 NOTE,
30 WP5: Modelling of non-targeted responses Mark Little intracellular and local intercellular communication and damage mechanisms intercellular communication mechanisms in vitro extracellular signalling mechanims in vivo genomic instability mechanisms in vivo 06/07/2007 NOTE,
31 WP5 main questions 1. Quantitatively test working hypotheses on mechanisms underlying non-targeted effects (bystander effects, genomic instability, adaptive response and non-cancer diseases) 2. Assess role in determining deviations from linear nothreshold hypothesis 3. Address tissues in which effects might arise, also mechanisms (intracellular stress response, signalling molecules etc) that might explain what is observed. 06/07/2007 NOTE,
32 WP5 Tasks Task 5.0 Modeller- experimentalist interaction (all): devise experiments that allow modellers to discriminate between models, and ascertain model parameters Task 5.1 Intracellular and local intercellular communication and damage mechanisms (GSF, ISS): elucidate intracellular mechanisms that might account for non-targeted effects, and integrate into better understood mechanisms for targeted effects (DNA damage and repair) 06/07/2007 NOTE,
33 WP5 tasks Task 5.2 Intercellular communication mechanisms in vitro (UNIPV, RR HF): evaluate candidate intercellular signalling mechanisms that might account for non-targeted effects (in particular bystander effect), and way these can be modulated Task 5.3 Extracellular signalling mechanisms in vivo (ICFM): devise models for non-targeted effects at organ or tissue level, taking account of mechanisms proposed in subgroups. In particular, develop number of candidate models of radiation-induced cardiovascular disease 06/07/2007 NOTE,
34 WP 6: Integration activities Kevin Prise development and better use of existing radiobiological facilities strengthening collaborative RTD activity supporting training and mobility of scientists educating the next generation of European radiobiologists on non-targeted effects 06/07/2007 NOTE,
35 Infrastructures within NOTE Charged particle microbeams (Leipzig and Northwood) Soft X-ray microbeam (Belfast) Small animal low dose facility (Chalk River) Low level exposure facility (Rome) Proteomics and genomics facilities (Helsinki) 06/07/2007 NOTE,
36 NOTE Training Course Protocols and Pitfalls in the study of Non-targeted Effects of Radiation th September, Crete General overview lectures on Non-targeted effects External lecturers including Bill Morgan / Christian Streffer Review talks on specific end-points with emphasis on protocols, data interpretation Break-out sessions on technical aspects with emphasis on pitfalls and problems Wrap up and general discussion session Targeted at research students and post-docs 06/07/2007 NOTE,
37 WP 7: Dissemination and exploitation activities Oleg Belyakov a public NOTE website, NOTE Newsletter, Press releases a workshop on the conceptualisation of the new paradigm (2008) a workshop on the relevance of non-targeted effects for radiation protection (2010) 06/07/2007 NOTE,
38 WP7 structure and links with other WPs WP6 Integration activities: Infrastructures, training and mobility WP2 Mechanisms of non-targeted effects WP3 Non-cancer diseases WP4 Factors modifying non-targeted responses WP5 Modelling of non-targeted effects WP7 Dissemination and exploitation activities Task 1 Communication with public Task 2 Conceptualisation of new paradigm Task 3 Relevance for radiation protection End-users General public Scientific community Radiation protection community Decision makers 06/07/2007 NOTE,
39 NOTE website A new NOTE IP website with public and secure areas was launched in April 2007 at 06/07/2007 NOTE,
40 NOTE-related news for scientific community, media and general public The first newsletter was released in May 2007; appears every half a year Subscribe the Newsletter at the NOTE web site! NOTE Newsletter 06/07/2007 NOTE,
41 Future directions... High versus low doses High versus low dose rate Cell cultures -> 3-D models -> tissues -> animals -> human data Tissue responses, effect of microstructure Non-targeted responses involve complex interactions, need for new holistic approaches Generation of hypothesis for mechanistic studies using systems biological approaches ( discovery science ) Mathematical modelling of genomics and proteomics data obtained during NOTE project 06/07/2007 NOTE,
42 Low-dose risk: Increasing the power of epidemiology High background in cancer incidence -> very large populations needed to detect small increases Confounding factors may mask risks Limitations in dosimetry, especially in environmental and protracted exposures -> hampers detection of risk Quantification of risk at low doses is very challenging Combine information from epidemiology and radiation biology (mechanisms, dose response, susceptibility)?? 06/07/2007 NOTE,
43 Key questions from the radiation protection policy point of view For cancer risk: is there a deviation from LNT at low doses? Can ionising radiation cause non-cancer diseases or modify their risk at low / intermediate doses? Are there differences in the radiation sensitivity between individuals? International collaboration is essential to solve these issues (Europe, US, Japan, Canada...) 06/07/2007 NOTE,
Non targeted effects of ionising radiation Integrated Project
 Non targeted effects of ionising radiation Integrated Project 2006-2010 A new paradigm of Radiation Biology Targeted effects Classical paradigm of radiation biology DNA damage occurs during or very shortly
Non targeted effects of ionising radiation Integrated Project 2006-2010 A new paradigm of Radiation Biology Targeted effects Classical paradigm of radiation biology DNA damage occurs during or very shortly
William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc.
 Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting
 BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Dose-Response Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University
 Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University Outline Bystander effects and genomic instability In vivo relevance and evidence The fish model
Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University Outline Bystander effects and genomic instability In vivo relevance and evidence The fish model
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program
 U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
Introduction to European DoReMi programme on low dose risk
 Introduction to European DoReMi programme on low dose risk Prof. Sisko Salomaa DoReMi Coordinator STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority, Finland ICRR2015, Kyoto, Japan Aim of DoReMi to promote
Introduction to European DoReMi programme on low dose risk Prof. Sisko Salomaa DoReMi Coordinator STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority, Finland ICRR2015, Kyoto, Japan Aim of DoReMi to promote
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Non-Targeted Effects. Break out Session 1 H.Métivier Rapporteur
 Non-Targeted Effects Break out Session 1 H.Métivier Rapporteur Non-Targeted Effects The group discussed the non-targeted effects and their potential impacts on RP system. However, after a fruitful and
Non-Targeted Effects Break out Session 1 H.Métivier Rapporteur Non-Targeted Effects The group discussed the non-targeted effects and their potential impacts on RP system. However, after a fruitful and
Genomic Instability and Bystander Effect Implications for Radiation Protection. S. Salomaa
 Genomic Instability and Bystander Effect Implications for Radiation Protection S. Salomaa STUK Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority, Research and Environmental Surveillance, P.O.Box 14, FIN-00881 Helsinki,
Genomic Instability and Bystander Effect Implications for Radiation Protection S. Salomaa STUK Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority, Research and Environmental Surveillance, P.O.Box 14, FIN-00881 Helsinki,
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis
 Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
Cataract following low dose ionising radiation exposures: Mechanistic understanding and current research
 Cataract following low dose ionising radiation exposures: Mechanistic understanding and current research Liz Ainsbury, PHE CNSC/CRPA Webinar: Lens of the eye 21 st March 2018 Human Lens Diameter ~9-10
Cataract following low dose ionising radiation exposures: Mechanistic understanding and current research Liz Ainsbury, PHE CNSC/CRPA Webinar: Lens of the eye 21 st March 2018 Human Lens Diameter ~9-10
LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1
 J. Radiat. Res., 47: Suppl., B19 B24 (2006) Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1 Christian STREFFER* Genomic instability/malformation/transgenerational
J. Radiat. Res., 47: Suppl., B19 B24 (2006) Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1 Christian STREFFER* Genomic instability/malformation/transgenerational
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350.
 Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy
 Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
María José Mesa López
 María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to. Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority
 Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to ionizing radiation Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Objectives: Identify clastogenic factors in blood
Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to ionizing radiation Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Objectives: Identify clastogenic factors in blood
MELODI statement 2018 Gap analysis
 MELODI statement 2018 Gap analysis MELODI (Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative) is a European Platform dedicated to low dose ionizing radiation risk research. The purpose of the MELODI Association
MELODI statement 2018 Gap analysis MELODI (Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative) is a European Platform dedicated to low dose ionizing radiation risk research. The purpose of the MELODI Association
Are non-targeted effects important in radiation protection? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour McMaster University Canada
 Are non-targeted effects important in radiation protection? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour McMaster University Canada Non-targeted radiation effects Inter-animal/plant signaling Effects in neighbouring
Are non-targeted effects important in radiation protection? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour McMaster University Canada Non-targeted radiation effects Inter-animal/plant signaling Effects in neighbouring
Radiation Protection Research. From FP6 to FP7. Neale Kelly
 Radiation Protection Research From FP6 to FP7 Neale Kelly Risks at low and protracted doses Topic % Radiobiology 46 Epidemiology 25 Medical uses 7 Risk and emergency management Other topics Radioecology
Radiation Protection Research From FP6 to FP7 Neale Kelly Risks at low and protracted doses Topic % Radiobiology 46 Epidemiology 25 Medical uses 7 Risk and emergency management Other topics Radioecology
Advances in biological dosimetry
 Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation
 The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Edouard Azzam New Jersey Medical School Newark, USA Two phenomena have been recently implicated
The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Edouard Azzam New Jersey Medical School Newark, USA Two phenomena have been recently implicated
The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE
 The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE Andrea Ottolenghi, Klaus Trott, Giorgio Baiocco, Vere Smyth Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy On behalf of the ANDANTE project MELODI
The ANDANTE project: a multidisciplinary approach to neutron RBE Andrea Ottolenghi, Klaus Trott, Giorgio Baiocco, Vere Smyth Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy On behalf of the ANDANTE project MELODI
Modelling of Biological Processes
 Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
Radiation induced bystander effects adaptive responses and low dose risk
 Radiation induced bystander effects adaptive responses and low dose risk Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour Medical Physics and Applied Radiation Sciences McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario Canada
Radiation induced bystander effects adaptive responses and low dose risk Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour Medical Physics and Applied Radiation Sciences McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario Canada
CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
 CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION Ron Mitchel Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River,
CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION Ron Mitchel Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River,
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Identification and isolation of susceptibility genes involved in radiation-induced cancer in humans (SUS GENES IN RAD CAR) Contract N o FIGH-CT1999-00002
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Identification and isolation of susceptibility genes involved in radiation-induced cancer in humans (SUS GENES IN RAD CAR) Contract N o FIGH-CT1999-00002
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus
 Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Jan 3 rd Wed Mapping disease genes I: inheritance patterns and linkage analysis
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Jan 3 rd Wed Mapping disease genes I: inheritance patterns and linkage analysis
Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses
 Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses "Frédéric Joliot-Curie" National Research Institute for Radiobiology and Radiohygiene, Budapest, Hungary The structure of the immune system INNATE
Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses "Frédéric Joliot-Curie" National Research Institute for Radiobiology and Radiohygiene, Budapest, Hungary The structure of the immune system INNATE
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus
 Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Module I: Mapping and characterizing simple genetic diseases Jan 4 th Wed Mapping
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Module I: Mapping and characterizing simple genetic diseases Jan 4 th Wed Mapping
MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low dose Initiative. First Draft of Strategic Research Agenda (SRA) Date: 11 October 2010
 MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low dose Initiative First Draft of Strategic Research Agenda (SRA) Date: 11 October 2010 Authors: Dietrich AVERBECK, IRSN/CEA Consultant, Leader of WP2 of DoReMi, Emeritus
MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low dose Initiative First Draft of Strategic Research Agenda (SRA) Date: 11 October 2010 Authors: Dietrich AVERBECK, IRSN/CEA Consultant, Leader of WP2 of DoReMi, Emeritus
Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation
 EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2006 Report Volume II Scientific Annexes C, D and E EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations
EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR 2006 Report Volume II Scientific Annexes C, D and E EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION United Nations
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage
 Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs. Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica
 Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Risks of X-rays examinations during pregnancy: scientific background
 Stralingsbescherming in de radiologie Röntgenonderzoeken en zwangerschap Herfstsymposium 21 oktober 2017 FANC Brussel Risks of X-rays examinations during pregnancy: scientific background Dr Patrick Smeesters
Stralingsbescherming in de radiologie Röntgenonderzoeken en zwangerschap Herfstsymposium 21 oktober 2017 FANC Brussel Risks of X-rays examinations during pregnancy: scientific background Dr Patrick Smeesters
Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements
 Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements Kevin M. Prise Centre for Cancer Research & Cell Biology, Queen s University Belfast Outline Definition of bystander
Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements Kevin M. Prise Centre for Cancer Research & Cell Biology, Queen s University Belfast Outline Definition of bystander
The EU NoE DoReMi where are we now?
 The EU NoE DoReMi where are we now? Sisko Salomaa STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority FINLAND MELODI workshop 2011, Rome MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative Open RTD platform
The EU NoE DoReMi where are we now? Sisko Salomaa STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority FINLAND MELODI workshop 2011, Rome MELODI Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative Open RTD platform
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned. Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago
 The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
What is radiation quality?
 What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
Threshold doses and circulatory disease risks
 Threshold doses and circulatory disease risks J.H. Hendry Christie Medical Physics and Engineering, Christie Hospital, Manchester M20 4BX, UK; e-mail: jhendry2002uk@yahoo.com Abstract Tissue reactions
Threshold doses and circulatory disease risks J.H. Hendry Christie Medical Physics and Engineering, Christie Hospital, Manchester M20 4BX, UK; e-mail: jhendry2002uk@yahoo.com Abstract Tissue reactions
Chapter 7. What is Radiation Biology? Ionizing Radiation. Energy Transfer Determinants 09/21/2014
 Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
The use of radiation microbeams to investigate the bystander effect in cells and tissues
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 580 (2007) 446 450 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima The use of radiation microbeams to investigate the bystander effect in cells and tissues M. Folkard
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 580 (2007) 446 450 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima The use of radiation microbeams to investigate the bystander effect in cells and tissues M. Folkard
1/31/2014. Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public
 Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
A Commentary on: A History of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) Low Dose Radiation Research Program: Dr. Antone L.
 A Commentary on: A History of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) Low Dose Radiation Research Program: 1998 2008 Dr. Antone L. Brooks 1 1. Retired, Washington State University 1 6802 West 13 th
A Commentary on: A History of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) Low Dose Radiation Research Program: 1998 2008 Dr. Antone L. Brooks 1 1. Retired, Washington State University 1 6802 West 13 th
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program
 U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager EFCOG Radiation Protection Subgroup 13-15 March 2012 Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research DOE s Low
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager EFCOG Radiation Protection Subgroup 13-15 March 2012 Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research DOE s Low
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology
 The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Study of lung cancer risk and residential radon exposure (Radon Epidemiology) Contract N o FIGH-CT1999-00008 Final report (summary) Work performed as
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Study of lung cancer risk and residential radon exposure (Radon Epidemiology) Contract N o FIGH-CT1999-00008 Final report (summary) Work performed as
Radiation Protection Dosimetry Advance Access published December 13, 2006
 Radiation Protection Dosimetry Advance Access published December 13, 2006 Radiation Protection Dosimetry (2006), 1 of 7 doi:10.1093/rpd/ncl433 A MODEL FOR THE INDUCTION OF CHROMOSOME ABERRATIONS THROUGH
Radiation Protection Dosimetry Advance Access published December 13, 2006 Radiation Protection Dosimetry (2006), 1 of 7 doi:10.1093/rpd/ncl433 A MODEL FOR THE INDUCTION OF CHROMOSOME ABERRATIONS THROUGH
Report OPERRA Workshop: Modelling of pathogenesis
 Report OPERRA Workshop: Modelling of pathogenesis Markus Eidemüller a, Christian Kaiser a, E. Georg Luebeck b, William Paul Accomando c, Kristian Unger a, Mark van de Wiel d, Jonas Behr e, Marc Chadeau-Hyam
Report OPERRA Workshop: Modelling of pathogenesis Markus Eidemüller a, Christian Kaiser a, E. Georg Luebeck b, William Paul Accomando c, Kristian Unger a, Mark van de Wiel d, Jonas Behr e, Marc Chadeau-Hyam
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY
 LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Ionizing Radiation. Nuclear Medicine
 Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
Institute of Radiation Biology. Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes DoReMi Course 2014
 Institute of Radiation Biology Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes DoReMi Course 2014 Hippocrates: Cause is systemic excess of black humor. Paracelsus challenges the humor theory. Suggests external
Institute of Radiation Biology Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes DoReMi Course 2014 Hippocrates: Cause is systemic excess of black humor. Paracelsus challenges the humor theory. Suggests external
RADIATION-INDUCED BYSTANDER EFFECTS: EVIDENCE FOR AN ADAPTIVE RESPONSE TO LOW DOSE EXPOSURES?
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 4 Issue 4 Article 5 12-2006 RADIATION-INDUCED BYSTANDER EFFECTS: EVIDENCE FOR AN ADAPTIVE RESPONSE TO LOW DOSE EXPOSURES? Carmel Mothersill McMaster University,
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 4 Issue 4 Article 5 12-2006 RADIATION-INDUCED BYSTANDER EFFECTS: EVIDENCE FOR AN ADAPTIVE RESPONSE TO LOW DOSE EXPOSURES? Carmel Mothersill McMaster University,
EAS Congress Innsbruck Highlights: A programme to excite, inspire and inform!
 Press release 84 th European Atherosclerosis Society Congress, Innsbruck, Austria For circulation 29 th May, 2016. 84 th Annual Congress of the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) May 29 th - June 1
Press release 84 th European Atherosclerosis Society Congress, Innsbruck, Austria For circulation 29 th May, 2016. 84 th Annual Congress of the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) May 29 th - June 1
Threshold doses and circulatory disease risks
 Threshold doses and circulatory disease risks Jolyon Hendry Christie Hospital Medical Physics and Engineering Manchester UK 17/10/2013 ICRP 2013 1 Threshold Dose (TD) TD 1% ICRP 41 (1984), 60 (1991), 103
Threshold doses and circulatory disease risks Jolyon Hendry Christie Hospital Medical Physics and Engineering Manchester UK 17/10/2013 ICRP 2013 1 Threshold Dose (TD) TD 1% ICRP 41 (1984), 60 (1991), 103
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3
 Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure
 Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
Radiation Health Effects
 Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons
 Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Certificate of Advanced Studies in Personalized Molecular Oncology
 Certificate of Advanced Studies in Personalized Molecular Oncology Certificate of Advanced Studies (CAS) in Personalized Molecular Oncology Overview Cutting-edge technologies, like next-generation-sequencing
Certificate of Advanced Studies in Personalized Molecular Oncology Certificate of Advanced Studies (CAS) in Personalized Molecular Oncology Overview Cutting-edge technologies, like next-generation-sequencing
Strategic Research Agenda of the Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative (MELODI) 2017
 Strategic Research Agenda of the Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative (MELODI) 2017 M. Kreuzer, A. Auvinen, S. Bouffler, E. Cardis, M. Durante, J.R. Jourdain, M. Harms-Ringdahl, B. Madaz, R.
Strategic Research Agenda of the Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative (MELODI) 2017 M. Kreuzer, A. Auvinen, S. Bouffler, E. Cardis, M. Durante, J.R. Jourdain, M. Harms-Ringdahl, B. Madaz, R.
Radiation-induced bystander effects: evidence for an adaptive response to low dose exposures? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour
 Radiation-induced bystander effects: evidence for an adaptive response to low dose exposures? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour Medical Physics and Applied Radiation Sciences Unit, McMaster University,
Radiation-induced bystander effects: evidence for an adaptive response to low dose exposures? Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour Medical Physics and Applied Radiation Sciences Unit, McMaster University,
Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter
 Ohio UNIVERSITY Fall 2018 Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter Alan Watts Radiation Safety Officer In This Issue: Instruction Concerning Risks From Occupational Radiation Exposure... pg.1-5 = Required = Optional
Ohio UNIVERSITY Fall 2018 Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter Alan Watts Radiation Safety Officer In This Issue: Instruction Concerning Risks From Occupational Radiation Exposure... pg.1-5 = Required = Optional
Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 17, 40-46 (2004) Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1 SHU-ZHENG LIU 2, SHUN-ZI JIN, AND XIAO-DONG LIU Department of Radiation Biology, Jilin University
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 17, 40-46 (2004) Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1 SHU-ZHENG LIU 2, SHUN-ZI JIN, AND XIAO-DONG LIU Department of Radiation Biology, Jilin University
Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology
 Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology This set of 88 slides is based on Chapter 14 authored by N. Suntharalingam, E.B. Podgorsak, J.H. Hendry of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics:
Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology This set of 88 slides is based on Chapter 14 authored by N. Suntharalingam, E.B. Podgorsak, J.H. Hendry of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics:
Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation. Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic
 Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) 2007 National Academy of Science National Research
Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) 2007 National Academy of Science National Research
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT
 RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW
 RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW PILLALAMARRI ILA Earth Atmospheric & Planetary Sciences Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 IAP
RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW PILLALAMARRI ILA Earth Atmospheric & Planetary Sciences Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 IAP
rare diseases research through National Plans and Strategies
 Recommendations to support rare diseases research through National Plans and Strategies Dr Domenica Taruscio EUROPLAN Coordinator Director of the Italian Centre for Rare Diseases, Italian National Institute
Recommendations to support rare diseases research through National Plans and Strategies Dr Domenica Taruscio EUROPLAN Coordinator Director of the Italian Centre for Rare Diseases, Italian National Institute
Radiation Carcinogenesis
 Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH AND CONSUMERS DIRECTORATE-GENERAL INTERIM REPORT 02_2013
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH AND CONSUMERS DIRECTORATE-GENERAL EXECUTIVE AGENCY FOR HEALTH AND CONSUMERS Health unit Contract number: 2010 21 02 Acronym: QUANDHIP INTERIM REPORT 02_2013 Proposal title: Quality
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH AND CONSUMERS DIRECTORATE-GENERAL EXECUTIVE AGENCY FOR HEALTH AND CONSUMERS Health unit Contract number: 2010 21 02 Acronym: QUANDHIP INTERIM REPORT 02_2013 Proposal title: Quality
Estimates of Risks LONG-TERM LOW DOSE EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION
 Estimates of Risks LONG-TERM LOW DOSE EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION Low Level Radiation Exposure Single exposure of 10 rad or less Larger exposures delivered over periods of days or longer (low dose
Estimates of Risks LONG-TERM LOW DOSE EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION Low Level Radiation Exposure Single exposure of 10 rad or less Larger exposures delivered over periods of days or longer (low dose
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Strategic Research Agenda of the Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative (MELODI)
 Strategic Research Agenda of the Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative (MELODI) - 2015 M. Kreuzer, D. Averbeck, I. Balashazy, S. Bouffler, E. Cardis, P. Jacob, J.R. Jourdain, M. Harms-Ringdahl,
Strategic Research Agenda of the Multidisciplinary European Low Dose Initiative (MELODI) - 2015 M. Kreuzer, D. Averbeck, I. Balashazy, S. Bouffler, E. Cardis, P. Jacob, J.R. Jourdain, M. Harms-Ringdahl,
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
Cancer Research in the EU Framework Programmes for RTD
 Cancer Research in the EU Framework Programmes for RTD Action against cancer: European platform Maria Vidal, MD, PhD Deputy Head of Unit Medical and public health research Health Directorate DG Research
Cancer Research in the EU Framework Programmes for RTD Action against cancer: European platform Maria Vidal, MD, PhD Deputy Head of Unit Medical and public health research Health Directorate DG Research
SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER
 Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
GENE-RAD-RISK FINAL REPORT. Reporting period: e.g. 01/06/08-30/11/09. Date of issue of this report: 15/01/11
 (Contract No: 012926) FINAL REPORT Author: Ausrele Kesminiene Reporting period: e.g. 01/06/08-30/11/09 Date of issue of this report: 15/01/11 Start date of project: 01/06/05 Duration: 54 months Project
(Contract No: 012926) FINAL REPORT Author: Ausrele Kesminiene Reporting period: e.g. 01/06/08-30/11/09 Date of issue of this report: 15/01/11 Start date of project: 01/06/05 Duration: 54 months Project
Individual Sensitivity
 Individual Sensitivity Why do we care about Individual Sensitivity? This IS an issue at high doses (for deterministic effects in radiation therapy) It is not known whether Individual Sensitivity is an
Individual Sensitivity Why do we care about Individual Sensitivity? This IS an issue at high doses (for deterministic effects in radiation therapy) It is not known whether Individual Sensitivity is an
Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in vitro
 Radiat Environ Biophys (1986) 25:195-199 Radiation and Environmental Biophysics Springer-Verlag 1986 Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in
Radiat Environ Biophys (1986) 25:195-199 Radiation and Environmental Biophysics Springer-Verlag 1986 Change in frequency of radiation induced micronuclei during interphase of four-cell mouse embryos in
ERICA an overview. Brenda Howard, NERC. 1 EC Contract: FI6R-CT
 ERICA an overview Brenda Howard, NERC 1 ERICA: Environmental Risk from Ionising Contaminants: Assessment and Management Overall objective to provide an integrated approach to scientific, managerial and
ERICA an overview Brenda Howard, NERC 1 ERICA: Environmental Risk from Ionising Contaminants: Assessment and Management Overall objective to provide an integrated approach to scientific, managerial and
Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach. R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham
 Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch, AECL, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River
Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch, AECL, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Background Radiation in U.S. ~ msv/yr msv/yr ~0.02 ~0.02 msv msv/day /day (~2 m rem/day) mrem/day) NCRP 4
 Patient Safety Concerns in Diagnostic Radiology? Lawrence T. Dauer, PhD, CHP Assistant Attending Health Physicist Department of Medical Physics RAMPS/GNYCHPS Spring Symposium April 30, 2010 Benefits?
Patient Safety Concerns in Diagnostic Radiology? Lawrence T. Dauer, PhD, CHP Assistant Attending Health Physicist Department of Medical Physics RAMPS/GNYCHPS Spring Symposium April 30, 2010 Benefits?
BEIR VII: Epidemiology and Models for Estimating Cancer Risk
 National Cancer Institute U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health BEIR VII: Epidemiology and Models for Estimating Cancer Risk Ethel S. Gilbert National Cancer Institute
National Cancer Institute U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health BEIR VII: Epidemiology and Models for Estimating Cancer Risk Ethel S. Gilbert National Cancer Institute
Molecular Biology of Cancer. Code: ECTS Credits: 6. Degree Type Year Semester
 2018/2019 Molecular Biology of Cancer Code: 100863 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other comments on languages
2018/2019 Molecular Biology of Cancer Code: 100863 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry OT 4 0 Contact Name: Carles Arús Caralto Email: Carles.Arus@uab.cat Other comments on languages
Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Radiation. Tim Marshel R.T. (R)(N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT)
 Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Radiation Tim Marshel R.T. (R)(N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) SNMTS Approved MIIWIIQI: Effects of Long Term Exposure to Radiation 45 Hr PET Registry Review Course Reference
Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Radiation Tim Marshel R.T. (R)(N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) SNMTS Approved MIIWIIQI: Effects of Long Term Exposure to Radiation 45 Hr PET Registry Review Course Reference
Current and Planned NCRP Activities
 Current and Planned NCRP Activities David A. Schauer, Executive Director National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements Bethesda, Maryland Presentation at 2008 Mid-Atlantic States Radiation
Current and Planned NCRP Activities David A. Schauer, Executive Director National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements Bethesda, Maryland Presentation at 2008 Mid-Atlantic States Radiation
Task 2.4 Develompment of SRA, roadmap and priorities for research on dosimetry
 Task 2.4 Develompment of SRA, roadmap and priorities for research on dosimetry EJP CONCERT Kick-Off Meeting Oberschleißhei m, Germany 8. June 2015 W. Rühm Institute for Radiation Protection Helmholtz Zentrum
Task 2.4 Develompment of SRA, roadmap and priorities for research on dosimetry EJP CONCERT Kick-Off Meeting Oberschleißhei m, Germany 8. June 2015 W. Rühm Institute for Radiation Protection Helmholtz Zentrum
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
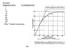 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Undiagnosed Rare Diseases: a bilateral project between. Italy (Istituto Superiore di Sanità) and USA (NIH)
 Undiagnosed Rare Diseases: a bilateral project between Italy (Istituto Superiore di Sanità) and USA (NIH) Domenica Taruscio & Marco Salvatore National Centre for Rare Diseases Istituto Superiore di Sanità,
Undiagnosed Rare Diseases: a bilateral project between Italy (Istituto Superiore di Sanità) and USA (NIH) Domenica Taruscio & Marco Salvatore National Centre for Rare Diseases Istituto Superiore di Sanità,
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Gene-radiation interactions: their influence on pre-menopausal breast cancer risk after Chernobyl (GENE-RAD-INTERACT) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00215 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Gene-radiation interactions: their influence on pre-menopausal breast cancer risk after Chernobyl (GENE-RAD-INTERACT) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00215 Final
