The Kinetic Signature of Toxicity of Four Heavy Metals and Their Mixtures on MCF7 Breast Cancer Cell Line
|
|
|
- Claribel Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, ; doi: /ijerph OPEN ACCESS Article International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health ISSN The Kinetic Signature of Toxicity of Four Heavy Metals and Their Mixtures on MCF7 Breast Cancer Cell Line Egbe Egiebor 1, Adam Tulu 1, Nadia Abou-Zeid 1, Isoken Tito Aighewi 2 and Ali Ishaque 1, * 1 2 Department of Natural Sciences, University of Maryland Eastern Shore, Princess Anne, MD 21853, USA; s: honeyspringsbv@yahoo.com (E.E.); adamtulu@yahoo.com (A.T.); nzeid06@yahoo.com (N.A.-Z.) Department of Biology, Chemistry and Environmental Health Sciences, Benedict College, Columbia, SC 29204, USA; aighewii@benedict.edu This paper is an extended version of paper presented at the Ninth International Symposium on Recent Advances in Environmental Health Research, Jackson, MS, USA; September * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; abishaque@mail.umes.edu. Received: 11 October 2012; in revised form: 30 November 2012 / Accepted: 4 December 2012 / Published: 21 October 2013 Abstract: This study evaluated the kinetic signature of toxicity of four heavy metals known to cause severe health and environmental issues cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg) lead (Pb) arsenic (As) and the mixture of all four metals (Mix) on MCF7 cancer cells, in the presence and absence of the antioxidant glutathione (GSH). The study was carried out using real time cell electronic sensing (RT-CES). RT-CES monitors in real time the electrical impedance changes at the electrode/culture medium interface due to the number of adhered cells, which is used as an index of cell viability. Cells were seeded for 24 h before exposure to the metals and their mixtures. The results showed that in the presence and absence of cellular glutathione, arsenic was the most cytotoxic of all five treatments, inducing cell death after 5 h of exposure. Lead was the least cytotoxic in both scenarios. In the presence of cellular GSH, the cytotoxic trend was As > Cd > MIX > Hg > Pb, while in the absence of GSH, the cytotoxic trend was As > Hg > MIX > Cd > Pb. The findings from this study indicate the significance of glutathione-mediated toxicity of the metals examined particularly for mercury and may be clinically relevant for disorders such as autism spectrum disorder where decreased glutathionebased detoxification capacity is associated with increased mercury intoxication.
2 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, Keywords: heavy metals; real time electronic cell sensing; glutathione; L-buthionine sulphoximine 1. Introduction Among heavy metals, cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), lead (Pb) and arsenic (As) are some of the most toxic elements due to their persistence in the environment. They cause oxidative and nitrosative stress [1 3] and damage macromolecules in cells which consequently lead to cell death by apoptosis or necrosis [4]. Although the toxicity of individual heavy metals on organisms are of serious ecological consequences, metals rarely occur alone, most often occuring as mixtures [5]. Metal mixtures substantially complicate the risk assessment process for these elements and very few researchers have studied the environmental effects of mixtures of heavy metals. Information on potential adverse health effects associated with intake of mixture of most frequently found metals contaminant is not known. Hence, it is imperative to study heavy metals not only individually, but also in mixtures. Metal metabolism has significant effects on metal toxicity. Protective processes at the molecular and cellular levels may not affect cellular homeostasis even after metal exposure. A studied example that is known to modify the susceptibility to metals is glutathione (GSH) [6]. GSH can interfere with toxic metals by altering the rates of metal uptake and elimination [7] and it can protect against oxidative stress resulting from metal-catalysed redox reactions [8]. The goal of this study was to understand the kinetic signature of toxicity of four heavy metals (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) and the mixture of all four metals (Mix) on MCF7 cells, in the presence and absence of cellular glutathione, using real time cell electronic sensing (RTCES). The present study highlights the viability of MCF7 cells that were exposed to metals and their mixture in real time. To study the effect of the absence of GSH in the cell, cellular GSH synthesis was inhibited by exposing the cells to L-buthionine sulfoximine (LBSO) for 24 h. LBSO is a specific γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase inhibitor that irreversibly inhibits the rate-limiting step of glutathionine biosynthesis and depletes the intracellular GSH pool in both cultured cells and in whole animals. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Chemicals Atomic absorption standards (Acros Organics, NJ, USA) consisted of arsenic 1 mg/l in 2% KOH, cadmium 1 mg/l in 0.5 N nitric acid, lead 1 mg/l in 2% nitric acid and mercury 1 mg/l in 10% nitric acid. L-Buthionine sulfoximine (LBSO) was purchased from Toronto Research Chemicals (North York, ON, Canada) Cell Lines and Culturing Reagent MCF7 cell lines were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATTC, Manassas, VA, USA). Minimum Essential Medium (MEM) alpha 1x, Dulbecco s Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS), MEM without phenol, and penicillin streptomycin were purchased from GIBCO Invitrogen (Grand
3 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, Island, NY, USA). Trypsin-EDTA and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were purchased from ATTC. MCF7 cells were grown in MEM alpha 1 supplemented with 10.0% FBS and 1.0% penicillin streptomycin. The cells were grown in a humidified incubator kept at the temperature of 37 C and 5% carbon dioxide Description of Exposure Studies Real-Time Cell Electronic Sensing (RT-CES) The in vitro cell viability effect of individual and mixture with/without LBSO on MCF7 cells were determined by RT-CES cytotoxicity assay. Cells in the presence of individual metals at concentrations from 0 µg/ml to 21.7 µg/ml were monitored by measurements of electrical impedance (ACEA Biosciences Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) every 10 min for 96 h. Continuous recording of impedance in cells was reflected by cell index value [9] Testing the Kinetic Response of the Individual Metals on MCF7 Cells To determine the individual toxicity of the metals, MCF7 cells were seeded in a 16x E-plate device and grown in the incubator for 24 h for metal treatment. To create a negative control, the last row of cell culture plate contained the media and cells but was not exposed to any metal. After 24 h, the media in the seeded cells was dumped, 180 µl of fresh media was added to each well and 50 µl of serially diluted metals (concentrations ranging from 0 µg/ml 21.7 µg/ml) was also added to give a final volume of 230 µl. Using four seeded plates (one for each metal), The first row of the plates had the highest concentration of the individual metals and concentrations of As, Cd, Hg, and Pb decreased from row 1 to row 7. Row 8 was not treated with any metals. The cells were incubated for 96 h. The procedure was carried out in duplicates and repeated twice for each of the chemicals to make sure the trend of toxicity was similar Testing the Kinetic Response of Quaternary Mixture of Metals on MCF7 Cells A mixture of the four metals was made by mixing As, Cd, Hg, and Pb stock solutions in the ratio of their Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL), that is 10, 5, 2 and 15 ppb, respectively. A serial dilution of the mixture was made such that the starting concentrations for As, Cd, Hg, and Pb in mixture were 250, 125, 50 and 375 mg/l, respectively. MCF7 cells were seeded in a 16x E-plates for 24 h and were treated with decreasing concentration of the mixture as mentioned above. The treated cells were incubated for 96 h. The procedure was carried out in duplicates and repeated twice Testing the Kinetic Response of Individual and Mixture of Metals on LBSO Pretreated MCF7 Cells To determine the toxicity of the individual and composite mixture of metals in the absence of glutathione (GSH), 2.5 mm of GSH-depleting agent LBSO was used to seed the cells prior to exposure to the chemicals. The appropriate concentration of which did not kill more than 5% of the cells was predetermined to be 2.5 mm in prior experiments. MCF7 cells were seeded and incubated for 24 h
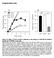
4 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, using the growth medium containing 2.5 mm LBSO. Thereafter, each plate was treated with decreasing concentrations of the four metals as described previously. The treated cells were incubated for 96 h. 3. Results 3.1. Kinetic Response of Individual and Composite Mixture of Metals on MCF7 Cells To characterize the kinetic signature of each of the four chemicals (Cd, Hg, Pb and As) and the mixture of all four (Mix), MCF7 cells were exposed to different concentrations of each chemical and dynamically monitored over 96 h using real time cell electronic sensing (RT-CES). RT-CES measures cell viability in real time using electrical impedance [9]. Using the aforementioned methods, the four highly toxic chemicals and their mixture were found to be cytotoxic within the concentration range that was tested. The kinetics response of MCF7 was different for each chemical. Cadmium, one of the more notorious chemicals, of serious concern due to its ability to cause lung and prostate cancer, was cytotoxic after 12 h at the highest concentration of 21.7 µg/ml (red, Figure 1). At the concentration of 10.8 µg/ml (light green), cadmium induced cell death after 34 h of exposure to MCF7 cells. Lower concentrations of cadmium ranging from 0.34 ppm to 5.4 ppm did not show any visible effect on the cells. Monitoring the kinetic signature of each chemical on MCF7 cells in real time, the results showed that arsenic which is known to be associated with different types of cancers, cardiovascular diseases and neurological disorders [10], had the worst effects on the cells (Figure 2). Figure 1. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for Cadmium (Cd) in MCF7 cells monitored by the RT-CES system.10,000 cells/well were plated in 16-well strips for the RT-CES cytotoxicity assay. Different compound concentrations in µg/ml are indicated by different colors. Red = 21.7, light green = 10.8, blue = 5.4, yellow = 2.7, turquoise = 1.3, pink = 0.68, burgundy = 0.34, green = control.
5 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, Figure 2. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for arsenic (As) in MCF7 cells as described in Figure 1 legend. The highest concentration of 21.7 µg/ml (red) induced cytotoxic effects after just 2 h of exposure and induced total cell death after 5 h. At concentrations of 10.8 µg/ml (light green) and 5.4 µg/ml (blue), arsenic induced total cell death at 10 h and 20 h after exposure respectively. Lower concentrations of arsenic ranging 0.34 ppm to 2.7 µg/ml showed slower onset of cytotoxicity but induced obvious cell death. Mercury which has been linked with various types of tissue damages [11], showed no visible effect on cell viability (Figure 3). However,the highest concentration of mercury 21.7 µg/ml (red) inhibited cell proliferation but did not cause any cell death or decrease in cell number. From our results (Figure 4), lead, which is known for its neurotoxic effects, showed cytotoxic effects at the highest concentration of 21.7 µg/ml (red) after about 34 h of exposure but all other concentrations did not induce any visible cell death. Figure 3. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for mercury (Hg) in MCF7 cells as described in Figure 1 legend.
6 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, Figure 4. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for lead (Pb) in MCF7 cells as described in Figure 1 legend. This study also examined the effects of the combination of all four chemicals on MCF7 cell lines (Figure 5). Though there was a slow onset of cytotoxicity, the four higher concentrations of the mixture induced cell death after 72 h of exposure. The three lower concentrations of the mixture did not have any visible effect on cell viability. Figure 5. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for mixture (Mix) in MCF7 as described in Figure 1 legend Kinetic Response of Individual and Quaternary Mixture of Metals on LBSO Pretreated MCF7 Cells To characterize the kinetic signature of each of the four chemicals (Cd, Hg, Pb and As) and their mixture (Mix) in the absence of cellular glutathione, MCF7 cells was pretreated with LBSO
7 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, (a compound that irreversibly inhibits GSH synthesis) for 24 h and the cells were exposed to different concentrations of each chemical and their quaternary mixture. The cytotoxic effects of each chemical and their mixture on MCF7 cells were dynamically monitored in real time for 96 h. Following the method that was described previously, the individual chemicals and their mixture (except lead) were found to be cytotoxic within the concentration range that was tested. The kinetics response of LBSO treated MCF7 cells was different for each chemical. Cadmium (Figure 6), arsenic (Figure 7), mercury (Figure 8) and the mixture of all four chemicals (mix) (Figure 10) induced severe cytotoxic effects on MCF7 cells, while lead (Figure 9) showed a visible decrease in cell number 40 h after exposure to the highest concentration. The result shows that mercury and arsenic had severe cytotoxicity after only 4 h of exposure. All concentrations (0.34 ppm 21.7 ppm) of arsenic were fully cytotoxic after 32 h of exposure. After 32 h of exposure, the four higher concentrations (2.7 µg/ml 21.7 µg/ml) of mercury induced cytotoxic effects while the lower three concentrations (0.034 µg/ml 1.3 µg/ml) did not have any effects on the cells. The higher two concentrations (10.8 ppm 21.7 ppm) of cadmium induced cytotoxic effect after 6 h of exposure, while the lower concentration did not reveal any visible effects on MCF-7 cells. In the case of the mixture of all four chemicals (mix), the higher three concentrations induced cell death after 32 h of exposure, while the lower concentration showed neither a decrease in cell number nor an increase in cell proliferation. The highest concentration (21.7 ppm) of lead showed a little decrease in cell number after 40 h of exposure, but all other concentrations did not show any visible effect on MCF-7 cells. Figure 6. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for cadmium in LBSO-treated MCF7 cells monitored by the RT-CES system. 10,000 cells/well were plated in 16-well strips for the RT-CES cytotoxicity assay. Different compound concentrations in µg/ml are indicated by different colors. Red = 21.7, light green = 10.8, blue = 5.4, yellow = 2.7, turquoise = 1.3, pink = 0.68, burgundy = 0.34, green = control.
8 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, Figure 7. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for arsenic in LBSO-treated MCF7 cells as described in Figure 6 legend. Figure 8. Kinetics of cytotoxic responses for mercury in LBSO-treated MCF7 cells as described in Figure 6 legend.
9 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, Figure 9. Kinetics of cytotoxicity responses for lead in LBSO-treated MCF7 cells as described in Figure 6 legend. Figure 10. Kinetics of cytotoxicity responses for mixture in LBSO-treated MCF7 cells as described in Figure 6 legend. 4. Discussion and Conclusions Exposure of cells to heavy metals may immediately lead to necrosis or apoptosis, but sometimes, cells may undergo series of events like the synthesis of more glutathione molecules that could lead to their survival. Studies by scientists have widely demonstrated that the exposure to heavy metals shares
10 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, several primary mechanisms of toxicity, including the production of reactive oxygen species, reaction with intracellular thiols and competing with essential metals in biological systems [12,13]. This study, determined the kinetic signature of toxicity of four heavy metals and their mixture (Hg, Cd, As, Pb and Mix) on MCF-7 breast cancer cells in the presence and absence of glutathione. From the results it was obvious that cells that were treated with the glutathione-scavenging agent LBSO before chemical exposure, exhibited more cell death at a shorter time period than cells that were exposed to the metals alone. The results showed that when MCF-7 cells were exposed to only cadmium the highest concentration of 21.7 µg/ml induced full cytoxicity after 12 h of exposure, the next concentration of 10.8 µg/ml exhibited cytotoxic effects after 34 h of exposure and the lower concentrations of 0.34 ppm 5.4 ppm did not reveal any cytotoxic effects. In contrast, when MCF7 cells were exposed to the glutathione-scavenging compound LBSO before being exposed to cadmium, the two higher concentrations (10.8 µg/ml and 21.7 µg/ml) were fully cytotoxic after only 6 h of exposure. Interestingly, arsenic was more cytotoxic on MCF-7 cells than cadmium both in the presence and absence of glutathione. The higher three concentrations of arsenic ( µg/ml) induced cytotoxic effects after 5 h of exposure and after 48 h, all concentrations were cytotoxic. In contrast, when cellular glutathione was scavenged, the higher three concentrations of arsenic ( µg/ml) became cytotoxic at only 4 h while all other concentrations induced cytotoxicity after 24 h of exposure. None of the concentrations of mercury had any obvious effects on MCF-7 cells when cellular GSH was present. In contrast, when cells were pretreated with LBSO before exposure to mercury, the result revealed that Hg was cytotoxic at the highest concentration of 21.7 ppm after only 4 h of exposure, while the next three concentrations ( µg/ml) induced total cytotoxic effects after 32 h of exposure. No concentrations of lead showed any signs of cytotoxicity, but when the cells were treated with LBSO before being exposed to lead, the highest concentration of 21.7 µg/ml indicated a slight decrease in cell number after 40 h of exposure. The higher incidence of cell death occurring in the presence of LBSO may be due to the fact that LBSO scavenges cellular glutathione and potentiates the effects of toxic chemicals [14]. Our result is in accordance with the findings of Lee et al., [15], who discovered that there was an up regulation of glutathione in arsenic treated Chinese hamster ovary cells. In addition, research by [16] found that there was an increase in the activities of glutathione when leydig cells were exposed to cadmium. Increased glutathione activities is in cells exposed to heavy metals may be the reason why MCF7 cells exposed to heavy metals alone showed more resistance than cells that were pretreated with LBSO before metal exposure. Glutathione may have helped the cells fight against reactive oxygen species that exposure to the metals may have generated, hence, the reduced cell death when glutathione was not scavenged. The tripeptide (glutathione) scavenges hydroxyl radicals, detoxifies hydrogen peroxides and lipid hydroperoxides by the activity of glutathione peroxidase and is able to regenerate other antioxidant molecules [17]. Glutathione can also bind with metals like Hg to form the GSHmetal complex which is then pumped out of the cells [14]. Studies has also shown an increase in GSH when NKR-52E cells were treated with Hg and Pb but treatment with Hg depleted more GSH and induces more oxidative stress than Pb because Hg had more affinity for GSH [18]. This may be why our result showed more cell death when glutathione was scavenged from the cells before exposure to mercury than when the cells were exposed to mercury alone. The mercury treated cells may have been able to survive because the metals may have been bound to glutathione molecules and pumped out of
11 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, the cells to prevent cell death. On the other hand, when glutathione was absent from the cells, mercury had a drastic effect on the cells causing almost immediate cell death. The observation of glutathione's importance in protecting against mercury induced toxicity may be of particular importance for clinical disorders such as autism spectrum disorders. Previous studies by [19] on subjects diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder revealed that they had decreased glutathione-based detoxification capacity, particularly of mercury, and as a consequence had elevated mercury body-burden. The observations from the present study provide cellular support for how impaired glutathione-based detoxification in autism spectrum disorders may result in mercury intoxication. In the case of the mixture of the four chemicals, the higher three concentrations inhibited cell viability when cellular GSH was intact, but when GSH was scavenged, the mixture induced cytotoxic effects less than 10 h after exposure. The result showed that the onset of cell death in cells exposed to the mixture was sooner in cells treated with LBSO than in those that were not treated with LBSO. From our results, the cytotoxic effects of the metals on MCF7 cells in the presence of glutathione is as follows As > Cd > MIX > Hg > Pb whereas when glutathione is scavenged, the cytotoxic effects of the metals is as follows As > Hg > MIX > Cd > Pb. Cells that were treated with LBSO before being exposed to the chemicals may have experienced more cell death because of the absence of glutathione and the cells may not have had the ability to fight off ROS generation which in turn leads to cell death. Although cells that were exposed only to the chemicals showed cell death, but it took a longer time and only occurred at high chemical concentrations. Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1. Stohs, S.J.; Bagchi, D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of heavy metals. Free. Radical Biol. Med. 1995, 18, Ercal, N.; Gurer-Orhan, H.; Aykin-Burns, N. Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: Mechanisms involved in metal induced oxidative damage. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, Pompella, A.; Visvikis, A.; Paolicchi, A.; de Tata, V.; Casini, A.F. The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, Pulido, M.D.; Parrish, A.R. Metal-induced apoptosis: Mechanisms. Mutat. Res. 2003, 533, Ishaque, A.; Johnson, L.; Gerald, T.; Boucaud, D.; Okoh, J.; Tchounwou, P. Assessment of Individual and Combined Toxicities of Four Non-Essential Metals (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) in the Microtox Assay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2006, 3, Kang, Y.J.; Enger, M.D. Effect of cellular glutathione depletion on cadmium-induced cytotoxicity in human lung carcinoma cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 1987, 3, Hsu, J.M. Lead toxicity as related to glutathione metabolism. J. Nutr. 1981, 111, Winston, D.W.; Giulio, R.T. Prooxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquat. Toxicol. 1991, 19,
12 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, Xing, J.Z.; Zheu, L.; Jackson, J.A.; Gabos, S.; Sun, X.J.; Wang, X.B. Dynamic monitoring of cytotoxicity on microelectronic sensors. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, Schwartz, R.A. Arsenic and the skin. Int. J. Dermatol. 1997, 36, Guo, T.L.; Miller, M.A.; Shapiro, I.M.; Shenker, B.J. Mercuric chloride induces apoptosis in human T lymphocytes: Evidence of mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1989, 153, Flora, S.; Mittal, M.; Metha, A. Heavy metal induced oxidative stress and its possible reversal by chelation therapy. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, Wang, G.; Fowler, B.A. Roles of biomarkers in evaluating interactions among mixtures of lead, cadmium and arsenic. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 233, Pu, Y.; Hour, T.; Chen, J.; Huang, C.; Guan, J.; Lu, S. Cytotoxicity of arsenic to transitional carcinoma cells. Urology 2002, 60, Lee, T.C.; Wei, M.L.; Chang, W.J.; Ho, I.C.; Lo, J.F.; Jan, K.Y.; Huang, H. Elevation of glutathione levels and glutathione S-transferase activity in arsenic resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 1989, 25, Yang, J.M.; Arnush, M.; Chen, Q.Y.; Wu, X.D.; Pang, B.; Jiang, X.Z. Cadmium induced damage to primary cultures of rat Leydig cells. Reprod. Toxicol. 2003, 17, Masella, R.; di Benedetto, R.; Varì, R.; Filesi, C.; Giovannini, C. Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological system: Involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, Stacchiotti, A.; Lavazza, A.; Rezzani, R.; Borsani, E.; Rodella, L.F.; Bianchi, R. Mercuric chloride-induced alterations in stress protein distribution in rat kidney. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 19, Geier, D.A.; King, P.G.; Geier, M.R. Mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired oxidative-reduction activity, degeneration, and cell death in human neuronal and fetal cells induced by low-level exposure to Thimerosal and other metal compounds. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2009, 91, by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
MTS assay in A549 cells
 Project: VIGO MTS assay in A549 cells Detection of cell viability/activity AUTHORED BY: DATE: Cordula Hirsch 20.01.2014 REVIEWED BY: DATE: Harald Krug 10.04.2014 APPROVED BY: DATE: DOCUMENT HISTORY Effective
Project: VIGO MTS assay in A549 cells Detection of cell viability/activity AUTHORED BY: DATE: Cordula Hirsch 20.01.2014 REVIEWED BY: DATE: Harald Krug 10.04.2014 APPROVED BY: DATE: DOCUMENT HISTORY Effective
IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES
 13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
13 13 IMPACT OF FLUORIDE AND SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE ON THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN RAT RIB-CAGE CHONDROCYTES Yanni Yu, a Binjie Meng a Guizhou, China SUMMARY: Chondrocytes of rib-cage cartilage from Wistar rats
Glutathione Assay Kit
 Glutathione Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1649 250 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Glutathione Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1649 250 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
Alpha Lipoic Acid Snapshot Monograph
 vitamins minerals nutrients Alpha Lipoic Acid Snapshot Monograph Alpha lipoic Acid Most Frequent Reported Uses: - Antioxidant - Peripheral neuropathy - Improves insulin signaling and regulation of appetite
vitamins minerals nutrients Alpha Lipoic Acid Snapshot Monograph Alpha lipoic Acid Most Frequent Reported Uses: - Antioxidant - Peripheral neuropathy - Improves insulin signaling and regulation of appetite
Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2016, 7(2): 49-53 ISSN: 2088 0197 Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin Laeli
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2016, 7(2): 49-53 ISSN: 2088 0197 Anti-Aging Activity Of Cucurbita moschata Ethanolic Extract Towards NIH3T3 Fibroblast Cells Induced By Doxorubicin Laeli
Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit
 Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0882 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0882 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
ROS Activity Assay Kit
 ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS
 CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
CHAPTER 3 IN VITRO ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF FLOWER EXTRACTS OF COUROUPITA GUIANENSIS 3. INTRODUCTION Plants are the basic source of knowledge of modern medicine. Almost all the parts of the plant, namely
EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells
 EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells Okezie I. Arouma a) and Irfan Rahman b) a) Department of Neuroinflammation, Division of Neuroscience & Psychological Medicine,
EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells Okezie I. Arouma a) and Irfan Rahman b) a) Department of Neuroinflammation, Division of Neuroscience & Psychological Medicine,
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D.
 Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
State of the art ingredients fast friendly service
 ALPHA-LIPOIC ACID An Efficient Antioxidant α-lipoic acid also known as thioctic acid, plays an important role in metabolic processes. It functions as a co-factor for a number of key enzymes that help in
ALPHA-LIPOIC ACID An Efficient Antioxidant α-lipoic acid also known as thioctic acid, plays an important role in metabolic processes. It functions as a co-factor for a number of key enzymes that help in
Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT
 Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Glutathione Regulation
 The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
OxiSelect Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Product Manual OxiSelect Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-343 5 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Oxidative stress is a physiological
Product Manual OxiSelect Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-343 5 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Oxidative stress is a physiological
Supporting Information Nitric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines
 upporting Information itric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines Priya udhesh a, Kaviyarasan Tamilarasan a, Palaniappan Arumugam a and
upporting Information itric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines Priya udhesh a, Kaviyarasan Tamilarasan a, Palaniappan Arumugam a and
Mechanistic Toxicology
 SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis aubl
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 169-176 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 169-176 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis
FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS
 Fluoride Vol. 37 No. 1 7 12 2004 Research Report 7 FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS I Inkielewicz, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: Eight-week old male
Fluoride Vol. 37 No. 1 7 12 2004 Research Report 7 FLUORIDE EFFECTS ON GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE AND LIPID PEROXIDATION IN RATS I Inkielewicz, a J Krechniak a,b Gdańsk, Poland SUMMARY: Eight-week old male
NM interference in the DCF assay
 Project: VIGO NM interference in the DCF assay Quenching effects DCF AUTHORED BY: DATE: Cordula Hirsch 20.01.14 REVIEWED BY: DATE: Harald Krug 09.04.2014 APPROVED BY: DATE: DOCUMENT HISTORY Effective Date
Project: VIGO NM interference in the DCF assay Quenching effects DCF AUTHORED BY: DATE: Cordula Hirsch 20.01.14 REVIEWED BY: DATE: Harald Krug 09.04.2014 APPROVED BY: DATE: DOCUMENT HISTORY Effective Date
ab Lipoxygenase Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit
 ab133087 Lipoxygenase Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the detection of hydroperoxides produced in the lipoxygenation reaction using a purified Lipoxygenases. This product is for
ab133087 Lipoxygenase Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the detection of hydroperoxides produced in the lipoxygenation reaction using a purified Lipoxygenases. This product is for
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
5þ ; AA, ascorbic acid.
 A B C SUPPLEMENTAL FIG. S1. Synergistic effect of MnTMPyP, AA, and GSH on PC-3 cell proliferation. PC-3 cells were incubated with different concentrations of AA (A) and GSH (B) with MnTMPyP for various
A B C SUPPLEMENTAL FIG. S1. Synergistic effect of MnTMPyP, AA, and GSH on PC-3 cell proliferation. PC-3 cells were incubated with different concentrations of AA (A) and GSH (B) with MnTMPyP for various
International Journal Of Recent Scientific Research
 International Journal Of Recent Scientific Research ISSN: 0976-3031 Volume: 7(5) May -2016 NEW ERA ABOUT TREATMENT - EVOLUATION OF ANTICANCER PROPERTIES OF EVERGREEN MEDICINAL PLANT ANNONA MURICATA (GRAVIOLA)
International Journal Of Recent Scientific Research ISSN: 0976-3031 Volume: 7(5) May -2016 NEW ERA ABOUT TREATMENT - EVOLUATION OF ANTICANCER PROPERTIES OF EVERGREEN MEDICINAL PLANT ANNONA MURICATA (GRAVIOLA)
Acrolein is an environmental toxicant, mainly found in smoke released from
 SHAH, HALLEY, M.S. Protection of HepG2 Cells from Acrolein Toxicity by CDDO-Im Via Glutathione-Mediated Mechanism. (2013) Directed by Dr. Zhenquan Jia. 56pp. Acrolein is an environmental toxicant, mainly
SHAH, HALLEY, M.S. Protection of HepG2 Cells from Acrolein Toxicity by CDDO-Im Via Glutathione-Mediated Mechanism. (2013) Directed by Dr. Zhenquan Jia. 56pp. Acrolein is an environmental toxicant, mainly
HT Glutathione Assay Kit
 Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT Glutathione Assay Kit Colorimetric assay for total, reduced and oxidized glutathione. Sufficient reagents for tests. Table of
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT Glutathione Assay Kit Colorimetric assay for total, reduced and oxidized glutathione. Sufficient reagents for tests. Table of
Available Online at CODEN: IJRSFP (USA) Vol. 9, Issue, 1(I), pp , January, 2018.
 ISSN: 976-331 Available Online at http://www.recentscientific.com CEN: IJRSFP (USA) International Journal of Recent Scientific Research Vol. 9, Issue, 1(I), pp. 2347-23474, January, 218 Research Article
ISSN: 976-331 Available Online at http://www.recentscientific.com CEN: IJRSFP (USA) International Journal of Recent Scientific Research Vol. 9, Issue, 1(I), pp. 2347-23474, January, 218 Research Article
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
MTS assay in THP-1 cells
 Project: VIGO MTS assay in THP-1 cells Detection of cell viability/activity AUTHORED BY: DATE: Cordula Hirsch 20.01.2014 REVIEWED BY: DATE: Harald Krug 10.04.2014 APPROVED BY: DATE: DOCUMENT HISTORY Effective
Project: VIGO MTS assay in THP-1 cells Detection of cell viability/activity AUTHORED BY: DATE: Cordula Hirsch 20.01.2014 REVIEWED BY: DATE: Harald Krug 10.04.2014 APPROVED BY: DATE: DOCUMENT HISTORY Effective
6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Free radicals are chemical species containing one or more unpaired electrons, like hydrogen atom, most transition metal ions, nitric oxide and oxygen, with two unpaired electrons.
6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Free radicals are chemical species containing one or more unpaired electrons, like hydrogen atom, most transition metal ions, nitric oxide and oxygen, with two unpaired electrons.
Europium Labeling Kit
 Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Modulating the inflammatory properties of activated microglia with Docosahexaenoic acid and Aspirin
 Pettit et al. Lipids in Health and Disease 213, 12:16 RESEARCH Open Access Modulating the inflammatory properties of activated microglia with Docosahexaenoic acid and Aspirin Lauren K Pettit 1, Christopher
Pettit et al. Lipids in Health and Disease 213, 12:16 RESEARCH Open Access Modulating the inflammatory properties of activated microglia with Docosahexaenoic acid and Aspirin Lauren K Pettit 1, Christopher
Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International
 Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International Ethanol and Glutathione Reduced glutathione plays a critical role in cellular detoxification processes including the metabolism of peroxides,
Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International Ethanol and Glutathione Reduced glutathione plays a critical role in cellular detoxification processes including the metabolism of peroxides,
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
Lankenau Institute for Medical Research Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Lankenau Institute for Medical Research nnual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Lankenau Institute for Medical Research received
Lankenau Institute for Medical Research nnual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Lankenau Institute for Medical Research received
Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit
 Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2522 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hemoglobin detection kit is designed to quantitatively measure all forms of hemoglobin present in blood
Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2522 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hemoglobin detection kit is designed to quantitatively measure all forms of hemoglobin present in blood
Anti-cancer activity of Aya Thambira Chendooram (ATC) in in-vitro cell line against Breast Carcinoma
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 5, Issue 1-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.01.010
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 5, Issue 1-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.01.010
MATERIAL AND METHODS
 MATERIAL AND METHODS Material and Methods Glucose induced cataract was chosen as a model for the present study. A total of 210 fresh goat lenses were analyzed. Sample Collection: Goat eyeballs were obtained
MATERIAL AND METHODS Material and Methods Glucose induced cataract was chosen as a model for the present study. A total of 210 fresh goat lenses were analyzed. Sample Collection: Goat eyeballs were obtained
Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells
 Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Antioxidant Products
 Antioxidant Products Introduction Introduction Antioxidant Total Antioxidant Status (TAS) Ransel Ransod Glutathione Reductase Antioxidants help defend living organisms against free radical attack. Many
Antioxidant Products Introduction Introduction Antioxidant Total Antioxidant Status (TAS) Ransel Ransod Glutathione Reductase Antioxidants help defend living organisms against free radical attack. Many
Graphene Quantum Dots-Band-Aids Used for Wound Disinfection
 Supporting information Graphene Quantum Dots-Band-Aids Used for Wound Disinfection Hanjun Sun, Nan Gao, Kai Dong, Jinsong Ren, and Xiaogang Qu* Laboratory of Chemical Biology, Division of Biological Inorganic
Supporting information Graphene Quantum Dots-Band-Aids Used for Wound Disinfection Hanjun Sun, Nan Gao, Kai Dong, Jinsong Ren, and Xiaogang Qu* Laboratory of Chemical Biology, Division of Biological Inorganic
THE DETOX QUBE WITH EDTA
 THE DETOX QUBE WITH EDTA ADVANCED HEAVY METAL DETOXIFICATION KIT PERFECT DELIVERY PERFECT PATHWAY PERFECT PROTOCOL INSIDE THE DETOX QUBE WITH EDTA Kit Item Liposomal Glutathione Liposomal Vitamin C with
THE DETOX QUBE WITH EDTA ADVANCED HEAVY METAL DETOXIFICATION KIT PERFECT DELIVERY PERFECT PATHWAY PERFECT PROTOCOL INSIDE THE DETOX QUBE WITH EDTA Kit Item Liposomal Glutathione Liposomal Vitamin C with
Fructose-6-Phosphate Colorimetric Assay Kit
 Fructose-6-Phosphate Colorimetric Assay Kit Catalog No. KM0060 Detection and Quantification of Fructose-6-Phosphate Concentrations in Biological Samples. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
Fructose-6-Phosphate Colorimetric Assay Kit Catalog No. KM0060 Detection and Quantification of Fructose-6-Phosphate Concentrations in Biological Samples. Research Purposes Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic
ab Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells
 ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 17 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Lara Abdallat Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 P a g e Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP) Or Hexose Monophosphate Shunt In this lecture We will talk about the
number 17 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Lara Abdallat Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 P a g e Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP) Or Hexose Monophosphate Shunt In this lecture We will talk about the
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Dr. Ing. Branislav Ruttkay-Nedecký
 Název: Školitel: Metalothionein Dr. Ing. Branislav Ruttkay-Nedecký Datum: 31.1.2014 Reg.č.projektu: CZ.1.07/2.4.00/31.0023 NanoBioMetalNet Název projektu: Partnerská síť centra excelentního bionanotechnologického
Název: Školitel: Metalothionein Dr. Ing. Branislav Ruttkay-Nedecký Datum: 31.1.2014 Reg.č.projektu: CZ.1.07/2.4.00/31.0023 NanoBioMetalNet Název projektu: Partnerská síť centra excelentního bionanotechnologického
A Long-Term and Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor Protects against Myocardial. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
 Supporting Information A Long-Term and Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor Protects against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Xiaotian Sun 1 *, Wenshuo Wang 2, Jing Dai 3, Sheng Jin 4, Jiechun Huang
Supporting Information A Long-Term and Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor Protects against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Xiaotian Sun 1 *, Wenshuo Wang 2, Jing Dai 3, Sheng Jin 4, Jiechun Huang
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
 The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652
 Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
HT Glutathione Assay Kit
 IFU0 Rev Status: RELEASED printed //0 ::0 AM by Trevigen Document Control Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT Glutathione Assay Kit Colorimetric assay for total,
IFU0 Rev Status: RELEASED printed //0 ::0 AM by Trevigen Document Control Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT Glutathione Assay Kit Colorimetric assay for total,
APPENDIX Heparin 2 mg heparin was dissolved in 0.9 % NaCl (10 ml). 200 µl of heparin was added to each 1 ml of blood to prevent coagulation.
 APPENDIX 1 Preparation of reagents 1.1. Preparation of dosing solution Nonylphenol 15 mg of Nonylphenol was dissolved in olive oil (10 ml) and used as stock solution. The stock solution was serially diluted
APPENDIX 1 Preparation of reagents 1.1. Preparation of dosing solution Nonylphenol 15 mg of Nonylphenol was dissolved in olive oil (10 ml) and used as stock solution. The stock solution was serially diluted
Risks of Copper and Iron Toxicity during Aging in Humans. Chemical Research in Toxicology February 15, 2010; Vol. 23; No. 2; pp.
 Risks of Copper and Iron Toxicity during Aging in Humans 1 Chemical Research in Toxicology February 15, 2010; Vol. 23; No. 2; pp. 319 326 George J. Brewer Departments of Human Genetics and Internal Medicine,
Risks of Copper and Iron Toxicity during Aging in Humans 1 Chemical Research in Toxicology February 15, 2010; Vol. 23; No. 2; pp. 319 326 George J. Brewer Departments of Human Genetics and Internal Medicine,
ab Complex II Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit
 ab109908 Complex II Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Complex II activity in samples from Human, Rat, Mouse and Cow This product is for research
ab109908 Complex II Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Complex II activity in samples from Human, Rat, Mouse and Cow This product is for research
THE DETOX QUBE HEAVY METAL DETOXIFICATION KIT PERFECT DELIVERY PERFECT PATHWAY PERFECT PROTOCOL
 THE DETOX QUBE HEAVY METAL DETOXIFICATION KIT PERFECT DELIVERY PERFECT PATHWAY PERFECT PROTOCOL quicksilverscientific.com 1 2 quicksilverscientific.com INSIDE THE DETOX QUBE Kit Item Liposomal Glutathione
THE DETOX QUBE HEAVY METAL DETOXIFICATION KIT PERFECT DELIVERY PERFECT PATHWAY PERFECT PROTOCOL quicksilverscientific.com 1 2 quicksilverscientific.com INSIDE THE DETOX QUBE Kit Item Liposomal Glutathione
NIS/WW Report 1 1 of 11. Report 1. Testing of Willard s Water for antioxidant capacity and cellular uptake of selected nutrients.
 NIS/WW Report 1 1 of 11 October 18, 2012. Report for: John Willard WW Industries, Inc. PO Box 4040 Rapid City, South Dakota 57709 Phone: (888) 379-4552 Fax: (605) 343-0109 Email: john@drwillard.com Web:
NIS/WW Report 1 1 of 11 October 18, 2012. Report for: John Willard WW Industries, Inc. PO Box 4040 Rapid City, South Dakota 57709 Phone: (888) 379-4552 Fax: (605) 343-0109 Email: john@drwillard.com Web:
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines
 Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
The cytotoxic effects of cadmium chloride on the human lung carcinoma (Calu-6) cell line
 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, October 2008; 3(2): 49-53 Received: Mar 2008 Accepted: Jul 2008 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, October 2008; 3(2): 49-53 Received: Mar 2008 Accepted: Jul 2008 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 CHAPTER VI SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION CHAPTER 6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION "The doctor of the future will no longer treat the human frame with drugs, but rather will cure and prevent disease with nutrition."
CHAPTER VI SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION CHAPTER 6. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION "The doctor of the future will no longer treat the human frame with drugs, but rather will cure and prevent disease with nutrition."
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
EconovaPlus Fertiliser
 EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
EconovaPlus Fertiliser The complete plant growth fertiliser, bio-stimulater & carbon control solution. A bio-fertiliser based on the need for organic mineral complexes in the soil. Manufactured by building
Data sheet. TBARS Assay kit. (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Kit Contents. MDA-TBA Adduct. 2-Thiobarbituric Acid. Cat. No: CA995.
 Data sheet Cat. No: CA995 TBARS Assay kit (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Introduction Oxidative stress in the cellular environment results in the formation of highly reactive and unstable lipid hydroperoxides.
Data sheet Cat. No: CA995 TBARS Assay kit (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Introduction Oxidative stress in the cellular environment results in the formation of highly reactive and unstable lipid hydroperoxides.
Synergistic effects of antioxidative peptides from rice bran
 Synergistic effects of antioxidative peptides from rice bran Pichamon Kiatwuthinon 1,*, Neeracha Lapanusorn 1, Anunyaporn Phungsom 1, Wirawan Tinanchai 1 1 Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science,
Synergistic effects of antioxidative peptides from rice bran Pichamon Kiatwuthinon 1,*, Neeracha Lapanusorn 1, Anunyaporn Phungsom 1, Wirawan Tinanchai 1 1 Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science,
High Content Imaging : Meaningful pictures for relevant results in dermocosmetology
 High Content Imaging : Meaningful pictures for relevant results in dermocosmetology We deliver High Content screening services with exhaustive, high quality and robust phenotypic data. Nathalie MAUBON,
High Content Imaging : Meaningful pictures for relevant results in dermocosmetology We deliver High Content screening services with exhaustive, high quality and robust phenotypic data. Nathalie MAUBON,
CHEM 105 Module 11 QUIZ
 CHEM 105 Module 11 QUIZ 1. Which of the following common kitchen chemicals are toxic at certain concentration or under certain biological conditions? A) table salt B) cane sugar C) baking soda D) All of
CHEM 105 Module 11 QUIZ 1. Which of the following common kitchen chemicals are toxic at certain concentration or under certain biological conditions? A) table salt B) cane sugar C) baking soda D) All of
Lankenau Institute for Medical Research Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Lankenau Institute for Medical Research Annual Progress Report: Formula Grant Reporting Period January, June, Formula Grant Overview The Lankenau Institute for Medical Research received $6,99 in formula
Lankenau Institute for Medical Research Annual Progress Report: Formula Grant Reporting Period January, June, Formula Grant Overview The Lankenau Institute for Medical Research received $6,99 in formula
ab Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 ab102530 Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of glutathione peroxidase activity in various samples. This product is for
ab102530 Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of glutathione peroxidase activity in various samples. This product is for
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 ab111749 Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Myeloperoxidase activity in various samples. This product is for
ab111749 Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Myeloperoxidase activity in various samples. This product is for
David Quig, PhD Doctor s Data, Inc.
 Basic Pharmacology of DMSA, DMPS and Ca-EDTA David Quig, PhD Doctor s Data, Inc. Basic Toxicology Exposure Assimilation Retention Toxicity Exposure Toxicity Low-level Exposure & Retention Exposure Assimilation
Basic Pharmacology of DMSA, DMPS and Ca-EDTA David Quig, PhD Doctor s Data, Inc. Basic Toxicology Exposure Assimilation Retention Toxicity Exposure Toxicity Low-level Exposure & Retention Exposure Assimilation
What Is Oxidative Stress?
 Oxidative Stress What Is Oxidative Stress? JMAJ 45(7): 271 276, 2002 Toshikazu YOSHIKAWA* and Yuji NAITO** Professor* and Associate Professor**, First Department of Medicine, Kyoto Prefectural University
Oxidative Stress What Is Oxidative Stress? JMAJ 45(7): 271 276, 2002 Toshikazu YOSHIKAWA* and Yuji NAITO** Professor* and Associate Professor**, First Department of Medicine, Kyoto Prefectural University
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Acetone and methanol fruit extracts of Terminalia paniculata inhibit HIV-1 infection in vitro Ankita Durge a, Pratiksha Jadaun a, Ashish Wadhwani a, Ashish A. Chinchansure b, Madhukar
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Acetone and methanol fruit extracts of Terminalia paniculata inhibit HIV-1 infection in vitro Ankita Durge a, Pratiksha Jadaun a, Ashish Wadhwani a, Ashish A. Chinchansure b, Madhukar
causing mercury toxicity. It prevents it. Title of Conference
 Ocean fish Title consumption of Presentation does not contribute to causing mercury toxicity. It prevents it. Title of Conference 65 th PFT Conference Presenter February 24, 2014 Monterey, Ca Date Nicholas
Ocean fish Title consumption of Presentation does not contribute to causing mercury toxicity. It prevents it. Title of Conference 65 th PFT Conference Presenter February 24, 2014 Monterey, Ca Date Nicholas
ab Glutathione Detection Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 ab 65322 Glutathione Detection Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Glutathione levels in various samples. This product is for research use
ab 65322 Glutathione Detection Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Glutathione levels in various samples. This product is for research use
Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic. etching of gold nanorods
 Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic etching of gold nanorods Xin Liu, Shuya Zhang, Penglong Tan, Jiang Zhou, Yan Huang, Zhou Nie* and Shouzhuo Yao State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic etching of gold nanorods Xin Liu, Shuya Zhang, Penglong Tan, Jiang Zhou, Yan Huang, Zhou Nie* and Shouzhuo Yao State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
AN ACTIVE SHELTER AGAINST POLLUTION V.16
 AN ACTIVE SHELTER AGAINST POLLUTION V.16 THE SKIN IS CONSTANTLY EXPOSED The skin is an interface and thus is constantly exposed to environmental agents: Sun radiation Smoke Air pollution Free radicals
AN ACTIVE SHELTER AGAINST POLLUTION V.16 THE SKIN IS CONSTANTLY EXPOSED The skin is an interface and thus is constantly exposed to environmental agents: Sun radiation Smoke Air pollution Free radicals
Source Variation in Antioxidant Capacity of Cranberries from Eight U.S. Cultivars
 33 Source Variation in Antioxidant Capacity of Cranberries from Eight U.S. Cultivars Peter J. Schaaf Faculty Sponsors: Margaret A. Maher and Ted Wilson, Departments of Biology/Microbiology ABSTRACT Antioxidants
33 Source Variation in Antioxidant Capacity of Cranberries from Eight U.S. Cultivars Peter J. Schaaf Faculty Sponsors: Margaret A. Maher and Ted Wilson, Departments of Biology/Microbiology ABSTRACT Antioxidants
Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells
 Supporting Information for Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells Sasa Zhu, Weiying Lin,* Lin Yuan State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Supporting Information for Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells Sasa Zhu, Weiying Lin,* Lin Yuan State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Open Access Inhibition of the Oxidation of Corn Oil Stripped of Tocopherols and Refined Olive Oil by Thiols
 The Open Food Science Journal, 2009, 3, 103-107 103 Open Access Inhibition of the Oxidation of Corn Oil Stripped of Tocopherols and Refined Olive Oil by Thiols Ioannis G. Roussis*,1, Despina Papadopoulou
The Open Food Science Journal, 2009, 3, 103-107 103 Open Access Inhibition of the Oxidation of Corn Oil Stripped of Tocopherols and Refined Olive Oil by Thiols Ioannis G. Roussis*,1, Despina Papadopoulou
EVALUATION OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF A 7% ACCELERATED HYDROGEN PEROXIDE-BASED FORMULATION AGAINST CANINE PARVOVIRUS
 Final report submitted to Virox Technologies, Inc. EVALUATION OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF A 7% ACCELERATED HYDROGEN PEROXIDE-BASED FORMULATION AGAINST CANINE PARVOVIRUS Syed A. Sattar, M.Sc., Dip. Bact., M.S.,
Final report submitted to Virox Technologies, Inc. EVALUATION OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF A 7% ACCELERATED HYDROGEN PEROXIDE-BASED FORMULATION AGAINST CANINE PARVOVIRUS Syed A. Sattar, M.Sc., Dip. Bact., M.S.,
Factors Affecting Oxidative Stability of Pork, Beef, and Chicken Meat
 Animal Industry Report AS 654 ASL R2257 2008 Factors Affecting Oxidative Stability of Pork, Beef, and Chicken Meat Byung R. Min Ki C. Nam Joseph C. Cordray Dong U. Ahn, duahn@iastate.edu Recommended Citation
Animal Industry Report AS 654 ASL R2257 2008 Factors Affecting Oxidative Stability of Pork, Beef, and Chicken Meat Byung R. Min Ki C. Nam Joseph C. Cordray Dong U. Ahn, duahn@iastate.edu Recommended Citation
Glutathione Reductase Assay Kit
 Glutathione Reductase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0881 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Glutathione Reductase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0881 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
MPO Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit
 MPO Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1337 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Background Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a member of the heme peroxidase superfamily
MPO Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1337 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Background Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a member of the heme peroxidase superfamily
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red)
 Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2525 200 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2525 200 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
CONSEQUENCES OF METHYL MERCURY EXPOSURE ON LUNG HISTO-ARCHITECTURE IN RAT Y. Nagamalleswari 1, V. Reddy Dhyana 2, V. Karunasri 3 and P.
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 2, 2017, 1095 1099 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) CONSEQUENCES OF METHYL MERCURY EXPOSURE ON LUNG HISTO-ARCHITECTURE IN RAT Y.
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 2, 2017, 1095 1099 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) CONSEQUENCES OF METHYL MERCURY EXPOSURE ON LUNG HISTO-ARCHITECTURE IN RAT Y.
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line
 Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals?
 The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
Montri Punyatong 1, Puntipa Pongpiachan 2 *, Petai Pongpiachan 2 Dumnern Karladee 3 and Samlee Mankhetkorn 4 ABSTRACT
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 676-681 (2008) Cytotoxicity of Crude Proanthocyanidin Extract from Purple Glutinous Rice Bran (Oryza sativa L.) (Kum Doi Saket) Compared with Cyanidin 3-Glucoside on X63 Myeloma
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 676-681 (2008) Cytotoxicity of Crude Proanthocyanidin Extract from Purple Glutinous Rice Bran (Oryza sativa L.) (Kum Doi Saket) Compared with Cyanidin 3-Glucoside on X63 Myeloma
Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit
 Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
Mechanisms of dopamine and dobutamine interference in biochemical tests that use peroxide and peroxidase to generate chromophore
 Clinical Chemistry 44:1 155 160 (1998) General Clinical Chemistry Mechanisms of dopamine and dobutamine interference in biochemical tests that use peroxide and peroxidase to generate chromophore Brad S.
Clinical Chemistry 44:1 155 160 (1998) General Clinical Chemistry Mechanisms of dopamine and dobutamine interference in biochemical tests that use peroxide and peroxidase to generate chromophore Brad S.
Investigations on its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potential
 - 1 - CITROZINE Investigations on its antioxidative and CITROFRESH SUPERCONCENTRATE anti-inflammatory potential Investigator and responsible for the correctness of the test protocol, results, conclusions
- 1 - CITROZINE Investigations on its antioxidative and CITROFRESH SUPERCONCENTRATE anti-inflammatory potential Investigator and responsible for the correctness of the test protocol, results, conclusions
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES
 ii LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES GENERAL INTRODUCTION Fig. 1 Effect of Pb on antioxidant enzymes and cofactors leading to inactivation of enzyme activity Fig. 2 Rationale between Pb exposures among low SES
ii LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES GENERAL INTRODUCTION Fig. 1 Effect of Pb on antioxidant enzymes and cofactors leading to inactivation of enzyme activity Fig. 2 Rationale between Pb exposures among low SES
