P53 IS UNSTABLE DURING METASTATIC DEVELOPMENT OF THE HUMAN BREAST CANCER: A COMPARISON BETWEEN THE PRIMARY TUMOR AND LYMPH NODE METASTASIS
|
|
|
- Morgan Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE P53 IS UNSTABLE DURING METASTATIC DEVELOPMENT OF THE HUMAN BREAST CANCER: A COMPARISON BETWEEN THE PRIMARY TUMOR AND LYMPH NODE METASTASIS ABSTRACT Veaceslav Fulga¹ 1 Department of Histology, Cytology and Embryology, Nicolae Testemitanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova Objective. The aim of this study was to highlight p53 expression during metastatic progression of invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (NST) and to evaluate its role in stratifying patients based on molecular classification. Material and Methods. The specimens, primary tumors and corresponding lymph node metastases (LNM) from 84 patients were immunohistochemically stained for estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)-2, basal cytokeratin CK5 and nuclear proteins Ki67, p53. Results. No statistical significant differences of p53 expression were found between the two compared sites, but the p53 instability was found in 11 cases (13.2%). Switch of molecular subtype was noticed in 22.62% of cases. Only 5 cases of p53 transitions, from positive to negative status, were involved in molecular subtypes switch, from Luminal B to Luminal A. Conclusions. The p53 marker and molecular subtypes are not stable during tumor progression. Breast cancer during its metastatic development can gain or lose the p53 expression and cases developed with p53 vanishing in metastasis prevailed. A link between p53 instability and molecular subtypes switch was found only between p53 loss and Luminal B to Luminal A transition. Key Words: p53, molecular subtypes, breast cancer, metastases. INTRODUCTION Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with different clinical outcomes. It is one of the most common cancers in females worldwide. Over- or underexpression of apoptotic genes can result with the lack of cell death, mechanism that has been also demonstrated in breast cancer. Beside of well-known prognostic factors, as histological type, tumor size, grade and vascular invasion, identification of new molecular markers has become the objective of many research studies. Such a potential marker is p53 protein. The p53 is one of the most intriguing potential factors involved in the metastatic process, which directly controls the transcription of genes responsible for cell adhesion, motility, invasion and anoikis. The wild-type p53 tumor suppressor protein acts in G1 cell cycle and in response to DNA damage promotes repairing or cell death. This protein is not expressed in normal breast based on immunohistochemical evaluation, due to its short time of expression (action). Loss of its function was associated with poor outcome in breast cancer [1]. Intriguing, but there are no data until now regarding the simultaneous expression of p53, ER, PR, HER2, CK5, of molecular subtypes in primary tumor and corresponding metastatic axillary lymph nodes. The purpose of the current study was to highlight p53 expression in the primary tumor and corresponding lymph node metastases (LNM) in association with ER, PR, HER2, basal cytokeratin CK5 status and molecular subtypes assessed by above mentioned surrogate markers. As a result we found that p53 marker and molecular subtypes are not stable during metastatic process. MATERIAL AND METHODS Patients. There were analyzed specimens of breast carcinoma and corresponding axillary lymph node metastases from 84 patients of years old (57.7±1.3, with a median of 58.5). All patients underwent a Madden modified radical mastectomy with lymph nodes dissection, without prior chemoand radiotherapy. Histopathological diagnosis was assessed by two pathologists and cases suitable for immunohistochemistry were carefully selected: all 84 cases were diagnosed as NST (no special type) of breast carcinoma, lobular and special types of cancer, as well equivocal results of staining/interpretation were excluded. Specimens processing and immunohistochemistry. The specimens were fixed in 10% buffered formalin and paraffin embedded (Paraplast High Melt, Leica Biosystems). Primary tumor and its LNM were placed in one block. The 5-µm thick sections were immunohistochemically assessed with 6 markers: ER (clone Er/6F11, Leica Biosystems), PR (clone Pr16, Leica Biosystems), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/polyclonal, DakoCytomation), marker of proliferation Ki67 (clone K2, Leica Biosystems), basal cytokeratin CK5 (clone XM26, Leica Biosystems) and pro-apoptotic protein p53 (p53/do-7, Leica Biosystems). Incubation with primary antibodies was followed by the use of HercepTest PharmDx Kit (DakoCytomation) and Bond Polymer Refine Detection System (Leica Biosystems, Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK). All cases were evaluated also by FISH 6 Research and Clinical Medicine, 2017 Vol. 1, Nr. 2
2 as international rules recommend (PathVysion HER- 2 DNA Probe Kit II, Abbott). Slides were processed automatically on Leica Bond-Max autostainer (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). The Harris modified hematoxylin solution (HHS32, SigmaAldrich) was used for counterstaining. Microscopic evaluation. The hormone receptors were scored in according to Allred et al. guideline of ER and PR assessment [2]. Cases scored as +1 to +3 were considered positive. The threshold of positivity was 10%. The HER2 expression was evaluated by LeicaBond Oracle HER2 IHC System (LeicaBiosystem). The HER2 status was interpreted according to American Society of Clinical Oncology recommendations [3]. Cases interpreted as +2 and +3 were considered positive. Leica HER2 control slides ensured the control and accuracy of our decisions. For Ki67 a 14% threshold was used. This marker, as well hormone receptors were counted using a semiquantitative method performed by Suciu et al. [4]. The basal cytokeratin CK5 was interpreted in accordance to Azoulay et al. recommendations [5]. Cases evaluated as +1 to +3 were considered positive. The p53 marker was assessed as Yamashita et al. purposed: 0 no specific staining; +1 less of 10% tumor cells are p53 positive; % of cells express p53; 3 more than 30% exhibit a specific nuclear pattern [6]. Breast stroma and lymph node lymphocytes served as positive control. Based on Goldhirsch et al. recommendation the molecular subtypes were clustered as follow: ER+ and/ or PR+, HER2, CK5-, Ki67<14% as Luminal A; ER+ and/or PR+, HER2+, CK5 as Luminal B/HER2; ER+ and/or PR+, HER2, CK5, Ki67>14% as Luminal B/ Ki67; ER+ and/or PR+, HER2+, CK5, Ki67>14% as Luminal B/HER2/Ki67; ER, PR, HER2+, CK5 as HER2-overexpressed; ER, PR, HER2 and CK5+ as Basal-like; ER, PR, HER2 and CK5- as 5NP (5-negative phenotype) [7]. Statistical analysis. For descriptive statistics (the mean and standard error of the mean, the median) and Pearson s correlation was used WinStat software (R. Fitch Software, Bad Krozingen, Germany). The p53 values from 2 sites were compared by t-dependent test. For all tests a value of p<0.05 was considered significant. Ethical issues. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Nicolae Testemitanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy from Chisinau, Republic of Moldova (approval number 21/13/ ). RESULTS The most frequent histological grade was G2, found in 45 cases (53.6%), G3 in 40.5% or 34 cases and G1 constitute 6%/5 cases. The p53 positive expression vs tumors histological grade was clustered as 1case or 1.2% with G1, 29 cases/34.5% with G2, 21 cases/25% with G3. The hormone receptors (ER, PR) had the highest rate of positivity compared to other analyzed markers in primary tumor. The p53 was determined as positive in majority of NST tumors 51 cases/60.7%. Its expression vs ER, PR, HER2 and CK5 is given in details in Figure 1. Fig.1. The p53 expression in relation to ER, PR, HER2 and CK5 scores at primary site. The numbers from table below indicate the number of cases (from 84). The Ki67 marker was considered positive ( 14) in 50 cases/59.52% of primary tumors. The negative p53 expression was supported in 12 cases/14.3% by a high proliferation rate and in 21 cases/25% by a Ki67 level less than 14. The positive p53 cases were a highly proliferating in 45.2% (38 cases) and low proliferating in 15.5% (13 cases). The most often subtype at primary site was Luminal B (45 cases/53.6%), followed by Luminal A (26 cases/31%) and hormone-negative group (13 cases/15.5%). The positive p53 marker had the highest expression in Luminal B/Ki67 group (27 cases/32.1%), followed in by Luminal A (9 cases/10.7%), Luminal B/ HER2/Ki67 (6 cases/8.3%) and HER2 (5 cases/6%) (Table 1). By comparing the p53 scores from both sites, t-test revealed no significant statistical differences (t=1.83, p<0.07). The comparison of molecular profile of primary tumor and its LNM revealed a transition of subtype to another one in 19 cases/22.62% (Table 1). Veaceslav Fulga 7
3 Table 1. Molecular subtypes, Ki67 activity and p53 evolution during breast cancer progression: a comparative study of primary tumor and corresponding metastases. Molecular subtype p53 Ki67 Tm Mt Tm Mt Tm Mt No % 5NP 5NP 3 3 >14 >14 1 1,2 5NP 5NP 3 3 >14 <14 1 1,2 5NP 5NP 0 0 <14 <14 1 1,2 BasalLike 5NP 0 0 >14 <14 1 1,2 BasalLike BasalLike 3 3 >14 >14 1 1,2 HER2 HER2 0 0 >14 >14 1 1,2 HER2 HER2 0 1 <14 >14 1 1,2 HER2 HER2 2 3 >14 >14 1 1,2 HER2 HER2 2 2 <14 >14 1 1,2 HER2 HER2 2 2 <14 <14 1 1,2 HER2 HER2 2 1 >14 >14 1 1,2 HER2 HER2 3 3 <14 >14 1 1,2 HER2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal A 5NP 0 0 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal A 0 0 <14 < ,7 Luminal A Luminal A 2 0 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal A 0 1 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal A 3 2 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal A 2 3 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal A 2 1 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal A 2 2 <14 <14 2 2,4 Luminal A Luminal A 3 3 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal B/HER2 2 2 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal B/Ki <14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal A Luminal B/Ki <14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2 Luminal A 0 0 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2 Luminal B/HER2 1 1 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2 Luminal B/HER2 0 0 <14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki67 HER2 3 3 >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki67 Luminal A 2 0 >14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki67 Luminal B/HER2 1 1 >14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki67 Luminal B/HER2/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki67 Luminal B/HER2/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki67 Luminal B/HER2/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/HER2/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 BasalLike 3 3 >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal A 2 0 >14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal A 3 3 >14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal A 0 0 >14 <14 2 2,4 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal A 2 2 >14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal A 3 0 >14 <14 2 2,4 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal A 1 0 >14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal A 1 1 >14 <14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 3 3,6 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 3 3,6 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 5 6,0 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 4 4,8 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 5 6,0 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 2 2,4 Luminal B/Ki67 Luminal B/Ki >14 >14 1 1,2 Note: Molecular subtypes shifted cases are selected with Bold and primed with gray color. The p53 transitions are selected with Bold, Italics and Underlined. Tm primary tumor, Mt metastases. 8 Research and Clinical Medicine, 2017 Vol. 1, Nr. 2 Total ,0
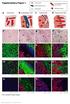
4 The p53 shifted in 11 cases/13.1% (Fig.2). In 8 cases/9.5% metastases lost p53 and in 3 cases/3.6% the tumor begins to express this marker in the metastatic site. A particular mention of 5 cases of p53 transition, from positive to negative status, that were involved in molecular subtypes switch, from Luminal B to Luminal A. The statistical assays revealed a significant, positive correlation of p53 expression with Ki67 activity (r=0.28, p=0.006) and negative correlations with ER (r=-0.22, p=0.002), PR (r=-0.20, p=0.003) and molecular subtype (r=-0.19, p=0.04). DISCUSSIONS Fig.2. The representative images of ER (assessed with Er/6F11 marker) and p53 (clone p53/do-7) transitions during metastatic progression, from positive status at primary site to negative in LNM. Note that primary tumor and its lymph node metastasis were processed on the same slide. DISCUSSIONS In previous studies we described in details that molecular subtypes and anti-apoptotic receptor BCL2 are unstable during metastatic development of breast cancer [8,9]. Now we focused the research on the pro-apoptotic marker p53. The p53 regulates cell proliferation and is considered the guardian of genome stability. By several transcription-regulating functions, including the induction of G1 cell cycle arrest by activation of p21 and by downregulation of BCL2 it induces the apoptosis in response to irreparable DNA damage. Due to its short life, the p53 protein is not usually detected immunohistochemically in normal tissues. The TP53 gene, which encodes p53 protein, is considered as the most frequent (more than 50%) mutated gene in human cancers. In breast cancers about one-third of cases have mutations in the TP53 gene, which are associated with high histological grade and clinical aggressiveness. Most TP53 alterations found in breast carcinomas are point mutations leading to the synthesis of a stable, mal-functional, and non-degradable protein that accumulates in tumor cells. The result of these mutations is detected by immunohistochemical assays as a nuclear accumulation of the protein. Yamashita et al. found that the expression of p53 is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer [6]. The authors noticed a significant correlation of p53 with HER2 and Ki67 level, in detriment of overall survival. Our study confirms the positive association of p53 expression with the proliferation activity. Silwal-Pandit et al. demonstrated that TP53 mutations have a different clinical relevance in molecular subtypes of breast cancer and suggest diverse roles for TP53 in the biology of breast cancer development [10]. TP53 mutations were associated with increased mortality in patients with Luminal B, HER2-enriched and normallike tumors, but not in cases with Luminal A and Basallike tumors. In addition, the presence of p53 was found to be an independent marker of poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive cases. In our cases predominated a negative correlation of p53 to ER and PR scores. The present study emphasized p53 instability during breast cancer metastatic development. In 11 cases p53 changed its expression, 8 of which evolved with p53 vanishing at metastatic site. A question arises then: does the malignant cell could repair p53 itself at metastatic site or primary tumor is heterogeneous by cellular components? In 2005 Weigelt et al. summarized the possible models of metastatic process development [11]. The prevailing model suggests that metastatic capacity is a late, acquired event in tumorigenesis. Other ideas consider that metastatic ability might be an inherent feature of tumors or breast cancer is intrinsically a systemic disease. The switch of markers expression in LNM, especially of p53 in our case pushes on us to debate the most appropriate metastatic model. The traditional and spontaneous models could be taken in consideration in case that tumor has the same markers expression at both sites (77.4% of cases). We correlated the markers expression from primary site with homonym receptors from LNM and in majority of cases received the same grade of association, which support the idea that in metastatic site is the same type of tumor. But what about the 22.6% of subtypes transitions, as well p53 and other receptor switches mentioned by Raica et al. [8]? In these cases probably the most applicable theories are of clonal dominance and genometastasis hypothesis. Anyway, it remains unclear which factors are triggering the acquiring or losing of tumors features in metastatic site. In summary, p53 marker and molecular subtypes are Veaceslav Fulga 9
5 not stable during tumor metastatic progression. Breast cancer can gain or lose the p53 expression and cases developed with p53 vanishing in metastasis, prevailed. A linkage of p53 instability and molecular subtypes switch was determined only between p53 loss and Luminal B to Luminal A transitions. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The author is thankful to Professor Marius Raica and entire team from the Department of Microscopic Morphology/Histology, Angiogenesis Research Center, Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara, Romania, by whose enormous support this work could be done. This work was sustained by Bilateral Cooperation Romania-Moldova grant /RoF of Academy of Sciences of Moldova. REFERENCES 1. Arun B, Kilic G, Yen C, Foster B, Yardley D, Gaynor R, Ashfaq R. Correlation of BCL2 and p53 expression in primary breast tumors and corresponding metastatic lymph nodes. Cancer 2003;98(12): Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol 1998;11: Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, et al. Recommendations for Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical PRactice Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol 2013;31(31): Suciu C, Muresan AM, Cornea R, Suciu O, Dema A, Raica M. Semi automated evaluation of Ki 67 index in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncol Lett 2014;7: Azoulay S, Laé M, Fréneaux P, Merle S, Al Ghuzlan A, Chnecker C, et al. KIT is highly expressed in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast, a basal-like carcinoma associated with a favorable outcome. Mod Pathol 2005;18(12): Yamashita H, Nishio M, Toyama T, Sugiura H, Zhang Z., Kobayashi S, Iwase H. Coexistence of HER2 over-expression and p53 protein accumulation is a strong prognostic molecular marker in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2004;6:R Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart- Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer. Ann Oncol 2013;24(9): Raica M, Cîmpean AM, Ceausu RA, Fulga V, Nica C, Rudico L, Saptefrati L. Hormone receptors and HER2 expression in primary breast carcinoma and corresponding lymph node metastasis: do we need both? Anticancer Res 2014;34(3): Fulga V, Ceausu AR, Cimpean AM, Saptefrati L, Raica M. B-cell lymphoma-2 receptor in human primary breast cancer and its lymph node metastases: more than a surrogate marker. Curierul medical 2017;1(60):3-9. ISSN [Epub ahead of print]. 10. Silwal-Pandit L, Vollan HK, Chin SF, Rueda OM, McKinney S, Osako T, et al. TP53 mutation spectrum in breast cancer is subtype specific and has distinct prognostic relevance. Clin Cancer Res 2014;20(13): Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van t Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer 2005;5(8): Research and Clinical Medicine, 2017 Vol. 1, Nr. 2
EXPRESSION OF CK5 BASAL CYTOKERATIN DURING METASTATIC DEVELOPMENT OF BREAST CARCINOMA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EXPRESSION OF CK5 BASAL CYTOKERATIN DURING METASTATIC DEVELOPMENT OF BREAST CARCINOMA Veaceslav Fulga 1 *, Amalia Raluca Balica 2, Anca Maria Cîmpean 2, Lilian Șaptefrați 1, Marius Raica
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EXPRESSION OF CK5 BASAL CYTOKERATIN DURING METASTATIC DEVELOPMENT OF BREAST CARCINOMA Veaceslav Fulga 1 *, Amalia Raluca Balica 2, Anca Maria Cîmpean 2, Lilian Șaptefrați 1, Marius Raica
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer
 Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Elmer ress Original Article World J Oncol. 2017;8(3):71-75 A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Utility of AJCC 8th Edition Cancer Staging System for Breast Cancer Hui Hu a, Wei Wei a, Xin Yi a, Ling Xin
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours
 Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K)
 Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Molecular classification of breast cancer implications for pathologists. Sarah E Pinder
 Molecular classification of breast cancer implications for pathologists Sarah E Pinder Courtesy of CW Elston Histological types Breast Cancer Special Types 17 morphological special types 25-30% of all
Molecular classification of breast cancer implications for pathologists Sarah E Pinder Courtesy of CW Elston Histological types Breast Cancer Special Types 17 morphological special types 25-30% of all
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing. Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine)
 Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy
 Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
Case Series Clinical and pathological portraits of axillary presentation breast cancer and effects of preoperative systemic therapy Ling Xu 1*, Fang Li 1,2*, Yinhua Liu 1, Xuening Duan 1, Jingming Ye 1,
Recent advances in breast cancers
 Recent advances in breast cancers Breast cancer is a hetrogenous disease due to distinct genetic alterations. Similar morphological subtypes show variation in clinical behaviour especially in response
Recent advances in breast cancers Breast cancer is a hetrogenous disease due to distinct genetic alterations. Similar morphological subtypes show variation in clinical behaviour especially in response
# Best Practices for IHC Detection and Interpretation of ER, PR, and HER2 Protein Overexpression in Breast Cancer
 #1034 - Best Practices for IHC Detection and Interpretation of ER, PR, and HER2 Protein Overexpression in Breast Cancer Richard W. Cartun, MS, PhD Andrew Ricci, Jr, MD Department of Pathology Hartford
#1034 - Best Practices for IHC Detection and Interpretation of ER, PR, and HER2 Protein Overexpression in Breast Cancer Richard W. Cartun, MS, PhD Andrew Ricci, Jr, MD Department of Pathology Hartford
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience
 Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Kristen E. Muller, DO, Jonathan D. Marotti, MD, Vincent A. Memoli, MD, Wendy A. Wells, MD, and Laura J. Tafe, MD
 AJCP / Original Article Impact of the 2013 ASCO/CAP HER2 Guideline Updates at an Academic Medical Center That Performs Primary HER2 FISH Testing Increase in Equivocal Results and Utility of Reflex Immunohistochemistry
AJCP / Original Article Impact of the 2013 ASCO/CAP HER2 Guideline Updates at an Academic Medical Center That Performs Primary HER2 FISH Testing Increase in Equivocal Results and Utility of Reflex Immunohistochemistry
Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67 and p53 Expressions to Histopathology Grading of Breast Cancer in Makassar, Indonesia
 Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Question 1 A. ER-, PR-, HER+ B. ER+, PR+, HER2- C. ER-, PR+, HER2- D. ER-, PR-, HER2- E. ER-, PR+, HER2+
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Question 1 The tumor depicted on the next slide
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Question 1 The tumor depicted on the next slide
Prognostic implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes in male breast cancer
 JBUON 2017; 22(2): 377-382 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes in male
JBUON 2017; 22(2): 377-382 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes in male
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer
 Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Journal of Advance Research in Medical & Health Science
 ER, PR, cerb-b2, ki-67, p53, Bcl-2, CYCLIN-D1 EXPRESSIONS IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMAS AND COMPARISON WITH THE CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL PARAMETERS 1 Özgür İlhan Çelik, 2 Serkan Yaşar Çelik, 3 Yelda
ER, PR, cerb-b2, ki-67, p53, Bcl-2, CYCLIN-D1 EXPRESSIONS IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMAS AND COMPARISON WITH THE CLINICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL PARAMETERS 1 Özgür İlhan Çelik, 2 Serkan Yaşar Çelik, 3 Yelda
Immunohistochemical Expression of Hormone Receptors and The Histological Characteristics of Biochemically Hormone Receptor Negative Breast Cancers
 Breast Cancer Vol. 14 No. 1 January 2007 Original Article Immunohistochemical Expression of Hormone Receptors and The Histological Characteristics of Biochemically Hormone Receptor Negative Breast Cancers
Breast Cancer Vol. 14 No. 1 January 2007 Original Article Immunohistochemical Expression of Hormone Receptors and The Histological Characteristics of Biochemically Hormone Receptor Negative Breast Cancers
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts
 Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
 JBUON 2018; 23(4): 877-882 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
JBUON 2018; 23(4): 877-882 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti. Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS
 Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Carcinoma mammario: le istologie non frequenti Valentina Guarneri Università di Padova IOV-IRCCS Histological diversity of breast adenocarcinomas Different histological types are defined according to specific
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Pathology. AGO e. V. in der DGGG e.v. sowie in der DKG e.v.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Immunohistochemistry in Breast Pathology- Brief Overview of the Technique and Applications in Breast Pathology
 SMGr up Immunohistochemistry in Breast Pathology- Brief Overview of the Technique and Applications in Breast Pathology Bhanumathi K Rao 1 * 1 Department of Biochemistry, JSS Medical College, a constituent
SMGr up Immunohistochemistry in Breast Pathology- Brief Overview of the Technique and Applications in Breast Pathology Bhanumathi K Rao 1 * 1 Department of Biochemistry, JSS Medical College, a constituent
HistoCyte Laboratories Ltd
 HistoCyte Laboratories Ltd Progesterone Receptor: The neglected breast receptor! Dr Ian Milton & Colin Tristram November 2018 UKNEQAS Autumn meeting Introduction Progesterone is an important prognostic
HistoCyte Laboratories Ltd Progesterone Receptor: The neglected breast receptor! Dr Ian Milton & Colin Tristram November 2018 UKNEQAS Autumn meeting Introduction Progesterone is an important prognostic
XXV Congreso de la Sociedad Española de Anatomía Patológica y División Española de la International Academy of Pathology
 XXV Congreso de la Sociedad Española de Anatomía Patológica y División Española de la International Academy of Pathology NUEVOS FENOTIPOS DEL CÁNCER DE MAMA: NUEVOS PROBLEMAS PARA EL PATÓLOGO? Tienen actualmente
XXV Congreso de la Sociedad Española de Anatomía Patológica y División Española de la International Academy of Pathology NUEVOS FENOTIPOS DEL CÁNCER DE MAMA: NUEVOS PROBLEMAS PARA EL PATÓLOGO? Tienen actualmente
Applications of IHC. Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin
 Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Pathology Dept.
 Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Pathology Dept. Judith Sandbank M.D. Pathology Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center ISRAEL jsandbank@asaf.health.gov.il 2 nd IBDC, 9 th February, 2012 Pathology as
Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Pathology Dept. Judith Sandbank M.D. Pathology Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center ISRAEL jsandbank@asaf.health.gov.il 2 nd IBDC, 9 th February, 2012 Pathology as
Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the. Subtypes. Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy
 Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the Classification of Molecular Subtypes Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy We know it is many diseases Breast cancer is
Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the Classification of Molecular Subtypes Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy We know it is many diseases Breast cancer is
Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors)
 Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors) Kael Mikesell, DO McKay-Dee Hospital May 14, 2015 Outline Update to DNA Testing
Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors) Kael Mikesell, DO McKay-Dee Hospital May 14, 2015 Outline Update to DNA Testing
Low ER+ Breast Cancer. Is This a Distinct Group? Nika C. Gloyeske, MD, David J. Dabbs, MD, and Rohit Bhargava, MD ABSTRACT
 Low ER+ Breast Cancer Is This a Distinct Group? Nika C. Gloyeske, MD, David J. Dabbs, MD, and Rohit Bhargava, MD From the Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA.
Low ER+ Breast Cancer Is This a Distinct Group? Nika C. Gloyeske, MD, David J. Dabbs, MD, and Rohit Bhargava, MD From the Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA.
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer.
 Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4. Clinical Case: Pathologic Features
 Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Histological Type. Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer. Nottingham Tenovus Primary Breast Cancer Study. Survival (%) Ian Ellis
 Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological Type
Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological Type
Cancer Cell Research 16 (2017)
 Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Relationship between molecular classification and clinicopathological features of young and medium-elderly breast cancer patients Lili Li
Available at http:// www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN 2161-2609 Relationship between molecular classification and clinicopathological features of young and medium-elderly breast cancer patients Lili Li
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide
 Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor survival in breast cancer patients
 Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Estrogen Receptor, Progesterone Receptor, and Her-2/neu Oncogene Expression in Breast Cancers Among Bangladeshi Women
 Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2010 Estrogen Receptor, Progesterone Receptor, and Her-2/neu Oncogene Expression in Breast Cancers Among Bangladeshi Women
Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2010 Estrogen Receptor, Progesterone Receptor, and Her-2/neu Oncogene Expression in Breast Cancers Among Bangladeshi Women
A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast
 Original Research Article A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast E. Rajesh Goud 1, M. Muralidhar 2*, M. Srinivasulu 3 1Senior
Original Research Article A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast E. Rajesh Goud 1, M. Muralidhar 2*, M. Srinivasulu 3 1Senior
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Edith Peterson Mitchell, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine and Medical Oncology Program Leader, Gastrointestinal Oncology Department
Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Edith Peterson Mitchell, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine and Medical Oncology Program Leader, Gastrointestinal Oncology Department
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments
 FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
Clinical pathological and epidemiological study of triple negative breast cancer
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajay A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 217 Jun;5(6):2657-2661 www.msjonline.org pissn 232-71 eissn 232-12 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/232-12.ijrms2172465
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajay A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 217 Jun;5(6):2657-2661 www.msjonline.org pissn 232-71 eissn 232-12 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/232-12.ijrms2172465
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Expression of androgen receptors in primary breast cancer
 Annals of Oncology 21: 488 492, 2010 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp510 Published online 3 November 2009 Expression of androgen receptors in primary breast cancer S. Park 1, J. Koo 2, H. S. Park 1, J.-H. Kim 1,
Annals of Oncology 21: 488 492, 2010 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp510 Published online 3 November 2009 Expression of androgen receptors in primary breast cancer S. Park 1, J. Koo 2, H. S. Park 1, J.-H. Kim 1,
10/15/2012. Biologic Subtypes of TNBC. Topics. Topics. Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical relevance
 Biologic Subtypes of TNBC Andrea L. Richardson M.D. Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Topics Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical
Biologic Subtypes of TNBC Andrea L. Richardson M.D. Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Topics Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical
Breast Cancer. Excess Estrogen Exposure. Alcohol use + Pytoestrogens? Abortion. Infertility treatment?
 Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen Exposure Nulliparity or late pregnancy + Early menarche + Late menopause + Cystic ovarian disease + External estrogens exposure + Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen
Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen Exposure Nulliparity or late pregnancy + Early menarche + Late menopause + Cystic ovarian disease + External estrogens exposure + Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen
The Expression of Basal Cytokeratins in Breast Cancers
 Global Journal of Medical Research: C Microbiology and Pathology Volume 17 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of Medical Research: C Microbiology and Pathology Volume 17 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Molecular Characterization of Breast Cancer: The Clinical Significance
 Molecular Characterization of : The Clinical Significance Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville
Molecular Characterization of : The Clinical Significance Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville
System-wide Ownership Group: Allina Health Breast Program Committee. Hospital Division Quality Council: August 2018
 Oncology Clinical Service Line System-wide Consensus Guidelines: Evaluation and Management of Breast Lumpectomy and Mastectomy Specimens by Surgeons and Pathologists These guidelines apply to clinical
Oncology Clinical Service Line System-wide Consensus Guidelines: Evaluation and Management of Breast Lumpectomy and Mastectomy Specimens by Surgeons and Pathologists These guidelines apply to clinical
Ki-67 is a biological tumor marker that reflects tumor
 Evaluation of Ki-67 Index in Core Needle Biopsies and Matched Breast Cancer Surgical Specimens Soomin Ahn, MD; Junghye Lee, MD; Min-Sun Cho, MD, PhD; Sanghui Park, MD, PhD; Sun Hee Sung, MD, PhD Context.
Evaluation of Ki-67 Index in Core Needle Biopsies and Matched Breast Cancer Surgical Specimens Soomin Ahn, MD; Junghye Lee, MD; Min-Sun Cho, MD, PhD; Sanghui Park, MD, PhD; Sun Hee Sung, MD, PhD Context.
Breast cancer: Antibody selection, protocol optimzation controls and EQA
 Breast cancer: Antibody selection, protocol optimzation controls and EQA Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry Oud St. Jan/ Old St. John Brugge (Bruges), Belgium June 13th 15nd 2018 Rasmus Røge,
Breast cancer: Antibody selection, protocol optimzation controls and EQA Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry Oud St. Jan/ Old St. John Brugge (Bruges), Belgium June 13th 15nd 2018 Rasmus Røge,
Radiation Therapy for the Oncologist in Breast Cancer
 REVIEW ARTICLE Chonnam National University Medical School Sung-Ja Ahn, M.D. Adjuvant Tamoxifen with or without in Patients 70 Years of Age with Stage I ER-Positive Breast Cancer: Efficacy Outcomes (10
REVIEW ARTICLE Chonnam National University Medical School Sung-Ja Ahn, M.D. Adjuvant Tamoxifen with or without in Patients 70 Years of Age with Stage I ER-Positive Breast Cancer: Efficacy Outcomes (10
Assessment Run B HER2 IHC
 Assessment Run B24 2017 HER2 IHC Material The slide to be stained for HER2 comprised the following 5 materials: IHC: HER2 Score* (0, 1+, 2+, 3+) FISH: HER2 gene/chr 17 ratio** 1. Breast carcinoma, no.
Assessment Run B24 2017 HER2 IHC Material The slide to be stained for HER2 comprised the following 5 materials: IHC: HER2 Score* (0, 1+, 2+, 3+) FISH: HER2 gene/chr 17 ratio** 1. Breast carcinoma, no.
Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer
 Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer Kathy S. Albain, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Dean s Scholar Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Cardinal Bernardin
Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer Kathy S. Albain, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Dean s Scholar Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Cardinal Bernardin
Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 2010
 Original Article Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 21 * DMRT clinical oncology, MSc. pathology. Summary:
Original Article Overview of breast cancerpatients and their prognostic factors treated in Baghdad teaching hospital/ oncology department in the year 21 * DMRT clinical oncology, MSc. pathology. Summary:
2016 Korean Breast Cancer Society. All rights reserved. eissn
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Dis 2016 December; 4(2): 70-76 JBD Journal of Breast Disease Reliability of Core Needle Biopsy in Evaluating Estrogen Receptor, Progesterone Receptor, and Human Epidermal Growth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Breast Dis 2016 December; 4(2): 70-76 JBD Journal of Breast Disease Reliability of Core Needle Biopsy in Evaluating Estrogen Receptor, Progesterone Receptor, and Human Epidermal Growth
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium. Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin
 UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
Her-2/neu expression and its correlation with ER status and various clinicopathological parameters
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00106.X Her-2/neu expression and its correlation with ER status and various clinicopathological parameters Kriti Chauhan 1,*, Monika Garg 2, Abhimanyu
Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00106.X Her-2/neu expression and its correlation with ER status and various clinicopathological parameters Kriti Chauhan 1,*, Monika Garg 2, Abhimanyu
Breast cancer diagnostic solutions Deliver diagnostic confidence
 Breast cancer diagnostic solutions Deliver diagnostic confidence 2 Breast cancer diagnostic solutions Roche Tissue Diagnostics is committed to improving outcomes in breast cancer Breast cancer...the most
Breast cancer diagnostic solutions Deliver diagnostic confidence 2 Breast cancer diagnostic solutions Roche Tissue Diagnostics is committed to improving outcomes in breast cancer Breast cancer...the most
FISH mcgh Karyotyping ISH RT-PCR. Expression arrays RNA. Tissue microarrays Protein arrays MS. Protein IHC
 Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Prevalence of molecular subtypes and prognosis of invasive breast cancer in north-east of Morocco: retrospective study
 BMC Research Notes This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Prevalence of molecular
BMC Research Notes This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Prevalence of molecular
Outcomes of Trastuzumab Therapy for 6 and 12 Months in Indonesian National Health Insurance System Clients with Operable HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.4.1151 Trastuzumab RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcomes of Trastuzumab Therapy for 6 and 12 Months in Indonesian National Health Insurance System Clients with Operable HER2-Positive Breast
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.4.1151 Trastuzumab RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcomes of Trastuzumab Therapy for 6 and 12 Months in Indonesian National Health Insurance System Clients with Operable HER2-Positive Breast
CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS
 CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS S. Chahbouni¹, A. Amarti 2, N. Hammas 3, L. Chbani 3, H. El fatemi 3 1 Department
CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS S. Chahbouni¹, A. Amarti 2, N. Hammas 3, L. Chbani 3, H. El fatemi 3 1 Department
Intro to Cancer Therapeutics
 An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry
 Nat Met, April 2014 Nat Med, April 2014 Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry Journal Club Timo Böge Overview Introduction Conventional Immunohistochemistry
Nat Met, April 2014 Nat Med, April 2014 Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry Journal Club Timo Böge Overview Introduction Conventional Immunohistochemistry
Quality in Control. ROS1 Analyte Control. Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024
 Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Study of expression of P53 in Gastric Carcinoma As a prognostic indicator
 Original Research Article Study of expression of P53 in Gastric Carcinoma As a prognostic indicator K. Padma Malini 1*, Srivani 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
Original Research Article Study of expression of P53 in Gastric Carcinoma As a prognostic indicator K. Padma Malini 1*, Srivani 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer
 Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer
 Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological
Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological
Estrogen receptor (ER)
 Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: Assessment Run B26 2018 Estrogen receptor (ER) No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity* 1. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Tonsil 1-5% Weak
Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: Assessment Run B26 2018 Estrogen receptor (ER) No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity* 1. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Tonsil 1-5% Weak
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Ki-67 Expression and Its Association with Conventional Prognostic Markers in Bhagyashri R Hungund
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Ki-67 Expression and Its Association with Conventional Prognostic Markers in Bhagyashri R Hungund
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF GENERAL MEDICINE DOCTOR S DEGREE THESIS ABSTRACT
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF GENERAL MEDICINE DOCTOR S DEGREE THESIS ABSTRACT CLINICAL, HISTOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY IN A GROUP OF PATIENTS WITH BREAST CANCERS
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF GENERAL MEDICINE DOCTOR S DEGREE THESIS ABSTRACT CLINICAL, HISTOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY IN A GROUP OF PATIENTS WITH BREAST CANCERS
Intratumoral Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer: A Case Report and Molecular Discussion
 Original Case Report Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; July October 20152018; 6(3): 9(4): 339-343 Intratumoral Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer: A Case Report and Molecular Discussion Akbar Safaei,
Original Case Report Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; July October 20152018; 6(3): 9(4): 339-343 Intratumoral Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer: A Case Report and Molecular Discussion Akbar Safaei,
Introduction. Wilfred Truin 1 Rudi M. H. Roumen. Vivianne C. G. Tjan-Heijnen 2 Adri C. Voogd
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2017) 164:133 138 DOI 10.1007/s10549-017-4220-x EPIDEMIOLOGY Estrogen and progesterone receptor expression levels do not differ between lobular and ductal carcinoma in patients
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2017) 164:133 138 DOI 10.1007/s10549-017-4220-x EPIDEMIOLOGY Estrogen and progesterone receptor expression levels do not differ between lobular and ductal carcinoma in patients
Carcinome du sein Biologie moléculaire. Thomas McKee Service de Pathologie Clinique Genève
 Carcinome du sein Biologie moléculaire Thomas McKee Service de Pathologie Clinique Genève Pathology Diagnostic Prognostic information Predictive information The information provided depends on the available
Carcinome du sein Biologie moléculaire Thomas McKee Service de Pathologie Clinique Genève Pathology Diagnostic Prognostic information Predictive information The information provided depends on the available
Heather M. Gage, MD, Avanti Rangnekar, Robert E. Heidel, PhD, Timothy Panella, MD, John Bell, MD, and Amila Orucevic, MD, PhD
 HER2 POSITIVE BREAST CARCINOMA IN THE PRE AND POST ADJUVANT ANTI-HER-2 THERAPY ERA: A SINGLE ACADEMIC INSTITUTION EXPERIENCE IN THE SETTING OUTSIDE OF CLINICAL TRIALS Heather M. Gage, MD, Avanti Rangnekar,
HER2 POSITIVE BREAST CARCINOMA IN THE PRE AND POST ADJUVANT ANTI-HER-2 THERAPY ERA: A SINGLE ACADEMIC INSTITUTION EXPERIENCE IN THE SETTING OUTSIDE OF CLINICAL TRIALS Heather M. Gage, MD, Avanti Rangnekar,
Poly ADP-ribose Polymerase PARP Staining for Immunohistological Investigation of Primary Breast Cancer
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 2, 83 91, June 2013 Original Poly ADP-ribose Polymerase PARP Staining for Immunohistological Investigation of Primary Breast Cancer Genki TSUKUDA 1 2, Yuko DATE 1, Kunio ASONUMA
Showa Univ J Med Sci 25 2, 83 91, June 2013 Original Poly ADP-ribose Polymerase PARP Staining for Immunohistological Investigation of Primary Breast Cancer Genki TSUKUDA 1 2, Yuko DATE 1, Kunio ASONUMA
Re-Classification of Carcinoma of Breast According To Molecular Classification and Its Correlation with Histologic Features.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.PT13 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Re-Classification of Carcinoma of Breast According To Molecular Classification and Its Correlation with Histologic
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.PT13 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Re-Classification of Carcinoma of Breast According To Molecular Classification and Its Correlation with Histologic
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Assessment Run B HER2 IHC
 Assessment Run B26 208 HER2 IHC Material The slide to be stained for HER2 comprised the following 5 materials: IHC: HER2 Score* (0, +, 2+, 3+) FISH: HER2 gene/chr 7 ratio**. Breast carcinoma, no. 2+..3
Assessment Run B26 208 HER2 IHC Material The slide to be stained for HER2 comprised the following 5 materials: IHC: HER2 Score* (0, +, 2+, 3+) FISH: HER2 gene/chr 7 ratio**. Breast carcinoma, no. 2+..3
Hacia la personalización en el tratamiento del cáncer de mama Qué aportan los biomarcadoresen la actualidad?
 Hacia la personalización en el tratamiento del cáncer de mama Qué aportan los biomarcadoresen la actualidad? Primera Parte Federico Rojo XVI Jornada sobre el Cáncer de Mama: Personalización en el Cáncer
Hacia la personalización en el tratamiento del cáncer de mama Qué aportan los biomarcadoresen la actualidad? Primera Parte Federico Rojo XVI Jornada sobre el Cáncer de Mama: Personalización en el Cáncer
Synopsis: However there are huge published articles breast carcinoma in female population,
 Male Invasive Breast Carcinoma: Nine Years Experience at a Single Center in Turkey S Yigit 1, D Etit 1, B Kucukzeybek 1, AE Yenipazar 1,Y Kucukzeybek 2, AA Sarı 1, A Alacacıoglu 2 Affiliations: 1 Department
Male Invasive Breast Carcinoma: Nine Years Experience at a Single Center in Turkey S Yigit 1, D Etit 1, B Kucukzeybek 1, AE Yenipazar 1,Y Kucukzeybek 2, AA Sarı 1, A Alacacıoglu 2 Affiliations: 1 Department
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of YourCare Health Plan
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: HER-2 TESTING IN INVASIVE BREAST OR PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: HER-2 TESTING IN INVASIVE BREAST OR PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases,
Evaluation of HER2/neu oncoprotein in serum and tissue samples of women with breast cancer: Correlation with clinicopathological parameters
 Evaluation of HER2/neu oncoprotein in serum and tissue samples of women with breast cancer: Correlation with clinicopathological parameters Mehdi Farzadnia, Naser TayyebiMeibodi, Fatemeh HomayiShandiz,
Evaluation of HER2/neu oncoprotein in serum and tissue samples of women with breast cancer: Correlation with clinicopathological parameters Mehdi Farzadnia, Naser TayyebiMeibodi, Fatemeh HomayiShandiz,
Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
 Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Product Introduction
 Product Introduction Product Codes: HCL026, HCL027 and HCL028 Contents Introduction to HER2 2 HER2 immunohistochemistry 3 Cell lines as controls 5 HER2 Analyte Control DR IHC 7 HER2 Analyte Control DR
Product Introduction Product Codes: HCL026, HCL027 and HCL028 Contents Introduction to HER2 2 HER2 immunohistochemistry 3 Cell lines as controls 5 HER2 Analyte Control DR IHC 7 HER2 Analyte Control DR
HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
Characterization of immunohistochemical markers in triple negative breast carcinomas
 JBUON 2013; 18(4): 886-890 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characterization of immunohistochemical markers in triple negative breast
JBUON 2013; 18(4): 886-890 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characterization of immunohistochemical markers in triple negative breast
Tumour markers in breast carcinoma correlate with grade rather than with invasiveness
 doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2001.1995, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com Tumour markers in breast carcinoma correlate with grade rather than with invasiveness F Wärnberg
doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2001.1995, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on http://www.bjcancer.com Tumour markers in breast carcinoma correlate with grade rather than with invasiveness F Wärnberg
Determination of HER2 Amplification by In Situ Hybridization. When Should Chromosome 17 Also Be Determined?
 Anatomic Pathology / FISH f o r HER2: Wh e n to Use Ch r o m o s o m e 17 Determination of HER2 Amplification by In Situ Hybridization When Should Chromosome 17 Also Be Determined? John M.S. Bartlett,
Anatomic Pathology / FISH f o r HER2: Wh e n to Use Ch r o m o s o m e 17 Determination of HER2 Amplification by In Situ Hybridization When Should Chromosome 17 Also Be Determined? John M.S. Bartlett,
The Clinical Significance of. Triple-negative Phenotype on. Cancer Patients
 The Clinical Significance of Triple-negative Phenotype on Prognosis of Young Age( 35) Breast Cancer Patients IM-KYUNG KIM Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University The Clinical Significance
The Clinical Significance of Triple-negative Phenotype on Prognosis of Young Age( 35) Breast Cancer Patients IM-KYUNG KIM Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei University The Clinical Significance
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
