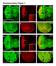
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
|
|
|
- Helen Haynes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue specific genes for each one of the 30 tissues analyzed. (b) Plot representation of the weighed expression of the colon genes versus skin genes. Circle highlights COLO741 cells showing high skin score. (c) Log2 expression of the skin-specific tyrosinase (TYR) gene in 152 cell lines. Circle highlights COLO741 cells showing an outlier expression profile for the TYR gene. (d) Plot representation of the weighed expression of the colon genes versus small intestine genes. Circle highlights Hutu80 cells displaying high small intestine score.
2 Supplementary Figure 2. Cetuximab response curves in 150 CRC cell lines. 150 cell lines of colorectal origin were treated with increasing concentrations of cetuximab for 4 days and cell viability was assessed by measuring ATP content. Data are expressed as percent viability compared with medium-only treated cells. Based on their response cells can be classified in sensitive (red lines); partially sensitive (green lines) and resistant (blue lines) to cetuximab treatment.
3 Supplementary Figure 3. Cetuximab effect on CRC cell lines. (a) Cell viability of each CRC cell line at clinical relevant concentration of 10µg/ml of cetuximab after 4 days of treatment (indicated by yellow dots) closely parallel AUC values. (b-e) Analysis of cell viability after 4-5 days of cetuximab treatment indicates net loss of cells compared to the number of cells at time 0, in three representative sensitive cell models, even at clinical relevant dose of 10 µg/ml of cetuximab (b-d); while cetuximab exerts mainly a cytostatic effect (reduction of growth rate) on the intermediate cell lines LIM1215 (e). Data are expressed as percent viability compared to the number of cells at day 0.
4 Supplementary Figure 4: Expression based classification of Assignment of CRC cell lines. to intrinsic subtypes according to five expression-based CRC classifiers. (a) CRCassigner (CRCA) is the reference classifier. Enrichment matrix (Bonferroni-corrected hypergeometric p- values) comparing members of CRCA subtype versus others expression-based CRC classifiers. Orange highlighting indicates enrichment p-values< 0.05, green highlighting indicates depletion p-values< (b) Graphic representation of the consensus across the intrinsic subtypes identified in cell lines by CRCassigner (CRCA) by Sadanandam et al. and other four different classification systems. The number of cell lines significantly assigned to each subtype (FDR<0.2) is reported.
5 Supplementary Figure 5. Characterization of oncogenic TPM3-NTRK1 gene fusion in KM12 cells. (a) RNA seq analysis identified gene fusion event between exon 7 of the TPM3 gene and the exon10 of NTRK1 gene in the KM12 CRC cell line. (b) PCR on the cdna of KM12 cell lines confirmed the TPM3-NTRK1 gene rearrangements. KM12SM cells, a derivate of the KM12 cells, were used as positive control. (c) Break apart FISH analysis of TPM3-NTRK1 in KM12 cells shows clear separation of green (5 ) and red (3 ) signals corresponding to the NTRK1 gene. Scale bars, 10µm. (d) Western blot analysis confirmed overexpression of the TRKA protein (codified by NTRK1 gene) in KM12 cells, at a molecular weight compatible with TPM3-NTRK1 translocation. (e) RNAi knockdown of NTRK1 inhibits cell proliferation of KM12 cells harboring thetpm3-ntrk1 fusion gene. KM12 cells were analyzed by ATP lite proliferation assay 5 days after transfection with NTRK1-specific pooled sirnas, scrambled sirna, or transfection reagent (mock). Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. si-rna mediated downregulation of NTRK1 levels were verified by western blot. (f) KM12 cells, resistant to the EGFR inhibitor cetuximab, are sensitive to the TRK inhibitor CEP701. Cell viability was assessed by measuring ATP content after 5 days of treatment. Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (g) CEP701 treatment downregulates MAPK and PI3K pathways in KM12 cells harboring NTRK1 genetic rearrangment. KM12 cells were treated with 1µM CEP701 for 12h, after which whole-cell extracts were subjected to western blot analysis.
6 Supplementary Figure 6. Oncogenic addiction to FGFR2 genetic amplification. (a) gdna RTPCR identified FGFR2 gene copy number increase in the NCIH716 CRC cell line. (b) Western blot analysis confirmed overexpression of FGFR2 protein in the NCIH716 cells. (c) RNAi knockdown of FGFR2 inhibits NCIH716 cell proliferation overexpressing the tyrosine kinase receptor. Cells were analyzed by ATP lite proliferation assay 5 days after transfection with FGFR2-specific pooled sirnas, scrambled sirna, or transfection reagent (mock). Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. si-rna mediated downregulation of FGFR2 levels were verified by western blot analysis. (d) NCIH716 cell lines, resistant to EGFR inhibitor cetuximab, are sensitive to FGFR inhibitor AZD4547. Cell viability was assessed by measuring ATP content after 5 days of treatment. Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (e) AZD4547 treatment downregulates MAPK and PI3K pathways in NCIH716 cells harboring FGFR2 gene copy number increase. NCIH716 cells were treated with 0.5µM AZD4547 for 12h, after which whole-cell extracts were subjected to western blot analysis.
7 Supplementary Figure 7. Oncogenic addiction to overexpressed NTRK2 and RET kinases. (a) RNAi knockdown of NTRK2 inhibits cell proliferation of SNU503 cell line. SNU503 cells were analyzed by ATP lite 5 days after transfection with NTRK2-specific pooled sirnas, or transfection reagent (mock). Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. si-rna mediated downregulation of NTRK2 levels were verified by cdna RTPCR. (b) SNU503 cells, resistant to the EGFR inhibitor cetuximab, are sensitive to the TRK inhibitor CEP701. Cell viability was assessed by measuring ATP content after 5 days of treatment. Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (c) Treatment with TRK inhibitor CEP701 initiates apoptosis in NTRK2-dependent SNU503 CRC cells. Protein lysates were analyzed by western blot after 3 days of treatment with 1µM CEP701. (d) Western blot analysis confirmed overexpression of RET protein in NCIH716 cells. (e) NCIH716 cells, resistant to the EGFR inhibitor cetuximab, are sensitive to the RET inhibitor ponatinib and to the FGFR inhibitor AZD4547. Cell viability was assessed by measuring ATP content after 5 days of treatment. Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (f) RNAi knockdown of RET inhibits cell proliferation in the NCIH716 cells. NCIH716 cells were analyzed by ATP lite proliferation assay 5 days after transfection with RET-specific pooled sirnas, scrambled sirna, or transfection reagent (mock). Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. si-rna mediated downregulation of RET levels were verified by western blot analysis.
8 Supplementary Figure 8. Functional validation of KIT and PDGFRA overexpression. (a) Western blot analysis confirmed overexpression of KIT protein in HCA24 cell lines. (b) RNAi knockdown of KIT inhibits cell proliferation in HCA24 cells. HCA24 cells were analyzed by ATP lite 5 days after transfection with KIT-specific pooled sirnas, scrambled sirna, or transfection reagent (mock). Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. si-rna mediated downregulation of KIT levels were verified by western blot. (c) RNAi knockdown of KIT initiates apoptosis in KIT-dependent HCA24 CRC cell lines. Protein lysates were analyzed by western blot 3 days after transfection with KIT-specific pooled sirnas, scrambled sirna, or transfection reagent (mock). (d) HCA24 cells, resistant to the EGFR inhibitor cetuximab, are resistant also to the KIT kinase inhibitors nilotinib or imatinib. Cell viability was assessed by measuring ATP content after 5 days of treatment. Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments. (e) Western blot analysis confirmed overexpression of PDGFRA protein in CACO2 cell lines. (f-g) CACO2 cells are not addicted to the PDGFRA overexpression. RNAi knockdown of PDGFRA failed to induce apoptosis. Protein lysates were analyzed by western blot 3 days after transfection with PDGFRA-specific pooled sirnas, scrambled sirna, or transfection reagent (mock). (h) CACO2 cell lines, resistant to the EGFR inhibitor cetuximab, are resistant also to the PDGFRA kinase inhibitors nilotinib or imatinib. Cell viability was assessed by measuring ATP content after 5 days of treatment. Data are expressed as average ± s.d. of three independent experiments.
9 Supplementary Figure 9. Full lengths western blot of Figure 4. (4e) C10 CRC cells overexpress ALK protein. (4f) RNAi knockdown of ALK inhibits cell proliferation of C10 cell line harboring the EML4-ALK fusion gene. (4h) Crizotinib treatment downregulates MAPK and PI3K pathways in C10 cells.
10 Supplementary Figure 10. Full lengths western blot of Supplementary Figure 5. (S5d) KM12 CRC cells overexpress TRKA protein. (S5e) RNAi knockdown of TRKA inhibits cell proliferation of KM12 cell line harboring the TPM3-NTRK1 fusion gene. (S5g) CEP701 treatment downregulates MAPK and PI3K pathways in KM12 cells.
11 Supplementary Figure 11. Full lengths western blot of Supplementary Figure 6. (S6b) NCIH716 CRC cells overexpress FGFR2 protein. (S6c) RNAi knockdown of FGFR2 inhibits cell proliferation of NCIH716 cell line harboring the FGFR2 gene amplification. (S6e) AZD4547 treatment downregulates MAPK and PI3K pathways in NCIH716 cells.
12 Supplementary Figure 12. Full lengths western blot of Supplementary Figure 7. (S7c) Treatment with TRK inhibitor CEP701 initiates apoptosis in NTRK2-dependent SNU503 CRC cells. (S7d) NCIH716 CRC cells overexpress RET protein. (S7f) RNAi knockdown of RET inhibits cell proliferation of NCIH716 cell line harboring the RET overexpression
13 Supplementary Figure 13. Full lengths western blot of Supplementary Figure 8. (S8a) HCA24 CRC cells overexpress KIT protein. (S8b) RNAi knockdown of KIT inhibits cell proliferation of HCA24 cells. (S8c) RNAi knockdown of KIT initiates apoptosis in KIT-dependent HCA24 CRC cells. (S8e) CACO2 CRC cells overexpress PDGFRA protein. (S8bf) RNAi knockdown of PDGFRA does not affect cell proliferation of CACO2 cells. (S8g) RNAi knockdown of PDGFRA does not induce apoptosis in CACO2 CRC cells.
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
The molecular landscape of colorectal cancer cell lines unveils clinically actionable kinase targets
 Received 1 Oct 2014 Accepted 23 Mar 2015 Published 30 Apr 2015 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8002 The molecular landscape of colorectal cancer cell lines unveils clinically actionable kinase targets Enzo Medico 1,2,
Received 1 Oct 2014 Accepted 23 Mar 2015 Published 30 Apr 2015 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8002 The molecular landscape of colorectal cancer cell lines unveils clinically actionable kinase targets Enzo Medico 1,2,
RXDX-101 & RXDX-102. Justin Gainor, MD February 20 th, 2014
 RXDX-101 & RXDX-102 Justin Gainor, MD February 20 th, 2014 Background Chromosomal fusions are important oncogenic drivers in NSCLC - ALK Rearrangements (4-6%) - ROS1 Rearrangements (1-2%) - RET Rearrangements
RXDX-101 & RXDX-102 Justin Gainor, MD February 20 th, 2014 Background Chromosomal fusions are important oncogenic drivers in NSCLC - ALK Rearrangements (4-6%) - ROS1 Rearrangements (1-2%) - RET Rearrangements
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3967
 Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL-
 Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1. Int6 gene silencing efficiency. (A) Western Blot analysis of Int6 expression at different times after sirna transfection. Int6 expression is strongly silenced in Int6
Supplementary Information Figure S1. Int6 gene silencing efficiency. (A) Western Blot analysis of Int6 expression at different times after sirna transfection. Int6 expression is strongly silenced in Int6
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung
 Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Supplementary Figure 1. A. Bar graph representing the expression levels of the 19 indicated genes in the microarrays analyses comparing human lung immortalized broncho-epithelial cells (AALE cells) expressing
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Frequency(%) KRAS G12 KRAS G13 KRAS A146 KRAS Q61 KRAS K117N PIK3CA H1047 PIK3CA E545 PIK3CA E542K PIK3CA Q546. EGFR exon19 NFS-indel EGFR L858R
 Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4078
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental Figure S1A Notch1
 Supplemental Figure S1A Notch1 erage) epth of Cove ormalized De Log1(No Notch exons Figure S1: A) Relative coverage of Notch1 and Notch 2 exons in HCC2218, HCC1187, MB157, MDA-MB157 cell lines. Blue color
Supplemental Figure S1A Notch1 erage) epth of Cove ormalized De Log1(No Notch exons Figure S1: A) Relative coverage of Notch1 and Notch 2 exons in HCC2218, HCC1187, MB157, MDA-MB157 cell lines. Blue color
Clinical response to entrectinib in a patient with NTRK1-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
 Clinical response to entrectinib in a patient with NTRK1-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Anna F. Farago, Manish Patel, Todd M. Bauer, Stephen V. Liu, Alexander Drilon, Jennifer Wheler, Sai-Hong
Clinical response to entrectinib in a patient with NTRK1-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Anna F. Farago, Manish Patel, Todd M. Bauer, Stephen V. Liu, Alexander Drilon, Jennifer Wheler, Sai-Hong
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well
 Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Aliccia Bollig-Fischer, PhD Department of Oncology, Wayne State University Associate Director Genomics Core Molecular Therapeutics Program Karmanos
 Aliccia Bollig-Fischer, PhD Department of Oncology, Wayne State University Associate Director Genomics Core Molecular Therapeutics Program Karmanos Cancer Institute Development of a multiplexed assay to
Aliccia Bollig-Fischer, PhD Department of Oncology, Wayne State University Associate Director Genomics Core Molecular Therapeutics Program Karmanos Cancer Institute Development of a multiplexed assay to
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. Relative cell viability. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng SCR shyap1-1 shyap
 Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
Dr C K Kwan. Associate Consultant, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, HKSAR Honorary member, Targeted Therapy Team, ICR, UK
 HA Convention 2013 Dr C K Kwan MBChB, FRCR, FHKCR, FHKAM, MPM, CPI, MAppMgt(Hlth) Associate Consultant, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, HKSAR Honorary member, Targeted Therapy Team, ICR, UK To personalize cancer
HA Convention 2013 Dr C K Kwan MBChB, FRCR, FHKCR, FHKAM, MPM, CPI, MAppMgt(Hlth) Associate Consultant, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, HKSAR Honorary member, Targeted Therapy Team, ICR, UK To personalize cancer
Implementation of nation-wide molecular testing in oncology in the French Health care system : quality assurance issues & challenges
 Implementation of nation-wide molecular testing in oncology in the French Health care system : quality assurance issues & challenges Frédérique Nowak - 21 october 2015 "Putting Science into Standards event:
Implementation of nation-wide molecular testing in oncology in the French Health care system : quality assurance issues & challenges Frédérique Nowak - 21 october 2015 "Putting Science into Standards event:
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
Origin of oncogenes? Oncogenes and Proto-oncogenes. Jekyll and Hyde. Oncogene hypothesis. Retroviral oncogenes and cell proto-oncogenes
 Oncogenes and Proto-oncogenes Jekyll and Hyde A double edged sword Origin of oncogenes? Oncogene hypothesis Retroviral oncogenes and cell proto-oncogenes (v-onc) (c-onc) The role of c-onc in cancer How
Oncogenes and Proto-oncogenes Jekyll and Hyde A double edged sword Origin of oncogenes? Oncogene hypothesis Retroviral oncogenes and cell proto-oncogenes (v-onc) (c-onc) The role of c-onc in cancer How
Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer
 S1 of S6 Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer Shang-Gin Wu, Tzu-Hua Chang, Meng-Feng Tsai, Yi-Nan Liu, Chia-Lang
S1 of S6 Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer Shang-Gin Wu, Tzu-Hua Chang, Meng-Feng Tsai, Yi-Nan Liu, Chia-Lang
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor
 Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Lab Approach for Basket Trials in Advanced Tumors. Mohamed Salama M.D. Professor of Pathology, University of Utah
 Lab Approach for Basket Trials in Advanced Tumors Mohamed Salama M.D. Professor of Pathology, University of Utah Objectives Discuss how to support basket trials as a pathology department Basket trials
Lab Approach for Basket Trials in Advanced Tumors Mohamed Salama M.D. Professor of Pathology, University of Utah Objectives Discuss how to support basket trials as a pathology department Basket trials
PID1 increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells in a manner that involves NFκB
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: PID1 increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells in a manner that involves NFκB Jingying Xu, Xiuhai Ren, Anup Singh Pathania, G. Esteban Fernandez,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: PID1 increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells in a manner that involves NFκB Jingying Xu, Xiuhai Ren, Anup Singh Pathania, G. Esteban Fernandez,
1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance. 13/10/2017 Sara Redaelli
 Dott.ssa Sara Redaelli 13/10/2017 1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance Tumor Heterogeneity: Oncogenic Drivers in NSCLC The Promise of Genotype-Directed Therapy
Dott.ssa Sara Redaelli 13/10/2017 1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance Tumor Heterogeneity: Oncogenic Drivers in NSCLC The Promise of Genotype-Directed Therapy
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Current and future applications of Molecular Pathology. Kathy Walsh Clinical Scientist NHS Lothian
 Current and future applications of Molecular Pathology Kathy Walsh Clinical Scientist NHS Lothian Molecular Pathology in Solid tumours Cancer type Genes tested Purpose Associated treatments Non small cell
Current and future applications of Molecular Pathology Kathy Walsh Clinical Scientist NHS Lothian Molecular Pathology in Solid tumours Cancer type Genes tested Purpose Associated treatments Non small cell
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy
 Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
ALK Fusion Oncogenes in Lung Adenocarcinoma
 ALK Fusion Oncogenes in Lung Adenocarcinoma Vincent A Miller, MD Associate Attending Physician, Thoracic Oncology Service Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, New York The identification of
ALK Fusion Oncogenes in Lung Adenocarcinoma Vincent A Miller, MD Associate Attending Physician, Thoracic Oncology Service Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, New York The identification of
Downregulation of the small GTPase SAR1A: a key event underlying alcohol-induced Golgi fragmentation in hepatocytes
 Downregulation of the small GTPase SAR1A: a key event underlying alcohol-induced Golgi fragmentation in hepatocytes Armen Petrosyan 1*, Pi-Wan Cheng 1,3, Dahn L. Clemens 2,3 & Carol A. Casey 2,3 1 Department
Downregulation of the small GTPase SAR1A: a key event underlying alcohol-induced Golgi fragmentation in hepatocytes Armen Petrosyan 1*, Pi-Wan Cheng 1,3, Dahn L. Clemens 2,3 & Carol A. Casey 2,3 1 Department
Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer
 Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer No disclosures Objectives Understand how FISH and NGS provide complementary data for the evaluation of lung cancer Recognize the challenges of performing testing
Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer No disclosures Objectives Understand how FISH and NGS provide complementary data for the evaluation of lung cancer Recognize the challenges of performing testing
PLX7486 Background Information October Candidate for CRUK Combinations Alliance
 PLX7486 Background Information October 2015 Candidate for CRUK Combinations Alliance 1 Oct 2015 Plexxikon s Development Pipeline Compound Target Cancer Indication Stage of Development Pre- IND Ph1 Ph2
PLX7486 Background Information October 2015 Candidate for CRUK Combinations Alliance 1 Oct 2015 Plexxikon s Development Pipeline Compound Target Cancer Indication Stage of Development Pre- IND Ph1 Ph2
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
GENETIC TESTING FOR TARGETED THERAPY FOR NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER (NSCLC)
 CANCER (NSCLC) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
CANCER (NSCLC) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
Drug Resistance in ALK- and ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancers. Alice T. Shaw, MD PhD Director, Center for Thoracic Cancers September 16, 2017
 Drug Resistance in ALK- and ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancers Alice T. Shaw, MD PhD Director, Center for Thoracic Cancers September 16, 2017 ALK and ROS1 are Related Tyrosine Kinases, and Both are Targeted
Drug Resistance in ALK- and ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancers Alice T. Shaw, MD PhD Director, Center for Thoracic Cancers September 16, 2017 ALK and ROS1 are Related Tyrosine Kinases, and Both are Targeted
Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors
 Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Quality in Control. ROS1 Analyte Control. Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024
 Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Quality in Control ROS1 Analyte Control Product Codes: HCL022, HCL023 and HCL024 Contents What is ROS1? 2 The Role of ROS1 in Cancer 3 ROS1 Assessment 3 ROS1 Analyte Control Product Details 4 ROS1 Analyte
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, China; 5 Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China; 6 Department of Pathology, University of Michigan
 Overexpression of FAM83H-AS1 indicates poor patient survival and knockdown impairs cell proliferation and invasion via MET/EGFR signaling in lung cancer Jie Zhang 1,2, Shumei Feng 3, Wenmei Su 4, Shengbin
Overexpression of FAM83H-AS1 indicates poor patient survival and knockdown impairs cell proliferation and invasion via MET/EGFR signaling in lung cancer Jie Zhang 1,2, Shumei Feng 3, Wenmei Su 4, Shengbin
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San
 Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information - chimeric fusion transcript in human gastric cancer promotes tumorigenesis through activation of PI3K/AKT signaling Sun Mi Yun, Kwiyeom Yoon, Sunghoon Lee, Eunjeong Kim, Seong-Ho
Supplementary Information - chimeric fusion transcript in human gastric cancer promotes tumorigenesis through activation of PI3K/AKT signaling Sun Mi Yun, Kwiyeom Yoon, Sunghoon Lee, Eunjeong Kim, Seong-Ho
WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors
 Research article WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors Jamie N. Anastas, 1,2 Rima M. Kulikauskas, 3 Tigist Tamir, 4 Helen Rizos, 5 Georgina V. Long, 5 Erika M. von Euw,
Research article WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors Jamie N. Anastas, 1,2 Rima M. Kulikauskas, 3 Tigist Tamir, 4 Helen Rizos, 5 Georgina V. Long, 5 Erika M. von Euw,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Generation of cetuximab-resistant cells and analysis of singlecell clones. Cetuximab-sensitive cells (LIM1215 and OXCO-2) were chronically treated with cetuximab
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Generation of cetuximab-resistant cells and analysis of singlecell clones. Cetuximab-sensitive cells (LIM1215 and OXCO-2) were chronically treated with cetuximab
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test
 Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
5 th July 2016 ACGS Dr Michelle Wood Laboratory Genetics, Cardiff
 5 th July 2016 ACGS Dr Michelle Wood Laboratory Genetics, Cardiff National molecular screening of patients with lung cancer for a national trial of multiple novel agents. 2000 NSCLC patients/year (late
5 th July 2016 ACGS Dr Michelle Wood Laboratory Genetics, Cardiff National molecular screening of patients with lung cancer for a national trial of multiple novel agents. 2000 NSCLC patients/year (late
Detection of clinically relevant gene fusions with the
 Detection of clinically relevant gene fusions with the HTG EdgeSeq ALKPlus Assay EU Introduction Numerous mutations have been shown to drive oncogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Measuring
Detection of clinically relevant gene fusions with the HTG EdgeSeq ALKPlus Assay EU Introduction Numerous mutations have been shown to drive oncogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Measuring
Personalized Genetics
 Personalized Genetics Understanding Your Genetic Test Results Tracey Evans, MD September 29, 2017 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 2 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 3 It s not
Personalized Genetics Understanding Your Genetic Test Results Tracey Evans, MD September 29, 2017 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 2 Genetics 101 Punnett Square Genetic Pedigree 3 It s not
Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know
 Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know Stephen P. Ethier, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, MUSC Director, MUSC Center for Genomic Medicine Genomics and
Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know Stephen P. Ethier, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, MUSC Director, MUSC Center for Genomic Medicine Genomics and
Evolution of Pathology
 1 Traditional pathology Molecular pathology 2 Evolution of Pathology Gross Pathology Cellular Pathology Morphologic Pathology Molecular/Predictive Pathology Antonio Benivieni (1443-1502): First autopsy
1 Traditional pathology Molecular pathology 2 Evolution of Pathology Gross Pathology Cellular Pathology Morphologic Pathology Molecular/Predictive Pathology Antonio Benivieni (1443-1502): First autopsy
HSL-Advanced Diagnostics 2018 / 19 Test & Service List
 HSL-Advanced Diagnostics 2018 / 19 Test & Service List 2018/19 TEST & SERVICE LIST Haematoxylin & Eosin H&E H&E per slide Routine Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical demonstration of an antigen in
HSL-Advanced Diagnostics 2018 / 19 Test & Service List 2018/19 TEST & SERVICE LIST Haematoxylin & Eosin H&E H&E per slide Routine Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical demonstration of an antigen in
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
Identification of Novel Variant of EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in NSCLC: Potential Benefits of the RT-PCR Method
 International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Novel Variant of EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in NSCLC: Potential Benefits of the RT-PCR Method Martin K. H. Maus 1, 2, Craig Stephens
International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Novel Variant of EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in NSCLC: Potential Benefits of the RT-PCR Method Martin K. H. Maus 1, 2, Craig Stephens
Figure S1 A. MGH092-1 (Biopsy) MGH092-1B (Cell Line)
 a/f3 G1del ell viability (% control) a/f3 G1R ell viability (% control) Figure S1 MGH9-1 (iopsy) MGH9-1 (ell Line) G1del LK G1del (c.33_35delggg) Reference MGH9-1 D 5 rizotinib I 5 = 5. nm eritinb I 5
a/f3 G1del ell viability (% control) a/f3 G1R ell viability (% control) Figure S1 MGH9-1 (iopsy) MGH9-1 (ell Line) G1del LK G1del (c.33_35delggg) Reference MGH9-1 D 5 rizotinib I 5 = 5. nm eritinb I 5
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.
 Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
Molecular Diagnostics in Lung Cancer
 Molecular Diagnostics in Lung Cancer Mutations in lung carcinomas and their impact on diagnosis and treatment With special thanks to: Barbara Chaitin, MD Medical Director, Esoteric Services AmeriPath Orlando,
Molecular Diagnostics in Lung Cancer Mutations in lung carcinomas and their impact on diagnosis and treatment With special thanks to: Barbara Chaitin, MD Medical Director, Esoteric Services AmeriPath Orlando,
p.r623c p.p976l p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r2922w p.r2370h p.c1201y p.a868v p.s952* RING_C BP PHD Cbp HAT_KAT11
 ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
Megan S. Lim MD PhD. Translating Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics of Malignant Lymphoma into Clinical Application
 Translating Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics of Malignant Lymphoma into Clinical Application Megan S. Lim MD PhD FRCPC Department of Pathology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Proteomics is a multi-faceted
Translating Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics of Malignant Lymphoma into Clinical Application Megan S. Lim MD PhD FRCPC Department of Pathology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Proteomics is a multi-faceted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature8645 Physical coverage (x haploid genomes) 11 6.4 4.9 6.9 6.7 4.4 5.9 9.1 7.6 125 Neither end mapped One end mapped Chimaeras Correct Reads (million ns) 1 75 5 25 HCC1187 HCC1395 HCC1599
doi: 1.138/nature8645 Physical coverage (x haploid genomes) 11 6.4 4.9 6.9 6.7 4.4 5.9 9.1 7.6 125 Neither end mapped One end mapped Chimaeras Correct Reads (million ns) 1 75 5 25 HCC1187 HCC1395 HCC1599
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays
 SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays Detect all cancer-relevant variants in a single SureSelect assay SNV Indel TL SNV Indel TL Single DNA input Single AIO assay Single data analysis
SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays Detect all cancer-relevant variants in a single SureSelect assay SNV Indel TL SNV Indel TL Single DNA input Single AIO assay Single data analysis
Additional methods appearing in the supplement are described in the Experimental Procedures section of the manuscript.
 Supplemental Materials: I. Supplemental Methods II. Supplemental Figure Legends III. Supplemental Figures Supplemental Methods Cell Culture and Transfections for Wild Type and JNK1-/-,JNK2-/- MEFs: The
Supplemental Materials: I. Supplemental Methods II. Supplemental Figure Legends III. Supplemental Figures Supplemental Methods Cell Culture and Transfections for Wild Type and JNK1-/-,JNK2-/- MEFs: The
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/393/rs9/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Identification of potential drug targets for tuberous sclerosis complex by synthetic screens combining CRISPR-based knockouts
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/393/rs9/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Identification of potential drug targets for tuberous sclerosis complex by synthetic screens combining CRISPR-based knockouts
