Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(2): /ISSN: /IJCEP
|
|
|
- Chastity Webb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(2): /ISSN: /IJCEP Original Article Immunohistochemical expression of PAX5 and TdT by Merkel cell carcinoma and pulmonary small cell carcinoma: a potential diagnostic pitfall but useful discriminatory marker Ravindra Kolhe 1, Michelle D Reid 2, Jeffrey R Lee 3, Cynthia Cohen 2, Preetha Ramalingam 1,4 1 Department of Pathology, Georgia Health Sciences University, Augusta, GA; 2 Department of Pathology, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 3 Department of Pathology, Charlie Norwood Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Augusta, GA, United States; 4 The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX Received November 26, 2012; Accepted December 15, 2012; Epub January 15, 2013; Published February 1, 2013 Abstract: Background: Merkel cell carcinoma is a high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of skin that is characterized by immature cells which, because of its striking morphologic similarity, may be confused with other small round blue cell tumors such as pulmonary small cell carcinoma or lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Immunohistochemistry is therefore paramount to ensuring accurate diagnostic distinction between these tumors. The aim of our study was to evaluate and compare the expression of PAX5 and Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), in Merkel cell carcinoma and pulmonary small cell carcinoma. Design: PAX5 and TdT immunohistochemical stains were performed on 27 Merkel cell carcinomas and 10 pulmonary small cell carcinomas. Results: PAX5 was expressed in 24/27 (89%) Merkel cell carcinomas and 0/10 (0%) pulmonary small cell carcinomas. TdT was expressed in 21/27 (78%) Merkel cell carcinomas and 9/10 (90%) pulmonary small cell carcinomas. Conclusions: Our study confirms that PAX5 and TdT expression can be expressed in a high percentage of Merkel cell carcinomas and so when positive are not diagnostic of lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. When dealing with metastatic lesions, PAX5 negativity would favor a diagnosis of pulmonary small cell carcinoma over Merkel cell carcinoma. In addition, TTF-1 negative pulmonary small cell carcinoma is to be differentiated from Merkel cell carcinoma. Keywords: Merkel cell carcinoma, PAX5, TdT, small cell carcinoma, lung Introduction Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) of the skin is an aggressive cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma which was first reported in 1972 by Toker, who coined the term trabecular carcinoma of the skin [1]. MCC predominantly affects elderly Caucasians and has a propensity for local recurrence and regional lymph node metastasis. These tumors are most commonly found on sun-exposed areas of the head and neck or extremities, but can occur at virtually any site. In addition to ultraviolet radiation, immunosuppression has been suggested as a likely cause of Merkel cell carcinoma, with reports of up to a 13-fold increase in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection [2]. Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma typically present with rapidly growing, painless, red to purple colored cutaneous nodules or plaques. Like other neuroendocrine neoplasms, Merkel cell carcinoma shares histologic features with cutaneous small blue round cell tumors in that they are characterized by a dermal and subcutaneous infiltrate of monotonous cells that have high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, fine stippled chromatin and high proliferation rate. The differential diagnosis for Merkel cell carcinoma includes other small blue round cell tumors such as neuroblastoma, metastatic carcinoid, amelanotic melanoma, Ewing sarcoma, pulmonary small cell carcinoma (PSCC) and lymphomas including lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL).
2 Immunohistochemical stains are extremely helpful in distinguishing Merkel cell carcinoma from both lymphoblastic lymphoma and pulmonary small cell carcinoma with a panel of markers including, cytokeratin 7 (CK7), cytokeratin 20 (CK20), thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF- 1), and lymphocyte common antigen (CD45/ LCA). PAX5, a member of the paired box gene family, is located on chromosome 9q13 and plays an important role in B-cell ontogeny. In addition to this primary function, PAX5 has been detected in the spinal cord and mesencephalon-rhombencephalon boundary by in situ hybridization [3]. Earlier reports have demonstrated PAX5 expression in MCC and a subset of PSCC [4]. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), a DNA polymerase, catalyzes the elongation of nucleotide chains with its actions being most pronounced during the early development of B and T cells during immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements. TdT expression has recently been reported in both MCC as well as PSCC [5]. To our knowledge no single study has reported the expression patterns of PAX5 and TdT in MCC and PSCC, which is the goal of this paper. Materials and methods We retrieved 27 cases of Merkel cell carcinoma and 10 cases of pulmonary small cell carcinoma from the pathology files of Georgia Health Sciences University, Augusta, GA, Charlie Norwood Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC), Augusta, GA and Emory University Hospital, Atlanta, GA between 1999 and The study was approved by the Human Assurance Committee of each institution. Original slides were reviewed and the diagnoses confirmed by two reference pathologists. Neuroendocrine markers (synaptophysin, chromogranin, CD56), keratin markers (pancytokeratin, low-molecular-weight cytokeratin, CK7, CK20), TTF-1 and CD45 were variably performed at the time of initial diagnosis. These stains were also reviewed for the purpose of the study. Seven cases of Merkel cell carcinoma and 10 pulmonary small cell carcinoma from Georgia Health Sciences University and Charlie Norwood VAMC were stained with PAX5 (Clone- Table 1. Expression of PAX5 and TdT in Merkel cell carcinoma and pulmonary small cell carcinoma Diagnosis PAX5 TdT Merkel cell carcinoma 24/27 (89%) 21/27 (78%) Pulmonary small cell carcinoma 0/10 (0%) 9/10 (90%) TdT, Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. SP-34, 1:100, Biocare Medicals, Walnut Creek, CA.) and TdT (Clone- SP-3, 1:100, DAKO, Carpentaria, CA). Formalin-fixed paraffinembedded blocks were sectioned at 4μm and sections mounted on treated slides. Immunohistochemistry was performed using the standard avidin-biotin complex method on a DAKO autostainer (DAKO, Carpinteria, CA). Antigen retrieval consisted of pretreatment with target retrieval solution, ph 6.0. Bound antibody was detected with DAB+ substrate kit (DAKO Carpinteria, CA). Positive controls for PAX5 (tonsil) and TdT (cervical lymph node involved by lymphoblastic lymphoma) and negative controls with primary antibody replaced with Tris buffer were simultaneously run. The cases of Merkel cell carcinoma (n=20) from Emory University were stained using TdT (polyclonal antibody, 1:40 dilution, DAKO, Carpinteria, CA) and PAX5 (clone 24, Cell Marque, Rocklin, CA, RTU). After antigen retrieval, sections (5 micron) of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue were incubated with TdT for 15 minutes, with post primary polymer for 8 minutes, blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 5 minutes (Bonded Polymer Refine Detection Kit (DAB chromogen), (Leica Microsystems, Bannockburn, IL) with 3,3-diaminobenzidine 9DAB, brown chromogen, and hematoxylin as counterstain for 5 minutes. All steps were performed on the Leica Bond Max III automated system. Incubations were performed at room temperature; between incubations, sections were washed with Tris-buffered saline (Bond wash solution). Positive controls for PAX5 (tonsil) and TdT (case of lymphoblastic lymphoma) and negative controls with primary antibody replaced with Tris buffer were simultaneously run. All slides were assessed for extent of nuclear staining of PAX5 and TdT in the neoplastic cells as follows: 0: no staining, 1+: 1% to 25%, 2+: 26% to 50%, 3+: greater than 50%. Nuclear staining intensity was also evaluated and was 143 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(2):
3 Table 2. Expression of immunohistochemical stains performed for the diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma and pulmonary small cell carcinoma Diagnosis Pancytokeratin CK20 Synaptophysin Chromogranin TTF-1 Merkel cell carcinoma 5/6 (83%) 15/16 (94%) 14/14 (100%) 9/9 (100%) 0/10 (0%) Pulmonary small cell carcinoma 2/2 (100%) NP 5/5 (100%) 6/6 (100%) 2/2 (100%) NP, not performed. scored as: negative (-), weak (1+), moderate (2+) or strong (3+). Results PAX5 was expressed in 24/27 (89%) Merkel cell carcinoma and 0/10 (0%) of pulmonary small cell carcinoma. TdT was expressed in 21/27 (78%) Merkel cell carcinomas and 9/10 (90%) pulmonary small cell carcinoma (Table 1). In the Merkel cell carcinoma cohort, diffuse (>50%), strong (2-3+) PAX5 positivity was seen in 11 of 27 (40%) cases, and diffuse, strong TdT staining was seen in 12 of 27 (44%) cases. Eight of 10 (80%) of pulmonary small cell carcinoma showed diffuse, strong positivity for TdT. Immunohistochemical results for pancytokeratin, CK20, synaptophysin, chromogranin, and TTF-1 are summarized in Table 2 and Figure 1. Discussion In this study, we report the expression of PAX5 and TdT in a cohort of Merkel cell carcinomas and pulmonary small cell carcinomas. Both markers are typically associated with B- lymphoblastic lymphoma. TdT is an intranuclear template-independent DNA polymerase that catalyzes the elongation of nucleotide chains by repetitive addition of deoxyribonucleotides to the 3 -OH-terminated segment of DNA in mammalian cells. TdT has been found to span at least 65 kb and is located on chromosome 10 q23-q25 [6]. It has greatest activity in early B cells and T cells during the phase of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements and is expressed in normal thymic T cells. The most notable example of expression of TdT in human tumors is in lymphoblastic lymphoma, but nuclear expression has also been described in acute myeloid leukemia, some cases of medulloblastoma, CD56+/CD4+ hematodermic neoplasm, rare cases of pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma, and Ewing sarcoma [7-10]. Sur et al reported strong nuclear TdT expression in 53% (8/15) of Merkel cell carcinomas. Six of their cases morphologically resembled blastic hematologic malignancies with large- to intermediate-sized cells showing vesicular nuclei and one or two prominent nucleoli. This morphology in conjunction with TdT positivity could result in an erroneous diagnosis of a blastic hematological malignancy in the skin. A subsequent study by Bernd et al reported similar nuclear TdT immunoreactivity in 10 of 28 (36%) cases of Merkel cell carcinoma [11]. In the present study, we found that TdT was positive in the majority (89%) of Merkel cell carciomas. The expression of TdT in both Merkel cell carcioma and pulmonary small cell carcinoma is particularly notable because its uniformly strong nuclear staining was frequently at intensities mimicking those seen in lymphoblastic lymphoma. The latter observation emphasizes the caution that must be exercised when interpreting PAX5 and TdT positivity in the setting of any small round blue cell tumor. Differentiating Merkel cell carcinoma from metastatic pulmonary small cell carcinoma can sometimes be challenging as both tumors have a neuroendocrine phenotype. Other discriminatory immunohistochemical stains can be helpful in this differential such as CK20 and TTF1. Merkel cell carcinomas are typically positive for CK20 (~ 97%) and show a characteristic paranuclear dot-like positivity but are negative for TTF-1. The converse is typically true of pulmonary small cell carcinoma; rare positivity has been reported [12]. Furthermore, up to a third of Merkel cell carcinomas can be negative for CK20, and CK7 has been reported to be positive in up to 25% of Merkel cell carcinomas [13-16]. Thyroid transcription factor -1 (TTF-1) is typically negative in Merkel cell carcinoma, but up to 20% of pulmonary small cell carcinomas are also negative for TTF-1 [5, 17], thus limiting its usefulness in differentiating these tumors. PAX5, as a marker of B cells, was initially reported by Torlakovic et al in 2002 [18]. He also reported PAX5 expression in non-hematopoiet- 144 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(2):
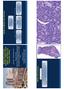
4 PAX5 and TdT expression in Merkel cell carcinoma Figure 1. A. Merkel cell carcinoma showing neoplastic cells with finely stippled chromatin, indistinct nucleoli and high mitotic activity (Hematoxylin & Eosin, magnification x200). B. Pulmonary small cell carcinoma showing malignant cells with high N/C ratio, salt-and-pepper chromatin and characteristic crush artifact (Hematoxylin & Eosin, magnification x200). C. Cytokeratin 20 positivity in Merkel cell carcinoma with typical paranuclear dot-like staining pattern (magnification x400). D. Diffuse positivity for synaptophysin in Merkel cell carcinoma (magnification x400). E. Merkel cell carcinoma showing diffuse, strong nuclear staining for PAX5 (magnification x200). F. Merkel cell carcinoma showing strong nuclear staining for TdT (magnification x400). G. Pulmonary small cell carcinoma with diffuse positive nuclear staining for TdT (magnification x200). H. Pulmonary small cell carcinoma demonstrating negative staining for PAX5 (magnification x200). 145 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(2):
5 ic tumors such as neuroendocrine tumors, Merkel cell carcinoma, and mesonephric tumors [18, 19]. Dong et al [4] later also reported the expression of PAX5 in neuroendocrine carcinomas such as Merkel cell carcinoma (93.5%) and small cell carcinoma (73.3%). An interesting finding in our study was that pulmonary small cell carcinomas were mostly positive for TdT (90%) but none were positive for PAX5. Dong et al [4] found PAX5 reactivity in greater than two thirds (~74%) of PSCC. In their study, they confirmed the presence of PAX5 mrna by real time RT-PCR in 8 cases of Merkel cell carcinoma, but no cases of pulmonary small cell carcinoma were tested. The antibody clones used in our and Dong et al s studies are not the same (monoclonal anti-pax5 antibody, clone 24, BD Biosciences versus monoclonal anti-pax5 antibody, clone SP-34, Biocare Medicals, Walnut Creek, CA, respectively) and this could possibly explain the difference in staining patterns that were observed. Given this significant discrepancy, additional studies using different PAX5 clones are needed to determine the true incidence of PAX5 positivity in pulmonary small cell carcinoma. In conclusion, co-expression of TdT and PAX5 by Merkel cell carcinoma may result in its misdiagnosis as B- lymphoblastic lymphoma, particularly since the latter is often negative for CD45, a frequently used lymphoid marker. When confronted with a cutaneous small round blue cell tumor in which an immature hematologic malignancy such as B- lymphoblastic lymphoma is in the differential diagnosis, the use of an immunohistochemical panel including CD34, CD79a, CD10, CK20 as well as neuroendocrine markers is strongly recommended. In our hands, PAX5 and TdT positivity in conjunction with the expression of neuroendocrine markers, suggests a diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma rather than pulmonary small cell carcinoma, when evaluating cutaneous small round blue cell tumors. PAX5 may therefore represent an additional marker to facilitate the distinction between Merkel cell carcinoma and pulmonary small cell carcinoma. Address correspondence to: Dr. Preetha Ramalingam, Department of Pathology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 1515 Holcombe Blvd, Box 85, Houston, TX 77030, USA. Phone: ; Fax: ; pramalingam@mdanderson.org References [1] Toker C. Trabecular carcinoma of the skin. Arch Dermatol 1972; 105: [2] Engels EA, Frisch M, Goedert JJ, Biggar RJ and Miller RW. Merkel cell carcinoma and HIV infection. Lancet 2002; 359: [3] Gerard M, Abitbol M, Delezoide AL, Dufier JL, Mallet J and Vekemans M. PAX-genes expression during human embryonic development, a preliminary report. C R Acad Sci III 1995; 318: [4] Dong HY, Liu W, Cohen P, Mahle CE and Zhang W. B-cell specific activation protein encoded by the PAX-5 gene is commonly expressed in merkel cell carcinoma and small cell carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 2005; 29: [5] Sidiropoulos M, Hanna W, Raphael SJ and Ghorab Z. Expression of TdT in Merkel cell carcinoma and small cell lung carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 2011; 135: [6] Isobe M, Huebner K, Erikson J, Peterson RC, Bollum FJ, Chang LM and Croce CM. Chromosome localization of the gene for human terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase to region 10q23-q25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1985; 82: [7] Suzumiya J, Ohshima K, Kikuchi M, Takeshita M, Akamatsu M and Tashiro K. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase staining of malignant lymphomas in paraffin sections: a useful method for the diagnosis of lymphoblastic lymphoma. J Pathol 1997; 182: [8] Budke H, Orazi A, Neiman RS, Cattoretti G, John K and Barberis M. Assessment of cell proliferation in paraffin sections of normal bone marrow by the monoclonal antibodies Ki-67 and PCNA. Mod Pathol 1994; 7: [9] Orazi A, Cattoretti G, John K and Neiman RS. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase staining of malignant lymphomas in paraffin sections. Mod Pathol 1994; 7: [10] Braziel RM, Keneklis T, Donlon JA, Hsu SM, Cossman J, Bollum FJ and Jaffe ES. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase in non-hodgkin s lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol 1983; 80: [11] Bernd HW, Krokowski M, Feller AC, Bartsch S and Thorns C. Expression of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase in Merkel cell carcinomas. Histopathology 2007; 50: [12] Bobos M, Hytiroglou P, Kostopoulos I, Karkavelas G and Papadimitriou CS. Immunohistochemical distinction between merkel cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma of the lung. Am J Dermatopathol 2006; 28: [13] Beer TW. Merkel cell carcinomas with CK20 negative and CK7 positive immunostaining. J 146 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(2):
6 Cutan Pathol 2009; 36: ; author reply 387. [14] Calder KB, Coplowitz S, Schlauder S and Morgan MB. A case series and immunophenotypic analysis of CK20-/CK7+ primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin. J Cutan Pathol 2007; 34: [15] Jensen K, Kohler S and Rouse RV. Cytokeratin staining in Merkel cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study of cytokeratins 5/6, 7, 17, and 20. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000; 8: [16] Cheuk W, Kwan MY, Suster S and Chan JK. Immunostaining for thyroid transcription factor 1 and cytokeratin 20 aids the distinction of small cell carcinoma from Merkel cell carcinoma, but not pulmonary from extrapulmonary small cell carcinomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001; 125: [17] Torlakovic E, Torlakovic G, Nguyen PL, Brunning RD and Delabie J. The value of anti-pax-5 immunostaining in routinely fixed and paraffinembedded sections: a novel pan pre-b and B- cell marker. Am J Surg Pathol 2002; 26: [18] Torlakovic E, Slipicevic A, Robinson C, DeCoteau JF, Alfsen GC, Vyberg M, Chibbar R and Florenes VA. Pax-5 expression in nonhematopoietic tissues. Am J Clin Pathol 2006; 126: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(2):
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells. Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital
 Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Cytokeratin 20 negative Merkel cell carcinoma consistent with negative Merkel cell polyomavirus
 CASE REPORT eissn 2384-0293 Yeungnam Univ J Med 2017;34(2):293-297 https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2017.34.2.293 Cytokeratin 20 negative Merkel cell carcinoma consistent with negative Merkel cell polyomavirus
CASE REPORT eissn 2384-0293 Yeungnam Univ J Med 2017;34(2):293-297 https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2017.34.2.293 Cytokeratin 20 negative Merkel cell carcinoma consistent with negative Merkel cell polyomavirus
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology. Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport
 From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Positive Cells in Human Tonsils
 Hematopathology / TDT-POSITIVE TONSIL CELLS Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Positive Cells in Human Tonsils James A. Strauchen, MD, and Lorraine K. Miller, PhD Key Words: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl
Hematopathology / TDT-POSITIVE TONSIL CELLS Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Positive Cells in Human Tonsils James A. Strauchen, MD, and Lorraine K. Miller, PhD Key Words: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl
Financial disclosures
 Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchc Geisel School of
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchc Geisel School of
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2.
 Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement
 Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Update on Merkel cell carcinoma
 Merkel cell carcinoma: Diagnosis, staging, sentinel lymph node biopsy and prognostic markers Michael T. Tetzlaff MD, PhD Associate Professor Departments of Pathology (Dermatopathology) and Translational
Merkel cell carcinoma: Diagnosis, staging, sentinel lymph node biopsy and prognostic markers Michael T. Tetzlaff MD, PhD Associate Professor Departments of Pathology (Dermatopathology) and Translational
Case 2. Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset
 Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
Merkel cell carcinoma: Diagnosis, staging, sentinel lymph node biopsy and prognostic markers
 Merkel cell carcinoma: Diagnosis, staging, sentinel lymph node biopsy and prognostic markers Michael T. Tetzlaff MD, PhD Associate Professor Departments of Pathology (Dermatopathology) and Translational
Merkel cell carcinoma: Diagnosis, staging, sentinel lymph node biopsy and prognostic markers Michael T. Tetzlaff MD, PhD Associate Professor Departments of Pathology (Dermatopathology) and Translational
3/27/2017. Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical History:
 Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Problem 1: Differential of Neuroendocrine Carcinoma 3/23/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Differential of Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Alain C. Borczuk,MD Weill Cornell Medicine Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control
Differential of Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Alain C. Borczuk,MD Weill Cornell Medicine Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control
3/24/2017 DENDRITIC CELL NEOPLASMS: HISTOLOGY, IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, AND MOLECULAR GENETICS. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 DENDRITIC CELL NEOPLASMS: HISTOLOGY, IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, AND MOLECULAR GENETICS Jason L. Hornick, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Surgical Pathology and Immunohistochemistry Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor
DENDRITIC CELL NEOPLASMS: HISTOLOGY, IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, AND MOLECULAR GENETICS Jason L. Hornick, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Surgical Pathology and Immunohistochemistry Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
The Panel Approach to Diagnostics. Lauren Hopson International Product Specialist Cell Marque Corporation
 The Panel Approach to Diagnostics Lauren Hopson International Product Specialist Cell Marque Corporation Cell Marque Rocklin, California About Cell Marque: IVD primary antibody manufacturer Distributors
The Panel Approach to Diagnostics Lauren Hopson International Product Specialist Cell Marque Corporation Cell Marque Rocklin, California About Cell Marque: IVD primary antibody manufacturer Distributors
Estrogen receptor (ER)
 Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: Assessment Run B26 2018 Estrogen receptor (ER) No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity* 1. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Tonsil 1-5% Weak
Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: Assessment Run B26 2018 Estrogen receptor (ER) No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity* 1. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Tonsil 1-5% Weak
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Respiratory Tract Cytology
 Respiratory Tract Cytology 40 th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK Momin T. Siddiqui M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Director of Cytopathology Emory University Hospital, Atlanta,
Respiratory Tract Cytology 40 th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK Momin T. Siddiqui M.D. Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Director of Cytopathology Emory University Hospital, Atlanta,
Unknown Case 6. Ann T. Moriarty, MD
 Unknown Case 6 Ann T. Moriarty, MD Unknown Case 6 61 year old male with an enlarged cervical lymph node. He has a history of lung carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma and lymphoma. Case 6 Image 1: Fine needle
Unknown Case 6 Ann T. Moriarty, MD Unknown Case 6 61 year old male with an enlarged cervical lymph node. He has a history of lung carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma and lymphoma. Case 6 Image 1: Fine needle
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma
 * * Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma A Case Report Chun-Ming Lin Shu-Hui Wang Tseng-tong Kuo* Ching-Chi Chi Hsin-Chun Ho Hong-Shang Hong Blastic natural killer (NK) cell lymphoma / leukemia is a rare
* * Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma A Case Report Chun-Ming Lin Shu-Hui Wang Tseng-tong Kuo* Ching-Chi Chi Hsin-Chun Ho Hong-Shang Hong Blastic natural killer (NK) cell lymphoma / leukemia is a rare
Case Report A Case of p63 Positive Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma of the Bladder
 Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 4348208, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4348208 Case Report A Case of p63 Positive Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma of the Bladder Chelsey D. Deel,
Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 4348208, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4348208 Case Report A Case of p63 Positive Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma of the Bladder Chelsey D. Deel,
Case 18. M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is:
 Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Cytokeratin 19 (CK19)
 Assessment Run 34 202 Cytokeratin 9 (CK9) Material The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Thyroid gland, 2. Appendix, 3. Esophagus, 4. Papillary thyroid carcinoma, 5 & 6. Pancreatic neuroendocrine
Assessment Run 34 202 Cytokeratin 9 (CK9) Material The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Thyroid gland, 2. Appendix, 3. Esophagus, 4. Papillary thyroid carcinoma, 5 & 6. Pancreatic neuroendocrine
A Report of a Rare Case of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma of the Oral Cavity
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 0 1 2 )5 (1 ):9 8-1 0 2 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G CASE REPORT A Report of a Rare Case of Anaplastic
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 0 1 2 )5 (1 ):9 8-1 0 2 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G CASE REPORT A Report of a Rare Case of Anaplastic
Immunopathology of Lymphoma
 Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF1) Assessment run
 Thyroid transcription factor- (TTF) Assessment run 39 203 The slide to be stained for TTF comprised:. Thyroid gland, 2. Liver, 3. Normal lung, 4. Lung adenocarcinoma 5. Colon adenocarcinoma, 6 & 7. Lung
Thyroid transcription factor- (TTF) Assessment run 39 203 The slide to be stained for TTF comprised:. Thyroid gland, 2. Liver, 3. Normal lung, 4. Lung adenocarcinoma 5. Colon adenocarcinoma, 6 & 7. Lung
DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA. Case Reports Clinical history. Materials and Methods
 DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA A Metastatic Renal Carcinoid Tumor Presenting as Breast Mass: A Diagnostic Dilemma Farnaz Hasteh, M.D., 1 Robert Pu, M.D., Ph.D., 2 and Claire W. Michael, M.D. 2 * We present clinicopathological
DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA A Metastatic Renal Carcinoid Tumor Presenting as Breast Mass: A Diagnostic Dilemma Farnaz Hasteh, M.D., 1 Robert Pu, M.D., Ph.D., 2 and Claire W. Michael, M.D. 2 * We present clinicopathological
Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas
 Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Role of immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis of malignant small round cell tumor: a study of 38 cases
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Patel A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3833-3839 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151452
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Patel A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3833-3839 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151452
Case year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid
 Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
Case 4 Diagnosis 2/21/2011 TGB
 Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
Supplemental materials
 Supplemental materials 1 Supplemental Fig. 1 Immunogram This immunogram summarizes patient clinical data and immune parameters at corresponding time points for Patient IMF-32. The top panel illustrates
Supplemental materials 1 Supplemental Fig. 1 Immunogram This immunogram summarizes patient clinical data and immune parameters at corresponding time points for Patient IMF-32. The top panel illustrates
Applications of IHC. Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin
 Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Cutaneous metastases. Thaddeus Mully. University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology
 Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma
 Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
Mihaela Onciu, MD, Robert B. Lorsbach, MD, PhD, E. Charlene Henry, HTL(ASCP)QIHC, and Frederick G. Behm, MD. Abstract
 Hematopathology / TDT-POSITIVE CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Positive Lymphoid Cells in Reactive Lymph Nodes From Children With Malignant Tumors Incidence, Distribution Pattern,
Hematopathology / TDT-POSITIVE CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Positive Lymphoid Cells in Reactive Lymph Nodes From Children With Malignant Tumors Incidence, Distribution Pattern,
Estrogen receptor (ER)
 Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: Assessment B25 208 Estrogen receptor (ER) No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity*. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Tonsil < 2-5% Weak to strong
Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: Assessment B25 208 Estrogen receptor (ER) No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity*. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Tonsil < 2-5% Weak to strong
THYROID TUMOR DIAGNOSIS: MARKER OF THE MONTH CLUB
 THYROID TUMOR DIAGNOSIS: MARKER OF THE MONTH CLUB CHARACTERISTIC OF THE IDEAL TUMOR MARKER Specific Sensitive Easy to perform Easy to interpret Adaptable to FNA Reasonable cost (CHEAP) THYROID TUMOR MARKERS
THYROID TUMOR DIAGNOSIS: MARKER OF THE MONTH CLUB CHARACTERISTIC OF THE IDEAL TUMOR MARKER Specific Sensitive Easy to perform Easy to interpret Adaptable to FNA Reasonable cost (CHEAP) THYROID TUMOR MARKERS
Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
 Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy.
 November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4)
 Assessment Run 43 205 Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4) The slide to be stained for SALL4 comprised:. Appendix, 2. Testis, 3. Renal clear cell carcinoma, 4. Seminoma, 5. Intratubular germ cell neoplasia (IGCN),
Assessment Run 43 205 Sal-like protein 4 (SALL4) The slide to be stained for SALL4 comprised:. Appendix, 2. Testis, 3. Renal clear cell carcinoma, 4. Seminoma, 5. Intratubular germ cell neoplasia (IGCN),
Distinction of pulmonary small cell carcinoma from poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical approach
 & 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Distinction of pulmonary small cell carcinoma from poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical
& 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Distinction of pulmonary small cell carcinoma from poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical
C.L. Davis Foundation Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course
 C.L. Davis Foundation 2015 Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course IHC Resources IHC Identification Targets Antibodies Antibodies 1 Antibodies Specimens Antigen Retrieval Unmasks antigen epitopes Methods
C.L. Davis Foundation 2015 Descriptive Veterinary Pathology Course IHC Resources IHC Identification Targets Antibodies Antibodies 1 Antibodies Specimens Antigen Retrieval Unmasks antigen epitopes Methods
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery
 Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
NEW IHC A n t i b o d i e s
 NEW IHC Antibodies TABLE OF CONTENTS NEW IHC ANTIBODIES from Cell Marque CITED1 (5H6).... 1 Claudin 7 (5D10F3).... 1 GATA1 (4F5).... 1 Transgelin (2A10C2).... 1 NEW IHC ANTIBODIES using RabMAb Technology
NEW IHC Antibodies TABLE OF CONTENTS NEW IHC ANTIBODIES from Cell Marque CITED1 (5H6).... 1 Claudin 7 (5D10F3).... 1 GATA1 (4F5).... 1 Transgelin (2A10C2).... 1 NEW IHC ANTIBODIES using RabMAb Technology
Assessment Run CK19
 Assessment Run 29 200 CK9 The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Appendix, 2. Thyroid gland, 3. Pancreas, 4. Ductal breast carcinoma, 5. Esophagus, 6. Papillary thyroid carcinoma. All tissues were
Assessment Run 29 200 CK9 The slide to be stained for CK9 comprised:. Appendix, 2. Thyroid gland, 3. Pancreas, 4. Ductal breast carcinoma, 5. Esophagus, 6. Papillary thyroid carcinoma. All tissues were
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Thyroid: possible thymic origin, so-called ITET/CASTLE 2012/03/22
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Thyroid: possible thymic origin, so-called ITET/CASTLE 2012/03/22 History of ITET/CASTLE First Report Gross Appearance and Prognosis 1) Miyauchi A et al: Intrathyroidal epithelial
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Thyroid: possible thymic origin, so-called ITET/CASTLE 2012/03/22 History of ITET/CASTLE First Report Gross Appearance and Prognosis 1) Miyauchi A et al: Intrathyroidal epithelial
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Estrogen receptor (ER)
 Assessment Run B7 204 Estrogen receptor (ER) Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity*. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Breast carcinoma 0%
Assessment Run B7 204 Estrogen receptor (ER) Material The slide to be stained for ER comprised: No. Tissue ER-positivity* ER-intensity*. Uterine cervix 80-90% Moderate to strong 2. Breast carcinoma 0%
Primary enteric adenocarcinoma with predominantly signet ring features of the lung: A case report with clinicopathological and molecular findings
 CASE REPORT Primary enteric adenocarcinoma with predominantly signet ring features of the lung: A case report with clinicopathological and molecular findings Makoto Nagashima 1, Ayako Moriyama 1, Yasuo
CASE REPORT Primary enteric adenocarcinoma with predominantly signet ring features of the lung: A case report with clinicopathological and molecular findings Makoto Nagashima 1, Ayako Moriyama 1, Yasuo
Mojca Velikonja Jože Pižem
 Mojca Velikonja Jože Pižem An 81-year old woman presented with an exophytic, wart-like skin lesion on her neck that she had observed for one year. Cryotherapy had been applied twice, but proved unsuccessful.
Mojca Velikonja Jože Pižem An 81-year old woman presented with an exophytic, wart-like skin lesion on her neck that she had observed for one year. Cryotherapy had been applied twice, but proved unsuccessful.
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY Original Article Mantle Cell Lymphoma Morphologic Findings in Bone Marrow Involvement JAY WASMAN, MD, 1 NANCY S. ROSENTHAL, MD,' AND DIANE C. FARHI, MD 2 Although mantle cell lymphoma (MCL),
HEMATOPATHOLOGY Original Article Mantle Cell Lymphoma Morphologic Findings in Bone Marrow Involvement JAY WASMAN, MD, 1 NANCY S. ROSENTHAL, MD,' AND DIANE C. FARHI, MD 2 Although mantle cell lymphoma (MCL),
Technology from Abcam
 CD2 (EP222) CD2 is one of the earliest T-cell lineage restricted antigens to appear during T-cell differentiation and only rare CD2+ cells can be found in the bone marrow. Anti-CD2 is a pan-t-cell antigen
CD2 (EP222) CD2 is one of the earliest T-cell lineage restricted antigens to appear during T-cell differentiation and only rare CD2+ cells can be found in the bone marrow. Anti-CD2 is a pan-t-cell antigen
Assessment Run GATA3
 Assessment Run 44 2015 GATA3 Material The slide to be stained for GATA3 comprised: 1. Tonsil 2. Kidney, 3. Urothelial carcinoma, 4. Breast ductal carcinoma, 5. Colon adenocarcinoma All tissues were fixed
Assessment Run 44 2015 GATA3 Material The slide to be stained for GATA3 comprised: 1. Tonsil 2. Kidney, 3. Urothelial carcinoma, 4. Breast ductal carcinoma, 5. Colon adenocarcinoma All tissues were fixed
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. This case was provided by Treant Hospital, Bethesda, Hoogeveen, The Netherlands
 Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma This case was provided by Treant Hospital, Bethesda, Hoogeveen, The Netherlands ADS-01504 Rev. 001 2016 Hologic, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma This case was provided by Treant Hospital, Bethesda, Hoogeveen, The Netherlands ADS-01504 Rev. 001 2016 Hologic, Inc. All rights reserved. Overview Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Pepsin Solution ready-to-use
 SIE HABEN DIE VISION, WIR HABEN DIE SUBSTANZ. Pepsin Solution Single component Pepsin Solution: only one component refrigerator stable Pepsin is a commonly used digestive enzyme for immunohistochemical
SIE HABEN DIE VISION, WIR HABEN DIE SUBSTANZ. Pepsin Solution Single component Pepsin Solution: only one component refrigerator stable Pepsin is a commonly used digestive enzyme for immunohistochemical
WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic Adenocarcinoma to Body Fluids
 Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
Composite mantle cell and follicular lymphoma. A case report
 Human Pathology (2009) 40, 259 263 www.elsevier.com/locate/humpath Case study Composite mantle cell and follicular lymphoma. A case report Raquel B. Ilgenfritz MD a,, Agnès Le Tourneau MD a, Michel Arborio
Human Pathology (2009) 40, 259 263 www.elsevier.com/locate/humpath Case study Composite mantle cell and follicular lymphoma. A case report Raquel B. Ilgenfritz MD a,, Agnès Le Tourneau MD a, Michel Arborio
Lung Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (lu-alk)
 Assessment Run 5 207 Lung Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (lu-alk) Material The slide to be stained for lu-alk comprised:. Appendix, 2. Tonsil, 3. Merkel cell carcinoma, 4. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma with
Assessment Run 5 207 Lung Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (lu-alk) Material The slide to be stained for lu-alk comprised:. Appendix, 2. Tonsil, 3. Merkel cell carcinoma, 4. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma with
Differential diagnosis of HCC
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Quest for an Ideal Immunohistochemical Panel Sanjay Kakar, MD UCSF Differential diagnosis of HCC Hepatocellular lesions Adenoma, FNH, HG dysplasia Adenocarcinoma CholangioCA, metastasis
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Quest for an Ideal Immunohistochemical Panel Sanjay Kakar, MD UCSF Differential diagnosis of HCC Hepatocellular lesions Adenoma, FNH, HG dysplasia Adenocarcinoma CholangioCA, metastasis
Immunohistochemistry in Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors. Sahar Rassi Zankoul, MD
 Immunohistochemistry in Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors Sahar Rassi Zankoul, MD Introduction Bone tumors represent a wide variety of tumors of various origins and malignant potentials. These different tumor
Immunohistochemistry in Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors Sahar Rassi Zankoul, MD Introduction Bone tumors represent a wide variety of tumors of various origins and malignant potentials. These different tumor
Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice
 Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice Stephen S. Raab, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Eastern Health and Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John s, NL and University of Washington,
Lung Cytology: Lessons Learned from Errors in Practice Stephen S. Raab, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Eastern Health and Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John s, NL and University of Washington,
, , 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung
 Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung M Papotti, L Righi, & M Volante University of Turin at San Luigi Hospital TORINO NETs OF THE LUNG Menu - Spectrum of NE lung tumors - CARCINOID TUMORS - SCLC /LCNEC
Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung M Papotti, L Righi, & M Volante University of Turin at San Luigi Hospital TORINO NETs OF THE LUNG Menu - Spectrum of NE lung tumors - CARCINOID TUMORS - SCLC /LCNEC
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Squamous entities of the thyroid: Reactive to Neoplastic Michelle D. Williams Associate Professor Dept of Pathology, Head & Neck Section University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosure of Relevant
Squamous entities of the thyroid: Reactive to Neoplastic Michelle D. Williams Associate Professor Dept of Pathology, Head & Neck Section University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosure of Relevant
Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Lebanon Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of H&N Nov /7/2011. Broad Classification:
 H&N Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Classification and Diagnostic Considerations Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Broad Classification: A. Epithelial:
H&N Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Classification and Diagnostic Considerations Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Broad Classification: A. Epithelial:
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Myeloperoxidase
 Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Myeloperoxidase Product Code: NCL-L-MYELO Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom (
Novocastra Liquid Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Myeloperoxidase Product Code: NCL-L-MYELO Leica Biosystems Newcastle Ltd Balliol Business Park West Benton Lane Newcastle Upon Tyne NE12 8EW United Kingdom (
Neuroendocrine Lung Tumors Myers
 Diagnosis and Classification of Neuroendocrine Lung Tumors Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor Director, Anatomic Pathology & MLabs University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI myerjeff@umich.edu
Diagnosis and Classification of Neuroendocrine Lung Tumors Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor Director, Anatomic Pathology & MLabs University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI myerjeff@umich.edu
Pulmonary Salivary Gland Type Tumors With Features of Malignant Mixed Tumor (Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma) A Clinicopathologic Study of Five Cases
 Anatomic Pathology / Pulmonary Salivary Gland Type Tumors Pulmonary Salivary Gland Type Tumors With Features of Malignant Mixed Tumor (Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma) A Clinicopathologic Study of Five
Anatomic Pathology / Pulmonary Salivary Gland Type Tumors Pulmonary Salivary Gland Type Tumors With Features of Malignant Mixed Tumor (Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma) A Clinicopathologic Study of Five
Assessment Run C1 2017
 Assessment Run C1 2017 PD-L1 The first assessment in this new NordiQC Companion module C1 focused on the accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays performed by the participating laboratories to identify patients
Assessment Run C1 2017 PD-L1 The first assessment in this new NordiQC Companion module C1 focused on the accuracy of the PD-L1 IHC assays performed by the participating laboratories to identify patients
Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms
 Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Chapter 4 Cerebral Parenchymal Lesions: I. Metastatic Neoplasms After one has reasonably ruled out the possibility of a nonneoplastic diagnosis (see Chap. 3), one is left with considering a diagnosis of
Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic skin*
 J Cutan Pathol 2005: 32: 50 54 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Denmark Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic
J Cutan Pathol 2005: 32: 50 54 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Denmark Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Cluster designation 5 staining of normal and non-lymphoid neoplastic
NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA
 + NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA + INTRODUCTION + NEUROENDOCRINE FEATURES IN BREAST CARCINOMA Incidence of 2-5% Seen in various histopathological types of breast carcinoma Seen in both
+ NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATED BREAST CARCINOMA + INTRODUCTION + NEUROENDOCRINE FEATURES IN BREAST CARCINOMA Incidence of 2-5% Seen in various histopathological types of breast carcinoma Seen in both
A Toriyama et al. 1 / 15 Utility of PAX8 mouse monoclonal antibody in the diagnosis of thyroid, thymic, pleural,
 A Toriyama et al. 1 / 15 Utility of PAX8 mouse monoclonal antibody in the diagnosis of thyroid, thymic, pleural, and lung tumors: a comparison with polyclonal PAX8 antibody Akane Toriyama, 1,3 Taisuke
A Toriyama et al. 1 / 15 Utility of PAX8 mouse monoclonal antibody in the diagnosis of thyroid, thymic, pleural, and lung tumors: a comparison with polyclonal PAX8 antibody Akane Toriyama, 1,3 Taisuke
Assessment Run B HER2 IHC
 Assessment Run B24 2017 HER2 IHC Material The slide to be stained for HER2 comprised the following 5 materials: IHC: HER2 Score* (0, 1+, 2+, 3+) FISH: HER2 gene/chr 17 ratio** 1. Breast carcinoma, no.
Assessment Run B24 2017 HER2 IHC Material The slide to be stained for HER2 comprised the following 5 materials: IHC: HER2 Score* (0, 1+, 2+, 3+) FISH: HER2 gene/chr 17 ratio** 1. Breast carcinoma, no.
ROLE OF TTF-1, CK20, AND CK7 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY
 Y.C. Su, Y.C. Hsu, and C.Y. Chai ROLE OF TTF-1, CK20, AND CK7 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA Yue-Chiu Su 1, Yu-Chang Hsu 2, and Chee-Yin Chai 1,3 Departments
Y.C. Su, Y.C. Hsu, and C.Y. Chai ROLE OF TTF-1, CK20, AND CK7 IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY FOR DIAGNOSIS OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA Yue-Chiu Su 1, Yu-Chang Hsu 2, and Chee-Yin Chai 1,3 Departments
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
DETERMINATION OF A LYMPHOID PROCESS
 Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Chapter 2 Applications of Touch Preparation Cytology to Intraoperative Consultations: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Tissues for Evaluation of Hematolymphoid Disorders INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chap. 1,
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Primary Spinal T-Cell Rich B-Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report
 Primary Spinal T-Cell Rich B-Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report Pages with reference to book, From 148 To 149 Suhail Muzaffar,Irshad Nabi Soomro,Naila Kayani,Shahid Siddiqui ( Departments of Pathology, The Aga
Primary Spinal T-Cell Rich B-Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report Pages with reference to book, From 148 To 149 Suhail Muzaffar,Irshad Nabi Soomro,Naila Kayani,Shahid Siddiqui ( Departments of Pathology, The Aga
Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test
 753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
Immunohistochemical Profile of Lung Tumors in Image Guided Biopsies
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1342 Immunohistochemical Profile of Lung Tumors in Image Guided Biopsies T. Pavithra 1 *, A. Dhanalakshmi 1, C. Lalitha 1, K.B. Lavanya 1 and S. Shifa 2 Department
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1342 Immunohistochemical Profile of Lung Tumors in Image Guided Biopsies T. Pavithra 1 *, A. Dhanalakshmi 1, C. Lalitha 1, K.B. Lavanya 1 and S. Shifa 2 Department
Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7100-7104 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001717 Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case Jenny
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7100-7104 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001717 Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case Jenny
# Best Practices for IHC Detection and Interpretation of ER, PR, and HER2 Protein Overexpression in Breast Cancer
 #1034 - Best Practices for IHC Detection and Interpretation of ER, PR, and HER2 Protein Overexpression in Breast Cancer Richard W. Cartun, MS, PhD Andrew Ricci, Jr, MD Department of Pathology Hartford
#1034 - Best Practices for IHC Detection and Interpretation of ER, PR, and HER2 Protein Overexpression in Breast Cancer Richard W. Cartun, MS, PhD Andrew Ricci, Jr, MD Department of Pathology Hartford
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
The unknown primary tumour: IHC classification part I, the primary panel - Antibody selection, protocol optimization, controls and EQA
 The unknown primary tumour: IHC classification part I, Mogens Vyberg Professor of Clinical Pathology Director of NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital, Aalborg, Denmark the primary panel - Antibody selection,
The unknown primary tumour: IHC classification part I, Mogens Vyberg Professor of Clinical Pathology Director of NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital, Aalborg, Denmark the primary panel - Antibody selection,
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Assessment Run
 Assessment Run 50 2017 S100 Material The slide to be stained for S100 comprised: 1. Appendix, 2. Tonsil, 3. Schwannoma, 4-5. Malignant melanoma, 6. Colon adenocarcinoma. All tissues were fixed in 10% neutral
Assessment Run 50 2017 S100 Material The slide to be stained for S100 comprised: 1. Appendix, 2. Tonsil, 3. Schwannoma, 4-5. Malignant melanoma, 6. Colon adenocarcinoma. All tissues were fixed in 10% neutral
Financial disclosures
 Mesenchymal Neoplasms with Melanocytic Differentiation By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel
Mesenchymal Neoplasms with Melanocytic Differentiation By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel
