Obesity Modulates microrna Expression. in the Visceral Adipose of Humans and Mice. Honors Thesis Research
|
|
|
- Geraldine Andrews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Obesity Modulates microrna Expression in the Visceral Adipose of Humans and Mice Honors Thesis Research Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for graduation with Honors Research Distinction in the undergraduate college of The Ohio State University By Dheeraj Duggineni The Ohio State University May 2013 Project Advisor: Dr. Sanjay Rajagopalan, College of Medicine
2 ABSTRACT Objective: Previous studies have indicated that dysregulation of mirnas in visceral adipose tissue of mice and omental/subcutaneous adipose tissue of humans are linked to obesity and insulin resistance. In this study, we profile the differential mirna expression of obese IR bariatric patients and propose mechanisms of mirna transport that may play a role in systemic inflammation/insulin resistance. Methods and Results: Whole visceral adipose tissue from lean and obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery was analyzed for mirna expression. Four mirnas (mir- 223, mir-486, mir-15b, and mir-451) were upregulated in obese patients and found to be overexpressed in the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of the visceral adipose tissue. The overexpression of mir-223 in the SVF was also confirmed in a mouse model. Expression of mir-223 was found to be upregulated in mouse liver tissue, but not in mouse muscle tissue, human blood monocytes, or human adipocytes. Isolation of human plasma exosomes revealed mir-223 was selectively overexpressed relative to the other three mirnas. Conclusions: In this paper, we profile previously unreported obesity-related mirna upregulation in the stromal vascular fraction of human visceral adipose tissue. Our results provide evidence that mirna dysregulation during chronic obesity may play a key role in regulation of inflammation and insulin resistance of not only adipose tissue but of other tissues as well. We also show preferential enrichment of mir in the plasma exosome compartment and introduce the possibility of mirna transport from viscera to distal metabolic organs.
3 INTRODUCTION Chronic obesity represents a growing worldwide problem and is considered the sixth most important risk factor contributing to overall burden of disease [1]. Impacts on life expectancy due to obesity have namely been attributed to development of cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. However, obesity also results in a wide variety of pathophysiological conditions including insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, systemic inflammation, and metabolic disorders [1,2,3]. Obesity-related visceral adipose tissue changes include a significant infiltration of inflammatory immune cells (T cells and macrophages), adipocyte hypertrophy, and increased adipocyte cell death. Infiltrating macrophages and T-cells secrete inflammatory cytokines and the resulting inflammatory effects within adipose tissue have been well documented [4,5,6,7]. Using mouse models, the role of inflammatory cells / visceral adipose inflammation has been shown to be etiologically relevant in dietinduced obesity (DIO) and insulin resistance (IR) [8,9]. Understanding the pathogenic changes that occur in the visceral adipose during DIO is essential to developing effective therapeutics targeting IR/T2DM. MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small, ~22 nucleotide, highly-conserved, non-coding strands of RNA thought to play an important role in post-transcriptional regulation of a variety of cellular processes in eukaryotic organisms [10]. By base-pairing with complimentary seed sites within target mrnas, mirnas can cause degradation of the mrna strand or translational repression [11,12,13]. An estimated 30% of the human genome is thought to be regulated by mirnas. Of particular interest for this study,
4 mirnas have been shown to play critical roles in regulation of adipogenesis, lipid metabolism, and inflammatory response [14,15]. Thus dysregulation of mirnas in the obese state may play a role in visceral adipose inflammation and tissue dysfunction, potentiating metabolic disease development and/or progression. Previous studies have indicated that dysregulation of mirnas in visceral adipose tissue of mice and omental/subcutaneous adipose tissue of humans are linked to obesity and insulin resistance [16,17]. In particular, one study analyzed mirna modulation after DIO in mice and found 22 differentially-expressed mirnas compared to lean counterparts [18]. Further studies have identified dysregulation of mirnas in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue of non-obese hyperglycemic individuals when compared to non-obese normoglycemic individuals [19]. Evidence suggests that adipose tissue mirna dysregulation is linked to obesity and insulin resistance, especially in mouse models. In this study, we profile the differential mirna expression of obese IR bariatric patients. Moreover, we show conservation of mirna regulation in a mouse model by analyzing adipose, liver, and muscle tissue. We show preferential enrichment of mir in the plasma exosome compartment and introduce the possibility of mirna transport from viscera to distal metabolic organs.
5 METHODS AND MATERIALS Human Participants Visceral adipose tissue was obtained from the greater omentum of patients undergoing hernia repairs or bariatric surgery. Patients were stratified based on BMI (lean, BMI<30; obese, BMI 40). Fasting blood was drawn the morning of surgery by venipuncture and plasma isolated using centrifugation. The Office of Responsible Research Practices, Human Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Ohio State University under OSU protocol #2008H0177, has approved this study and its procedures. Human informed consent was obtained. Human Tissue Processing A portion of whole adipose sample was digested using collagenase and separated by centrifugation into stromal vascular fraction (SVF) and adipocyte/fat fraction (FF). The SVF, containing macrophages, monocytes, T-cells, B-cells, and endothelial progenitor cells were lysed in TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies) and frozen at -80 C until needed. The adipocyte fraction (FF) was frozen separately at -80 C. Mouse Tissue Previously banked mouse muscle, liver, and adipose tissue from ob/ob knockout mice (a genetic model of spontaneous obesity) and wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 controls were analyzed. The samples were from obesity experiments previously performed in the lab.
6 RNA Isolation Prior to RNA isolation, tissue was homogenized in one milliliter TRIzol reagent before lipids were removed via centrifugation. To extract RNA, chloroform (200 µl) was added to samples containing TRIzol. Centrifugation (12,000 x g, 15 min, 4 C) separated aqueous and organic layers. RNA was precipitated from the aqueous layer using isopropyl alcohol. Linear acrylamide was used to increase RNA yield. The RNA pellet was washed in ethanol before air drying. RNA was dissolved in RNase free water and quantified using Nanodrop microvolume spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific). Purity of samples was determined by 260/280 and 260/230 ratios which measure DNA and protein contamination, respectively. RNA was stored at -80. Exiqon mirna Analysis 1 µg of RNA from human whole visceral adipose was hybridized to an Exiqon mircury LNA Array 5th generation (product number A ( A / A, slide batch 33011) using mirbase mirplus. Analysis of the scanned slides showed that the labeling was successful as all capture probes for the control spike-in oligo nucleotides produced signals in the expected range. The quantified signals (background corrected) were normalized using the global Lowess (LOcally WEighted Scatterplot Smoothing) regression algorithm. In the expression matrix, all capture probes with both Hy3 (sample) and Hy5 (common reference pool) signals lower than 1.5x of the median signal intensity of the given slide were excluded from analysis. Only log2(hy3/hy5) ratios which passed the filtering criteria on variation across samples were used. Student s t-test was performed between lean and obese patient groups. The
7 mirnas with mean expression level change above 1.3-fold, and p value < 0.05 were further selected to check their correlation with patient phenotypic traits (BMI, CRP level, fasting insulin level, and HOMA index). RT PCR for mirna-specific cdna MicroRNA specific cdna was generated via the ABI TaqMan MicroRNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems). Briefly, 1 µl of 10X Reverse Transcriptase buffer, 0.75 µl of 10mM DNTPs, 0.5 µl of Reverse Transcriptase enzyme, 0.09 µl of RNase inhibitor, and 1.5 µl of microrna specific primer were used to create a 3.84 µl RT master mix per sample. Then, 6.16 µl of RNA sample at 1 ng/ µl was added to the master mix to create a 10 µl reaction per sample. Samples were loaded into a thermocycler and reverse transcription reaction as described by the manufacturer was performed. Resulting microrna cdna samples were kept frozen at -80 C until needed. qpcr Assay for mirna cdna Quantitative PCR via ABI Taqman Probe Assay (Applied Biosystems) was performed to measure expression of target micrornas in the tissue samples relative to a reference snrna (RNU44). ABI Taqman Probe master mix (5.0 µl per reaction) mixed with 20X microrna specific probe (0.5 µl per reaction) was used alongside 4.5 µl of microrna specific cdna to create a 10 µl reaction. Each sample was tested in duplicate. Expression of microrna was quantified via fold change relative to RNU44.
8 RT PCR for Total cdna Total cdna was generated from each RNA sample in order to test for gene expression. Briefly, a 5.0 µl master mix reaction composed of 1.0 µl of 10X RT Buffer, 1.0 µl of 10mM DNTPs, 1.0 µl of 10X ABI Random Primers (Applied Biosystems), 0.5 µl of Reverse Transcriptase enzyme, and 1.5 µl of RNase free H 2 0 was used per sample. Then, 350 ng of total RNA in a total volume of 5.0 µl H 2 0 was added to the master mix to create a 10 µl reaction per sample. Samples were loaded into a thermocycler and reverse transcription reaction was performed as per the manufacturers directions. Resulting total cdna samples were kept frozen at -80 C until needed. qpcr for Gene Expression Quantitative PCR via SYBR Green Assay (Integrated Technologies) was performed to measure relative gene expression in tissue samples. Reactions consisting of 5.0 µl of SYBR Green master mix, 0.1 µl each of Forward and Reverse Primer, and 5.0 µl of total cdna from samples were performed in duplicate per sample. Gene expression is expressed as fold change relative to B-actin housekeeping gene. Isolation of Plasma Exosomes Plasma was isolated from freshly collected EDTA-anti-coagulated blood. Differential centrifugation (16,500xg, 20 ; 0.22 um filtration; 120,000xg, 180 ) yielded secreted microvesicles (exosomes nm in size) and lipoproteins. RNA was isolated from exosomal pellet via Exiqon mircury RNA isolation kit. mir-specific cdna was synthesized using equal volumes of RNA. mirna expression was quantified by mirna qpcr analysis as previously described.
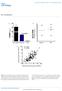
9 RESULTS Exiqon Array Profiling of Patients Exiqon array data was analyzed by a consulting bioinformatics specialist who determined that 12 micrornas passed the threshold of mean fold change > 1.3 and p- value < 0.05 between the lean and obese groups with three micrornas being downregulated (mir-299-3p, mirplus-e1067, and mirplus-e1076) and nine up-regulated (mir-202, -15b, -451, -24-2*, 1184, -187*, p, -10b, and -223). Hierarchical biclustering organized patients independent of group, re-arranging both axes by the correlation of expression profiling patterns (Figure 1). Hierarchical bi-clustering separated lean (blue) and obese (black) samples to groups relatively faithfully, with the exception of patient V28 and V14. Biomorphic characteristics of the sample population used in this experiment are shown in Table 1. Pearson correlation calculations were performed between data obtained from adipose tissue microrna expression profiling and BMI, fasting insulin, CRP, and HOMA-IR. Of particular interest for this study were mir-223, mir-451, mir-15b, and mir-486, all of which correlated highly to the analyzed biomarkers (Table 2).
10 Figure 1. Heirarchial biclustering of heatmap data of 12 significantly changed mirnas automatically clusters lean and obese groups. This is indicative of correlation between mirnas and obesity. Table 1. Biomorphic comparison of patients for Exiqon analysis Lean Obese Age 41.7±6 47.6±5 Gender 4F; 2M 5F; 1M BMI 27±0.6 50±3* Glucose 90±10 143±20* Insulin 3.4± ±3.1* HOMA-IR 0.77± ±1.3* QUICKI 0.43± ±0.01* HemA1c 5.6± ±1 TG 123±31 144±32 CRP 2.4± ±3.4 TC 171±9 168±14 HDL 44±4.3 41±7.5
11 LDL 102±11 98±10 TZD 0 3 Table 2. Pearson correlation coefficients of significant correlations between mirna expression and the patient phenotypical traits. mir BMI Fasting Insulin HOMA CRP mir p= p= p=0.038 mir-486-5p 0.74 p= p= p= p=0.021 mir p= p= p= p=0.046 mir-15b 0.74 p= p= p= p=0.040 Determining the source of obesity-related mir-223 expression To determine which fraction of adipose tissue is responsible for increases of mir- 223 expression, lean (n=7) and obese (n=7) stromal vascular fraction (SVF) and fat fraction (FF) samples from the same patients were analyzed via qpcr for expression of mir-223. A significant increase in mir-223 expression was observed in the SVF obese samples (4.9-fold increase, p-value < 0.05) relative to SVF lean samples (Figure 2A). However, no difference was observed between the lean and obese groups in the FF samples relative to each other or relative to SVF lean samples. This indicates that SVF fraction is responsible for the observed increases in mir-223. Expression of mir-223 in monocytes isolated from patient blood samples were also analyzed (Figure 2B). No difference was found in these samples.
12 Fold Change mir-223 Expression in SVF and FF LN OB Fold Change mir-223 Expression in Blood Monocytes SVF FF 0.0 Lean Obese Figure 2. Quantitative PCR was used to measure mir-223 expression in SVF and FF of both lean and obese patients (A). Fold change is expressed relative to levels of SVF LN. The same patients used for SVF LN and OB were also used in the FF LN and OB. n=7 for each LN and OB group. Expression of mir-223 was also analyzed in blood monocytes. No difference was found. qpcr Verification of Exiqon Data Quantitative PCR analysis of RNA isolated from the SVF of lean and obese patients indicates there is a significant (p-value < 0.05) upregulation of mir223 (3.3-fold increase), mir15b (2.4-fold increase), mir451 (2.4-fold increase), and mir486 (2.3-fold increase) in obese patients when compared to their lean counterparts (Figure 3). These results were confirmed in replicate experiments. RNU44 was used as the housekeeping mirna in these experiments. Biomorphic characteristics of the sample population used in this experiment are shown in Table 3.
13 A mir-223 B mir Fold Change 2 1 Fold Change SVF LN SVF OB n=14 n=18 0 SVF LN SVF OB n=15 n=16 C mir-15b D mir Fold Change 2 1 Fold Change SVF LN SVF OB n=13 n=16 0 SVF LN SVF OB n=17 n=17 Figure 3. Relative mir-223 (A), mir-486 (B), mir-15b (C), and mir-451 (D) expression in SVF of lean and obese patients was measured via ABI TaqMan Probe qpcr kit. RNU44 was used as the houskeeping gene. Table 1. Biomorphic comparison of patients used for qpcr analysis Lean Obese Age 47.1± ±10 Gender 9F;10M 10F; 9M BMI 25.1±2 52.1±8* Glucose 88±8 132±36* Insulin 4.5± ±12* HOMA-IR 1.0± ±5* QUICKI 0.4± ±0.05* HemA1c 5.4± ±1 TG 86±74 124±56 CRP 2.0± ±5.4 TC 173±54 163±29 HDL 52±16 37±7.5* LDL 103±47 101±28
14 TZD 0 5 mir-451 is Highly Expressed in SVF Quantitative PCR was used to analyze expression all four micrornas of interest (mir223, mir451, mir15b, mir486) relative to each other in SVF samples (n=3). This was achieved by running reactions on one plate and normalizing fold difference relative to the lowest expressed microrna, as identified by CT value. These reactions were run in duplicate. Mir-451 is expressed over 40 times higher than the other micrornas of interest (Figure 4). This dramatic difference in expression suggests a more important physiological role for mir451. Relative microrna Expression in SVF 80 Fold Change mir-486 mir-223 mir-15b mir-451 Figure 4. Quantative PCR was used to assess relative expression levels of micrornas of interest in the SVF. Fold change is expressed relative to mir-486 expression levels (i.e. mir-486 fold change is 1). For each microrna, n=3. Same patient samples were used for each microrna
15 mir-486 Gene Target Expression unchanged in human samples Quantitative PCR via SYBR Green was performed on SVF LN and OB samples to test for expression of SIRT-1, a putative gene target of mir-486 and an important glucose mediated cell cycle regulator [19]. No change was observed in gene expression between lean and obese patients (Figure 5). Thus any observed changes in SIRT-1 protein expression or SIRT-1 activity may be due to post-transcriptional regulation as is the case for most mirna regulated genes. Mouse Model Corroborates mir-223 Differential Expression RNA isolated from ob/ob and WT mouse whole visceral adipose tissue was analyzed for mir-223 expression. There was a 2-fold increase in mir-223 expression in the ob/ob mouse adipose tissue when compared to wild-type counterparts. Furthermore, analysis of liver tissue found a 3-fold increase in mir-223 expression in ob/ob mice. These data suggest that the liver may play a vital role in mir-223-modulated insulin resistance. Analysis of muscle tissue from ob/ob and WT mice found no difference in mir-223 expression (Figure 6).
16 Fold Change Murine mir-223 Expression Adipose Liver Muscle 0 WT ob/ob Figure 6. qpcr analysis reveals significant increase in mir-223 expression in adipose and liver tissue of ob/ob mice when compared to the WT control. n=8/group Plasma Exosomes Derived from Obese humans are preferentially enriched in mir-223 Exosomal RNA isolated from plasma was analyzed for mirnas of interest via ABI TaqMan Probe qpcr. All mirnas of interest (mir-223, mir-451, mir-15b, mir- 486) were expressed in the exosomes (Figure 7A). However, only mir-223 was differentially expressed between lean and obese samples. There was approximately a 9-fold (p-value < 0.05) increase of mir-223 expression in obese samples compared to lean samples (Figure 7B).
17 mir-223/1.5 ml of plasma (Ct Value) mirna Expression in Exosomes mir-486 mir-15b mir-451 mir-223 Lean Obese Fold Change Relative mir-223 Expression in Exosome LN OB LN OB Figure 7. mir-486, mir-15b, mir-451, and mir-223 are all expressed in exosomes isolated from human plasma (A). mir-223 expression is increased 9-fold in the exosomes.
18 DISCUSSION In this study we profile mirnas in human adipose tissue that are differentially expressed in lean and obese patients. We then used a mouse model to confirm that this expression is conserved. Our results provide evidence that mirna dysregulation during chronic obesity may play a key role in regulation of inflammation and insulin resistance of not only adipose tissue but of other tissues as well. Exiqon data showed significantly increased expression of mir-223, mir-486, mir-451, and mir-15b in in the visceral adipose tissue of obese patients compared to their lean counterparts. Pearson correlation curves indicated that all four mirnas have strong correlations with BMI, fasting insulin, and C-reactive protein and all but mir-223 have a strong correlation to HOMA-IR. These correlations suggest that expression of the mirnas is correlated with obesity (as measured by BMI), insulin resistance (as measure by fasting insulin and HOMA-IR), and inflammation (as measure by C-reactive protein). Because of the correlations of these four mirnas to relevant biomarkers, we pursued further analysis to characterize their adipose expression. We determined that mir-223 was differentially expressed in the SVF of lean and obese patients but not in the FF or the blood monocytes. SVF is primarily composed of a mixed population of monocytes, macrophages, T-cells, and pre-adipocytes. Thus, the data suggests that this population of cells is solely responsible for the upregulation of mir-223 expression in the whole adipose rather than adipocytes which are primarily found in the FF. Based on previous studies, these results were expected. Recent studies have implicated mir-223 as critical regulator of macrophage activation. Putative
19 gene targets of mir-223 suggest that this mirna plays a central role in regulation of ubiquitination/protein degradation (via FBXw7) and insulin signaling (via IRS-1) [19] mir-223 has also been shown to be highly expressed in myeloid cell populations [20]. Because mir-223 was highly expressed in SVF as opposed to FF, and because the other mirnas of interest have previously been found in cells that comprise the SVF, we tested the SVF of a larger population of human samples for mirna expression. Our results corroborated the Exiqon differential expression of mirnas. Comparing relative expression levels of the mirnas in the SVF found that mir-451 was much more highly expressed in the SVF than any other mirna tested. This suggests that mir-451 may have a key pathophysiological role in adipose dysfunction. Evidence from previous studies indicate that mir-451 upregulation is induced by inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and type 1 Interferons [21]. Furthermore, mir-451 overexpression in gliomas have resulted in a downstream reduction of PI3K/AKT signaling [22]. This pathway is central to cell growth, apoptosis, and proliferation. Thus the high mir-451 expression found in the SVF could potentially be related to key role that mir-451 plays in overall cell function. Moreover, increases in mir-451, as is the case with the obese group, could result in apoptosis not only potentiating inflammation of the visceral adipose tissue but also significantly contributing to adipose dysfunction. Our mouse model studies not only indicate that obesity related mir-223 expression increase is a conserved finding in adipose tissue but that mir-223 expression is also increased in other tissue. It is important to note that increased mir- 223 expression in the liver as a result of chronic obesity has not been previously described. The liver is a key organ in glucose metabolism and is rich in innate immune
20 cells. mir-223 dysregulation within this organ could result in changes in pathways relevant to DIO-IR. Our study reveals that mir-223 is expressed in both adipose and liver tissue and previous studies have shown that mir-223 is expressed in mouse macrophages (both bone marrow derived and cell lines) as well as human hepatic cell lines. However, obesity induced differential mir-223 expression seems to be localized to specific tissues and cannot be found in circulating blood monocytes. Thus we proposed a novel mechanism of mir-223 obesity related modulation of insulin sensitivity via a visceral adipose tissue derived, mir-223 rich, exosome delivery to distant tissues. Our data shows a 9-fold increase in the expression of mir-223 in plasma derived exosomes thus providing preliminary evidence to support such a hypothesis. Exosomal delivery of mirnas in general is not a novel mechanism. mirna containing exosomes have been shown to exert paracrine-like effects in cardiovascular disease and cancer [23]. Macrophages have been known to regularly endocytose circulating exosomes and exosomal communication has been well characterized in immune systems [24,25]. Exosomal transport of mir-223 derived from the visceral adipose could provide a direct link between localized and systemic inflammation/insulin resistance. The challenge in diabetes and obesity has always been to find mechanistic links between local and systemic regulation. Obesity in general is pathologically localized to deposits of adipose tissue. Resulting adipose dysfunction is also localized. However, if mir-223 plays a central role in potentiating adipose dysfunction, then transport of mir-223 out of the adipose via exosomes provides a mechanistically sound link between local and systemic. Furthermore, mir-223 was found to be increased in the SVF. These cell
21 population have direct access to the blood and thus transport of mir-223 by secreted exosomes can prove to be truly systemic in scope. The challenge now will be to provide more evidence of visceral adipose tissue derived mir-223 transport by increasing sample size and characterizing destinations of the mirna. Also, modulation of target genes needs to be analyzed to provide support to the idea that localized dysfunction can lead to systemic problems. Although the relative expression of the other mirnas were not changed between lean and obese patients, this does not discount the potential for these mirnas to play roles in adipose dysfunction or systemic problems. Although this study provides a compelling profile of mirna modulation exhibited during chronic obesity, these data can only provide preliminary/hypothetical framework of mechanistic effects of mirna dysregulation. Modulation of putative gene targets of these mirnas as predicted by DIANA program has yet to confirmed. To this end, 3 UTR luciferase assays need to be conducted for all mirnas and target genes. Of particular interest and relevance is the canonical mtor pathway that is involved in cell apoptosis, lipid metabolism, inflammation, and glucose metabolism. Furthermore, profiling of FF for all mirnas can provide evidence to corroborate the data the suggests that SVF plays a much more significant role in the potentiation of adipose dysfunction and insulin resistance than FF. This study provides significant evidence for the multidimensional/multisystem role of mirnas in chronic obesity. Current trends are shifting from viewing diseases as localized problems to being more systemically relevant with a centrally regulating mechanism. Specifically, obesity by itself is not a burdensome disease. However, development of insulin resistance, inflammatory diseases, type 2 diabetes, and
22 cardiovascular diseases as a result of chronic obesity does create a significant burden. Finding the potential mechanisms of regulation of these systemic issues stemming from obesity as we believe exosomal mir-223 transport may exhibit can provide targets for drugs that provide a multisystem benefits. Furthermore, our mrna profiling of chronically obese patients can provide other targets of interest for treating insulin resistance and preventing the development of type 2 diabetes.
23 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like to thank Dr. Sanjay Rajagopalan for his continued support and for always pushing me to do better. His guidance throughout my undergraduate career has been integral to my growth as a scientist and a student. I would like to also thank Dr. Jeffrey Deiuliis for his phenomenal mentorship, support, and overall role in my development in the laboratory. Finally I would like to thank Ms. Jessica Rutsky and Dr. Andrei Maiseyeu for their help in making this project possible.
24 REFERENCES 1) Haslam, David W., and W Philip T. James. "Obesity." The Lancet (2005): ) Winer, Shawn, Yin Chan, Geoffrey Paltser et. al. "Normalization of Obesityassociated Insulin Resistance through Immunotherapy." Nature Medicine 15.8 (2009): ) Kintscher, U., M. Hartge, and K. Hess. "T-lymphocyte Infiltration in Visceral Adipose Tissue: A Primary Event in Adipose Tissue Inflammation and the Development of Obesity-Mediated Insulin Resistance." Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 28.7 (2008): ) Deiuliis J, Shah Z, Shah N, Needleman B, Mikami D, Narula V, Perry K, Hazey J, Kampfrath T, Kollengode M, Sun Q, Satoskar AR, Lumeng C, Moffatt-Bruce S, and Rajagopalan S. Visceral adipose inflammation in obesity is associated with critical alterations in tregulatory cell numbers. PLoS One 6: e16376, ) Nishimura, Satoshi, Ichiro Manabe, and Mika Nagasaki. "CD8+ Effector T Cells Contribute to Macrophage Recruitment and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity." Nature Medicine 15.8 (2009): ) Wu, H., S. Ghosh, X. D. Perrard, L. Feng, G. E. Garcia, J. L. Perrard, J. F. Sweeney, L. E. Peterson, L. Chan, C. W. Smith, and C. M. Ballantyne. "T-Cell Accumulation and Regulated on Activation, Normal T Cell Expressed and Secreted Upregulation in Adipose Tissue in Obesity." Circulation (2007): ) Viviane Zorzanelli Rocha and Eduardo J. Folco, Inflammatory Concepts of Obesity, International Journal of Inflammation, vol. 2011, Article ID , 14 pages, doi: /2011/ ) Kawasaki, N., R. Asada, A. Saito, and S. Kanemoto. "Obesity-induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Causes Chronic Inflammation in Adipose Tissue." Scientific Reports 2 (2012): 9) Shah, A., N. Mehta, and M. P. Reilly. "Adipose Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Cardiovascular Disease." Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 32.6 (2008): ) Krol, Jacek, Inga Loedige, and Witold Filipowicz. "The Widespread Regulation of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Function and Decay." Nature Reviews Genetics (2010) 11) Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microrna targets. Cell. 2005;120: ) Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS, Johnson JM. Microarray analysis shows that some micrornas downregulate large numbers of target mrnas.nature. 2005; 13) Bartel, David P. "MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions." Cell136.2 (2009): ) Krutzfeldt J, and Stoffel M. MicroRNAs: a new class of regulatory genes affecting metabolism. Cell Metab 4: 9-12, ) O'Connell, Ryan M., Dinesh S. Rao, and David Baltimore. "MicroRNA Regulation of Inflammatory Responses." Annual Review of Immunology 30 (2012):
25 16) Chartoumpekis DV, Zaravinos A, Ziros PG, Iskrenova RP, Psyrogiannis AI, Kyriazopoulou VE, and Habeos IG. Differential Expression of MicroRNAs in Adipose Tissue after Long-Term High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. PLoS One 7: e34872, ) Kloting N, Berthold S, Kovacs P, Schon MR, Fasshauer M, Ruschke K, Stumvoll M, and Bluher M. MicroRNA expression in human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue. PLoS One 4: e4699, ) Kim, YJ, SH Hwang, SY Lee, KK Shin, and JS Jung. "MiR-486-5p Induces Replicative Senescence of Human Adipose Tissue-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Its Expression Is Controlled by High Glucose." Stem Cells and Development (2011) 19) La Rocca G, Shi B, Badin M, De Angelis T, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Baserga R. Growth inhibition by micrornas that target the insulin receptor substrate-1. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(14): ) Shi B, Prisco M, Calin G, Liu CG, Russo G, Giordano A, et al. Expression profiles of micro RNA in proliferating and differentiating 32D murine myeloid cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207(3): ) Rosenberger, CM, RL Podyminogin, G. Navarro, and A. Aderem. "MiR-451 Regulates Dendritic Cell Cytokine Responses to Influenza Infection." Journal of Immunology (2012) 22) Tian, Y., Y. Nan, L. Han, A. Zhang, and C. Kang. "MicroRNA MiR-451 Downregulates the PI3K/AKT Pathway through CAB39 in Human Glioma."International Journal of Oncology 40.4 (2012):
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits
 Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr)
 Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT) and NQO1-null (NQO1-/-) mice.
 competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo. Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale
 Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
The Role of micrornas in Pain. Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan
 The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplemental Figure 1. Body weight and blood glucose parameters of chow-diet (CD)
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION LEGENDS Supplemental Figure. Body weight and blood glucose parameters of chow-diet (CD) fed and high-fat diet (HFD) fed mice. (A) Body weight was measured at the beginning of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION LEGENDS Supplemental Figure. Body weight and blood glucose parameters of chow-diet (CD) fed and high-fat diet (HFD) fed mice. (A) Body weight was measured at the beginning of
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing. Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM
 MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit
 Datasheet EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Datasheet EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization
 A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit
 Datasheet EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Datasheet EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits
 ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits Cat # EQ806A-1, EQ806TC-1, EQ808A-1 User Manual Storage: Please see individual components Version 2 8/14/2018 A limited-use label license covers this
ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits Cat # EQ806A-1, EQ806TC-1, EQ808A-1 User Manual Storage: Please see individual components Version 2 8/14/2018 A limited-use label license covers this
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Products for cfdna and mirna isolation. Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma
 MACHEREY-NAGEL Products for cfdna and mirna isolation Bioanalysis Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma n Flexible solutions for small and large blood plasma volumes n Highly efficient recovery
MACHEREY-NAGEL Products for cfdna and mirna isolation Bioanalysis Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma n Flexible solutions for small and large blood plasma volumes n Highly efficient recovery
From reference genes to global mean normalization
 From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays
 Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays Lu Zhang b, Lei Guo a, Leming Shi a, Weida Tong a, Yongming Sun b, Gary
Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays Lu Zhang b, Lei Guo a, Leming Shi a, Weida Tong a, Yongming Sun b, Gary
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Exosome DNA Extraction Kits
 Exosome DNA Extraction Kits Summary Section 5 Introduction 40 EXO-DNAc 41 EXO-DNA 43 Introduction Genomic DNA Extractiom Kits Ordering informations Products can be purchased directly in our on-line shop:
Exosome DNA Extraction Kits Summary Section 5 Introduction 40 EXO-DNAc 41 EXO-DNA 43 Introduction Genomic DNA Extractiom Kits Ordering informations Products can be purchased directly in our on-line shop:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 -. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
-. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Ct=28.4 WAT 92.6% Hepatic CE (mg/g) P=3.6x10-08 Plasma Cholesterol (mg/dl)
 a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
Benchmark study: Exiqon mircury LNA microrna arrays vs. Supplier A s DNA based capture probes. Includes comparison of:
 Benchmark study: Exiqon mircury LNA microrna arrays vs. Supplier A s DNA based capture probes Includes comparison of: I. II. III. Signal levels Relative quantification False differences For complete experimental
Benchmark study: Exiqon mircury LNA microrna arrays vs. Supplier A s DNA based capture probes Includes comparison of: I. II. III. Signal levels Relative quantification False differences For complete experimental
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Genetic Analysis of Anxiety Related Behaviors by Gene Chip and In situ Hybridization of the Hippocampus and Amygdala of C57BL/6J and AJ Mice Brains
 Genetic Analysis of Anxiety Related Behaviors by Gene Chip and In situ Hybridization of the Hippocampus and Amygdala of C57BL/6J and AJ Mice Brains INTRODUCTION To study the relationship between an animal's
Genetic Analysis of Anxiety Related Behaviors by Gene Chip and In situ Hybridization of the Hippocampus and Amygdala of C57BL/6J and AJ Mice Brains INTRODUCTION To study the relationship between an animal's
A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer
 Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A
 MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models. Yu Wu
 Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast cancer cells
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Ambient Temperature Stabilization of RNA derived from Jurkat, HeLa and HUVEC Cell Lines for Use in RT-qPCR Assays
 Ambient Temperature Stabilization of RNA derived from Jurkat, HeLa and HUVEC Cell Lines for Use in RT-qPCR Assays C. Litterst 1, H. Martinez, B. Iverson and R. Nuňez 1 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Life Science
Ambient Temperature Stabilization of RNA derived from Jurkat, HeLa and HUVEC Cell Lines for Use in RT-qPCR Assays C. Litterst 1, H. Martinez, B. Iverson and R. Nuňez 1 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Life Science
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer mirnas to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis
 Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer mirnas to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis Tanja Wagner 1 Introduction 2 Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) non-haematopoietic, multipotent stem
Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer mirnas to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis Tanja Wagner 1 Introduction 2 Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) non-haematopoietic, multipotent stem
BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SPRING 2017
 THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SPRING 2017 Stephen M Bergin PhD Candidate Activation of Hypothalamic BDNF Modulates Lymphocyte Immunity February 17 th, 2017 Room 105, Biomedical
THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SPRING 2017 Stephen M Bergin PhD Candidate Activation of Hypothalamic BDNF Modulates Lymphocyte Immunity February 17 th, 2017 Room 105, Biomedical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supp. Fig. 1. Autoimmunity. Tolerance APC APC. T cell. T cell. doi: /nature06253 ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 TCR CD28
 Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.
![Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9. Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.](/thumbs/90/103696086.jpg) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin
 Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, M.D., Ph.D Department of Hematopathology The University of Texas M.
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, M.D., Ph.D Department of Hematopathology The University of Texas M.
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Product Manual. Omni-Array Sense Strand mrna Amplification Kit, 2 ng to 100 ng Version Catalog No.: Reactions
 Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
EXOTESTTM. ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids
 DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL DIAGNOSTIC TEST USING PODOCYTURIA AS A BIOMARKER FOR DETECTION OF KIDNEY DAMAGE. An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL DIAGNOSTIC TEST USING PODOCYTURIA AS A BIOMARKER FOR DETECTION OF KIDNEY DAMAGE An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by EESHA FAROOQI Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL DIAGNOSTIC TEST USING PODOCYTURIA AS A BIOMARKER FOR DETECTION OF KIDNEY DAMAGE An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by EESHA FAROOQI Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
Supplementary Information. MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
 Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers
 Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM HCV
 METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE HCV Steatosis Insulin resistance Arun J Sanyal M.D. Chairman, Div. of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE HCV Steatosis Insulin resistance Arun J Sanyal M.D. Chairman, Div. of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO. Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu ABSTRACT
 Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
Insight into cancer research from discovery to validation
 Insight into cancer research from discovery to validation 1 Exosomes in cancer research: from exosome isolation to biomarker discovery Zheng Songyue, PhD Technical Sales Specialists Life Technologies The
Insight into cancer research from discovery to validation 1 Exosomes in cancer research: from exosome isolation to biomarker discovery Zheng Songyue, PhD Technical Sales Specialists Life Technologies The
PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature
 PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. RNAzol BD is a reagent for isolation of total RNA from whole blood, plasma or serum of human
PRODUCT: RNAzol BD for Blood May 2014 Catalog No: RB 192 Storage: Store at room temperature PRODUCT DESCRIPTION. RNAzol BD is a reagent for isolation of total RNA from whole blood, plasma or serum of human
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome. and Type-2 Diabetes
 A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
Milk micro-rna information and lactation
 Christophe Lefèvre, BioDeakin,. Deakin University, Geelong VIC Australia Milk micro-rna information and lactation New Signals in milk? - Markers of milk and lactation status? - Signal infant development?
Christophe Lefèvre, BioDeakin,. Deakin University, Geelong VIC Australia Milk micro-rna information and lactation New Signals in milk? - Markers of milk and lactation status? - Signal infant development?
Cardiovascular. Diseases. a simple and standardized kit qpcr analysis of circulating platelet-derived micrornas
 microrna Biomarkers of Platelet Function Neurodegenerative Diseases Cardiovascular Diseases Musculoskeletal Diseases a simple and standardized kit qpcr analysis of circulating platelet-derived micrornas
microrna Biomarkers of Platelet Function Neurodegenerative Diseases Cardiovascular Diseases Musculoskeletal Diseases a simple and standardized kit qpcr analysis of circulating platelet-derived micrornas
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
CRS4 Seminar series. Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4. Biomedicine. Bioinformatics. Paolo Uva July 11, 2012
 CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
Human Leptin ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA/cfRNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. R1072 Highlights High-quality cell-free DNA and RNA are easily and robustly purified from up to 3 ml of plasma, serum, or other biological
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA/cfRNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. R1072 Highlights High-quality cell-free DNA and RNA are easily and robustly purified from up to 3 ml of plasma, serum, or other biological
Micro RNA Research. Ken Kosik. Harriman Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology and Biomolecular Sciences & Engr.
 Ken Kosik Harriman Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology and Biomolecular Sciences & Engr. Program Co-Director, Neurosciences Research Institute Micro RNA Research Neuroscience
Ken Kosik Harriman Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology and Biomolecular Sciences & Engr. Program Co-Director, Neurosciences Research Institute Micro RNA Research Neuroscience
Supplementary Table 2. Conserved regulatory elements in the promoters of CD36.
 Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
Human Rotavirus A. genesig Standard Kit. Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests. Primerdesign Ltd. For general laboratory and research use only
 TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells
 CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
THE USE OF WT1-QPCR TO MEASURE AND DETECT MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA. Ava Greco
 THE USE OF WT1-QPCR TO MEASURE AND DETECT MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA Ava Greco REVIEW OF LITERATURE What is Leukemia? Abnormal growth of cells in the blood stream Progresses rapidly
THE USE OF WT1-QPCR TO MEASURE AND DETECT MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA Ava Greco REVIEW OF LITERATURE What is Leukemia? Abnormal growth of cells in the blood stream Progresses rapidly
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017
 mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
