Impact of NM23-M1 "knock-out" on metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma: a transgenic approach
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact of NM23-M1 "knock-out" on metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma: a transgenic approach
2 NM23-M1 "knock- out" mice (without NDPK A) Experimental models of hepatocarcinogenesis Chemical model (Diethylnitrosamine, DEN) : single IP injection in 15-days-old mice (10 g/g body weight). Double transgenic mice : ASV/NM23-M1 / breeding of NM23-M1 "knock-out" mice with ASV mice expressing specifically in the liver the SV40 large T antigen under the control of antithrombin III promoter and developping hepatocellular carcinoma (P. Briand).
3 Primary tumor development in DEN-treated and ASV mice No difference in tumor primary formation between NM23-M1 +/+ and NM23-M1 -/- mice.
4 Immunohistochemical analysis with Hep-Par 1 antibody Only the lung nodules of ASV mice are hepatocarcinoma metastases.
5 Metastatic dissemination in ASV mice Highly significant increase in the metastatic incidence in ASV/NM23-M1 -/- mice.
6 NM23 silencing and consequences in epithelial cancer cell models
7 NM23-H1 silencing and cell scattering (1) HepG2 cells
8 NM23-H1 silencing and cell scattering (2) C Si 24h 48h 72h 24h 48h 72h NM23-H1 silenced cells show a random spatial distribution
9 NM23-H1 silencing and cell scattering (3) PLC/PRF/5 cells HCT8/S11 cells NM23-H1 silenced cells are scattered and show cellular extensions
10 NM23-H1 silencing and intercellular adhesion HepG2 cells fast aggregation assay slow aggregation assay
11 NM23-H1 silencing and intercellular adhesion HCT8/S11 cells fast aggregation assay slow aggregation assay Inhibition of intercellular adhesion by NM23-H1 silencing
12 NM23-H1 silencing and adherens junctions NM23-H1 silencing induces the disruption of adherens junction complexes
13 NM23-H1 silencing and adherens junctions NM23-H1 silencing induces -catenin-tcf/lef-1 transactivation through a GSK-3 -independent mechanism
14 NM23-H1 silencing and cell motility HepG2 cells NM23-H1 silenced cells exhibit higher motility
15 NM23-H1 silencing and cell motility HCT8/S11 cells NM23-H1 silencing induces directional migration
16 NM23-H1 silencing and actin cytoskeleton Fluorescence microscopy Scanning electron microscopy NM23-H1 silencing induces filopodia-like structures and Rac1 activation
17 NM23-H1 silencing and invasion Matrigel Native collagen I -NM23-H1 silencing induces invasion in matrigel and collagen I. -Conditioned media from control and silenced cells does not promote invasion.
18 NM23-H2 silencing and invasion Native collagen I NM23-H2 silencing does not induce invasion in collagen I.
19 NM23 silencing, invasion and NDPK activity H1: invasion H1 H2 H2: no invasion H1 H2 20% 15% 52% 38% The NDPK intrinsic activity of NM23-H1 only represents a minor fraction of the global cellular NDPK activity
20 NM23-H1 silencing, invasion and signaling HepG2 cells HCT8/S11 cells Involvement of MAPK, PI3K, Rho/ROCK, and Src in invasion induced by NM23-H1 silencing
21 NM23-H1 silencing, invasion and signaling Hyperactivation of MAPK and PI3K/Akt/S6K induced by NM23-H1 silencing
22 NM23-H1 silencing and invadopodia (1)
23 NM23-H1 silencing and invadopodia (2) Depletion of NM23-H1 stimulates matrix degradation, invadopodia formation and invasion in a MT1-MMPdependent manner
24 NM23-H1 silencing and invasion in other studies Invasion induced by NM23-H1 silencing -in melanoma cell lines (Bakalian et al, 2007) -in lung cancer cell lines (Ma et al, 2008) -in trophoblast cells (Xie et al, 2010) Microarray analysis: MMP-1 and MMP-2 upregulated genes, E-cadherin downregulated gene (Ma et al, 2008) NM23-H1 silencing induced increased levels of activated FGF receptor (Hsu et al, 2006)
25 NM23-H1 silencing and proliferation Flow cytometry Soft agar assay No effect on anchorage -dependent and -independent growth
26 NM23-H1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (1)
27 NM23-H1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (2)
28 NM23-H1 in colon carcinoma (1)
29 NM23-H1 in colon carcinoma (2) Loss or reduction of NM23-H1 at the invasive front of clinical tumors in comparison to the central body of the tumor
30 Phénotype épithélial (NM23-H1 >0) E-cadhérine -caténine Cohésion et polarité épithéliale NM23-H1 Déstabilisation des jonctions adhérentes (Ecadhérine). Translocation nucléaire ( -caténine) Phénotype mésenchymateux (NM23-H1 <0) Dispersion cellulaire MEC TEM partielle Motilité INVASION Collagène type I Matrigel Gélatine Invadopodes (MT1-MMP) Perte de NM23-H1 au front invasif de tumeurs primaires Src Rac1-GTP MEK PI3K p38 ERK Akt LEF-TCF (Wnt) MT1-MMP Tiam-1 JNK -caténine
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development
 Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development Sen-Yung Hsieh, MD, PhD Liver Research Unit Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Taoyuan, Taiwan Aims To identify genes controlling tumor
Functional Genomics : PTPRF-Mediated Contact Inhibition in HCC development Sen-Yung Hsieh, MD, PhD Liver Research Unit Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Taoyuan, Taiwan Aims To identify genes controlling tumor
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Cancer Biology Course. Invasion and Metastasis
 Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Supplementary Figure 1: Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points
 A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
Quantitative Data Analysis Assignment Sample Newessays.co.uk
 Absorbance Quantitative Data Analysis Assignment Sample Newessays.co.uk Part A: Results of the Study Is there a difference of curve profile between the MTT assay and the cell number? What do the different
Absorbance Quantitative Data Analysis Assignment Sample Newessays.co.uk Part A: Results of the Study Is there a difference of curve profile between the MTT assay and the cell number? What do the different
A RENAISSANCE FOR SRC
 A RENAISSANCE FOR SRC Timothy J. Yeatman The c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and activated in a large number of human malignancies and has been linked to the development of cancer and
A RENAISSANCE FOR SRC Timothy J. Yeatman The c-src non-receptor tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and activated in a large number of human malignancies and has been linked to the development of cancer and
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition
 EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Virchow s Hypothesis lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation
 Virchow s Hypothesis 1863 lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation Barrett s esophagus/ Esophageal adenocarcinoma PSC / Cholangiocarcinoma Viral hepatitis
Virchow s Hypothesis 1863 lymphorecticular infiltration of cancer reflected the origin of cancer at sites of inflammation Barrett s esophagus/ Esophageal adenocarcinoma PSC / Cholangiocarcinoma Viral hepatitis
TITLE: The Cadherin Interaction as a Rate Limiting Step in Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0403 TITLE: The Cadherin Interaction as a Rate Limiting Step in Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Liver PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher R. Shepard CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0403 TITLE: The Cadherin Interaction as a Rate Limiting Step in Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Liver PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher R. Shepard CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Hsin-Lin Cheng 1,2, Chiao-Wen Lin 3,4, Jia-Sin Yang 1,2, Ming-Ju Hsieh 1,5, Shun-Fa Yang 1,2, Ko-Hsiu Lu 6,7
 /, Vol. 7, No. 9 Zoledronate blocks geranylgeranylation not farnesylation to suppress human osteosarcoma U2OS cells metastasis by EMT via Rho A activation and FAK-inhibited JNK and p38 pathways Hsin-Lin
/, Vol. 7, No. 9 Zoledronate blocks geranylgeranylation not farnesylation to suppress human osteosarcoma U2OS cells metastasis by EMT via Rho A activation and FAK-inhibited JNK and p38 pathways Hsin-Lin
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 1), pp: 915-932 Non-toxic dose of liposomal honokiol suppresses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through destabilizing EGFR and inhibiting the downstream pathways Jianhong Yang
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 1), pp: 915-932 Non-toxic dose of liposomal honokiol suppresses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through destabilizing EGFR and inhibiting the downstream pathways Jianhong Yang
Positive and Negative Regulators of Metastasis
 Positive and Negative Regulators of Metastasis J. Carl Barrett Laboratory of Biosystems and Cancer Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute TIME SCALE OF TUMOR PROGRESSION CHEMOPREVENTION PERIOD
Positive and Negative Regulators of Metastasis J. Carl Barrett Laboratory of Biosystems and Cancer Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute TIME SCALE OF TUMOR PROGRESSION CHEMOPREVENTION PERIOD
Cancer invasion: Growth factor-induced mechanisms and targeting by image-guided surgery. Julia Odenthal
 Cancer invasion: Growth factor-induced mechanisms and targeting by image-guided surgery Julia Odenthal Cover design: Julia Odenthal Cover image: UT-SCC58 spheroid cultured in a 3D collagen matrix and stained
Cancer invasion: Growth factor-induced mechanisms and targeting by image-guided surgery Julia Odenthal Cover design: Julia Odenthal Cover image: UT-SCC58 spheroid cultured in a 3D collagen matrix and stained
Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines
 Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines Dra Martha Robles Flores Department of Biochemistry Facultad de Medicina Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Tissue anatomy of the
Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines Dra Martha Robles Flores Department of Biochemistry Facultad de Medicina Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Tissue anatomy of the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Cell Polarity and Cancer
 Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
1. The metastatic cascade. 3. Pathologic features of metastasis. 4. Therapeutic ramifications. Which malignant cells will metastasize?
 1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium. Rosita Winkler
 Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Justyna Sikorska, Damian Gaweł, Hanna Domek, Magdalena Rudzińska and Barbara Czarnocka *
 Sikorska et al. BMC Cancer (2019) 19:85 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5239-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Podoplanin (PDPN) affects the invasiveness of thyroid carcinoma cells by inducing ezrin, radixin
Sikorska et al. BMC Cancer (2019) 19:85 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5239-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Podoplanin (PDPN) affects the invasiveness of thyroid carcinoma cells by inducing ezrin, radixin
PAX8-PPARγ Fusion Protein in thyroid carcinoma
 Sidney H. Ingbar Lecture, ATA 10/17/2013: PAX8-PPARγ Fusion Protein in thyroid carcinoma Ronald J. Koenig, MD, PhD Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology & Diabetes University of Michigan Learning Objectives
Sidney H. Ingbar Lecture, ATA 10/17/2013: PAX8-PPARγ Fusion Protein in thyroid carcinoma Ronald J. Koenig, MD, PhD Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology & Diabetes University of Michigan Learning Objectives
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Cell Cyc Cell Cy l c e
 Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation 1 Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 2 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
Mechanisms of Cell Proliferation 1 Cell Cycle G 2 S G 1 2 Multi-cellular organisms depend on cell division/proliferation; Each organism has a developmental plan that determines its behavior and properties;
N-cadherin in cancer metastasis, its emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a therapeutic target in cancer
 Mrozik et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:939 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4845-0 REVIEW N-cadherin in cancer metastasis, its emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a therapeutic
Mrozik et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:939 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4845-0 REVIEW N-cadherin in cancer metastasis, its emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a therapeutic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Department of Pathology, Wan Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei 116, Taiwan; 2
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2530-2558; doi:10.3390/ijms16022530 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms EGCG Inhibits Proliferation, Invasiveness
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2530-2558; doi:10.3390/ijms16022530 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms EGCG Inhibits Proliferation, Invasiveness
DNA Microarray Analysis of the Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition of Mesothelial Cells in a Rat Model of Peritoneal Dialysis
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 27, 2011 Toshimi Imai, Ichiro Hirahara, Yoshiyuki Morishita, Akira Onishi, Makoto Inoue, Shigeaki Muto, Eiji Kusano DNA Microarray Analysis of the Epithelial Mesenchymal
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 27, 2011 Toshimi Imai, Ichiro Hirahara, Yoshiyuki Morishita, Akira Onishi, Makoto Inoue, Shigeaki Muto, Eiji Kusano DNA Microarray Analysis of the Epithelial Mesenchymal
CXC chemokine (ligand/receptor)
 List of abbreviations -MEM alpha-modified minimal essential AKT protein kinase B (also abbreviated PKB) AMC 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin AP-1 activator protein 1 ARF ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding
List of abbreviations -MEM alpha-modified minimal essential AKT protein kinase B (also abbreviated PKB) AMC 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin AP-1 activator protein 1 ARF ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding
Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention
 REVIEW J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1 12, 2004 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention YOUHUA LIU Division of Cellular
REVIEW J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1 12, 2004 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention YOUHUA LIU Division of Cellular
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 November 21.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 March ; 15(3): 178 196. doi:10.1038/nrm3758. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial mesenchymal transition
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 March ; 15(3): 178 196. doi:10.1038/nrm3758. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial mesenchymal transition
 Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer
 Research article Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer Punita Dhawan, 1 Amar B. Singh, 2 Natasha G. Deane, 1,3 YiRan No, 1 Sheng-Ru Shiou, 1 Carl Schmidt,
Research article Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer Punita Dhawan, 1 Amar B. Singh, 2 Natasha G. Deane, 1,3 YiRan No, 1 Sheng-Ru Shiou, 1 Carl Schmidt,
WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer
 WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer Jamie N. Anastas 1,2,3,4 and Randall T. Moon 1,2,4 Abstract Since the initial discovery of the oncogenic activity of WNT1 in mouse mammary glands,
WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer Jamie N. Anastas 1,2,3,4 and Randall T. Moon 1,2,4 Abstract Since the initial discovery of the oncogenic activity of WNT1 in mouse mammary glands,
Yanrong Su *, Nathan R. Hopfinger, Theresa D. Nguyen, Thomas J. Pogash, Julia Santucci-Pereira and Jose Russo *
 Su et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:314 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0988-8 RESEARCH Open Access Epigenetic reprogramming of epithelial mesenchymal transition in
Su et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:314 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0988-8 RESEARCH Open Access Epigenetic reprogramming of epithelial mesenchymal transition in
INTEGRIN SIGNALLING DURING TUMOUR PROGRESSION
 INTEGRIN SIGNALLING DURING TUMOUR PROGRESSION Wenjun Guo and Filippo G. Giancotti Abstract During progression from tumour growth to metastasis, specific integrin signals enable cancer cells to detach from
INTEGRIN SIGNALLING DURING TUMOUR PROGRESSION Wenjun Guo and Filippo G. Giancotti Abstract During progression from tumour growth to metastasis, specific integrin signals enable cancer cells to detach from
EMT AND CANCERS. Terrence P McGarty White Paper No 157 January, 2019
 EMT AND CANCERS Terrence P McGarty White Paper No 157 January, 2019 The epithelial to mesenchymal transition, EMT, is a process that has been closely linked to cancer metastasis. We examine its current
EMT AND CANCERS Terrence P McGarty White Paper No 157 January, 2019 The epithelial to mesenchymal transition, EMT, is a process that has been closely linked to cancer metastasis. We examine its current
Loss of RhoA promotes skin tumor formation. Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization. a. Representative IF images of F-actin staining of big and small control (left) and RhoA ko tumors
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization. a. Representative IF images of F-actin staining of big and small control (left) and RhoA ko tumors
The Role of Metastasis Suppressor CD82 in the Deactivation of the c-met Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer
 Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Masters Theses Graduate Research and Creative Practice 4-27-2017 The Role of Metastasis Suppressor CD82 in the Deactivation of the c-met Signaling Pathway
Grand Valley State University ScholarWorks@GVSU Masters Theses Graduate Research and Creative Practice 4-27-2017 The Role of Metastasis Suppressor CD82 in the Deactivation of the c-met Signaling Pathway
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Hippocampal sections from new-born Pten+/+ and PtenFV/FV pups were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and were imaged at (a) low and (b) high
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Hippocampal sections from new-born Pten+/+ and PtenFV/FV pups were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and were imaged at (a) low and (b) high
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
IJC International Journal of Cancer
 IJC International Journal of Cancer Steps in prostate cancer progression that lead to bone metastasis Jung-Kang Jin 1,2, Farshid Dayyani 1 and Gary E. Gallick 1,2 1 Department of Genitourinary Medical
IJC International Journal of Cancer Steps in prostate cancer progression that lead to bone metastasis Jung-Kang Jin 1,2, Farshid Dayyani 1 and Gary E. Gallick 1,2 1 Department of Genitourinary Medical
Biobehavioral Pathways in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
 Biobehavioral Pathways in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Susan K. Lutgendorf, Ph.D. Departments of Psychology, Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Urology and Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center University of Iowa
Biobehavioral Pathways in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Susan K. Lutgendorf, Ph.D. Departments of Psychology, Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Urology and Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center University of Iowa
WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors
 Research article WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors Jamie N. Anastas, 1,2 Rima M. Kulikauskas, 3 Tigist Tamir, 4 Helen Rizos, 5 Georgina V. Long, 5 Erika M. von Euw,
Research article WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors Jamie N. Anastas, 1,2 Rima M. Kulikauskas, 3 Tigist Tamir, 4 Helen Rizos, 5 Georgina V. Long, 5 Erika M. von Euw,
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0371 TITLE: The Role of Src in Mammary Epithelial Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Leonard Kusdra, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The University of California Berkeley,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0371 TITLE: The Role of Src in Mammary Epithelial Tumorigenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Leonard Kusdra, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The University of California Berkeley,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Molecular principles of cancer invasion and metastasis (Review)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 34: 881-895, 2009 881 Molecular principles of cancer invasion and metastasis (Review) MATHIAS FELIX LEBER 1 and THOMAS EFFERTH 2 1 University of Mainz, Mainz; 2 German
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 34: 881-895, 2009 881 Molecular principles of cancer invasion and metastasis (Review) MATHIAS FELIX LEBER 1 and THOMAS EFFERTH 2 1 University of Mainz, Mainz; 2 German
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank
 @QMBCI bartscancerinstitute 3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank Richard Grose Barts Cancer Institute Ed Carter Normal Breast Architecture Calponin / CK8 Myoepithelial
@QMBCI bartscancerinstitute 3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank Richard Grose Barts Cancer Institute Ed Carter Normal Breast Architecture Calponin / CK8 Myoepithelial
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
TITLE: Hyaluronan-CD44 Interactions Decrease the Metastatic Potential of Breast Cancer Cells
 Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0455 TITLE: Hyaluronan-CD44 Interactions Decrease the Metastatic Potential of Breast Cancer Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jose I. Lopez CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The University
Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0455 TITLE: Hyaluronan-CD44 Interactions Decrease the Metastatic Potential of Breast Cancer Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jose I. Lopez CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The University
A Specific Inhibitor of TGF-B Receptor Kinase, SB , as a Potent Antitumor Agent for Human Cancers 1
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Neoplasia. Vol. 7, No. 5, May 2005, pp. 509 521 509 www.neoplasia.com A Specific Inhibitor of TGF-B Receptor Kinase, SB-431542, as a Potent Antitumor Agent for Human Cancers 1 Sunil K.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Neoplasia. Vol. 7, No. 5, May 2005, pp. 509 521 509 www.neoplasia.com A Specific Inhibitor of TGF-B Receptor Kinase, SB-431542, as a Potent Antitumor Agent for Human Cancers 1 Sunil K.
SOLUBLE E-CADHERIN AS A MICROENVIRONMENTAL FACTOR WHICH ENHANCES TUMOR PROGRESSION. Pratima U. Patil
 SOLUBLE E-CADHERIN AS A MICROENVIRONMENTAL FACTOR WHICH ENHANCES TUMOR PROGRESSION by Pratima U. Patil A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the
SOLUBLE E-CADHERIN AS A MICROENVIRONMENTAL FACTOR WHICH ENHANCES TUMOR PROGRESSION by Pratima U. Patil A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the
Apoptosis inhibitor 5 increases metastasis via Erk-mediated MMP expression
 BMB Reports BMB Rep. 2015; 48(6): 330-335 www.bmbreports.org Apoptosis inhibitor 5 increases metastasis via Erk-mediated MMP expression Kwon-Ho Song 1,3,#, Seok-Ho Kim 2,#, Kyung Hee Noh 1,3,#, Hyun Cheol
BMB Reports BMB Rep. 2015; 48(6): 330-335 www.bmbreports.org Apoptosis inhibitor 5 increases metastasis via Erk-mediated MMP expression Kwon-Ho Song 1,3,#, Seok-Ho Kim 2,#, Kyung Hee Noh 1,3,#, Hyun Cheol
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells. Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari
 Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0212 TITLE: Wnt/Beta-Catenin, Foxa2, and CXCR4 Axis Controls Prostate Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiuping Yu CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0212 TITLE: Wnt/Beta-Catenin, Foxa2, and CXCR4 Axis Controls Prostate Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiuping Yu CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt University
Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
Regulation of EMT by TGFb in cancer
 FEBS Letters 586 (2012) 1959 1970 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Review Regulation of EMT by TGFb in cancer Carl-Henrik Heldin a,, Michael Vanlandewijck a, Aristidis Moustakas a,b a Ludwig Institute
FEBS Letters 586 (2012) 1959 1970 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Review Regulation of EMT by TGFb in cancer Carl-Henrik Heldin a,, Michael Vanlandewijck a, Aristidis Moustakas a,b a Ludwig Institute
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S100A9
 Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
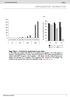 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for
 INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
The role of microrna in metastatic processes of non-small cell lung carcinoma
 The role of microrna in metastatic processes of non-small cell lung carcinoma Zuzana Pastorkova a, Jozef Skarda a, Jozef Andel b Background. MicroRNAs are small non-coding one-stranded RNA molecules that
The role of microrna in metastatic processes of non-small cell lung carcinoma Zuzana Pastorkova a, Jozef Skarda a, Jozef Andel b Background. MicroRNAs are small non-coding one-stranded RNA molecules that
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling
 Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway
 Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
IN VIVO ANALYSIS OF THE ROLE OF TENASCIN-C IN TUMORIGENESIS
 IN VIVO ANALYSIS OF THE ROLE OF TENASCIN-C IN TUMORIGENESIS Inauguraldissertation zur Erlangung der Würde eines Doktors der Philosophie vorgelegt der Philosophisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät der
IN VIVO ANALYSIS OF THE ROLE OF TENASCIN-C IN TUMORIGENESIS Inauguraldissertation zur Erlangung der Würde eines Doktors der Philosophie vorgelegt der Philosophisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät der
Prostaglandin E 2 reduces radiation-induced epithelial apoptosis through a mechanism involving AKT activation and bax translocation
 Research article Prostaglandin E 2 reduces radiation-induced epithelial apoptosis through a mechanism involving AKT activation and bax translocation Teresa G. Tessner, Filipe Muhale, Terrence E. Riehl,
Research article Prostaglandin E 2 reduces radiation-induced epithelial apoptosis through a mechanism involving AKT activation and bax translocation Teresa G. Tessner, Filipe Muhale, Terrence E. Riehl,
Intercellular indirect communication
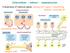 Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Screening of novel thalidomide analogues with label-free assays and appling in the in vivo model of hepatocellular carcinoma.
 Screening of novel thalidomide analogues with label-free assays and appling in the in vivo model of hepatocellular carcinoma Lajos István Nagy Ph.D thesis summary Supervisor: László Puskás, PhD, DSc Scientific
Screening of novel thalidomide analogues with label-free assays and appling in the in vivo model of hepatocellular carcinoma Lajos István Nagy Ph.D thesis summary Supervisor: László Puskás, PhD, DSc Scientific
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Should the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) pathway be activated or silenced in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer?
 Should the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) pathway be activated or silenced in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer? Sonja Kesselmans. S2242362. Bachelorscriptie. 20-06-2014 Supervisor: Marcel van
Should the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) pathway be activated or silenced in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer? Sonja Kesselmans. S2242362. Bachelorscriptie. 20-06-2014 Supervisor: Marcel van
PhD THESIS Epigenetic mechanisms involved in stem cell differentiation
 Romanian Academy Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology "Nicolae Simionescu" PhD THESIS Epigenetic mechanisms involved in stem cell differentiation Coordinator: Acad. Maya Simionescu PhD Student:
Romanian Academy Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology "Nicolae Simionescu" PhD THESIS Epigenetic mechanisms involved in stem cell differentiation Coordinator: Acad. Maya Simionescu PhD Student:
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy. Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI
 A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
Rearrangements of the Actin Cytoskeleton and E-Cadherin Based Adherens Junctions Caused by Neoplasic Transformation Change Cell Cell Interactions
 Rearrangements of the Actin Cytoskeleton and E-Cadherin Based Adherens Junctions Caused by Neoplasic Transformation Change Cell Cell Interactions Dmitry V. Ayollo., Irina Y. Zhitnyak., Jury M. Vasiliev,
Rearrangements of the Actin Cytoskeleton and E-Cadherin Based Adherens Junctions Caused by Neoplasic Transformation Change Cell Cell Interactions Dmitry V. Ayollo., Irina Y. Zhitnyak., Jury M. Vasiliev,
The crosstalk between p38 and Akt signaling pathways orchestrates EMT by regulating SATB2 expression in NSCLC cells
 706212TUB0010.1177/1010428317706212Tumor BiologyKucuksayan and Akca research-article20172017 Original Article The crosstalk between p38 and Akt signaling pathways orchestrates EMT by regulating SATB2 expression
706212TUB0010.1177/1010428317706212Tumor BiologyKucuksayan and Akca research-article20172017 Original Article The crosstalk between p38 and Akt signaling pathways orchestrates EMT by regulating SATB2 expression
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
